Evaluating Landscape Gene Perception in Traditional Villages for Sustainable Development: A Methodological Framework Integrating Game Theory and the Cloud Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Area and Methods
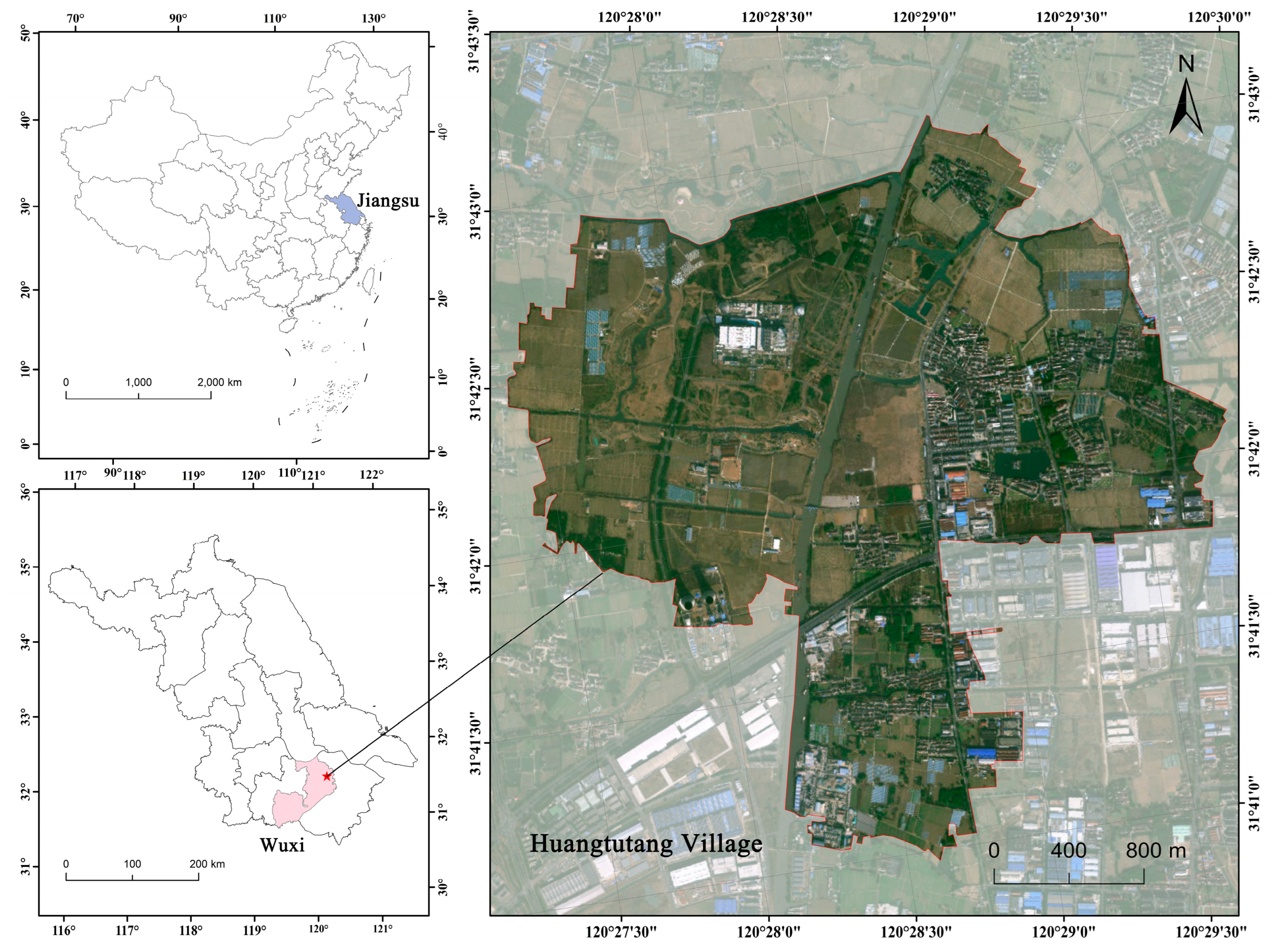
2.1. Overview of the Research Area
2.2. Research Methods
2.2.1. Landscape Gene Theory and Its Identification
2.2.2. Subjective and Objective Weighting Methods
- The Analytic Hierarchy Process
- 2.
- Entropy Method
2.2.3. Game Theory-Based Combined Weighting
2.2.4. Cloud Model
2.3. Research Framework
3. Construction of Landscape Gene Identification and Evaluation System for Huangtutang Village
3.1. Landscape Gene Identification and Translation
3.1.1. Environmental Pattern: Interwoven Water Networks and the Integration of Commerce and Development
3.1.2. Spatial Layout Characteristics: Grid-like Streets and Clustered Layouts Interwoven with Water Systems
3.1.3. Architectural Character: Republican-Era Esthetics Featuring Blue Bricks, Gray Tiles, and Wooden and Stone Components
3.1.4. Cultural Characteristics: Dual Narratives of Historical Accounts and Local Traditions
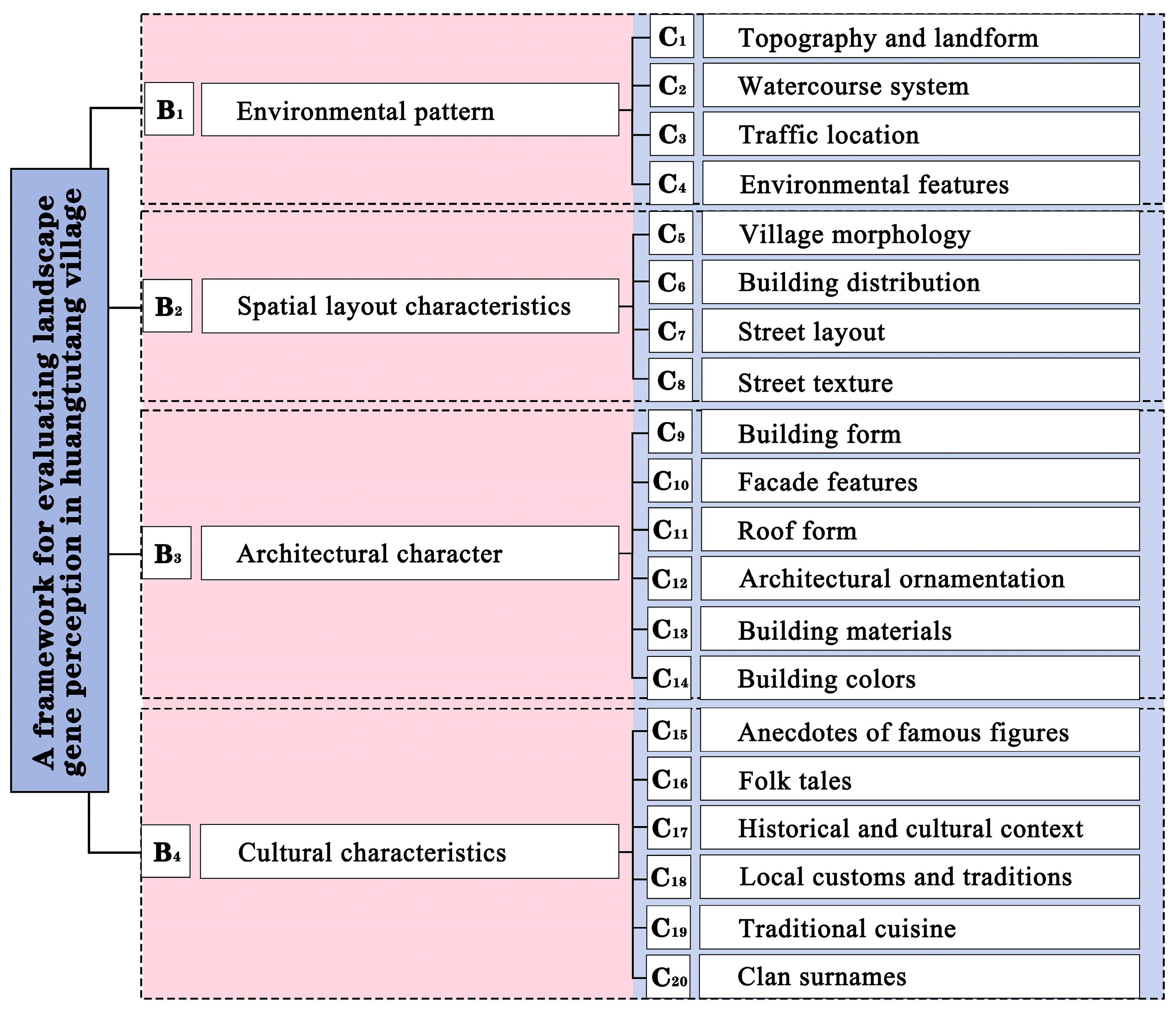
3.2. Construction of the Landscape Gene Perception Evaluation System
4. Landscape Gene Perception Evaluation of Huangtutang Village
4.1. Calculation of Combined Weights
4.2. Comprehensive Cloud Model Evaluation
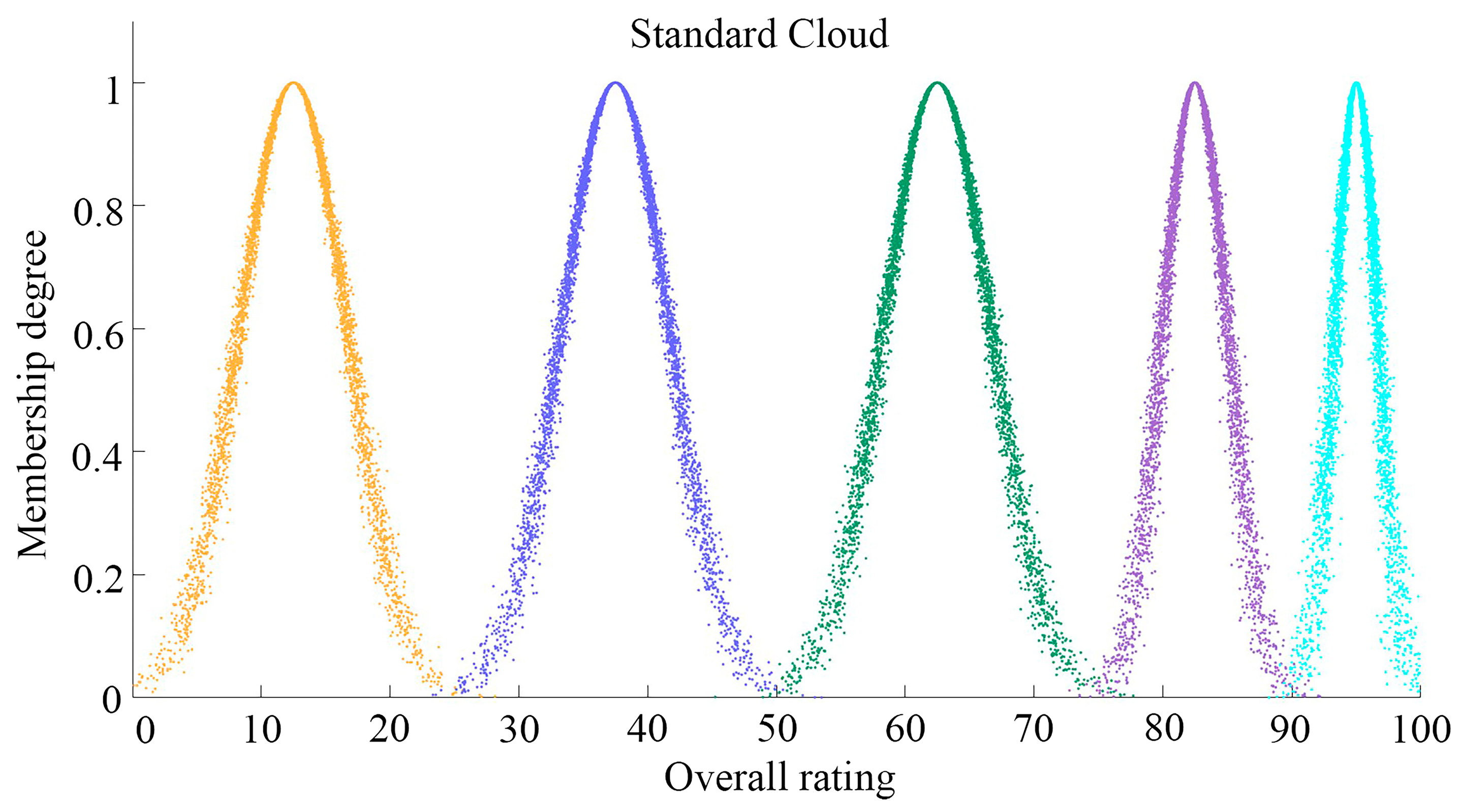
4.2.1. Establishment of Evaluation Criteria and Standard Cloud Grades
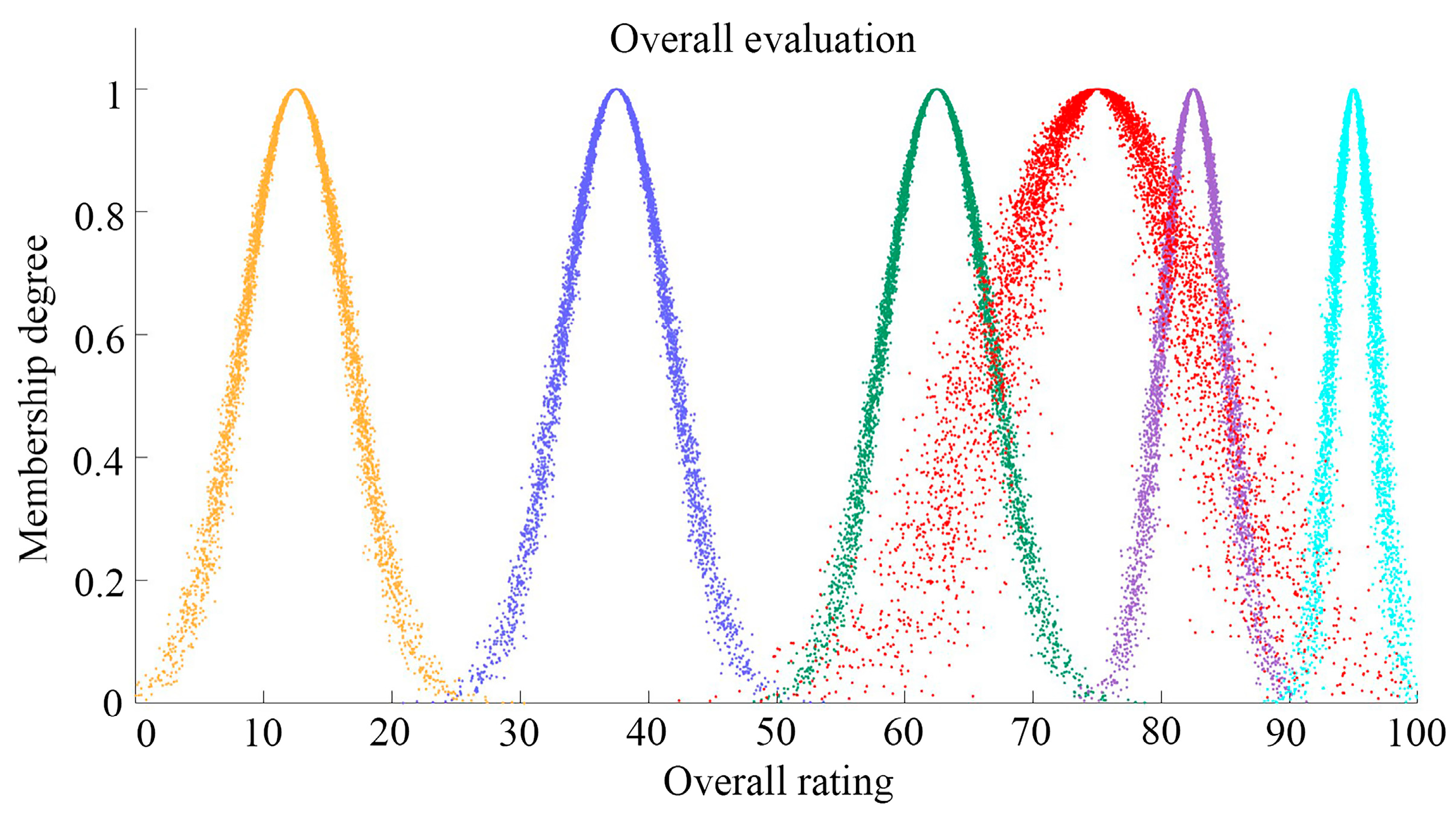
4.2.2. Calculation of Individual Indicator Clouds and Comprehensive Cloud
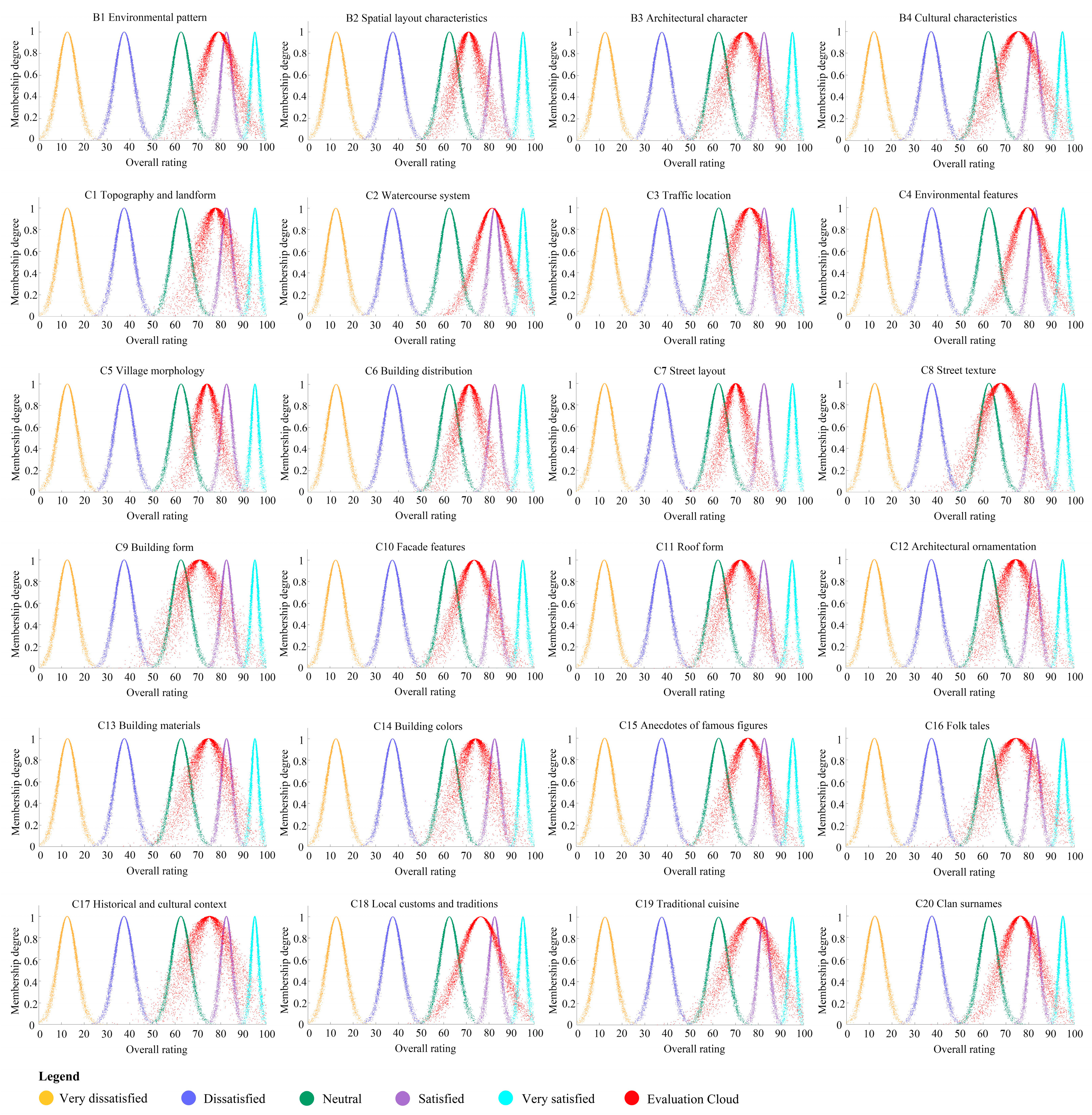
4.3. Results Analysis
4.3.1. Perception Evaluation Results of “Environmental Pattern”
4.3.2. Perception Evaluation Results of “Spatial Layout Characteristics”
4.3.3. Perception Evaluation Results of “Architectural Character”
4.3.4. Perception Evaluation Results of “Cultural Characteristics”
5. Discussion
5.1. Protection and Development Strategies for Huangtutang Village Based on Perception Evaluation
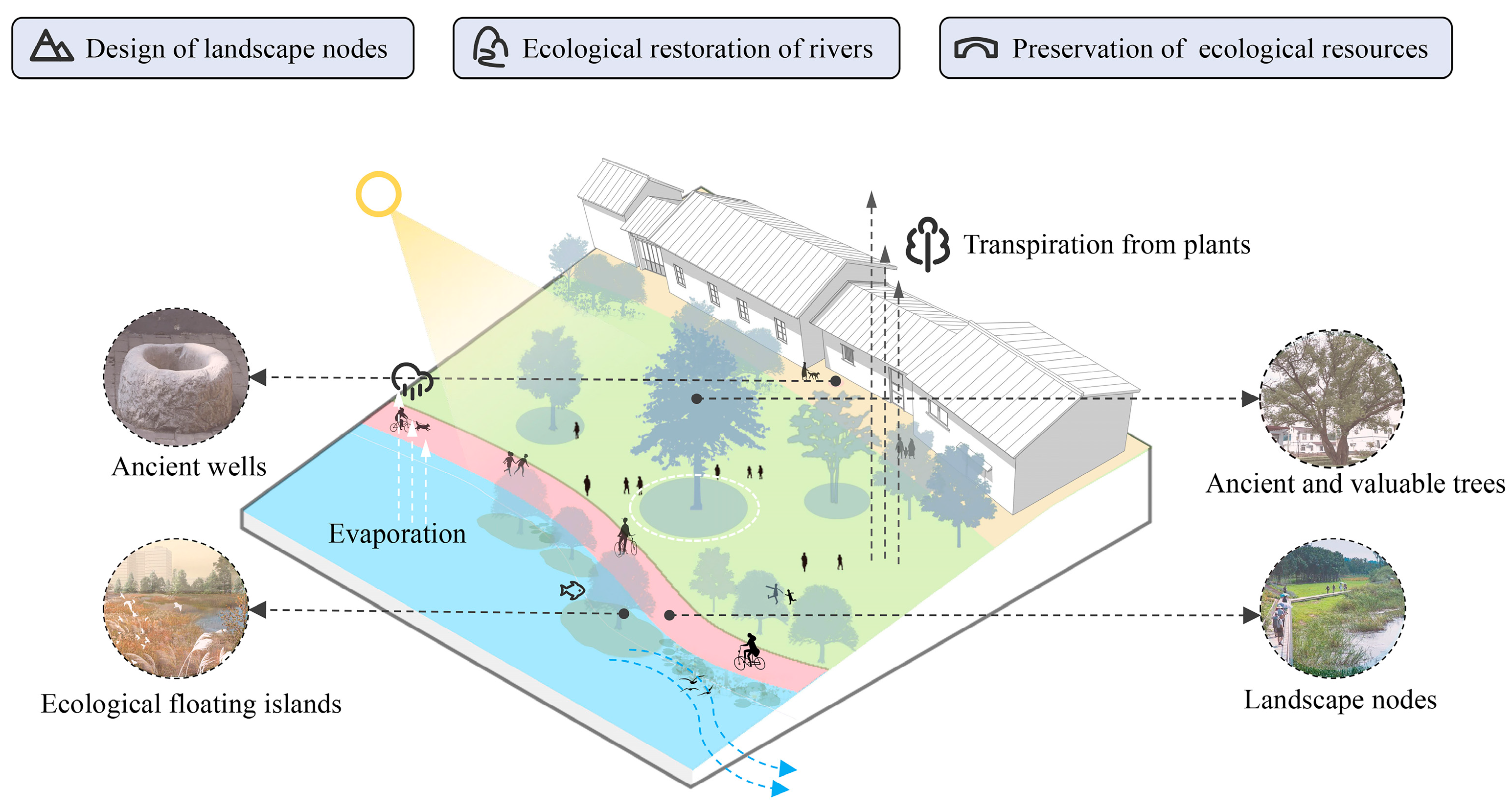
5.1.1. Restoration of Damaged Ecological Environments
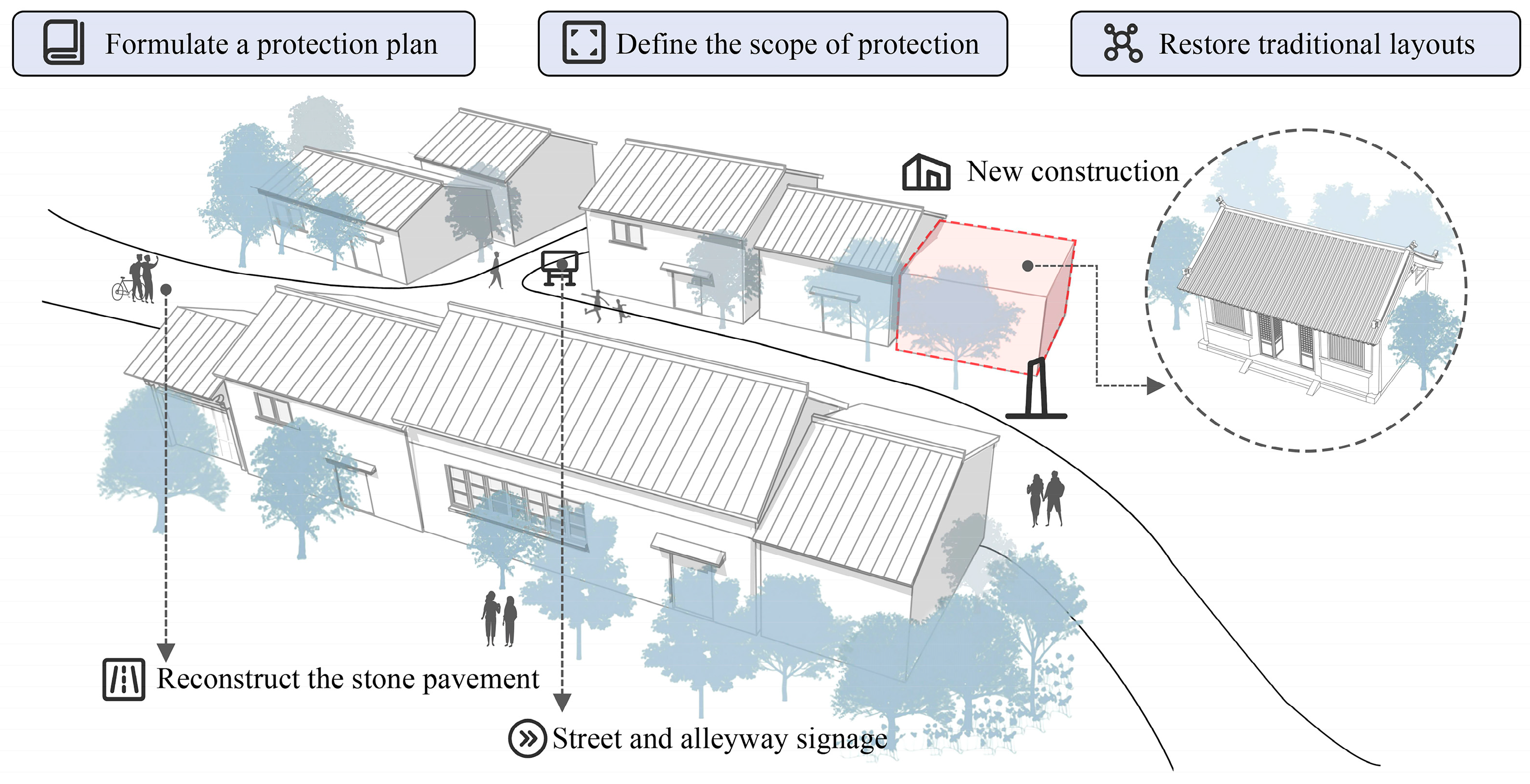
5.1.2. Repairing Fragmented Historical Textures
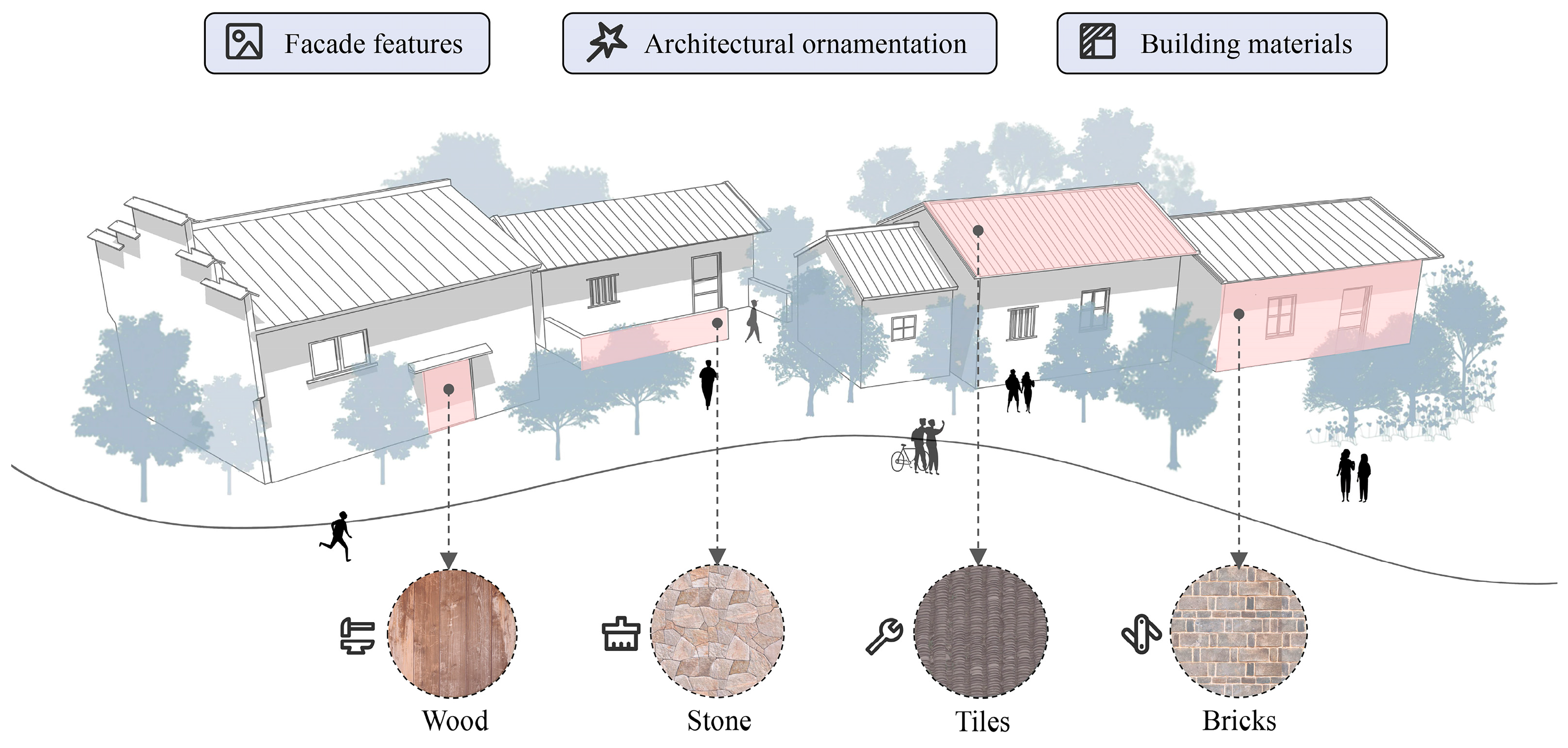
5.1.3. Preservation and Inheritance of Architectural Heritage
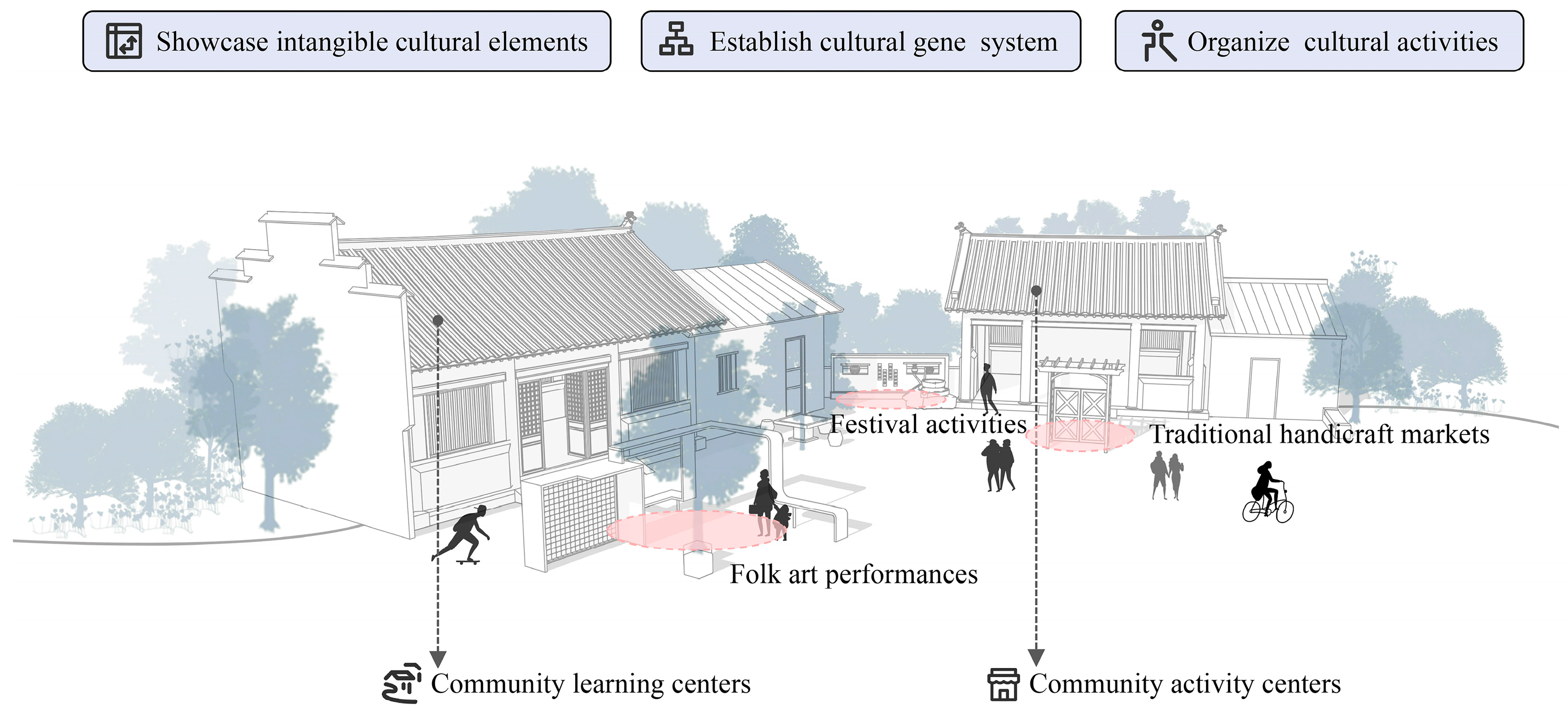
5.1.4. Continuation of Diverse Historical Contexts
5.2. Applications and Contributions of Landscape Gene Perception Evaluation for Traditional Villages
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Target Layer | Criterion Layer | Factor Layer | Subjective Weight | Objective Weight | Combined Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landscape Gene Perception Evaluation System for Huangtutang Village | B1 Environmental pattern | C1 Topography and landform | 0.0271 | 0.0658 | 0.0534 |
| C2 Watercourse system | 0.036 | 0.0684 | 0.0580 | ||
| C3 Traffic location | 0.0231 | 0.0415 | 0.0356 | ||
| C4 Environmental features | 0.0575 | 0.1028 | 0.0882 | ||
| B2 Spatial layout characteristics | C5 Village morphology | 0.0662 | 0.0537 | 0.0577 | |
| C6 Building distribution | 0.0444 | 0.0195 | 0.0275 | ||
| C7 Street layout | 0.0679 | 0.0576 | 0.0609 | ||
| C8 Street texture | 0.0334 | 0.0171 | 0.0224 | ||
| B3 Architectural character | C9 Building form | 0.0595 | 0.0114 | 0.0269 | |
| C10 Facade features | 0.1082 | 0.0810 | 0.0898 | ||
