Physicochemical Properties of Alkali-Activated Ground-Granulated Blast Furnace Slag (GGBS)/High-Calcium Fly Ash (HCFA) Cementitious Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experiments
2.1. Material
2.2. The Mixture Ratio and the Sample Preparation
2.2.1. Mix Design and Specimen Preparation
2.2.2. Mechanical Properties Test and Durability Test Design
2.3. Test the Equipment and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microscopic Analysis of Composite Cementitious Materials and Their Mechanical Properties
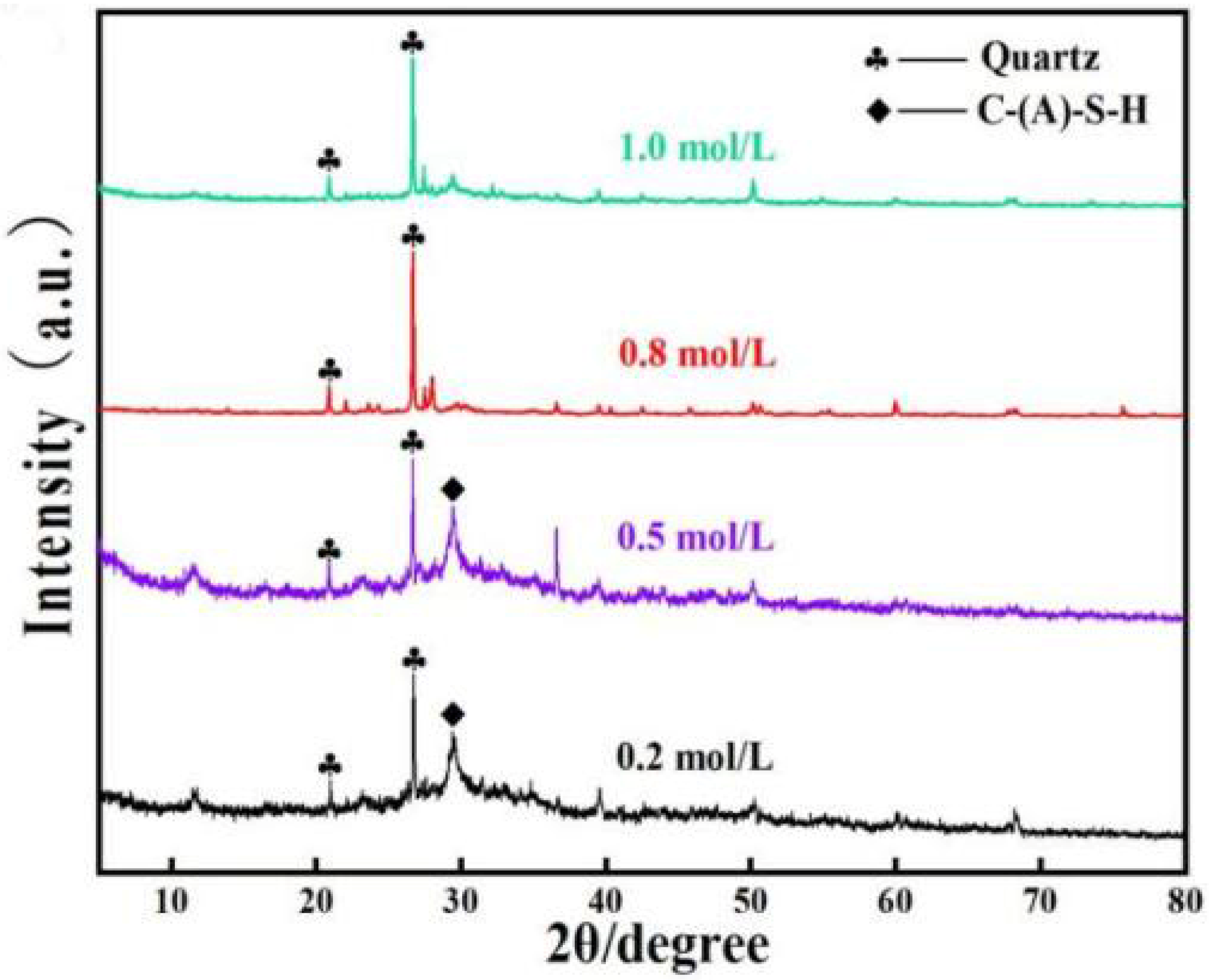
3.1.1. XRD Analysis
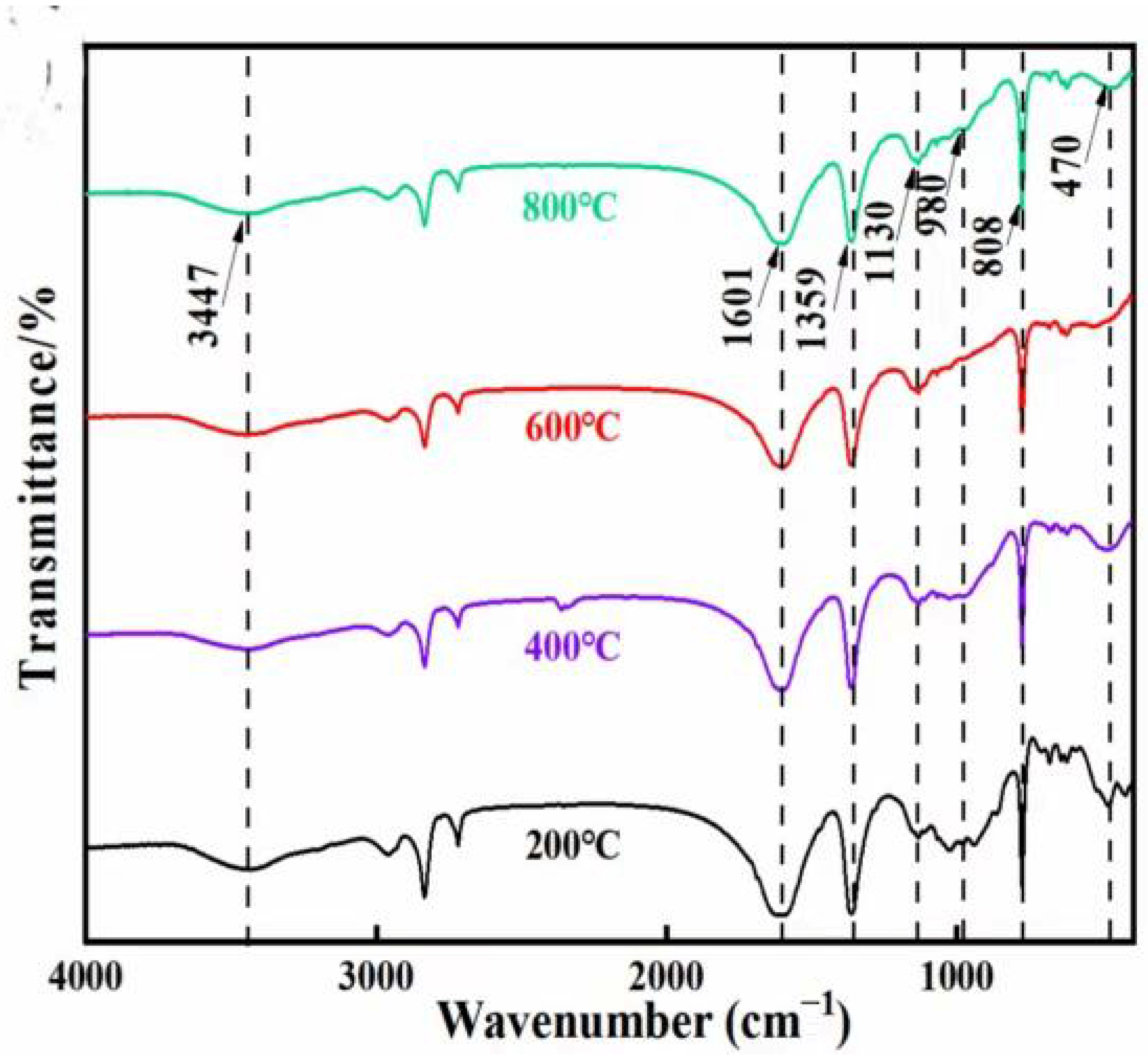
3.1.2. FTIR Analysis
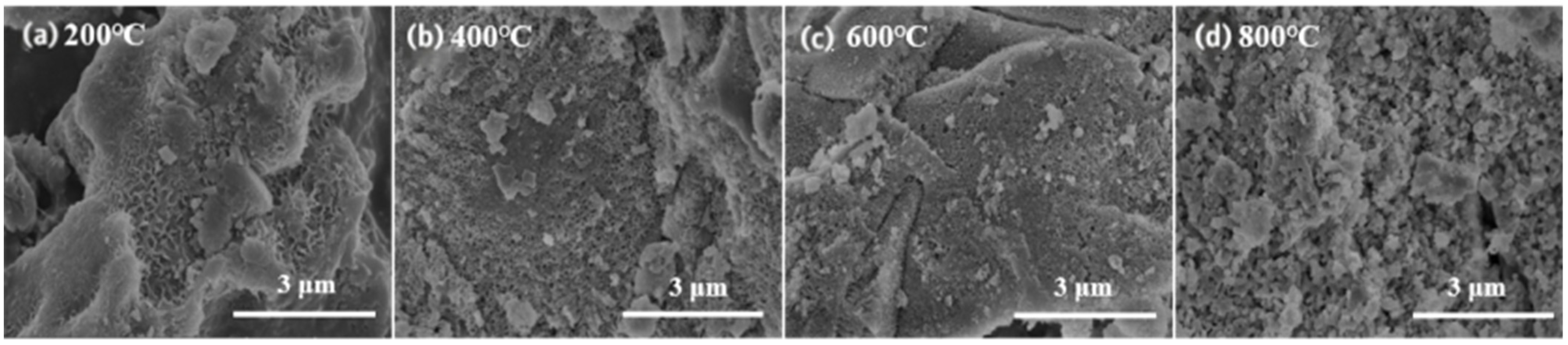
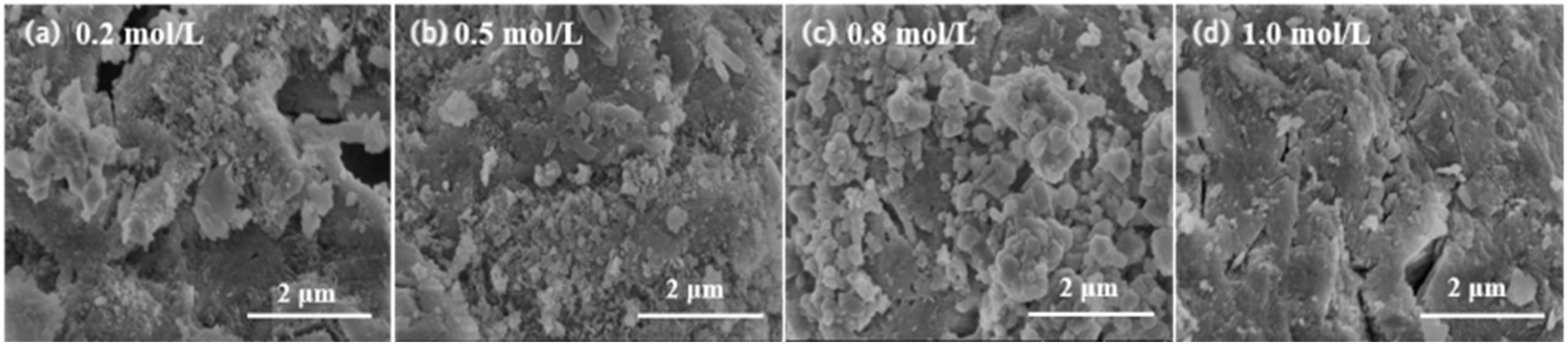
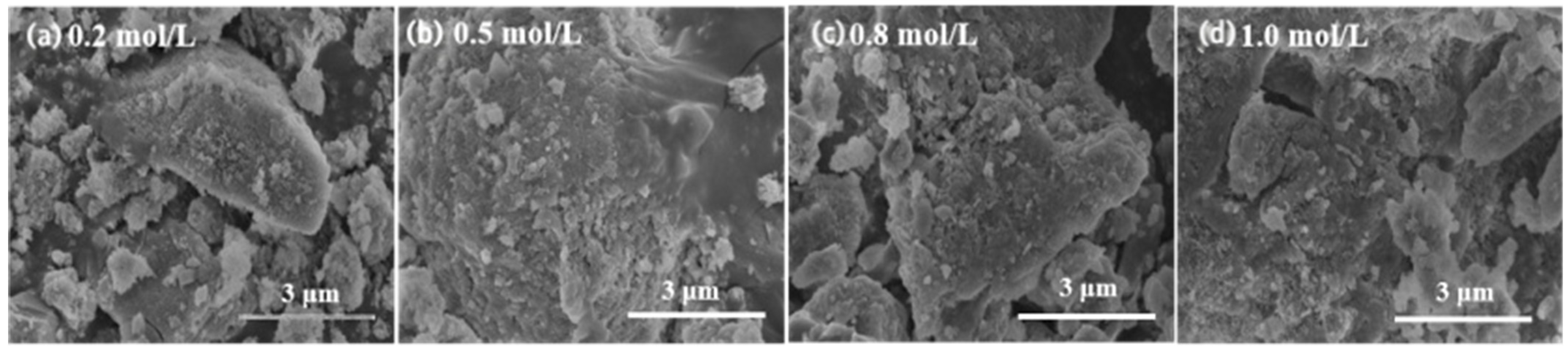
3.1.3. SEM Analysis
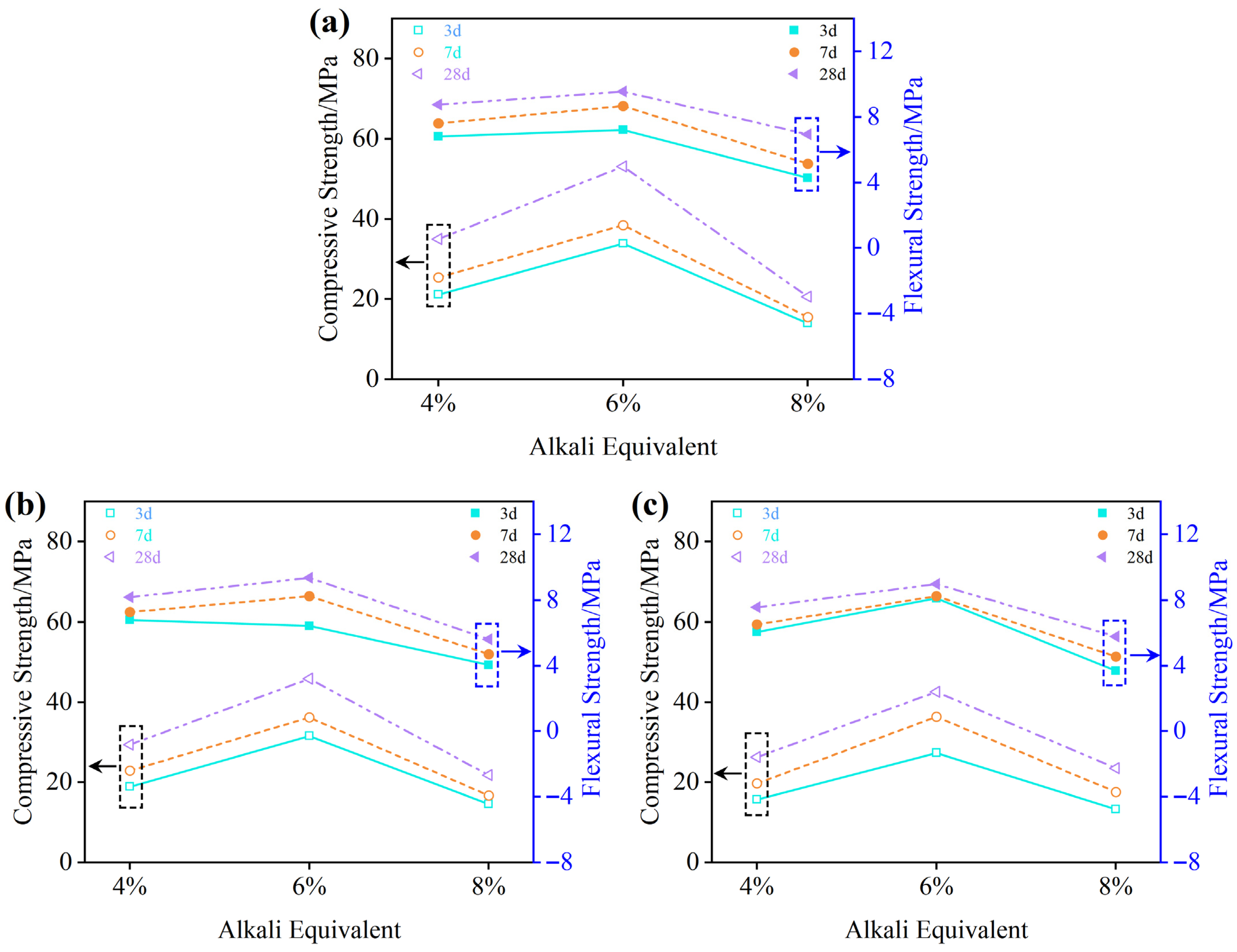
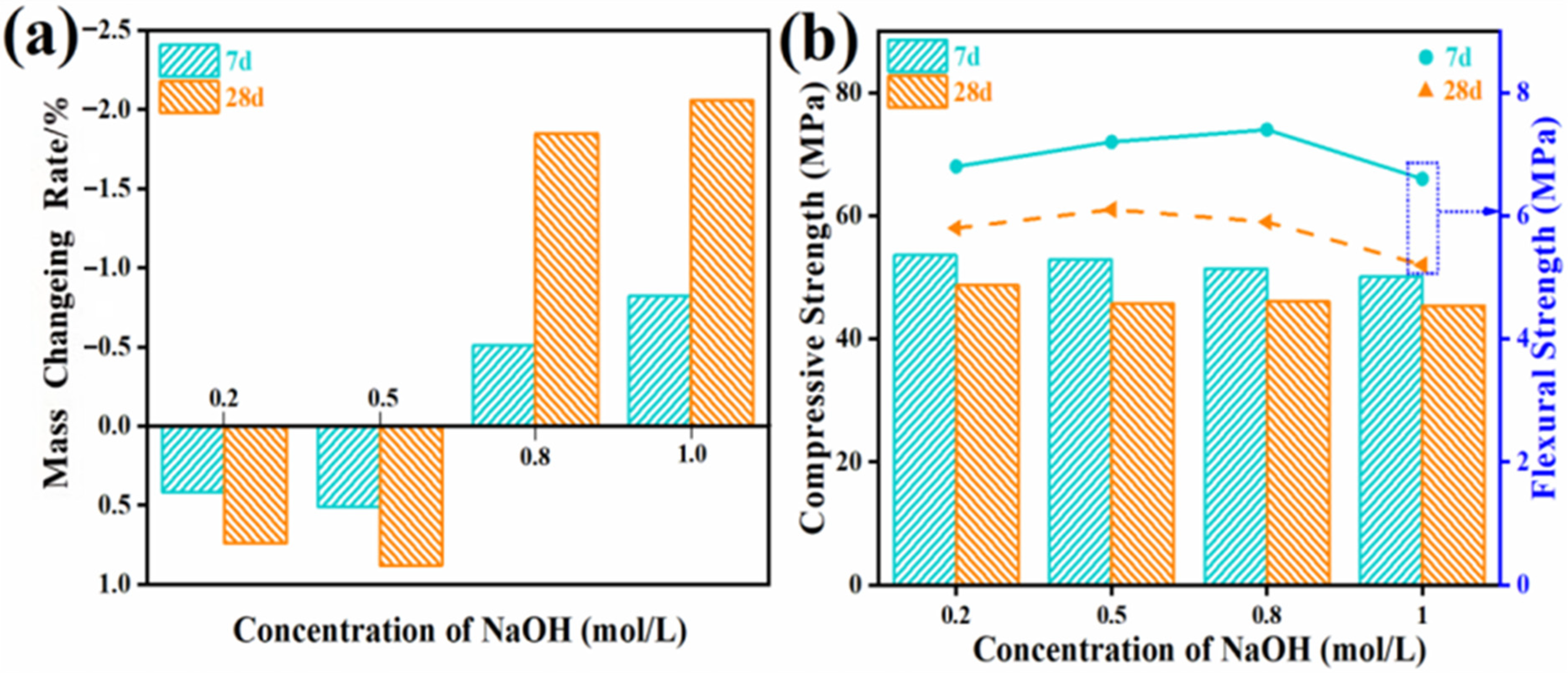
3.1.4. Mechanical Performance Analysis
3.2. Durability of Composite Gel Materials
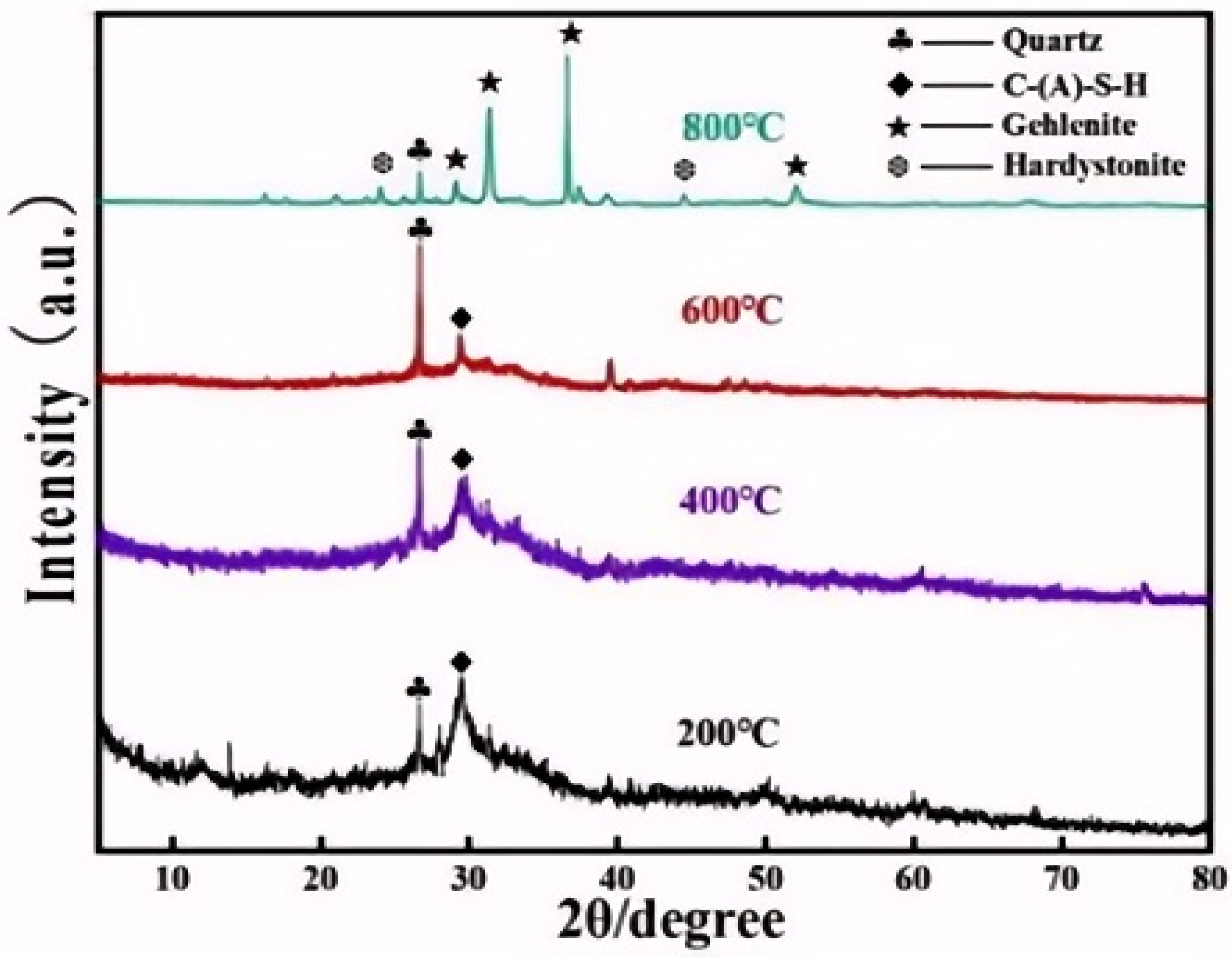
3.2.1. XRD Analysis
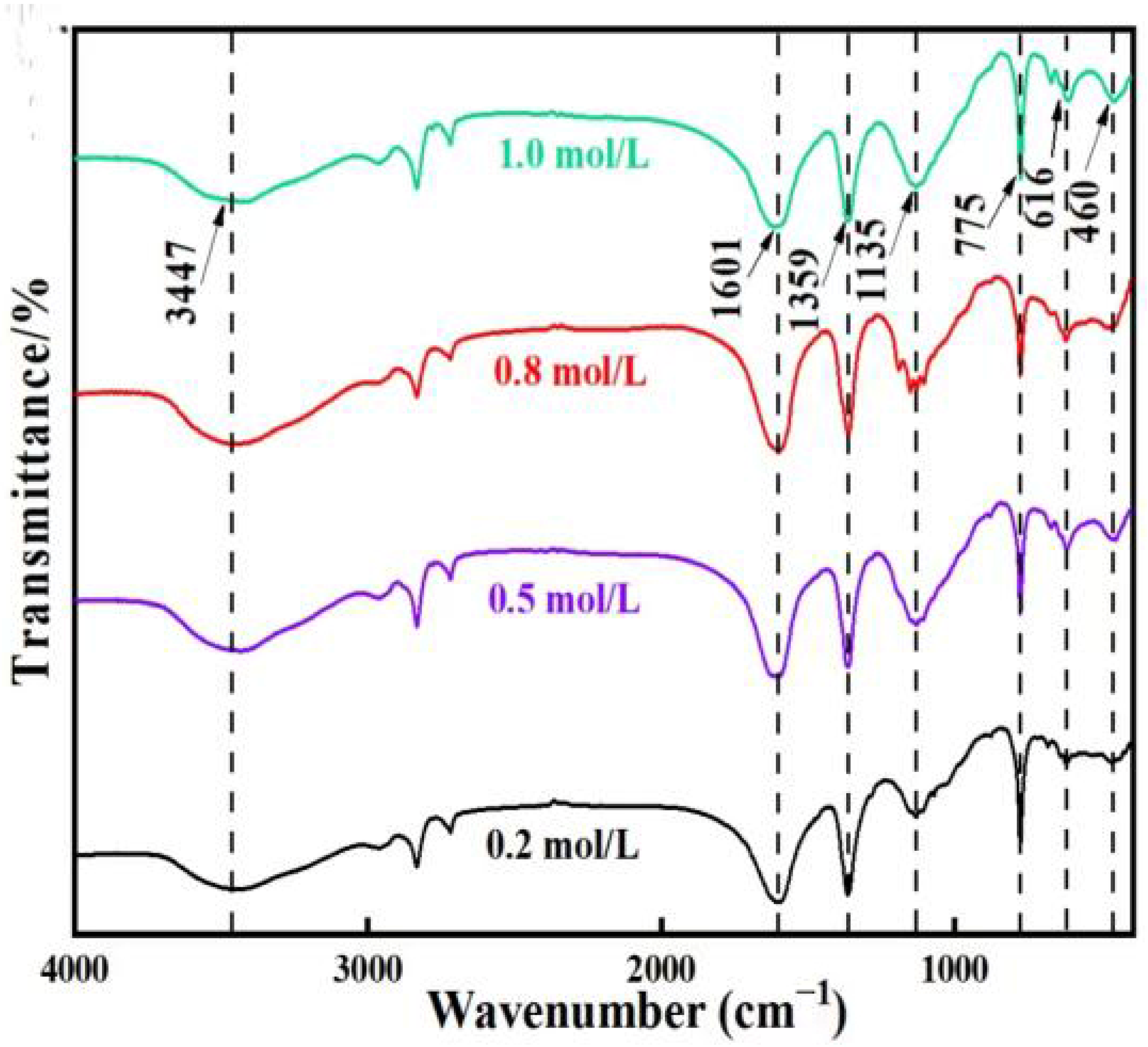
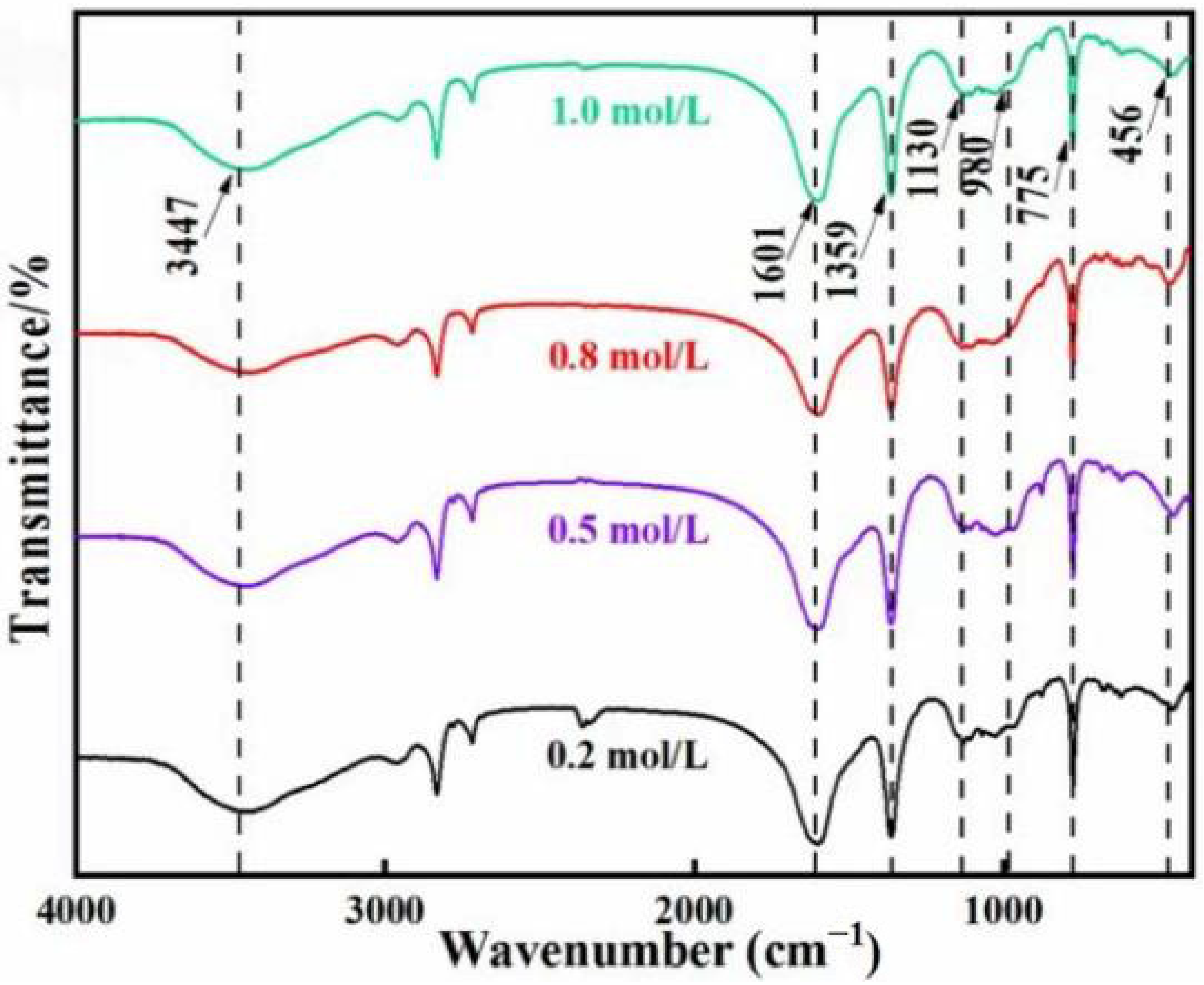
3.2.2. FTIR Analysis
3.2.3. SEM Analysis
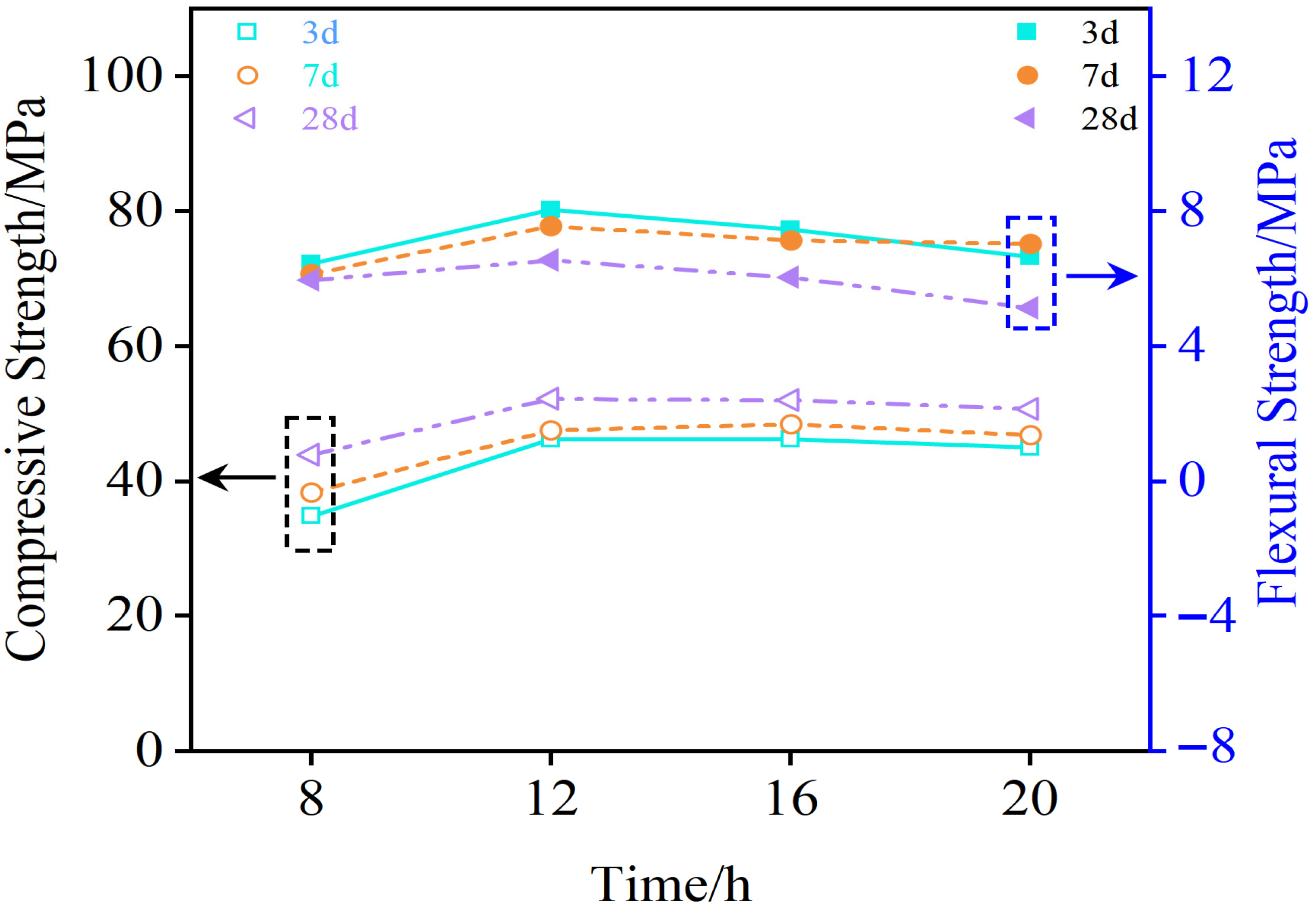
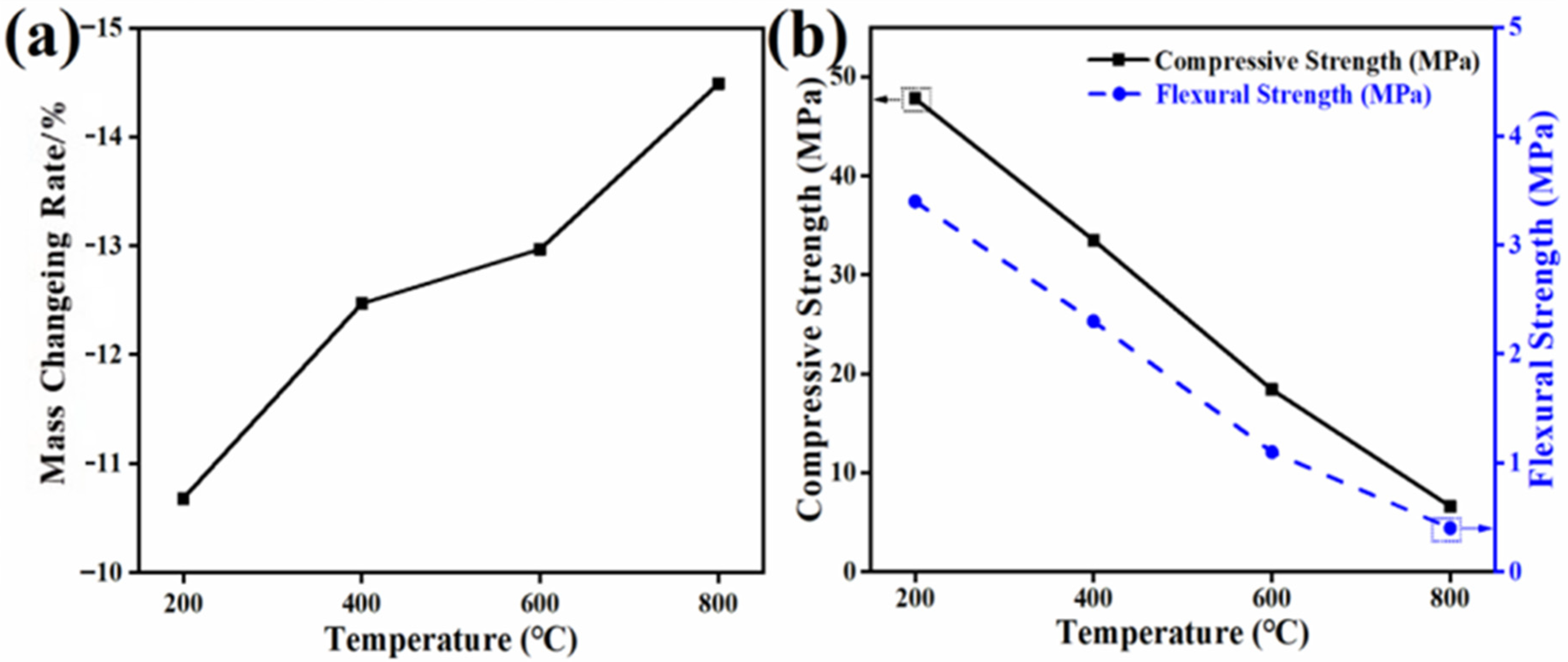
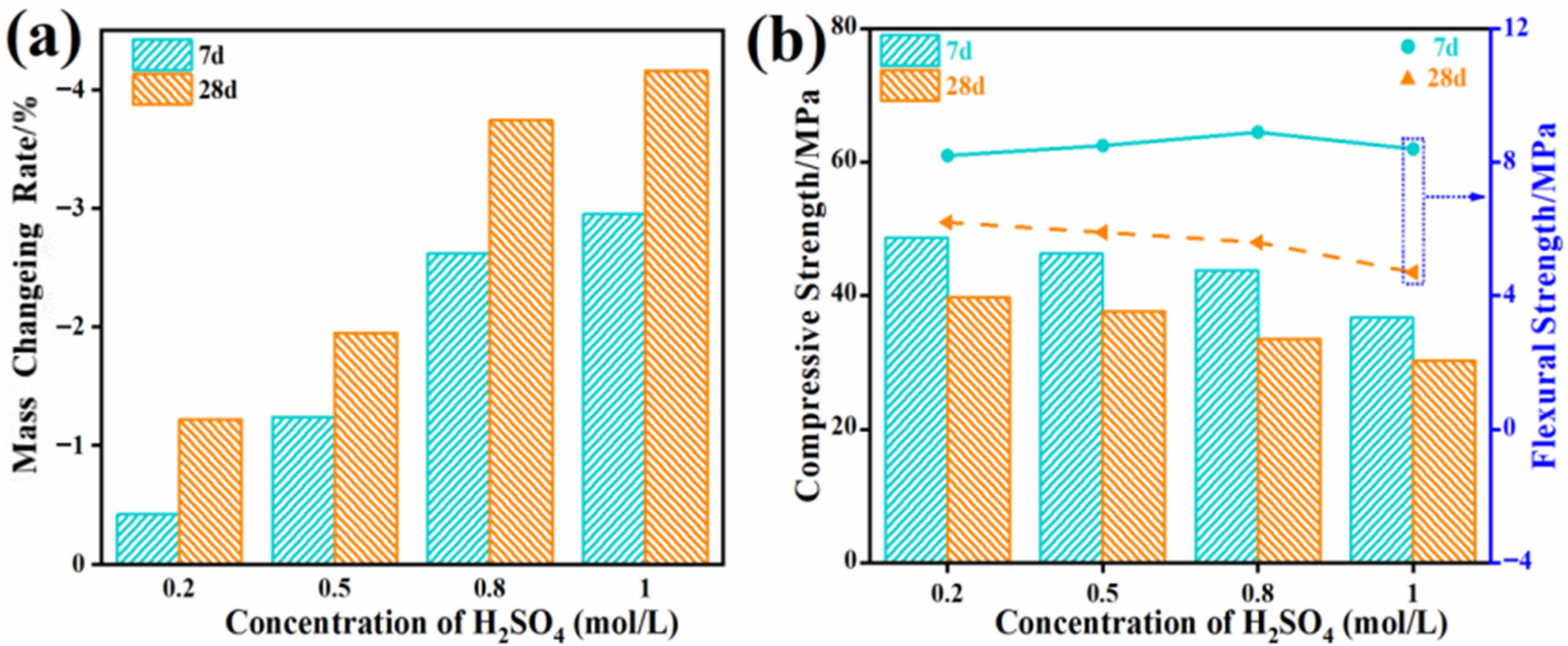
3.2.4. Durability Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gluth, G.J.G.; Mundra, S.; Henning, R. Chloride binding by layered double hydroxides (LDH/AFm phases) and alkali-activated slag pastes: An experimental study by RILEM TC 283-CAM. Mater. Struct. 2024, 57, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habert, G.; Miller, S.A.; John, V.M.; Provis, J.L.; Favier, A.; Horvath, A.; Scrivener, K.L. Environmental impacts and decarbonization strategies in the cement and concrete industries. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakira, U.; Zheng, K.; Xie, N.; Birgisson, B. Development of high-strength geopolymers from red mud and blast furnace slag. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 383, 135439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guan, X.; Zhu, M.; Gao, J.; Zhao, D. Mechanism on Activation of Coal Gangue Admixture. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5436482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudawaba, F.; Gomaa, E.; Gheni, A.A.; Feys, D.; ElGawady, M.A. Evaluation of fresh properties of high calcium content fly ash-based alkali-activated 3D-Printed mortar. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 104, 112244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yang, H.; Luo, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, G.; Liu, K. Interfacial Behavior of Slag, Fly Ash, and Red Mud-Based Geopolymer Mortar with Concrete Substrate: Mechanical Properties and Microstructure. Buildings 2024, 14, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathee, M.; Misra, A.; Kolleboyina, J.; Sarma, P.S.K. Study of mechanical properties of geopolymer mortar prepared with fly ash and GGBS. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 93, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Fu, T. Effect of Steel Slag on the Properties of Alkali-Activated Slag Material: A Comparative Study with Fly Ash. Materials 2024, 17, 2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, Y.; Li, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y. Photocatalysis in alkali activated cementitious materials. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 46, 103749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Shicheng, S. A Review of the Current Status of Research on Alkali-Activated Cementitious Materials. Green Build. Mater. 2019, 11, 16+18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; He, Y.; Cui, X.-M.; Liu, J.-H.; Liu, Q. Design, preparation, and performance of marine resource-based alkali-activated cementitious materials. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 97, 110822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, I.; Kohail, M.; El-Feky, M.; Rashad, A.; Khalaf, M.A. A review on alkali-activated slag concrete. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 1475–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. Research on road performance of alkali-activated cementitiousmaterials mixed with fly ash. Shangdong Jiaotong Keji 2023, 4, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Khajeh, A.; Ebrahimi, S.A.; MolaAbasi, H.; Chenari, R.J.; Payan, M. Effect of EPS beads in lightening a typical zeolite and cement-treated sand. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 8615–8632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyadasa, P.W.; Manalo, A.C.; Lokuge, W.; Aravinthan, V.; Gerdes, A.; Kaltenbach, J.; Galvan, B.A. Macro and microstructural evolution of low-calcium fly ash-based geopolymer mortar exposed to sulphuric acid corrosion. Cem. Concr. Res. 2024, 178, 107436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Tao, Z.; Cao, Y.-F.; George, L.; Wuhrer, R. High-temperature performance of alkali-activated binders of fly ash and calcium aluminate. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 14389–14398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, O.A. Effects of the Curing Regime, Acid Exposure, Alkaline Activator Dosage, and Precursor Content on the Strength Development of Mortar with Alkali-Activated Slag and Fly Ash Binder: A Critical Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosrati, S.A.; Negahdar, A.; Negahdar, H. Stabilizing the clayey sand contaminated with heavy metals by zeolite and rice husk ash absorbents. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanj, A.; Chenari, M.J.; Zolfalizadeh, M.; Salimi, M.; Hosseinpour, I.; Payan, M. Experimental study on freeze-thaw durability of high plasticity clay treated with waste glass powder and waste tire textile fibers. Results Eng. 2025, 27, 106221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeshokan, M.O.; Arum, C. Comparison between the Compressive Strength of Binary and Ternary Alkaline-activated Pozzolanic Concrete. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2023, 27, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Zhang, M. Multiscale micromechanical analysis of alkali-activated fly ash-slag paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 135, 106141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomayri, T. Mechanical and microstructure characteristics of alkali-activated coal ash with α-phase ultrafine Al2O3 nanoparticles and basalt fibres. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2022, 16, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Q. Mechanical Properties and Damage Layer Thickness of Green Concrete under a Low-Temperature Environment. Materials 2022, 15, 7409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kancir, I.V.; Serdar, M. Contribution to Understanding of Synergy between Red Mud and Common Supplementary Cementitious Materials. Materials 2022, 15, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surehali, S.; Simon, A.; Ramasamy, R.K.; Neithalath, N. A Comparison of the Effect of Activator Cations (Sodium and Potassium) on the Fresh and Hardened Properties of Mine Tailing-Slag Binders. Constr. Mater. 2023, 3, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitarz, M.; Castro-Gomes, J.; Hager, I. Strength and Microstructure Characteristics of Blended Fly Ash and Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag Geopolymer Mortars with Na and K Silicate Solution. Materials 2022, 15, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurda, R.; Silva, R.V.; de Brito, J. Incorporation of Alkali-Activated Municipal Solid Waste Incinerator Bottom Ash in Mortar and Concrete: A Critical Review. Materials 2020, 13, 3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Y.; Qi, T.; Shen, L.; Liu, G.; Peng, Z.; Li, X. Coal fly ash resource utilization: Structure of siloxy group of high-modulus sodium silicate solution. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 171, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas-Casarez, C.; Arredondo-Rea, S.; Ramos-Ortiz, G.; Corral-Higuera, R.; Cruz-Enríquez, A.; Gómez-Soberón, J.; Velusamy, J.; Zárraga-Núñez, R.; Campos-Gaxiola, J. Excitation-dependent photoluminescent properties in geopolymers with addition of Eu2+ Dy3+ co-doped strontium silicoaluminate. Mater. Lett. 2019, 250, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthieswaran, N.; Moorthy, N.; Renisha, M.; Chinnadurai, M. Optimization of Strength Properties of Reactive Powder Concrete by Response Surface Methodology. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. 2024, 29, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S. The application of high calcium fly ash in modern concrete. Sichuan Build. Mater. 2020, 46, 15–16. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Jin, Y. Phase Analysis of Alkali-Activated Slag Hybridized with Low-Calcium and High-Calcium Fly Ash. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Guan, W.; Wang, W.; Xu, X.; Song, Y.; Liu, H.; Su, H.; Zhao, B.; Hou, D. Review of the Backfill Materials in Chinese Underground Coal Mining. Minerals 2023, 13, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekara, C.; Atzarakis, P.; Lokuge, W.; Law, D.W.; Setunge, S. Novel Analytical Method for Mix Design and Performance Prediction of High Calcium Fly Ash Geopolymer Concrete. Polymers 2021, 13, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, S.Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Gang, L. Study on the Preparation and Strength Characteristics of High-Calcium Fly Ash Geopolymer. Wall Mater. Innov. Build. Energy Effic. 2019, 11, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 18046-2017; Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag Used for Cement, Mortar and Concrete. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Yang, N. The physical and chemical basis of alkali-gel materials (I). J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 1996, 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, N. The physical and chemical basis of alkali-gel materials (II). J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 1996, 459–465. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 50081-2019; Standard for Test Methods of Concrete Physical and Mechanical Properties. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Verma, N.K.; Rao, M.C.; Kumar, S. Effect of Curing Regime on Compressive Strength of Geopolymer Concrete. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 982, 012031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabanshchikov, Y.G.; Usanova, K.Y.; Umarov, S.; Salimbayev, M.; Bazarov, D. Properties of concrete containing high-calcium fly ash artificial aggregate. E3S Web Conf. 2023, 401, 03016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Tao, Y.; Ju, L.; Yang, H. Macro–micro investigation on stabilization sludge as subgrade filler by the ternary blending of steel slag and fly ash and calcium carbide residue. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 447, 141496, ISSN 0959-6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xiang, E.; Yang, C.; Huang, H.; Jiang, J.; Lyu, J. Radial variation in the sorption behavior of water-saturated bamboo with graded fibrous structure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 494, 143324, ISSN 0950-0618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Tian, X.; Li, J.; Gao, W.; Yue, Y.; Kang, J. Influence of Al2O3/SiO2 Ratio on the Structure and Properties of Na+/K+ Ion Exchange Na2O-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2 Glasses. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2024, 39, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viet, H.V.; Le Van, Q. Early strength enhancement of high-volume fly ash mortar using accelerating admixtures. Transp. Commun. Sci. J. 2024, 75, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 17671-2021; Test Method of Cement Mortar Strength (ISO Method). Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Khajeh, A.; Chenari, R.J.; Payan, M.; MolaAbasi, H. Assessing the effect of lime-zeolite on geotechnical properties and microstructure of reconstituted clay used as a subgrade soil. Phys. Chem. Earth 2023, 132, 103501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, Y.; Sun, J.; Cui, Q.; Yu, R.; Liu, Y. Mechanisms of concentration control alkali activated fly ash stabilized saline soil in seasonally frozen regions. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, H.; Ngo, D.; Gin, S.; Kim, S.H. Spectral changes in Si–O–Si stretching band of porous glass network upon ingress of water. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2020, 527, 119722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, G.; Chen, D.; Gao, K.