Digital Technologies in Urban Regeneration: A Systematic Literature Review from the Perspectives of Stakeholders, Scales, and Stages
Abstract
1. Introduction
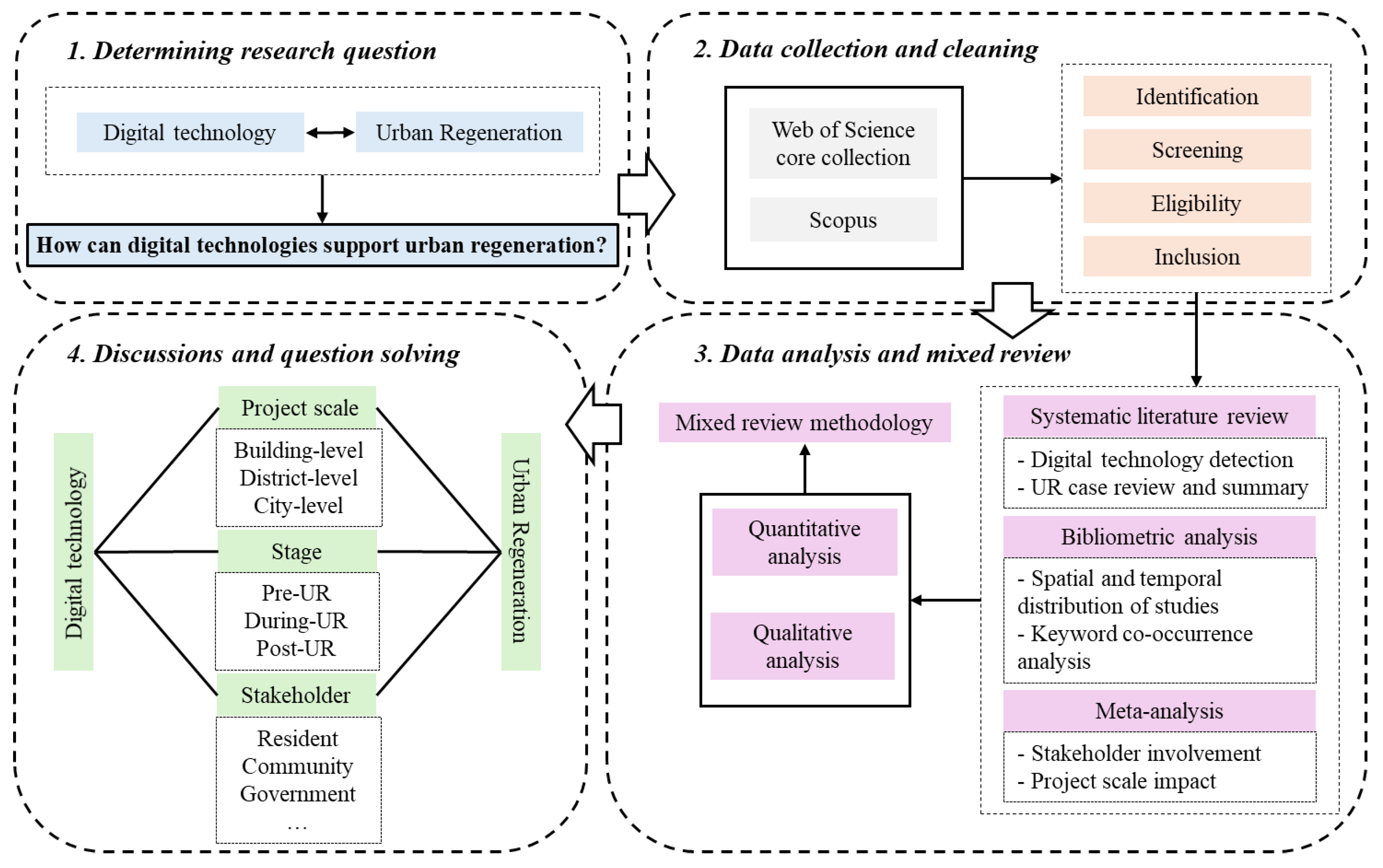
2. Methodology
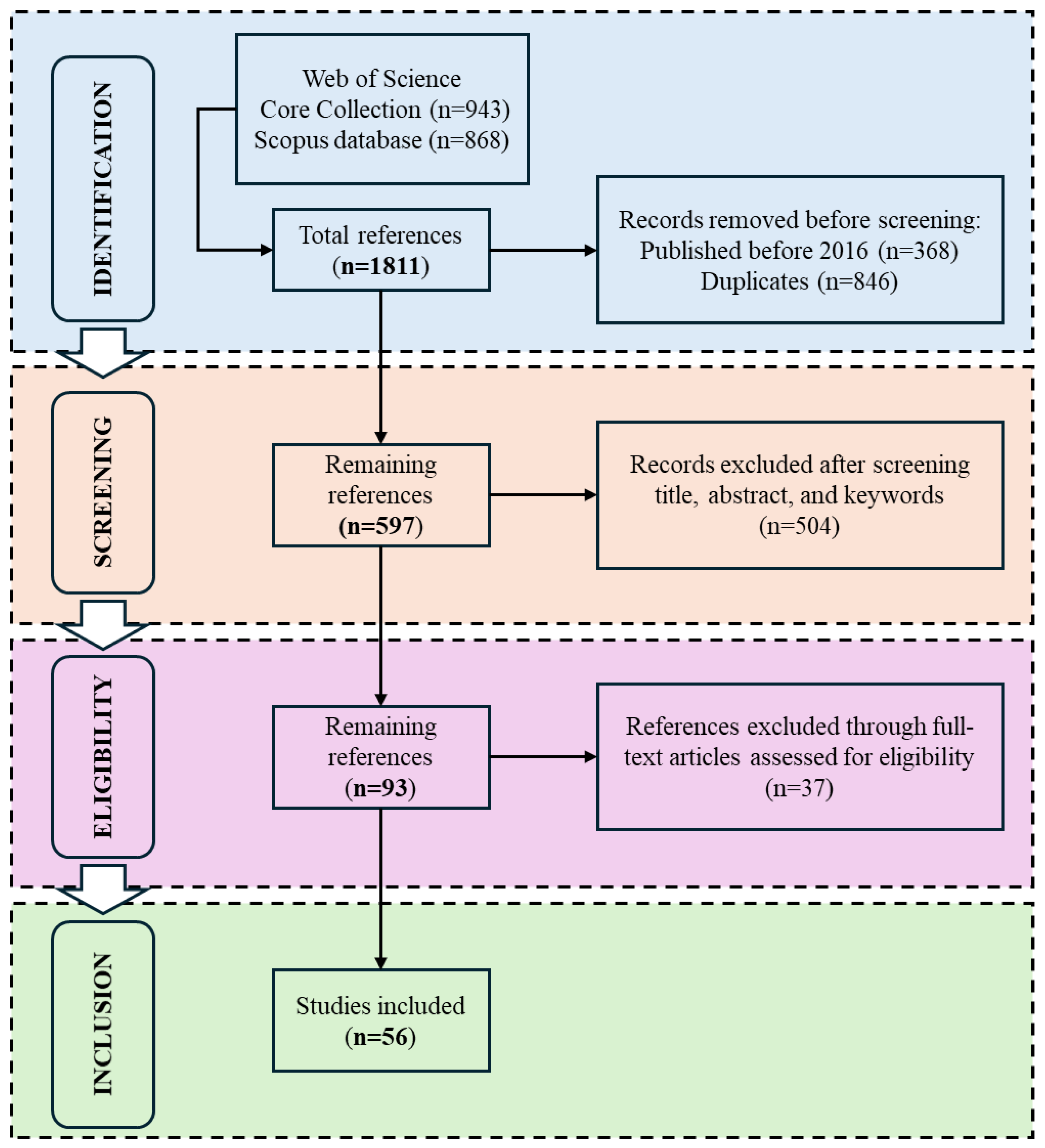
2.1. Systematic Literature Review
2.2. Bibliometric Analysis
2.3. Meta-Analysis Framework
3. Data Analysis and Results
3.1. Systematic Review of DT in UR
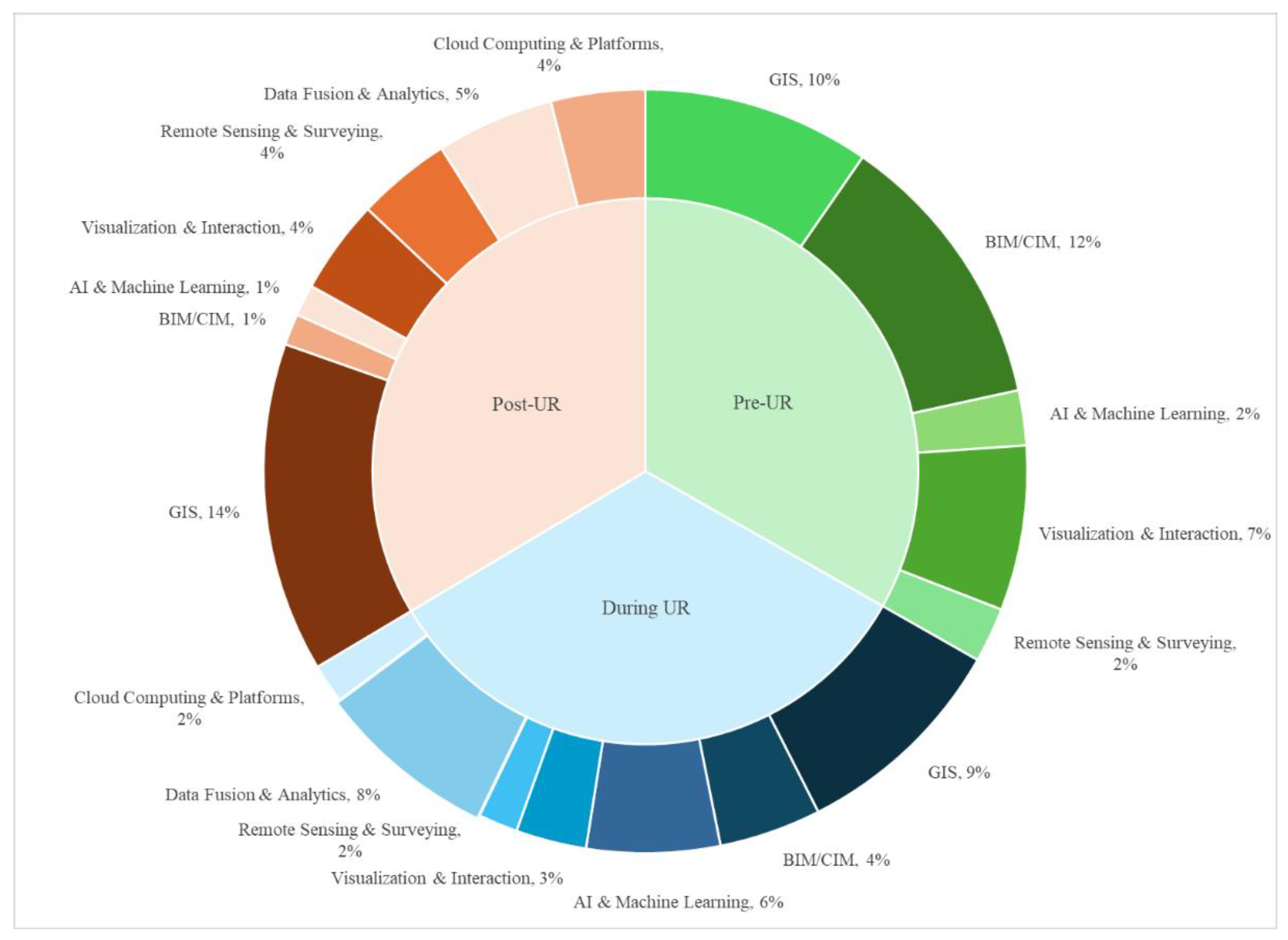
3.1.1. Pre-UR Stage
3.1.2. During-UR Stage
3.1.3. Post-UR Stage
3.2. Results of Bibliometric Analysis
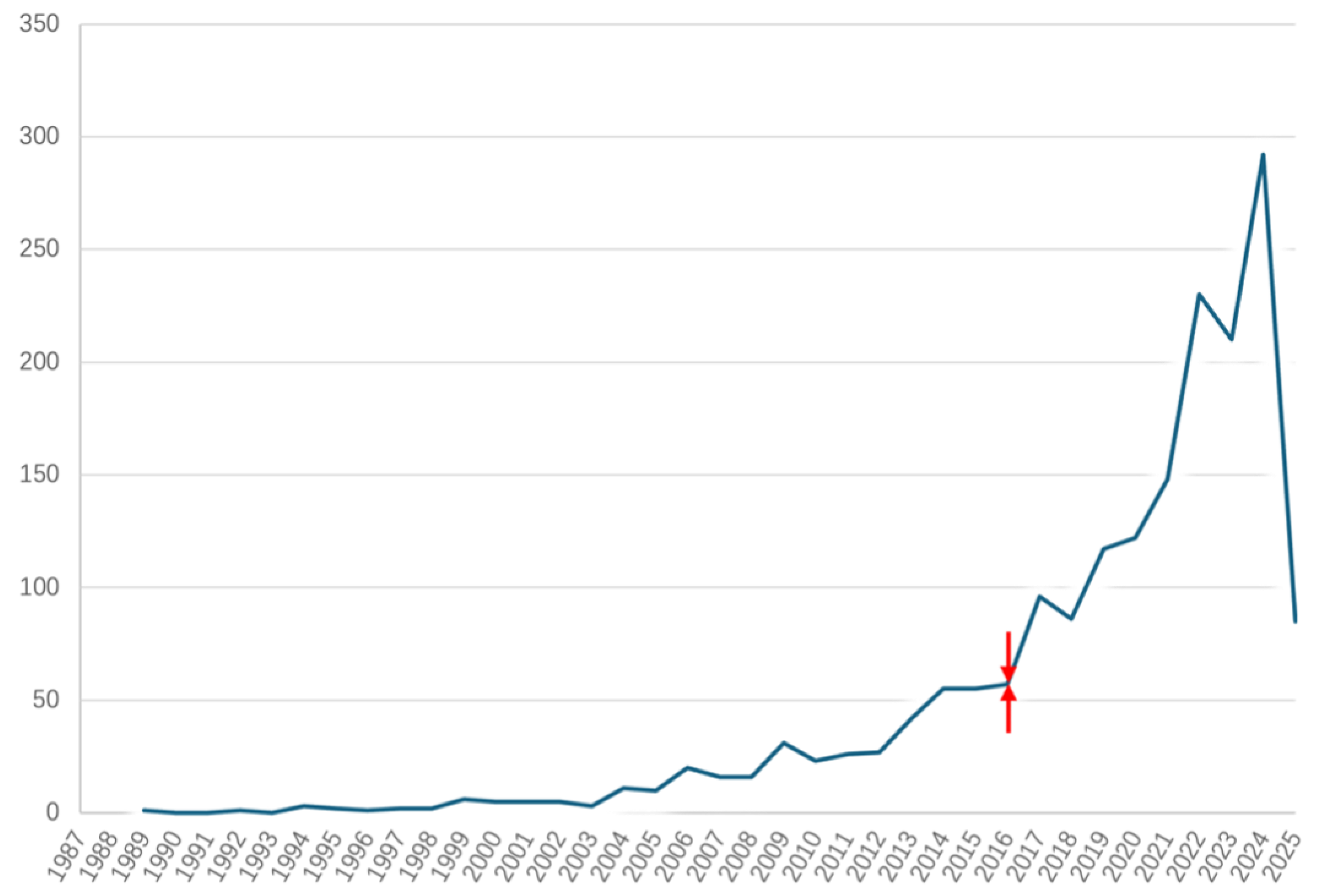
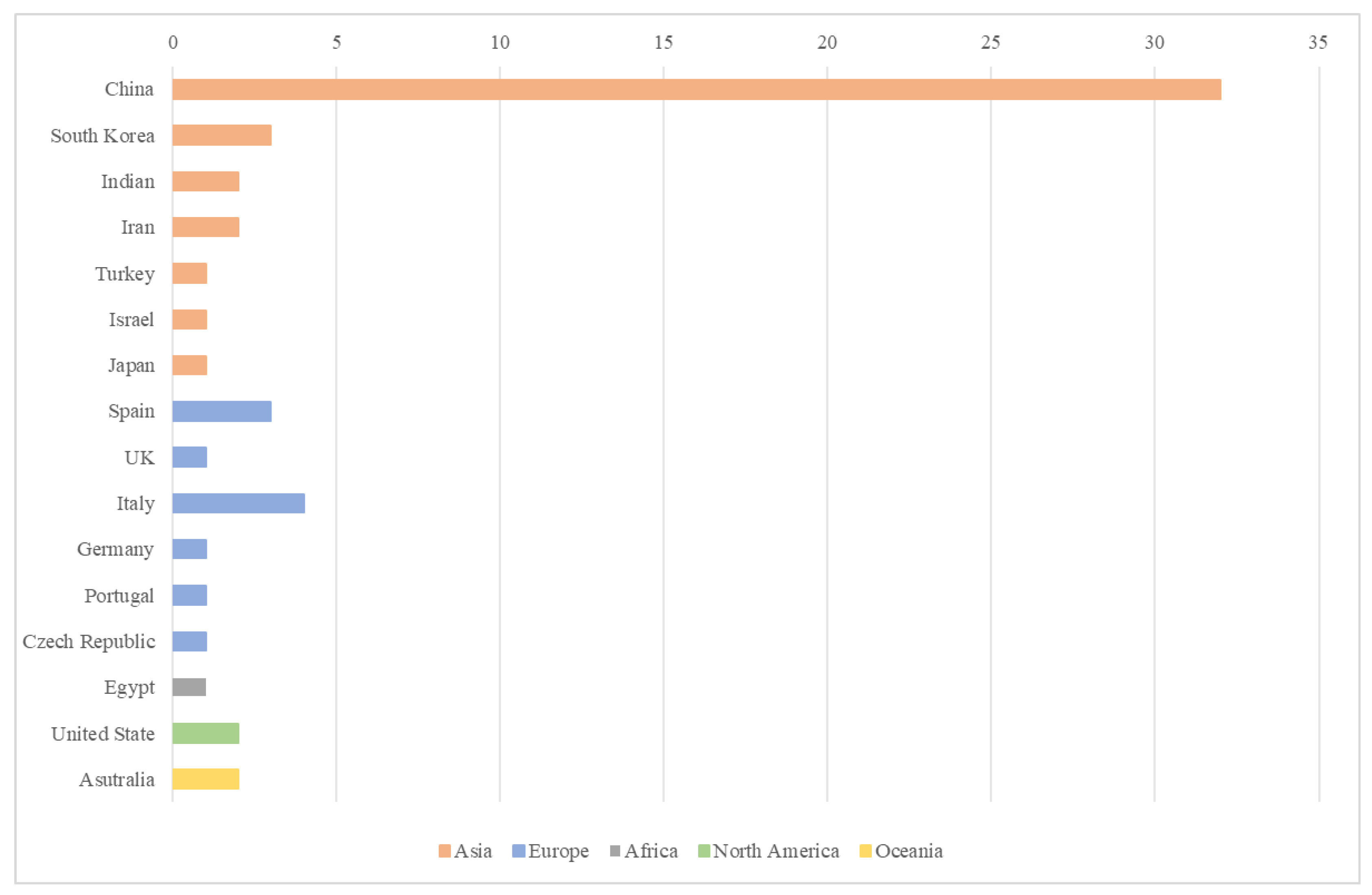
3.2.1. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Studies
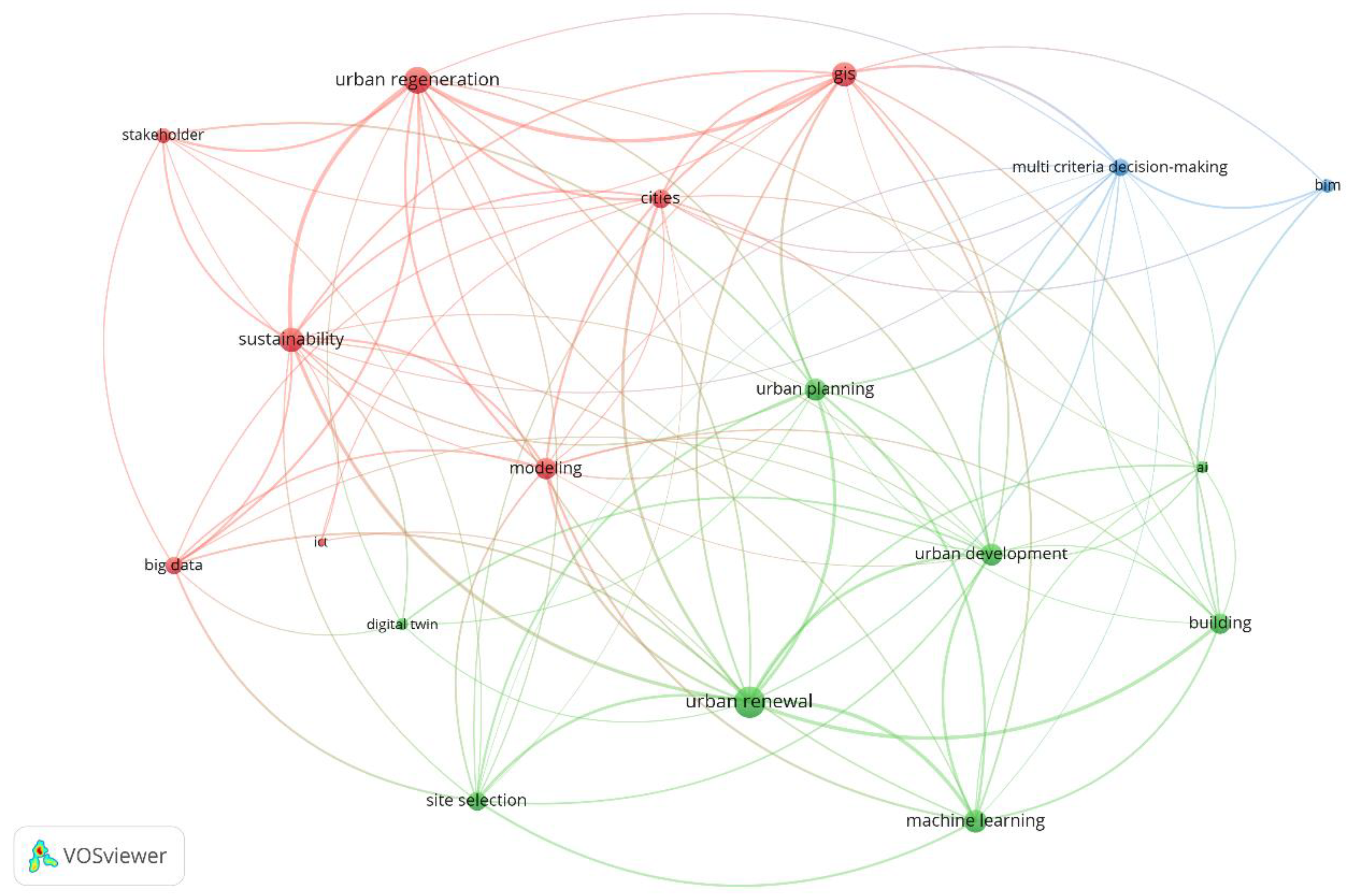
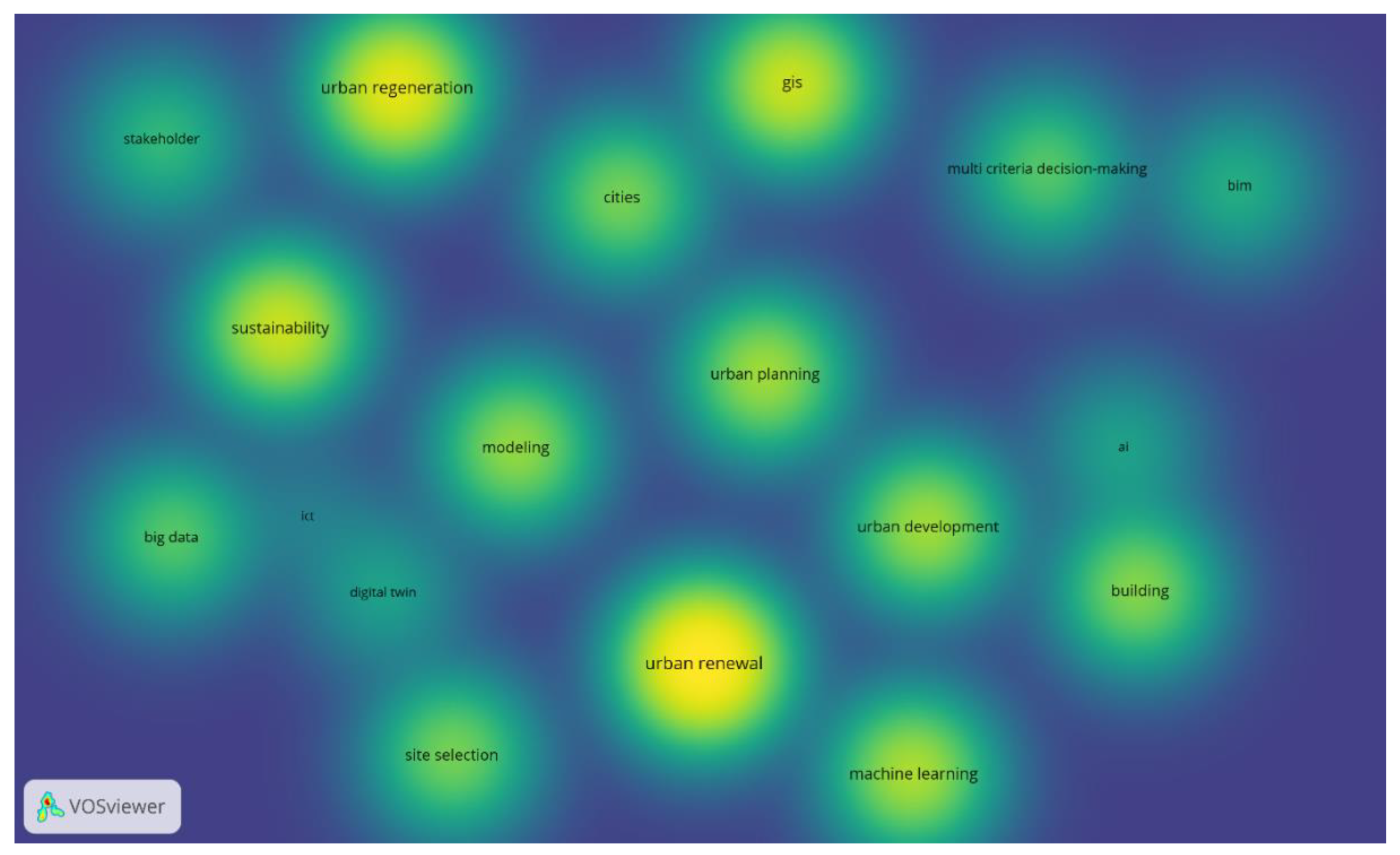
3.2.2. Keyword Co-Occurrence Analysis
3.3. Meta-Analysis
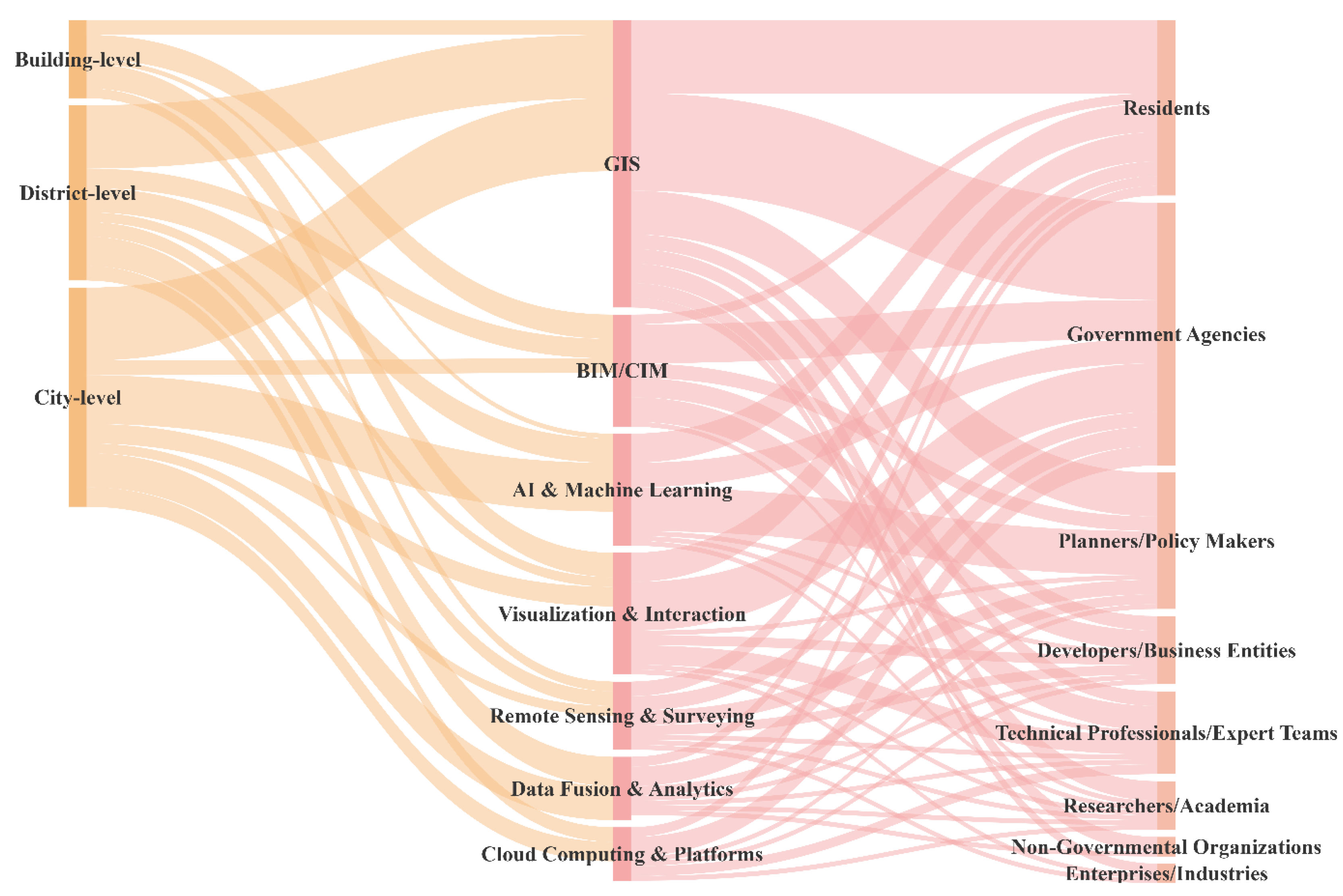
3.3.1. Project Scale and Digital Technology Adoption
3.3.2. Stakeholder Involvement and Digital Strategies
4. Discussion
4.1. Challenges in Applying Digital Technologies to Support UR
4.1.1. Stakeholder-Related Challenges
4.1.2. Scale-Dependent Technology Adoption Challenges
4.1.3. Stage-Specific Implementation Challenges
4.2. Research Gaps and Future Direction
4.2.1. Lack of Systematic Management Framework
4.2.2. Insufficient Integration of Advanced AI Technologies
4.2.3. Cross-Scale Integration and Adaptive Technology Deployment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Author and Year | Stage | Scale | Stakeholder | Digital Technology | Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wu & Leng, 2025 [43] | Pre-UR | Micro-level Macro-level | Residents Planners/Policy Makers Government Agencies | BIM/CIM | China |
| Wang et al., 2025 [28] | Pre-UR | Meso-level | Residents Planners/Policy Makers | Visualization and Interaction | China |
| Sun et al., 2025 [27] | Pre-UR | Meso-level | Planners/Policy Makers | GIS AI and Machine Learning | China |
| Manna et al., 2025 [37] | Pre-UR | Meso-level | Residents Planners/Policy Makers | AI and Machine Learning | India |
| Li et al., 2025 [60] | Pre-UR | Macro-level | Government Agencies Planners/Policy Makers | GIS | China |
| Chen et al., 2025 [61] | Pre-UR During-UR | Meso-level | Government Agencies | BIM/CIM Visualization and Interaction Cloud Computing and Platforms | China |
| Zhou et al., 2024 [40] | Pre-UR During-UR | Macro-level | Residents Government Agencies Planners/Policy Makers | AI and Machine Learning | China |
| Zhao et al., 2024 [33] | Pre-UR | Macro-level | Residents Government Agencies Developers/Business Entities | BIM/CIM | China |
| Zhang et al., 2024 [46] | Pre-UR | Meso-level | Planners/Policy Makers Technical Professionals/Expert Teams | BIM/CIM | China |
| Yilmaz & Alkan, 2024 [62] | Pre-UR | Macro-level | Residents Government Agencies Researchers/Academia | AI and Machine Learning Cloud Computing and Platforms | Turkey |
| Ye et al., 2024 [63] | Pre-UR | Macro-level | Government Agencies Planners/Policy Makers | AI and Machine Learning | China |
| Teklemariam, 2024 [64] | During-UR | Macro-level | Residents Government Agencies Non-Governmental Organizations | GIS | Africa |
| Mutani et al., 2024 [52] | Post-UR | Macro-level | Residents Planners/Policy Makers Researchers/Academia | GIS AI and Machine Learning | Italy |
| Lin & Song, 2024 [65] | Pre-UR | Micro-level | Planners/Policy Makers | Visualization and Interaction AI and Machine Learning | China |
| Lin et al., 2024 [55] | During-UR | Macro-level | Planners/Policy Makers | GIS Remote Sensing and Surveying AI and Machine Learning | China |
| Hu et al., 2024 [25] | Pre-UR | Meso-level | Residents Planners/Policy Makers Government Agencies | Visualization and Interaction Remote Sensing and Surveying | China |
| Chen et al., 2024 [66] | Post-UR | Micro-level | Residents Planners/Policy Makers Government Agencies | GIS Data Fusion and Analytics Cloud Computing and Platforms | China |
