Eco-Friendly Bitumen Composites with Polymer and Rubber Waste for Sustainable Construction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Mixtures
2.3. Methods
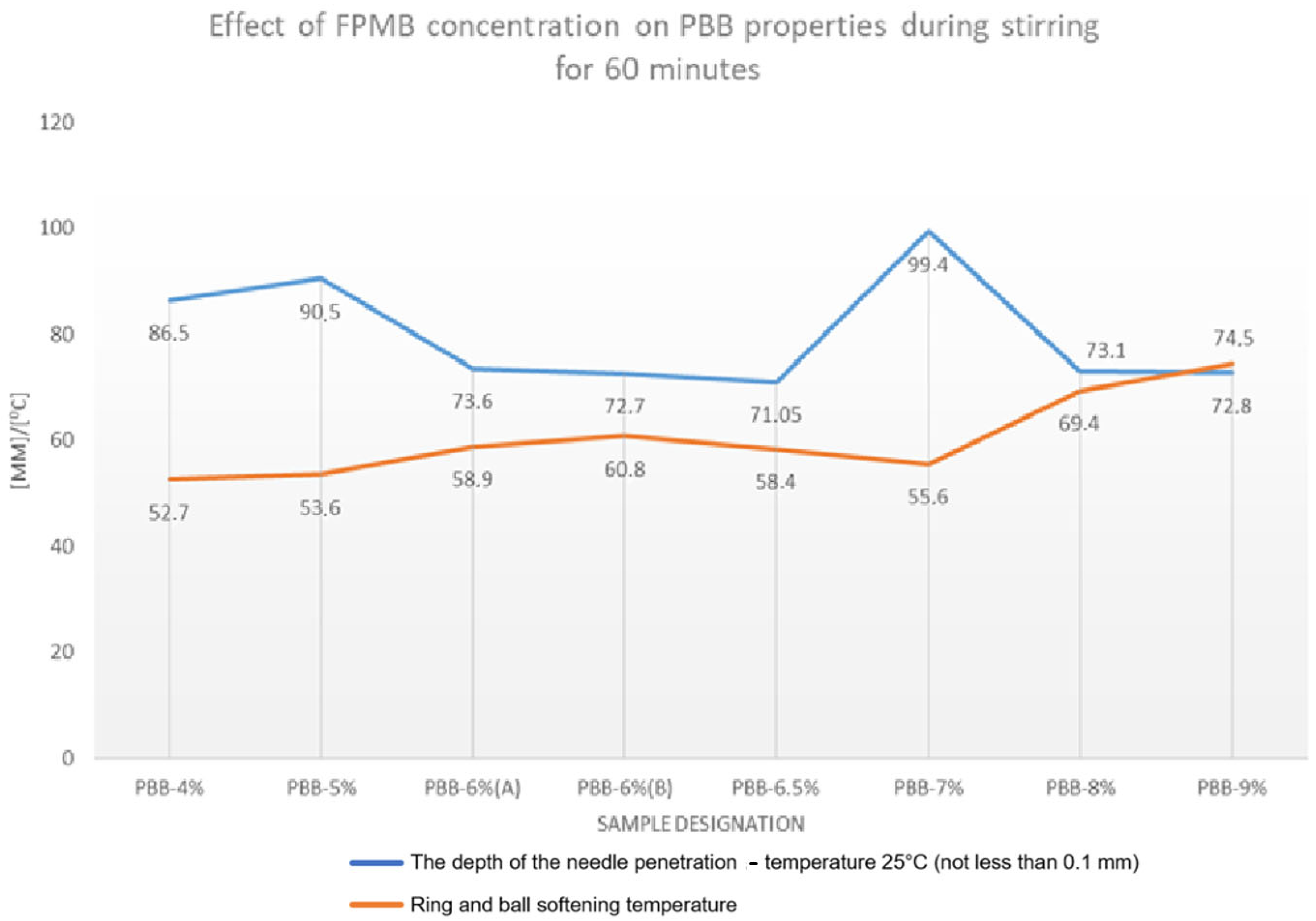
3. Results
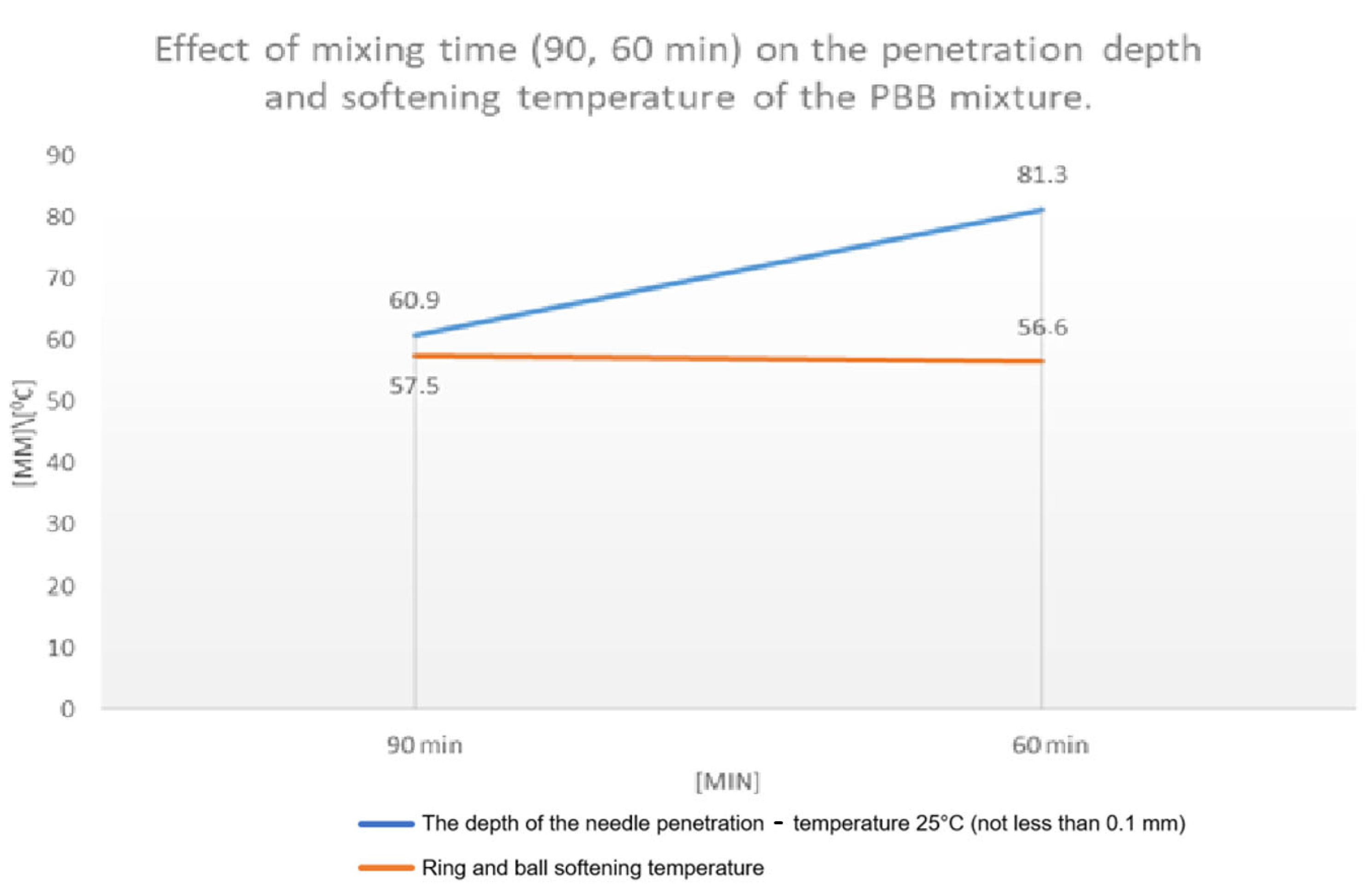
- 90 min: The penetration depth is 60.9 mm, indicating high hardness of the material. The softening temperature is 57.5 °C, close to the standard, providing acceptable heat resistance.
- 30 min: The penetration depth increases to 81.3 mm, reflecting a softer structure. The softening temperature is 56.6 °C, slightly below the standard, indicating a decrease in heat resistance.
4. Discussion
- The softening temperature before aging was 70.6 °C, but after aging, it decreased to 59 °C, indicating a decrease in the heat resistance of the material.
