Effects of Stray Current on Chloride Ingress in Underground Reinforced Concrete Structures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Modeling
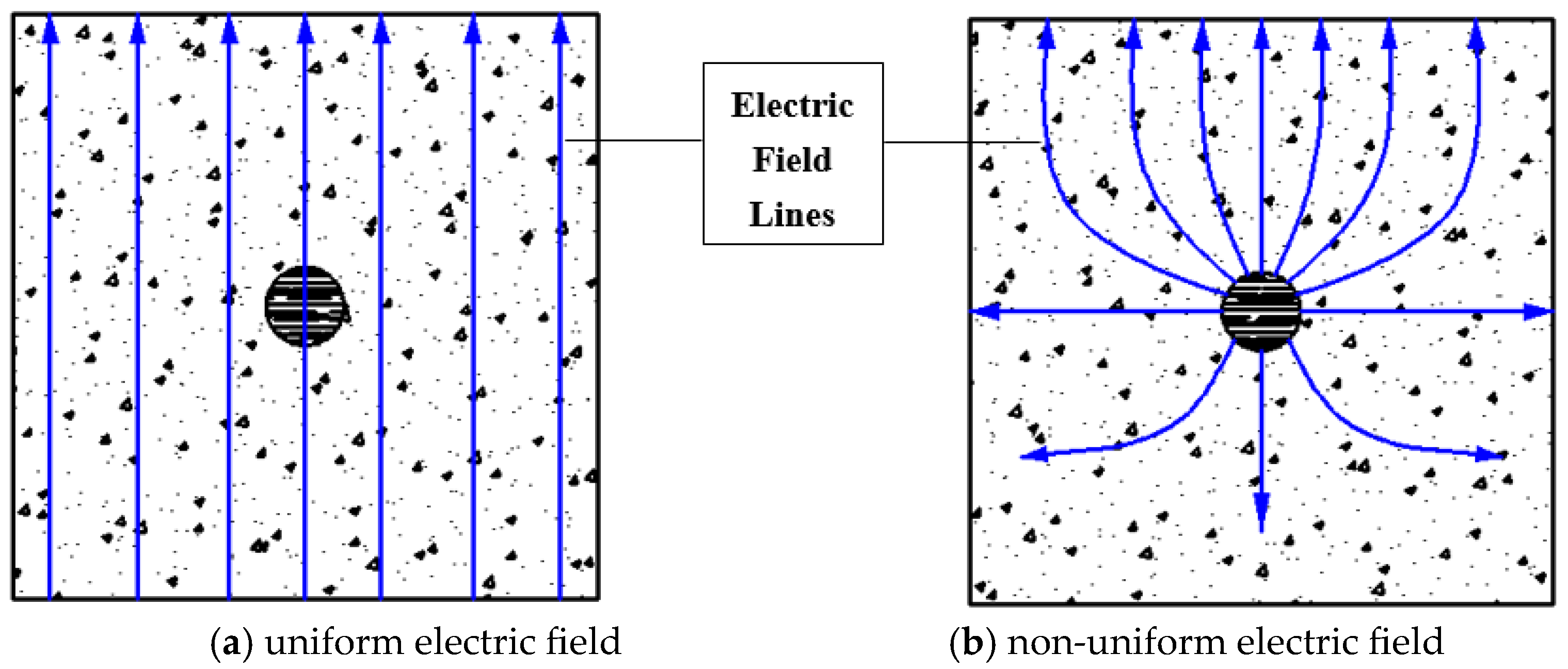
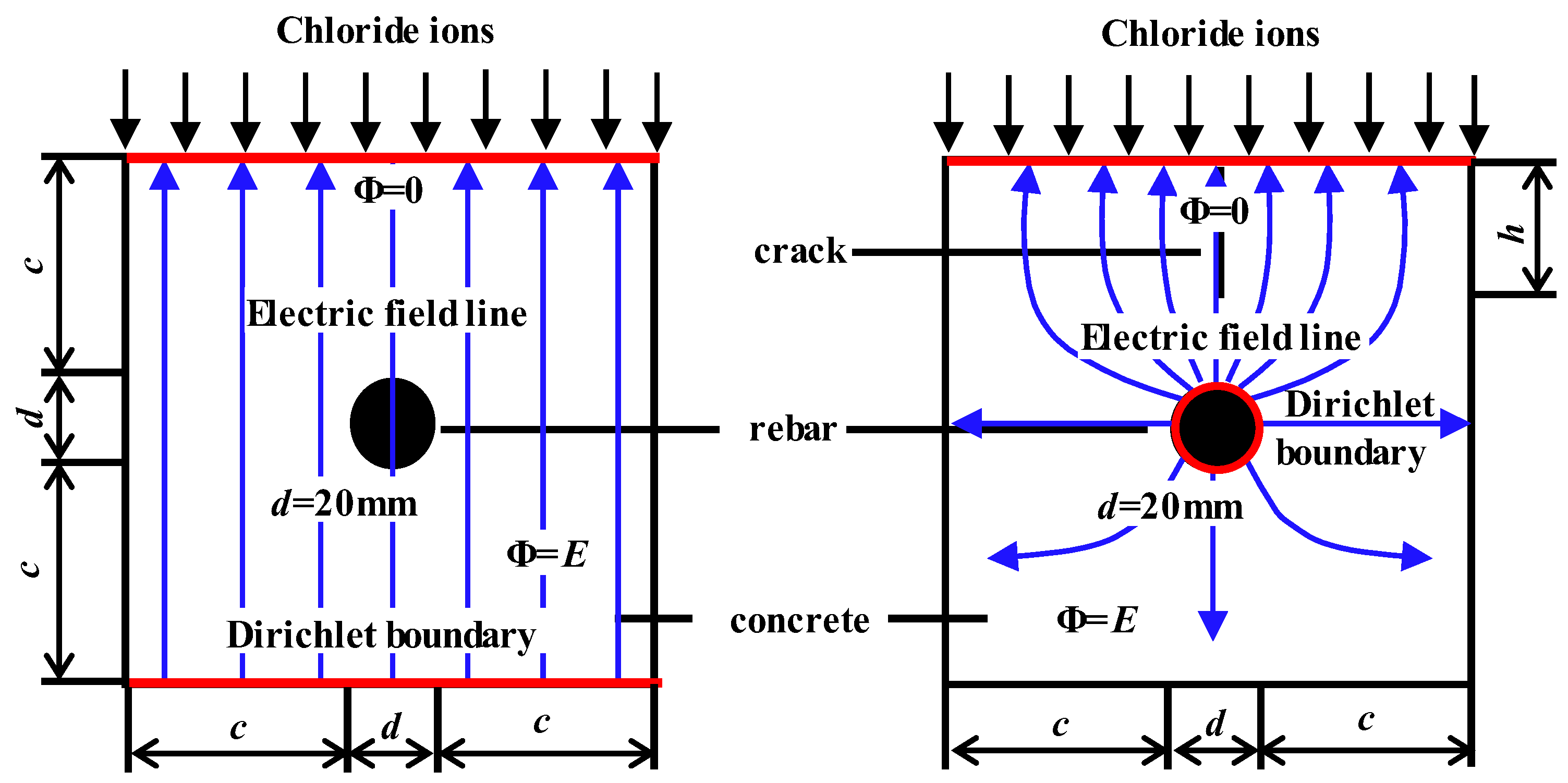
2.1. Stray Current
2.2. Chloride Ingress Model
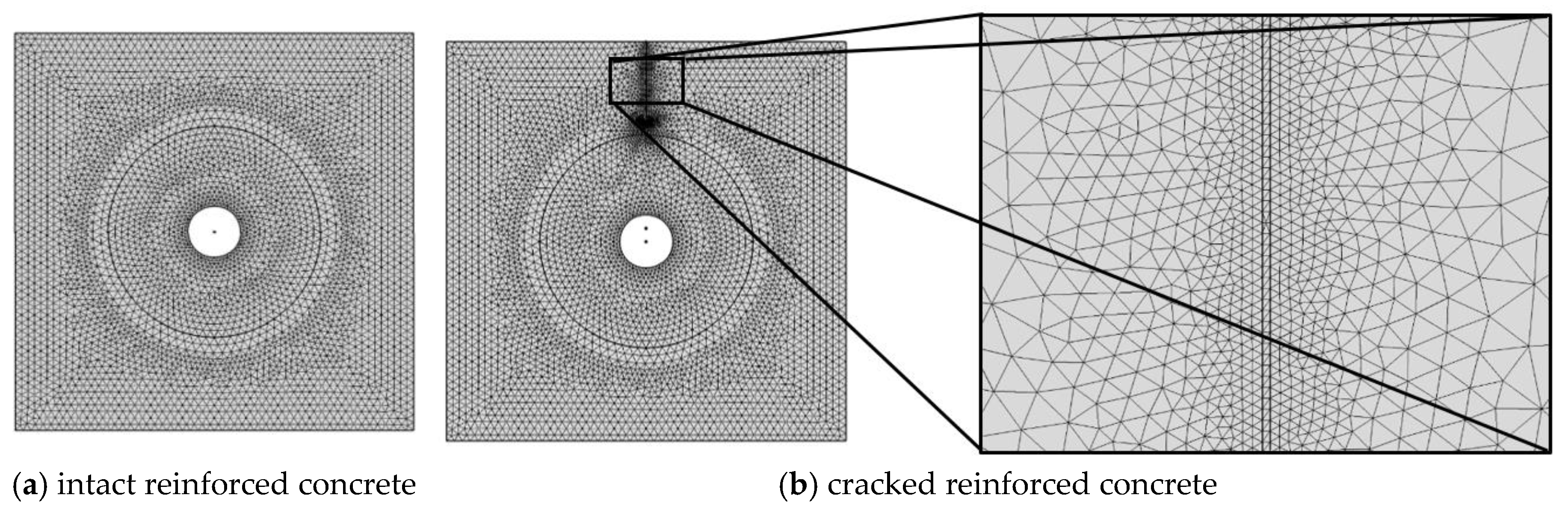
2.3. Finite Element Model
| Parameters | Values or Ranges |
|---|---|
| Rebar diameter d (mm) | 20 |
