Seasonal Effects of Window-to-Wall Ratio and Glazing Combinations on Office Building Performance in Qingdao
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Building Model
2.2. Envelope Parameters of the Model
2.3. Internal Load Settings for Energy Consumption Simulation
2.4. Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
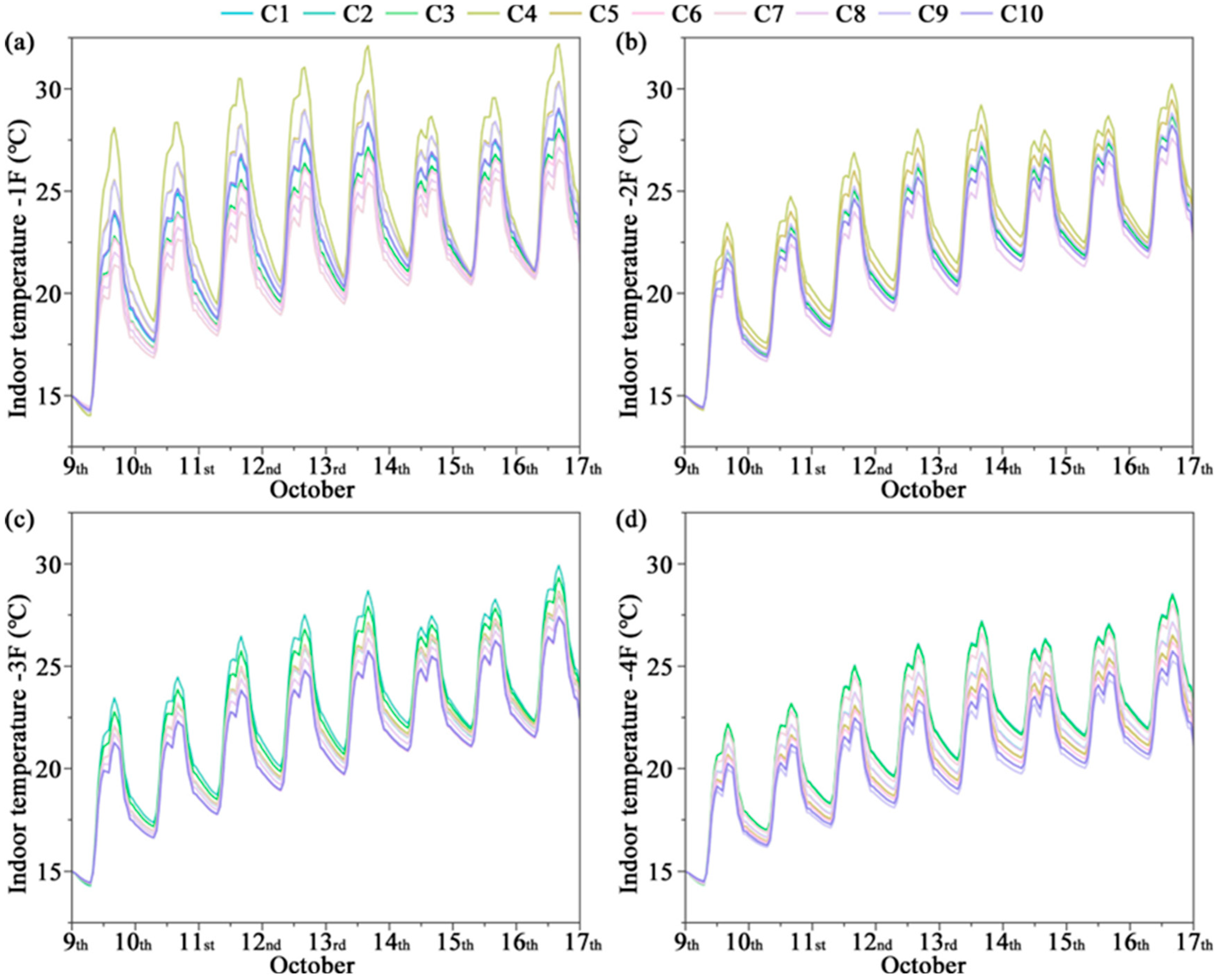
3.1. Indoor Temperature
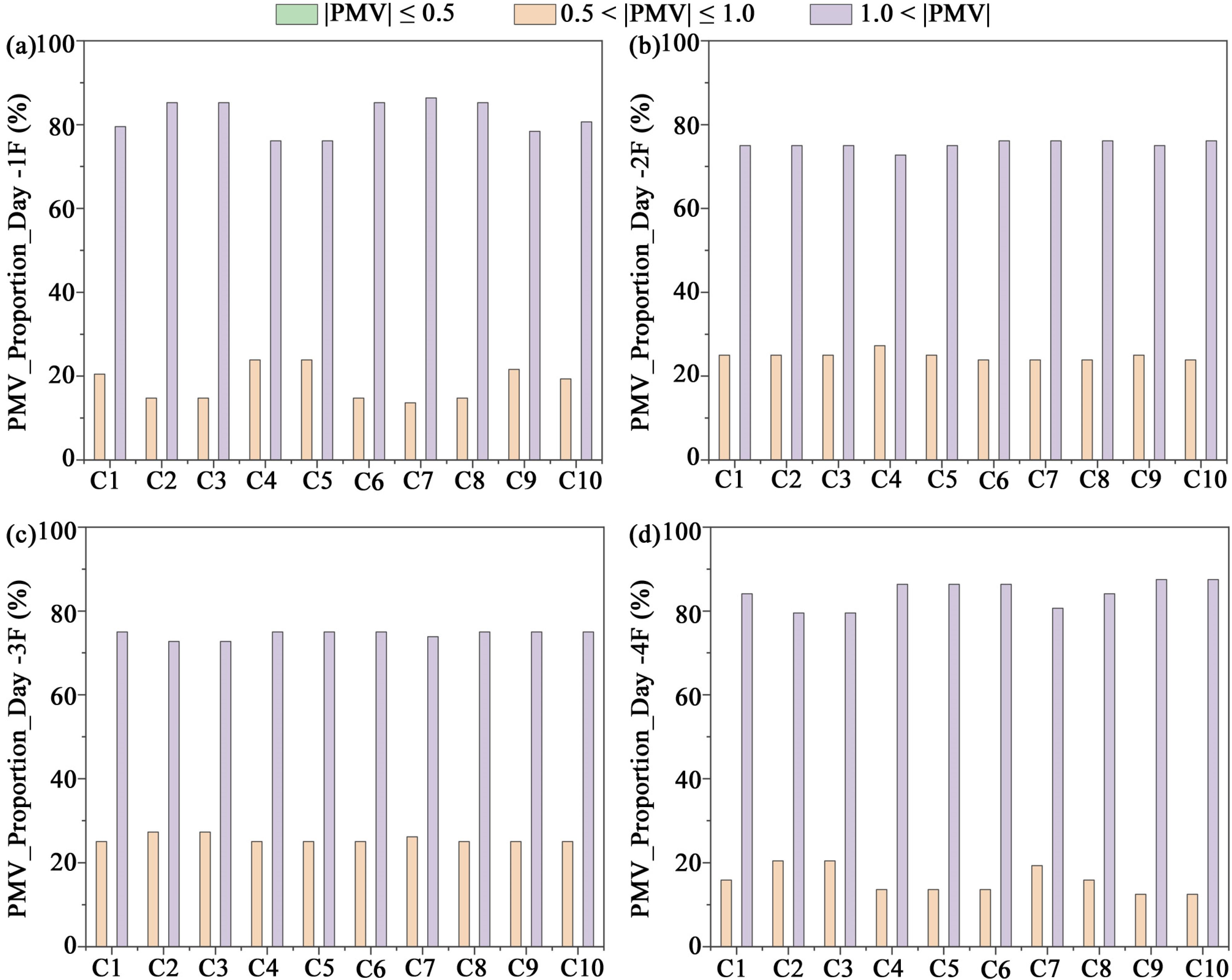
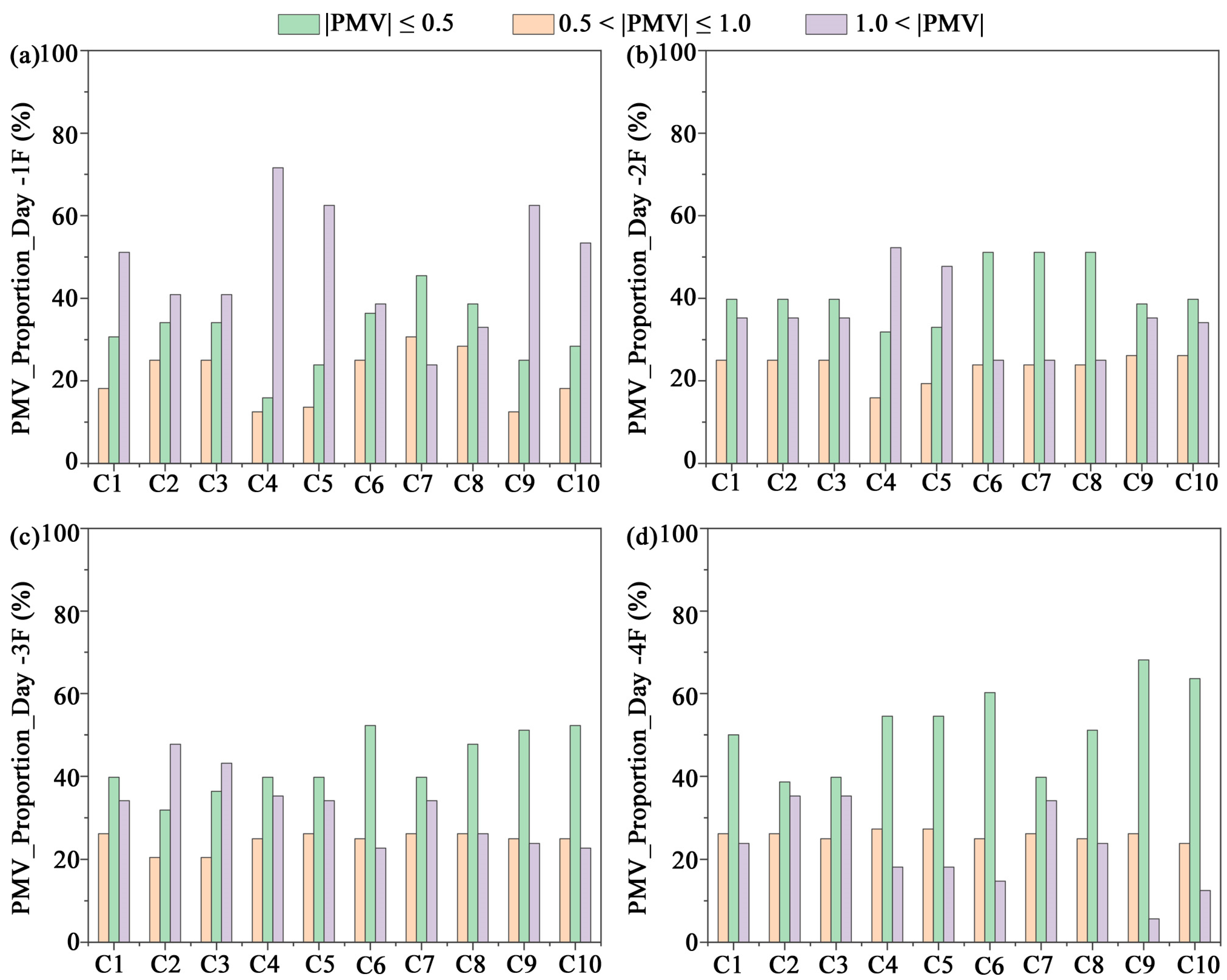
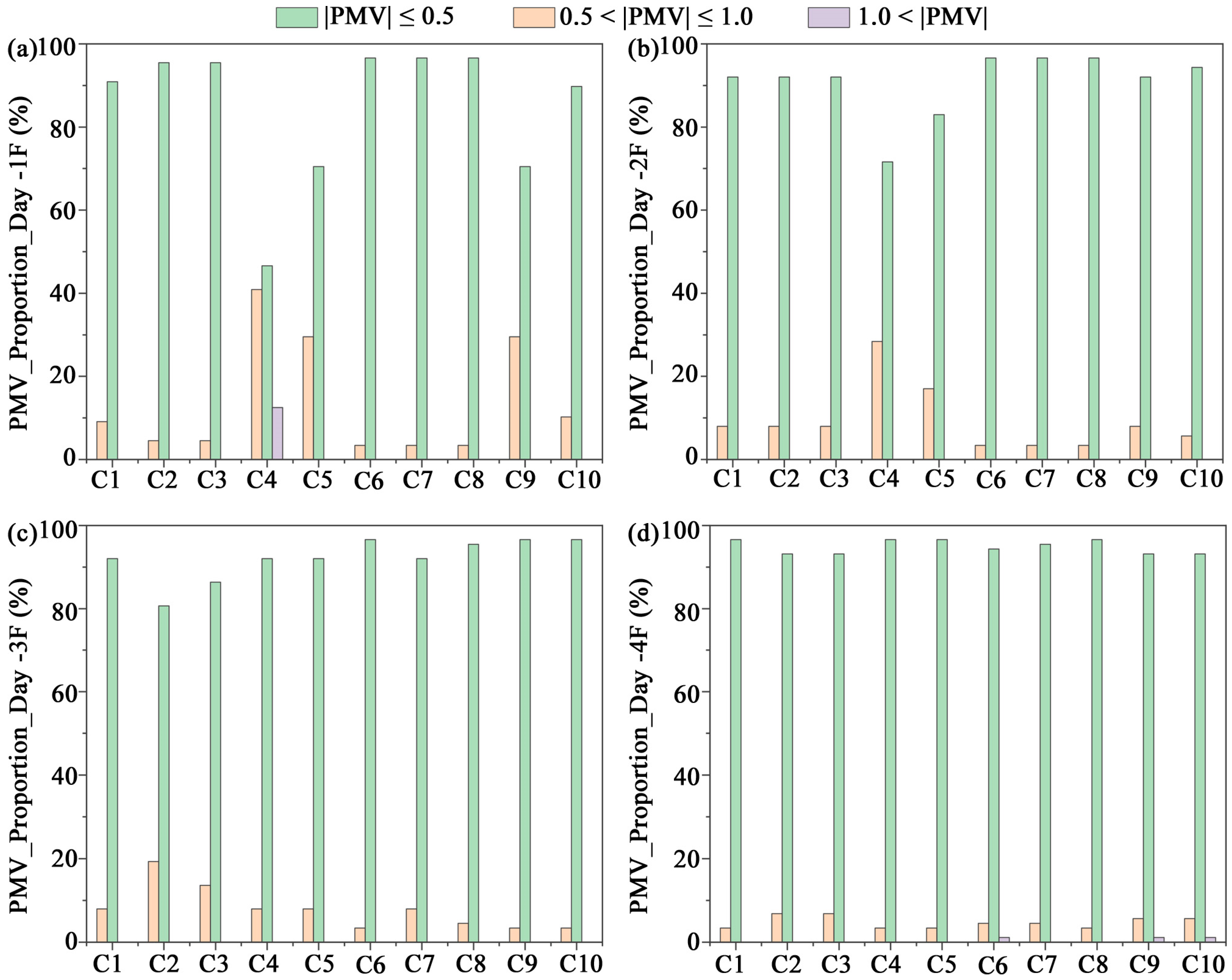
3.2. PMV
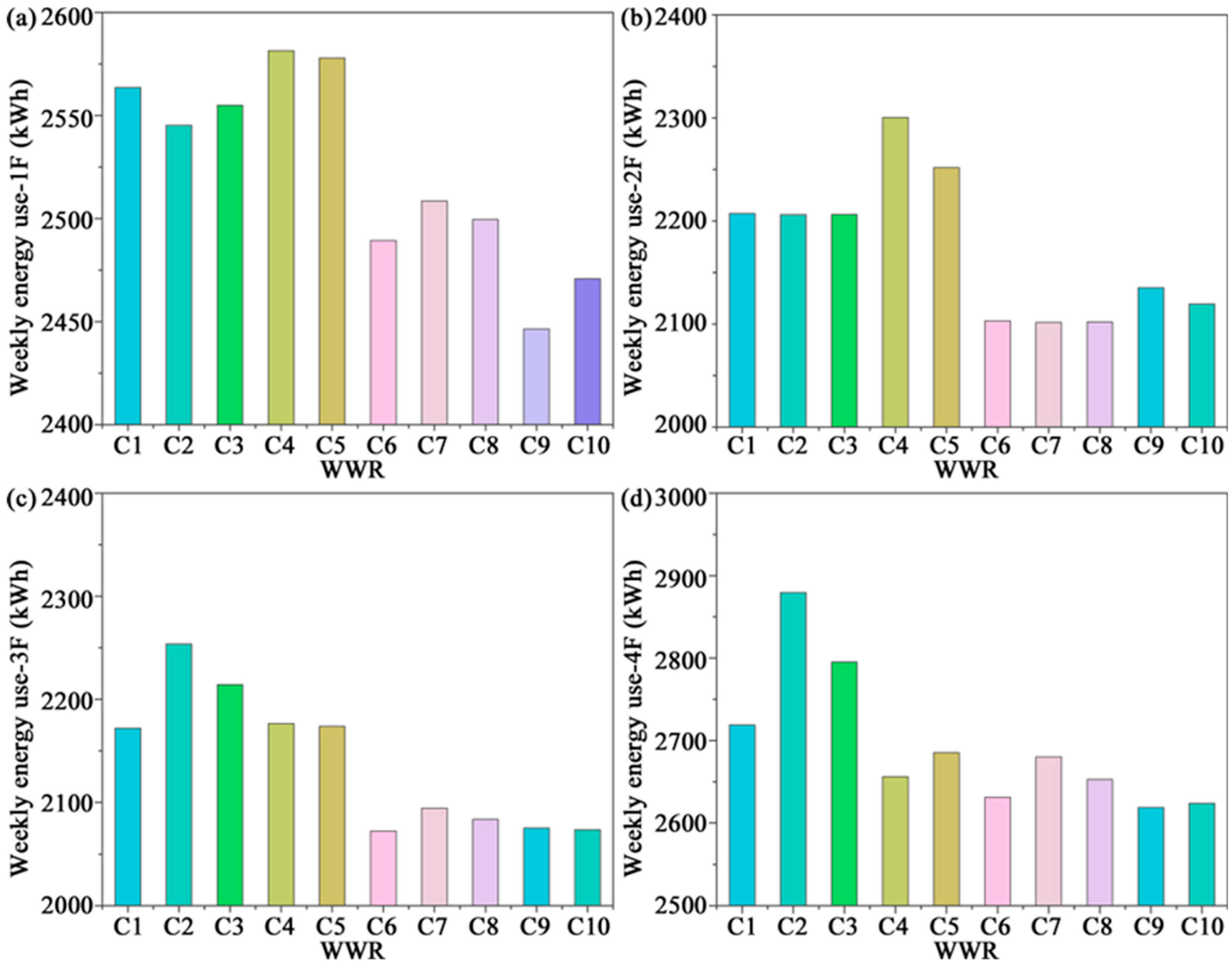
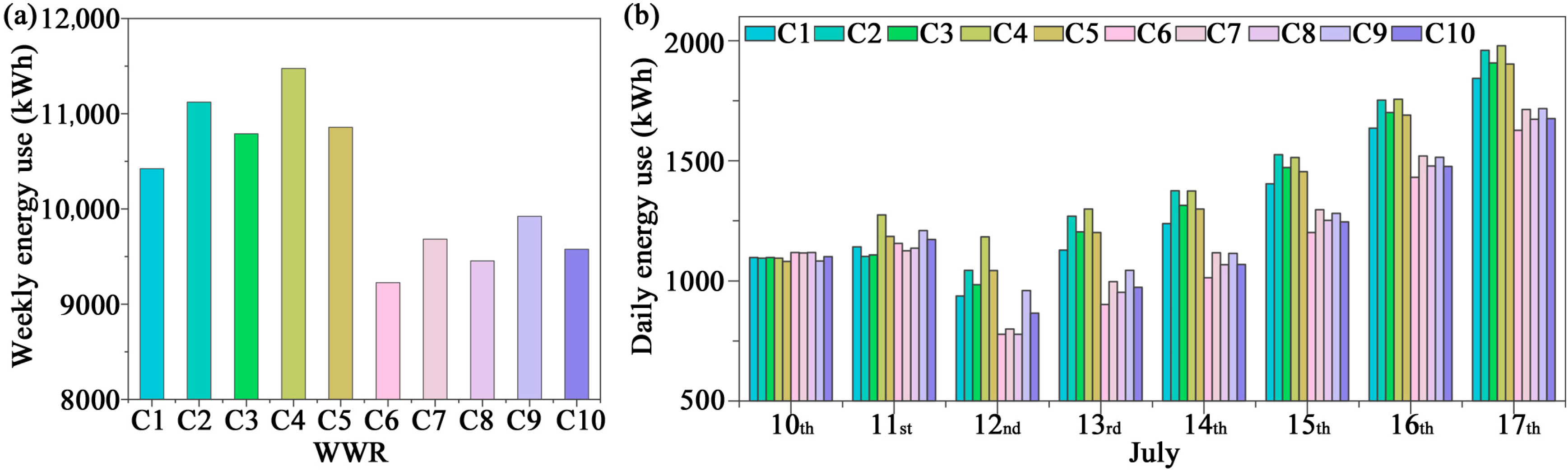
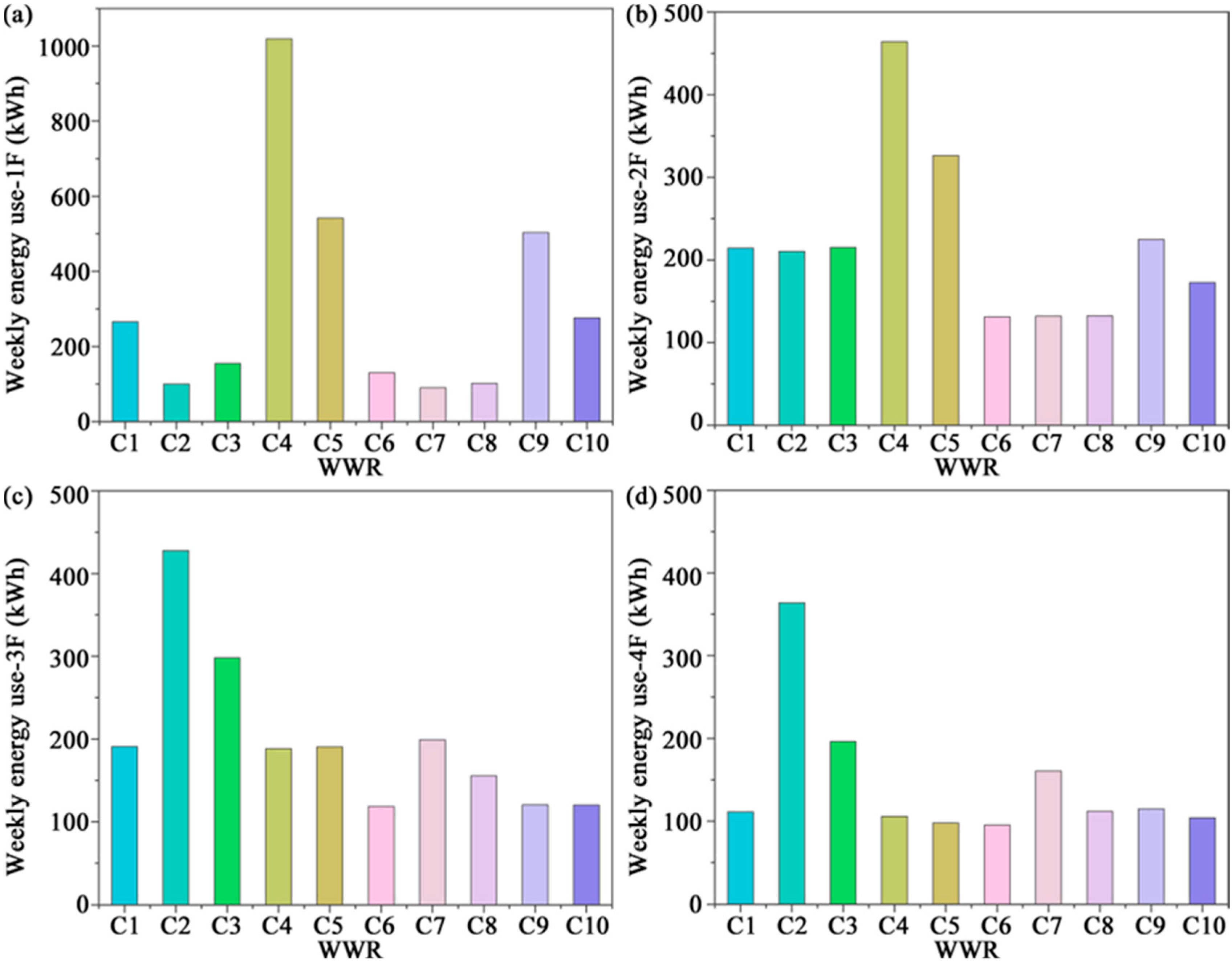
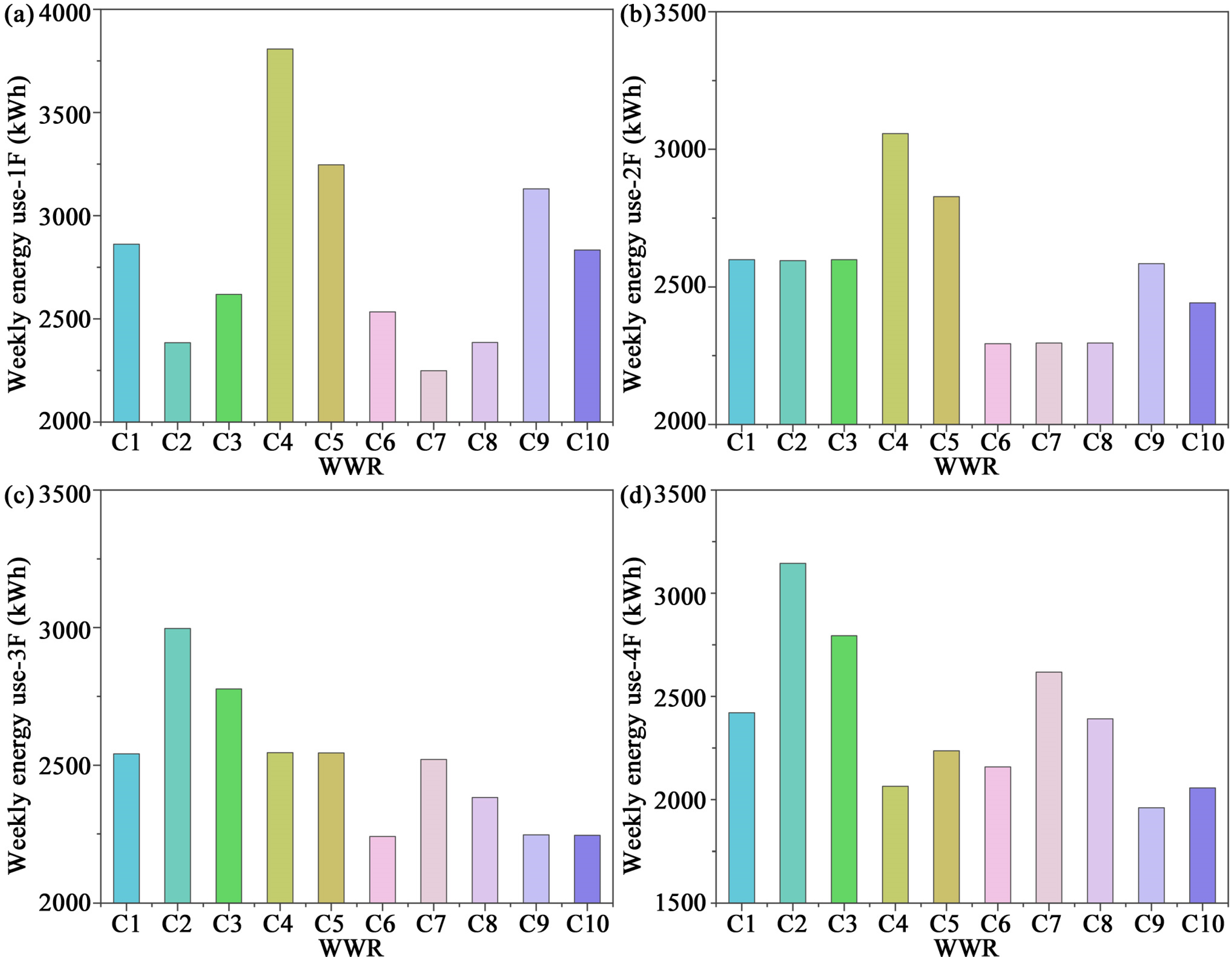
3.3. Energy Consumption
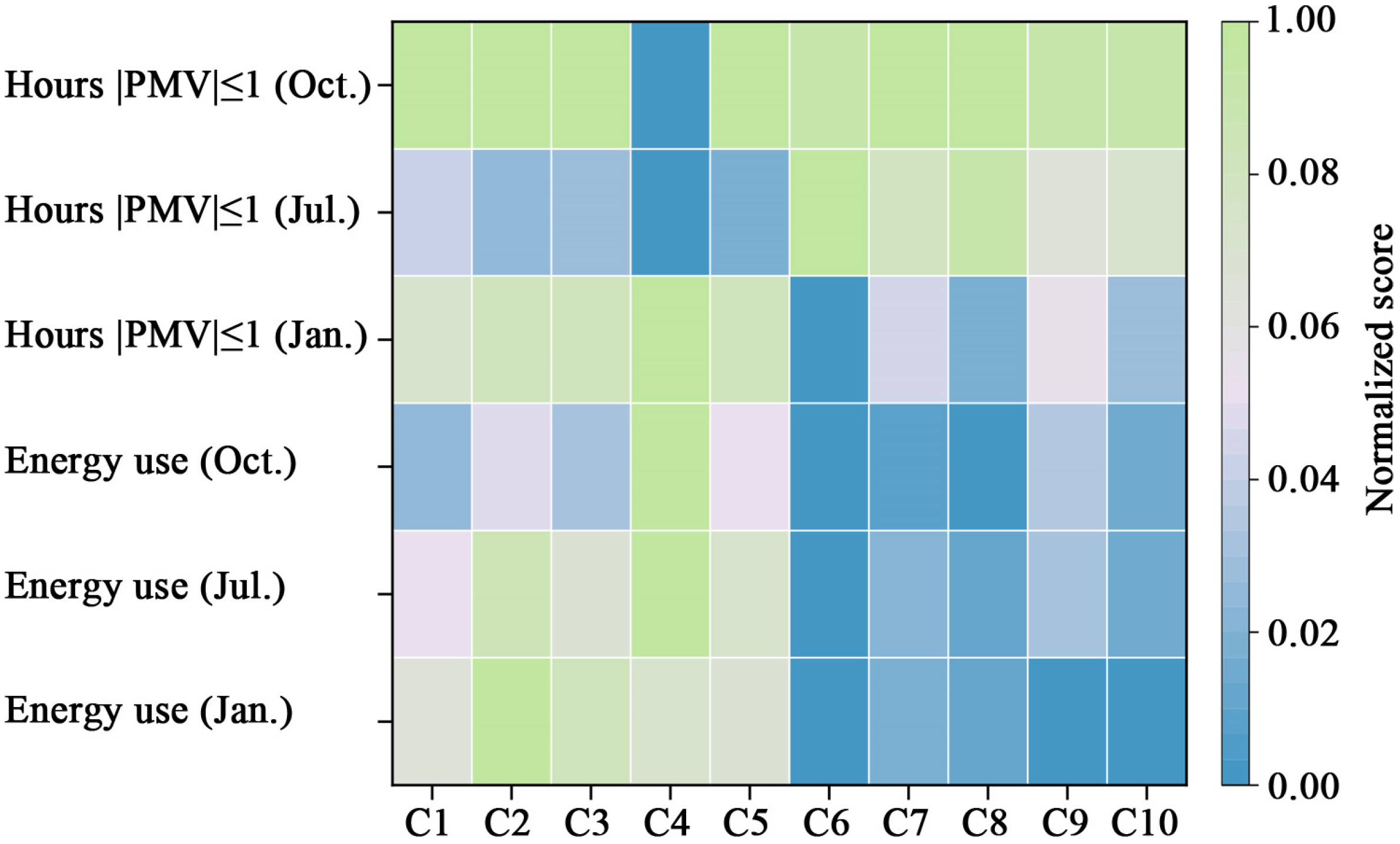
3.4. Summary
4. Discussion
4.1. Seasonal Differences in Thermal Environment Responses
4.2. The Impact of WWR on Thermal Performance
4.3. The Impact of Glazing Type on Thermal Performance
4.4. Design Implications
4.5. Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Significant inter-floor and seasonal differences in thermal environment were observed. In Qingdao’s winter, low outdoor temperatures combined with strong ground heat loss caused the first floor to experience the largest fluctuations, with a pronounced diurnal temperature range. In summer (July), under typical hot conditions, peak indoor temperatures reached 36.07 °C and the diurnal variation exceeded 22.6 °C, highlighting the large thermal fluctuations characteristic of temperate monsoon climates. In October, although the overall climate was milder, the diurnal variation still induced slight overheating on the first floor.
- (2)
- In the hot summer with large diurnal variations, low WWR combined with double glazing effectively suppressed overheating and improved comfort; specifically, with WWR = 30% and double glazing, the proportion of comfortable hours (|PMV| ≤ 0.5) reached 51.14%. In winter, due to the combined effects of low ambient temperatures and daytime solar radiation, higher WWR improved passive solar gains and enhanced daytime comfort. However, in the transitional season (October), excessively high WWR easily led to overheating because of the large diurnal temperature swing.
- (3)
- In January, it reduced total building loads by 366–500 kWh compared with single glazing. In climates with both heating and cooling demands and large diurnal variations, the overall trend showed that smaller WWR generally reduced energy consumption. However, large variations in WWR across floors disrupted thermal stability and markedly increased energy demand. Notably, single glazing exhibited stronger passive solar gains in winter daytime; if nighttime heat loss could be effectively mitigated, overall energy efficiency could potentially be improved.
- (4)
- In summer and the transitional season, energy consumption differences were more volatile. In particular, during October, the combination of single glazing with a strongly increasing WWR pattern resulted in energy consumption that was 2.69 times higher than the measured baseline, underscoring the strong sensitivity of energy performance to WWR and glazing configurations.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Daily Energy Use (kWh) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | |
| 10th | 210.57 | 220.01 | 215.43 | 192.02 | 203.24 | 210.85 | 219.93 | 215.49 | 192.43 | 201.71 |