| C11 Roof form | 0.0651 | 0.0609 | 0.0623 | ||
| C12 Architectural ornamentation | 0.1081 | 0.0930 | 0.0979 | ||
| C13 Building materials | 0.0596 | 0.0527 | 0.0549 | ||
| C14 Building colors | 0.0479 | 0.0463 | 0.0468 | ||
| B4 Cultural characteristics | C15 Anecdotes of famous figures | 0.0313 | 0.0127 | 0.0186 | |
| C16 Folk tales | 0.0279 | 0.0442 | 0.0390 | ||
| C17 Historical and cultural context | 0.0311 | 0.0392 | 0.0366 | ||
| C18 Local customs and traditions | 0.0518 | 0.1051 | 0.0880 | ||
| C19 Traditional cuisine | 0.0196 | 0.0222 | 0.0214 | ||
| C20 Clan surnames | 0.0343 | 0.0047 | 0.0142 |
| Indicators | Weight | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 Environmental pattern | 79.025 | 7.424 | 1.310 | 0.2352 |
| B2 Spatial layout characteristics | 70.990 | 5.881 | 1.427 | 0.1685 |
| B3 Architectural character | 73.612 | 8.138 | 2.042 | 0.3785 |
| B4 Cultural characteristics | 75.759 | 9.443 | 1.725 | 0.2173 |
| C1 Topography and landform | 75.043 | 7.875 | 1.720 | 0.0534 |
| C2 Watercourse system | 77.653 | 6.77 | 2.256 | 0.0580 |
| C3 Traffic location | 81.361 | 7.384 | 0.732 | 0.0356 |
| C4 Environmental features | 76.139 | 8.066 | 1.810 | 0.0882 |
| C5 Village morphology | 79.509 | 7.588 | 0.955 | 0.0577 |
| C6 Building distribution | 73.912 | 5.349 | 1.230 | 0.0275 |
| C7 Street layout | 71.259 | 5.800 | 1.449 | 0.0609 |
| C8 Street texture | 70.097 | 5.341 | 1.365 | 0.0224 |
| C9 Building form | 67.676 | 8.827 | 1.817 | 0.0269 |
| C10 Facade features | 70.708 | 9.261 | 2.689 | 0.0898 |
| C11 Roof form | 73.569 | 8.007 | 1.344 | 0.0623 |
| C12 Architectural ornamentation | 72.384 | 8.110 | 1.997 | 0.0979 |
| C13 Building materials | 74.537 | 7.979 | 2.207 | 0.0549 |
| C14 Building colors | 74.630 | 8.470 | 2.261 | 0.0468 |
| C15 Anecdotes of famous figures | 74.102 | 7.731 | 2.410 | 0.0186 |
| C16 Folk tales | 75.333 | 8.112 | 1.607 | 0.0390 |
| C17 Historical and cultural context | 74.444 | 10.420 | 2.296 | 0.0366 |
| C18 Local customs and traditions | 75.125 | 9.545 | 2.979 | 0.0880 |
| C19 Traditional cuisine | 76.361 | 9.214 | 0.943 | 0.0214 |
| C20 Clan surnames | 76.944 | 10.293 | 1.807 | 0.0142 |
| Target layer | 75.043 | 7.875 | 1.72 | 1.0000 |
References
- Setijanti, P.; Defiana, I.; Setyawan, W.; Silas, J.; Firmaningtyas, S.; Ernawati, R. Traditional settlement livability in creating sustainable living. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 179, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tang, C.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, X. Comprehensive evaluation of the cultural inheritance level of tourism-oriented traditional villages: The example of Beijing. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2023, 48, 101166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xiang, H.; Xiang, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, J. Development types and design guidelines for the conservation and utilization of spatial environment in traditional villages in Southern China. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2024, 23, 1699–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ge, J.; Bai, M.; Yao, M.; He, L.; Chen, M. Toward classification-based sustainable revitalization: Assessing the vitality of traditional villages. Land Use Policy 2022, 116, 106060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zhou, J.; Deng, Y. Heritage values of ancient vernacular residences in traditional villages in Western Hunan, China: Spatial patterns and influencing factors. Build. Environ. 