Hierarchical Prediction of Subway-Induced Ground Settlement Based on Waveform Characteristics and Machine Learning with Applications to Building Safety
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodologies
2.1. Evaluation Indices of Model Accuracy
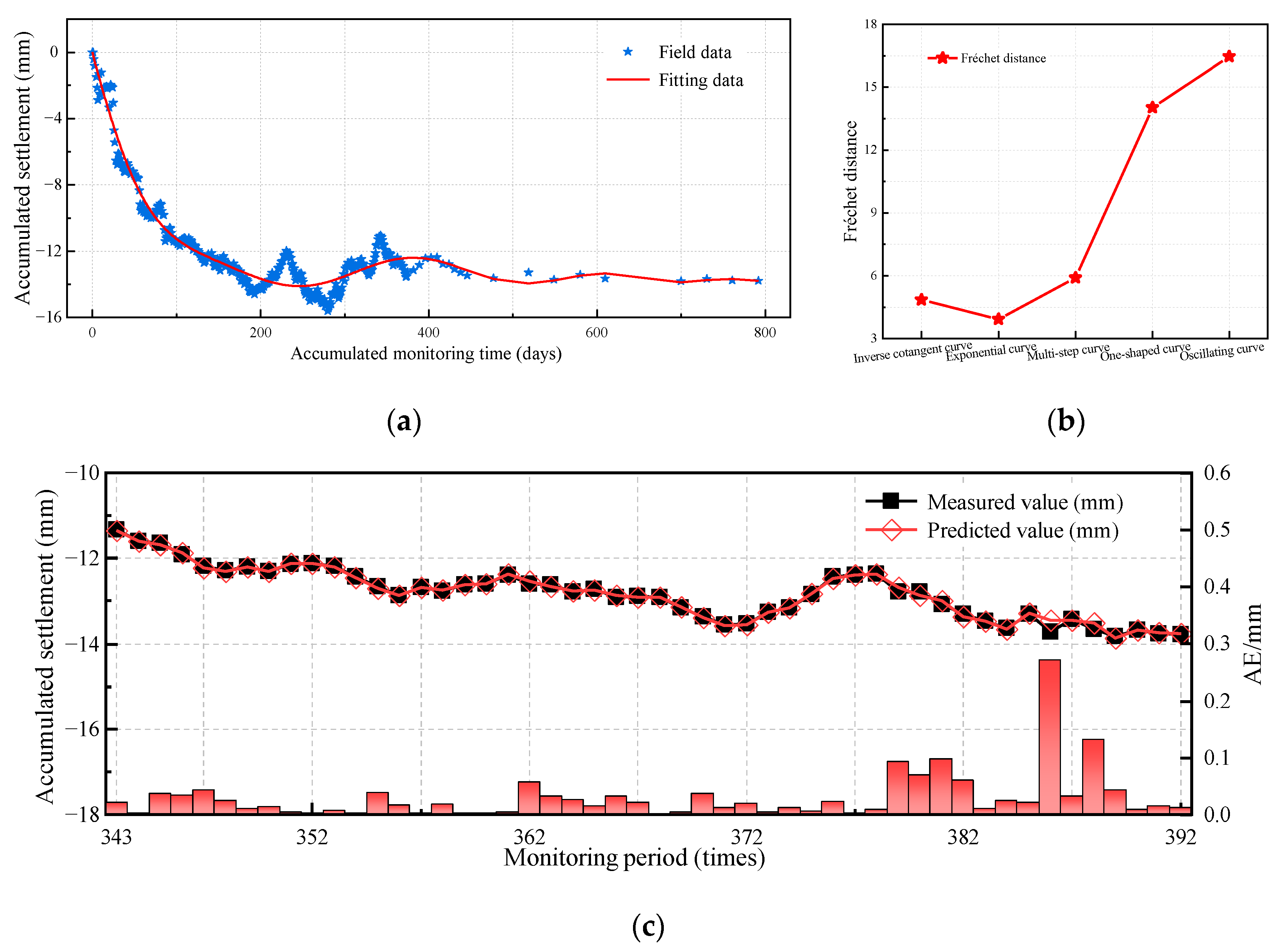
2.2. Fréchet Distance

2.3. Prediction Modules
2.3.1. CI Noise Reduction Model
2.3.2. ARIMA Model
2.3.3. AM-LSTM Model
2.3.4. GA-SVR Model
2.3.5. PSO-BP Model
3. Research Overview
3.1. Project Background
3.2. Data Source
4. Result Analyses
4.1. Classification of Settlement Curves
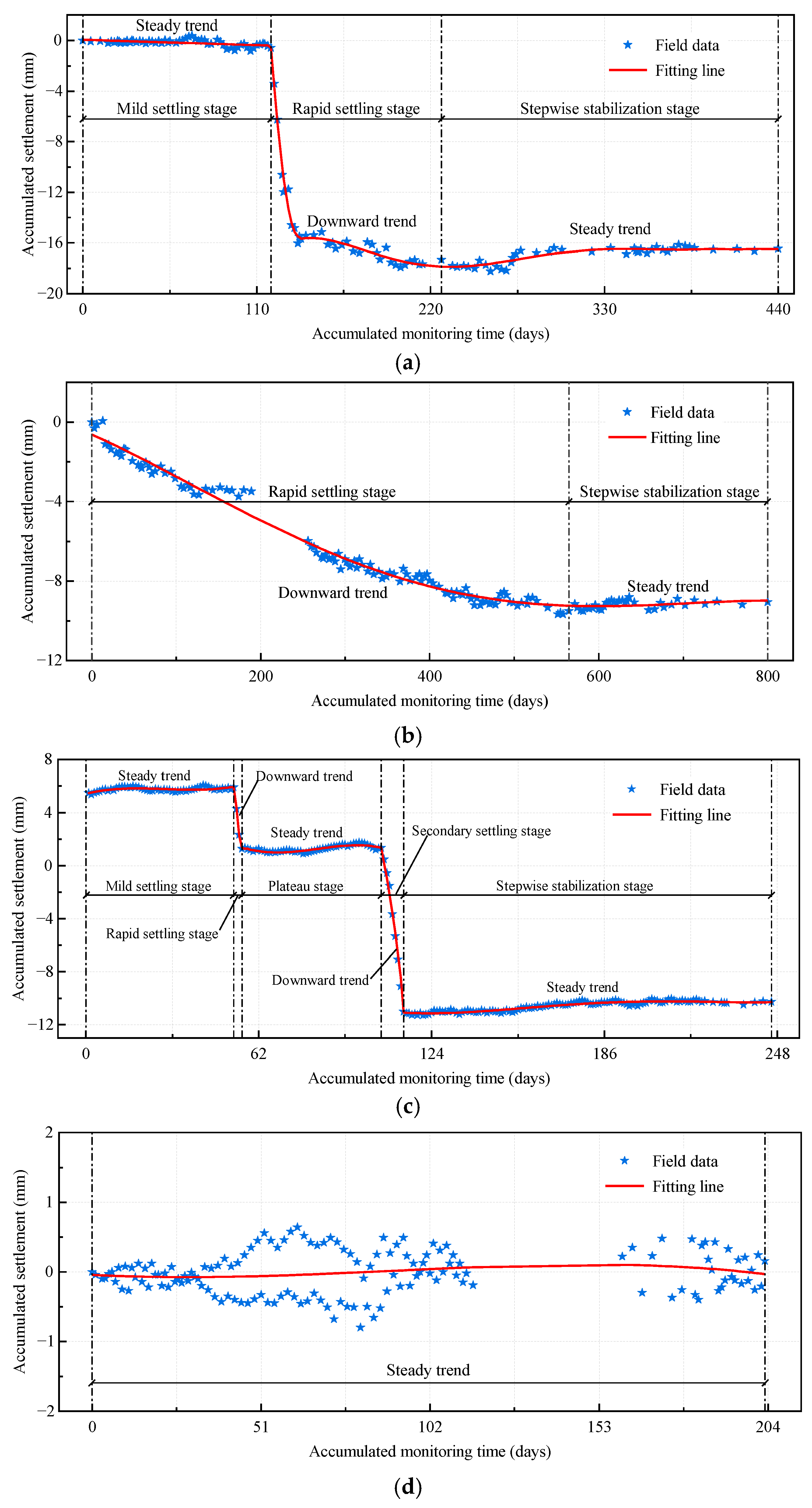
4.1.1. Fluctuation Characteristics
4.1.2. Classification Results of Subway Settlement Curves
4.1.3. Settlement Curve Classification Criteria
4.2. Selection of Optimal Module
4.3. Validation of the Subway Settlement Layering Prediction Model
4.3.1. Main Module Determination
4.3.2. Selective Module Prediction
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, W.; Hu, Y.; Hu, C.; Yang, M. An Agent-Based Simulation of Deep Foundation Pit Emergency Evacuation Modeling in the Presence of Collapse Disaster. Symmetry 2018, 10, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wu, R.; Congress, S.S.C.; Du, Q.; Cai, G.; Li, Z. Design Optimization of the Soil Nail Wall-Retaining Pile-Anchor Cable Supporting System in a Large-Scale Deep Foundation Pit. Acta Geotech. 2021, 16, 2251–2274. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.; Xiao, Y.; Lan, T.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Xiang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z. Predicting Soft Soil Settlement with a FAGSO-BP Neural Network Model. Buildings 2025, 15, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Wang, Y.; Niu, X.; Sha, S.; Yu, J. Prediction of Ground Surface Settlement by Shield Tunneling Using XGBoost and Bayesian Optimization. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 114, 105020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, H.; Wang, J.; Feng, J. A Model Based on Neural Network to Predict Surface Settlement During Subway Station Construction: A Case Study of the Dongba-Zhongjie Station in Beijing, China. Buildings 2025, 15, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, R.N.; Moh, Z.-C. Prediction of Long-Term Settlements Induced by Shield Tunneling. J. Geoengin. 2006, 1, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.; Liu, J. Deformation Monitoring and Control of Geotechnical Engineering Based on Intelligent Optimal Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2019 11th International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation (ICMTMA), Qiqihar, China, 28–29 April 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 341–344. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Du, X.; Li, P. Predictions of Ground Surface Settlement for Shield Tunnels in Sandy Cobble Stratum Based on Stochastic Medium Theory and Empirical Formulas. Undergr. Space 2023, 11, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.; Ma, J.; Han, M. Online Prediction of Noisy Time Series: Dynamic Adaptive Sparse Kernel Recursive Least Squares from Sparse and Adaptive Tracking Perspective. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2020, 91, 103547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Kasama, K.; Wang, G.; Takahashi, A. Assessing the Influence of Geotechnical Uncertainty on Existing Tunnel Settlement Caused by New Tunneling Underneath. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2025, 155, 106189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kwon, K.; Pham, K.; Oh, J.-Y.; Choi, H. Surface Settlement Prediction for Urban Tunneling Using Machine Learning Algorithms with Bayesian Optimization. Autom. Constr. 2022, 140, 104331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Ding, H.; Miao, L.; Gong, C. Predictive Model for the Surface Settlement Caused by the Excavation of Twin Tunnels. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 114, 104014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Hossain, M.B.; Chon, K.H. AR and ARMA Model Order Selection for Time-Series Modeling with ImageNet Classification. Signal Process. 2021, 183, 108026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Chen, X.; Lu, D.; Zhang, D.; Su, D. Theoretical Prediction of Ground Settlements Due to Shield Tunneling in Multi-Layered Soils Considering Process Parameters. Undergr. Space 2024, 16, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, J.; Shi, Z.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Jin, D.; Dong, G. Prediction of Surface Settlement Induced by Large-Diameter Shield Tunneling Based on Machine-Learning Algorithms. Geofluids 2022, 2022, 4174768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, R.; Wu, C.; Goh, A.T.C.; Lacasse, S.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H. State-of-the-Art Review of Soft Computing Applications in Underground Excavations. Geosci. Front. 2020, 11, 1095–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Xu, B.; Kong, F.; Ma, Y. Intelligent Prediction Method for Settlement Curves of Shield Tunnel Based on Machine Learning Algorithms. J. Beijing Univ. Technol. 2024, 50, 1285–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado-Vara, R.; Martin Del Rey, A.; Pérez-Palau, D.; de-la-Fuente-Valentín, L.; Corchado, J.M. Web Traffic Time Series Forecasting Using LSTM Neural Networks with Distributed Asynchronous Training. Mathematics 2021, 9, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, F.; Haq, S.; Rakib, M.; Ahmed, T.; Jamal, Z.; Siam, Z.S.; Hasan, R.T.; Adnan, M.S.G.; Dewan, A.; Rahman, R.M. Water Level Forecasting Using Spatiotemporal Attention-Based Long Short-Term Memory Network. Water 2022, 14, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yuan, J. Soil Disturbance and Ground Movement under Shield Tunnelling and Its Intelligent Prediction by Using ANN Technology. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2001, 23, 261–267. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.P.; Li, J.P.; Liu, G.Y.; Zhou, P. Prediction of Dredged Soil Settlement Based on Improved BP Neural Network. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1337, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagmur, N.; Musaoglu, N. The Comparison of ARIMA and LSTM in Forecasting of Long-Term Surface Movements Derived from PSINSAR. In Proceedings of the Earth Observing Systems XXVIII, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 August 2023; p. 31. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.-D.; Hua, S.-S.; Yan, J.-S. Long-Term Settlement of Subway Tunnel and Prediction of Settlement Trough in Coastal City Shanghai. In Proceedings of the GeoShanghai 2018 International Conference: Multi-physics Processes in Soil Mechanics and Advances in Geotechnical Testing, Shanghai, China, 27–30 May 2018; Hu, L., Gu, X., Tao, J., Zhou, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 458–467, ISBN 978-981-13-0094-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, X.; Zhang, R.; Shama, A.; Li, S.; Xie, L.; Lv, J.; Fu, Y.; Wu, R.; Liu, G. Ground Deformation Pattern Analysis and Evolution Prediction of Shanghai Pudong International Airport Based on PSI Long Time Series Observations. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Qin, Y.; Meng, X.; Xie, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y. Prediction Model of Land Surface Settlement Deformation Based on Improved LSTM Method: CEEMDAN-ICA-AM-LSTM (CIAL) Prediction Model. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0298524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, P.; Liu, F.; Zhang, J. Land Subsidence Prediction Model Based on the Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network Optimized Using the Sparrow Search Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-S.; Yuan, Y.; Long, M.; Yao, R.-H.; Jia, L.; Liu, M. Prediction of Surface Settlement around Subway Foundation Pits Based on Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Deep Learning Models. Comput. Geotech. 2024, 168, 106149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fréchet, M. Sur Quelques Points Du Calcul Fonctionnel. Rend. Circ. Matem. Palermo 1906, 22, 1–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiter, T.; Mannila, H. Computing Discrete Fréchet Distance. 1994. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:16010565 (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Gudmundsson, J.; Van Renssen, A.; Saeidi, Z.; Wong, S. Translation Invariant Fréchet Distance Queries. Algorithmica 2021, 83, 3514–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weise, J.; Mostaghim, S. Many-Objective Pathfinding Based on Fréchet Similarity Metric. In Evolutionary Multi-Criterion Optimization; Ishibuchi, H., Zhang, Q., Cheng, R., Li, K., Li, H., Wang, H., Zhou, A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 12654, pp. 375–386. ISBN 978-3-030-72061-2. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Hasanipanah, M.; Bakhshandeh Amnieh, H.; Brindhadevi, K.; Tahir, M.M. GA-SVR: A Novel Hybrid Data-Driven Model to Simulate Vertical Load Capacity of Driven Piles. Eng. Comput. 