Economic and Low-Carbon Cementitious Materials Based on Hot–Stuffy Steel Slag
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Material
2.2. Preparation of Cementitious Materials
2.3. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Setting Times
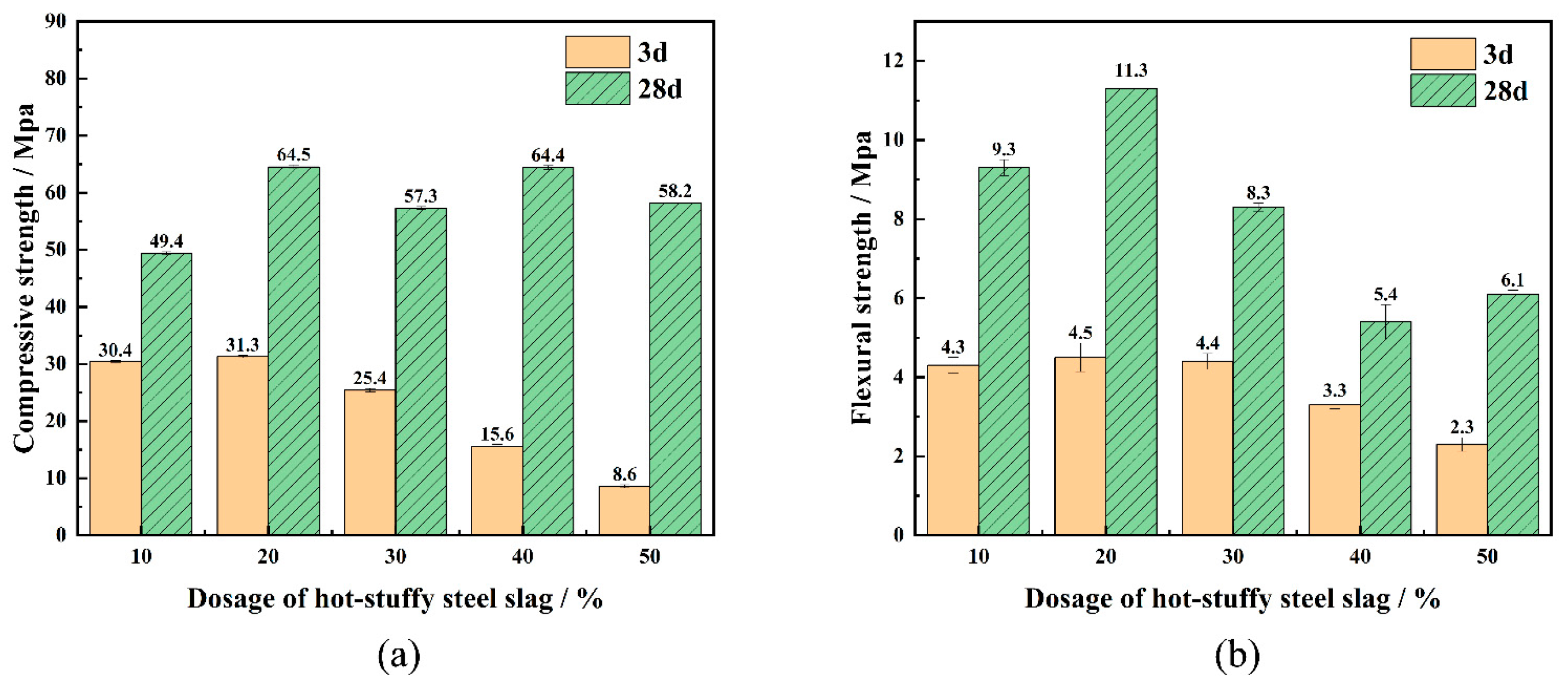
3.2. Compressive Strength and Flexural Strength
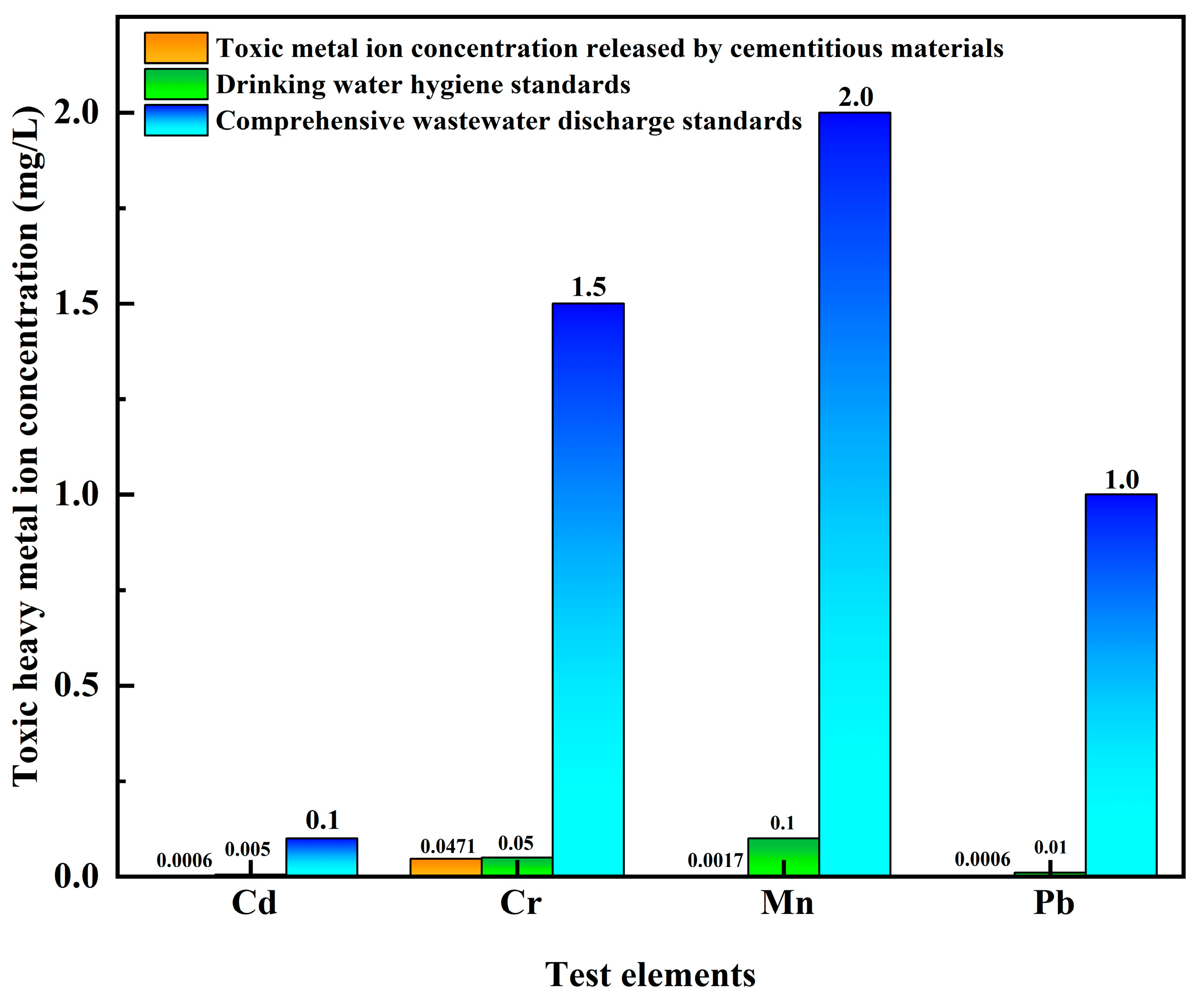
3.3. Ion Concentration Measurement
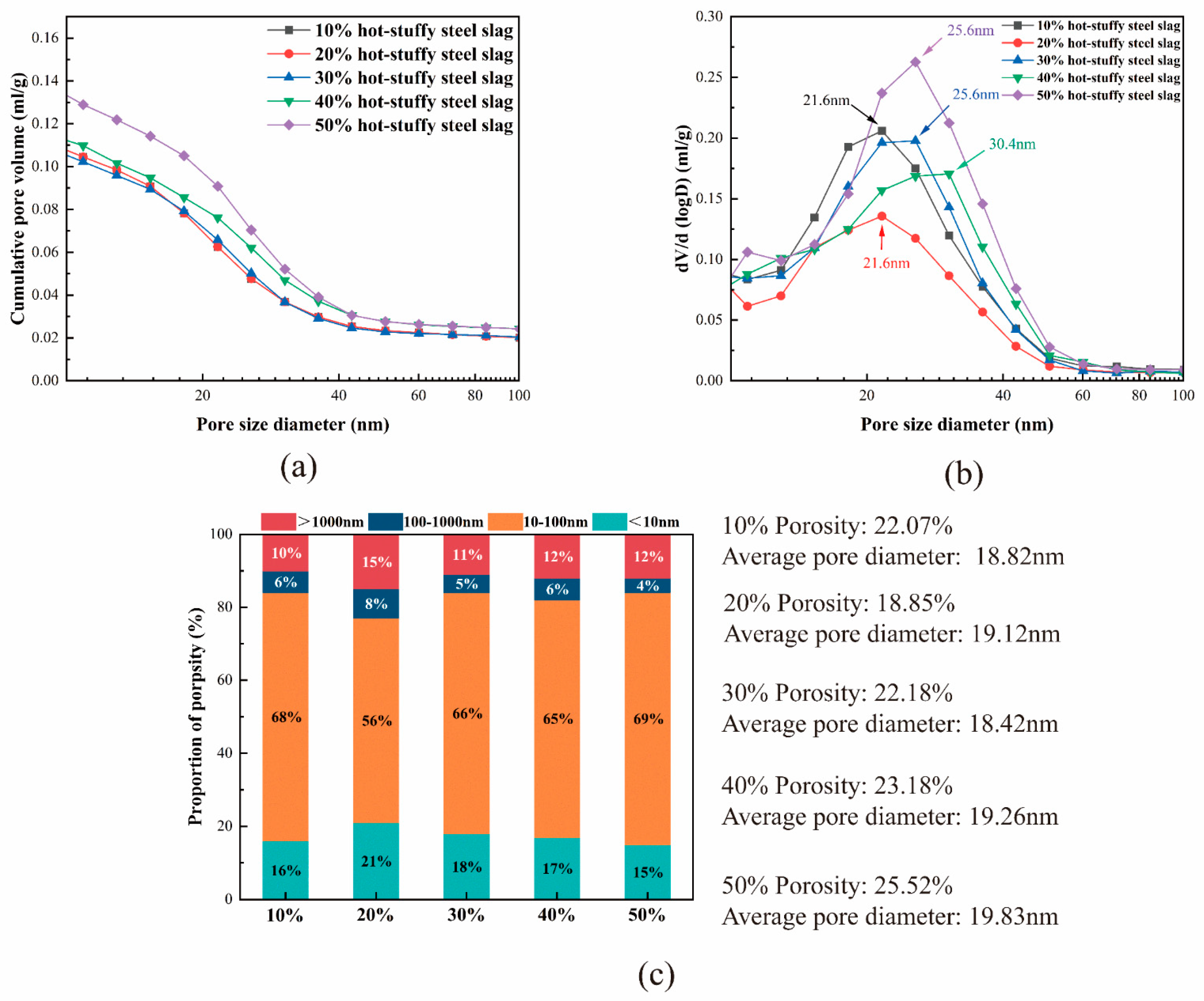
3.4. MIP
3.5. SEM and EDS Analysis
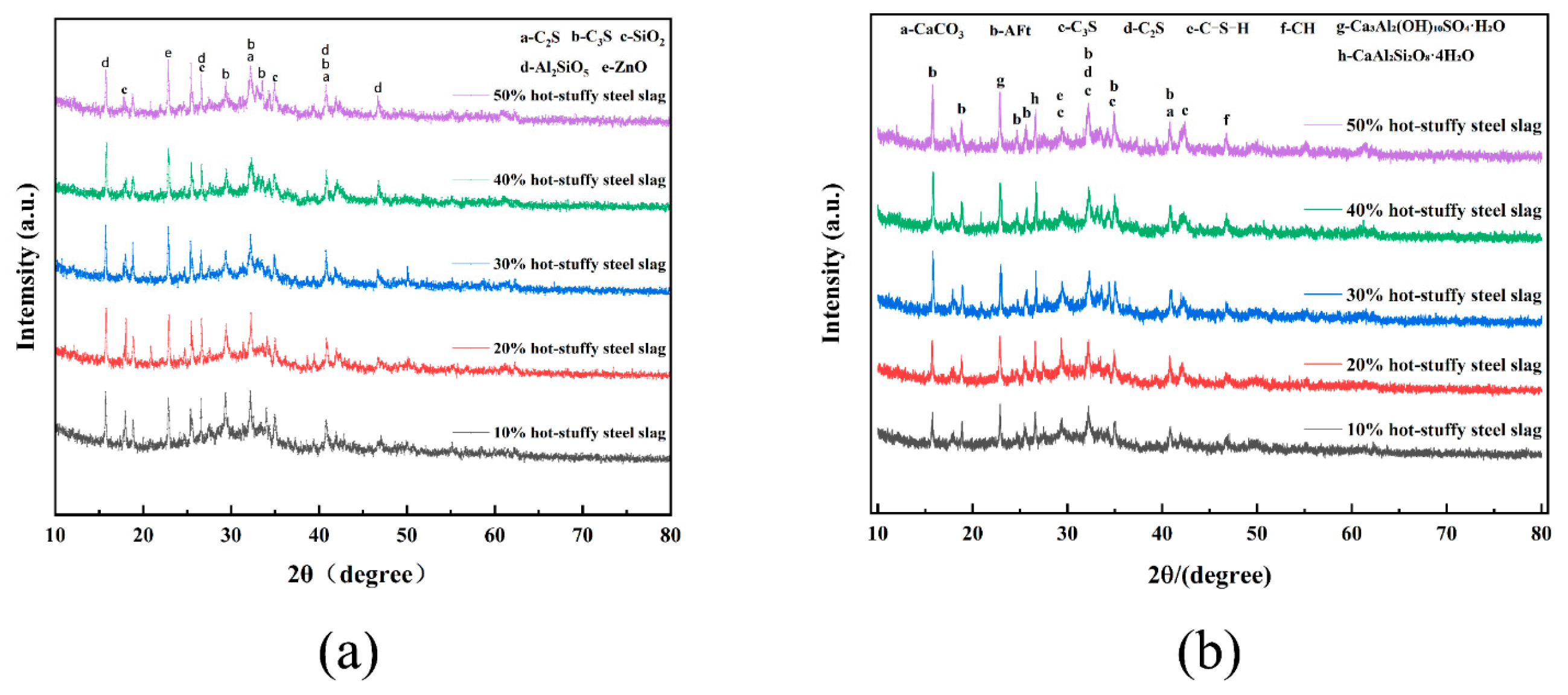
3.6. XRD Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gencel, O.; Karadag, O.; Oren, O.H.; Bilir, T. Steel slag and its applications in cement and concrete technology: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 283, 122783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremona, R.; De Lena, E.; Conversano, A.; Spinelli, M.; Romano, M.C.; Gatti, M. Techno-economic assessment of high temperature heat pumps integrated in MEA-based post-combustion CO2 capture for cement plant. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2025, 16, 100446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Mi, R.; Zhang, D.; Li, J.; Mao, Y.; Wang, W. Performance comparison of solid waste-derived sulfoaluminate cement and Portland cement under air curing and CO2 curing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 482, 141629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, T.S.; Sheridan, C.M.; van Dyk, L.D. Basic oxygen furnace slag: Review of current and potential uses. Miner. Eng. 2020, 149, 106234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, F. Enhanced environmental and self-healing performance of asphalt mixture using steel slag as the substrate of functional coatings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 489, 142427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hu, W.; Ni, W. On the use of blast furnace slag and steel slag in the preparation of green artificial reef concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Wei, C.; Wu, P.; Cao, Z.; Shao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z. Application and mechanism analysis of steel slag in resource recovery and environmental remediation: A review. Miner. Eng. 2025, 227, 109268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Dai, T.; Shen, L.; Jiang, L. Benefits of using steel slag in cement clinker production for environmental conservation and economic revenue generation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 282, 124538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Xu, G.; Cheng, H.; Wang, J.; Wan, Y.; Chen, H. An Overview of Utilization of Steel Slag. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 16, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Bao, Y.; Wang, M. Steel slag in China: Treatment, recycling, and management. Waste Manag. 2018, 78, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Y.; Li, C.; Zou, J.; Wang, W.; Yu, T. Evaluation of the impact factors on the leaching risk of steel slag and its asphalt mixture. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e01067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Huang, W.; Wang, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, S. Feasibility of pretreated steel slag for asphalt pavement application and risk assessment of hazardous substance leaching. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. Hydration behavior and cementitious properties of steel slag: From an early age to a long-term. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Kwon, E.E.; Lee, J. Upcycling steel slag into construction materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 444, 137882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, V.A.; Borges, P.H.R. Recent advances in the reuse of steel slags and future perspectives as binder and aggregate for alkali-activated materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 281, 122605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Wei, R.; Cheng, T.; Sun, R.; Zhang, H.; Long, H. The positive contributions of steel slag in reducing carbon dioxide emissions in the steel industry: Waste heat recovery, carbon sequestration, and resource utilization. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yao, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, L. Utilization of steel slag as coarse aggregate and filler in stone mastic asphalt (SMA) mixture: Engineering performance, environmental impact and economic benefits analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 450, 141891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Shao, J.; Liu, M.; Zhu, H.; Li, M.; Ma, R.; Liang, L.; Mao, J.; Wang, D. The improvement on the properties and heavy metal solidification of phosphogypsum-steel slag cementitious material: Enhancement from Bi-directional carbonation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 457, 139435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, X.; Yang, Y.; Ruan, J.; Zou, Y.; Wu, S.; Chen, F.; Zhu, R. Enhanced ammonia removal in tidal flow constructed wetland by incorporating steel slag: Performance, microbial community, and heavy metal release. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 922, 171333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Ye, G. Enhancing the reaction of municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) bottom ash in blast furnace slag-based alkali-activated blends: A novel strategy and underlying mechanism. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2025, 160, 106056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Shen, J. Micromorphology and microstructure of coal fly ash and furnace bottom slag based light-weight geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 242, 118168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, S.; Lim, T.Y.D.; Sabet Divsholi, B. Durability and mechanical properties of high strength concrete incorporating ultra fine Ground Granulated Blast-furnace Slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 40, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhao, H.; Hao, B.; Gao, S.; Liu, R.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, P.; Wang, C.; Shen, P. Study on the mechanical properties and failure behavior of slag cement under dynamic and static loads. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 47, 113189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Jiao, F.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Z. A new technology for solidification and separation of calcium fluoride from overhaul slag: Synergistic desulfurization gypsum roasting and flotation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 117881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yin, T.; Lin, C.; Tan, H.; Hariana, H. CO2 mineralization characteristics of Ca2+-rich leachate from desulfurization gypsum and the regulation of CaCO3 crystal and morphology. J. Cryst. Growth 2025, 667, 128273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koralegedara, N.H.; Pinto, P.X.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Al-Abed, S.R. Recent advances in flue gas desulfurization gypsum processes and applications—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, G.U.; Kim, H.J.; Yu, H.J.; Pyo, S. Utilization of steelmaking slag in cement clinker production: A review. J. CO2 Util. 2024, 84, 102842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, S.; Zhao, J. Insights to compressive strength, impermeability and microstructure of micro-expansion steel slag cement under constraint conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 326, 126540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhang, D.; Shen, W.; Huang, J.; Tang, X.; Yang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wang, Y. Investigation on industrial trial production of multi-phased clinker with crude granular steel slag. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 337, 130467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.-C.; Geng, Y.; Bin, R.-L.; Li, G.-D.; Wang, Y.-Y. Effects of mineral admixtures on time-dependent behavior of high-strength self-compacting concrete-filled steel tubes. Eng. Struct. 2025, 335, 120327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazloom, M.; Ramezanianpour, A.A.; Brooks, J.J. Effect of silica fume on mechanical properties of high-strength concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2004, 26, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Shao, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Du, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X. Preparation of low-carbon precast concrete with high-content red mud and steel slag mineral admixtures. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 108, 112931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; He, R. Experimental study on manufactured sand concrete containing mineral admixture under freeze-thaw cycles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 453, 138759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Y.; Chang, W. Creep model of high-strength concrete containing supplementary cementitious materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 202, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, B.; Fan, X.; Yuwen, C.; Hou, K.; Chen, W.; Liu, X.; Guo, S.; Zhang, L. High-value utilization of steel slag and red mud: Recovery of platinum from spent aluminum-based catalyst by pyrometallurgy. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson Ponnu Durai, T.; Kandasamy, S.; Rajendran Startha Christabel, A. Enhanced mechanical properties in green concrete through innovative blends of GGBFS, alccofine, and metakaolin. Hybrid Adv. 2025, 11, 100520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TC-242-MDC, R.T.C. RILEM draft recommendation: TC-242-MDC multi-decade creep and shrinkage of concrete: Material model and structural analysis*. Mater. Struct. 