Upper Shallow Foundation Pit Engineering: Utilization and Evaluation of Portal Frame Anti-Heave Structures
Abstract
1. Introduction
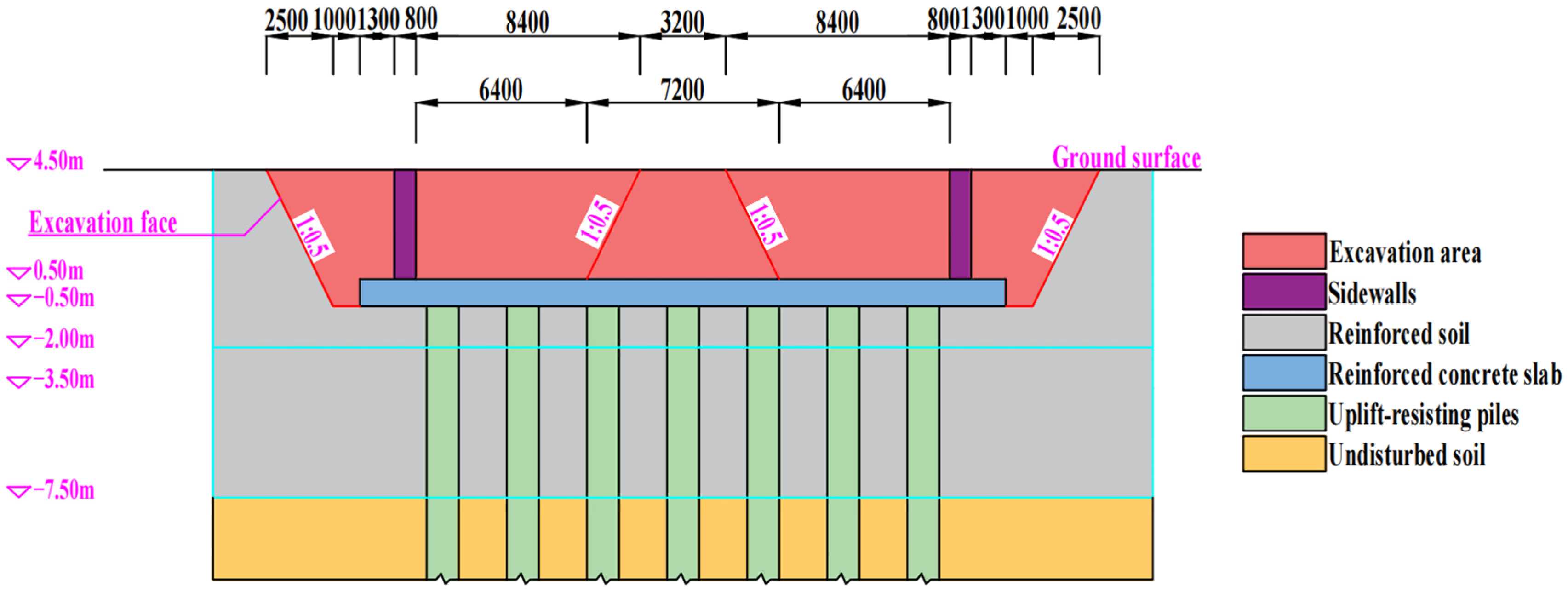
2. Case Study on the Application of Portal Frame Anti-Heave Structures
2.1. Stratum Parameters
2.2. Deformation Control Measures for Existing Tunnels
2.3. Foundation Pit Unloading Ratio
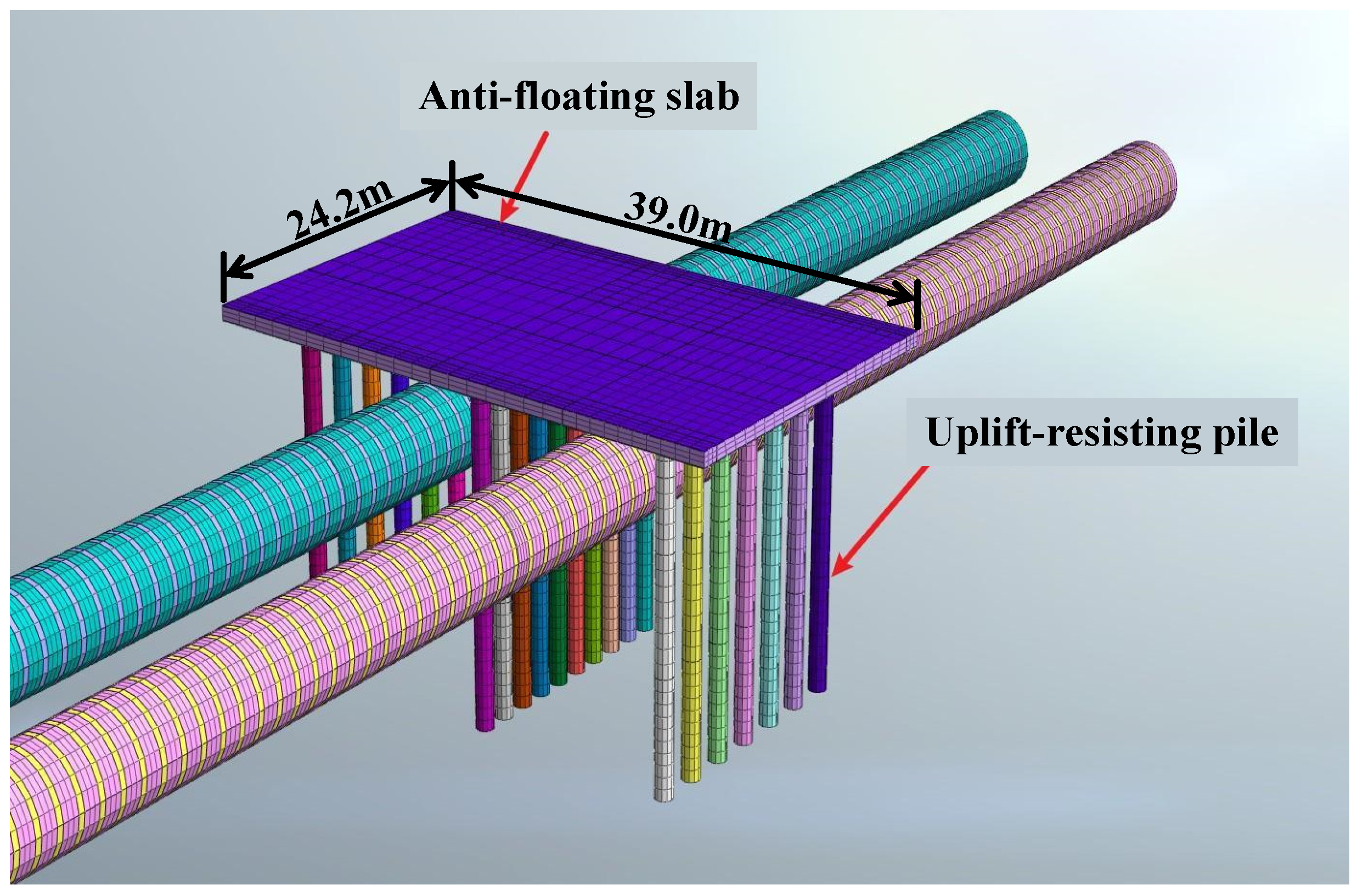
2.4. Uplift-Resisting Pile Parameters
2.5. Anti-Floating Slab Parameters
3. Numerical Orthogonal Experimental Scheme
3.1. Constitutive Model
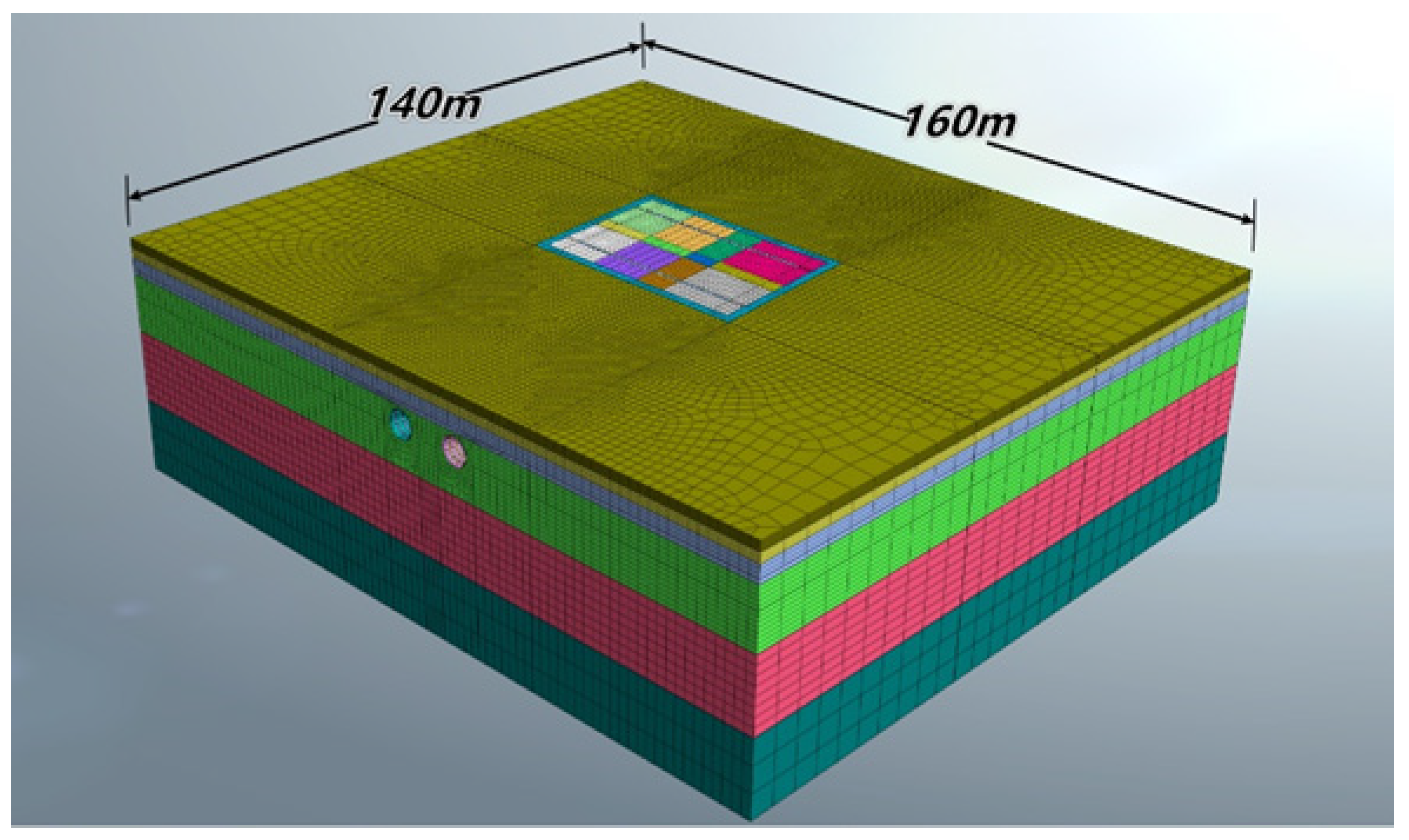
3.2. Case Project Overview
3.3. Model Parameters
3.4. Construction Process Simulation
3.5. Orthogonal Experimental Scheme
4. Deformation Response of Existing Tunnels
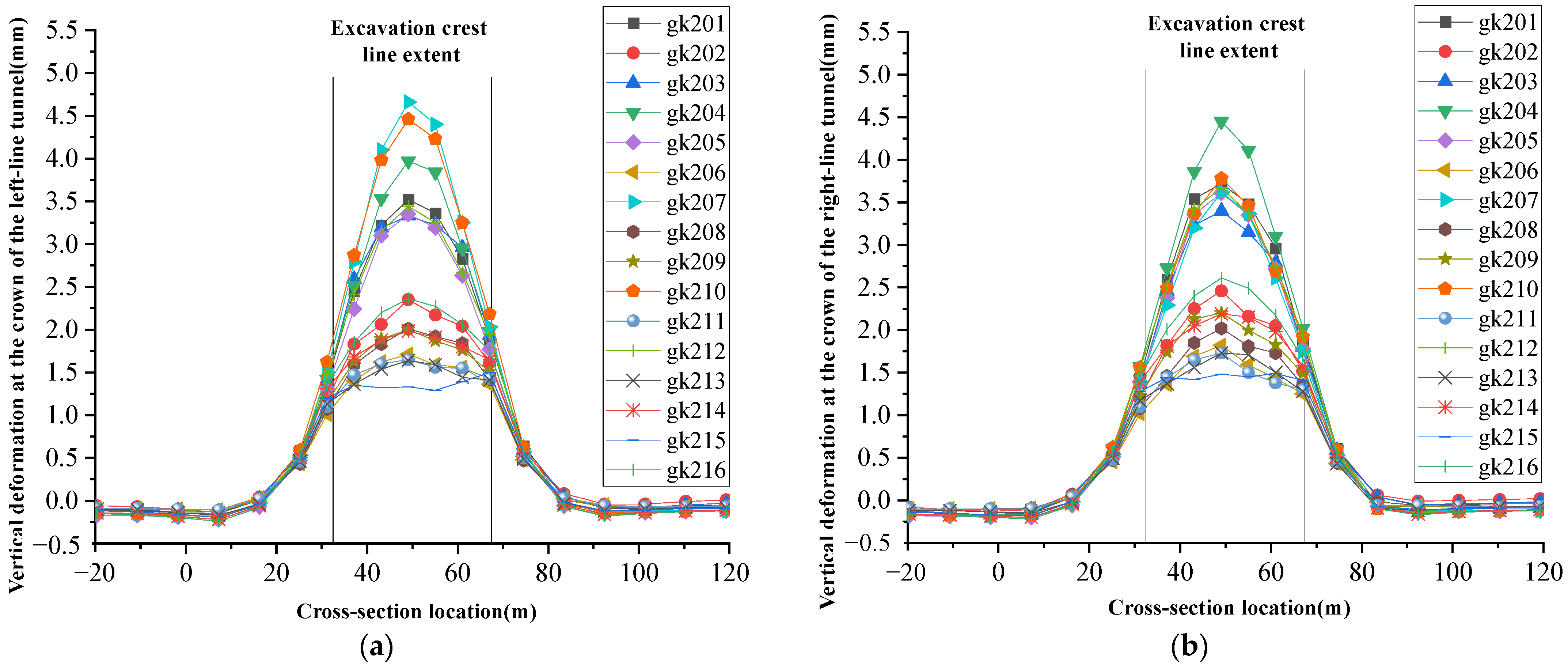
4.1. Tunnel Deformation Distribution