| 11st | 207.22 | 227.66 | 217.77 | 165.15 | 190.84 | 213.85 | 229.30 | 221.77 | 181.66 | 197.99 |
| 12nd | 229.31 | 251.77 | 240.88 | 183.66 | 211.45 | 236.92 | 253.55 | 245.44 | 202.44 | 219.90 |
| 13rd | 298.96 | 296.59 | 297.68 | 303.79 | 301.14 | 289.75 | 292.64 | 291.20 | 284.71 | 287.25 |
| 14th | 333.13 | 323.27 | 328.13 | 350.44 | 340.94 | 317.86 | 316.62 | 317.26 | 320.38 | 319.39 |
| 15th | 403.22 | 380.00 | 391.46 | 445.42 | 421.56 | 379.44 | 369.85 | 374.59 | 398.46 | 389.43 |
| 16th | 411.10 | 409.25 | 410.42 | 408.99 | 412.15 | 401.70 | 403.32 | 402.67 | 396.42 | 399.91 |
| 17th | 470.12 | 436.72 | 453.16 | 531.95 | 496.67 | 439.00 | 423.38 | 431.11 | 469.96 | 455.19 |
| Total | 2563.63 | 2545.27 | 2554.93 | 2581.42 | 2577.99 | 2489.37 | 2508.59 | 2499.53 | 2446.46 | 2470.77 |
| Daily Energy Use (kWh) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | |
| 10th | 242.49 | 242.38 | 242.40 | 238.77 | 240.46 | 241.22 | 241.11 | 241.16 | 236.33 | 238.70 |
| 11st | 210.00 | 209.81 | 209.90 | 200.08 | 204.74 | 211.74 | 211.58 | 211.65 | 202.67 | 207.12 |
| 12nd | 202.93 | 202.81 | 202.83 | 192.23 | 197.26 | 204.49 | 204.39 | 204.43 | 194.71 | 199.52 |
| 13rd | 241.84 | 241.80 | 241.79 | 249.90 | 245.63 | 230.75 | 230.65 | 230.70 | 231.67 | 231.17 |
| 14th | 262.82 | 262.56 | 262.64 | 280.15 | 271.17 | 245.12 | 244.85 | 244.95 | 251.61 | 248.38 |
| 15th | 323.82 | 323.52 | 323.62 | 354.92 | 339.12 | 297.56 | 297.31 | 297.39 | 313.21 | 305.49 |
| 16th | 338.97 | 338.78 | 338.83 | 358.33 | 348.33 | 320.99 | 320.77 | 320.84 | 331.03 | 326.19 |
| 17th | 384.32 | 384.45 | 384.37 | 426.11 | 405.10 | 350.96 | 350.97 | 350.93 | 374.07 | 362.83 |
| Total | 2207.19 | 2206.11 | 2206.38 | 2300.49 | 2251.81 | 2102.83 | 2101.63 | 2102.05 | 2135.30 | 2119.40 |
| Daily Energy Use (kWh) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | |
| 10th | 241.86 | 237.65 | 239.69 | 241.92 | 241.89 | 240.70 | 235.46 | 238.02 | 240.73 | 240.72 |
| 11st | 209.53 | 198.51 | 203.99 | 209.66 | 209.56 | 211.69 | 201.90 | 206.73 | 211.74 | 211.71 |
| 12nd | 201.60 | 189.78 | 195.65 | 201.81 | 201.67 | 203.71 | 193.04 | 198.33 | 203.80 | 203.72 |
| 13rd | 238.86 | 245.75 | 242.32 | 239.16 | 238.97 | 228.32 | 228.22 | 228.22 | 228.49 | 228.39 |
| 14th | 257.62 | 273.03 | 265.49 | 258.22 | 257.85 | 240.62 | 245.53 | 243.07 | 240.98 | 240.78 |
| 15th | 316.77 | 345.73 | 331.58 | 317.68 | 317.15 | 291.33 | 305.06 | 298.27 | 291.93 | 291.63 |
| 16th | 330.50 | 347.69 | 339.50 | 331.63 | 330.99 | 313.26 | 321.31 | 317.41 | 314.06 | 313.65 |
| 17th | 375.24 | 415.53 | 395.98 | 376.45 | 375.76 | 342.46 | 363.91 | 353.41 | 343.38 | 342.94 |
| Total | 2171.98 | 2253.67 | 2214.2 | 2176.53 | 2173.84 | 2072.09 | 2094.43 | 2083.46 | 2075.11 | 2073.54 |
| Daily Energy Use (kWh) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | |
| 10th | 280.18 | 278.26 | 278.78 | 282.57 | 281.26 | 278.42 | 272.92 | 275.43 | 281.92 | 280.13 |
| 11st | 266.53 | 252.41 | 258.93 | 275.54 | 270.87 | 268.01 | 254.36 | 260.90 | 275.79 | 271.84 |
| 12nd | 269.09 | 253.1 | 260.37 | 279.55 | 274.09 | 270.74 | 255.07 | 262.52 | 279.76 | 275.17 |
| 13rd | 307.71 | 321.54 | 313.75 | 303.58 | 305.31 | 299.03 | 299.85 | 298.93 | 300.20 | 299.46 |
| 14th | 330.82 | 358.72 | 344.07 | 319.48 | 324.83 | 316.46 | 325.33 | 320.40 | 313.72 | 314.91 |