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, Y.; Fan, S.; Tang, L.; Jia, H. The Effects of Diatomite as an Additive on the Macroscopic Properties and Microstructure of Concrete. Materials 2023, 16, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Nedeljković, M.; Ye, G. Pore solution composition of alkali-activated slag/fly ash pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 115, 230–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Luan, M.; Yang, K.; Li, J. Temperature-sensitively dissolving of GGBS in neutral and alkali media. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 418, 135353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Feng, P.; Li, W.; Geng, G.; Huang, J.; Gao, Y.; Mu, S.; Hong, J. Effects of pH on the nano/micro structure of calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) under sulfate attack. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 140, 106306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xi, X.; Yang, S. Research Progress in Corrosion Mechanism of Reinforced Alkali-Activated Concrete Structures. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2021, 2, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
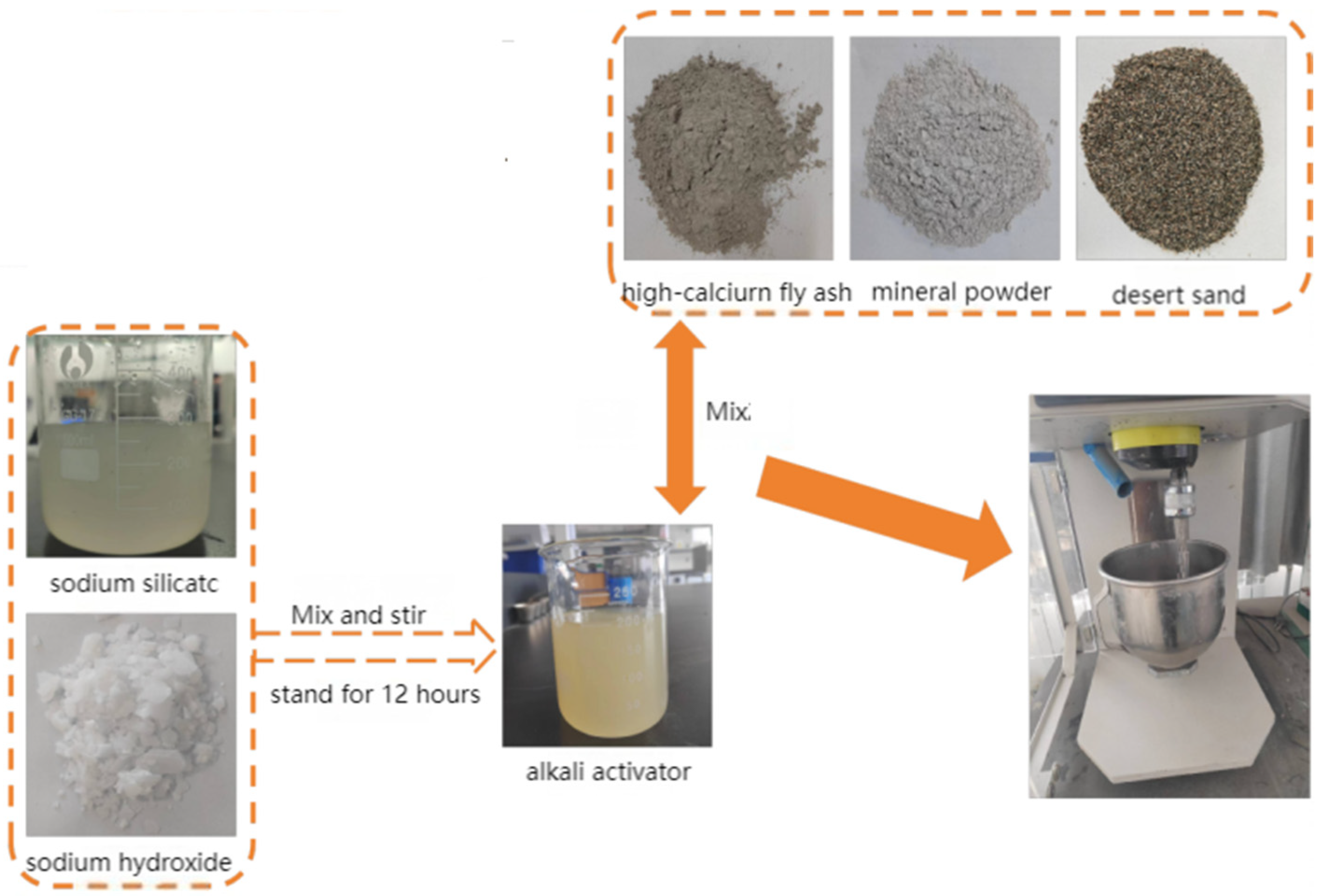


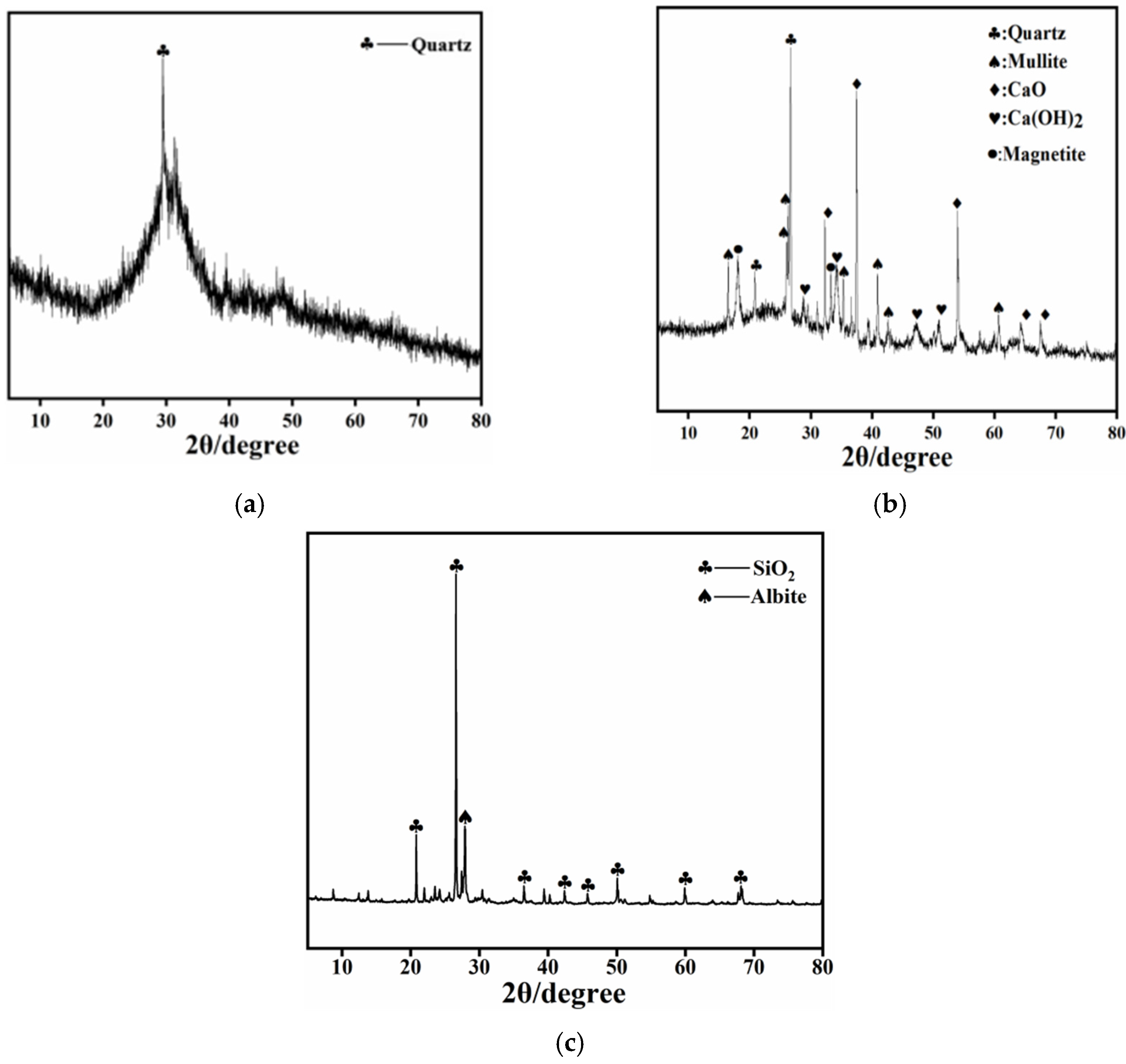
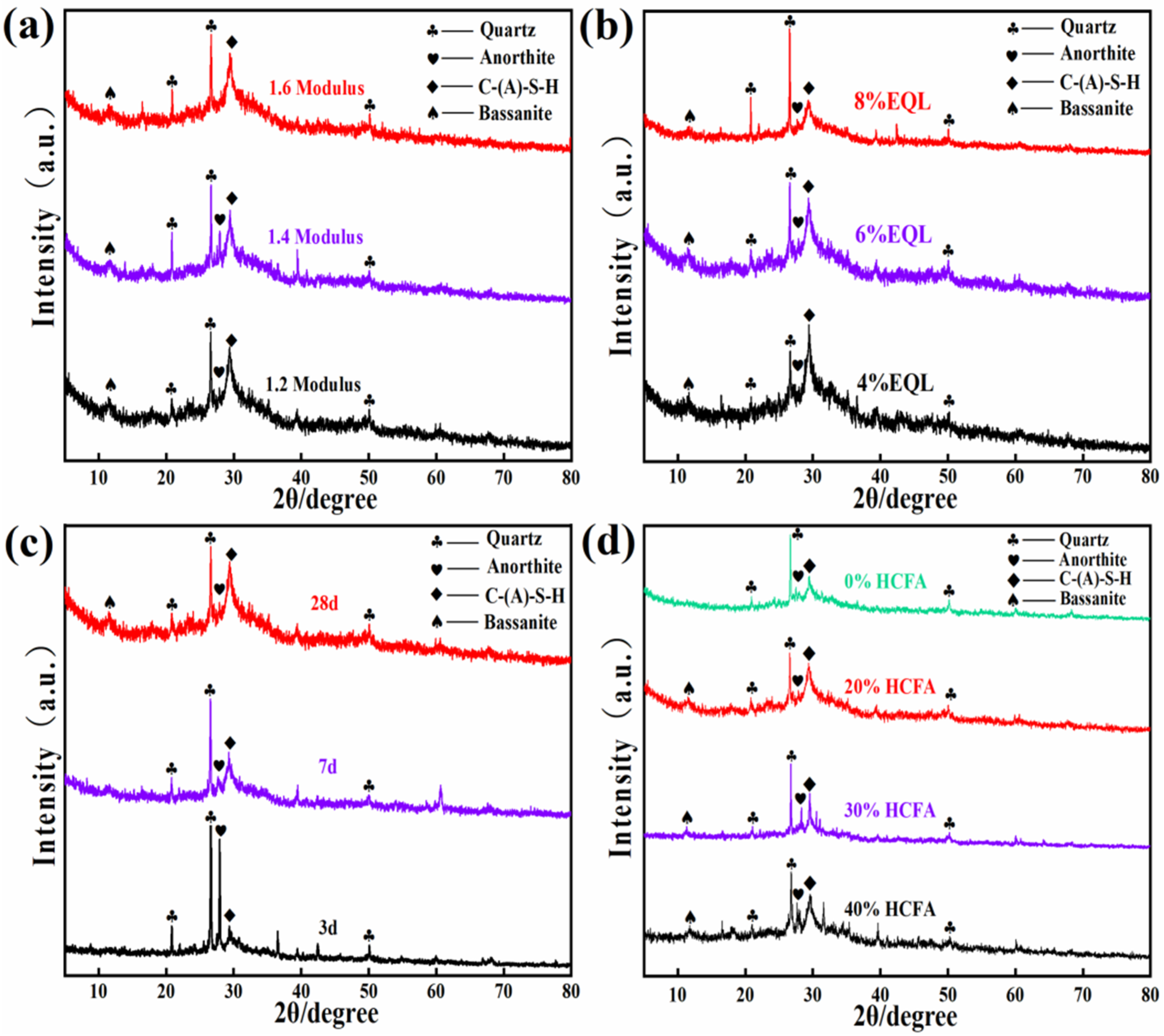
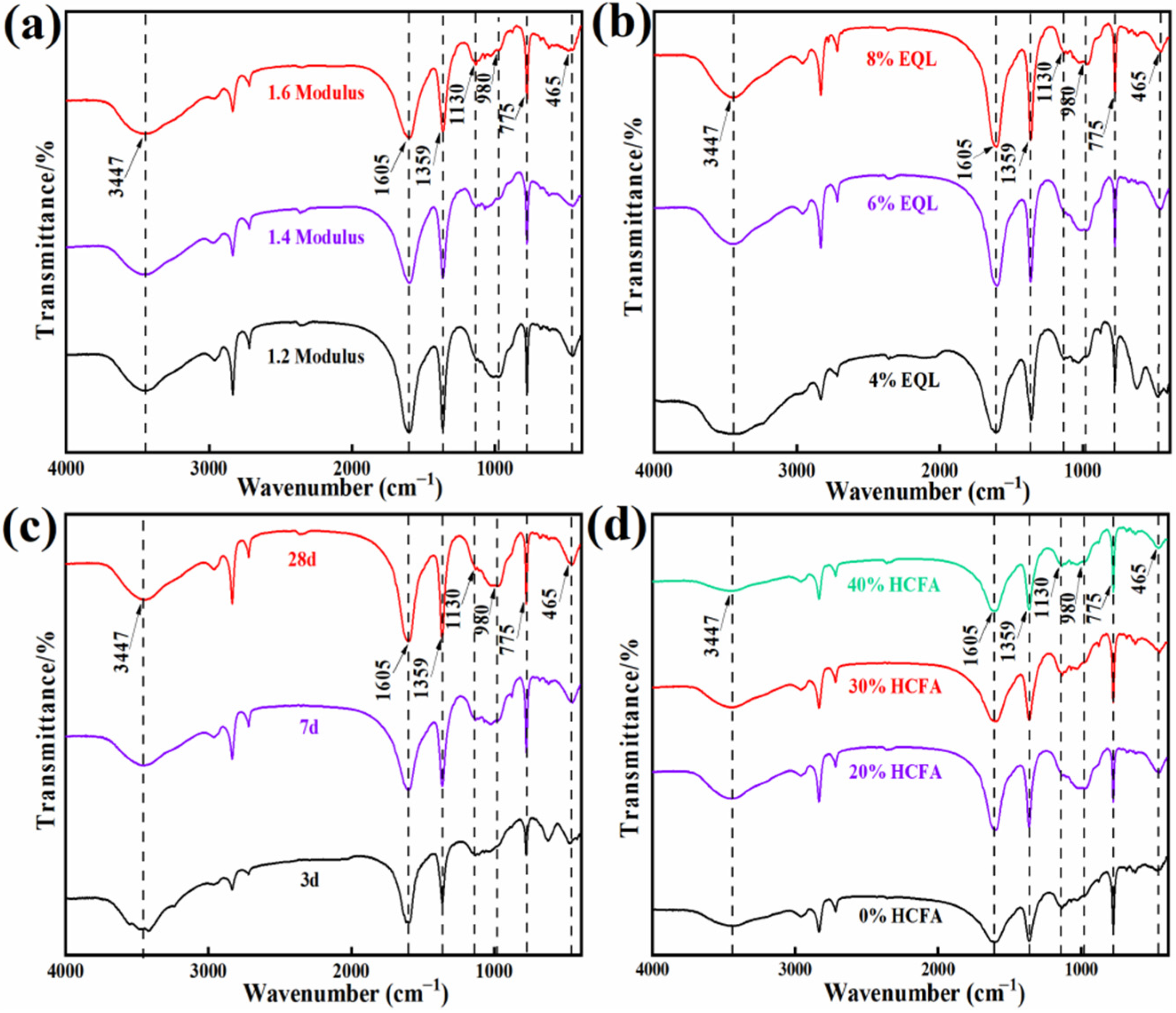
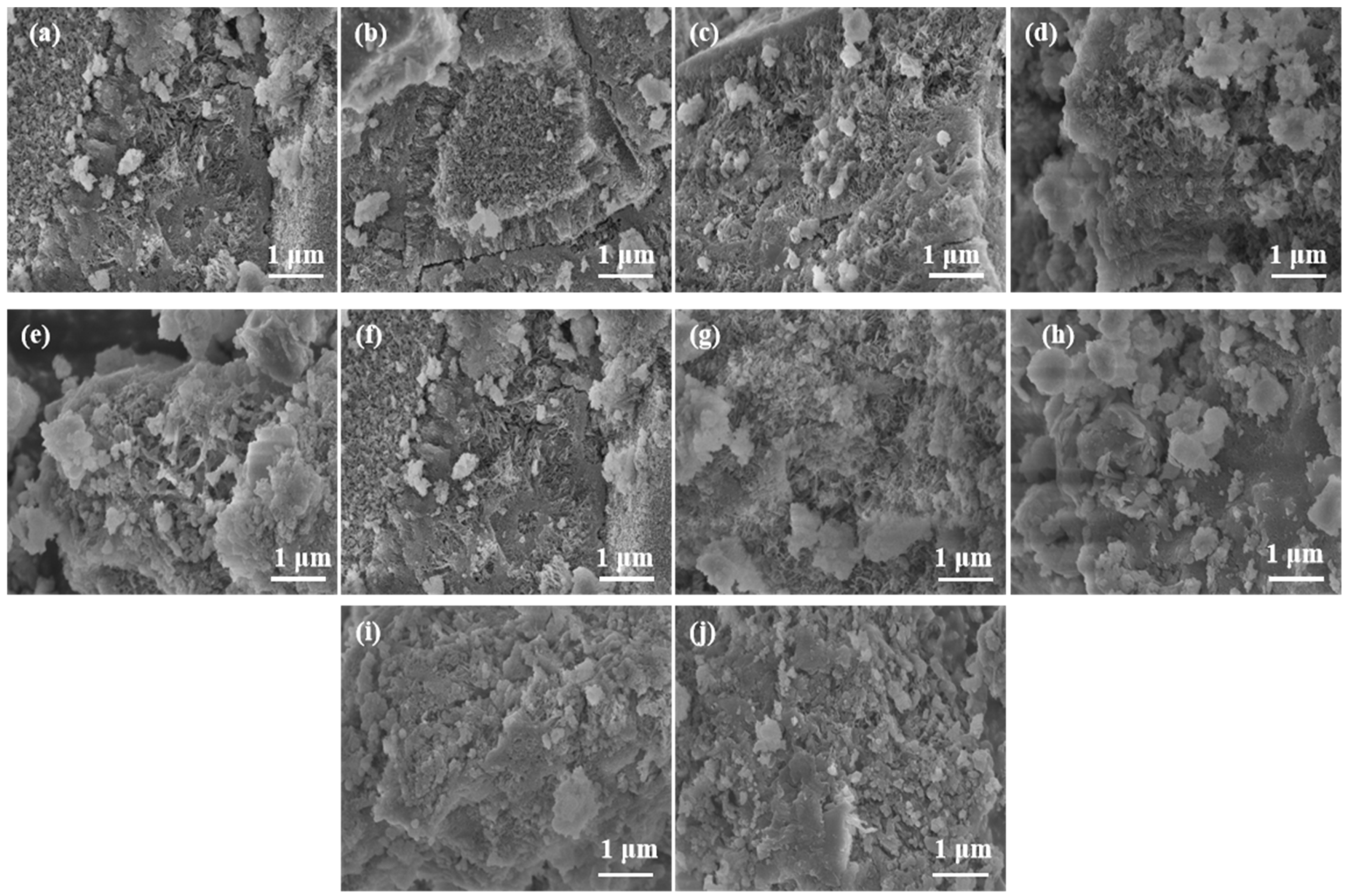



| Parameter | GB/T 18046-2017 | The Detection Value |
|---|---|---|
| Specific area (m2/kg) | ≥400 | 429.00 |
| The flow (%) | ≥95 | 98.00 |
| Activity index/%(28 d) | ≥95 | 98.50 |
| Density (g/cm3) | ≥2.8 | 3.10 |
| Loss on ignition % | ≤1.0 | 0.84 |
| Water content % | ≤1.0 | 0.45 |
| Chemical Composition | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | Fe2O3 | MgO | K2O | TiO2 | SO3 | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GGBS | 34.50 | 17.70 | 34.00 | 1.03 | 6.01 | - | - | 0.04 | - |
| HCFA | 39.12 | 19.71 | 28.42 | 6.62 | 1.32 | 1.66 | 0.87 | 0.84 | - |
| Tuokexun Desert Sand | 73.10 | 14.63 | 2.69 | 2.13 | 1.37 | 2.96 | - | - | 2.70 |
