Abstract
To address environmental pollution issues and optimize the utilization of waste biomass resources, this study proposes a novel eco-friendly sound-absorbing material based on maple leaf waste and tests its sound absorption performance. The fibers were extracted from maple leaf waste through a wet decomposition and grinding process. Metallurgical microscopy was employed to observe the microstructural characteristics of maple leaf fibers to identify the potential synergistic effect. The effects of two key factors—sample thickness and mass density—on sound absorption performance were investigated. The sound absorption coefficients were measured using the transfer function method in a dual-microphone impedance tube to evaluate their sound-absorbing performance. Experimental results demonstrate that the prepared maple leaf fibers, as acoustic materials, exhibit excellent acoustic performance across a wide frequency range, with an average sound absorption coefficient of 0.7. Increasing sample thickness improves the sound absorption coefficient in low- and mid-frequency ranges. Additionally, increased sample mass density was found to enhance acoustic performance in low- and mid-frequency bands. This study developed an eco-friendly material with lightweight and efficient acoustic absorption properties using completely biodegradable maple leaf waste. The results provide high-performance, economical, and ecologically sustainable solutions for controlling building and traffic noise while promoting the development of eco-friendly acoustic materials.
1. Introduction
Urbanization-induced noise pollution has emerged as a major global public health challenge, posing significant threats to human health, including hearing impairment, cardiovascular diseases, and ecological imbalance. Addressing this urgent challenge necessitates the development of sustainable, high-efficiency sound-absorbing materials. Conventional absorbers such as mineral wool and glass fibers are associated with substantial energy consumption during production, potential environmental contamination risks, and non-biodegradable waste accumulation. Repurposing waste plant fibers for developing novel green sound-absorbing materials not only fulfills noise mitigation requirements but also aligns with circular economy principles. This approach offers an innovative pathway for noise control, integrating ecological sustainability, economic viability, and superior performance with enabling efficient resource valorization and a reduced environmental footprint.
In recent years, investigations into the acoustic properties of sustainable plant-based fibers have revealed their potential as effective sound-absorbing materials. Literature reviews by Eun-Suk Jang et al. document that the sound absorption of lignocellulosic materials (e.g., coir, kenaf, and rice husk) improves with greater thickness, especially at low- to mid-frequencies. It also shows that a higher density at a given thickness and a larger air gap behind the material enhances low-frequency performance [1]. Numerous natural fibers exhibit substantial acoustic absorption capabilities. Lignocellulosic fibers including poplar seed, pineapple leaf, and hemp fibers serve as sustainable alternatives to conventional glass wool, with porous microstructure enabling effective sound energy dissipation. Notably, hemp fiber demonstrates a stable sound absorption coefficient exceeding 0.8 [2]. Loofah fiber panels with macro porous structures, when installed on 30% of ceilings and 65% of side walls, reduced mean reverberation time from 4.0 s to 0.7 s [3]. Sugarcane bagasse composites demonstrate notable structural stability and exceptional acoustic attenuation performance across low-to-mid frequency ranges, achieving a sound absorption coefficient consistently above 0.7 [4]. Natural fibers (hemp, wool, reed, and cork) demonstrate viability as environmentally sustainable and renewable materials, with wool fiber achieving α = 0.9 at mid-frequencies [5]. Hemp particles with calcium oxide demonstrate size dependent acoustic properties, with a systematic evaluation of particle size distribution effects. Characterization revealed multiscale porosity enabling consistent effective acoustic absorption at targeted frequency bands [6]. Jute fiber has emerged as a promising acoustic material due to its inherent sound-absorbing characteristics. Novel jute fiber matrix panels show that the peak of the acoustic absorption coefficient increases with the depth of the shot holes, and remains above 0.7 between 750 and 1500 Hz [7]. Addressing sustainable construction demands, rice straw was fabricated into thermal-acoustic insulation panels. Under 5 bar pressure, those bonded with PP (paper pulp) adhesive