- The depth of needle penetration decreased from 81 mm to 69 mm, indicating an increase in the hardness of the bitumen after aging. This suggests that the structure of the mixture becomes denser, but the heat resistance worsens.
- The softening temperature before aging was 58.9 °C, and after aging, it increased to 61.4 °C. This indicates an improvement in the heat resistance of the material and an increase in its resistance to high temperatures.
- The depth of needle penetration significantly decreased from 73.6 mm to 49.3 mm, indicating a significant increase in the stiffness of the mixture. This may be due to the strengthening of the bitumen structure after aging.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EVA | ethylene-vinyl acetate |
| LCA | Life Cycle Analysis |
| PBB | polymer–bitumen binder |
| PE | polyethylene |
| PP | polypropylene |
| RAP | recycled asphalt pavement |
| SBS | styrene–butadiene–styrene |
Appendix A. Used Laboratory Device

References
- Yang, Q.; Lin, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Xie, N.; Shi, X. A Review of Polymer-Modified Asphalt Binder: Modification Mechanisms and Mechanical Properties. Clean. Mater. 2024, 12, 100255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.H.; Jakarni, F.M.; Muniandy, R.; Hassim, S. A Review on the Application of Natural Rubber as Asphalt Modifier. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1075, 012031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Birgisson, B.; Kringos, N. Polymer Modification of Bitumen: Advances and Challenges. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 54, 18–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiada, W.; Liu, H.; Ezzat, H.; Al-Khateeb, G.G.; Shane Underwood, B.; Shanableh, A.; Samarai, M. Review of the Superpave Performance Grading System and Recent Developments in the Performance-Based Test Methods for Asphalt Binder Characterization. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 319, 126063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsheyab, M.A.; Khasawneh, M.A.; Abualia, A.; Sawalha, A. A Critical Review of Fatigue Cracking in Asphalt Concrete Pavement: A Challenge to Pavement Durability. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2024, 9, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochare, R.; Dhone, K.; Parolkar, R. Green Roads Revolution: Innovating Rubber and Bitumen Production for Sustainable and Durable Infrastructure. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ning, Z.; Feng, X.; He, X.; Tan, S. Methods for Improving Storage Stability of Rubber Bitumen: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 449, 141595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olalekan, S.T.; Olatunde, A.A.; Kolapo, S.K.; Omolola, J.M.; Olukemi, O.A.; Ayanniyi Mufutau, A.; Olaosebikan, O.O.; Saka, A.A. Durability of Bitumen Binder Reinforced with Polymer Additives: Towards Upgrading Nigerian Local Bitumen. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilema, M.; Yuen, C.W.; Alharthai, M.; Al-Saffar, Z.H.; Al-Sabaeei, A.; Yusoff, N.I.M. A Review of Rubberised Asphalt for Flexible Pavement Applications: Production, Content, Performance, Motivations and Future Directions. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valerievna, K.E.; Vladimirovna, Z.O.; Yurievich, B.V. Involvement of Products of Chemical Processing of Polymer Waste in the Composition of Building Materials. Egypt. J. Pet. 2024, 33, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed Adnan Hayder, A.-R.; Alexandra Olegovna, S.; Igorevna, Z.V.; Wako Bleck Junior, H. Study of the Dispersion of Bitumens Modified with Secondary Polyethylene Terephthalate. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1374, 012032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, A.; Kutay, M.E.; Anctil, A. Environmental Assessment of Asphalt Mixtures Modified with Polymer Coated Rubber from Scrap Tires. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 418, 138090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sienkiewicz, M.; Borzędowska-Labuda, K.; Wojtkiewicz, A.; Janik, H. Development of Methods Improving Storage Stability of Bitumen Modified with Ground Tire Rubber: A Review. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 159, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuano, L.; Magatti, G.; Perucca, M.; Dettori, M.; Mantecca, P. Use of Recycled Plastics as a Second Raw Material in the Production of Road Pavements: An Example of Circular Economy Evaluated with Lca Methodology. Procedia Environ. Sci. Eng. Manag. 