Mechanical Behavior of Geopolymers Containing Soil and Red Mud Stabilized by Alkali Activation
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Source | Raw Materials | Remarks |
| Kandalai and Patel (2025) [12] | RM, ground-granulated blast furnace slag (GGBS), black cotton soil, NaOH | Geomechanical and microstructural tests were conducted to evaluate an expansive soil stabilized with RM and GGBS |
| Hao et al. (2025) [19] | RM, fly ash, copper- and cadmium-contaminated soils | A geopolymer based on solid waste materials was designed for solidification of heavy metal contaminated soils |
| Kandalai and Patel (2025) [13] | RM, GGBS, black cotton soil, NaOH | Strength, durability and leachate tests were carried out to investigate an expansive soil stabilized with RM and GGBS |
| Hai et al. (2024) [10] | RM, water glass, GGBS, NaOH | Effects of water glass modulus and slag replacement ratio on mechanical properties of RM-based geopolymers were elucidated |
| Li et al. (2024) [20] | RM, fly ash, GGBFS, sodium silicate, NaOH, naphthalene superplasticizer | The influential mechanisms of RM and slag on strength and permeability of geopolymer mixtures were elucidated |
| Luo et al. (2022) [21] | RM, chromium slag, GGBS, sodium silicate | A geopolymer with high content of RM was used to solidify/stabilize the heavy metal Cr in the chromium slag. |
| Zhang et al. (2022) [22] | RM, fly ash, NaOH | The feasibility of RM-based geopolymers as pile materials for composite foundations was verified by laboratory and field tests |