exhibited superior low-frequency sound absorption, with an absorption coefficient of 0.51 [8]. Polylactic acid (PLA) bio-composites reinforced with plant fibers exhibit sound absorption coefficients approaching 0.4 in the 100–500 Hz range. The composites demonstrate significantly improved acoustic attenuation performance in higher-frequency bands exceeding 1000 Hz [9]. Rice waste fibers (5–15 wt%) were incorporated as reinforcement in flexible polyurethane foam through controlled blending. The 5 wt% rice fiber composites exhibited a 25–30% increase in acoustic absorption properties compared with the unreinforced form [10]. Tire-derived fibers from recycled rubber granules exhibit superior sound absorption owing to their macro porous architecture. Optimal absorption occurs at low binder concentrations, with an absorption coefficient of 0.85 [11]. Multilayer absorbers fabricated from coal bottom ash establish innovative waste valorization pathways, demonstrating an inverse correlation between elevated porosity and reduced static airflow resistivity in bottom ash-derived composites [12]. Nonwoven composites manufactured from recycled cotton–polyester textile waste deliver integrated acoustic attenuation and thermal insulation functionality, with porous assemblies exhibiting outstanding high-frequency absorption efficiencies above 2000 Hz [13]. Post-consumer denim waste was fiberized and consolidated with phenolic resin into sound absorbers. The absorption coefficients increased monotonically with surface density and bulk density, achieving values up to 0.7. Performance was further enhanced by increasing the resin content at a constant bulk density [14]. Cellulose acetate materials regenerated from discarded cigarette filters demonstrate excellent broadband absorption, attaining near-ideal absorption coefficients throughout the tested spectrum range of 500–6400 Hz [15]. Acoustic specimens fabricated from reclaimed denim fibers and waste jute fibers exhibit exceptional sound absorption performance, with experimental results confirming that the absorption coefficients of both materials exceeded 0.8, surpassing those of commercial glass wool benchmarks [16]. Composites incorporating fruit kernels (olive, cherry, peach) and coconut fiber exhibited average sound absorption coefficients of above 0.5 in a defined frequency band, reaching approximately 0.7 in the case of cherry kernels [17]. Wood-reinforced cement board (WRCB), utilizing renewable wood fibers, provides a sustainable sound-absorbing solution. Studies indicate that WRCB with 30–50 mm thickness and 400–500 kg/m3 density achieves near-ideal absorption in the 1000–2000 Hz range [18].
Current research has utilized plant fibers as fillers in the fabrication of composites. There is limited research on the acoustic properties of individual plant fibers, with studies predominantly concentrating on the optimization of specific frequency bands. Comprehensive spectral analysis of plant fiber acoustic performance remains largely unexplored. Maple trees, taxonomically classified as acer species within the sapindaceae family, serve as ecologically and economically important species worldwide. As key components of Northern Hemisphere temperate forests, they occupy vital ecological niches [19]. In China, acer species predominantly occur in the northeastern provinces and southwestern high-altitude regions. Occupying approximately 12–18 million hectares, they comprise 5.5–8.2% of China’s forested cover, yielding 2.4–3.6 million tons of annual leaf litter. The distribution area of maple trees across the country is illustrated in Table 1, where it is evident that the area is characterized by abundant leaf litter resources. Current disposal methods generate toxic gas emissions (CO, PM2.5, VOCs), eliminating potential valorization opportunities. While waste fiber-reinforced acoustic materials have advanced significantly, few existing studies have investigated dying maple leaves as primary sound-absorbing media.

Table 1.
The distribution area of maple trees in China.
This study investigates the potential application of maple leaf waste as acoustic materials, aiming to fully utilize this discarded biomass resource while achieving organic waste recycling and reuse. A method for extracting fibers from maple leaf waste was developed, enabling the fabrication of eco-friendly sound absorbers. The sound absorption coefficients were measured using the transfer function method in a dual-microphone impedance tube to evaluate their sound-absorbing performance and analyze parameter influence. This study innovatively proposes a maple fiber-based sound absorber, offering an architectural acoustic solution that combines ecological benefits with economic feasibility.
