Behavior of Demountable and Replaceable Fabricated RC Beam with Bolted Connection Under Mid-Span Compression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
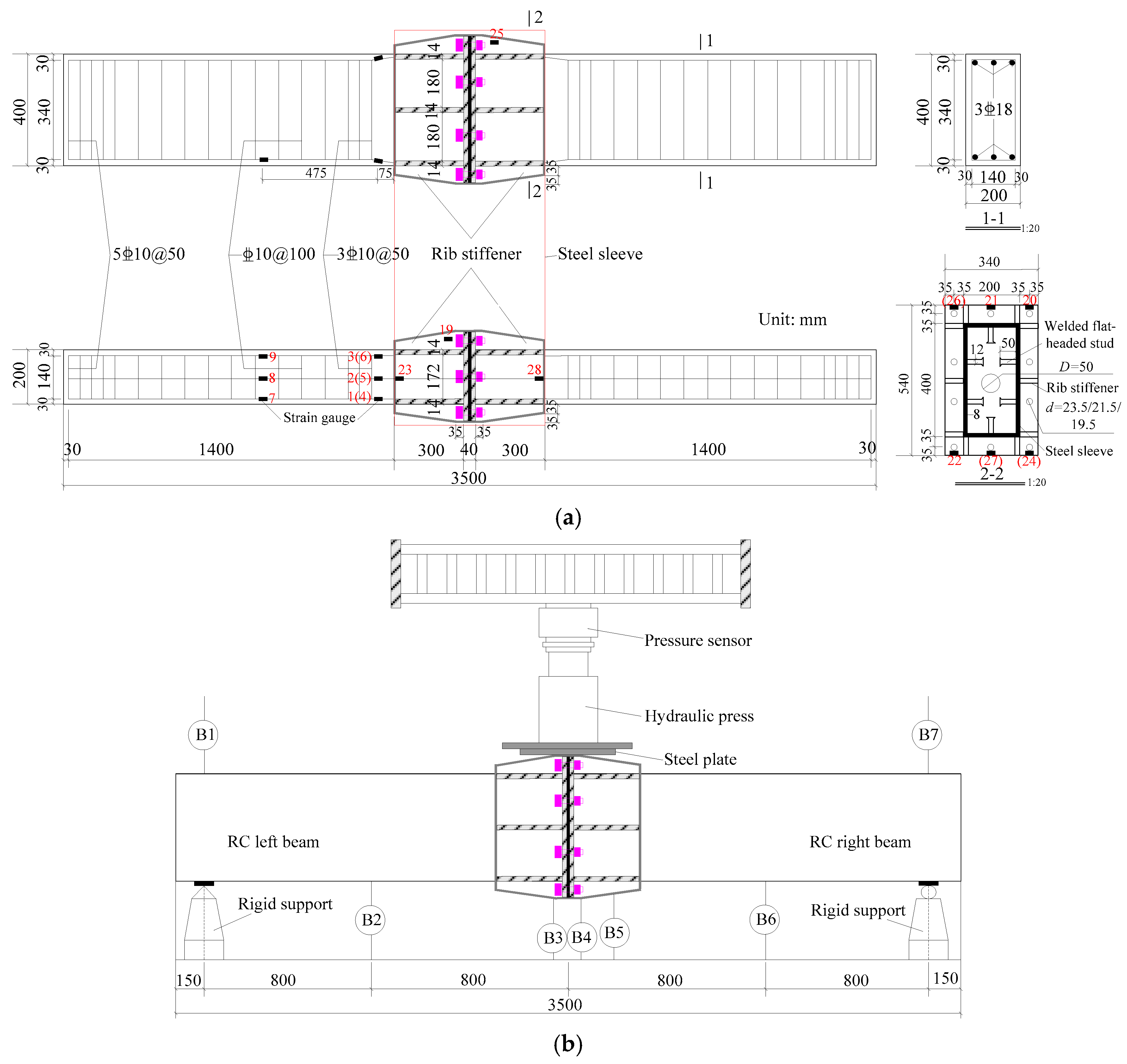
2.1. Specimen Designed
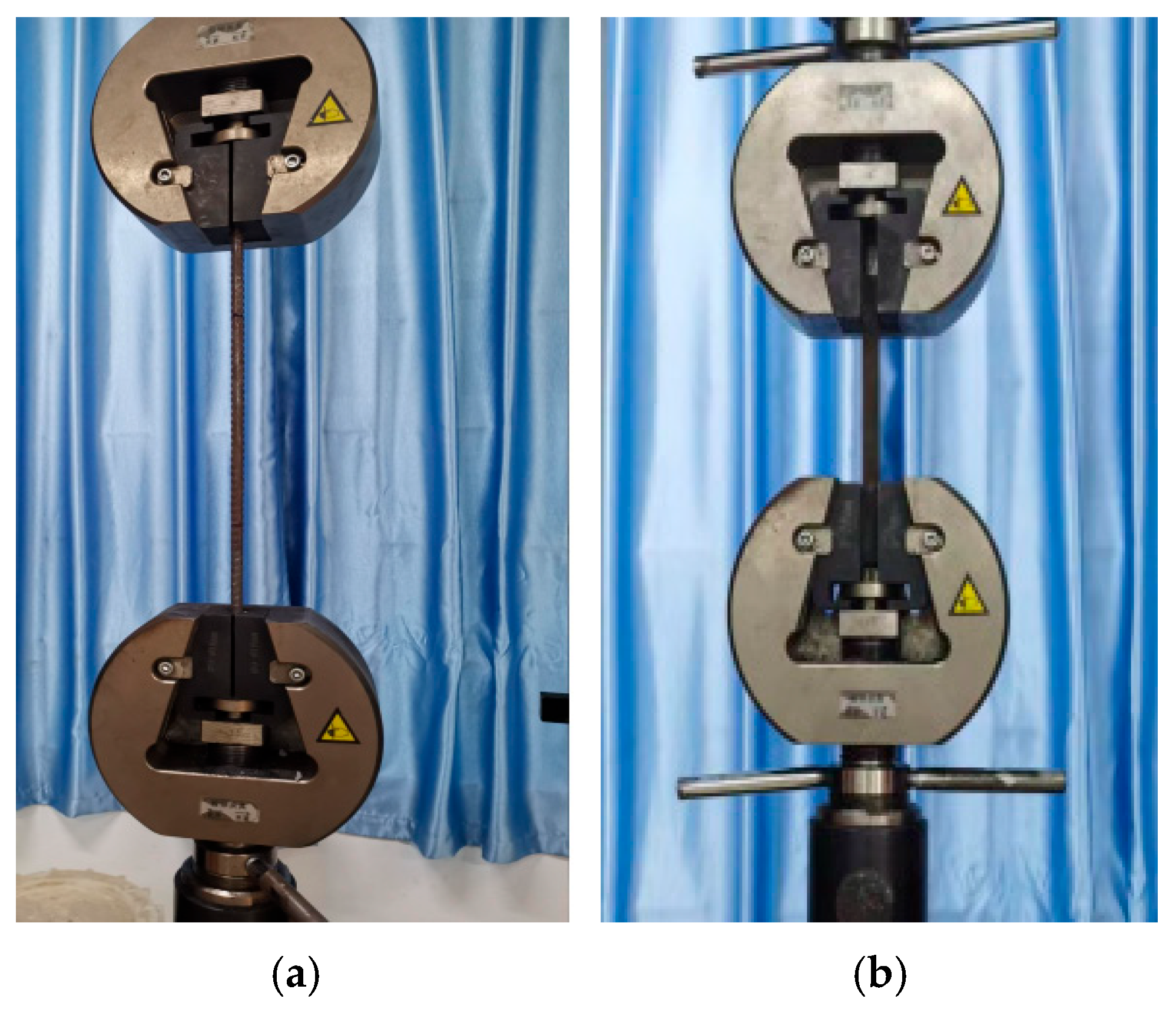
2.2. Material Property
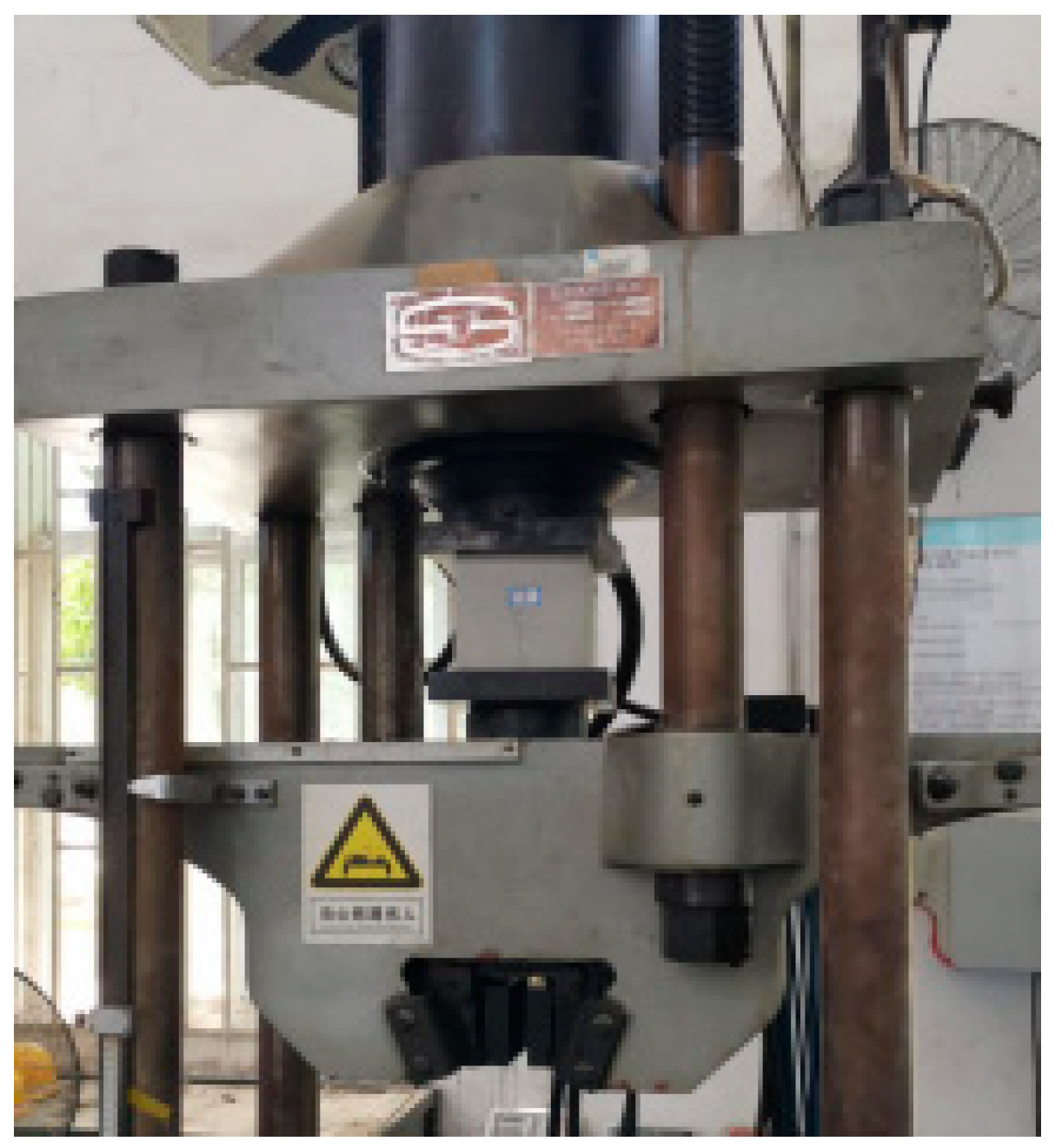
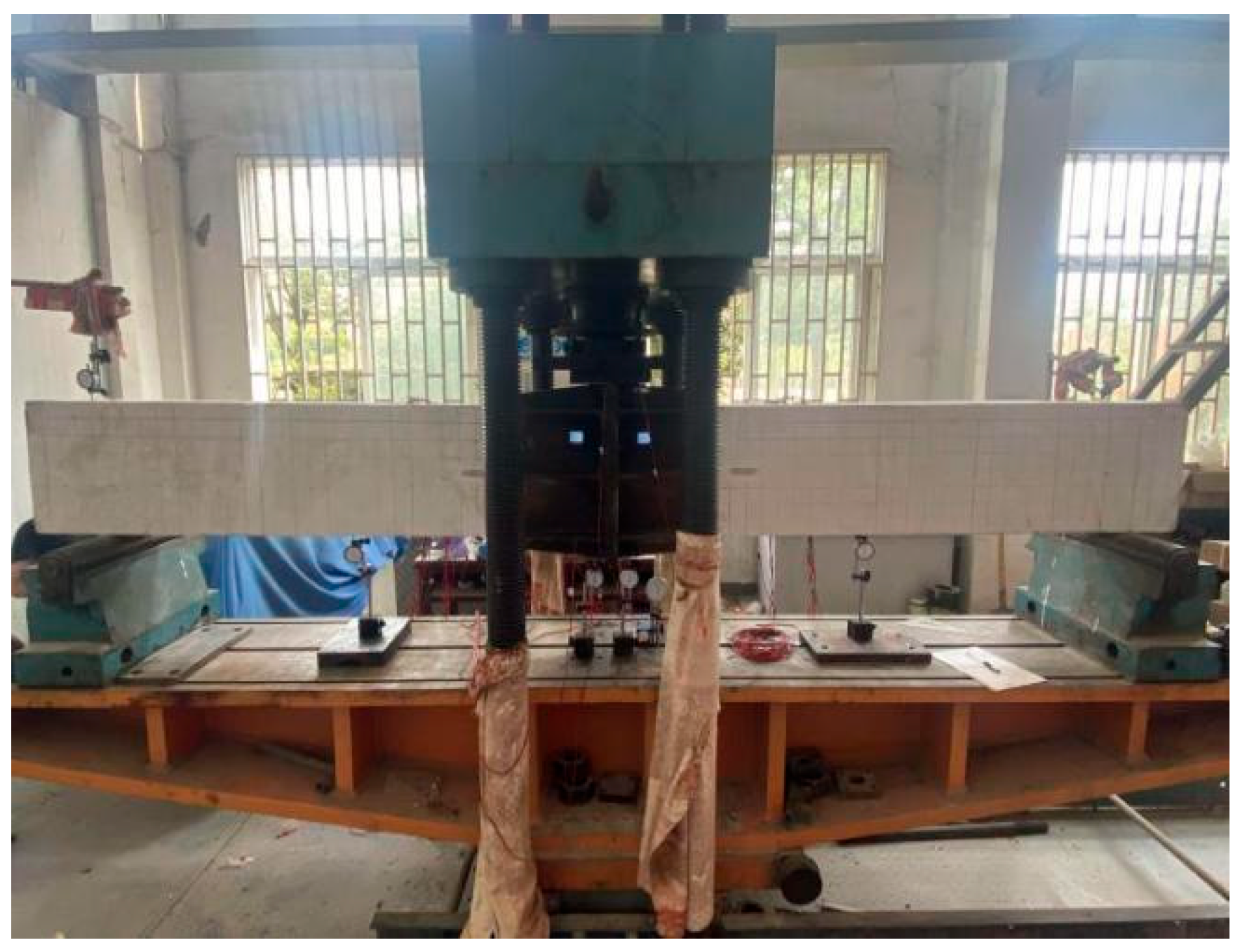
2.3. Test Loading Setup and Protocol
3. Analysis of Test Results
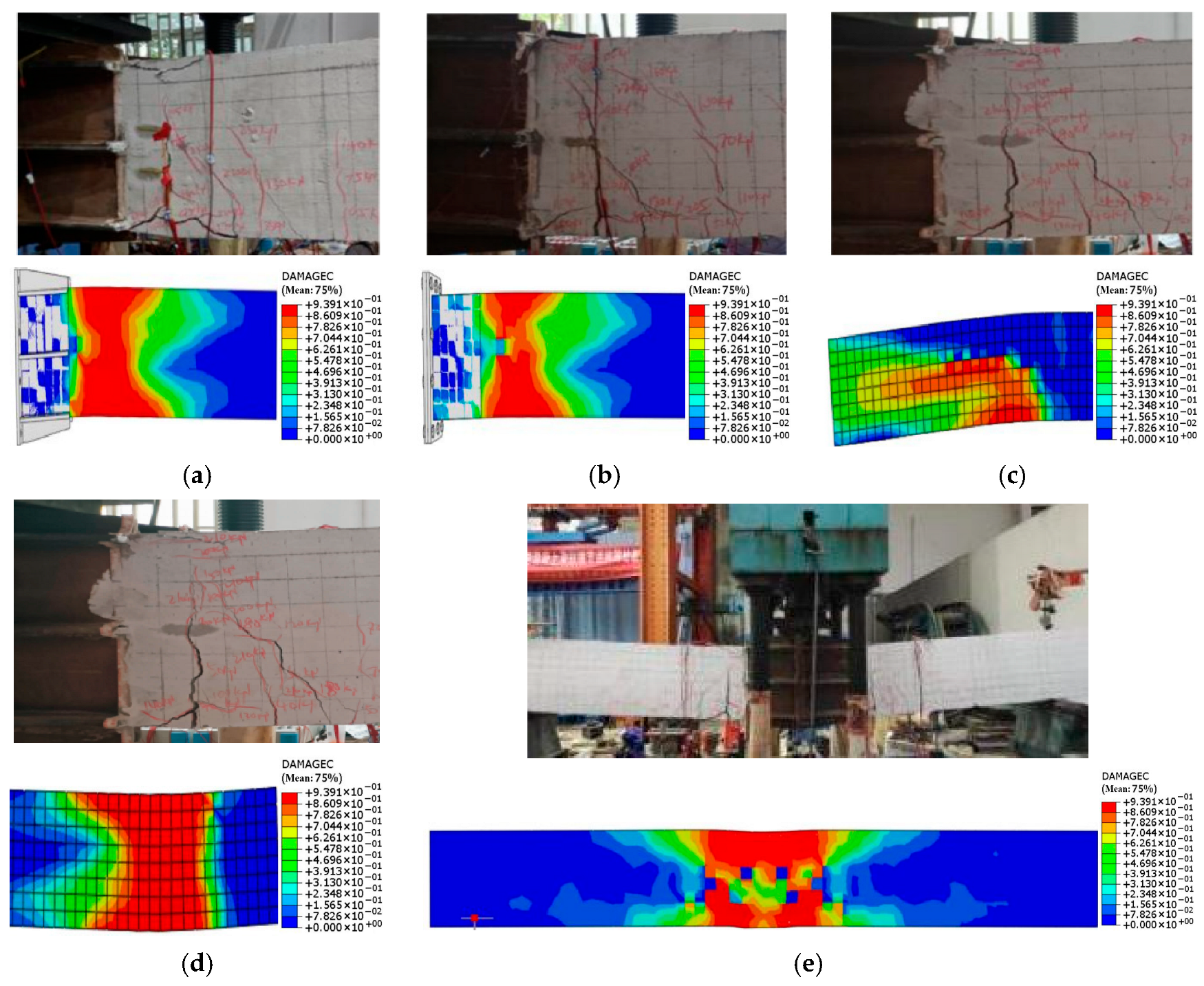
3.1. Failure Phenomena
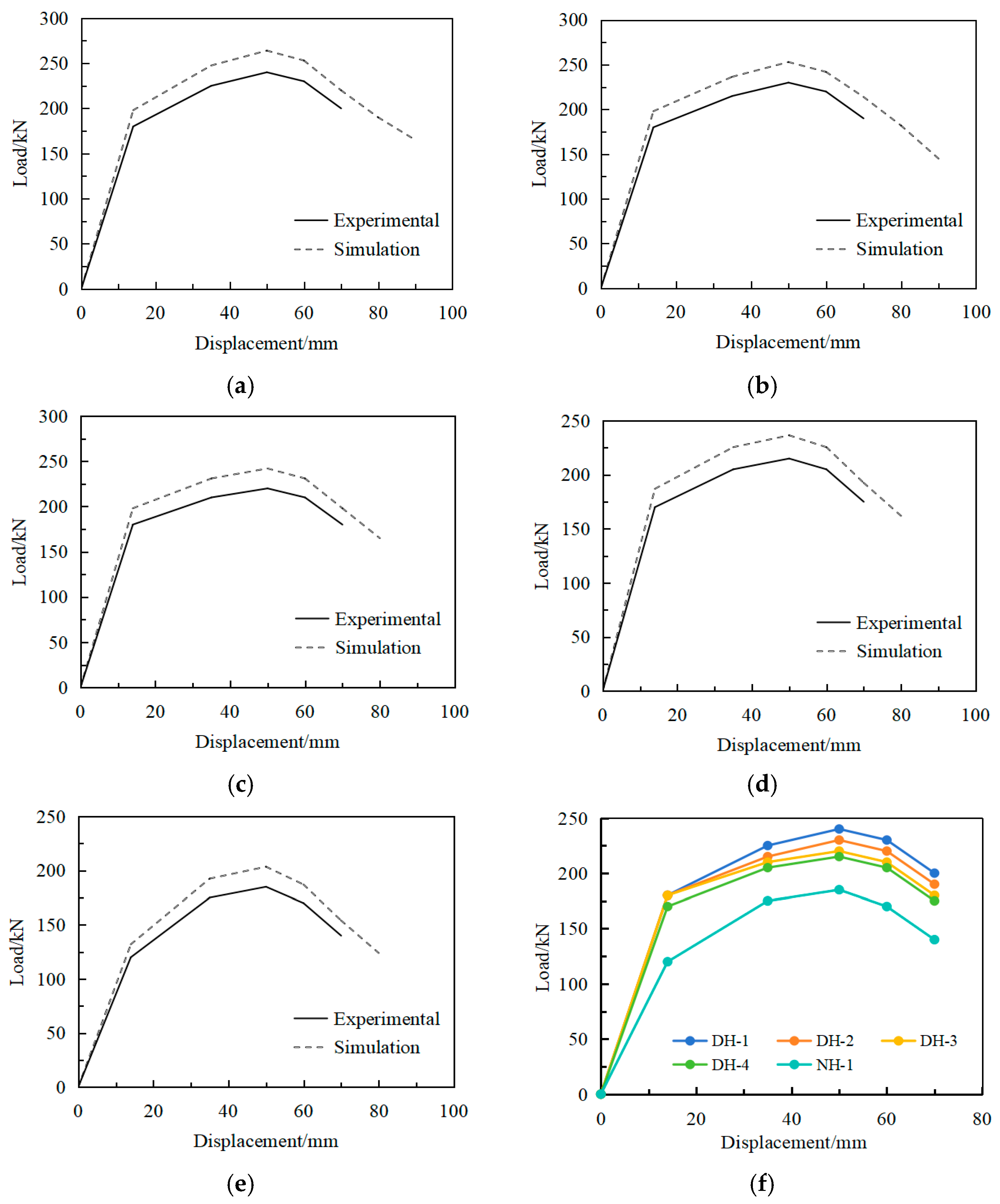
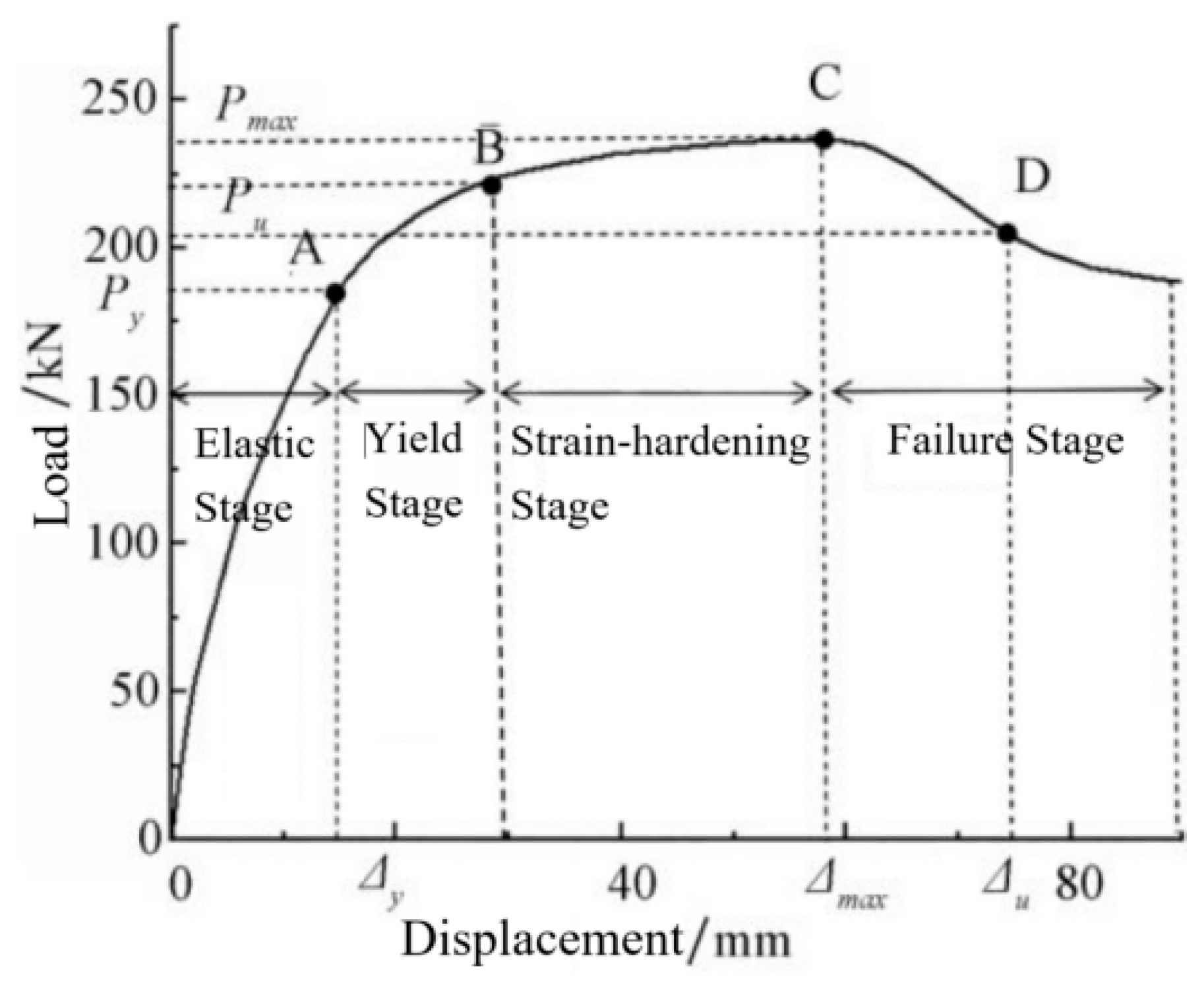
3.2. Experimental and Simulated of Load–Displacement Curves
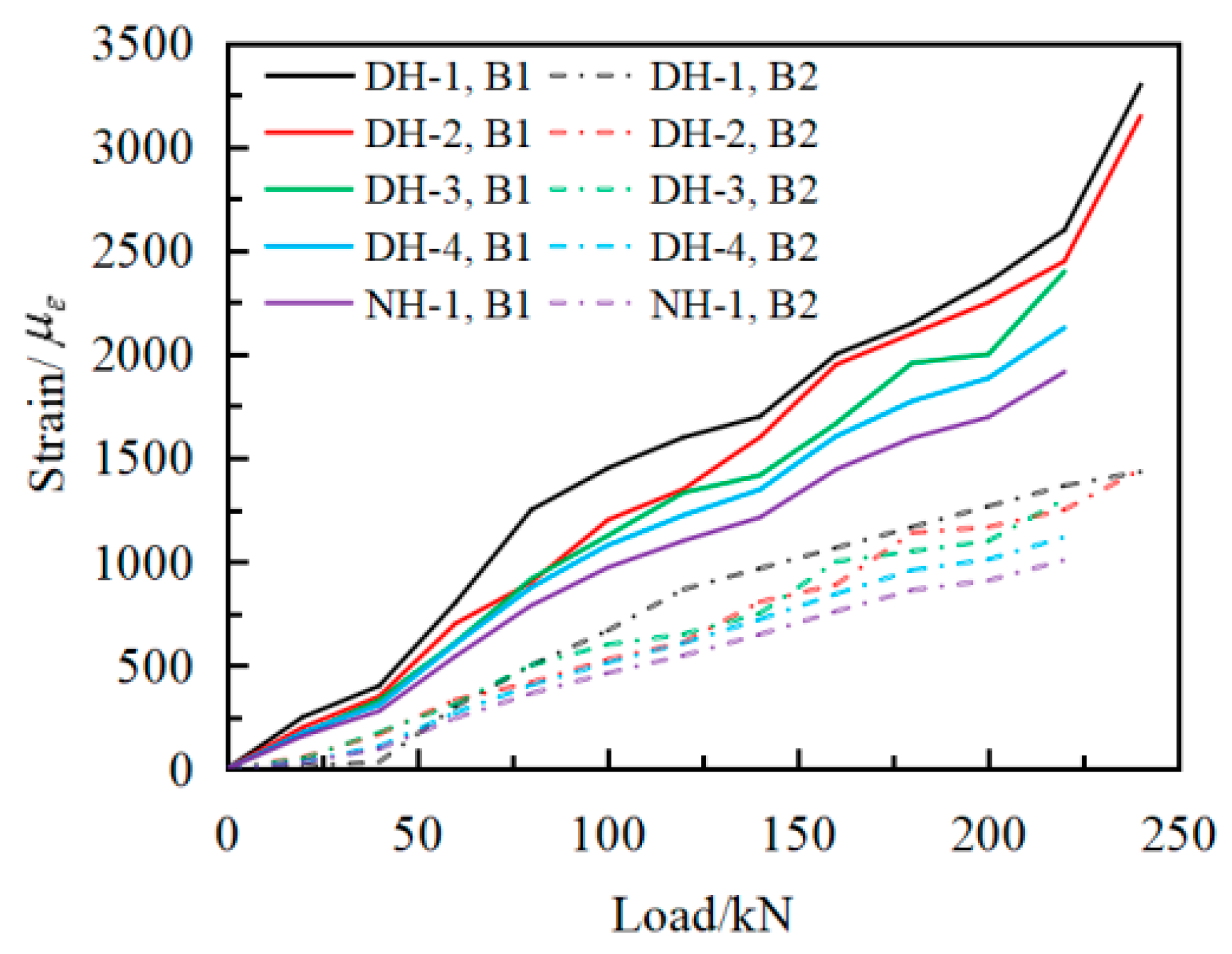
3.3. Load–Strain Analysis of Steel Reinforcement and Connecting Plate
4. Numerical Simulation Analysis
4.1. Element Type Selection
4.2. Constitutive Models
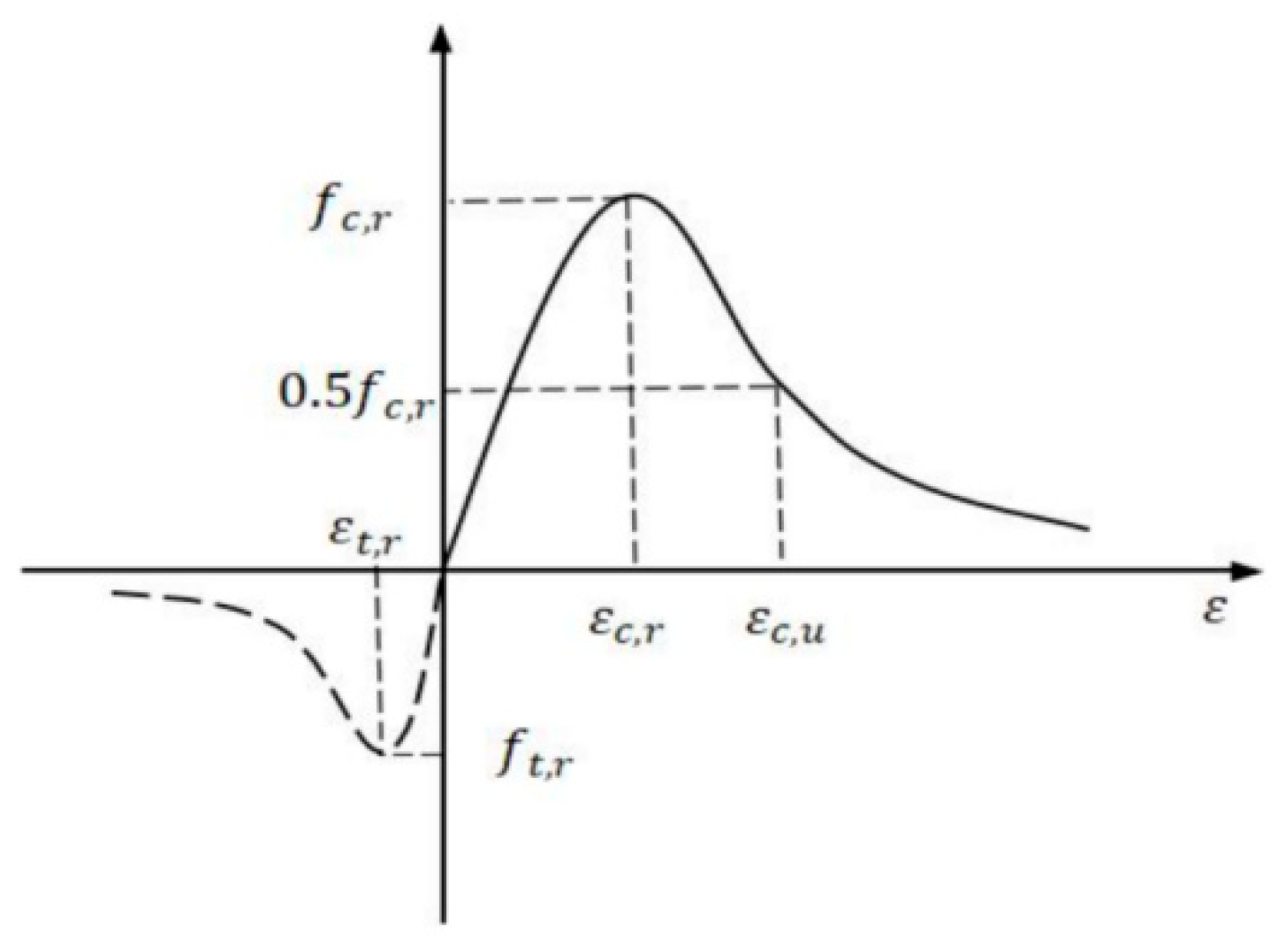
4.2.1. Concrete
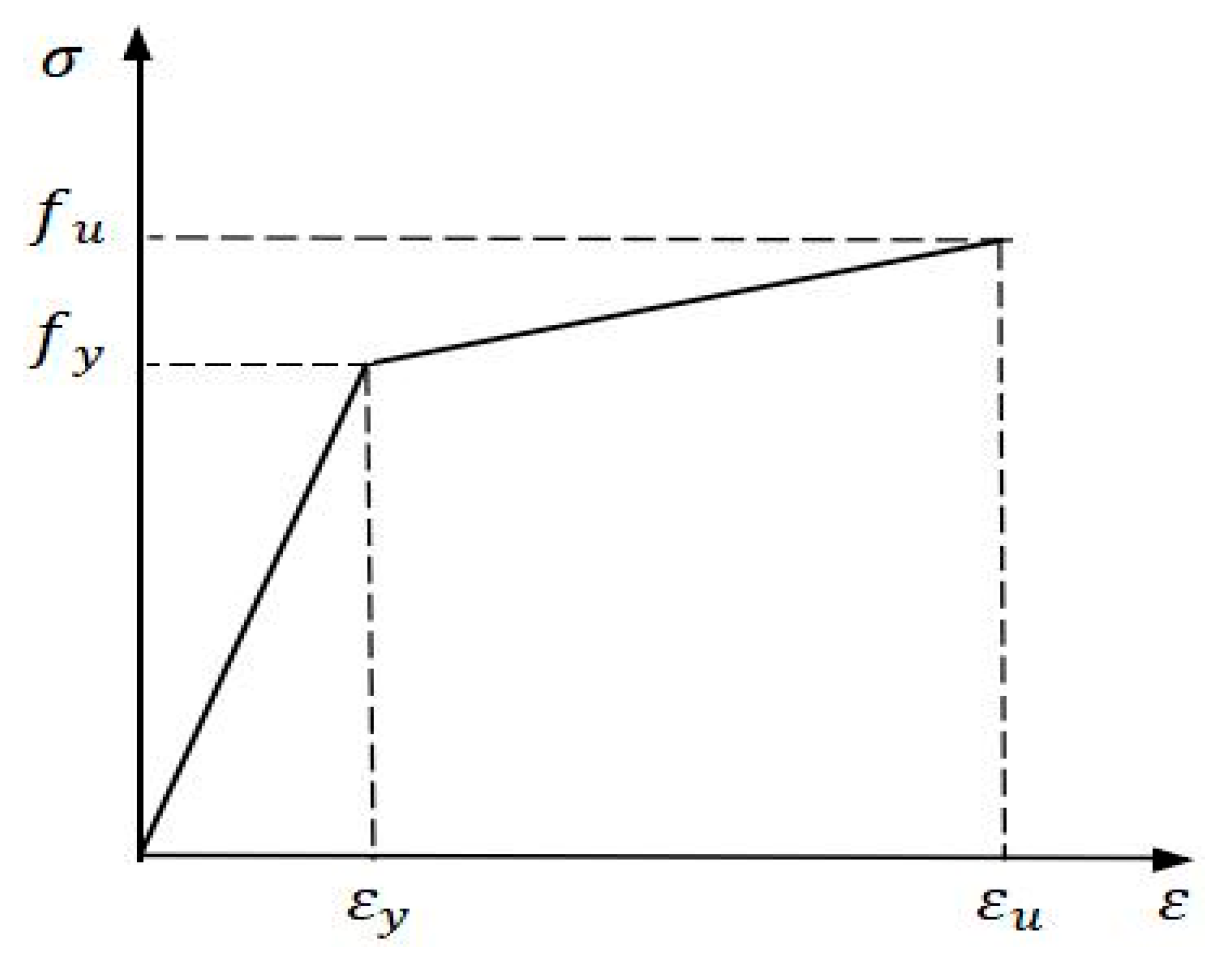
4.2.2. Reinforcement Steel and Bolts
4.3. Contact Settings
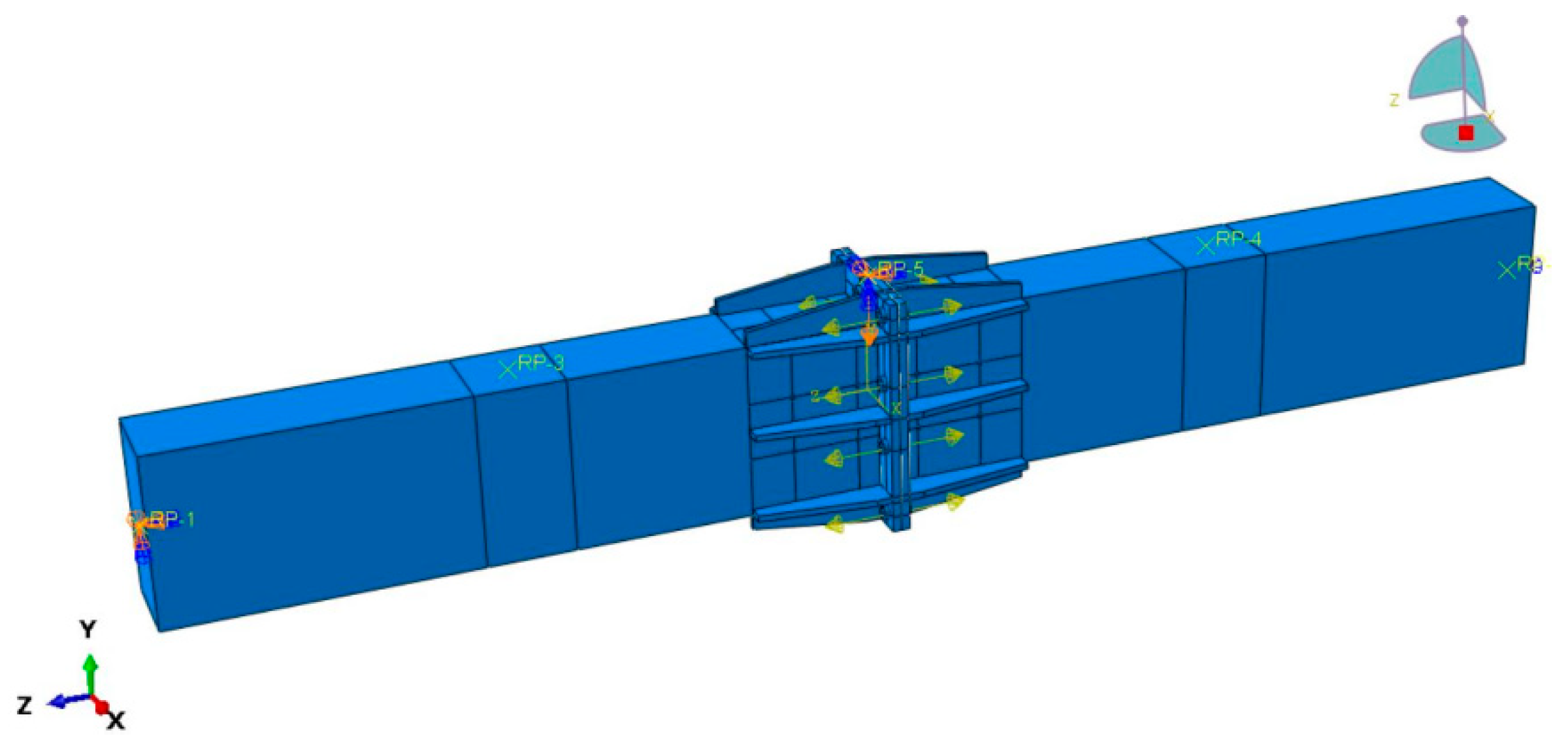
4.4. Loading Protocol and Boundary Conditions
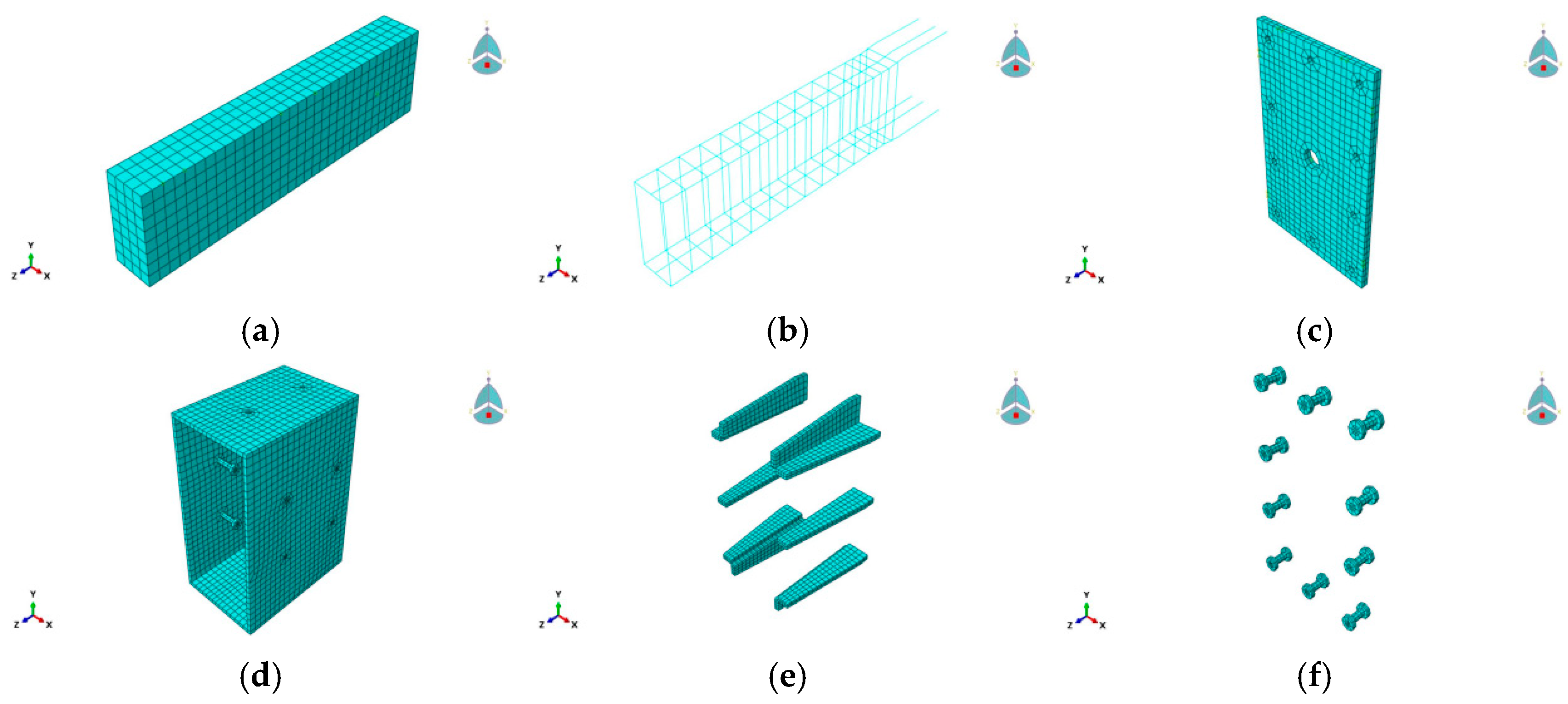
4.5. Meshing Approach
4.6. Numerical Model Validation
4.6.1. Failure Mode Comparison
4.6.2. Ultimate Load Comparison
4.6.3. Comparative Analysis of Experimental and Simulated Load–Displacement Curves