2021, 37, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Wang, Y.; Song, C.; Wang, T.; Shen, Y. Prediction of Surface Subsidence Based on PSO-BP Neural Network. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2400, 012046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Hu, M.; Zhang, H. Comparison of ARIMA and LSTM in Predicting Structural Deformation of Tunnels during Operation Period. Data 2023, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yue, J.; Zhou, Q. Dam Deformation Prediction Using SVM and ARIMA Combined Model. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2021, 13, 5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, Z. Improve the LSTM Trajectory Prediction Accuracy through an Attention Mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference & Expo (ITEC), Anaheim, CA, USA, 15–17 June 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 190–195. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Cui, J.; Zeng, T.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, F.; Guo, J.; Chen, Z.; et al. Land Subsidence Prediction in Zhengzhou’s Main Urban Area Using the GTWR and LSTM Models Combined with the Attention Mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Lin, Y.; Feng, N.; Song, C.; Wan, H. Attention Based Spatial-Temporal Graph Convolutional Networks for Traffic Flow Forecasting. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 922–929. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Li, Z.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Geng, Z. Novel Long Short-Term Memory Model Based on the Attention Mechanism for the Leakage Detection of Water Supply Processes. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern Syst. 2024, 54, 2786–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, A.; Sanku, R.; Sridevi, M.; Manusubramanian, S.; Chandar, S.K. Real-Time Human Action Prediction Using Pose Estimation with Attention-Based LSTM Network. SIViP 2024, 18, 3255–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V.N.; Vapnik, V. Statistical Learning Theory; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.-T.; Zhao, H.; Li, S. Modeling Non-Linear Displacement Time Series of Geo-Materials Using Evolutionary Support Vector Machines. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2004, 41, 1087–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Wen, X.; Li, C.; Shao, J.; Xu, J. Predicting the Energy Consumption in Buildings Using the Optimized Support Vector Regression Model. Energy 2023, 273, 127188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Zheng, H.; Liu, X. The Collapse Deformation Control of Granite Residual Soil in Tunnel Surrounding Rock: A Case Study. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 28, 2034–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.-S.; Chen, X.; Jiang, B.-Y.; Liang, G.-Q. Hybrid Genetic Algorithm and Support Vector Regression for Predicting the Shear Capacity of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Beam. Soft Comput 2024, 28, 1023–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Li, Q.; Zhao, T. Deformation Extent Prediction of Roadway Roof during Non-Support Period Using Support Vector Regression Combined with Swarm Intelligent Bionic Optimization Algorithms. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2024, 145, 105585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jia, C.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, H.; Gao, J. Investigation on the Deformation Mechanism of the Full-Section Tunnel Excavation in the Complex Geological Environment Based on the PSO-BP Neural Network. Env. Earth Sci 2023, 82, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Dai, Y.; Xu, M.; Mo, Y. Tunnel Surface Settlement Forecasting with Ensemble Learning. Sustainability 2019, 12, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Hang, D.; Wei, Y.-J.; Zhang, X.-L.; Ma, S.-Y.; Liu, Z.-X.; Zhou, S.-X.; Han, Z. Settlement Prediction of Existing Metro Induced by New Metro Construction with Machine Learning Based on SHM Data: A Comparative Study. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2023, 13, 1447–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Han, M.; Deng, Y. A Hybrid GAN-Inception Deep Learning Approach for Enhanced Coordinate-Based Acoustic Emission Source Localization. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapidis, G.M.; Naoum, M.C.; Papadopoulos, N.A.; Golias, E.; Karayannis, C.G.; Chalioris, C.E. A Novel Approach to Monitoring the Performance of Carbon-Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Retrofitting in Reinforced Concrete Beam–Column Joints. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Indicator Characteristics | Inverse Cotangent Curve | Exponential Curve | Multi-Step Curve | One-Shaped Curve | Oscillating Curve |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Value/mm | 0.062 | −0.62 | 5.913 | 0.101 | 4.332 |
| Minimum Value/mm | −17.87 | −9.264 | −11.137 | −0.075 | −1.345 |
| Mean/mm | −9.295 | −6.837 | −3.876 | −0.016 | 1.585 |
| Variance | 66.613 | 8.167 | 51.254 | 0.003 | 2.161 |
| Standard Deviation | 8.162 | 2.858 | 7.159 | 0.051 | 1.47 |
| Root Mean Square | 12.370 | 7.410 | 8.141 | 0.053 | 2.162 |
| Peak/mm | 17.932 | 8.644 | 17.049 | 0.176 | 5.676 |
| Skewness | 0.193 | 0.993 | 0.229 | 0.491 | 0.037 |
| Waveform Factor | 1.330 | 1.084 | 1.139 | 1.128 | 1.19 |
| Peak Factor | 0.005 | −0.084 | 0.726 | 1.903 | 2.003 |
| Pulse Factor | 0.007 | −0.091 | 0.827 | 2.147 | 2.383 |
| Margin factor | 0.01 | −0.097 | 0.925 | 2.368 | 2.658 |
| Cliff Factor | 1.822 | 1.326 | 1.54 | 1.611 | 2.329 |
| Trend Characteristics | Stable–decline–stable trend | Decline–stable trend | Stable–decline–stable–decline–stable trend | Stable trend | Damping trend |
| Parameter | Inverse Cotangent Curve | Exponential Curve | Multi-Step Curve | One-Shaped Curve | Oscillating Curve |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample size | 132 | 146 | 230 | 144 | 115 |
| ARIMA (p) | 2 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| ARIMA (q) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| ARIMA (d) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 2 |