2. Material and Sample Preparation
2.1. Extraction Procedures of Maple Leaf Fibers
The primary raw material was plant fibers extracted from maple leaf waste that naturally fell during autumn. The maple fiber extraction methodology is illustrated in Figure 1. The fiber extraction process begins with collecting fallen dry leaves and hydrating them through water soaking. The leaves are then treated with a 5% sodium hydroxide solution for one hour to soften the tissue and facilitate fiber separation. The post-treatment liquid was collected and neutralized to an environmentally benign solution through acid-base neutralization. Following alkaline treatment, the leaves undergo water rinsing and mechanical fiber separation through repeated crushing. A 10% sodium chlorate solution is subsequently introduced, with a two-minute soaking period for fiber decolorization. Residual sodium hypochlorite is finally neutralized and removed using a hydrogen peroxide solution wash. The extracted fibers were subjected to a 48 h drying period at 28 °C under ventilation to obtain purified fibers from maple leaves. Quantified fiber aliquots are then placed in cylindrical compression mold. Sustained pressure application yields the final fabricated sound absorber samples.

Figure 1.
Steps of the methodology for maple fiber extraction and sample fabrication. (1) fallen dry leaves collection; (2) fiber separation; (3) decolorization; (4) drying fiber quantization; (5) compression; and (6) sample.
2.2. Preparation of Sound Absorber Samples with Maple Leaf Fibers
This study investigates the acoustic properties of maple fiber-based sound absorbers as sustainable materials for broadband sound absorption and noise control applications. The extracted maple leaf fibers were compressed in a cylindrical mold to fabricate sound-absorbing samples matching the inner diameter (29 mm) of the impedance tube. Sample mass density directly influences porosity characteristics. Fiber mass was measured using an electronic scale, while sample volume was calculated from the inner diameter of the compression mold and the sample thickness. Mass density was then determined using the relation ρ = m/V. For quantitative sound absorption evaluation, maple leaf fibers of varying masses were placed in a compression mold. Prior to testing, a 50 N force was applied to the sample and maintained in a ventilated indoor area for 48 h to achieve a consistent density and the desired thickness under a constant compressive load. Sample bulk density was calculated from areal density divided by thickness [20], and the porosity (Φ) was evaluated by
where ρb denotes the bulk density and ρm signifies the density of the maple fiber, which is approximately 540 kg/m3, similar to the density of wood [21]. Figure 2 illustrates four thickness-varied samples and three mass density-varied specimens. The geometrical parameters of the samples are summarized in Table 2. All samples were designed with diameters matching the inner diameter of the impedance tube.
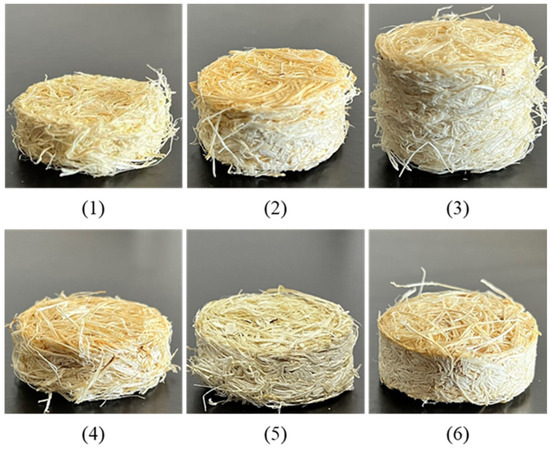
Figure 2.
Sound absorbers made from maple leaf fibers with different parameters. The geometrical sample 1~6 parameters are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
The geometric parameters of the sound absorber samples.
2.3. Microstructure Characterization of Maple Leaf Fibers
A metallographic microscope serves as a pivotal tool for characterizing material microstructural features via high-resolution imaging. Microstructural analysis was conducted using metallurgical microscopy (MX6RTW) to characterize maple leaf fiber morphologies, with results presented in Figure 3. Fiber samples were positioned on glass slides and examined at 50 and 200 magnifications, respectively.