2021, 188, 107473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, P.; Tan, M. Cultural landscape genome maps: A scientific language perspective of traditional settlements. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2024, 44, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Long, T.; Ișık, C.; Yan, J.; Zhong, Q. Promoting the sustainable development of traditional villages: Exploring the comprehensive assessment, spatial and temporal evolution, and internal and external impacts of traditional village human settlements in hunan province. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Xu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, G. Making rural micro-regeneration strategies based on resident perceptions and preferences for traditional village conservation and development: The case of Huangshan Village, China. Land 2021, 10, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jin, T.; Xiang, W.; Huang, Q. Exploring the dynamic evolutionary mechanism of game model on the protection of traditional villages. Reg. Sustain. 2022, 3, 188–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q. Research on the changes in cultural landscape of tourist-type traditional Chinese villages from the perspective of cultural memory: Taking Anzhen Village in Chongqing as an example. Land 2023, 12, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shan, Y.; Xia, S.; Cao, J. Traditional village morphological characteristics and driving mechanism from a rural sustainability perspective: Evidence from Jiangsu Province. Buildings 2024, 14, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, L. Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of traditional villages in Fujian Province, China. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Liu, Y.; Wan, Z.; Liang, W. Evaluation system and influencing paths for the integration of culture and tourism in traditional villages. J. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 2489–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wu, B. Revitalizing traditional villages through rural tourism: A case study of Yuanjia Village, Shaanxi Province, China. Tour. Manag. 2017, 63, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Sang, K.; Li, G.; Lin, G.; Luo, Q.; Giordano, A. Heritage evaluation and analysis based on entropy weight method: The study of Wengji ancient village in China. J. Hous. Built Environ. 2023, 38, 1843–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Shi, D. Rural heritage: Value, conservation and Revitalisation—From the perspective of the human-land relationship. Built Herit. 2019, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; She, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, S. Study on ecological adaptability of traditional village construction in Hainan volcanic areas. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2023, 22, 494–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Li, L.; Pang, Y. Analysis on climate adaptability of traditional villages in Lingnan, China--World Cultural Heritage Site of Majianglong Villages as example. Procedia Eng. 2017, 205, 2011–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.C.; Hsu, M.F.; Hsieh, C.M. An example of ecological wisdom in historical settlement: The wind environment of Huazhai village in Taiwan. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2017, 16, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Li, Z. Cultural ecology cognition and heritage value of huizhou traditional villages. Heliyon 2022, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cao, Y.; Li, G. An approach to developing and protecting linear heritage tourism: The construction of cultural heritage corridor of traditional villages in Mentougou District using GIS. Int. J. Geoheritage Parks 2023, 11, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, M. Ecomuseum, community museology, local distinctiveness, Hüsamettindere village, Bogatepe village, Turkey. J. Cult. Herit. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 5, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.L. On Construction and Utilization of Chinese Traditional Settlements Landscape’s Genetic Map. Ph.D. Thesis, Peking University, Beijing, China, 2011. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Fei, X.; Cheng, Y.; Kong, X.; Zhang, J. Cultural landscapes recognition and landscape genetic information chain analysis of traditional villages: A case study of Tanka Fishing village in Lingshui Li autonomous county. J. Nat. Resour. 2024, 39, 1760–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Tian, Y. Construction and characteristic analysis of landscape gene maps of traditional villages along ancient Qin-Shu roads, Western China. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zeng, C.; Liu, R. Environmental adaptation of traditional Chinese settlement patterns and its landscape gene mapping. Habitat Int. 2023, 135, 102808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, A.; Zhao, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C. Conservation of cave-dwelling village using Cultural Landscape Gene Theory. In Spatial Synthesis: Computational Social Science and Humanities; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 97–105. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Yang, F.; Long, X.; Liu, X.; Cheng, B.; Dou, Y. The organic renewal of traditional villages from the perspective of logical space restoration and physical space adaptation: A case study of Laoche village, China. Habitat Int. 2024, 144, 102988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Tan, M. A parameter to featuring the cultural landscape genes of traditional settlements in China: A perspective of geographical information. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, L.; Xiang, C.; Dai, W. Revitalizing rural landscapes: Applying cultural landscape gene theory for sustainable spatial planning in Linpu Village. Buildings 2024, 14, 2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, P.; Shen, X.; Liu, X.; Deng, Y.; Chen, Y. A Prototype Design of Gene Graphic Methodology for Ancient Village Landscapes Based on GIS. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2010, 12, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Josef, S.; Min, Q.; Tan, M.; Cheng, F. Visualizing the cultural landscape gene of traditional settlements in China: A semiotic perspective. Herit. Sci. 2021, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Deng, Y.; Liu, P.; Peng, H. The semiotic mechanism of cultural landscape genes of traditional settlements. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 789–803. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Liu, P.; Shen, X.; Zhou, W. Effect of traditional village landscape genes on tourists’ image construction: Case study of Zhangguying Village. J. Resour. Ecol. 2024, 15, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Chen, B.; Zhu, J.; Sun, L. Traditional Village research based on culture-landscape genes: A Case of Tujia traditional villages in Shizhu, Chongqing, China. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2024, 23, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, X.; Xu, X.; Mak, K.; Ruan, D. Construction and Application of Cultural Gene Library of Ancestral Hall in Canton Region. Teh. Vjesn. 2024, 31, 993–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Xia, X.; Wu, S. Genetic characteristics evaluation and planning design of traditional village cultural landscape: Taking Dongmen Fishing Village in Xiangshan, Zhejiang Province as an example. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2025, 24, 4572–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, C. The morphology of landscape. In The Cultural Geography Reader; Routledge: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, C.; Liu, P.; Huang, L.; Feng, S.; Li, Y. Features of architectural landscape fragmentation in traditional villages in Western Hunan, China. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhou, Y.; Xun, G. Evaluation of rural landscape resources based on cloud model and probabilistic linguistic term set. Land 2022, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.Y.; Lee, W.T.; Guizani, N.; Wang, T.M. Incentive mechanism for P2P file sharing based on social network and game theory. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2014, 41, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Lai, C.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.; He, Y. Surface water quality evaluation based on a game theory-based cloud model. Water 2018, 10, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.; Gan, W. A new cognitive model: Cloud model. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2009, 24, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Wang, J.Q. A linguistic intuitionistic cloud decision support model with sentiment analysis for product selection in E-commerce. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 21, 963–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, D.; Ding, H.; Singh, V.P.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, L. A cloud model-based approach for water quality assessment. Environ. Res. 2016, 148, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, S.; Feng, Y.; Li, Z.; Zheng, H.; Tan, J. An integrated decision-making method for product design scheme evaluation based on cloud model and EEG data. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2020, 43, 101028. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.; Ge, S.L.; Wang, N.X.; Yang, Z. Personalized product service scheme recommendation based on trust and cloud model. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 82581–82591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.W.; Zhen, J.; Zhang, J. Urban rail transit operation safety evaluation based on an improved CRITIC method and cloud model. J. Rail Transp. Plan. Manag. 2020, 16, 100206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gong, E.; Wang, D.; Teng, Y. Cloud model-based safety performance evaluation of prefabricated building project in China. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2018, 102, 3021–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Ding, M.; Zhang, Q. Flood risk assessment of urban cultural heritage based on PSR conceptual model with game theory and cloud model—A case study of Nanjing. J. Cult. Herit. 2022, 58, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Shao, Y.B.; Yang, C.; Zhao, C. The application of the game theory combination weighting-normal cloud model to the quality evaluation of surrounding rocks. Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 12, 1346536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X. Talking About Huangtutang; Jiangsu People’s Publishing House: Nanjing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Liu, C.; Deng, Y.; Shen, X.; Hu, Z.; Li, B. Study on ancient village’s protection and development which based on the concept of landscape-gene’s integrity. Econ. Geogr. 2009, 29, 1731–1736. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Dong, S. Study of landscape-image of Chinese ancient village. Geogr. Res. 1998, 17, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P. The Gene Expression and the Siqht ldentification ofthe Ancient Villages’ Cultural Landscape. J. Hengyang Norm. Univ. 2003, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P. The Landscape and Genes of Home: An In-Depth Interpretation of the Landscape Gene Map of Traditional Settlements; Commercial Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, P. The conceptual model and characterizations of landscape genome maps of traditional settlements in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2015, 70, 1592–1606. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, Y.; Liu, P. The Loess Plateau: Settlement Landscapes and Vernacular Culture; China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, P.; Deng, Y.; Zheng, W. A novel method for identifying and separating landscape genes from traditional settlements. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2015, 35, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. The analytic hierarchy process (AHP). J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1980, 41, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Poveda, C.A.; Lipsett, M.G. A review of sustainability assessment and sustainability/environmental rating systems and credit weighting tools. J. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Deng, H. Evaluating urban resource and environment carrying capacity by using an innovative indicator system based on eco-civilization—A case study of Guiyang. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 6941–6955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, X. Evaluation of water resources carrying capacity in Tarim River Basin under game theory combination weights. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, Y.; Wang, R.; Han, P. Measurement of water resources carrying capacity in Gugang Town of Central China based on human-water-agriculture framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Xiao, C.; Liang, X.; Yang, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Yao, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, W. Spatial-temporal evolution law analysis of resource and environment carrying capacity based on game theory combination weighting and GMD-GRA-TOPSIS model. Evidence from 18 cities in Henan Province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 439, 140820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D. Membership