Impact of Urban Elevated Complex Roads on Acoustic Environment Quality in Adjacent Areas: A Field Measurement Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
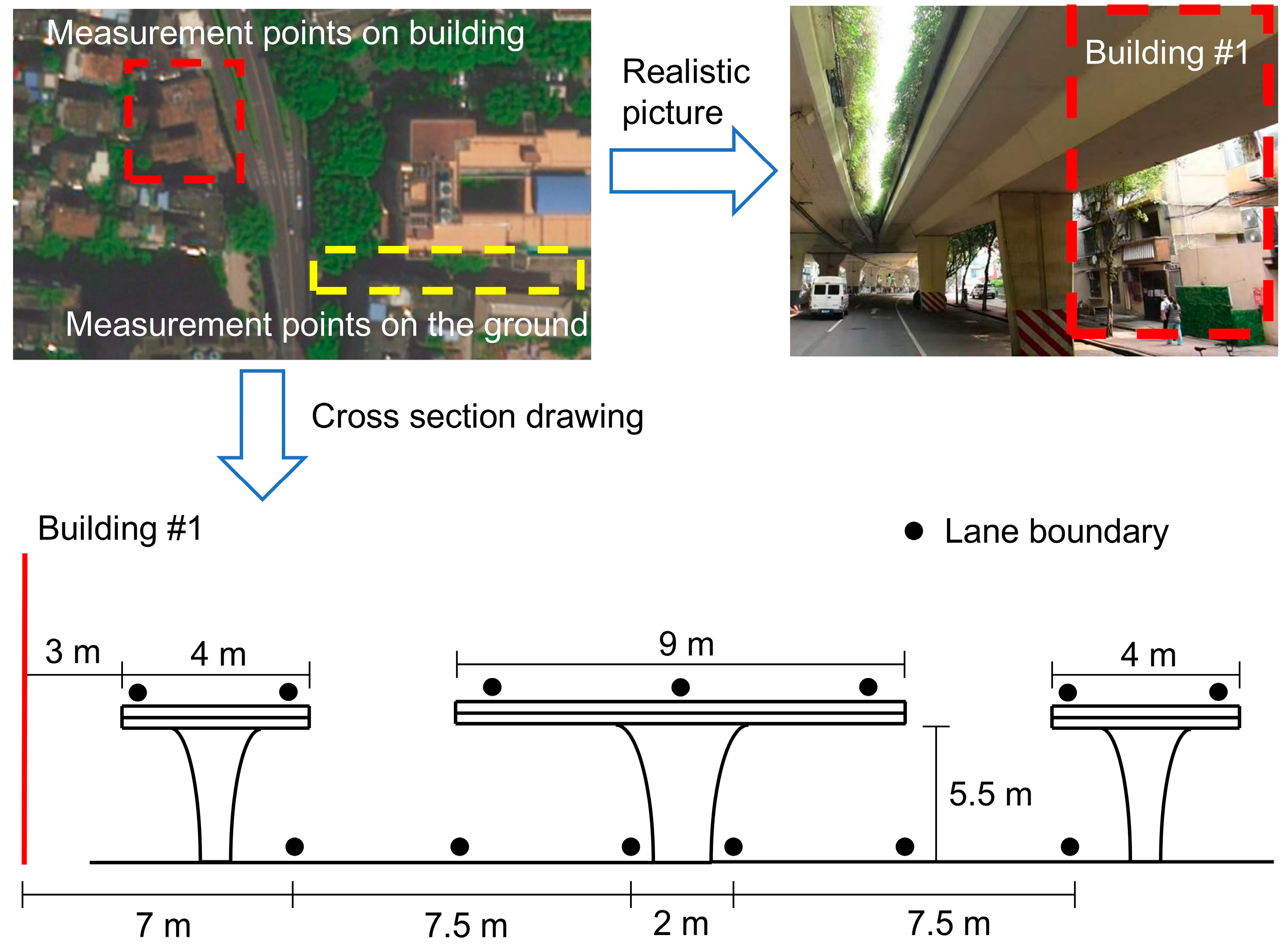
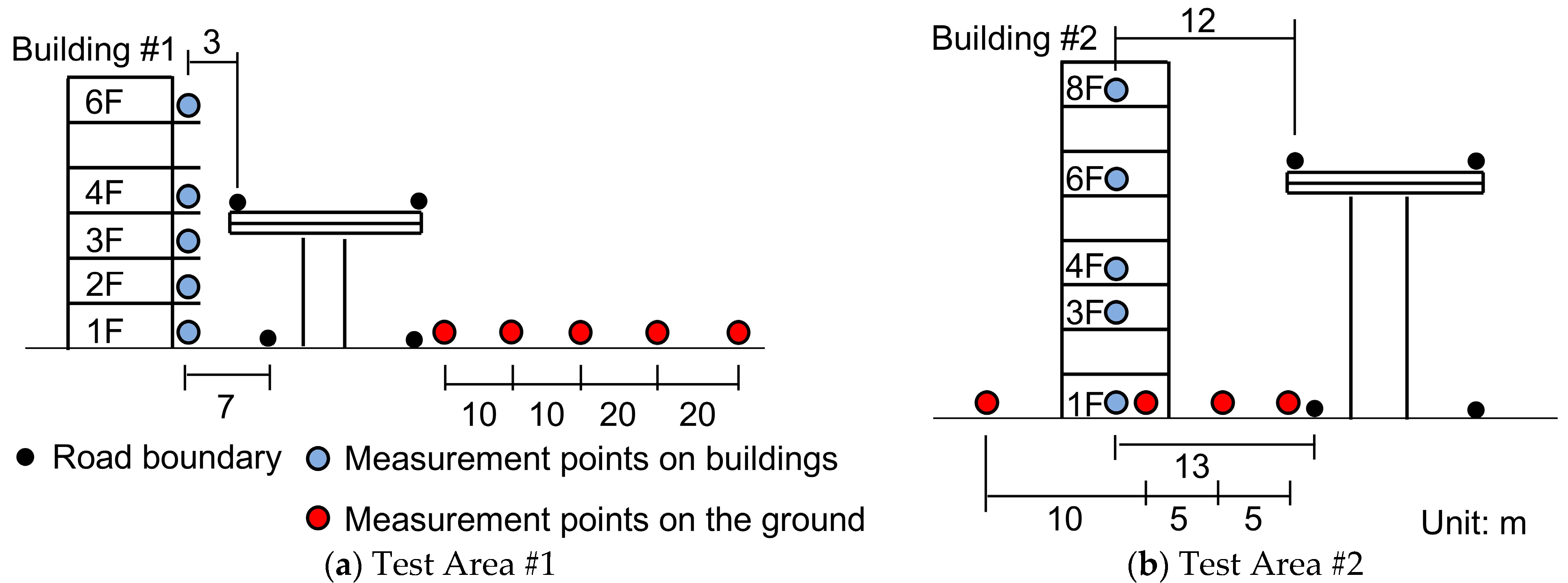
2.1. Location
2.2. Measurement Scheme
3. Results
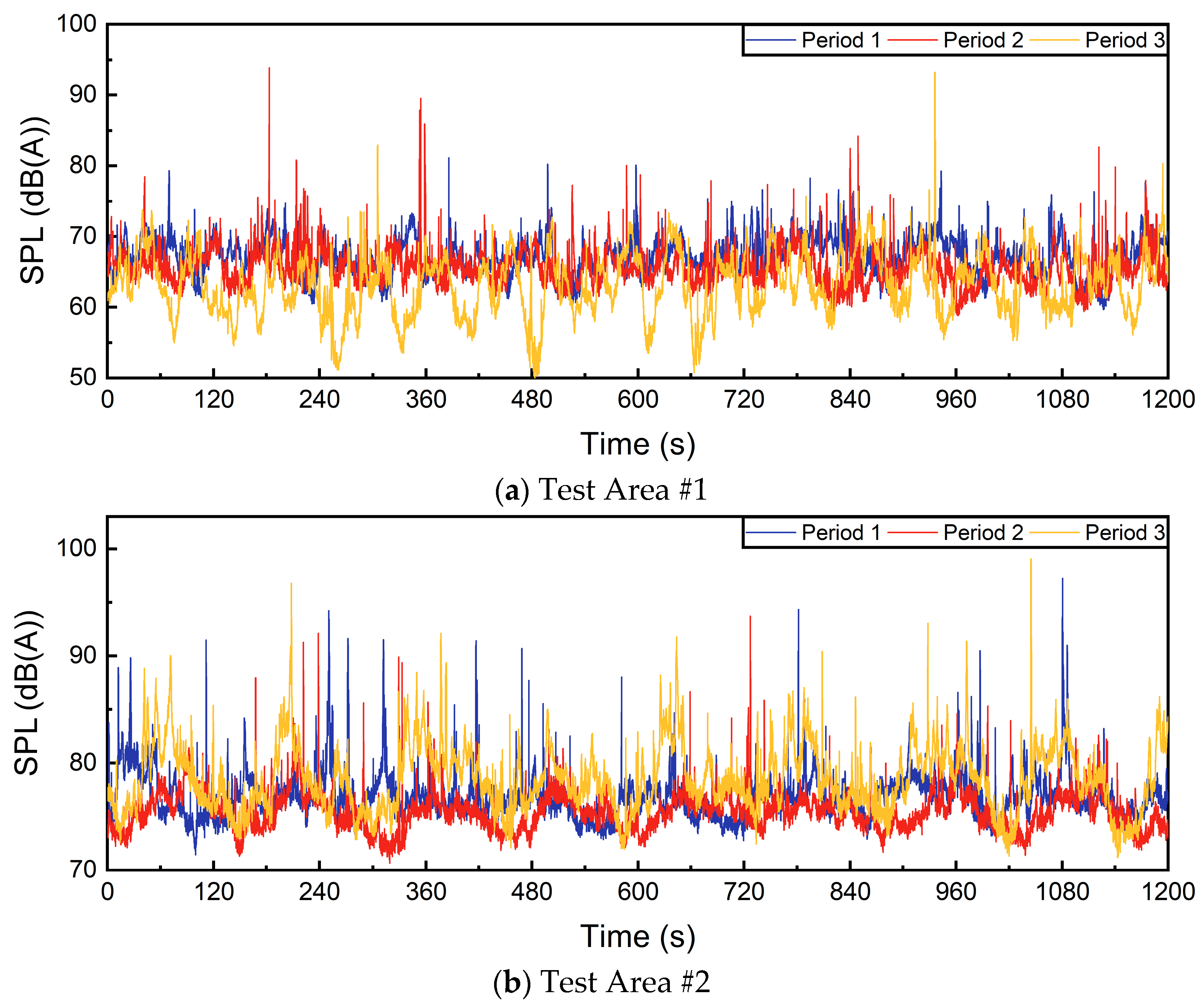
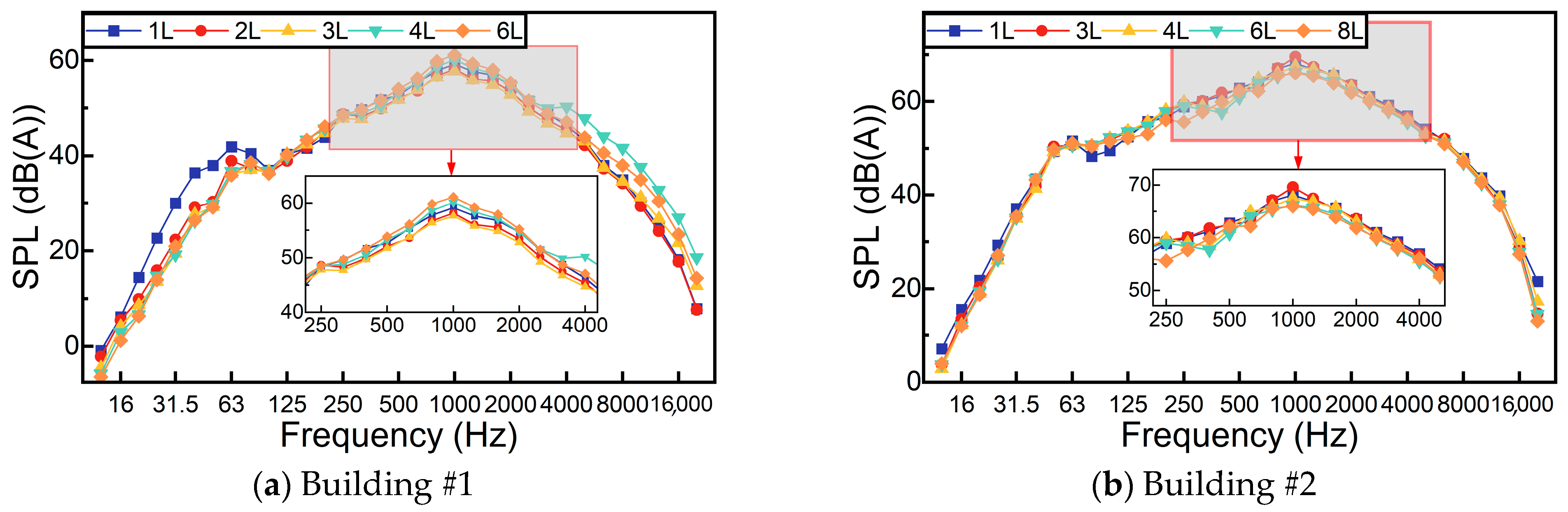
3.1. Characteristics of Traffic Noise in Urban Actual Traffic Operations
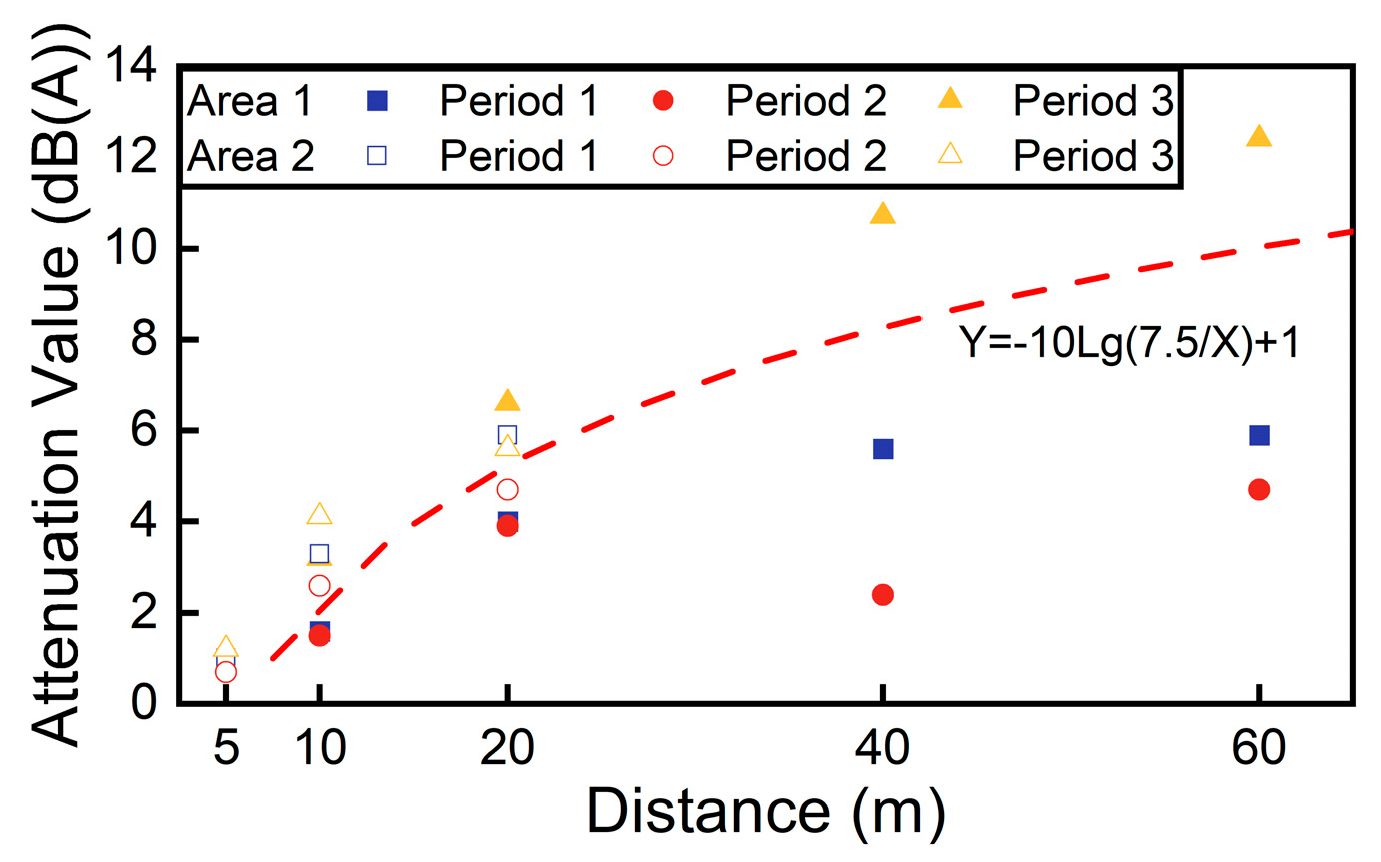
3.2. Noise Distance Attenuation Under Elevated Complex Roads
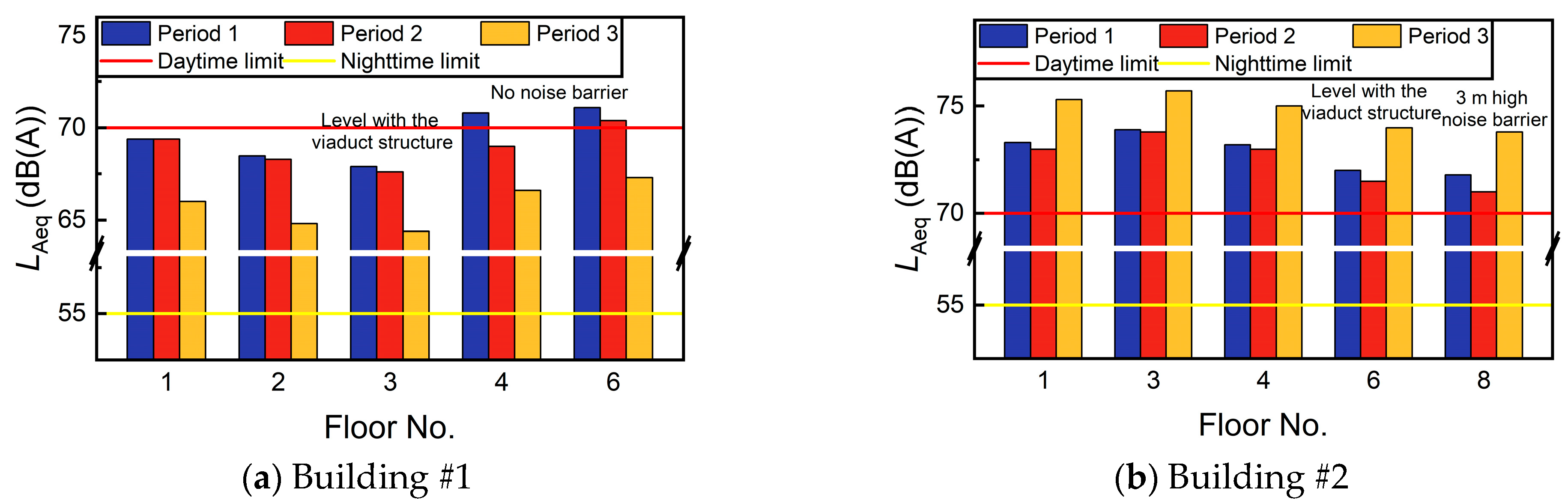
3.3. The Variation in Traffic Noise with Height
4. Discussion
4.1. How Can We Better Address Residential Noise Nuisance at Night?
4.2. Improvements Needed for Noise Prediction Methods in Adjacent Areas of Elevated Complex Roads
4.3. Comprehensive Design of Multiple Noise Reduction Measures Needed
5. Conclusions
- The distance attenuation of noise from elevated complex roads at ground level is not significantly different from that of general roads. By comparing the measured data with the predicted data, it is demonstrated that the distance attenuation formulas of the Chinese Sound Environment Guidelines and the US FHWA Road Noise Prediction Model remain applicable to elevated complex roads.
- Given the presence of noise barriers on many elevated roads adjacent to residential buildings, it is expected that the maximum noise levels will be concentrated within the height range underneath the viaduct. The reflection of noise from the viaduct structure results in the maximum noise level underneath the viaduct being in the middle of the viaduct height. In cases where there are no noise barriers, the noise level on the viaduct initially shows an increasing trend with height. However, with the installation of noise barriers, this upward trend is reversed and the noise level within the acoustic shadow zone gradually decreases as height increases.
- Within the frequency range of 250 to 4000 Hz, the sound pressure levels exhibit consistent variations with the total sound pressure level. Additionally, due to the lower speeds and lighter weights of urban road vehicles, little low-frequency noise pollution caused by viaduct vibration has been observed.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Test Area | Period | Height of Measurement Point Above Ground (m) | Distance from Road Boundary (m) | LAeq (dB(A)) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area #1 | Period 1 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 67.8 |
| 10 | 66.2 | |||
| 20 | 63.8 | |||
| 40 | 62.2 | |||
| 60 | 61.9 | |||
| Period 2 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 66.9 | |
| 10 | 65.4 | |||
| 20 | 63 | |||
| 40 | 64.5 (excluded) | |||
| 60 | 62.2 (excluded) | |||
| Period 3 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 66.1 | |
| 10 | 62.9 | |||
| 20 | 59.5 | |||