| 15th | 391.34 | 441.36 | 415.91 | 368.56 | 379.60 | 369.51 | 392.81 | 380.72 | 359.71 | 364.41 |
| 16th | 414.44 | 446.81 | 430.35 | 400.56 | 407.19 | 398.72 | 413.52 | 405.78 | 393.23 | 395.79 |
| 17th | 458.80 | 527.45 | 493.07 | 426.28 | 442.19 | 430.31 | 466.21 | 447.93 | 414.31 | 422.08 |
| Total | 2718.91 | 2879.65 | 2795.23 | 2656.12 | 2685.34 | 2631.2 | 2680.07 | 2652.61 | 2618.64 | 2623.79 |
| Daily Energy Use (kWh) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | |
| 10th | 261.58 | 277.84 | 271.34 | 269.14 | 247.36 | 271.83 | 280.33 | 276.33 | 247.06 | 259.17 |
| 11st | 294.66 | 273.31 | 281.27 | 410.61 | 337.39 | 280.01 | 276.97 | 273.44 | 339.58 | 299.50 |
| 12nd | 319.44 | 225.08 | 270.15 | 488.36 | 392.58 | 259.76 | 200.79 | 230.42 | 379.65 | 321.62 |
| 13rd | 349.46 | 261.27 | 305.21 | 499.07 | 414.55 | 291.14 | 235.80 | 263.22 | 395.95 | 346.31 |
| 14th | 353.73 | 275.82 | 314.63 | 486.48 | 411.66 | 299.90 | 251.47 | 275.69 | 391.30 | 348.08 |
| 15th | 377.91 | 311.50 | 344.69 | 490.80 | 427.52 | 330.57 | 289.64 | 310.14 | 407.91 | 371.48 |
| 16th | 429.03 | 359.19 | 393.87 | 551.44 | 481.83 | 378.89 | 336.97 | 357.84 | 459.83 | 421.22 |
| 17th | 476.50 | 400.55 | 438.07 | 611.73 | 534.17 | 421.52 | 376.97 | 399.05 | 508.57 | 466.70 |
| Total | 2862.31 | 2384.56 | 2619.23 | 3807.63 | 3247.06 | 2533.62 | 2248.94 | 2386.13 | 3129.85 | 2834.08 |
| Daily Energy Use (kWh) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | |
| 10th | 276.45 | 276.48 | 276.46 | 268.14 | 272.31 | 280.94 | 280.94 | 280.96 | 275.87 | 278.42 |
| 11st | 276.81 | 277.28 | 277.07 | 282.72 | 271.72 | 287.54 | 287.80 | 287.70 | 274.96 | 281.25 |
| 12nd | 226.93 | 225.18 | 226.15 | 313.56 | 271.63 | 180.93 | 180.55 | 180.72 | 231.59 | 201.94 |
| 13rd | 282.77 | 281.40 | 282.30 | 371.08 | 328.57 | 224.69 | 224.36 | 224.61 | 284.13 | 255.13 |
| 14th | 312.90 | 312.28 | 312.88 | 392.03 | 353.97 | 254.73 | 255.05 | 255.04 | 311.35 | 284.88 |
| 15th | 353.50 | 353.37 | 353.74 | 421.69 | 388.87 | 301.84 | 302.56 | 302.36 | 350.23 | 327.6 |
| 16th | 409.80 | 410.05 | 410.25 | 477.48 | 444.91 | 357.96 | 358.95 | 358.61 | 404.36 | 382.59 |
| 17th | 459.53 | 459.77 | 459.96 | 530.35 | 496.17 | 405.12 | 406.09 | 405.74 | 452.01 | 429.91 |
| Total | 2598.69 | 2595.81 | 2598.81 | 3057.05 | 2828.15 | 2293.75 | 2296.3 | 2295.74 | 2584.5 | 2441.72 |
| Daily Energy Use (kWh) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | |
| 10th | 276.57 | 268.42 | 272.48 | 276.55 | 276.57 | 281.05 | 276.08 | 278.59 | 281.04 | 281.03 |
| 11st | 279.05 | 278.79 | 271.38 | 278.69 | 278.88 | 289.44 | 278.13 | 283.78 | 289.16 | 289.29 |
| 12nd | 213.20 | 297.27 | 257.65 | 215.05 | 214.18 | 175.79 | 214.26 | 189.55 | 176.45 | 176.15 |
| 13rd | 267.37 | 355.04 | 313.92 | 268.65 | 268.18 | 210.09 | 266.07 | 239.64 | 212.06 | 211.24 |
| 14th | 300.50 | 380.40 | 343.11 | 301.25 | 301.15 | 240.96 | 297.56 | 270.79 | 242.49 | 241.98 |
| 15th | 344.64 | 414.46 | 382.02 | 345.04 | 345.18 | 291.66 | 340.98 | 317.66 | 292.76 | 292.49 |
| 16th | 404.18 | 473.99 | 441.45 | 404.26 | 404.52 | 351.03 | 399.02 | 376.29 | 351.81 | 351.70 |
| 17th | 456.13 | 528.75 | 494.79 | 456.18 | 456.43 | 400.62 | 449.08 | 426.07 | 401.28 | 401.22 |
| Total | 2541.64 | 2997.12 | 2776.8 | 2545.67 | 2545.09 | 2240.64 | 2521.18 | 2382.37 | 2247.05 | 2245.1 |
| Daily Energy Use (kWh) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | |
| 10th | 282.60 | 271.44 | 277.20 | 281.09 | 284.36 | 283.90 | 279.02 | 282.53 | 278.44 | 281.90 |
| 11st | 290.87 | 272.48 | 278.08 | 302.97 | 297.14 | 298.71 | 282.46 | 290.84 | 305.86 | 302.40 |
| 12nd | 177.18 | 296.64 | 230.62 | 166.35 | 164.91 | 161.73 | 203.64 | 176.68 | 171.70 | 165.89 |
| 13rd | 228.14 | 371.94 | 302.25 | 160.39 | 189.92 | 176.27 | 270.81 | 224.74 | 151.48 | 160.73 |
| 14th | 271.19 | 406.69 | 343.73 | 194.13 | 231.90 | 217.29 | 312.77 | 266.18 | 169.29 | 193.48 |
| 15th | 327.82 | 446.39 | 391.89 | 256.08 | 293.24 | 277.65 | 362.95 | 322.33 | 230.42 | 254.29 |
| 16th | 392.65 | 508.92 | 455.31 | 323.09 | 358.88 | 343.00 | 424.79 | 385.83 | 298.33 | 320.86 |
| 17th | 450.57 | 570.53 | 514.84 | 380.08 | 416.13 | 399.33 | 481.26 | 442.12 | 355.25 | 377.41 |
| Total | 2421.02 | 3145.03 | 2793.92 | 2064.18 | 2236.48 | 2157.88 | 2617.7 | 2391.25 | 1960.77 | 2056.96 |
| Daily Energy Use (kWh) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | |
| 10th | 13.03 | 22.37 | 18.76 | 44.07 | 10.34 | 19.72 | 22.85 | 23.54 | 10.50 | 12.81 |
| 11st | 22.92 | 43.28 | 34.94 | 59.34 | 14.62 | 36.34 | 46.55 | 41.98 | 15.37 | 20.91 |
| 12nd | 13.66 | 7.47 | 6.30 | 137.92 | 58.17 | 6.66 | 8.14 | 7.43 | 54.32 | 16.29 |
| 13rd | 27.42 | 0.00 | 5.20 | 153.97 | 81.82 | 2.16 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 74.55 | 30.52 |
| 14th | 52.46 | 1.31 | 20.49 | 182.20 | 109.72 | 13.42 | 0.00 | 1.99 | 99.19 | 53.76 |
| 15th | 27.42 | 0.00 | 5.20 | 153.97 | 81.82 | 2.16 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 74.55 | 30.52 |
| 16th | 27.57 | 1.63 | 13.65 | 97.69 | 58.41 | 9.29 | 0.00 | 1.69 | 55.65 | 29.72 |
| 17th | 80.98 | 24.13 | 50.30 | 189.70 | 127.06 | 40.52 | 12.71 | 25.42 | 118.91 | 81.88 |
| Total | 265.46 | 100.19 | 154.84 | 1018.86 | 541.96 | 130.27 | 90.25 | 102.05 | 503.04 | 276.41 |
| Daily Energy Use (kWh) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | |
| 10th | 17.79 | 17.80 | 17.80 | 10.29 | 13.86 | 23.15 | 23.14 | 23.15 | 17.43 | 22.09 |
| 11st | 40.82 | 41.06 | 40.95 | 26.99 | 35.00 | 46.99 | 47.12 | 47.04 | 39.81 | 43.46 |
| 12nd | 6.69 | 6.79 | 6.75 | 16.75 | 7.12 | 9.92 | 10.01 | 9.98 | 6.48 | 7.24 |
| 13rd | 2.58 | 2.04 | 2.35 | 51.90 | 20.19 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 4.61 | 0.00 |
| 14th | 25.28 | 23.90 | 25.06 | 97.33 | 61.90 | 0.67 | 0.58 | 0.61 | 28.92 | 11.19 |
| 15th | 2.58 | 2.04 | 2.35 | 51.90 | 20.19 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 4.61 | 0.00 |
| 16th | 32.76 | 31.79 | 33.41 | 73.79 | 55.73 | 7.84 | 8.01 | 8.11 | 36.12 | 21.13 |
| 17th | 85.86 | 84.91 | 86.51 | 135.00 | 112.32 | 42.61 | 43.18 | 43.42 | 86.71 | 67.62 |
| Total | 214.36 | 210.33 | 215.18 | 463.95 | 326.31 | 131.18 | 132.04 | 132.31 | 224.69 | 172.73 |
| Daily Energy Use (kWh) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | |
| 10th | 17.81 | 10.30 | 13.86 | 17.80 | 17.81 | 23.17 | 17.43 | 22.12 | 23.15 | 23.14 |
| 11st | 41.65 | 29.48 | 36.70 | 41.48 | 41.55 | 47.63 | 41.13 | 44.41 | 47.50 | 47.57 |
| 12nd | 7.13 | 12.21 | 6.35 | 7.02 | 7.08 | 10.48 | 7.12 | 7.74 | 10.36 | 10.42 |
| 13rd | 0.65 | 39.24 | 12.66 | 0.97 | 0.82 | 0.00 | 0.94 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 14th | 16.64 | 87.56 | 51.40 | 17.84 | 17.45 | 0.00 | 18.44 | 5.39 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 15th | 0.65 | 39.24 | 12.66 | 0.97 | 0.82 | 0.00 | 0.94 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 16th | 25.85 | 72.99 | 52.46 | 24.73 | 25.71 | 3.20 | 29.54 | 15.31 | 4.18 | 3.88 |