| Stray current field intensity E (V) | 0, 3, 5, 10 |
| Concrete cover thickness c (mm) | 60, 50, 40, 30 |
| Crack depth h (mm) | 10, 20, 30, 40 |
| Crack width w (µm) | 10, 30, 60, 90 |
| Environmental chloride concentration C0 (kg/m3) [49] | 16.53 |
| Chloride threshold Ct (kg/m3) [52] | 8.918 |
| Chloride diffusion coefficient D (m2/s) [56] | 6 × 10−12 |
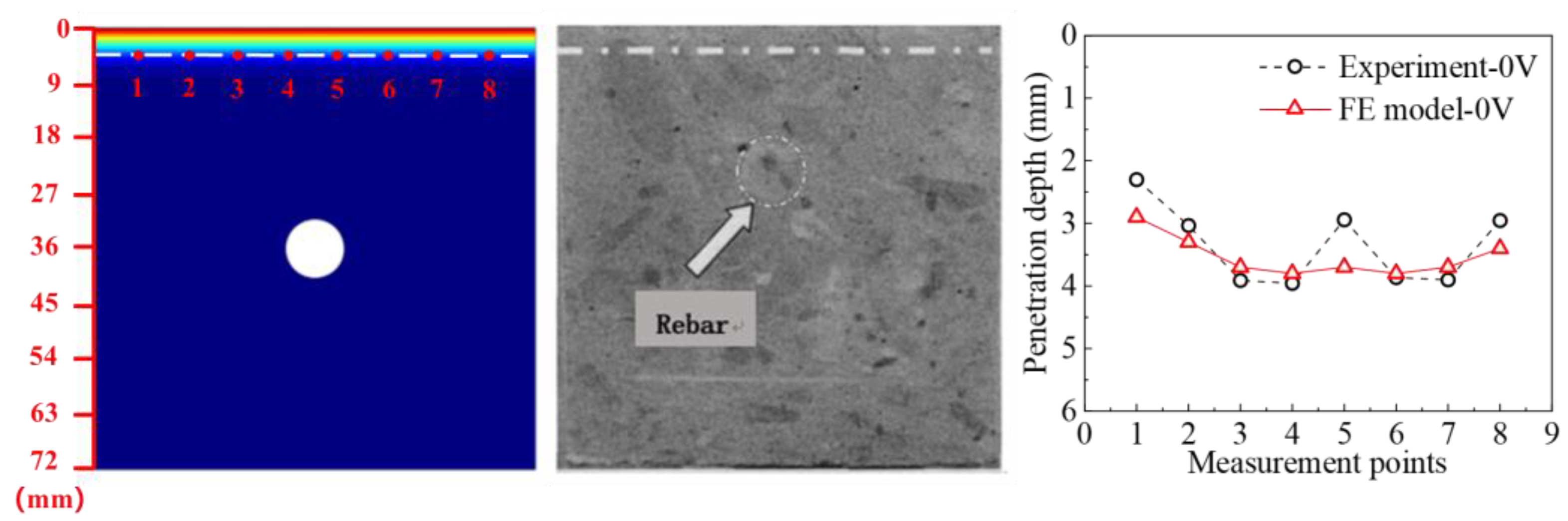
2.4. Model Verification