| Chao et al., 2024 [51] | During-UR | Meso-level | Residents | GIS Visualization and Interaction AI and Machine Learning | China |
| Carruthers & Wei, 2024 [36] | Pre-UR | Macro-level | Planners/Policy Makers | AI and Machine Learning | United State |
| Yu et al., 2023 [38] | Pre-UR | Micro-level | Planners/Policy Makers Professionals/Expert Teams | AI and Machine Learning Visualization and Interaction | China |
| Xueqiang et al., 2023 [67] | Pre-UR | Macro-level | Planners/Policy Makers Government Agencies | GIS | China |
| Tian et al., 2023 [68] | Pre-UR | Macro-level | Residents Government Agencies | Cloud Computing and Platforms | China |
| Shi et al., 2023 [26] | Pre-UR | Meso-level | Planners/Policy Makers | GIS Remote Sensing and Surveying AI and Machine Learning | China |
| Kim et al., 2023 [69] | During-UR | Meso-level | Residents | Cloud Computing and Platforms | South Korea |
| Faraji et al., 2023 [44] | Pre-UR | Macro-level | Planners/Policy Makers | BIM/CIM | Iran |
| Duan et al., 2023 [70] | Pre-UR | Micro-level | Residents | GIS | China |
| Dong et al., 2023 [71] | Pre-UR Post-UR | Macro-level | Enterprises/Industries | GIS | China |
| Chen et al., 2023 [72] | Pre-UR | Meso-level | Residents Government Agencies | GIS Visualization and Interaction | China |
| Allan et al., 2023 [35] | Pre-UR | Macro-level | Residents Planners/Policy Makers Government Agencies | GIS BIM/CIM Visualization and Interaction. AI and Machine Learning | Australia |
| Akl et al., 2023 [45] | Pre-UR | Micro-level | Planners/Policy Makers Government Agencies | GIS BIM/CIM Visualization and Interaction | Egypt |
| Zhang et al., 2022 [39] | Pre-UR | Meso-level | Planners/Policy Makers Government Agencies | GIS Visualization and Interaction AI and Machine Learning | China |
| Zhang & Lee, 2022 [73] | Pre-UR | Meso-level | Planners/Policy Makers | GIS Data Fusion and Analytics Cloud Computing and Platforms | China |
| Sütçüoğlu & Önaç, 2022 [74] | Pre-UR | Macro-level | Residents Planners/Policy Makers | GIS Data Fusion and Analytics | Turkey |
| Seve et al., 2022 [75] | Pre-UR | Meso-level | Residents | Data Fusion and Analytics Cloud Computing and Platforms | Spain |
| Sampaio et al., 2022 [48] | During-UR | Micro-level | Technical Professionals/Expert Teams | BIM/CIM Visualization and Interaction | Portugal |
| Shih et al., 2021 [76] | Pre-UR During-UR Post-UR | Meso-level Macro-level | Residents Planners/Policy Makers Non-Governmental Organizations | GIS Data Fusion and Analytics | China |
| Praharaj, 2021 [31] | Pre-UR Post-UR | Macro-level | Planners/Policy Makers Government Agencies | Data Fusion and Analytics | India |
| Porat & Shach-Pinsly, 2021 [77] | Pre-UR | Macro-level | Planners/Policy Makers Government Agencies | GIS Data Fusion and Analytics | Israel |
| Tiboni et al., 2020 [54] | Post-UR | Macro-level | Residents Government Agencies | GIS | Italy Portugal |
| Kim et al., 2020 [30] | Pre-UR During-UR Post-UR | Macro-level | Residents Government Agencies Researchers/Academia | GIS BIM/CIM Data Fusion and Analytics | South Korea |
| Kang et al., 2020 [78] | Pre-UR | Macro-level | Residents Government Agencies | GIS | South Korea |
| Dogan et al., 2020 [79] | Pre-UR | Meso-level | Residents Government Agencies | GIS AI and Machine Learning | Turkey |
| Boulanger et al., 2020 [53] | Pre-UR During-UR Post-UR | Micro-level | Residents Government Agencies Researchers/Academia Professionals/Expert Teams | GIS Data Fusion and Analytics Visualization and Interaction | Italy |
| Zhang et al., 2019 [80] | Pre-UR | Micro-level | Residents Planners/Policy Makers Professionals/Expert Teams | Visualization and Interaction | China |
| Xu et al., 2019 [81] | Pre-UR | Meso-level | Residents Planners/Policy Makers Developers/Business Entities | GIS Remote Sensing and Surveying | China |
| Wang & Fukuda, 2019 [55] | Pre-UR | Macro-level | Residents Government Agencies Researchers/Academia | GIS BIM/CIM | Japan |