| 17th | 80.40 | 136.74 | 111.95 | 77.55 | 79.46 | 33.95 | 83.52 | 60.52 | 35.41 | 35.24 |
| Total | 190.78 | 427.76 | 298.04 | 188.36 | 190.70 | 118.43 | 199.06 | 155.49 | 120.60 | 120.25 |
| Daily Energy Use (kWh) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | |
| 10th | 24.46 | 11.29 | 17.37 | 33.65 | 24.28 | 25.57 | 21.94 | 24.24 | 39.78 | 31.97 |
| 11st | 48.91 | 33.35 | 41.72 | 55.93 | 52.31 | 53.25 | 44.29 | 48.89 | 56.47 | 55.64 |
| 12nd | 10.41 | 8.49 | 6.77 | 11.54 | 11.60 | 11.42 | 7.36 | 10.49 | 12.14 | 11.43 |
| 13rd | 0.00 | 25.46 | 1.53 | 0.93 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.50 | 0.99 |
| 14th | 0.00 | 78.09 | 21.76 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 9.05 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 15th | 0.00 | 25.46 | 1.53 | 0.93 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.50 | 0.99 |
| 16th | 0.58 | 55.10 | 21.43 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 12.70 | 0.62 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 17th | 26.89 | 126.68 | 84.21 | 2.71 | 9.65 | 5.19 | 65.20 | 27.65 | 3.57 | 2.92 |
| Total | 111.25 | 363.92 | 196.32 | 105.69 | 97.84 | 95.43 | 160.54 | 111.89 | 114.96 | 103.94 |
References
- Tsinghua University. Building energy conservation research center. In 2020 Annual Report on China Building Energy Efficiency; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cappelletti, F.; Prada, A.; Romagnoni, P.; Gasparella, A. Passive performance of glazed components in heating and cooling of an open-space office under controlled indoor thermal comfort. Build. Environ. 2014, 72, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needell, D.R.; Phelan, M.E.; Hartlove, J.T.; Atwater, H.A. Solar power windows: Connecting scientific advances to market signals. Energy 2021, 219, 119567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zomorodian, Z.S.; Tahsildoost, M. Assessment of window performance in classrooms by long term spatial comfort metrics. Energy Build. 2017, 134, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hee, W.J.; Alghoul, M.A.; Bakhtyar, B.; Elayeb, O.; Shameri, M.A.; Alrubaih, M.S.; Sopian, K. The role of window glazing on daylighting and energy saving in buildings. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 323–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, A.R.; Rodrigues, E.; Gaspar, A.R.; Gomes, Á. A thermal performance parametric study of window type, orientation, size and shadowing effect. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2016, 26, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, K.W.; Cho, Y.H. A study on the proposes of energy analysis indicator by the window elements of office buildings in Korea. Energy Build. 2014, 73, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goia, F. Search for the optimal window-to-wall ratio in office buildings in different European climates and the implications on total energy saving potential. Sol. Energy 2016, 132, 467–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghoul, S.K.; Rijabo, H.G.; Mashena, M.E. Energy consumption in buildings: A correlation for the influence of window to wall ratio and window orientation in Tripoli, Libya. J. Build. Eng. 2017, 11, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Fu, W.; Meng, X. Climate adaptation analysis of the thermal performance of dynamic rotating latent-energy-storage envelope (DRLESE) in China. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2025, 71, 106254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Hu, C.; Meng, X. Formation analysis of cooling load from envelopes under air-conditioning intermittent operation. Sol. Energy 2025, 292, 113428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Hu, H.; Wang, X. China’s newest design of apartment buildings with modernized façade: A comparative evaluation of its energy performance in five major climate zones. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 117, 105954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, G.; Deng, Q. Multi-objective optimization of rural residential envelopes in cold regions of China based on performance and economic efficiency. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 61, 104937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shen, X.; Qu, K. Interpretable machine learning for predicting and optimizing residential building performance in cold regions. Energy Build. 2025, 116321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.T.; Li, L.J.; Liu, G.D.; Zhang, L. Exploration on an optimal Wall-window ratio in public buildings based on building energy consumption in Qingdao area. Build. Sci. 2016, 32, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, N.; Li, L.; Morandi, A.; Zhao, Y. A metamodel-based multi-objective optimization method to balance thermal comfort and energy efficiency in a campus gymnasium. Energy Build. 2021, 253, 111513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafian, T.; Moazzen, N. The impact of glazing ratio and window configuration on occupants’ comfort and energy demand: The case study of a school building in Eskisehir, Turkey. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 47, 101483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Hu, Y.; Liu, M.; Heiselberg, P. Influence of design parameters on the night ventilation performance in office buildings based on sensitivity analysis. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Chen, X.-N.; Xu, B.; Pei, G. Investigation of occupied/unoccupied period on thermal comfort in Guangzhou: Challenges and opportunities of public buildings with high window-wall ratio. Energy 2022, 244, 123186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, C.E.; Aries, M.B.; Van Loenen, E.J.; Hensen, J.L. Considerations on design optimization criteria for windows providing low energy consumption and high visual comfort. Appl. Energy 2012, 95, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, K.; Han, L.; Guo, L. The Climate Change in Qingdao during 1899–2015 and Its Response to Global Warming. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2018, 6, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- GB 50176-2016; Code for Thermal Design of Civil Buildings. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 50189-2015; Design Standard for Energy Efficiency of Public Buildings. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2015.
- ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 55-2004; Thermal Environmental Conditions for Human Occupancy. ASHRAE: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2004.