3. The Influence of Stray Current on Chloride Ingress
3.1. Chloride Ingress in Intact Concrete Under Stray Current
3.2. Chloride Ingress in Cracked Concrete Under Stray Current
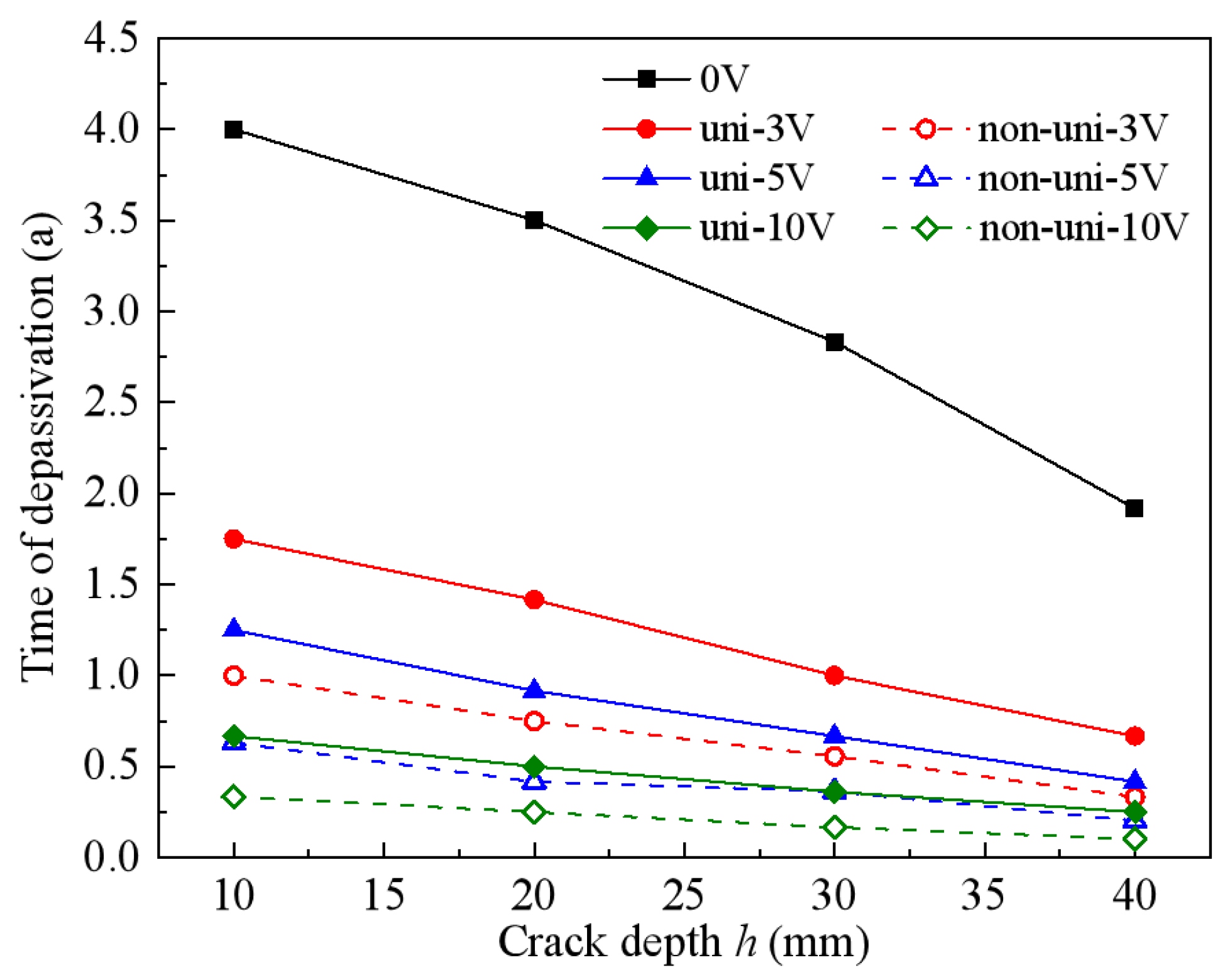
3.2.1. Combined Effects of Crack Depth and Stray Current on Chloride Ingress
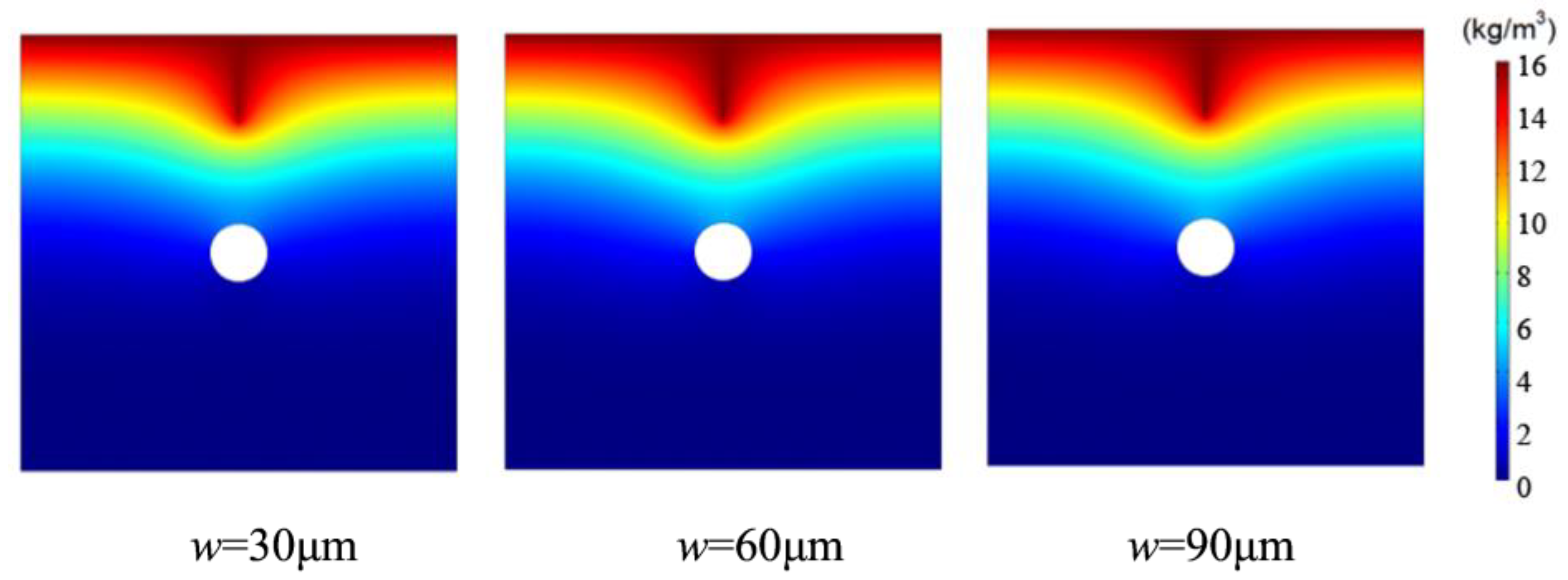
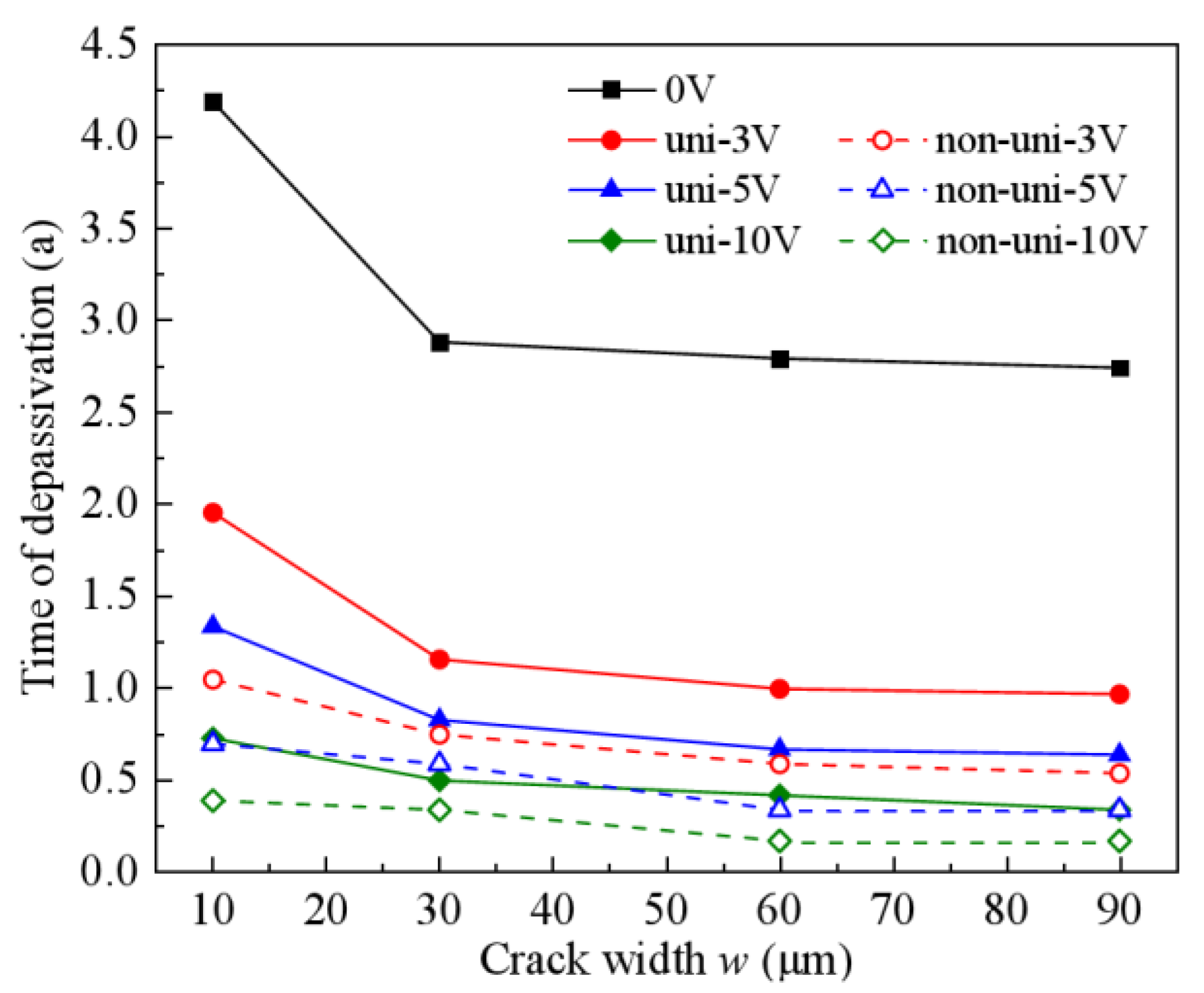
3.2.2. Combined Effects of Crack Width and Stray Current on Chloride Ingress