4.6.4. Mechanistic Analysis of Load–Displacement Curves
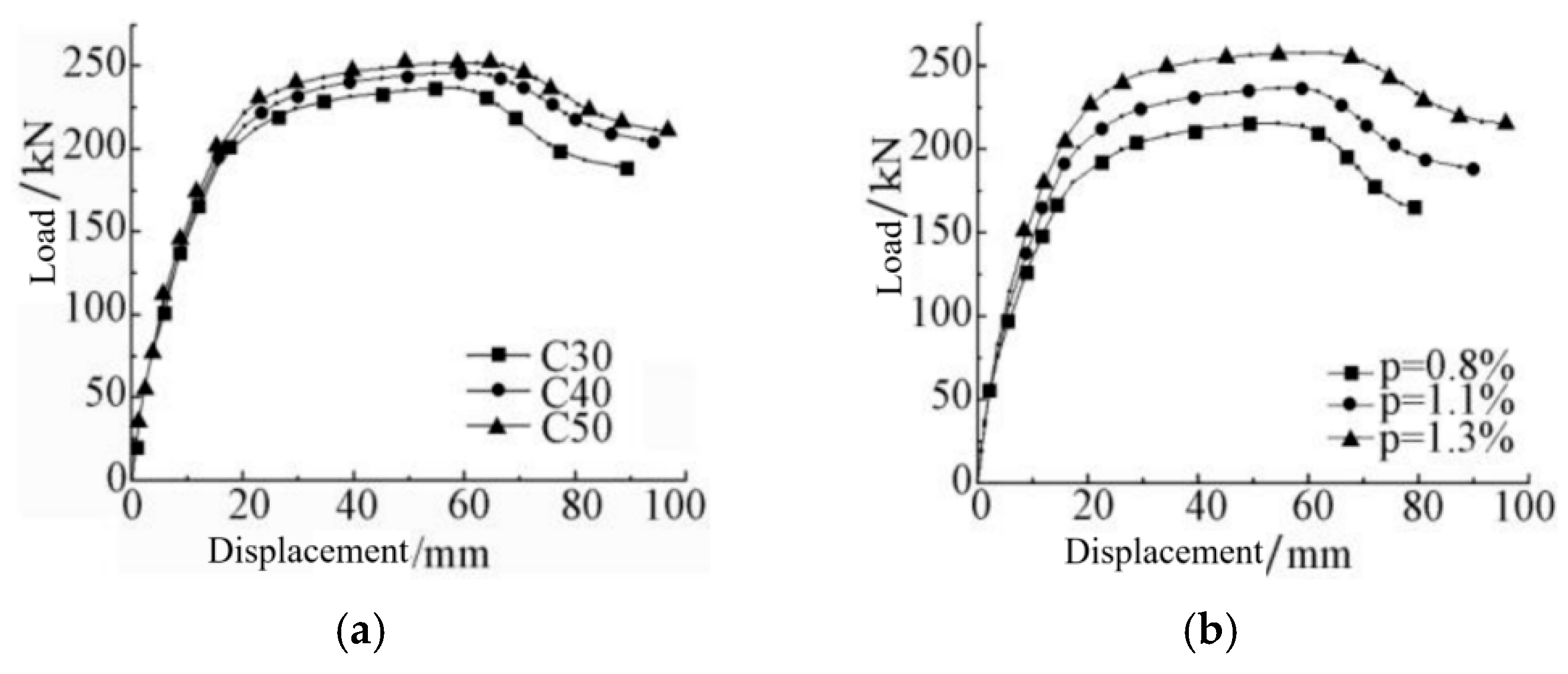
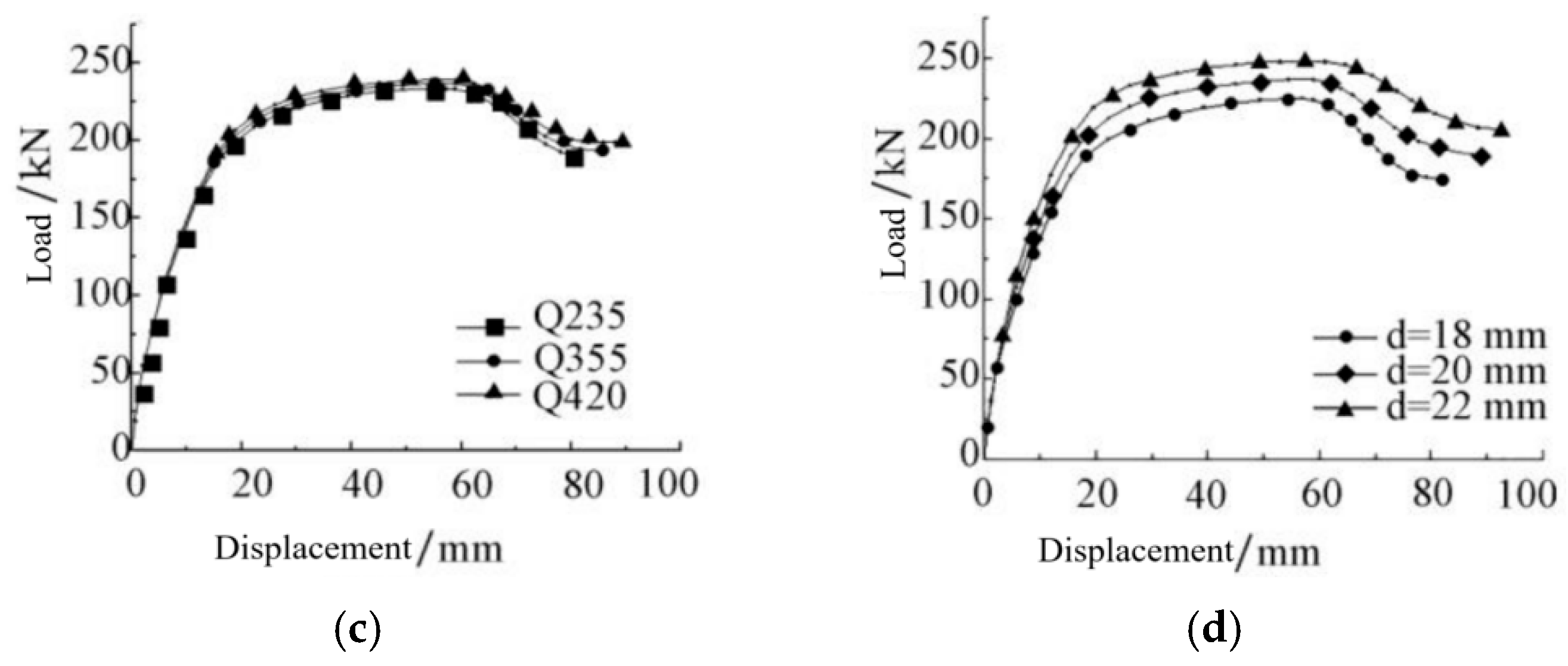
4.6.5. Parametric Analysis of Simulation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hossein, P.; Iman, H.; Reza, R. A new ductile moment-resisting connection for precast concrete frames in seismic regions: An experimental investigation. Eng. Struct. 2014, 70, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Research Status on Reinforcement Connection Form of Precast Concrete Shear Wall Structure. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 322, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Kuang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Pan, Z. Mechanical performance for defective and repaired grouted sleeve connections under uniaxial and cyclic loadings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 233, 117233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiao, S.; Gao, R.; Harries, K.A.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Q. Effects of grout sleeve defects and their repair on the seismic performance of precast concrete frame structures. Eng. Struct. 2021, 242, 112619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Li, S.; Jiang, K.; He, J.; Kong, F. Development and assessment of sustainable steel-concrete composite beams with novel demountable shear connections. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2024, 180, 108606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.-B.; Yan, J.-B. Developments of prefabricated steel-concrete composite beams with novel steel-yielding demountable bolt connectors. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2022, 190, 107123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataei, A.; Mahmoudy, S.A. Modeling of innovative bolted shear connectors in demountable cold-formed steel-concrete composite beams: Validation of finite element model and parametric study. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 110076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hou, C.; Peng, J.; Wang, Y.; Rasmussen, K.J.R. Recent advancements of inter-module connections for modular buildings: An overview and multi-dimensional assessment. Eng. Struct. 2025, 335, 120378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, S.; Lin, W.; Zeng, F. Experimental study on novel energy-dissipating prefabricated beam-column joints. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 17, 8151087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.-H.; Oh, M.-H.; Kim, M.-H.; Lee, H.-C. Flexural behavior of hybrid precast concrete beams with H-steel beams at both ends. Eng. Struct. 2010, 32, 2940–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.A.; Li, B.; Yip, W.K. Finite element analysis of precast hybrid-steel concrete connections under cyclic loading. Steel Constr. 2008, 23, 83–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy, U.; Tugrul, T. Precast concrete members with welded plate connections under reversed cyclic loading. PCI J. 1993, 38, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, M.; Castiglioni, C.A.; Kanyilmaz, A. Dissipative devices for earthquake resistant composite steel structures: Bolted versus welded solution. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2016, 14, 3613–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, M.; Castiglioni, C.A.; Kanyilmaz, A. Numerical investigations of repairable dissipative bolted fuses for earthquake resistant composite steel frames. Eng. Struct. 2017, 131, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Yoda, T.; Taniguchi, N. Fatigue tests on straight steel-concrete composite beams subjected to hogging moment. Steel Constr. 2013, 80, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, S.J.; Pennington, A. Partial factors for the design resistance of composite beams in bending. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2015, 105, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Huang, D.; Zhuang, L.; Fan, J.; Deng, N. Precast concrete connections for alleviating reinforcement congestion: A state-of-the-art review. Eng. Struct. 