- Liu, N.; Qin, Y. Building Thermal Environment; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Heydari, A.; Sadati, S.E.; Gharib, M.R. Effects of different window configurations on energy consumption in building: Optimization and economic analysis. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 35, 102099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustufa, A.; Anwar, M.; Khan, T.I. Energy optimization of an institutional building to reduce the energy and air conditioning demand. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Liu, Z.-A.; Zhang, L. Influence and sensitivity evaluation of window thermal parameters variations on economic benefits of insulation materials for building exterior walls–a case study for traditional dwelling in China. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2023, 46, 102207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhou, X.; Yan, D.; Guo, F.; Hong, T.; Jiang, Y. A systematic review of building energy sufficiency towards energy and climate targets. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 181, 113316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jiang, S.; Qiao, Y.; Ye, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y. Key drivers of life-cycle carbon emission for residential buildings in cold zone of China: A comparative study of thermal design and morphological design factors. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 111, 113449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Ding, W.; Liu, X.; Zeng, Y.; Adu, E.; Shao, H. Multi-objective optimization framework for the building envelope of public rental housing in China’s cold regions. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 104, 112261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Calautit, J.K.; Jimenez-Bescos, C. Examining the regulating impact of thermal mass on overheating, and the role of night ventilation, within different climates and future scenarios across China. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 9, 100534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamero-Salinas, J.; Monge-Barrio, A.; Sánchez-Ostiz, A. Overheating risk assessment of different dwellings during the hottest season of a warm tropical climate. Build. Environ. 2020, 171, 106664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hien, W.N.; Wang, L.; Chandra, A.N.; Pandey, A.R.; Wei, X. Effects of double glazed facade on energy consumption, thermal comfort and condensation for a typical office building in Singapore. Energy Build. 2005, 37, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawadhi, E.M. Using phase change materials in window shutter to reduce the solar heat gain. Energy Build. 2012, 47, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jiang, T.; Meng, Y.; Yang, R.; Tan, G.; Long, Y. Scalable thermochromic smart windows with passive radiative cooling regulation. Science 2021, 374, 1501–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, H.; Xu, W.; Li, A.; Lv, Y.; Liu, C. Analysis and optimization of external venetian blind shading for nearly zero-energy buildings in different climate regions of China. Sol. Energy 2021, 223, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, H.; Xu, W.; Li, A.; Chu, J.; Lv, Y. Sensitivity analysis and prediction of shading effect of external Venetian blind for nearly zero-energy buildings in China. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 41, 102401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Li, Q.; Xie, J.; Zhao, M.; Liu, J. Optimization of window-to-wall ratio with sunshades in China low latitude region considering daylighting and energy saving requirements. Appl. Energy 2019, 233, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, F.A.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, G.; Peng, C. An investigation of optimal window-to-wall ratio based on changes in building orientations for traditional dwellings. Sol. Energy 2020, 195, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; I Ezeh, C.; Deng, W.; Hong, S.-H.; Peng, Z.; Tang, Y. Correlation between building characteristics and associated energy consumption: Prototyping low-rise office buildings in Shanghai. Energy Build. 2020, 217, 109959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacker, J.N.; De Saulles, T.P.; Minson, A.J.; Holmes, M.J. Embodied and operational carbon dioxide emissions from housing: A case study on the effects of thermal mass and climate change. Energy Build. 2008, 40, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
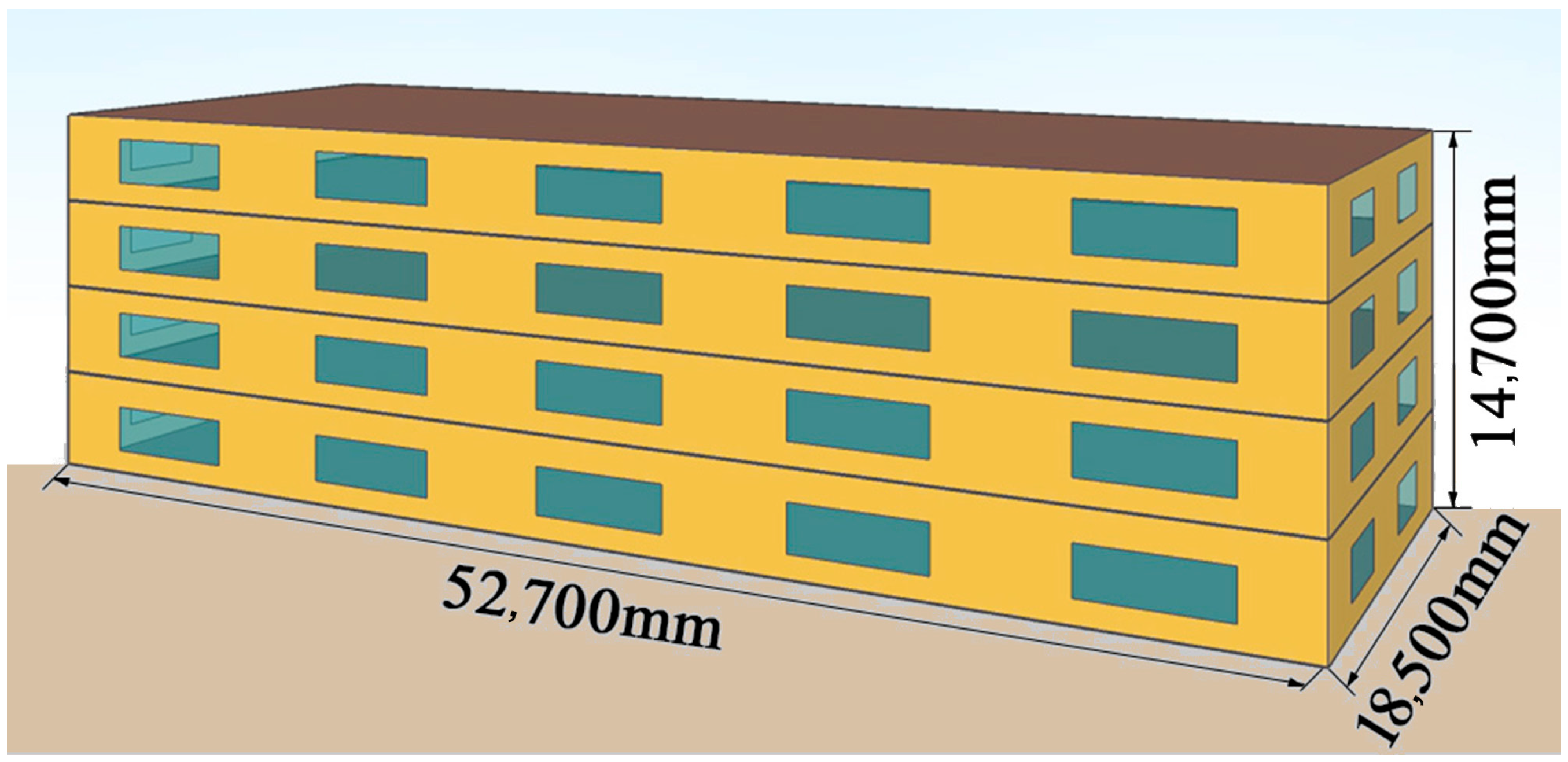

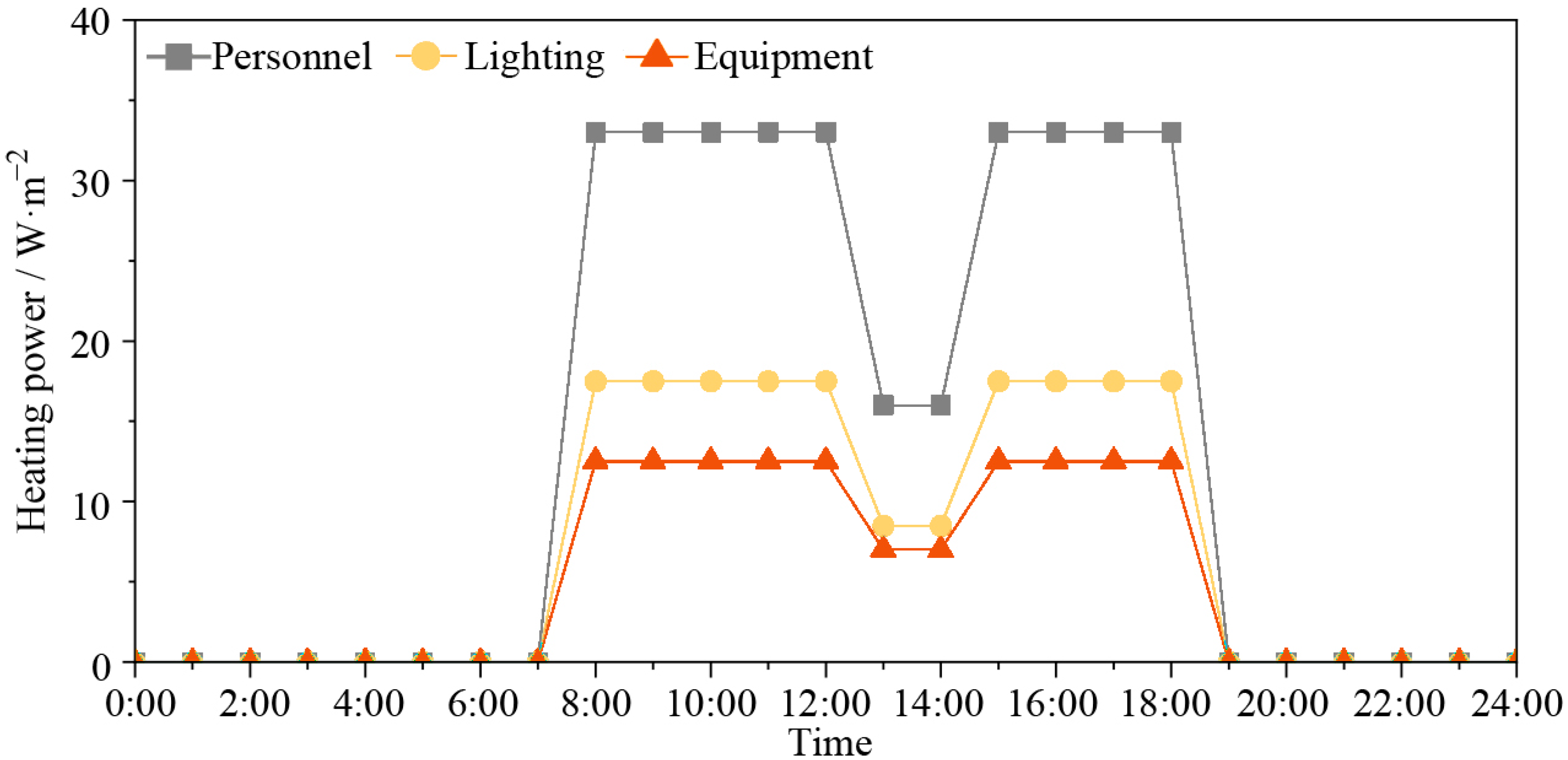
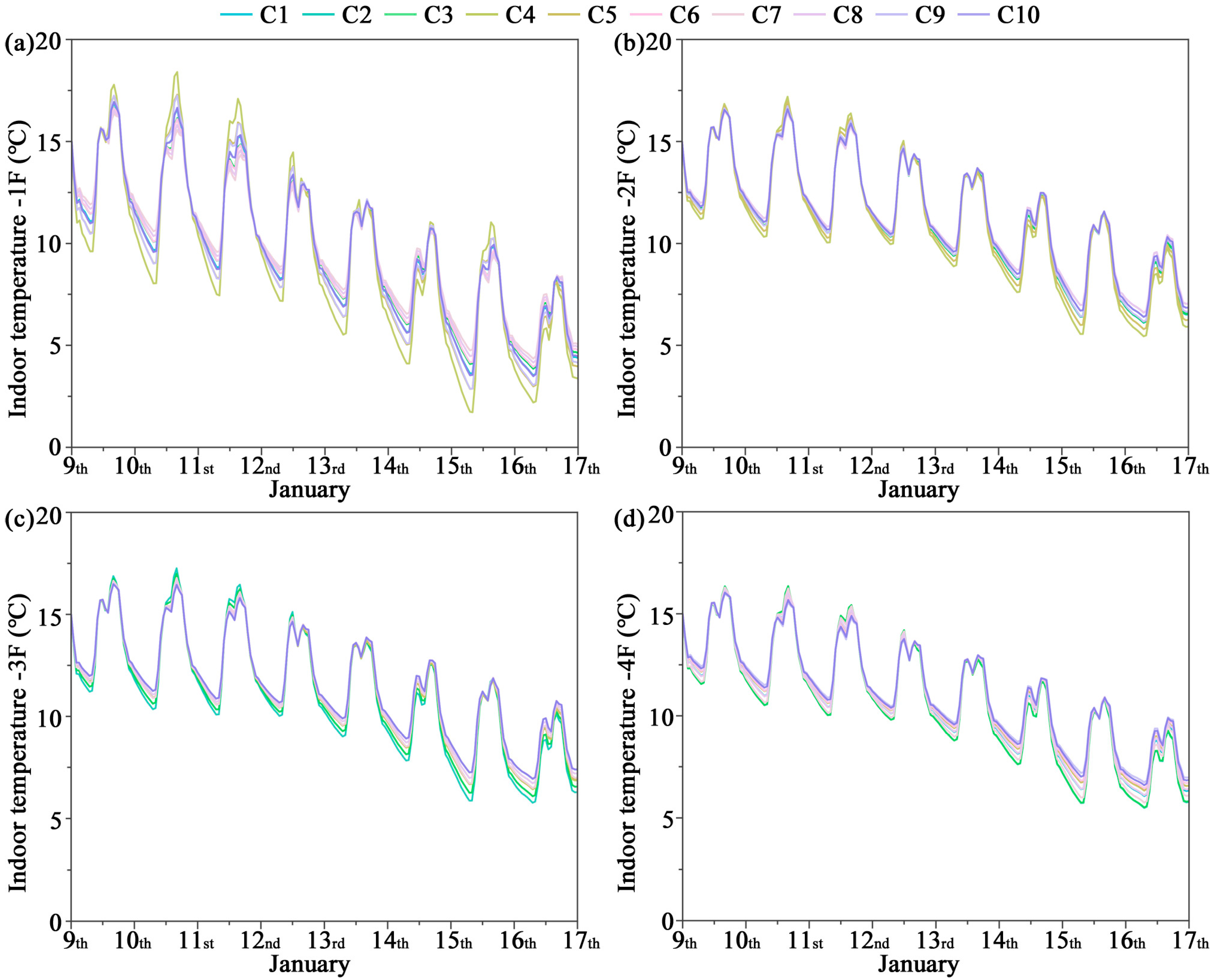
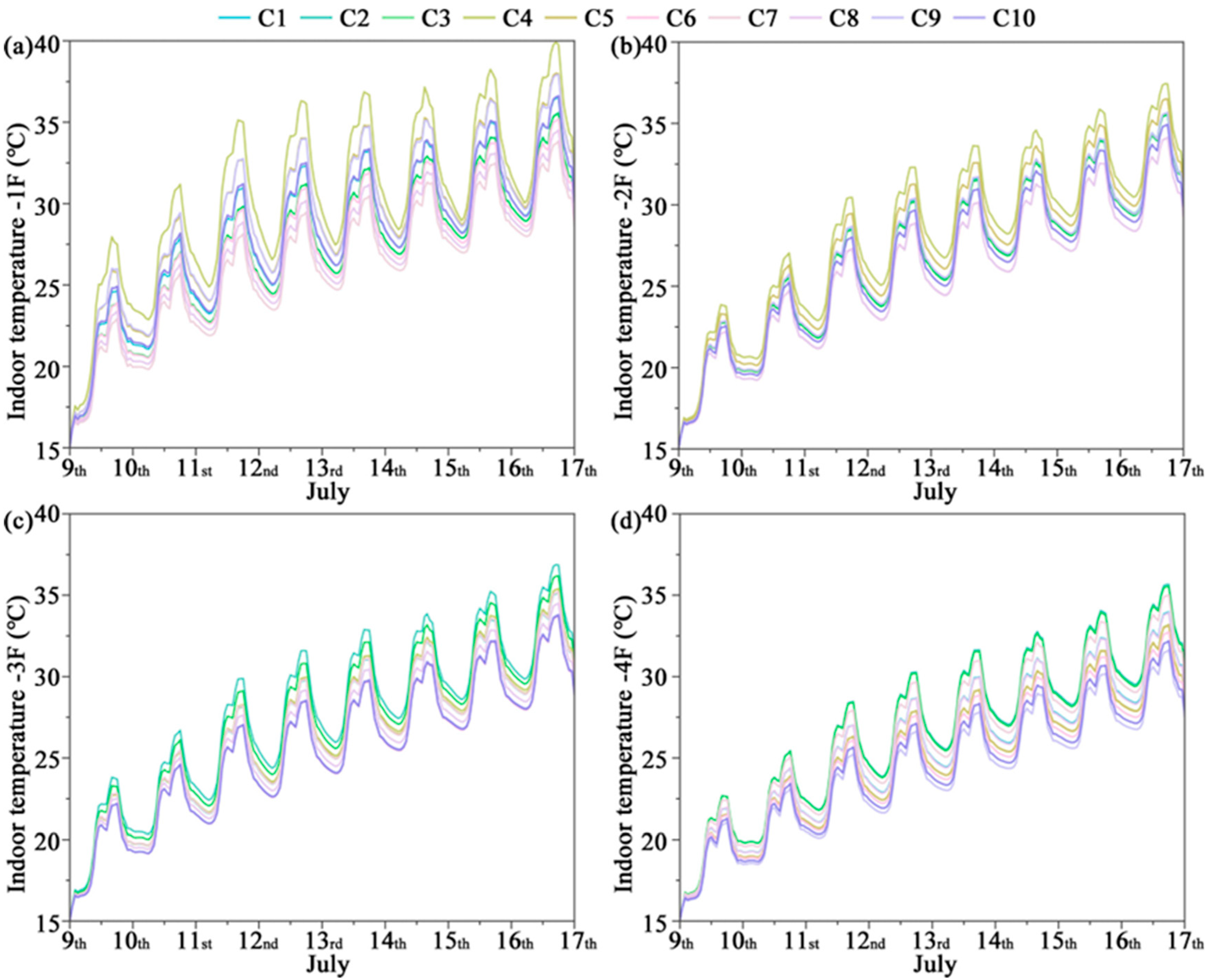



| Component | Total Thickness (mm) | U/W·m−2K−1 | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Roof (Top slab) | 155 | 0.224 | EPS + RC + mortar |
| Exterior wall | 320 | 0.485 | Plaster + insulation + brick |
| Type | U-value | Solar Transmittance | Visible Transmittance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Double 14011 | 1.240 | 0.354 | 0.529 |
| Single 102 | 5.690 | 0.823 | 0.855 |
| Temperature-Jan. (Mean) | Temperature-Jul. (Mean) | Temperature-Oct. (Mean) | Energy Use-Jan. (Total) | Energy Use-Jul. (Total) | Energy Use-Oct. (Total) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simulation | 10.88 °C | 25.70 °C | 21.38 °C | 27,118.91 kWh | 2421.02 kWh | 111.25 kWh |
| Measured | 11.03 °C | 26.83 °C | 22.15 °C | 2753.34 kWh | 2298.56 kWh | 98.57 kWh |
| CVRMSE | 5.33% | 3.41% | 4.48% | 5.25% | 8.62% | 6.21% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Z.; Gao, W. Seasonal Effects of Window-to-Wall Ratio and Glazing Combinations on Office Building Performance in Qingdao. Buildings 2025, 15, 3156. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173156
Liu X, Zhang N, Wang Z, Gao W. Seasonal Effects of Window-to-Wall Ratio and Glazing Combinations on Office Building Performance in Qingdao. Buildings. 2025; 15(17):3156. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173156
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xin, Nan Zhang, Zhongshuai Wang, and Weijun Gao. 2025. "Seasonal Effects of Window-to-Wall Ratio and Glazing Combinations on Office Building Performance in Qingdao" Buildings 15, no. 17: 3156. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173156
APA StyleLiu, X., Zhang, N., Wang, Z., & Gao, W. (2025). Seasonal Effects of Window-to-Wall Ratio and Glazing Combinations on Office Building Performance in Qingdao. Buildings, 15(17), 3156. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173156