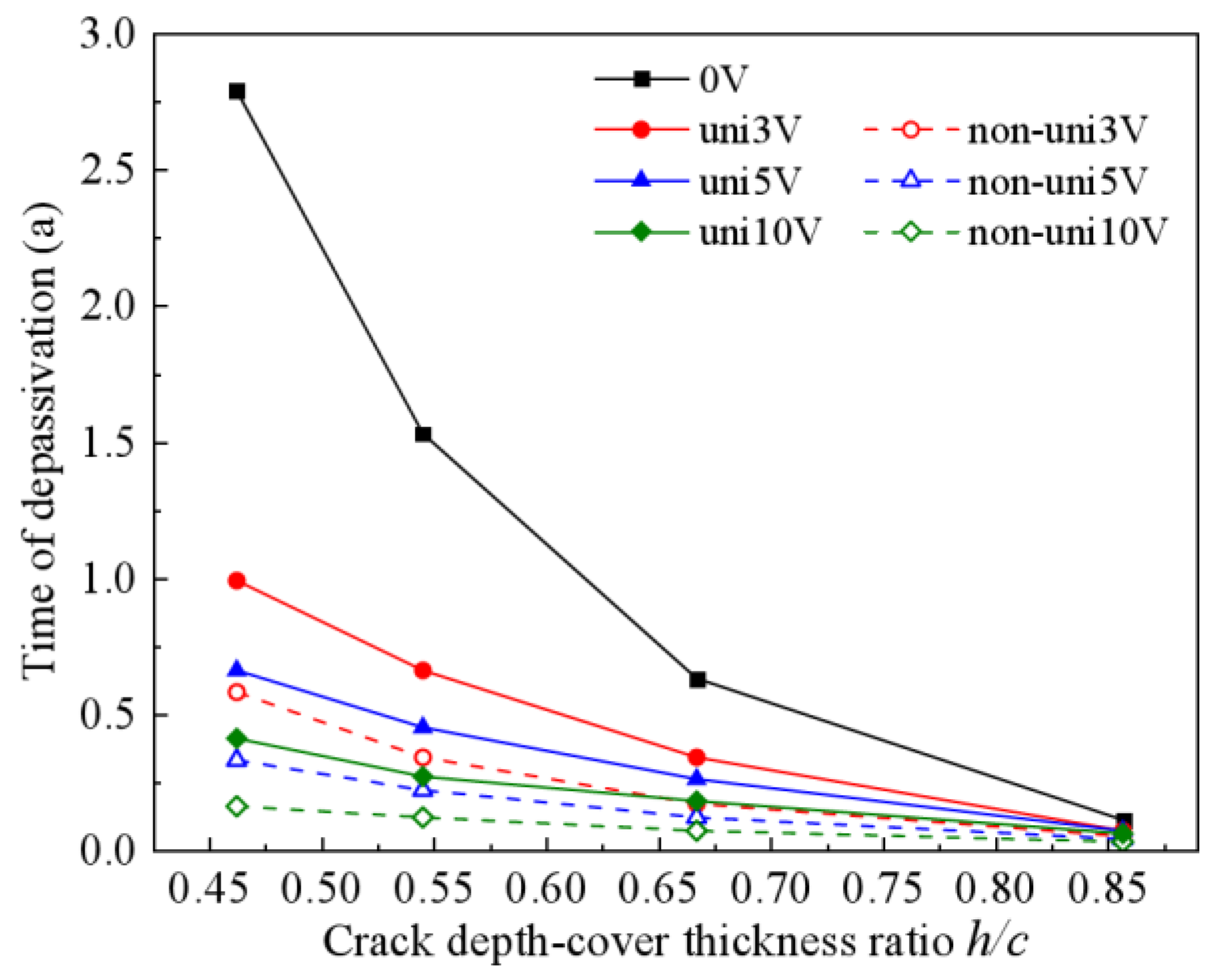
3.2.3. Combined Effects of h/c and Stray Current on Chloride Ingress
4. Deterioration Coefficient of Stray Current
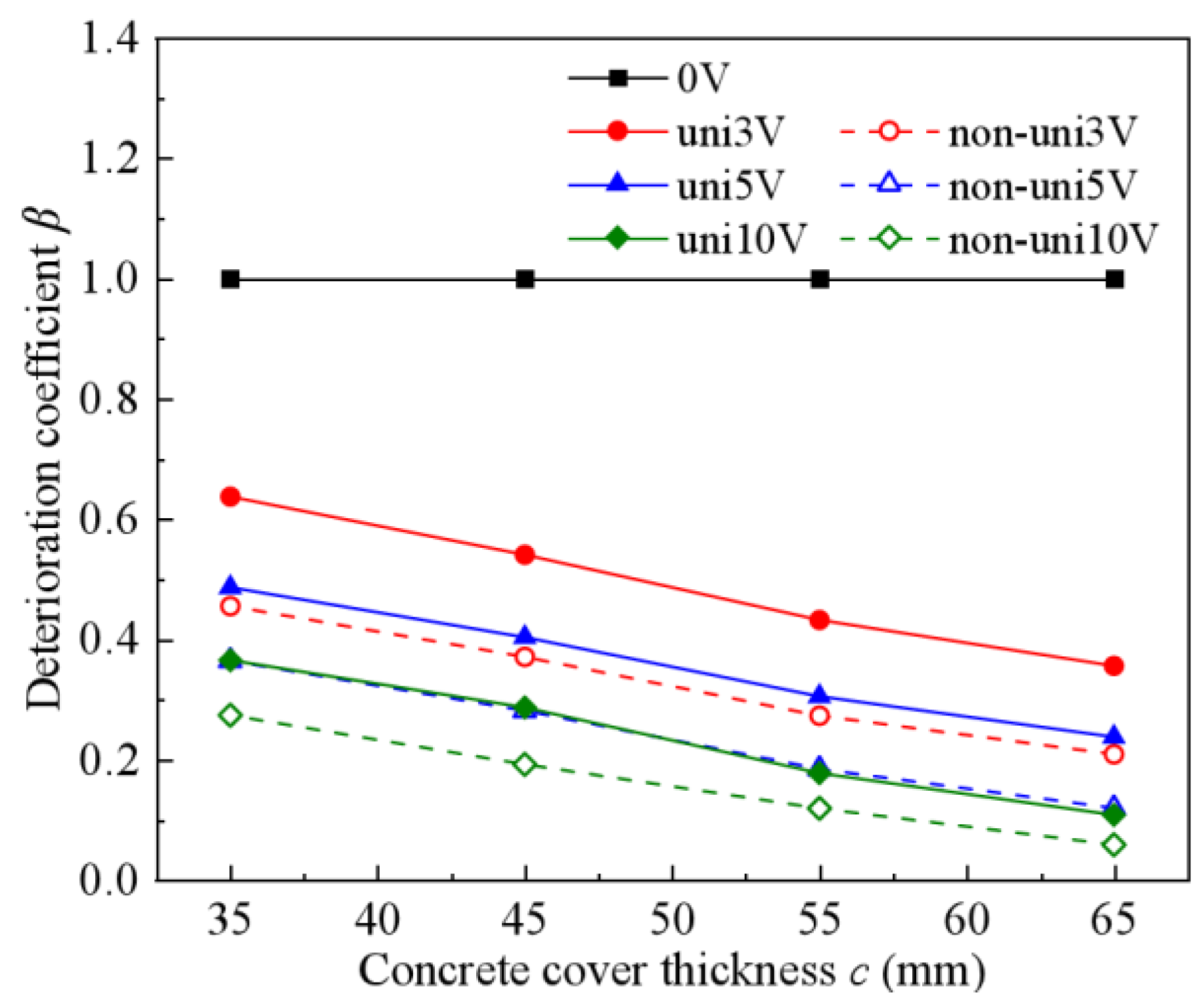
4.1. Effects of Stray Current and Concrete Cover Thickness on β in Intact RC Structures
4.2. Effects of Stray Current and Concrete Cover Thickness on β in Cracked RC Structures
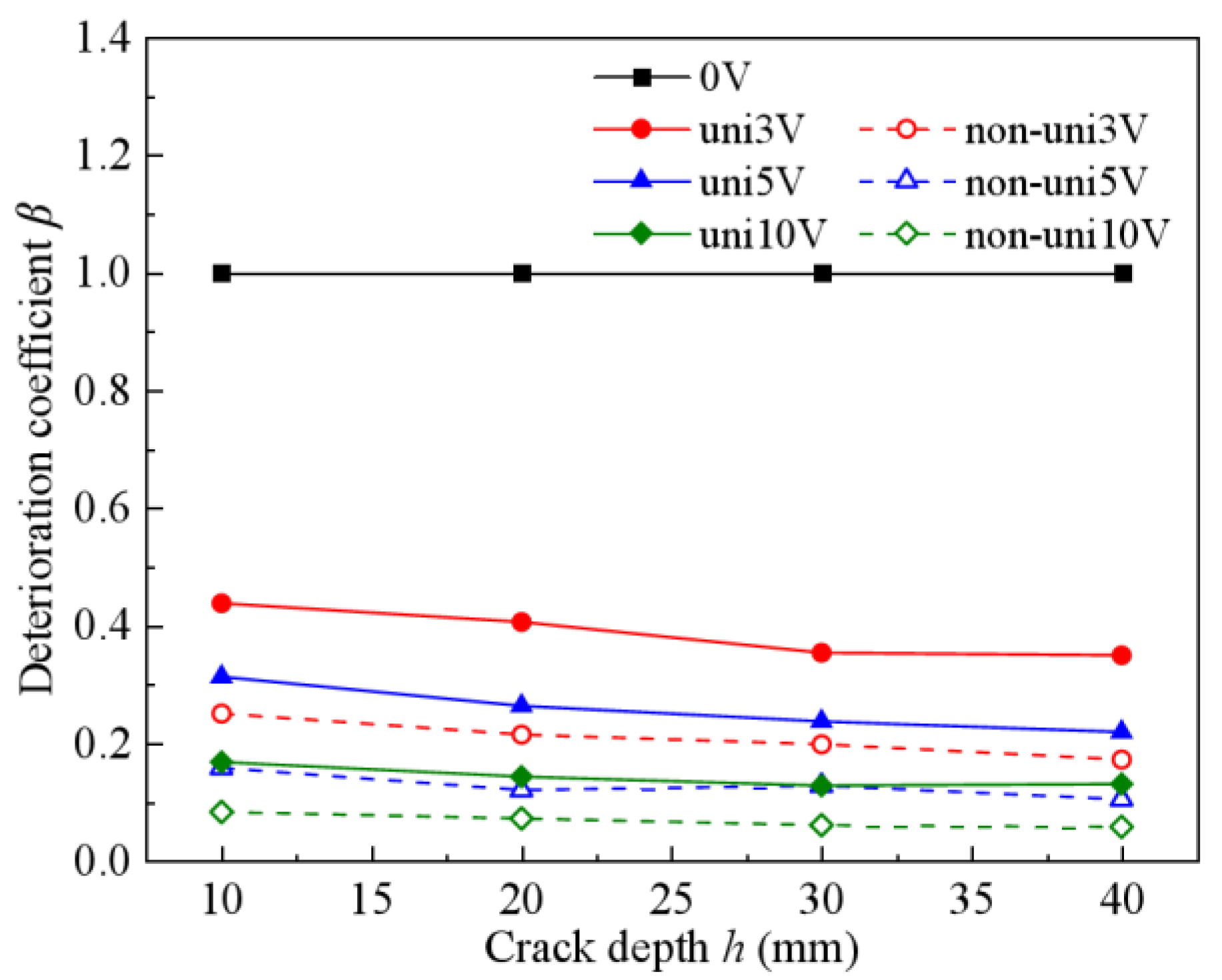