2025, 331, 119985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-H.-S.; Chen, B.-C.; Deng, Y.-X.; Cheng, J.-T.; Zhang, J.-P. Experimental Study on Shear and Tensile Behavior of T-Shaped Embedded-Nut Bolted Shear Connectors in Prefabricated Steel-Concrete Composite Beams. Eng. Mech. 2025, 42, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, T.-S.; Park, H.-G.; Hwang, H.-J.; Kang, S.-M. Plastic hinge relocation methods for emulative PC beam-column connections. J. Struct. Eng. 2016, 142, 04015111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 50010-2010; Code for Design of Concrete Structures. Architecture Industrial Press of China: Beijing, China, 2024. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 50081-2019; The Standard for Test Methods of Concrete Physical and Mechanical Properties. Architecture Industrial Press of China: Beijing, China, 2024. (In Chinese)
- ISO 1920-3:2019; Testing of Concrete Part 3: Making and Curing Test Specimens. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Huang, Y.; Mazzarolo, E.; Briseghella, B.; Zordan, T.; Chen, A. Experimental and numerical investigation of the cyclic behaviour of an innovative prefabricated beam-to-column joint. Eng. Struct. 2017, 150, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Marino, E.M.; Pan, P.; Liu, H.; Nie, X. Experimental study of a novel precast prestressed reinforced concrete beam-to-column joint. Eng. Struct. 2018, 156, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Zhang, B.; Liao, X. Cyclic loading response of precast concrete frame with composite beams prestressed by partially bonded draped tendons under high axial compression. Eng. Mech. 2025, 334, 120229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharos, P.A.; Egan, B.; Mccarthy, C.T. An analytical model for strength prediction in multi-bolt composite joints at various loading rates. Compos. Struct. 2014, 116, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Specimen | Casting Type | Stiffening Ribs | High-Strength Bolt Specifications | Bolt Grades |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DH-1 | Prefabricated | Y | M22 | 10.9 grade |
| DH-2 | Prefabricated | Y | M20 | 10.9 grade |
| DH-3 | Prefabricated | Y | M18 | 10.9 grade |
| DH-4 | Prefabricated | N | M20 | 10.9 grade |
| NH-1 | Cast-in-place | Y | M20 | 10.9 grade |
| Steel Type | Rebar Diameter/Steel Plate Thickness/mm | Yield Strength /MPa | Ultimate Strength /MPa | Elastic Modulus /MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRB400 | 10 | 408 | 549 | 2.00 × 105 |