| Bai et al. (2023) [23] | RM, fly ash, water glass, and NaOH | A RM–fly ash geopolymer with a strength high compressive strength was developed and physical/chemical mechanisms related to the high-strength characteristics were revealed |
| Kumar et al. (2021) [24] | RM combined with different types of precursors and alkali activators published in previous literature | Review paper on the utilization of RM for the production of geopolymer and alkali activated concrete |
| Liang and Ji (2021) [25] | RM, GGBS, lime, gypsum, water glass, NaOH, and river sand | Chloride ion permeability of geopolymer mortars containing RM was measured by two types of electric flux methods |
| Hoang et al. (2020) [26] | RM, fly ash, and NaOH | Investigation of the influence of heat curing and autoclave curing on RM-based geopolymer mixtures |
| Li et al. (2020) [27] | RM, coal metakaolin, sodium silicate, NaOH | The effects of different Na/Al molar ratios on mechanical properties and microstructure of geopolymer containing RM and coal metakaolin were investigated |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Program
2.2. Materials
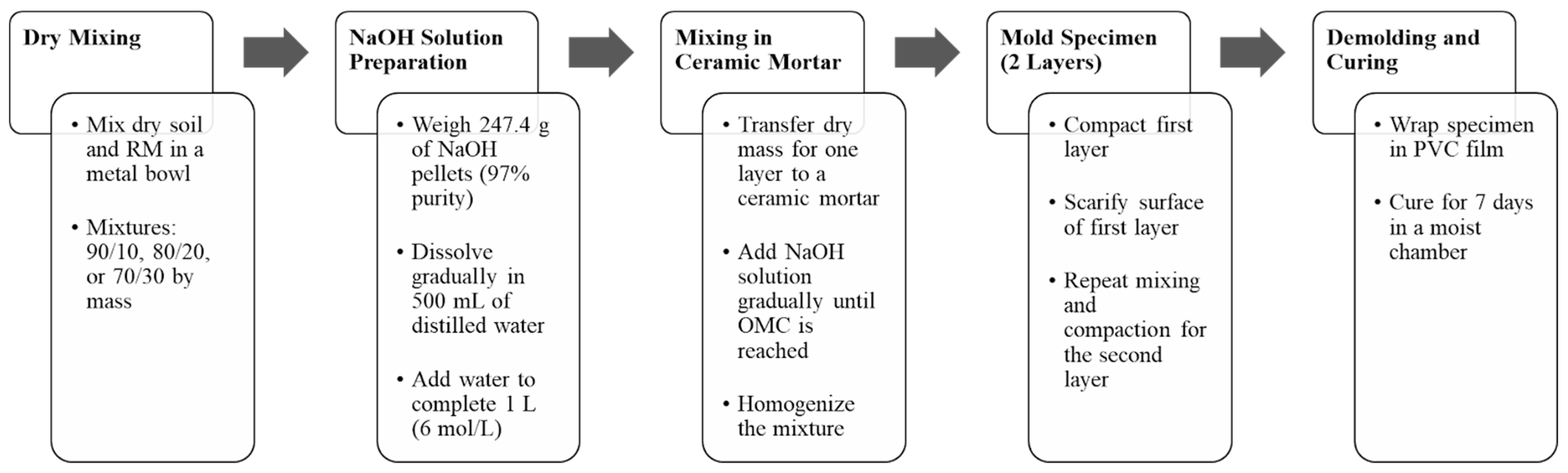
2.3. Mixture Procedures
2.4. Standard Proctor Compaction Test
2.5. Unconfined Compressive Strength Test
2.6. Mineralogical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Raw Materials Characterization
3.2. Mechanical Behavior
3.3. Microstructural Behavior
4. Conclusions
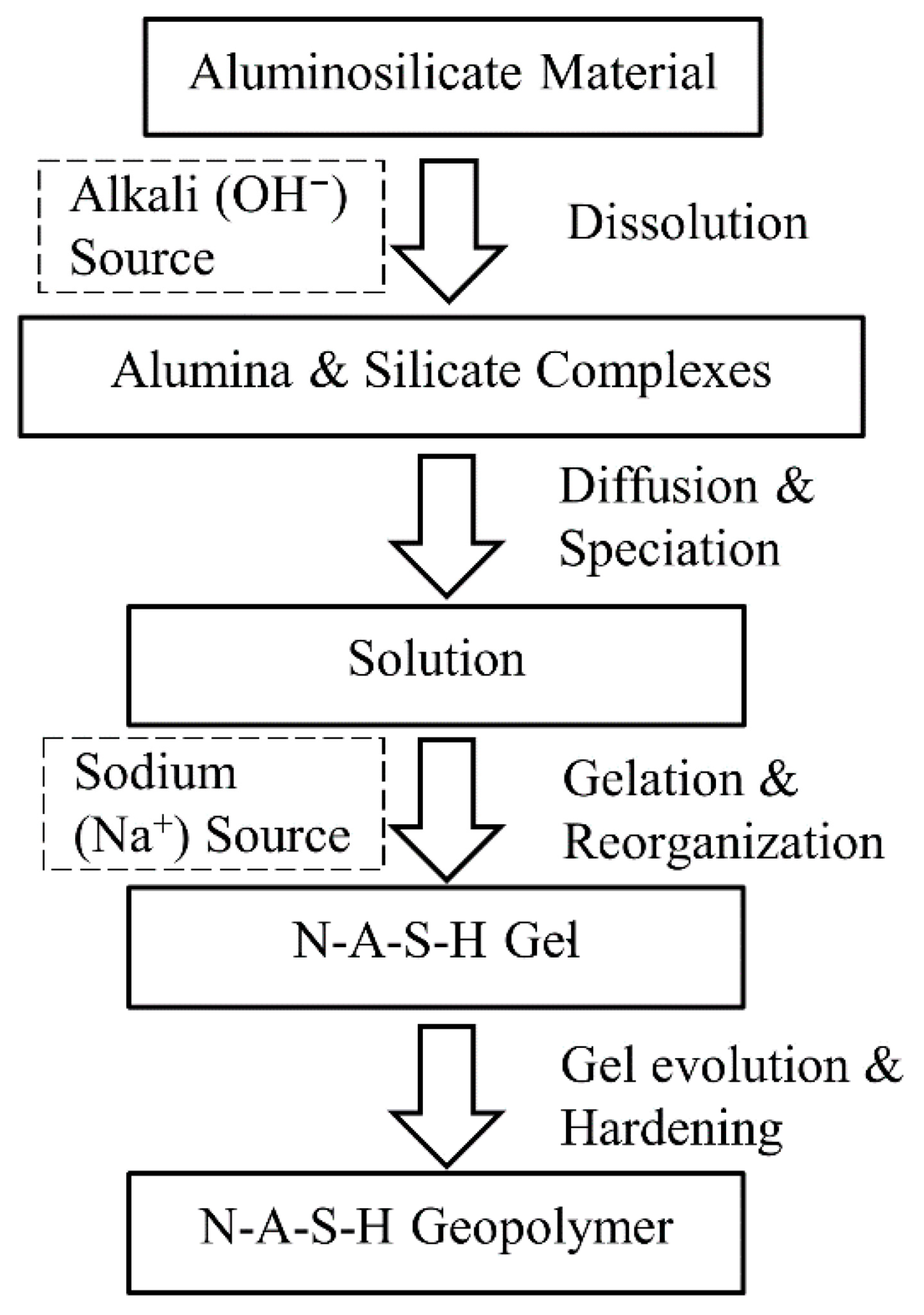
- The addition of NaOH significantly increased the UCS of the mixtures, confirming the positive role of alkaline activation in promoting particle bonding through the formation of N–A–S–H gels.