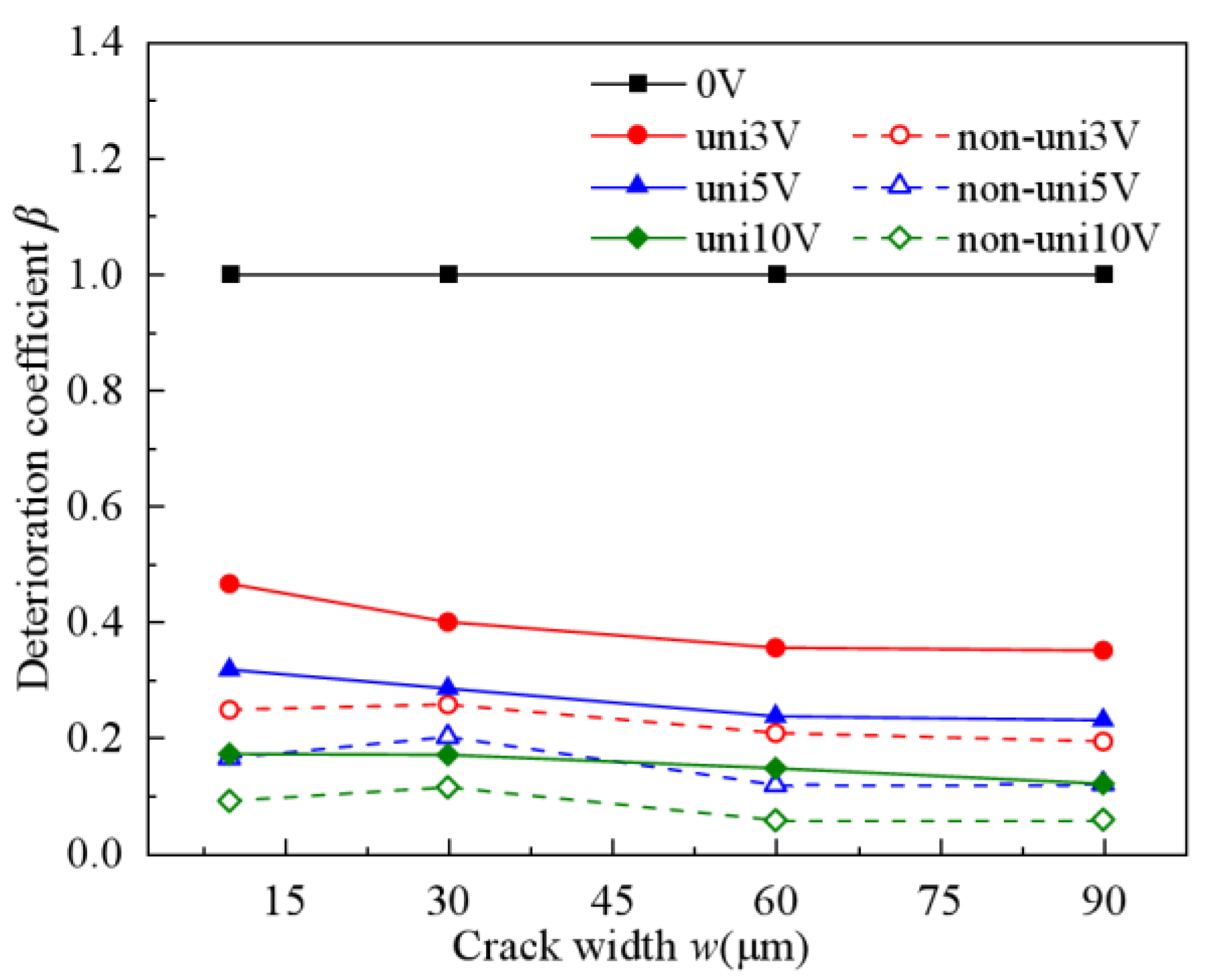
4.3. Effects of Stray Current and Crack Depth and Width on β in Cracked RC Structures
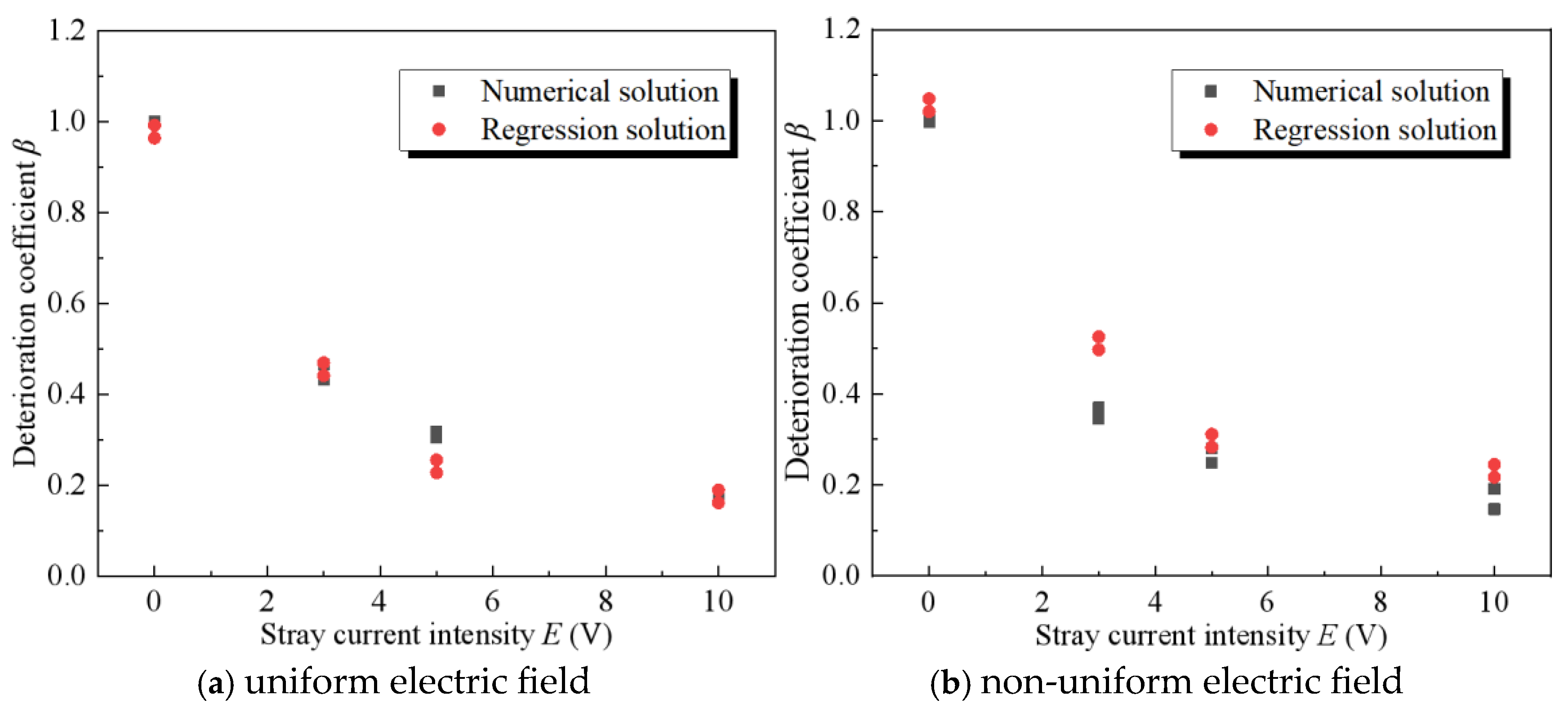
4.4. The Regression Formula for Stray Current Deterioration Coefficient β
5. Conclusions and Discussion
- Stray current intensity increasingly promotes chloride ingress. Non-uniform stray current fields accelerate ingress 20–50% faster than uniform fields at equivalent intensities.