2015, 48, 753–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Wang, J.; Sheng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, X. Synergistic enhancement of power factor and figure-of-merit in tin sulfide-expanded graphite cementitious composites by silica fume and fly ash. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2025, 321, 118567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, V.; Ardelean, I.; Bulátkó, A.; László, K.; Csík, A.; Janovics, R.; Kéri, M. Effect of metakaolin and fly ash on the early hydration and pore structure of Portland cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2025, 196, 107928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, M.; Samimi, K. Effect of silica fume on Self-compacting Earth Concrete: Compressive strength, durability and microstructural studies. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 472, 140815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, P.H.C.; Engvall, K.; Penha, F.M.; Kantarelis, E.; Nazir, S.M. Sustainable pathway towards red mud valorization through biomass thermochemical conversion and metals recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 434, 132847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.-F.; Wang, X.-F.; Ding, H.; Jia, Y.-J. Effect of calcined red mud on the mechanical properties and microstructure of ultra-high performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 484, 141891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavian, S.; Shirvani, M.A.; Gholampour, A. Influences of elevated temperature and re-curing on the compressive performance of lightweight concrete containing metakaolin: Experiments and prediction models. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 489, 142111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Liao, J.L.; Ju, J.T.; Dang, Y.J. Treatment process and utilization technology of steel slag in China and abroad. J. Iron Steel Res. 2013, 25, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, P.K.; Mudgal, M.; Ghosh, P.K. Assessing the viability of using BOF steel slag treated with tartaric acid as coarse aggregate in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 436, 136912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Guo, C.; Liu, S.; Li, M.; Wu, Y. Effect and mechanism of calcination on improving the hydration activity of titanium extraction slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 447, 138144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Wu, H.