Figure 3.
Metallographic microscope setup for microstructure observation.
2.4. Acoustic Performance Measurement of the Proposed Sound Absorber
To reduce experimental variability, three repeated measurements were conducted for each specimen, involving complete remounting into the impedance tube prior to each test. The sound absorption coefficient of the proposed sound absorber was evaluated using an experimental setup developed in accordance with ASTM-E-1050, as illustrated in Figure 4. The impedance tube (29 mm inner diameter) contained two microphones spaced 20 mm apart, enabling measurements across the 250–6400 Hz frequency range. It should be noted that this setup is effectively limited to frequencies above 250 Hz due to its diameter. Measurements at lower frequencies below 250 Hz would require the 100 mm inner diameter tube. Hence, the focus of this paper is only on high-frequency sound absorption performance. The excitation system utilized a function generator (DG952) to produce white noise, amplified by a power amplifier (PA50) and transduced through a loudspeaker (4 Ω/10 W). Two microphones (PCB, 130F20) were employed to measure the incident and reflected waves, with signal processing performed by a data acquisition system (DH5902N).
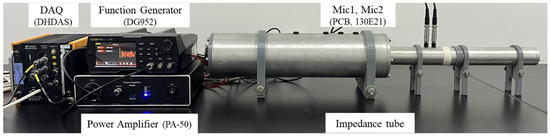
Figure 4.
Two-microphone impedance tube system.
Figure 5 presents a schematic of the impedance tube measurement system. The reflection coefficient (r) was derived from the complex transfer function (H12) between microphone signals. The transfer function (H12) is expressed by
where p1 and p2 represent the acoustic pressures measured by the two microphones, and x1 and x2 denote the distances from the reference plane (the sample position at x = 0) to each microphone. Herein,
where j denotes the imaginary unit, k0 is the wavenumber, s = x1 − x2 represents the distance between the two microphone sensors, l is the distance from the sample surface to the nearest microphone, f is frequency, and c0 is the speed of sound. The normal incident sound absorption coefficient is calculated by the formula α = 1 − |r|2 [22]. All measurements were performed at standard temperature and atmospheric pressure, with an air density of 1.202 kg/m3 and sound velocity of 343.24 m/s.
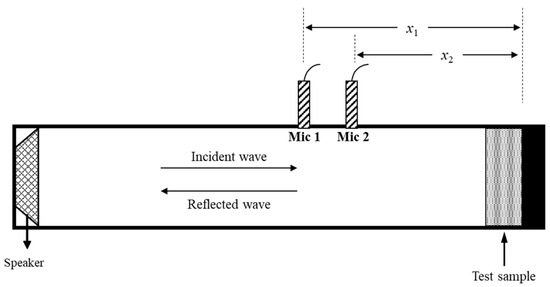
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of the impedance tube system.
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure of Maple Leaf Fibers
Figure 6 shows the microstructural characteristic of maple leaf fibers (sample 1) observed at various magnifications. The maple leaf fibers exhibited diameters ranging from 100 to 400 μm, with a median of 200 μm. The extracted maple leaf fibers exhibited a predominantly regular, flattened strip-like morphology with a concomitant disordered arrangement. At 200 magnification, an intricate hierarchical porous structure became evident within the fibers. These interconnected structural units form a distinctive gradient cavity system extending from surface to interior. The structure features a dense, homogeneous mesh network throughout the fiber matrix. When acoustic waves penetrate the fiber network, air molecules undergo an intense and repeated relative motion against fiber surfaces, generating substantial viscous friction resistance. This mechanism facilitates acoustic energy dissipation through conversion to thermal energy at molecular scales, enabling broadband sound absorption.

Figure 6.
Fiber structures at (a) 50 and (b) 200 magnification.