| Mesh Size (mm) | 0.075 | 0.15 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 1.18 | 2.36 | 4.75 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage of screening (%) | 0.6 | 1.2 | 2.8 | 19.1 | 89.4 | 99.0 | 100 |
| Number | GGBS (%) | HCFA (%) | Modulus of Aqueous Glass (n) | Base Equivalent (%) | Alkaline Stimulating Agent (g) | Water (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 80 | 20 | 1.2 | 4 | 81.74 | 182 |
| 2 | 80 | 20 | 1.2 | 6 | 123.46 | 160.34 |
| 3 | 80 | 20 | 1.2 | 8 | 164.21 | 138.78 |
| 4 | 80 | 20 | 1.4 | 4 | 81.74 | 182 |
| 5 | 80 | 20 | 1.4 | 6 | 123.46 | 160.34 |
| 6 | 80 | 20 | 1.4 | 8 | 164.21 | 138.78 |
| 7 | 80 | 20 | 1.6 | 4 | 81.74 | 182 |
| 8 | 80 | 20 | 1.6 | 6 | 123.46 | 160.34 |
| 9 | 80 | 20 | 1.6 | 8 | 164.21 | 138.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Si, Y.; Wu, H.; La, R.; Yang, B.; Liu, T.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Li, M. Physicochemical Properties of Alkali-Activated Ground-Granulated Blast Furnace Slag (GGBS)/High-Calcium Fly Ash (HCFA) Cementitious Composites. Buildings 2025, 15, 3265. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183265
Si Y, Wu H, La R, Yang B, Liu T, Huang Y, Zhou M, Li M. Physicochemical Properties of Alkali-Activated Ground-Granulated Blast Furnace Slag (GGBS)/High-Calcium Fly Ash (HCFA) Cementitious Composites. Buildings. 2025; 15(18):3265. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183265
Chicago/Turabian StyleSi, Yi, Hong Wu, Runtao La, Bo Yang, Ting Liu, Yong Huang, Ming Zhou, and Meng Li. 2025. "Physicochemical Properties of Alkali-Activated Ground-Granulated Blast Furnace Slag (GGBS)/High-Calcium Fly Ash (HCFA) Cementitious Composites" Buildings 15, no. 18: 3265. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183265
APA StyleSi, Y., Wu, H., La, R., Yang, B., Liu, T., Huang, Y., Zhou, M., & Li, M. (2025). Physicochemical Properties of Alkali-Activated Ground-Granulated Blast Furnace Slag (GGBS)/High-Calcium Fly Ash (HCFA) Cementitious Composites. Buildings, 15(18), 3265. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183265