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, T.; Ren, X.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Y. Effect of pressed-heat and stuffy slag powder on the properties of epoxy coating. Chin. J. Eng. 2024, 46, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Deng, A. Study on preparation and properties of unburned ceramsite with steel slag. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 677, 022067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Sha, A.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, W.; Hu, L.; Li, X. Utilization of steel slags to produce thermal conductive asphalt concretes for snow melting pavements. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 19077-2016; Particle Size Analysis-Laser Diffraction Methods. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Qi, L. Effects of temperature and carbonation curing on the mechanical properties of steel slag-cement binding materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Shukla, A.K.; Sharma, A.K.; Kadabinakatti, S. Enhancement of subgrade soil properties using coal bottom ash and basalt fiber for sustainable pavement applications. Transp. Eng. 2025, 21, 100377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Bao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, M. Preparation and characterization of low-activity coal bottom ash-based cementitious materials via orthogonal experiment. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 96, 110495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, C.; Wang, Y.; Du, M.; Luo, W.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, J. Study on the method of reinforcing recycled fine aggregate by wrapping slag and cement powder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 483, 141771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T1346-2011; Test Methods for Water Requirement of Normal Consistency, Setting Time and Soundness of the Portland Cement. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- GB/T 17671-1999; Method of Testing Cements-Determination of Strength. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 1999.