- The observed decrease in UCS with increasing RM content correlated with a declining Si/Al molar ratio (from 2.03 in M1 to 1.77 in M3), indicating reduced geopolymerization efficiency.
- XRD analysis indicated the dissolution of aluminosilicates and suggested the formation of amorphous gel phases, consistent with geopolymerization pathways and reinforcing the mechanisms behind UCS gains in mixtures containing NaOH.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodrigues, K.H.d.P.; da Silva, T.O.; Pitanga, H.N.; Pedroti, L.G.; Rodrigues, M.H.R. Experimental Study of Mixtures Soil-Industrial Waste Using Simplex Design for Application in Paving. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 78, 107761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, E.C.; da Silva, T.O.; Pitanga, H.N.; Pedroti, L.G.; Franco de Carvalho, J.M.; Nalon, G.H.; Duarte de Araújo, E.N.; Rodrigues, K.H.d.P. Chemical, Mineralogical, Microstructural and Engineering Properties of Tropical Soils Stabilised with the Combined and Individual Use of Different Types of Steel Slag. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2024, 25, 1507–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghoubi, E.; Yaghoubi, M.; Guerrieri, M.; Sudarsanan, N. Improving Expansive Clay Subgrades Using Recycled Glass: Resilient Modulus Characteristics and Pavement Performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 302, 124384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, E.C.; da Silva, T.O.; Pitanga, H.N.; Mendes, A.J.C.; Nalon, G.H.; Rodrigues, K.H.d.P. Stabilisation of Tropical Soils with Lime Mud: Materials Characterisation and Pavement Structural Analyses. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2025, 26, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.S.; Mendes, B.C.; da Silva, T.O.; Lopes, E.C.; Ferreira, F.A.; Pedroti, L.G. Use of Red Mud in Soil Stabilization for Pavement Through Alkali Activation. In Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials 2024; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 693–700. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, S.; Dhawan, N. Investigation of Mechanical and Thermal Activation on Metal Extraction from Red Mud. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2021, 27, e00246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Y.; Pei, L.; Liu, H.; Jiang, J.; Xu, H. Investigation on the Fabrication of Lightweight Aggregate with Acid-Leaching Tailings of Vanadium-Bearing Stone Coal Minerals and Red Mud. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 32, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagundes, J.T.; Santana, V.P.; Ferreira, G.A.; Brigolini, G.J. Synthesis and Characterization of Geopolymer from In Natura Red Mud and Glass Waste. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2024, 21, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Bai, B.; Du, Q. Durability Evaluation of a High-Performance Red Mud-Based Composite Material. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 39, 108684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, R.; Zheng, J.; Li, J.; Hui, C.; Liu, J. Preparation Mechanism and Properties of Thermal Activated Red Mud and Its Geopolymer Repair Mortar. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e02853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, P. Optimal Analysis of the Proportion between Modified Lime Mud and Active Mineral Additive in Mortar: Insights from Particle Size Distribution and Packing Density Modeling. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 91, 109500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandalai, S.; Patel, A. Geomechanical and Microstructural Behaviour of Expansive Soil Stabilized with Red Mud and GGBS: An Experimental Investigation. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2025, 50, 7965–7985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandalai, S.; Patel, A. Alkali Activation of Red Mud and GGBS Blends for Expansive Soil Stabilization: Strength, Durability and Leachate Studies. Indian Geotech. J. 2025, 26, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Huang, K.; Chen, F.; Li, L.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, K. Engineering Properties and Microstructure of Soils Stabilized by Red-Mud-Based Cementitious Material. Materials 2024, 17, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Wan, X.; Jiao, N.; Zhang, S.; Chen, W. Collaborative Effects of Red Mud and Phosphogypsum on Geotechnical Behavior of Cement-Stabilized Dredged Clay. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2024, 83, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, C.; Javadi, A.A.; Vinai, R.; Russo, G. Effects of Fly Ash Inclusion and Alkali Activation on Physical, Mechanical, and Chemical Properties of Clay. Materials 2022, 15, 4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukmak, P.