3.2. Influence of Sample Thickness on the Sound Absorption Coefficient
Figure 7 shows that the acoustic absorption coefficient increases significantly with maple fiber-based sound-absorber thickness across both low- and high-frequency ranges. This observed trend is consistent with the experimental findings summarized by Eun-Suk Jang et al. in the introduction. As the sample thickness increased from 10 mm to 20 mm, the peak sound absorption coefficient rose from 0.87 to 0.95. Concurrently, the absorption curve shifted toward lower frequencies. Within the 250–2000 Hz range, the sound absorption coefficient exhibited a substantial enhancement from 0.25 to 0.8 with increasing thickness. The 10 mm thickness sample exhibited a particularly pronounced sound absorption coefficient (α = 0.95) in the 3000–4000 Hz range. This behavior indicates the shorter wavelengths of high-frequency waves, which exhibit reduced penetration depth compared with low-frequency waves. Incident sound waves experience surface attenuation and reflection, limiting their penetration to superficial layers [23]. Increased sample thickness extends the propagation path of incident waves through the material. This longer path length enhances visco-thermal losses through inter-fiber friction. This is accompanied by increased friction and viscosity effects between fibers. Consequently, this mechanism promotes more efficient sound-to-thermal energy conversion and subsequent energy dissipation.
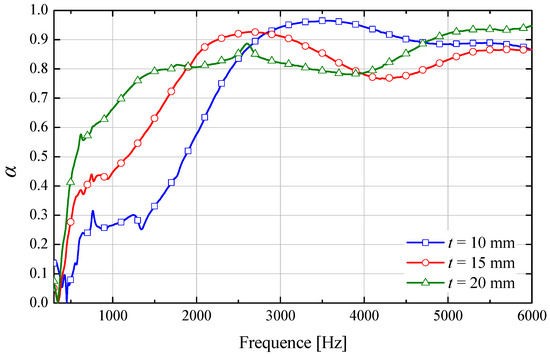
Figure 7.
Measured sound absorption coefficient of sample 1–3 for analyzing thickness effect.
3.3. Effect of Mass Density Effect on the Sound Absorption Coefficient
Figure 8 reveals that increasing the mass density of the maple fiber-based sound absorber induces a leftward shift in the absorption coefficient curve, particularly enhancing low- and mid-frequency absorption coefficients. Higher mass density reduces inter-fiber spacing, porosity, and average pore diameter, while increasing flow resistance. The elevated flow resistance inhibits wave penetration, promoting acoustic-to-thermal energy conversion primarily within the surface layers [24]. High-frequency sound waves exhibit limited penetration depth. As the flow resistivity of the sample increases, majority of the acoustic energy is reflected at the surface, allowing only a small fraction of high-frequency waves to enter the material, resulting in a decrease in the high-frequency sound absorption coefficient. For low- and mid-frequency waves propagating through the microporous structure, enhanced air–pore wall friction induces viscous energy dissipation, significantly improving absorption coefficients at these frequencies.
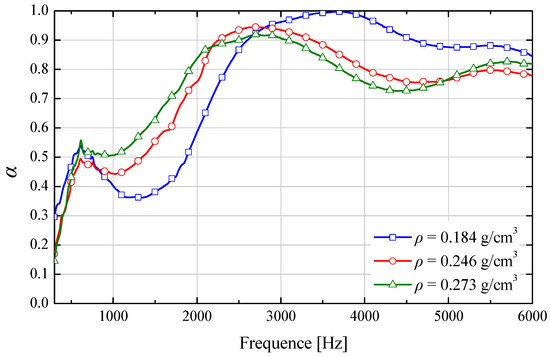
Figure 8.
Variation in sound absorption coefficient of samples 4–6 for analyzing mass density effect.
3.4. Comparison with Commercial Glass Wool
To compare the sound absorption properties of the proposed the maple fiber-based sound absorbers and commercial glass wool samples, specimens with a consistent diameter of 29 mm and thicknesses of 10 mm and 20 mm were prepared, as shown in Figure 9. The geometrical parameters of the samples are summarized in Table 3. Figure 10 indicates that the maple fiber specimens consistently achieved higher sound absorption coefficients across the frequency spectrum from 250 to 6000 Hz, with a particularly notable enhancement observed at the 10 mm thickness. This suggests that glass wool necessitates a greater thickness (above 20 mm) to deliver high acoustic absorption performance. This characteristic is in agreement with the results reported by Kim et al. [25] for glass wool. The comparative outcomes underscore the advantageous acoustic characteristics of maple fiber-based absorbers, especially in scenarios demanding reduced material thickness without compromising sound absorption efficiency.