| Wang et al., 2019 [49] | Pre-UR During-UR Post-UR | Meso-level | Residents Government Agencies Developers/Business Entities | GIS Data Fusion and Analytics | China |
| Ruiz-Pérez et al., 2019 [57] | Pre-UR During-UR Post-UR | Micro-level | Residents Government Agencies Developers/Business Entities | GIS Data Fusion and Analytics | Spain |
| Omidipoor et al., 2019 [34] | Pre-UR During-UR Post-UR | Macro-level | Developers/Business Entities | GIS Data Fusion and Analytics | Iran |
| Dowsett & Harty, 2019 [41] | Pre-UR During-UR | Micro-level | Developers/Business Entities Professionals/Expert Teams | BIM/CIM | UK |
| Ding et al., 2019 [47] | Pre-UR During-UR | Micro-level | Residents Professionals/Expert Teams | BIM/CIM Visualization and Interaction | China |
| Faltejsek et al., 2018 [42] | Pre-UR | Meso-level | Government Agencies Developers/Business Entities | BIM/CIM Visualization and Interaction | Czech Republic |
| Abarca-Alvarez et al., 2018 [82] | Pre-UR | Macro-level | Residents Planners/Policy Makers Government Agencies Developers/Business Entities | GIS Data Fusion and Analytics | Spain |
| Xu et al., 2017 [29] | Pre-UR | Micro-level | Residents Enterprises/Industries | GIS Remote Sensing and Surveying | China |
| Tsai, 2016 [83] | Pre-UR | Macro-level | Residents Planners/Policy Makers | GIS Visualization and Interaction | China |
| Trubka & Glackin, 2016 [32] | Pre-UR | Micro-level | Residents | BIM/CIM Visualization and Interaction | Australia |
References
- Couch, C.; Sykes, O.; Börstinghaus, W. Thirty years of urban regeneration in Britain, Germany and France: The importance of context and path dependency. Prog. Plan. 2011, 75, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.W.; Shen, G.Q.; Wang, H. A review of recent studies on sustainable urban renewal. Habitat Int. 2014, 41, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, P.; Sykes, H.; Granger, R. Urban Regeneration, 2nd ed.; SAGE Publications Ltd.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutra, S.; Ioakimidis, C.S. Unveiling the Potential of Machine Learning Applications in Urban Planning Challenges. Land 2023, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Liu, R.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. The Fundamental Issues and Development Trends of AI-Driven Transformations in Urban Transit and Urban Space. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 126, 106422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, G.; Arbolino, R.; Shi, L.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Ioppolo, G. Digital Technologies for Urban Metabolism Efficiency: Lessons from Urban Agenda Partnership on Circular Economy. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, S.; Witte, P. Digital technologies in urban planning and urban management. J. Urban Manag. 2023, 12, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kępczyńska-Walczak, A.; Walczak, B.M. Application of Visual Simulation in Urban Renewal Projects. Urban Des. Represent. 2017, 4, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berawi, M.A.; Miraj, P.; Sari, M. The Role Of Digital Technologies In Shaping Sustainable And Smarter Cities. CSID J. Infrastruct. Dev. 2020, 3, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DENİZ, D. The Importance of Digitalization for Sustaining Cultural Environments in Resilient Cities. Environ. Sci. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yi, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shrestha, A.; Martek, I.; Wei, L. An Evaluation of Urban Renewal Policies of Shenzhen, China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, E.; Brandão, A.; Pinto, P.T.; Lopes, S.S. Urban Planning Policies to the Renewal of Riverfront Areas: The Lisbon Metropolis Case. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y. Exploring the Key Factors Influencing Sustainable Urban Renewal from the Perspective of Multiple Stakeholders. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhu, J.; Duan, M.; Li, P.; Guo, X. Overcoming the Collaboration Barriers among Stakeholders in Urban Renewal Based on a Two-Mode Social Network Analysis. Land 2022, 11, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, K.M.A.; Daoud, A.O.; Singh, A.K.; Alhusban, M. Integrating digital mapping technologies in urban development: Advancing sustainable and resilient infrastructure for SDG 9 achievement—A systematic review. Alex. Eng. J. 2025, 116, 512–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moufid, O.; Praharaj, S.; Oulidi, H.J. Digital technologies in urban regeneration: A systematic review of literature. J. Urban Manag. 2025, 14, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiahou, X.; Chen, G.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Li, Q. Knowledge Management in Construction Quality Management: Current State, Challenges, and Future Directions. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2025, 72, 1069–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, P.; Jena, P.K.; Mishra, B.R. Systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis of energy efficiency. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 200, 114583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, A.; Thomas, J. Mixed Methods and Systematic Reviews: Examples and Emerging Issues. In SAGE Handbook of Mixed Methods in Social & Behavioral Research, 2nd ed.; Tashakkori, A., Teddlie, C., Eds.; SAGE Publications, Inc.: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- David Moher, A.L.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; the PRISMA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Phys. Ther. 2009, 89, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arezoo Aghaei Chadegani, H.S.; Yunus, M.M.; Farhadi, H.; Fooladi, M.; Farhadi, M.; Ebrahim, N.A. A Comparison between Two Main Academic Literature Collections: Web of Science and Scopus Databases. Asian Soc. Sci. 2013, 9, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, P.; Ryan, F.; Coughlan, M. Undertaking a literature review: A step-by-step approach. Br. J. Nurs. 2013, 17, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Singh, P.; Karmakar, M.; Leta, J.; Mayr, P. The journal coverage of Web of Science, Scopus and Dimensions: A comparative analysis. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 5113–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, O.; Kocaman, R.; Kanbach, D.K. How to design bibliometric research: An overview and a framework proposal. Rev. Manag. Sci. 2024, 18, 3333–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Yang, Z.L.; Xing, H.F.; Chen, Z.H.; Liu, W.K.; Ao, Z.R.; Liu, Y.F.; Li, J.J. Identifying urban villages: An attention-based deep learning approach that integrates remote sensing and street-level images. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2024, 39, 1247–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.J.; Cao, Q.; van Rompaey, A.; Pu, M.Q.; Ran, B.S. Modeling vibrant areas at nighttime: A machine learning-based analytical framework for urban regeneration. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 99, 104920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.K.; Lu, Y.F.; Qin, Y.; Lu, M.; Song, Z.Q.; Ding, Z.Q. Method for Evaluating Urban Building Renewal Potential Based on Multimachine Learning Integration: A Case Study of Longgang and Longhua Districts in Shenzhen. Land 2025, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.K.; Xia, N.; Hua, S.; Liang, J.L.; Ji, X.K.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, J.C. Hierarchical Recognition for Urban Villages Fusing Multiview Feature Information. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2025, 18, 3344–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Y.; Liu, M.; Hu, Y.M.; Li, C.L.; Xiong, Z.P. Changes of architectural landscape in renewal of old industrial zone in Tiexi district, Shen-Yang. China. J. Ecol. 2017, 36, 499–507. Available online: https://www.cje.net.cn/EN/abstract/abstract22624.shtml (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Kim, H.W.; McCarty, D.A.; Lee, J. Enhancing Sustainable Urban Regeneration through Smart Technologies: An Assessment of Local Urban Regeneration Strategic Plans in Korea. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praharaj, S. Area-Based Urban Renewal Approach for Smart Cities Development in India: Challenges of Inclusion and Sustainability. Urban Plan. 2021, 6, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubka, R.; Glackin, S. Modelling housing typologies for urban redevelopment scenario planning. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2016, 57, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xia, N.; Li, M.C. Assessing urban renewal opportunities by combining 3D building information and geographic big data. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2024, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidipoor, M.; Jelokhani-Niaraki, M.; Moeinmehr, A.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Choi, S.M. A GIS-based decision support system for facilitating participatory urban renewal process. Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 104150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, M.; Rajabifard, A.; Foliente, G. Urban regeneration and placemaking: A Digital Twin enhanced performance-based framework for Melbourne’s Greenline Project? Aust. Plan. 2023, 59, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, J.I.; Wei, H.X. What drives urban redevelopment activity? Evidence from machine learning and econometric analysis in three American cities. J. Geogr. Syst. 2024, 26, 565–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, H.; Mallick, S.K.; Sarkar, S.; Roy, S.K. Developing decision making framework on built-up site suitability assessment for urban regeneration in the industrial cities of Eastern India. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Zhan, X.; Tian, Z.; Wang, D. A Machine Learning-Based Approach to Evaluate the Spatial Performance of Courtyards—A Case Study of Beijing’s Old Town. Buildings 2023, 13, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Yang, L.Q.; Luo, R.Z.; Wu, H.Y.; Xu, J.Q.; Huang, C.Y.; Ruan, Y.J.; Zheng, X.W.; Yao, J.W. Estimating the outdoor environment of workers’ villages in East China using machine learning. Build. Environ. 2022, 226, 109738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Li, T.; Shi, J.; Zhan, H. Using deep learning to unravel the structural evolution of block-scale green spaces in urban renewal. Cities 2024, 150, 105030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowsett, R.M.; Harty, C.F. Assessing the implementation of BIM—An information systems approach. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2019, 37, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faltejsek, M.; Szeligova, N.; Vojvodikova, B. Application of building information modelling in planning of future use of underused areas. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Munic. Eng. 2018, 171, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.Z.; Leng, J.W. An Overview of Sustainable Urban Regeneration Development: A Synergistic Perspective of CIM and BIM. Buildings 2025, 15, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, A.; Arya, S.H.; Ghasemi, E.; Soleimani, H.; Rahnamayiezekavat, P. A Constructability Assessment Model Based on BIM in Urban Renewal Projects in Limited Lands. Buildings 2023, 13, 2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akl, M.H.; Sheta, S.A.; ElGizawi, L. Application of BIM/GIS-based Integrated Models on the Historic Urban Districts of Rosetta City, Egypt. Ital. J. Plan. Pract. 2023, 13, 24–46. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Cai, Y.Q.; Song, S.D.; Sun, L.L. An Urban Renewal Design Method Based on Carbon Emissions and Carbon Sink Calculations: A Case Study on an Environmental Improvement Project in the Suzhou Industrial Investment Science and Technology Park. Buildings 2024, 14, 2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.K.; Liu, S.; Liao, L.H.; Zhang, L. A digital construction framework integrating building information modeling and reverse engineering technologies for renovation projects. Autom. Constr. 