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Shen, S.-L.; Chindaprasirt, P.; Suksiripattanapong, C. Factors Influencing Strength Development in Clay–Fly Ash Geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, R.; Yadav, B.; Yadav, J.S.; Kumar, S. Red Mud Utilisation for Sustainable Construction and Soil Improvement: A Comprehensive Review. Discov. Sustain. 2024, 5, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Liu, X.; Dong, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; Chang, S. Study on the Solidification/Stabilization of Cu(II) and Cd(II)-Contaminated Soil by Fly Ash-Red Mud Based Geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 469, 140515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lei, Z.; Gao, M.; Sun, J.; Tong, L.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y. Designing Low-Carbon Fly Ash Based Geopolymer with Red Mud and Blast Furnace Slag Wastes: Performance, Microstructure and Mechanism. J. Envorn. Manag. 2024, 354, 120362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zhi, T.; Liu, L.; Mi, J.; Zhang, M.; Tian, C.; Si, Z.; Liu, X.; Mu, Y. Solidification/Stabilization of Chromium Slag in Red Mud-Based Geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 316, 125813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qin, L.; Nie, Q.; Wang, Y.; Jia, X. Experimental Research on the Bearing Properties of Red Mud Geopolymer Foundations. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 843189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Bai, F.; Nie, Q.; Jia, X. A High-Strength Red Mud–Fly Ash Geopolymer and the Implications of Curing Temperature. Powder Technol. 2023, 416, 118242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Saravanan, T.J.; Bisht, K.; Kabeer, K.I.S.A. A Review on the Utilization of Red Mud for the Production of Geopolymer and Alkali Activated Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 302, 124170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Ji, Y. Experimental Study on Durability of Red Mud-Blast Furnace Slag Geopolymer Mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 267, 120942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, M.D.; Do, Q.M.; Le, V.Q. Effect of Curing Regime on Properties of Red Mud Based Alkali Activated Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 259, 119779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Bai, X. Effects of Na/Al Ratio on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Red Mud-Coal Metakaolin Geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 263, 120653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Ye, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Yan, F.; Li, G.; Ren, X.; Li, J. Leaching Kinetics and Reactivity Regulation of Red Mud in an NaOH Solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 421, 135750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABNT NBR 7181; Soil—Grain Size Analysis. ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; São Paulo, Brazil, 2016; pp. 1–12.
- ABNT NBR 6459; Soil—Liquid Limit Determination. ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; São Paulo, Brazil, 2016.
- ABNT NBR 7180; Soil—Plasticity Limit Determination. ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; São Paulo, Brazil, 2016.
- ABNT NBR 6458; Gravel Grains Retained on the 4.8 Mm Mesh Sieve—Determination of the Bulk Specific Gravity, of the Apparent Specific Gravity and of Water Absorption. ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; São Paulo, Brazil, 2016.
- ABNT NBR 7182; Compaction Test—Procedures. ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; São Paulo, Brazil, 2020.
- Pratap, B. Analysis of Mechanical Properties of Fly Ash and Bauxite Residue Based Geopolymer Concrete Using ANN, Random Forest and Counter Propagation Neural Network. Asian J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 25, 4303–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konduru, H.; Karthiyaini, S.; Shanmugasundaram, M. Comparative Study of Silica Fume and Sodium Silicate as Replacement of Active Reactive Silica in Bauxite Residue Based Geopolymer Mortar. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frieda, F.S.; Greeshma, S. Graphene Oxide Reinforced Bauxite Tailings-Based Geopolymers: Mechanical and Microstructural Properties Investigations. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon. Nanostruct. 2025, 33, 843–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis of BiOX-Red Mud/Granulated Blast Furnace Slag Geopolymer Microspheres for Photocatalytic Degradation of Formaldehyde. Materials 2024, 17, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABNT NBR 12024; Soil-Cement—Molding and Curing of Cylindric Specimens—Procudure. ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; São Paulo, Brazil, 2012.
- DNIT ES 143; Paving—Soil-Cement Base Course—Service Specification. DNIT: Brasília, Brazil, 2022.