- Stray currents nonlinearly shorten rebar depassivation time. Crack depth and width effects are linear, with width becoming insignificant past a threshold. Crucially, depassivation time plunges 40–60% when crack depth-to-cover ratio exceeds 0.6.
- Stray current intensity dominates depassivation sensitivity, exceeding concrete cover thickness effects and far surpassing crack influences. Research in chloride-stray current environments should focus primarily on current intensity and cover thickness, treating crack parameters as secondary.
- The proposed regression formula for the deterioration coefficient β quantitatively characterizes the relationship between rebar depassivation time, stray current intensity, and concrete cover thickness. This enables effective durability evaluation of RC structures exposed to stray currents.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, X.; Wang, Z.; Fan, J.; Zhao, L.; Lin, D.; Zhao, J. Problems of durability and reinforcement measures for underground structures in China. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2011, 3, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, U.M. Steel corrosion in concrete—Achilles’ heel for sustainable concrete? Cem. Concr. Res. 2023, 172, 107239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Shi, C.; Schutter, G.D.; Audenaert, K.; Deng, D. Chloride binding of cement-based materials subjected to external chloride environment—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Cai, Z.; Wu, H.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z. Chloride transport and induced steel corrosion in recycled aggregate concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 282, 122547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luping, T.; Nilsson, L.O. Chloride binding capacity and binding isotherms of OPC pastes and mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 1993, 23, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouteiller, V.; Tissier, Y.; Marie-Victoire, E.; Chaussadent, T.; Joiret, S. The application of electrochemical chloride extraction to reinforced concrete—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 351, 128931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Qiao, G.; Niu, D.; Ou, J. Electrochemical corrosion control for reinforced concrete structures−a review. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 5723–5740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemena, G.G.; Jackson, D.R. Trial Application of Electrochemical Chloride Extraction on Concrete Bridgecomponents in Virginia. Bridge Piers. 2000. Available online: https://rosap.ntl.bts.gov/view/dot/19511 (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Chen, X.; Fu, F.; Wang, H.; Liang, Q.; Yu, A.; Qian, K.; Chen, P. A multi-phase mesoscopic simulation model for the long-term chloride ingress and electrochemical chloride extraction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 270, 121826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Hao, J. Experimental-numerical analysis of bending behavior of reinforced concrete beam with electrochemical chloride extraction-strengthening. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2021, 25, 2991–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida Souza, L.R.; de Medeiros, M.H.F.; Pereira, E.; Capraro, A.P.B. Electrochemical chloride extraction: Efficiency and impact on concrete containing 1% of NaCl. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 145, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswathy, V.; Lee, H.S.; Karthick, S.; Kwon, S.J. Extraction of chloride from chloride contaminated concrete through electrochemical method using different anodes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 158, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Jiang, C.; Gu, X.; Fang, J. Modeling electrochemical chloride extraction in surface carbonated concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 460, 142591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, E.; Li, W. A review on corrosion detection and protection of existing reinforced concrete (RC) structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 325, 126718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, S.; Guo, M.; Liang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Song, Z. Effect of electric current on the stability of bound chloride. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 103, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, N. Reinforced concrete structure composition analysis after electrochemical chloride extraction. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 8430–8438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xia, J.; Easterbrook, D.; Yang, J.; Li, L. Three-phase modelling of electrochemical chloride removal from corroded steel-reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 70, 410–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Wilkinson, S. Corrosion resistance of electrified railway tunnels made of steel fibre reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 230, 117006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Koleva, D.A.; Schlangen, E. Bond of steel-mortar interface interfered by stray current. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 150, 106591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Yu, S. Effect of DC stray current on rebar corrosion in cracked segment of shield tunnel. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 272, 121646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qin, G. Corrosion of underground infrastructures under metro-induced stray current: A review. Corros. Commun. 2024, 14, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Peng, W.; Xiao, C.; Ma, L.; Hou, J. Effect of electric field intensity on chloride binding capacity of concrete. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 4466–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delagrave, A.; Marchand, J.; Ollivier, J.-P.; Julien, S.; Hazrati, K. Chloride binding capacity of various hydrated cement paste systems. Adv. Cem. Based Mater. 1997, 6, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, L.; Kang, K.; Gao, D.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Mechanical properties and corrosion mechanism of steel fiber reinforced concrete (SFRC) subjected to stray current. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 96, 110519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Koleva, D.; van Breugel, K. A review on stray current-induced steel corrosion in infrastructure. Corros. Rev. 2017, 35, 397–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W. Research status of the corrosion effect of stray current on reinforced concrete. China Concr. Cem. Prod. 2025, 2, 19–25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, H.; Cai, Y.; Chen, X.; Wei, H. Review of stray current corrosion on reinforced concrete. Concrete 2019, 6, 31–36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Yang, B.; Chen, B.; Ding, C. Coupling effects of stray current and chloride ion on corrosion resistance of fiber reinforced mortar. J. Water Resour. Archit. Eng. 2016, 14, 11–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Chu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, D.; Jiang, L.; Zuo, Q.; Li, Y. Migration behavior of sulfate ion in cement-based materials under thecombined action of chloride salt and stray current. Concrete 2020, 5, 19–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, R.; Chen, Y.; Ma, X.; Kang, X. Stray current induced chloride ion transport and corrosion characteristics of cracked ultra-high performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 398, 132536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Jin, Z.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Hu, Y.; Du, Z. Study on corrosion of reinforcement in buried concrete under the action of stray current and chlorine salt. J. Xi’an Univ. Archit. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 55, 484–491. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Chen, J.; Li, T.; Shen, J.; Liu, Q.; Jin, W. Modelling the corrosion mechanism of steel bars in chloride-contaminated concrete with transverse cracks. Mag. Concr. Res. 2022, 75, 580–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ba, M.; Yi, B.; Liu, J. Experimental and numerical investigation on the effect of cracks on chloride diffusion and steel corrosion in concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 86, 108521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, J.; Yan, H.; Huang, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, B. Simulation of concrete cracking and chloride diffusion under uniaxial compression. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 96, 110329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Simulation of chloride diffusion in cracked concrete with different crack patterns. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1075452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Jin, L.; Liu, M.; Du, X.; Li, Y. Numerical investigation of chloride diffusivity in cracked concrete. Mag. Concr. Res. 2017, 69, 850–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, T.; Li, B.; Liu, W.; Yang, H.; Xu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Zhu, H. Coupling effect of concrete cracks and stray current on chloride-induced corrosion of rebar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 449, 138403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Xu, G.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, Z. Corrosion behavior of steel bars in simulated concrete pore solution under the coupling action of chloride salt and DC stray current. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 455, 139126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, R.; Wu, J.; Zhu, W. Experimental study on chloride migration in mortar phase of concrete for metro tunnel segment under the coexistence of stray current and salt solution. Concrete 2024, 7, 54–57. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zhu, X.; Xu, L.; Peng, W.; Zhao, G. Effect of stray current coupled with chloride concentration and temperature on the corrosion resistance of a steel passivation film. Electrochem. Commun. 2020, 118, 106793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Huang, Z.; Wang, R.; Yan, J.; Zhang, J. Grouting-based treatment of tunnel settlement: Practice in Shanghai. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 80, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fang, Z.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, Q.; Han, K.; Zhou, S. External sulfate attack on cement-based materials in underground structures with the stray current. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 465, 140284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapiro, I.; Eid, R.; Kovler, K. Passive protection of reinforced concrete columns against stray currents and chloride attack. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 472, 140814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Gao, L.; Cai, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, Y. Evolution of steel-mortar interface undergoing stray current. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 134117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.A. Effect of alternating current on corrosion of low alloy and carbon steels. Corrosion 1978, 34, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenna, A.; Beretta, S.; Bolzoni, F.; Pedeferri, M.; Ormellese, M. Effects of AC-interference on chloride-induced corrosion of reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 137, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, E.; Liu, X.; Lv, B.; Cheng, X. Effects of stray current on chloride ingress in cracked RC structures. Low. Temp. Archit. Technol. 2018, 40, 4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, E. Study on the Corrosion Behaviors of the Exitingpermanent Bolt Structure and Its Durability Evaluation. Master’s Thesis, China University of Petroleum (East China), Qingdao, China, 2019. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Yan, Y.; Wang, H. Chloride diffusion in the cracked concrete. In Fracture Mechanics of Concrete and Concrete Structures; Korea Concrete Institute: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2010; Available online: https://www.framcos.org/FraMCoS-7/07-05.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Němeček, J.; Kruis, J.; Koudelka, T.; Krejčí, T. Simulation of chloride migration in reinforced concrete. Appl. Math. Comput. 2018, 319, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerný, R.; Rovnaníková, P. Transport Processes in Concrete; Spon Press: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COMSOL Multiphysics®, Version 5.4. [Computer software]. COMSOL AB: Stockholm, Sweden, 2018. Available online: https://www.comsol.com/comsol-multiphysics (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Alonso, C.; Castellote, M.; Andrade, C. Chloride threshold dependence of pitting potential of reinforcements. Electrochim. Acta 2002, 47, 3469–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Feng, D.; Wu, G. A multi-physics dual-phase field model for chloride-induced localized corrosion process and cracking in reinforced concrete. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2025, 434, 117578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. A unified phasefield theory for the mechanics of damage and quasibrittle failure. J. Mech. Phys. Solids. 2017, 103, 72–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zi, G. A 2D mechano-chemical model for the simulation of reinforcement corrosion and concrete damage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 137, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Ding, Q.; Sun, J.; Sun, B. Transport characteristics of chloride ion in concrete with stray current. J. Build. Mater. 2010, 13, 121–124. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J. The Research on the Deteriorated Mechanisms of Reinforced Concrete in Stray Currents and Chloride Ion Coexisted Corrosion Environment. Ph.D. Thesis, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, China, 2008. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 1stOpt (First Optimization)®, Version 7.0. [Computer software]. 7D-Soft High Technology Inc.: Beijing, China, 2016. Available online: http://www.7d-soft.com/ (accessed on 1 July 2025).