2020, 7, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Mersha, D.A.; Sendekie, Z.B. High-Temperature Performance Enhancement of Bitumen by Waste PET-Derived Polyurethane. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 2022, 9567197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakar, M.R.; Mikhailenko, P.; Piao, Z.; Bueno, M.; Poulikakos, L. Analysis of Waste Polyethylene (PE) and Its by-Products in Asphalt Binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 280, 122492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.; Fini, E.H. State of the Art in the Application of Functionalized Waste Polymers in the Built Environment. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 177, 105967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.I.; Mir, M.S.; Mohanty, B. Application of Solid Waste Materials in Cold Bitumen Emulsion Mixtures for Cleaner Pavement Industry: A Comprehensive Review. Env. Sci Pollut Res 2024, 31, 48908–48927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korniejenko, K.; Nykiel, M.; Choinska, M.; Jexembayeva, A.; Konkanov, M.; Aruova, L. An Overview of Micro- and Nano-Dispersion Additives for Asphalt and Bitumen for Road Construction. Buildings 2023, 13, 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santagata, E.; Lanotte, M.; Baglieri, O. Evaluation of Swelling and Degradation Rates in Crumb Rubber Modified Bituminous Binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 458, 139573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Jin, T.; Cheng, H.; Li, M.; Wang, Z.; Sun, L. Performance Evolution and Technique Optimization of Crumb Rubber Modified Bitumen under Thermal Effect throughout the Production and Construction Process. Fuel 2025, 394, 135115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merijs-Meri, R.; Zicans, J.; Ivanova, T.; Berzina, R.; Bernava, A.; Žiganova, M.; Ābele, A.; Haritonovs, V. Manufacturing and Characterization of Asphalt Binders Designed on the Bases of Polymer Modified Bitumen with Cement By-Pass Dust and Fly Ash. In Eleventh International Conference on the Bearing Capacity of Roads, Railways and Airfields, Volume 3; CRC Press: London, UK, 2022; pp. 380–386. ISBN 978-1-003-22291-0. [Google Scholar]
- Yeganeh, S.; Ameri, M.; Dalmazzo, D.; Santagata, E. Experimental Investigation on the Use of Waste Elastomeric Polymers for Bitumen Modification. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, H.A.; Zaidi, S.B.A.; Ahmad, N. Eco-Efficient Modification of Asphalt Binders and Mixtures Using Elevated Ratios of Polyethylene Terephthalate and Crumb Rubber Waste: A Step towards Sustainable Roads. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2025, 10, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaan, N. Engineering Characterisation of Wearing Course Materials Modified with Waste Plastic. Recycling 2022, 7, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emelyanycheva, E.; Abdullin, A. The Modification of Road Petroleum Bitumen with Petrochemical Wastes and Polymers. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2021, 56, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Lapkovskis, V.; Mironovs, V.; Kasperovich, A.; Myadelets, V.; Goljandin, D. Crumb Rubber as a Secondary Raw Material from Waste Rubber: A Short Review of End-Of-Life Mechanical Processing Methods. Recycling 2020, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo, G.; Cifuentes, S.; Colorado, H.A. Ground Tire Rubber and Bitumen with Wax and Its Application in a Real Highway. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 1048–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Pham, A.; Stasinopoulos, P.; Giustozzi, F. Recycling Waste Plastics in Roads: A Life-Cycle Assessment Study Using Primary Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagurskyy, A.; Grynyshyn, O.; Khlibyshyn, Y.; Korchak, B. Ukraine Use of Rubber Crumb Obtained from Waste Car Tires for the Production of Road Bitumen and Roofing Materials from Residues of Ukrainian Oil Processing. Chem. Chem. Technol 2023, 17, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugin, K.G. Ensuring Environmental Safety When Using Polymer Waste in Technologies for Obtaining Building Materials. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1926, 012048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Riccardi, C.; Jiang, W. From Waste to Sustainable Pavement: Rejuvenation of Asphalt Binder Using Waste Engine Oil Residue and Crumb Rubber. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellawati, J.; Sumarti, M.; Menry, Y.; Surtipanti, S.; Kump, P. Application of X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometry in Multielement Analysis of Rubber Samples. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2001, 54, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhou, T.; Cao, L.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Z.; Dong, Z. Characterization of Emissions from Rubber Modified Asphalt and Their Impact on Environmental Burden: Insights into Composition Variability and Hazard Assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 477, 135336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bredács, M.; Barretta, C.; Castillon, L.F.; Frank, A.; Oreski, G.; Pinter, G.; Gergely, S. Prediction of Polyethylene Density from FTIR and Raman Spectroscopy Using Multivariate Data Analysis. Polym. Test. 2021, 104, 107406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, X.; Wang, X. FTIR Analysis of the Functional Group Composition of Coal Tar Residue Extracts and Extractive Residues. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, R.; Jones, D.L.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Li, Z.; Yan, C. Field Test on the Biodegradation of Poly(Butylene Adipate-Co-Terephthalate) Based Mulch Films in Soil. Polym. Test. 2021, 93, 107009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painter, P.C.; Starsinic, M.; Squires, E.; Davis, A.A. Concerning the 1600 Cm−1 Region in the i.r. Spectrum of Coal. Fuel 1983, 62, 742–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, P.; Xu, G.; Fu, L.; Feng, H.; Chen, X. Chemical Structure of Rubber Powder on the Compatibility of Rubber Powder Asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 392, 131769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Huang, W.; Zheng, M.; Hu, Y.; Yan, C.; Wang, J. Understanding the Particle Effects and Interaction Effects of Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt Regarding Bonding Properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 348, 128716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 12607-1:2024; Bitumens and Bituminous Binders—Determination of the Resistance to Hardening under Influence of Heat and Air—Part 1: RTFOT Method. CEN: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024.
- ASTM D0005-06E01; Test Method for Penetration of Bituminous Materials. D04 Committee ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013. [CrossRef]
- ASTM D0036-06; Test Method for Softening Point of Bitumen (Ring-and-Ball Apparatus). D08 Committee ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010. [CrossRef]
- 22245-90; Viscous Petroleum Road Bitumens. Specification. GOST: Obninsk, Russia, 1994. Available online: https://www.russiangost.com/p-15935-gost-22245-90.aspx (accessed on 20 July 2025).
- PN-EN 12591:2010; Asphalts and Asphalt Binders—Requirements for Road Asphalts. Polski Komitet Normalizacyjny: Warsaw, Poland, 2010.
- Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Qin, Y. Aging Mechanism of SBS Modified Asphalt Based on Chemical Reaction Kinetics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 91, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Cao, L.; Fini, E.H.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Dong, Z. Behaviors of Asphalt under Certain Aging Levels and Effects of Rejuvenation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 249, 118748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X. Investigation of Asphalt Oxidation Kinetics Aging Mechanism Using Molecular Dynamic Simulation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 377, 131159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samieadel, A.; Islam Rajib, A.; Phani Raj Dandamudi, K.; Deng, S.; Fini, E.H. Improving Recycled Asphalt Using Sustainable Hybrid Rejuvenators with Enhanced Intercalation into Oxidized Asphaltenes Nanoaggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.R.; Katman, H.Y.; Karim, M.R.; Koting, S.; Mashaan, N.S. A Review on the Effect of Crumb Rubber Addition to the Rheology of Crumb Rubber Modified Bitumen. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 2013, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cui, C.; Temitope, A.A.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, G.; Guo, P. Effect of SBS and Crumb Rubber on Asphalt Modification: A Review of the Properties and Practical Application. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. (Engl. Ed.) 2022, 9, 836–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Song, L.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y. Research Progress and Performance Evaluation of Crumb-Rubber-Modified Asphalts and Their Mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 361, 129687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No | Properties of Bitumen | Results |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Penetration (25 °C, 100 g, 5 s, 0.1 mm) [mm] | 117.6 |