| Number of training times for AL | 750 | 800 | 1200 | 850 | 600 |
| Number of particle swarm generations for GS | 12 | 14 | 20 | 12 | 12 |
| Number of particles per generation of GS | 11 | 11 | 12 | 12 | 10 |
| Optimal ε of GS | 0.181 | 0.07 | 0.574 | 0.046 | 0.029 |
| Optimal C of GS | 7.929 | 8.707 | 2.015 | 9.065 | 4.775 |
| Optimal G of GS | 3.788 | 69.884 | 7.048 | 4.159 | 30.505 |
| C1 = C2 of PB | 2.05 | 1.85 | 2.45 | 1.9 | 2 |
| Number of evolutions of PB | 5 | 8 | 10 | 7 | 4 |
| Maximum inertia weight of PB | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.8 |
| Minimum inertia weight of PB | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Curve Categories | Predictive Models | (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inverse cotangent curve | ARIMA | 0.0430 | 0.0461 | 0.9065 | 0.2794 |
| AM-LSTM | 0.0174 | 0.0166 | 0.9888 | 0.1003 | |
| GA-SVR | 0.0895 | 0.0892 | 0.7016 | 0.5407 | |
| PSO-BP | 0.0610 | 0.0600 | 0.8616 | 0.3641 | |
| Exponential curve | ARIMA | 0.0262 | 0.0214 | 0.9759 | 0.2324 |
| AM-LSTM | 0.0396 | 0.0359 | 0.9630 | 0.3911 | |
| GA-SVR | 0.0756 | 0.0733 | 0.7994 | 0.8077 | |
| PSO-BP | 0.0719 | 0.0568 | 0.8186 | 0.6219 | |
| Multi-step curve | ARIMA | 0.0844 | 0.0830 | 0.2232 | 0.8106 |
| AM-LSTM | 0.0464 | 0.0439 | 0.7652 | 0.4295 | |
| GA-SVR | 0.0296 | 0.0282 | 0.9046 | 0.2765 | |
| PSO-BP | 0.0276 | 0.0230 | 0.9169 | 0.2255 | |
| One-shaped curve | ARIMA | 0.0932 | 0.0731 | 0.8029 | 58.0732 |
| AM-LSTM | 0.0349 | 0.0271 | 0.9725 | 27.3645 | |
| GA-SVR | 0.0238 | 0.0238 | 0.9871 | 24.1412 | |
| PSO-BP | 0.0991 | 0.0869 | 0.7775 | 85.0881 | |
| Oscillating curve | ARIMA | 0.2729 | 0.2216 | 0.8485 | 24.7111 |
| AM-LSTM | 0.3248 | 0.2461 | 0.7855 | 21.7981 | |
| GA-SVR | 0.0104 | 0.0099 | 0.9998 | 1.5953 | |
| PSO-BP | 0.1857 | 0.1542 | 0.9299 | 29.1099 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, X.; Qin, Y.; Xie, L.; He, P.; Zhu, L. Hierarchical Prediction of Subway-Induced Ground Settlement Based on Waveform Characteristics and Machine Learning with Applications to Building Safety. Buildings 2025, 15, 3390. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183390
Meng X, Qin Y, Xie L, He P, Zhu L. Hierarchical Prediction of Subway-Induced Ground Settlement Based on Waveform Characteristics and Machine Learning with Applications to Building Safety. Buildings. 2025; 15(18):3390. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183390
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Xin, Yongjun Qin, Liangfu Xie, Peng He, and Liling Zhu. 2025. "Hierarchical Prediction of Subway-Induced Ground Settlement Based on Waveform Characteristics and Machine Learning with Applications to Building Safety" Buildings 15, no. 18: 3390. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183390
APA StyleMeng, X., Qin, Y., Xie, L., He, P., & Zhu, L. (2025). Hierarchical Prediction of Subway-Induced Ground Settlement Based on Waveform Characteristics and Machine Learning with Applications to Building Safety. Buildings, 15(18), 3390. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183390