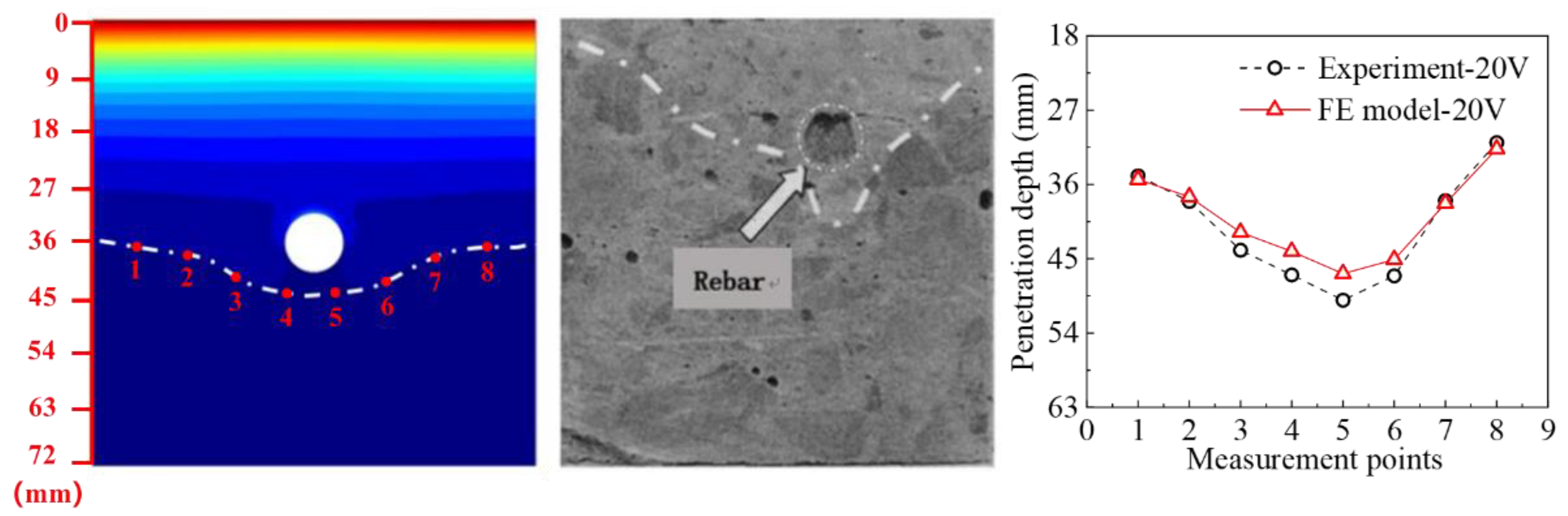
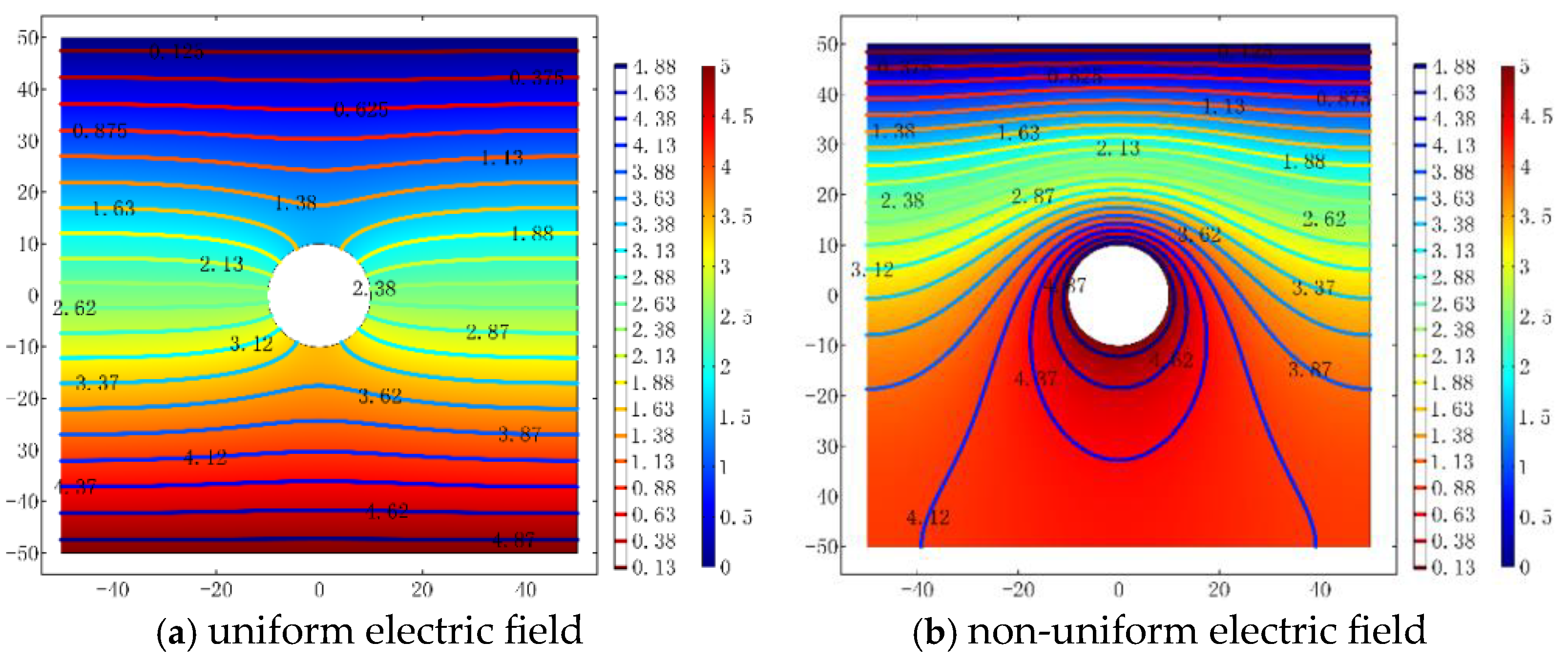
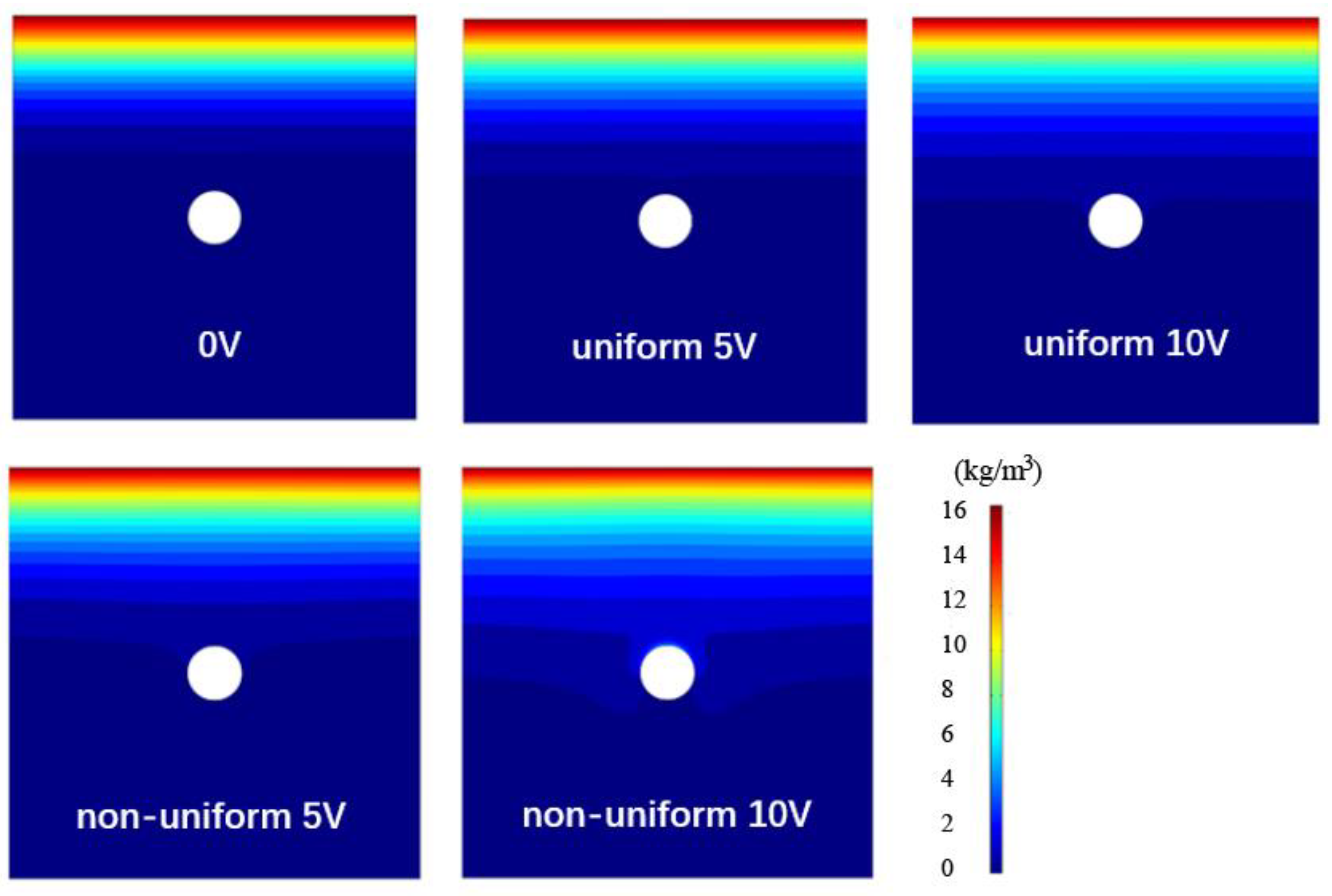
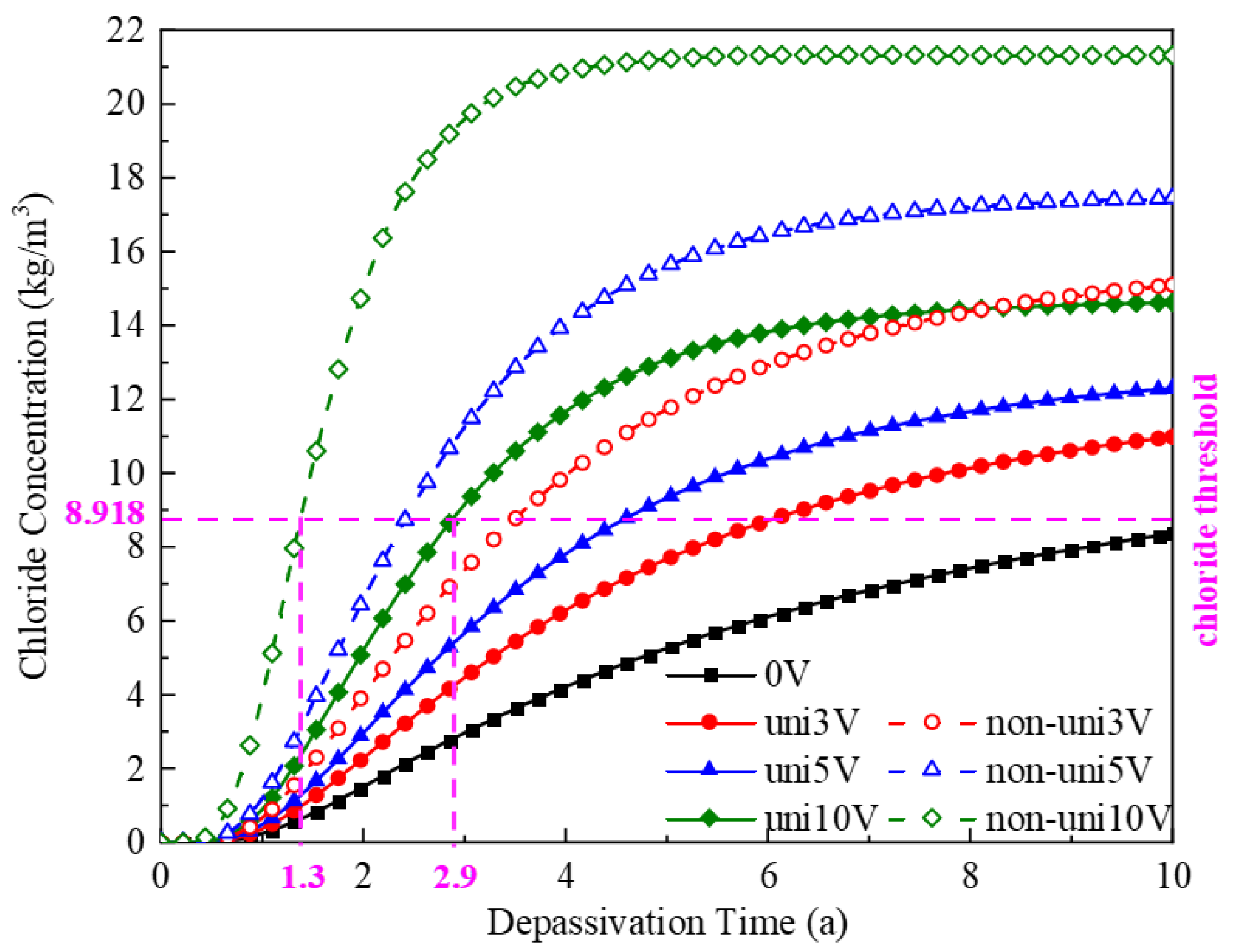


| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Rebar diameter d (mm) | 12 |
| Concrete cover thickness c (mm) | 30 |
| Stray current field intensity E (V) | 20 |
| Electrification time t (h) | 168 |
| Concentration of NaCl (%) | 8 |
| Concrete mix ratio—Cement (kg/m3) | 480 |
| Concrete mix ratio—Limestone (kg/m3) | 1056.9 |
| Concrete mix ratio—Sand (kg/m3) | 704.6 |
| Concrete mix ratio—Water (kg/m3) | 151.6 |
| Concrete mix ratio—Chemical admixture (%) | 1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, X.; Liu, X.; Xiang, E.; Chen, M.; Ma, C. Effects of Stray Current on Chloride Ingress in Underground Reinforced Concrete Structures. Buildings 2025, 15, 3301. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183301
Cheng X, Liu X, Xiang E, Chen M, Ma C. Effects of Stray Current on Chloride Ingress in Underground Reinforced Concrete Structures. Buildings. 2025; 15(18):3301. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183301
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Xudong, Xueying Liu, Enze Xiang, Minghao Chen, and Chuan Ma. 2025. "Effects of Stray Current on Chloride Ingress in Underground Reinforced Concrete Structures" Buildings 15, no. 18: 3301. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183301
APA StyleCheng, X., Liu, X., Xiang, E., Chen, M., & Ma, C. (2025). Effects of Stray Current on Chloride Ingress in Underground Reinforced Concrete Structures. Buildings, 15(18), 3301. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183301