- GB5749-2022; Standards for Drinking Water Quality. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- GB 8978-1996; Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 1996.





| Composition | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | Fe2O3 | SO3 | P2O5 | Heavy Metal | SSA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hot–stuffy steel slag | 9.64 | 7.57 | 44.23 | 4.50 | 26.72 | 0.34 | 1.53 | 0.58 | 297.6 |
| Coal bottom ash | 55.68 | 23.69 | 5.79 | 0.69 | 8.47 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 281.1 |
| Slag powder | 27.95 | 13.87 | 45.84 | 6.67 | 0.54 | 2.65 | 0.01 | 0.43 | 227.0 |
| Desulfurization gypsum | 1.18 | 0.49 | 49.56 | 0.10 | 0.24 | 46.24 | 0.01 | - | 224.3 |
| Cement | 23.89 | 8.23 | 54.83 | 4.42 | 3.73 | 3.10 | 0.13 | - | - |
| Sample No. | Hot–Stuffy Steel Slag | Cement | Slag Powder | Coal Bottom Ash | Desulfurization Gypsum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 28 | 42 | 10 | 10 |
| 2 | 20 | 24 | 36 | 10 | 10 |
| 3 | 30 | 20 | 30 | 10 | 10 |
| 4 | 40 | 16 | 24 | 10 | 10 |
| 5 | 50 | 12 | 18 | 10 | 10 |
| Heavy Metal Elements | Concentration | Hygienic Standards for Drinking Water | Comprehensive Sewage Discharge Standards |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.0006 | ≤0.005 | ≤0.1 |
| Cr | 0.0471 | ≤0.05 | ≤1.5 |
| Mn | 0.0017 | ≤0.1 | ≤2.0 |
| Pb | 0.0006 | ≤0.01 | ≤1.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Xu, C.; Wang, M.; Du, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, G. Economic and Low-Carbon Cementitious Materials Based on Hot–Stuffy Steel Slag. Buildings 2025, 15, 2931. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15162931
Zhang X, Xu C, Wang M, Du S, Li Y, Wang G. Economic and Low-Carbon Cementitious Materials Based on Hot–Stuffy Steel Slag. Buildings. 2025; 15(16):2931. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15162931
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xupeng, Changze Xu, Mingze Wang, Shirong Du, Yan Li, and Guoqing Wang. 2025. "Economic and Low-Carbon Cementitious Materials Based on Hot–Stuffy Steel Slag" Buildings 15, no. 16: 2931. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15162931
APA StyleZhang, X., Xu, C., Wang, M., Du, S., Li, Y., & Wang, G. (2025). Economic and Low-Carbon Cementitious Materials Based on Hot–Stuffy Steel Slag. Buildings, 15(16), 2931. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15162931