| 2 | Ring and ball softening temperature [°C] | 46.4 |
| No | Properties of Bitumen | Results |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Penetration (25 °C, 100 g, 5 s, 0.1 mm) [mm] | 110.2 |
| 2 | Ring and ball softening temperature [°C] | 46.6 |
| No | Oxide | Amount [%] | Standard Deviation [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SO3 | 76.34 | 0.00407 |
| 2 | P2O5 | 11.85 | 0.00247 |
| 3 | CaO | 5.49 | 0.00137 |
| 4 | SiO2 | 4.23 | 0.00182 |
| 5 | Na2O | 0.72 | 0.00514 |
| 6 | MgO | 0.46 | 0.00232 |
| 7 | Al2O3 | 0.33 | 0.00154 |
| 8 | HfO2 | 0.15 | 0.000740 |
| 9 | Fe2O3 | 0.10 | 0.000296 |
| Sample Designation | PBB-4% | PBB-5% | PBB-6% (A) | PBB-6% (B) | PBB-6.5% | PBB-7% | PBB-8% | PBB-9% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bitumen [%] | 96 | 95 | 94 | 94 | 93.5 | 93 | 92 | 91 |
| FPMB [%] | 4 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6.5 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| No | BND 60/90 (Pavlodar Petrochemical Plant LLP) + 6% FPMB | BND 60/90 (Caspi Bitum LLP) + 7% FPMB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass Before RTFOT [g] | Mass After RTFOT [g] | Change in Mass [%] | Mass Before RTFOT [g] | Mass After RTFOT [g] | Change in Mass [%] | |
| 1 | 194 | 194 | M1-0.00 | 192 | 191.9 | M1-0.05 |
| 2 | 201.6 | 201.5 | M2-0.05 | 195.1 | 195 | M2-0.05 |
| 3 | 202.5 | 202.2 | M3-0.15 | 190 | 190 | M3-0.00 |
| 4 | 195.1 | 195 | M4-0.05 | 192.3 | 192.3 | M4-0.00 |
| 5 | 191.2 | 191.2 | M5-0.00 | 194.6 | 194.5 | M5-0.05 |
| 6 | 201.5 | 201.4 | M6-0.05 | 191.8 | 191.7 | M6-0.05 |
| Ring and Ball Softening Temperature [°C] | |
|---|---|
| before | after |
| 70.6 | 59 |
| Needle penetration depth at 25 °C (not less than 0.1 mm) [mm] | |
| 81 | 69 |
| Ring and Ball Softening Temperature [°C] | |
|---|---|
| before | after |
| 58.9 | 61.4 |
| Needle penetration depth at 25 °C (not less than 0.1 mm) [mm] | |
| 73.6 | 49.3 |
| No | Properties of Bitumen | PN-EN 12591: 2010 50/70 [45] | PN-EN 12591: 2010 70/100 [45] | GOST 22245-90 BND 60/90 [44] | BND 60/90 (Caspi Bitum LLP) + 7% FPMB | BND 60/90 (Pavlodar Petrochemical Plant LLP) + 6% FPMB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Penetration (25 °C, 100 g, 5 s, 0.1 mm) [mm] | 50–70 | 70–100 | 61–90 | 81 | 73.6 |
| 2 | Ring and ball softening temperature [°C] | 46 ÷ 54 | 43 ÷ 51 | 47 | 70.6 | 58.9 |
| 3 | Remaining penetration after aging [%] | ≥50 | ≥46 | 20 (drop of penetration) | 69 | 49.3 |
| 4 | Increase in softening point after aging [°C] | ≤9 or ≤11 | ≤9 or ≤11 | 5 (defined as change) | 59 | 61.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seitenova, G.Z.; Dyussova, R.M.; Aspanbetov, D.A.; Jexembayeva, A.Y.; Korniejenko, K.; Aruova, L.; Sakanov, D.K. Eco-Friendly Bitumen Composites with Polymer and Rubber Waste for Sustainable Construction. Buildings 2025, 15, 2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15152608
Seitenova GZ, Dyussova RM, Aspanbetov DA, Jexembayeva AY, Korniejenko K, Aruova L, Sakanov DK. Eco-Friendly Bitumen Composites with Polymer and Rubber Waste for Sustainable Construction. Buildings. 2025; 15(15):2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15152608
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeitenova, Gaini Zhumagalievna, Rizagul Muslimovna Dyussova, Daulet Abaykhanovich Aspanbetov, Assel Yermekovna Jexembayeva, Kinga Korniejenko, Lyazat Aruova, and Darkhan Kuandykovich Sakanov. 2025. "Eco-Friendly Bitumen Composites with Polymer and Rubber Waste for Sustainable Construction" Buildings 15, no. 15: 2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15152608
APA StyleSeitenova, G. Z., Dyussova, R. M., Aspanbetov, D. A., Jexembayeva, A. Y., Korniejenko, K., Aruova, L., & Sakanov, D. K. (2025). Eco-Friendly Bitumen Composites with Polymer and Rubber Waste for Sustainable Construction. Buildings, 15(15), 2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15152608