- ABNT NBR 12025; Soil-Cement—Simple Compression Test of Cylindrical Specimens—Method of Test. ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; São Paulo, Brazil, 2012.
- Rohde, L.; Nunez, W.P.; Ceratti, J.A.P. Escória de Aciaria Elétrica: Uma Alternativa Aos Materiais Granulares Tradicionais. Transportes 2003, 11, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, L.; Nunez, W.P.; Ceratti, J.A.P. Electric Arc Furnace Steel Slag: Base Material for Low-Volume Roads. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2003, 1819, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, E.C.; da Silva, T.O.; Pitanga, H.N.; Pedroti, L.G.; Franco de Carvalho, J.M.; Nalon, G.H.; de Lima, G.E.S.; de Araújo, E.N.D. Stabilisation of Clayey and Sandy Soils with Ladle Furnace Slag Fines for Road Construction. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2022, 24, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.; Pitanga, H.; Santos, A.; Lima, D.; Silva, A. Use of Steel Waste for the Application in Urban Paving. Acta Scientiarum. Technol. 2019, 41, 37596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, C.M.M.; Mendes, B.C.; Pedroti, L.G.; Vieira, C.M.F. Evaluation of Geopolymer Composites, Based on Red Mud and Metakaolin, for Building Application. In Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials 2024: Process–Structure–Property Relations and New Technologies; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 421–430. [Google Scholar]
- ABNT NBR 12770; Soil—Determination of the Unconfined Compressive Strength of Cohesive Soil. ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; São Paulo, Brazil, 2022.
- Ye, N.; Yang, J.; Ke, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, Y.; Xiang, C.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Xiao, B. Synthesis and Characterization of Geopolymer from Bayer Red Mud with Thermal Pretreatment. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 97, 1652–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemougna, P.N.; Wang, K.; Tang, Q.; Cui, X. Synthesis and Characterization of Low Temperature (<800 °C) Ceramics from Red Mud Geopolymer Precursor. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 131, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Q.; Hu, W.; Ai, T.; Huang, B.; Shu, X.; He, Q. Strength Properties of Geopolymers Derived from Original and Desulfurized Red Mud Cured at Ambient Temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.-D.; Zeng, J.-J.; Huang, B.-T.; Huang, J.-Q.; Zhuge, Y.; Dai, J.-G. Bond Performance of FRP Bars in Plain and Fiber-Reinforced Geopolymer under Pull-out Loading. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 57, 104893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, A.; Sitharam, T. Effect of Red Mud-Based Geopolymer Binder on the Strength Development of Clayey Soil. In Proceedings of the 9th International Congress on Environmental Geotechnics, Chania, Greece, 25–28 June 2023; pp. 267–275. [Google Scholar]
- Gokul, V.; Steffi, D.A.; Kaviya, R.; Harni, C.V.; Dharani, S.M.A. Alkali Activation of Clayey Soil Using GGBS and NaOH. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 43, 1707–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y. Mechanical, Mineralogical, and Microstructural Characterization of Collapsible Loess Cured by NaOH Solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 421, 135678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasihnikoutalab, M.H.; Pourakbar, S.; Ball, R.J.; Unluer, C.; Cristelo, N. Sustainable Soil Stabilisation with Ground Granulated Blast-Furnace Slag Activated by Olivine and Sodium Hydroxide. Acta Geotech. 