clouds and membership cloud generators. Comput. Res. Dev. 1995, 32, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Meng, J.; Zhu, L.; Han, Z. Assessing progress towards sustainable development goals for Chinese urban land use: A new cloud model approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, X. Identification model of traditional village cultural landscape elements and its application from the perspective of living heritage—A case study of Chentian Village in Wuhan. Buildings 2024, 14, 3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, M.; Xie, G.; Liu, C. Landscape ecology analysis of traditional villages: A case study of Ganjiang River Basin. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xie, W.; Li, H. The spatial evolution process, characteristics and driving factors of traditional villages from the perspective of the cultural ecosystem: A case study of Chengkan Village. Habitat Int. 2020, 104, 102250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, H.; Lin, Y.; Xie, J.; Xie, Y.; Ding, Z. Exploring the association between the built environment and positive sentiments of tourists in traditional villages in Fuzhou, China. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 80, 102465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Aziz, N.F.; Huang, M.; Yu, L.; Liu, Z. Tourist perceptions of landscape in Chinese traditional villages: Analysis based on online data. J. Tour. Cult. Chang. 2024, 22, 232–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Ma, H.; Yang, L.; Luo, S. The influence of perceived physical and aesthetic quality of rural settlements on tourists’ preferences—A case study of zhaoxing dong village. Land 2023, 12, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jin, X.; Feng, Y. Landscape reconstruction of traditional village couplets based on image recognition algorithm. J. Opt. 2023, 52, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Gong, K.; Leng, J. Study on the inter-village space of a traditional village group in Huizhou Region: Hongguan Village group as an example. Front. Archit. Res. 2020, 9, 588–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Tian, Y.; Gao, B.; Wang, S.; Qi, Y.; Zou, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, R. A study on identifying the spatial characteristic factors of traditional streets based on visitor perception: Yuanjia Village, Shaanxi Province. Buildings 2024, 14, 1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.A.E. The architectural form and landscape as a harmonic entity in the vernacular settlements of Southwestern Saudi Arabia. Habitat Int. 2000, 24, 455–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Tan, D.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Z. Traditional village perception and protection behavior: The mediating role of local identity and the impact of different population differences. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2024, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Li, Z.; Xia, S.; Gao, M.; Ye, M.; Shi, T. Research on the spatial sequence of building facades in huizhou regional traditional villages. Buildings 2023, 13, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Liu, C. Assessment of visual quality and social perception of cultural landscapes: Application to Anyi traditional villages, China. Heritage Science. 