| HRB400 | 18 | 417 | 566 | 2.00 × 105 |
| Q355 | 8 | 365 | 484 | 2.02 × 105 |
| Q355 | 14 | 356 | 524 | 2.02 × 105 |
| Q355 | 20 | 389 | 531 | 2.02 × 105 |
| Specimen | Experimental Ultimate Load/kN | Simulated Ultimate Load/kN | Experimental-to-Simulated Ultimate Load Ratio | Relative Error /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DH-1 | 240 | 247.8 | 0.969 | 3.25 |
| DH-2 | 230 | 236.8 | 0.971 | 2.96 |
| DH-3 | 220 | 224.8 | 0.979 | 2.18 |
| DH-4 | 210 | 218.5 | 0.961 | 3.56 |
| NH-1 | 145 | 147.4 | 0.984 | 1.89 |
| Different Parameters | Py/kN | Δy/mm | Pmax/kN | Δmax/mm | Pu/kN | Δu/mm | K0/(kN·m)·rad−1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concrete strength | C30 | 181.98 | 14.12 | 236.80 | 58.96 | 201.28 | 76.14 | 31,133.43 |
| C40 | 188.28 | 14.27 | 246.39 | 62.47 | 209.43 | 86.53 | 31,230.21 | |
| C50 | 192.96 | 13.90 | 251.99 | 64.77 | 214.19 | 90.74 | 31,285.80 | |
| Reinforcement ratio | 0.8% | 163.57 | 13.94 | 215.66 | 54.47 | 183.31 | 70.33 | 29,925.15 |
| 1.1% | 181.98 | 14.12 | 236.80 | 58.96 | 201.28 | 76.14 | 31,133.43 | |
| 1.3% | 198.87 | 14.59 | 257.80 | 64.06 | 219.13 | 89.05 | 32,176.49 | |
| Steel strength | Q235 | 178.21 | 14.10 | 233.00 | 57.18 | 198.05 | 75.22 | 31,093.01 |
| Q335 | 181.98 | 14.12 | 236.80 | 58.96 | 201.28 | 76.14 | 31,133.43 | |