2020, 15, 1981–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Xiao, H. Treating Sulfate-Bearing Soil by Using Sodium Silicate and NaOH-Activated Ground Granulated Blast-Furnace Slag. Acta Geotech. 2024, 19, 3129–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonini de Araújo, M.; Tonatto Ferrazzo, S.; Mansur Chaves, H.; Gravina da Rocha, C.; Cesar Consoli, N. Mechanical Behavior, Mineralogy, and Microstructure of Alkali-Activated Wastes-Based Binder for a Clayey Soil Stabilization. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 362, 129757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. The Geopolymerisation of Alumino-Silicate Minerals. Int. J. Min. Process 2000, 59, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; He, J.; Gambrell, R.P. Synthesis, Characterization, and Mechanical Properties of Red Mud–Based Geopolymers. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board. 2010, 2167, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Lin, W.-T.; Liu, W. Effect of NaOH Concentration on Properties and Microstructure of a Novel Reactive Ultra-Fine Fly Ash Geopolymer. Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 2929–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, H.H.; Shahin, M.A.; Walske, M.L. Review of Fly-Ash-Based Geopolymers for Soil Stabilisation with Special Reference to Clay. Geosciences 2020, 10, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Liu, Z.; Tian, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, L. Review on the Impact of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer’s Reaction Chemistry, Nanostructure and Factors on Its Properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 412, 134760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.; van Deventer, J. Geopolymers: Structures, Processing, Properties and Industrial Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- van Riessen, A.; Jamieson, E.; Gildenhuys, H.; Skane, R.; Allery, J. Using XRD to Assess the Strength of Fly-Ash- and Metakaolin-Based Geopolymers. Materials 2025, 18, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Hossain, K.M.A. Physical, Compressive Strength, and Microstructural Characteristics of Alkali-Activated Engineered Composites Incorporating MgO, MWCNTs, and RGO. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Liu, M.; Purusottam, R.N.; Walls, J.D.; Pestana, L.R.; Suraneni, P. Composition-Structure Relationships for Calcium Aluminosilicate Glasses. Mater. Struct. 2025, 58, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristelo, N.; Glendinning, S.; Miranda, T.; Oliveira, D.; Silva, R. Soil Stabilisation Using Alkaline Activation of Fly Ash for Self Compacting Rammed Earth Construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 36, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jia, J.; Lu, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, L.; Guo, P.; Zhai, G. The Effect of Ionic Soil Stabilizer on Cement and Cement-Stabilized Iron Tailings Soil: Hydration Difference and Mechanical Properties. Materials 2025, 18, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consoli, N.C.; Festugato, L.; Filho, H.C.S.; Miguel, G.D.; Neto, A.T.; Andreghetto, D. Durability Assessment of Soil-Pozzolan-Lime Blends through Ultrasonic-Pulse Velocity Test. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04020223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consoli, N.C.; Carretta, M.S.; Leon, H.B.; Schneider, M.E.B.; Reginato, N.C.; Carraro, J.A.H. Behaviour of Cement-Stabilised Silty Sands Subjected to Harsh Environmental Conditions. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Geotech. Eng. 2020, 173, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, S.G.F.P.; Almeida, M.d.S.S.; Consoli, N.C.; Nascimento, T.Z.; Polido, U.F. Field and Laboratory Investigation of Highly Organic Clay Stabilized with Portland Cement. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04020063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samantasinghar, S.; Singh, S.P. Red Mud-Slag Blends as a Sustainable Road Construction Material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 375, 130926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khale, D.; Chaudhary, R. Mechanism of Geopolymerization and Factors Influencing Its Development: A Review. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 729–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Maslehuddin, M. An Overview of Factors Influencing the Properties of Alkali-Activated Binders. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 124972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxson, P.; Mallicoat, S.W.; Lukey, G.C.; Kriven, W.M.; van Deventer, J.S.J. The Effect of Alkali and Si/Al Ratio on the Development of Mechanical Properties of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymers. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 292, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiloğlu, H.A.; Kurucu, K.; Akbaş, D. Investigating the Effect of Polypropylene Fiber on Mechanical Features of a Geopolymer-Stabilized Silty Soil. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 28, 628–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariatmadari, N.; Hasanzadehshooiili, H.; Ghadir, P.; Saeidi, F.; Moharami, F. Compressive Strength of Sandy Soils Stabilized with Alkali-Activated Volcanic Ash and Slag. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2021, 33, 04021295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, N.; Kumar, T.; Nagaraju, V. Compressive Strength of High Plastic Clay Stabilized with Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer and Its Synthesis Parameters. In Transportation, Water and Environmental Geotechnics; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Xing, Z.; Wang, R.; Dai, S. The Effect of Various Si/Al, Na/Al Molar Ratios and Free Water on Micromorphology and Macro-Strength of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer. Materials 2021, 14, 3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxson, P.; Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C.; Mallicoat, S.W.; Kriven, W.M.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Understanding the Relationship between Geopolymer Composition, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 269, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxson, P.; Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C.; Separovic, F.; van Deventer, J.S.J. 29Si NMR Study of Structural Ordering in Aluminosilicate Geopolymer Gels. Langmuir 2005, 21, 3028–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Kang, J.; Shin, Y.; Yeo, T.; Heo, J.; Um, W. Effect of Si/Al Molar Ratio and Curing Temperatures on the Immobilization of Radioactive Borate Waste in Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Waste Form. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 458, 131884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racanelli, L. Obtaining Geopolymer from Amazonian Bauxite Washing Waste. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal do Pará, Belém, Brazil, 2022. (In Portuguese). [Google Scholar]