2019, 102, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, A.Z.; Constantino, G.B.; Almeida, N.M. 8D BIM Model in Urban Rehabilitation Projects: Enhanced Occupational Safety for Temporary Construction Works. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, J.K.; Wang, X.T.; Chen, Y.J. Cost-effectiveness analysis and evaluation of a ‘three-old’ reconstruction project based on smart system. Clust. Comput.-J. Netw. Softw. Tools Appl. 2019, 22, S7895–S7905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Lin, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, G.; Mei, Q.; Fu, Z. The Cost of Urban Renewal: Annual Construction Waste Estimation via Multi-Scale Target Information Extraction and Attention-Enhanced Networks in Changping District, Beijing. Remote. Sens. 2024, 16, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, H.; Xu, M.H.; Jin, S.T.; Kong, H. Understanding temporary residential mobility during urban renewal: Insights from a structured community survey and machine learning analysis. Appl. Geogr. 2024, 172, 103425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutani, G.; Scalise, A.; Sufa, X.; Grasso, S. Synergising Machine Learning and Remote Sensing for Urban Heat Island Dynamics: A Comprehensive Modelling Approach. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulanger, S.O.M.; Longo, D.; Roversi, R. Data evidence-based transformative actions in historic urban context—The bologna university area case study. Smart Cities 2020, 3, 1448–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiboni, M.; Botticini, F.; Sousa, S.; Jesus-Silva, N. A Systematic Review for Urban Regeneration Effects Analysis in Urban Cores. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Fukuda, H. Sustainable Urban Regeneration for Shrinking Cities: A Case from Japan. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Di, L.; Zhang, C.; Guo, L.; Zhao, H.; Islam, D.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Middleton, G. Modeling urban redevelopment: A novel approach using time-series remote sensing data and machine learning. Geogr. Sustain. 2024, 5, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Pérez, M.R.; Alba-Rodríguez, M.D.; Castaño-Rosa, R.; Solis-Guzmán, J.; Marrero, M. HEREVEA Tool for Economic and Environmental Impact Evaluation for Sustainable Planning Policy in Housing Renovation. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yue, J.; Wang, S.; Luo, Y.; Su, C.; Zhou, J.; Xu, D.; Lu, H. Development of Geographic Information System Architecture Feature Analysis and Evolution Trend Research. Sustainability 2024, 16, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dai, D.; Dong, J.; Hu, K. Research on the collaborative mechanism between site selection optimization model and control of green space planning under the background of urban renewal. Discov. Sustain. 2025, 6, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.N.; Wang, J.G.; Han, T.R.; Jin, X. Organic renewal of property plots in Chinese cities: Sustainable development of built environment via property value enhancement and digital twin construction. Indoor Built Environ. 2025, 34, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, O.; Alkan, M. Assessing the impact of unplanned settlements on urban renewal projects with GEE. Habitat Int. 2024, 149, 103095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.; Kweon, J.; He, J. Big data analysis and evaluation for vitality factors of public space of regenerated industrial heritage in Luoyang. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2024, 19, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teklemariam, N. Historic Preservation as Sustainable Urban Development in African Cities: A Technical and Technological Framework. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Song, M. Exploring the Potential of Generative Adversarial Networks in Enhancing Urban Renewal Efficiency. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ren, K.; Li, P.; Wang, H.; Zhou, P. Toward effective urban regeneration post-COVID-19: Urban vitality assessment to evaluate people preferences and place settings integrating LBSNs and POI. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xueqiang, W.; Ghani, M.Z.A.; Yuan, G.; Zaman, N.Q.; Sarkom, Y. Research On The Spatial Distribution Of Public Service Facilities In Nanchang Old City, China Based On Point Of Interest (Poi) Data. Plan. Malays 2023, 21, 432–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Liu, J.; Liang, Y.; Wu, Y. A participatory e-planning model in the urban renewal of China: Implications of technologies in facilitating planning participation. Environ. Plan. B-Urban Anal. City Sci. 2023, 50, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Seo, K.W. The Perception of Urban Regeneration by Stakeholders: A Case Study of the Student Village Design Project in Korea. Buildings 2023, 13, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Liao, J.; Liu, J.; Gao, X.; Shang, A.; Huang, Z. Evaluating the Spatial Quality of Urban Living Streets: A Case Study of Hengyang City in Central South China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.L.; Gao, X.Y.; Chen, X.W.; Lin, L.H. Industrial Park Renovation Strategy in a Poverty-Alleviated County Based on Inefficient Land Evaluation. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Pellegrini, P.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H.Q. Strategies for Sustainable Urban Renewal: Community-Scale GIS-Based Analysis for Densification Decision Making. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lee, M. Urban Renewal Design Based on Integration of Database Information under Data Mining. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 3494642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sütçüoğlu, G.G.; Önaç, A.K. A site selection model proposal for sustainable urban regeneration: Case study of Karşıyaka, İzmir, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 194, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seve, B.; Redondo, E.; Sega, R. A Taxonomy of Bottom-Up, Community Planning and Participatory Tools in the Urban Planning Context. Archit. City Environment 2022, 16, 48. Available online: https://upcommons.upc.edu/handle/2117/363276 (accessed on 20 April 2025). [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.M.; Treija, S.; Zaleckis, K.; Bratuškins, U.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Chiang, C.T.W.; Jankauskaitė-Jurevičienė, L.; Kamičaitytė, J.; Koroļova, A.; et al. Digital placemaking for urban regeneration: Identification of historic heritage values in Taiwan and The Baltic states. Urban Plan. 2021, 6, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porat, I.; Shach-Pinsly, D. Building morphometric analysis as a tool for urban renewal: Identifying post-Second World War mass public housing development potential. Environ. Plan. B-Urban Anal. City Sci. 2021, 48, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Kim, K.; Jung, J.; Son, S.; Kim, E.J. How Vulnerable Are Urban Regeneration Sites to Climate Change in Busan, South Korea? Sustainability 2020, 12, 4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, U.; Gungor, M.K.; Bostanci, B.; Yilmaz Bakir, N. GIS Based Urban Renewal Area Awareness and Expectation Analysis Using Fuzzy Modeling. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 54, 101945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.M.; Zhang, R.X.; Jeng, T.S.; Zeng, Z.Y. Cityscape protection using VR and eye tracking technology. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2019, 64, 102639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Y.; Liu, M.; Hu, Y.M.; Li, C.L.; Xiong, Z.P. Analysis of Three-Dimensional Space Expansion Characteristics in Old Industrial Area Renewal Using GIS and Barista: A Case Study of Tiexi District, Shenyang, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarca-Alvarez, F.J.; Campos-Sanchez, F.S.; Reinoso-Bellido, R. Demographic and dwelling models by Artificial Intelligence: Urban renewal opportunities in Spanish coast. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2018, 13, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.Y. Application of Gis with Typology in Urban Regeneration Process. ICIC Express Lett. Part B Appl. 2016, 7, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Categories | Names | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| GIS Technologies | Spatial Analysis, ArcGIS, POI Analysis, Geodatabase, Network Analysis | 28 |
| BIM/CIM Technologies | Building Information Modeling, City Information Modeling, Revit, 3D Modeling | 17 |
| AI and Machine Learning | Machine Learning, Random Forest, Deep Learning, GANs, Predictive Modeling | 16 |
| Visualization and Interaction | VR/AR, Digital Twin, Simulation (CFD/OpenFOAM), Spatial Syntax | 13 |
| Remote Sensing and Surveying | Remote Sensing (RS), LiDAR, Point Cloud, Satellite Imagery, Street View Imagery | 10 |
| Data Fusion and Analytics | Big Data Analytics, IoT Sensors, Social Media Mining, MCDA (AHP/TOPSIS) | 9 |
| Cloud Computing and Platforms | Cloud Computing, Mobile Apps, Web Platforms, Google Earth Engine (GEE) | 5 |
| Categories | Stakeholder | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Residents | Urban residents, citizens, community residents, the public, local residents, community members, students, the general public, tourists, etc. | 30 |
| Government Agencies | Local government, government departments, planning departments, management and planning departments, relevant government departments, municipal government, cultural heritage management departments, etc. | 33 |
| Planners/Policy Makers | Planners, urban planners, policy makers, urban decision makers, formulators, urban managers, etc. | 18 |
| Developers/Business Entities | Real estate developers, design and development companies, property owners, investors, managers, real estate stakeholders, etc. | 15 |
| Technical Professionals/Expert Teams | Technical personnel, industrial planning engineers, design teams, designers, urban builders and designers, technical partners, technical suppliers, construction workers, heritage experts, etc. | 14 |
| Researchers/Academia | Scientific researchers, academic researchers, academic teams, urban research scholars, etc. | 6 |
| Non-Governmental Organizations | Non-governmental organizations, communities, etc. | 3 |
| Enterprises/Industries | Industrial enterprises, factories, etc. | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiahou, X.; Ding, X.; Chen, P.; Qian, Y.; Jin, H. Digital Technologies in Urban Regeneration: A Systematic Literature Review from the Perspectives of Stakeholders, Scales, and Stages. Buildings 2025, 15, 2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142455
Xiahou X, Ding X, Chen P, Qian Y, Jin H. Digital Technologies in Urban Regeneration: A Systematic Literature Review from the Perspectives of Stakeholders, Scales, and Stages. Buildings. 2025; 15(14):2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142455
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiahou, Xiaer, Xingyuan Ding, Peng Chen, Yuchong Qian, and Hongyu Jin. 2025. "Digital Technologies in Urban Regeneration: A Systematic Literature Review from the Perspectives of Stakeholders, Scales, and Stages" Buildings 15, no. 14: 2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142455
APA StyleXiahou, X., Ding, X., Chen, P., Qian, Y., & Jin, H. (2025). Digital Technologies in Urban Regeneration: A Systematic Literature Review from the Perspectives of Stakeholders, Scales, and Stages. Buildings, 15(14), 2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142455