| 40 | 55.4 | |||
| 60 | 53.7 | |||
| Area #2 | Period 1 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 77.8 |
| 5 | 76.8 | |||
| 10 | 74.4 | |||
| 20 | 71.9 | |||
| Period 2 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 76 | |
| 5 | 75.3 | |||
| 10 | 73.4 | |||
| 20 | 71.3 | |||
| Period 3 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 79.9 | |
| 5 | 78.7 | |||
| 10 | 75.8 | |||
| 20 | 74.3 |
| Test Area | Period | Distance from Road Boundary (m) | Height of Measurement Point Above Ground (m) | LAeq (dB(A)) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area #1 | Period 1 | 3 | 1.5 (1L) | 69.4 |
| 4.1 (2L) | 68.5 | |||
| 6.7 (3L) | 67.9 | |||
| 9.3 (4L) | 70.8 | |||
| 14.5 (6L) | 71.1 | |||
| Period 2 | 3 | 1.5 (1L) | 69.4 | |
| 4.1 (2L) | 68.3 | |||
| 6.7 (3L) | 67.6 | |||
| 9.3 (4L) | 69 | |||
| 14.5 (6L) | 70.4 | |||
| Period 3 | 3 | 1.5 (1L) | 66 | |
| 4.1 (2L) | 64.8 | |||
| 6.7 (3L) | 64.4 | |||
| 9.3 (4L) | 66.6 | |||
| 14.5 (6L) | 67.3 | |||
| Area #2 | Period 1 | 13 | 1.5 (1L) | 73.3 |
| 7.8 (3L) | 73.9 | |||
| 10.6 (4L) | 73.2 | |||
| 16.2 (6L) | 72 | |||
| 21.8 (8L) | 71.8 | |||
| Period 2 | 13 | 1.5 (1L) | 73 | |
| 7.8 (3L) | 73.8 | |||
| 10.6 (4L) | 73 | |||
| 16.2 (6L) | 71.5 | |||
| 21.8 (8L) | 71 | |||
| Period 3 | 13 | 1.5 (1L) | 75.3 | |
| 7.8 (3L) | 75.7 | |||
| 10.6 (4L) | 75 | |||
| 16.2 (6L) | 74 | |||
| 21.8 (8L) | 73.8 |
References
- Phillips, B.B.; Bullock, J.M.; Osborne, J.L.; Gaston, K.J. Spatial extent of road pollution: A notional analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Kumari, N.; Sharma, P. A review of adverse effects of road traffic noise on human health. Fluct. Noise Lett. 2018, 17, 183001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobollik, M.; Hintzsche, M.; Wothge, J.; Myck, T.; Plass, D. Burden of disease due to traffic noise in Germany. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Das, P.P.; Foujdar, A. Association between road traffic noise and prevalence of coronary heart disease. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 2885–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.-T.; Wang, V.-S.; Chang, L.-T.; Chuang, K.-J.; Chuang, H.-C.; Liu, C.-S.; Bao, B.-Y.; Chang, T.-Y. Road Traffic Noise, Air Pollutants, and the Prevalence of Cardiovascular Disease in Taichung, Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Xu, Y.-N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.-K.; Liu, L. Experimental Study on the Effect of Urban Road Traffic Noise on Heart Rate Variability of Noise-Sensitive People. Front. Psychol. 2022, 12, 749224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Bai, L.; Oiamo, T.H.; Burnett, R.T.; Weichenthal, S.; Jerrett, M.; Kwong, J.C.; Goldberg, M.S.; Copes, R.; Kopp, A.; et al. Association Between Road Traffic Noise and Incidence of Diabetes Mellitus and Hypertension in Toronto, Canada: A Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e013021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-Y.; Cheng, W.