2024, 12, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhan, Q.; Du, G.; Wei, Y. The effects of involvement, authenticity, and destination image on tourist satisfaction in the context of Chinese ancient village tourism. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2024, 60, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Chu, S.; Du, X. Safeguarding traditional villages in China: The role and challenges of Rural Heritage preservation. Built Herit. 2019, 3, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Hu, Y. Production and inheritance of intangible cultural landscape gene in traditional villages: A case study of Huangdu village in Tongdong autonomous county. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 42, 208–215. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Lv, S.; Chen, Z.; Cui, J.; Li, W.; Liu, Y. Traditional Villages’ Cultural Tourism Spatial Quality Evaluation. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.J.; Leung, H.H. Becoming a traditional village: Heritage protection and livelihood transformation of a Chinese village. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shi, Q.; Wang, G. Exploration of the landscape gene characteristics of traditional villages along the Jinzhong section of the Wanli Tea Road from the perspective of the village temple system. Land 2024, 13, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, B.; Huang, Z.; Liu, J. Research on the Revitalization Path of Ethnic Villages Based on the Inheritance of Spatial Cultural Genes—Taking Tujia Village of Feng Xiang Xi in Guizhou Province as a Case Study. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Order of the Matrix | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R.I. | 0 | 0 | 0.52 | 0.89 | 1.12 | 1.24 |
| Landscape Gene Perception Evaluation Levels | Grade Intervals | Cloud Model Characteristic Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Very dissatisfied | [0.0, 25.0) | (12.5, 4.1667, 0.01) |
| Dissatisfied | [25.0, 50.0) | (37.5, 4.1667, 0.01) |
| Neutral | [50.0, 75.0) | (62.5, 4.1667, 0.01) |
| Satisfied | [75.0, 90.0) | (82.5, 2.5, 0.01) |
| Very satisfied | [90.0, 100.0] | (95.0, 1.1667, 0.01) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Chen, S.; Yu, L.; Brown, R.; Zhu, R. Evaluating Landscape Gene Perception in Traditional Villages for Sustainable Development: A Methodological Framework Integrating Game Theory and the Cloud Model. Buildings 2025, 15, 3441. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193441
Li X, Chen S, Yu L, Brown R, Zhu R. Evaluating Landscape Gene Perception in Traditional Villages for Sustainable Development: A Methodological Framework Integrating Game Theory and the Cloud Model. Buildings. 2025; 15(19):3441. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193441
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaobin, Siyi Chen, Lemin Yu, Robert Brown, and Rong Zhu. 2025. "Evaluating Landscape Gene Perception in Traditional Villages for Sustainable Development: A Methodological Framework Integrating Game Theory and the Cloud Model" Buildings 15, no. 19: 3441. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193441
APA StyleLi, X., Chen, S., Yu, L., Brown, R., & Zhu, R. (2025). Evaluating Landscape Gene Perception in Traditional Villages for Sustainable Development: A Methodological Framework Integrating Game Theory and the Cloud Model. Buildings, 15(19), 3441. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193441