- Karoui, O.; Andrejkovičová, S.; Pato, P.; Patinha, C.; Perná, I.; Řimnáčová, D.; Hajjaji, W.; Ascensão, G.; Rocha, F.; Mlayah, A. Alkali-Activated Geopolymers Based on Calcined Phosphate Sludges and Metakaolin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 45138–45161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Law, D.W.; Patnaikuni, I.; Gunasekara, C.; Tahmasebi Yamchelou, M. Low-Grade Clay as an Alkali-Activated Material. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




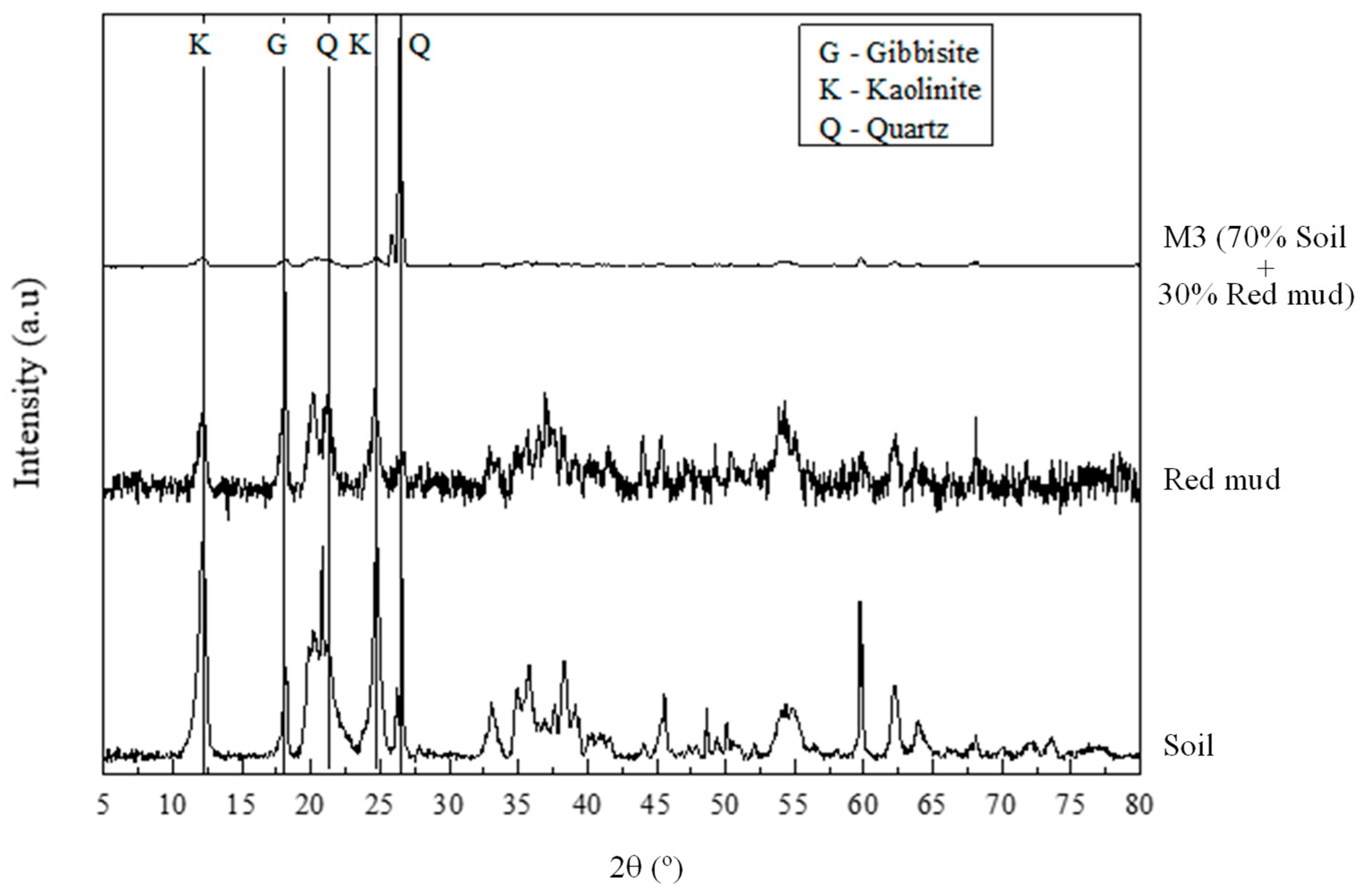

| Parameter | Soil | Red Mud | |
| Particle size distribution | % clay (ϕ < 0.002 mm) | 61 | 50 |
| % silt (0.002 mm < ϕ < 0.06 mm) | 14 | 38 | |
| % sand (0.06 mm < ϕ < 2 mm) | 25 | 12 | |
| % gravel (2 mm < ϕ < 60 mm) | 0 | 0 | |
| Atterberg limits | LL (%) | 78 | 64 |
| PL (%) | 43 | 42 | |
| PI (%) | 35 | 22 | |
| Specific gravity | 2.869 | 2.877 | |
| Maximum dry unit weight (kN/m3) | 13.95 | 13.33 | |
| Optimal moisture content (%) | 31.03 | 33.10 | |
| Free swell index (%) | 6.70 | - | |
| Classification | TRB | A-7-5 (20) | A-7-5 |
| USC | MH | MH | |
| MCT | LG′ | - | |
| Parameter | Soil | Red Mud | |
| Oxide percentages | (%) | 27.11 | 44.41 |
| (%) | 24.52 | 32.39 | |
| (%) | 12.47 | 15.56 | |
| CaO (%) | 0.02 | - | |
| MgO (%) | 1.28 | - | |
| (%) | 0.07 | 0.09 | |
| (%) | 1.55 | 3.62 | |
| (%) | 1.53 | 2.5 | |
| (%) | 0.04 | 0.9 | |
| Cl (%) | 0.27 | - | |
| Others (%) | 31.14 | 0.53 | |
| Loss on ignition (%) | 11.49 | 19.73 | |
| Series | OMC (%) | (%) | (%) | (kN/m3) | DC (%) | UCS (MPa) | Standard Deviation (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural soil | 31.0 | 30.6 | 0.42 | 13.9 | 99.07 | 0.30 | 0.009 |
| M1–90/10 | 30.3 | 30.7 | 0.43 | 14.1 | 100.68 | 3.05 | 0.079 |
| M2–80/20 | 31.9 | 31.7 | 0.20 | 14.0 | 100.36 | 2.61 | 0.029 |
| M3–70/30 | 31.0 | 30.7 | 0.28 | 13.9 | 100.84 | 2.23 | 0.093 |
| Red mud | 33.1 | 32.9 | 0.21 | 13.3 | 98.30 | 0.24 | 0.034 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, A.C.P.d.; Rodrigues, K.H.d.P.; Nalon, G.H.; Pitanga, H.N.; Silva, N.A.B.; Silva, T.O.d.; Lopes, E.C.; Rodrigues, M.H.R. Mechanical Behavior of Geopolymers Containing Soil and Red Mud Stabilized by Alkali Activation. Buildings 2025, 15, 3105. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173105
Silva ACPd, Rodrigues KHdP, Nalon GH, Pitanga HN, Silva NAB, Silva TOd, Lopes EC, Rodrigues MHR. Mechanical Behavior of Geopolymers Containing Soil and Red Mud Stabilized by Alkali Activation. Buildings. 2025; 15(17):3105. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173105
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Ana Carolina Pereira da, Klaus Henrique de Paula Rodrigues, Gustavo Henrique Nalon, Heraldo Nunes Pitanga, Natália Assunção Brasil Silva, Taciano Oliveira da Silva, Emerson Cordeiro Lopes, and Mateus Henrique Ribeiro Rodrigues. 2025. "Mechanical Behavior of Geopolymers Containing Soil and Red Mud Stabilized by Alkali Activation" Buildings 15, no. 17: 3105. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173105
APA StyleSilva, A. C. P. d., Rodrigues, K. H. d. P., Nalon, G. H., Pitanga, H. N., Silva, N. A. B., Silva, T. O. d., Lopes, E. C., & Rodrigues, M. H. R. (2025). Mechanical Behavior of Geopolymers Containing Soil and Red Mud Stabilized by Alkali Activation. Buildings, 15(17), 3105. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173105