-J.; Wu, C.-F.; Chang, T.-Y. Associations of Road Traffic Noise and Its Frequency Spectrum with Prevalent Depression in Taichung, Taiwan. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1116345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Huang, J.; Guo, M.; Tian, L.; Wang, J.; Wong, T.W.; Webster, C.; Leung, G.M.; Ni, M.Y. Contributions of Residential Traffic Noise to Depression and Mental Wellbeing in Hong Kong: A Prospective Cohort Study. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 338, 122641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sygna, K.; Aasvang, G.M.; Aamodt, G.; Oftedal, B.; Krong, N.H. Road Traffic Noise, Sleep and Mental Health. Environ. Res. 2014, 131, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.G.; Younes, M.; Aeschbach, D.; Elmenhorst, E.-M.; Müller, U.; Basner, M. Traffic Noise-Induced Changes in Wake-Propensity Measured with the Odds-Ratio Product (ORP). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Kempen, E.; Fischer, P.; Janssen, N.; Houthuijs, D.; van Kamp, I.; Stansfeld, S.; Cassee, F. Neurobehavioral Effects of Exposure to Traffic-Related Air Pollution and Transportation Noise in Primary Schoolchildren. Environ. Res. 2012, 115, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.-W.; Xue, W.-X.; Jiang, N.; Huang, S.; Zhang, S.-X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Dong, G.-H.; Cai, M.; Chen, Y.-J. Exposure to Road Traffic Noise and Behavioral Problems in Chinese Schoolchildren: A Cross-Sectional Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Zijlema, W.L.; Sørgjerd, E.P.; Doiron, D.; de Hoogh, K.; Hodgson, S.; Wolffenbuttel, B.; Gulliver, J.; Hansell, A.L.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; et al. Impact of Road Traffic Noise on Obesity Measures: Observational Study of Three European Cohorts. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annual Report on Prevention and Control of Noise Pollution in China 2024. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/hjzywr/202408/W020240829356736814731.pdf (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- Faulkner, J.; Murphy, E. Road traffic noise modelling and population exposure estimation using CNOSSOS-EU: Insights from Ireland. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 192, 108692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoatey, P.; Omidvarbona, H.; Baawain, M.S.; AI-Mayahi, A.; AI-Mamun, A.; AI-Harthy, I. Exposure assessment to road traffic noise levels and health effects in an arid urban area. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 35051–35064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.L.; Lam, K.C.; van Kamp, I. Quantification of the exposure and effects of road traffic noise in a dense Asian city: A comparison with western cities. Environ. Health 2015, 14, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.F.; Walker, E.D. Research in action-tourism and its impacts on the environmental soundscape-A community-initiated pilot study. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 105, 107450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Pan, Z.; Wang, G. A methodology to control urban traffic noise under the constraint of environmental capacity: A case study of a double-decision optimization model. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2015, 41, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnaccia, C.; Mascolo, A.; Aumond, P.; Can, A.; Rossi, D. From Early to Recent Models: A Review of the Evolution of Road Traffic and Single Vehicles Noise Emission Modelling. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2024, 10, 662–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, P.E.K.; Zannin, P.H.T. Evaluation of noise pollution in urban traffic hubs—Noise maps and measurements. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2015, 51, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, M.; Gao, X.; Gao, J.; Kang, J. Analysis of traffic noise spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors in high-density cities. Appl. Acoust. 2024, 217, 109838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Mak, C.M.; He, X. Analysis of urban road traffic noise exposure of residential buildings in Hong Kong over the past decade. Noise Health 2019, 21, 142–154. [Google Scholar]
- Di, G.; Liu, X.; Lin, Q.; Zheng, Y.; He, L. The relationship between urban combined traffic noise and annoyance: An investigation in Dalian, north of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 432, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; He, J.; He, C.; Cai, M. Evaluation of urban traffic noise pollution based on noise maps. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 87, 102516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, R.A.; Pimentel, R.L.; Lacerda, D.M.; Silva, W.M. Applicability of models to estimate traffic noise for urban roads. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2015, 13, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiff, M.; Hornikx, M.; Forssén, J. Excess attenuation for sound propagation over an urban canyon. Appl. Acoust. 2010, 71, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Pan, Z.; Liu, Z.; Hou, G.; Yang, H. Acoustic amenity analysis for high-rise building along urban expressway: Modeling traffic noise vertical propagation using neural networks. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 53, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhai, J.; Zhu, M. Characteristics and perception evaluation of the soundscapes of public spaces on both sides of the elevated road: A case study in Suzhou, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 84, 103996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.; Cao, R.; Wang, Q.; Peng, Z.; He, Y. Prediction of Noise Reduction Effect of Sound Barriers and Evaluation of Noise Annoyance. Fluct. Noise Lett. 2025, 24, 2550002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guangzhou Statistical Yearbook 2024. Available online: https://tjj.gz.gov.cn/datav/admin/home/www_nj/ (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- Cai, M.; Zou, J.; Xie, J.; Ma, X. Road traffic noise mapping in Guangzhou using GIS and GPS. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 87, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Cai, M. Evaluation of an urban traffic Noise-Exposed population based on points of interest and noise maps: The case of Guangzhou. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.M.; Luo, W.; Xie, J.; Lee, H.P. Urban traffic noise mapping using building simplification in the Panyu District of Guangzhou City, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 3096-2008; Environmental Quality Standard for Noise. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China/General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the Peoples Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Alsina-Pagès, R.M.; Benocci, R.; Brambilla, G.; Zambon, G. Methods for noise event detection and assessment of the sonic environment by the harmonica index. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zou, C.; He, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, Q. Traffic noise exposure of high-rise residential buildings in urban area. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 8502–8515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Wu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Wang, H. Study on the network acoustics environment effects of traffic management measures by a bilevel programming model. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 101, 105203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y. Traffic noise distribution characteristics of high-rise buildings along ultra-wide cross section highway with multiple noise reduction measures. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 20601–20620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Wu, D.; Zhang, H.; Shen, Y.; Mikio, Y. Low frequency noise radiation from traffic-induced vibration of steel double-box girder bridge. J. Vib. Control 2012, 18, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Sheng, X. Characterizing low-frequency structure-borne noise from multi-span bridges on high-speed railways. J. Cent. South Univ. 2024, 31, 976–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanok, S.; Berger, M.; Müller, U.; Schmid, M.; Weidenfeld, S.; Elmenhorst, E.-M.; Aeschbach, D. Road traffic noise impacts sleep continuity in suburban residents: Exposure-response quantification of noise-induced awakenings from vehicle pass-bys at night. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foraster, M.; Esnaola, M.; López-Vicente, M.; Rivas, I.; Álvarez-Pedrerol, M.; Persavento, C.; Sebastian-Galles, N.; Pujol, J.; Dadvand, P.; Sunyer, J. Exposure to road traffic noise and cognitive development in schoolchildren in Barcelona, Spain: A population-based cohort study. PLoS. Med. 2022, 19, e1004001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Z.; Cai, M. Dynamic traffic noise maps based on noise monitoring and traffic speed data. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2021, 94, 102796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balážiková, M.; Pačaiová, H.; Tomašková, M. A Proposal for Risk Assessment of Low-Frequency Noise in the Human–Machine–Environment System. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 13321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson Waye, K.; Bengtsson, J.; Rylander, R.; Hucklebridge, F.; Evans, P.; Clow, A. Low frequency noise enhances cortisol among noise sensitive subjects during work performance. Life Sci. 2002, 70, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, B.; Hassmén, P.; Soames Job, R.F. Sources and effects of low-frequency noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1996, 99, 2985–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wu, X.; Jiang, J. Lane restriction system to reduce the environmental cost of urban roads. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2023, 115, 103575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, K.; Wang, S. Replacing urban trucks via ground–air cooperation. Commun. Transp. Res. 2022, 2, 10080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hu, X.; Xue, G.; Guan, X. Truck–drone hybrid routing problem with time-dependent road travel time. Transp. Res. Part C Emer. 2022, 14, 103901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallas, M.A.; Chatagnon, R.; Lelong, J. Noise emission assessment of a hybrid electric mid-size truck. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 76, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lak, A.; Amiri, N.; Aghamolaei, R. Urban Elevated Highways in Residential Districts: New Developed Elevated Highways from Residents’ Perspectives. J. Urban Plann. Dev. 2022, 148, 05022006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi Baaj, M.; EI-Fadel, M.; Shazbak, S.M.; Saliby, E. Modeling Noise at Elevated Highways in Urban Areas: A Practical Application. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2001, 127, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.L.; Kang, J. Resistance of Villages to Elevated-Road Traffic Noise. J. Environ. Plan. Manage. 2018, 62, 492–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.-F.; He, H.-D.; Wang, H.-W.; Li, X.-B.; Peng, Z.-R. Characterizing temporal and vertical distribution patterns of traffic-emitted pollutants near an elevated expressway in urban residential areas. Build. Environ. 