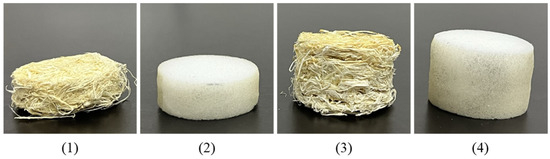
Figure 9.
Sound absorbers made from maple fiber fibers and glass wool with the thicknesses of 10 mm and 20 mm, respectively. The geometrical sample 1~4 parameters are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
The geometric parameters of glass wool samples.
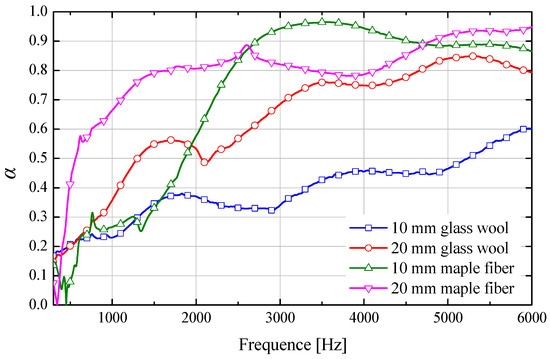
Figure 10.
Comparison of sound absorption coefficients between maple leaf fiber and glass wool at identical thicknesses (10 mm, 20 mm).
4. Conclusions
Conventional sound-absorbing materials are typically non-biodegradable and contribute to environmental pollution. To address these challenges while valorizing waste biomass, this study developed a novel sustainable sound-absorbing material extracted from maple leaf waste. This work systematically investigated the material’s acoustic properties to establish an experimental foundation for eco-friendly noise control applications. Maple leaf fibers were successfully extracted via sequential permeation treatment and mechanical grinding processes. The fibers were uniformly packed into cylindrical molding and compressed to form maple fiber-based sound absorber samples. The normal incident sound absorption coefficients were measured using a two-microphone impedance tube system employing the transfer function method. Results demonstrate that maple leaf fibers exhibit excellent broadband acoustic absorption capabilities. Absorption performance shows strong structural dependence, with enhancement observed at increased thicknesses and mass densities. The sound absorption coefficient increased significantly, within the 250–1000 Hz frequency band. This enhancement stems from an improved visco-thermal energy dissipation mechanism in thicker, denser structures. This study has certain limitations: acoustic measurements were restricted to 250–6400 Hz due to equipment constraints, resulting in incomplete low-frequency characterization below 250 Hz. Nonetheless, the use of maple leaf waste offers significant potential in supporting sustainable material development. The future development of maple leaf fiber-based sound absorbers lies in material modification for enhanced functionality, scalable production within circular economy frameworks, and extended applications in green buildings and transportation, ultimately promoting sustainability and reducing reliance on non-biodegradable acoustic materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.J. and Z.Z.; methodology, J.J. and Z.Z.; software, J.J. and Y.F.; validation, Y.F. and H.H.; formal analysis, Y.F. and H.H.; investigation, J.J. and Y.C.; resources, J.J.; data curation, J.J.; writing—original draft preparation, J.J. and Y.F.; writing—review and editing, J.J. and Z.Z.; visualization, Y.C.; supervision, Z.Z.; project administration, J.J.; funding acquisition, J.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Natural Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant No. ZR2022QA041), which is gratefully acknowledged by the authors.