| Q420 | 184.83 | 14.48 | 239.05 | 59.08 | 203.19 | 78.44 | 31,148.97 | |
| Bolt diameter | 18 mm | 172.01 | 14.03 | 224.80 | 56.57 | 190.08 | 70.98 | 30,629.81 |
| 20 mm | 181.98 | 14.12 | 236.80 | 58.96 | 201.28 | 76.14 | 31,133.43 | |
| 22 mm | 189.59 | 14.38 | 247.80 | 61.06 | 210.63 | 84.57 | 31,700.81 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, D.; Liang, Y.; Liu, H.; Peng, S. Behavior of Demountable and Replaceable Fabricated RC Beam with Bolted Connection Under Mid-Span Compression. Buildings 2025, 15, 2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15152589
Wu D, Liang Y, Liu H, Peng S. Behavior of Demountable and Replaceable Fabricated RC Beam with Bolted Connection Under Mid-Span Compression. Buildings. 2025; 15(15):2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15152589
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Dongping, Yan Liang, Huachen Liu, and Sheng Peng. 2025. "Behavior of Demountable and Replaceable Fabricated RC Beam with Bolted Connection Under Mid-Span Compression" Buildings 15, no. 15: 2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15152589
APA StyleWu, D., Liang, Y., Liu, H., & Peng, S. (2025). Behavior of Demountable and Replaceable Fabricated RC Beam with Bolted Connection Under Mid-Span Compression. Buildings, 15(15), 2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15152589