2020, 72, 106678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Shao, S. Study on noise reduction with paving different low noise pavement materials. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, U.; Żurek, B.Ś.; Ejsmont, J.A.; Ronowski, G. Tyre/road noise reduction of poroelastic road surface tested in a laboratory. In Proceedings of the Acoustics 2013—Victor Harbor, Victor Harbor, Australia, 17–20 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.; Han, S.; Luo, Y.; Han, X.; Xu, O. Evaluation of tire-pavement noise based on three-dimensional pavement texture characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 306, 124935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, T.; Meiarashi, S.; Namikawa, Y.; Hasebe, M. Reduction of equivalent continuous A-weighted sound pressure levels by porous elastic road surfaces. Appl. Acoust. 2005, 66, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fediuk, R.; Amean, M.; Vatin, N.; Vasilev, Y.; Lesovik, V.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Acoustic properties of innovative concretes: A review. Materials 2021, 14, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Xu, H.; Qin, X.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, J. Cross-scale study on the interaction behaviour of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash-asphalt mortar: A macro-micro approach. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2025, 26, 2469114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Qin, X.; Liu, Z.; Yin, Y. Damaging effect of fine grinding treatment on the microstructure of polyurea elastomer modifier used in asphalt binder. Measurement 2025, 242 Pt B, 115984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulikakos, L.D.; Athari, S.; Mikhailenko, P.; Kakar, M.R.; Bueno, M.; Piao, Z.; Pieren, R.; Heutschi, K. Effect of waste materials on acoustical properties of semi-dense asphalt mixtures. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2022, 102, 103154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faßbender, S.; Oeser, M. Investigation of the Reusability of a Polyurethane-Bound Noise-Absorbing Pavement in Terms of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement. Materials 2022, 15, 3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secchi, S.; Astolfi, A.; Calosso, G.; Casini, D.; Cellai, G.; Scamoni, F.; Scrosati, C.; Shtrepi, L. Effect of outdoor noise and façade sound insulation on indoor acoustic environment of Italian schools. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 126, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naish, D.A.; Tan, A.C.; Demirbilek, F.N. Simulating the effect of acoustic treatment types for residential balconies with road traffic noise. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 79, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggenschwiler, K.; Heutschi, K.; Taghipour, A.; Pieren, R.; Gisladottir, A.; Schäffer, B. Urban design of inner courtyards and road traffic noise: Influence of façade characteristics and building orientation on perceived noise annoyance. Build. Environ. 2022, 224, 109526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Hornikx, M.; van Renterghem, T.; Smyrnova, Y.; Forssén, J.; Cheal, C.; Botteldooren, D.; Yang, H.-S.; Jeon, J.Y.; Jang, H.S.; et al. Vegetation in urban streets, squares, and courtyards. In Environmental Methods for Transport Noise Reduction, 1st ed.; Nilsson, M., Bengtsson, J., Klaeboe, R., Eds.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Z.; Zhang, D.; Tu, D.; He, L.; Zou, C. Prediction of train-induced ground-borne vibration transmission considering parametric uncertainties. Probab. Eng. Mech. 2025, 79, 103731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zheng, B.; Jiang, B.; Jiang, S.; Zou, C. Effect of Non-Structural Components on Over-Track Building Vibrations Induced by Train Operations on Concrete Floor. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Test Area | Period | LAeq (dB(A)) | Lmax (dB(A)) | L10 (dB(A)) | L50 (dB(A)) | L90 (dB(A)) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area #1 | Period 1 | 67.8 | 80.2 | 70.2 | 67.1 | 63.5 |
| Period 2 | 66.9 | 92 | 68.6 | 65.4 | 62.7 | |
| Period 3 | 66.1 | 93.2 | 68.9 | 63.1 | 57.7 | |
| Area #2 | Period 1 | 77.8 | 96.3 | 79.2 | 76.6 | 74.6 |
| Period 2 | 76 | 92.9 | 77.5 | 75.4 | 73.3 | |
| Period 3 | 79.9 | 98.6 | 82.6 | 78.1 | 74.7 |
| Difference (dB(A)) | Distance (m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 40 | 60 | |
| Minimum | −0.7 | −1.4 | −1.7 | −4.1 |
| Maximum | 1.9 | 1.3 | 2.4 | 2.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, G.; He, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q. Impact of Urban Elevated Complex Roads on Acoustic Environment Quality in Adjacent Areas: A Field Measurement Study. Buildings 2025, 15, 2662. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15152662
Yang G, He L, Wang Y, Liu Q. Impact of Urban Elevated Complex Roads on Acoustic Environment Quality in Adjacent Areas: A Field Measurement Study. Buildings. 2025; 15(15):2662. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15152662
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Guangrui, Lingshan He, Yimin Wang, and Qilin Liu. 2025. "Impact of Urban Elevated Complex Roads on Acoustic Environment Quality in Adjacent Areas: A Field Measurement Study" Buildings 15, no. 15: 2662. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15152662
APA StyleYang, G., He, L., Wang, Y., & Liu, Q. (2025). Impact of Urban Elevated Complex Roads on Acoustic Environment Quality in Adjacent Areas: A Field Measurement Study. Buildings, 15(15), 2662. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15152662