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the paper.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to each participant for their active engagement.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Jang, E.S. Sound absorbing properties of selected green material: A review. Forests 2023, 14, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Hu, L.; Xiong, X.; Noman, M.T.; Mishra, R. Sound absorption properties of natural fibers: A review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halashi, K.; Taban, E.; Soltani, P.; Amininasab, S.; Samaei, E.; Moghadam, D.N.; Khavanin, A. Acoustic and thermal performance of luffa fiber panels for sustainable building applications. Build. Environ. 2024, 247, 111051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othmani, C.; Taktak, M.; Zain, A.; Hantati, T.; Dauchez, N.; Elnady, T.; Fakhfakh, T.; Haddar, M. Acoustic characterization of a porous absorber based on recycled sugarcane wastes. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 120, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, U.; Iannace, G. Acoustic characterization of natural fibers for sound absorption applications. Build. Environ. 2015, 94, 840–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glé, P.; Gourdon, E.; Arnaud, L. Acoustical properties of materials made of vegetable particles with several scales of porosity. Appl. Acoust. 2011, 72, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraj, L.; Jeyanthi, S.; Yogananda, A. An acoustical investigation of partial perforation in jute fiber composite panel. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 37, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawanwadeekul, S.; Jun-On, N.; Kongthavorn, P.; Sangkas, T.; Daothong, S. Chemical-free thermal-acoustic panels from agricultural waste for sustainable building materials. Microelectron. J. 2024, 12, 100245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G. Investigating polylactic acid foam-plant fiber composites for sound absorption and insulation. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6913. [Google Scholar]
- Olcay, H.; Kocak, E.D. Rice plant waste reinforced polyurethane composites for use as the acoustic absorption material. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 173, 107733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Mohamed, M.; Al Halo, N.; Benkreira, H. Acoustical properties of novel sound absorbers made from recycled granulates. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 127, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, C.; Leiva, C.; Vilches, L.F.; González Ganso, J.A. Approaching a methodology for the development of a multilayer sound absorbing device recycling coal bottom ash. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 115, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, S.; Kumar, S.S.; Melese, B.; Mekonnen, S.; Gedilu, M. Development of nonwoven composites from recycled cotton/polyester apparel waste materials for sound absorbing and insulating properties. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 180, 108126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, P.; Soltani, P.; Ghane, M.; Zarrebini, M. Porous resin-bonded recycled denim composite as an efficient sound-absorbing material. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 173, 107710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maderuelo-Sanz, R.; Gomez Escobar, V.; Miguel Meneses-Rodriguez, J. Potential use of cigarette filters as sound porous absorber. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 129, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, M.; Fatima, S.; Tandon, N. Recycled materials as a potential replacement to synthetic sound absorbers: A study on denim shoddy and waste jute fibers. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 159, 107070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, J.; Montava, I.; Juliá, E. Acoustic and thermal properties of panels made of fruit stones waste with coconut fiber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 426, 136054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, N.; Mirzaei, R.; Soltani, P. Acoustic and thermal performance of wood strands-rock wool-cement composite boards as eco-friendly construction materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 445, 137935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, I. Comprehensive review of maple trees: Evolution, biogeographical distribution, ecology, and economic significance with emphasis on canada. Indian J. Ecol. 2024, 15, 1418–1423. [Google Scholar]
- Lashgari, M.; Taban, E.; Sheikhmozafari, M.J. Wood chip sound absorbers: Measurements and models. Appl. Acoust. 2024, 220, 109963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, D.W. Highly variable bark-wood density relationships across tree species reflect tradeoffs in evolved tolerances to environmental stressors. Trees 2024, 38, 1223–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Wang, P.; Qiu, X.; Pan, J. Static flow resistivity measurements based on the ISO 10534.2 standard impedance tube. Build. Environ. 2015, 94, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, X.; Gao, Y. Structural Characteristics and Sound Absorption Properties of Waste Hemp Fiber. Coatings 2022, 12, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, X. Structure of Waste Hemp Stalks and Their Sound Absorbing Properties. Polymers 2022, 14, 4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-W.; Jeong, Y.-S. Experimental Study on the Comparison of the Material Properties of Glass Wool Used as Building Materials. Mater. Sci. 2014, 20, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).