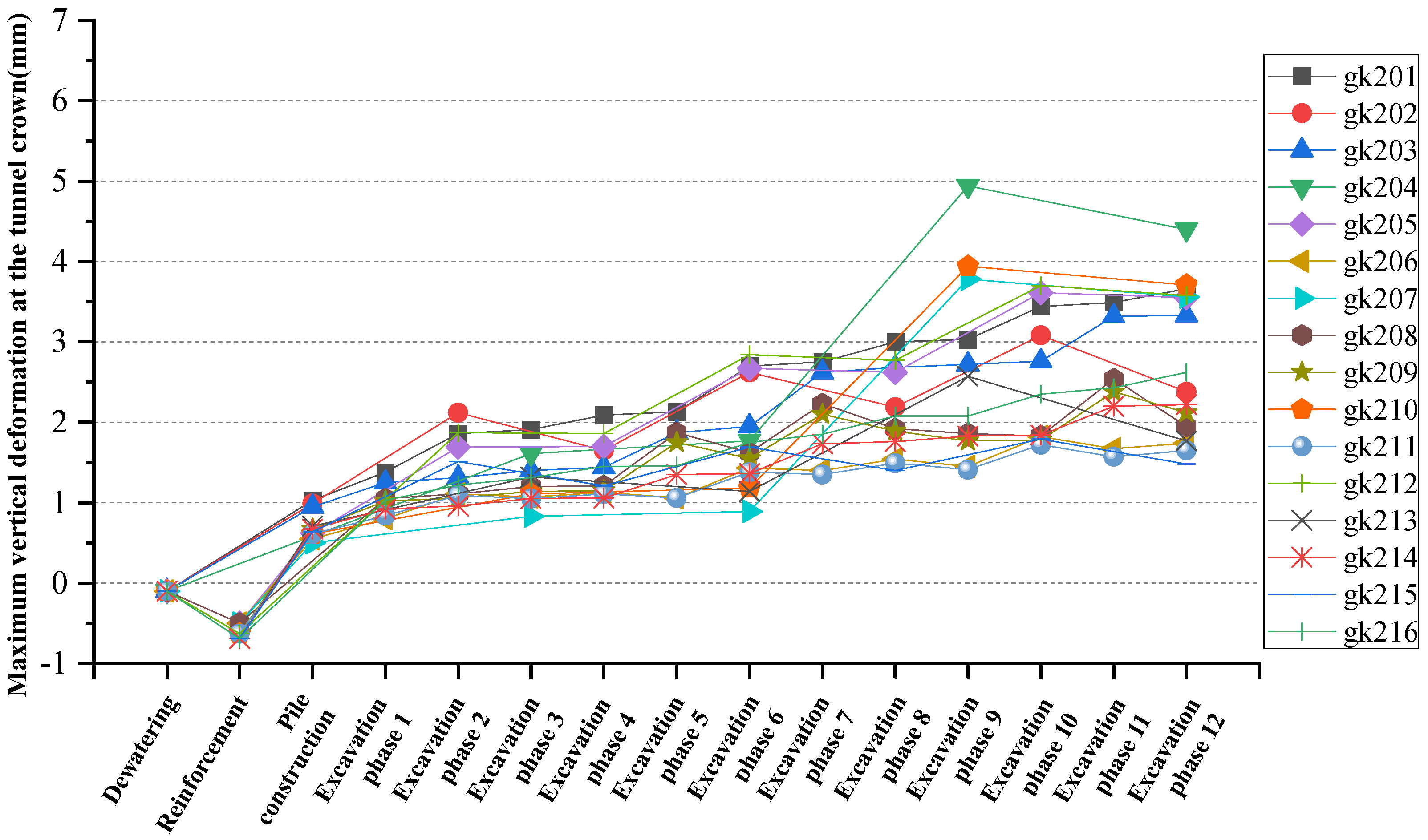
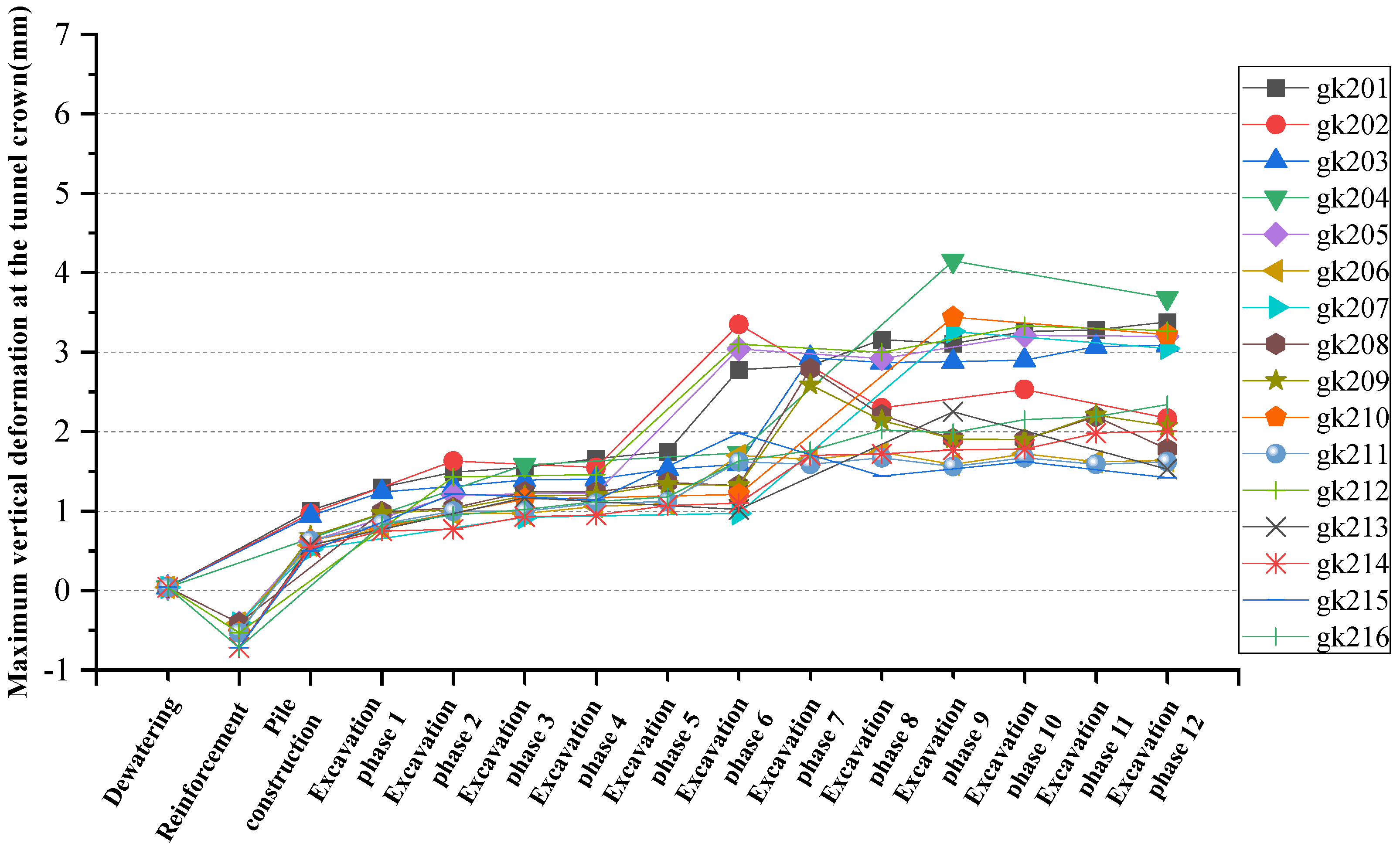
4.2. Development of Vertical Deformation of Tunnel Vault
5. Effectiveness Analysis of Control Measures Implementation
5.1. Overall Information on Tunnel Vertical Deformation Control
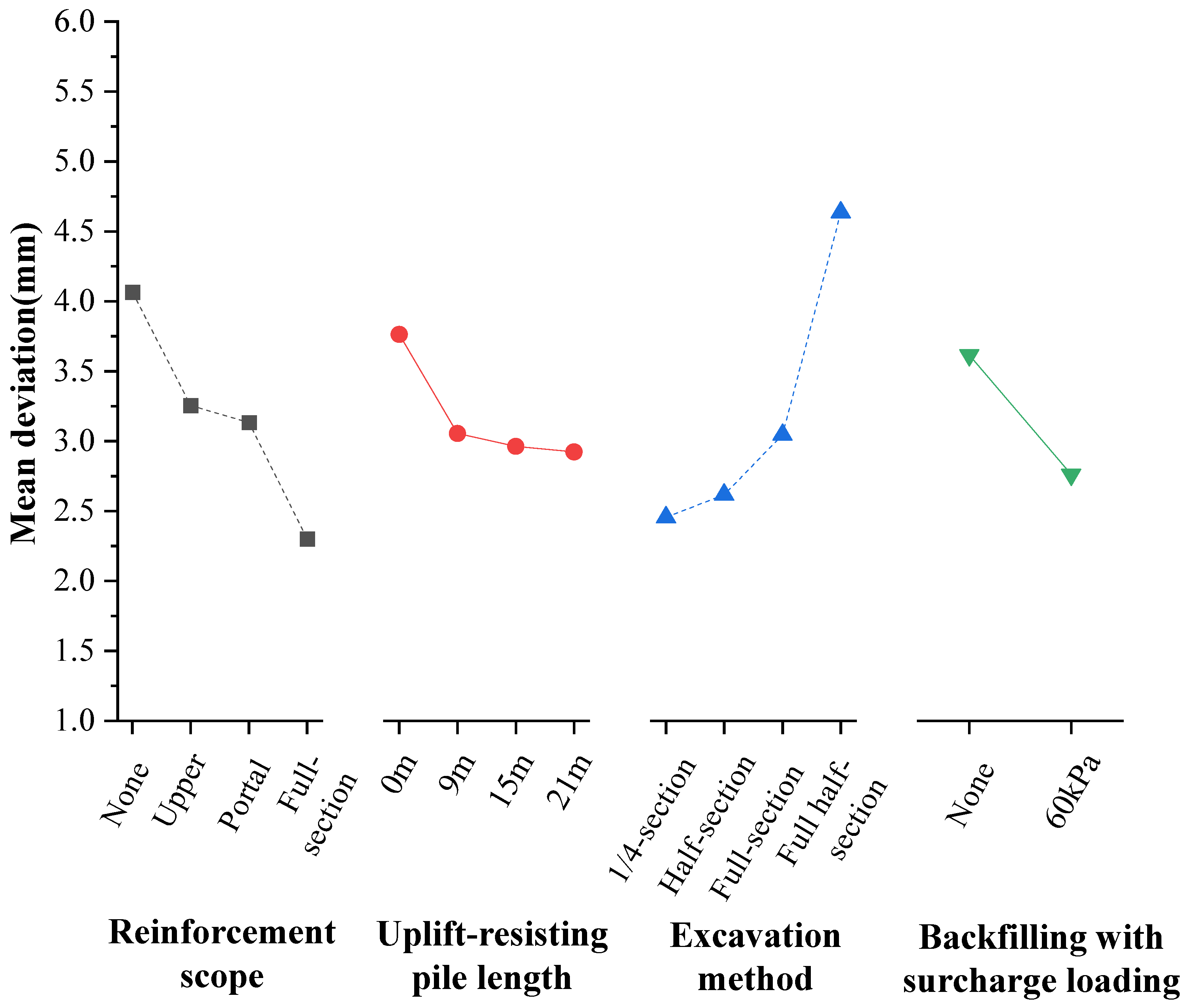
5.2. Range Analysis
5.3. Field-Measured Analysis of Control Effectiveness of Portal Frame Anti-Heave Structures
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Xie, C.; Qu, Y.; Lu, H.; Song, S. Study on Deformation of New Tunnels Overcrossing Existing Tunnels Underneath Operating Railways. Buildings 2024, 14, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, C.; Cui, S. Effect of New Tunnel Construction on Structural Performance of Existing Tunnel Lining. Geomech. Eng. 2020, 22, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Chen, R.; Wu, H.; Cheng, H. Deformation Behaviors of Existing Tunnels Caused by Shield Tunneling Undercrossing with Oblique Angle. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 89, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Jin, Z.; Wang, S. Seepage Effect on Progressive Failure of Shield Tunnel Face in Granular Soils by Coupled Continuum-Discrete Method. Comput. Geotech. 2024, 166, 106009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Tu, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, S. Stability Analysis for Excavation in Frictional Soils Based on Upper Bound Method. Comput. Geotech. 2024, 165, 105916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Chen, W. Effect of Inclined Layered Soils on Face Stability in Shield Tunneling Based on Limit Analysis. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 131, 104773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xue, B.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y. Numerical Study on the Behavior of an Existing Tunnel during Excavating Adjacent Deep Foundation Pit. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Rodriguez-Dono, A.; Song, F.; Zhou, Z. Time-Dependent Tunnel Deformations: Insights from in-Situ Tests and Numerical Analyses. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2025, 157, 106319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.W.W.; Shi, J.; Hong, Y. Three-Dimensional Centrifuge Modelling of Basement Excavation Effects on an Existing Tunnel in Dry Sand. Can. Geotech. J. 2013, 50, 874–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweiger, H.F.; Kummerer, C.; Otterbein, R.; Falk, E. Numerical Modelling of Settlement Compensation by Means of Fracture Grouting. Soils Found. 2004, 44, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komiya, K.; Soga, K.; Akagi, H.; Jafari, M.R.; Bolton, M.D. Soil Consolidation Associated with Grouting during Shield Tunnelling in Soft Clayey Ground. Géotechnique 2001, 51, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kelesh, A.M.; Mossaad, M.E.; Basha, I.M. Model of Compaction Grouting. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2001, 127, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Jiang, C.; Liu, Z.; Hu, J. Study on Construction Deformation Law of Shield Tunnel Overlapping through the Subway Tunnel. J. Transp. Sci. Eng. 2022, 38, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Lin, P.; Ding, C.; Shi, J. Study on Three-Dimensional Deformation Characteristics of Adjacent Operating Tunnel Caused by Foundation Pit Excavation. Railw. Eng. 2022, 62, 117–120. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Lan, G.; Liu, Y.; Chen, R.; Meng, F.; Xu, X. Field Performance of an Anti-Uplift Portal Frame in Control of the Tunnel Uplift Induced by Overlying Excavation. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 132, 104908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, R.; Cheng, H.; Wu, H.; Zhang, K. Analytical Solutions for Performance of Existing Shield Tunnel Subjected to Overlying Excavation under Anti-Uplift Portal Frame. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2024, 46, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Feng, D.; Liu, Y.; Lan, G.; Chen, R. Anti-Uplift Portal Frame in Control of Underlying Tunnel Deformation Induced by Foundation Pit Excavation. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. 2022, 56, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Luo, B.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Z. Theoretical Analysis of Stratum Horizontal Displacements Caused by Small Radius Curve Shield Tunneling. Comput. Geotech. 2024, 165, 105950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Luo, B.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, H. Case Study of Performance Assessment of Overlapping Shield Tunnels with a Small Curve Radius. Deep Undergr. Sci. Eng. 2024, 3, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qu, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z. Investigating the Damage to Masonry Buildings during Shield Tunneling: A Case Study in Hohhot Metro. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 160, 108147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z. Behaviour of Existing Tunnel Due to New Tunnel Construction Below. Comput. Geotech. 2019, 110, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Li, Q.; Wong, L.N.Y. Effects of Twin Tunnels Construction beneath Existing Shield-Driven Twin Tunnels. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2015, 45, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; He, C.; Zhu, H.; Sun, H. Longitudinal Equivalent Rigidity Analysis of Shield Tunnel Considering Transverse Characteristics. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2011, 33, 1870–1876. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Huang, X.; Schweiger, H.F. Numerical Analysis of the Influence of Deep Excavation on underneath Existing Road Tunnel. China Civ. Eng. J. 2012, 45, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



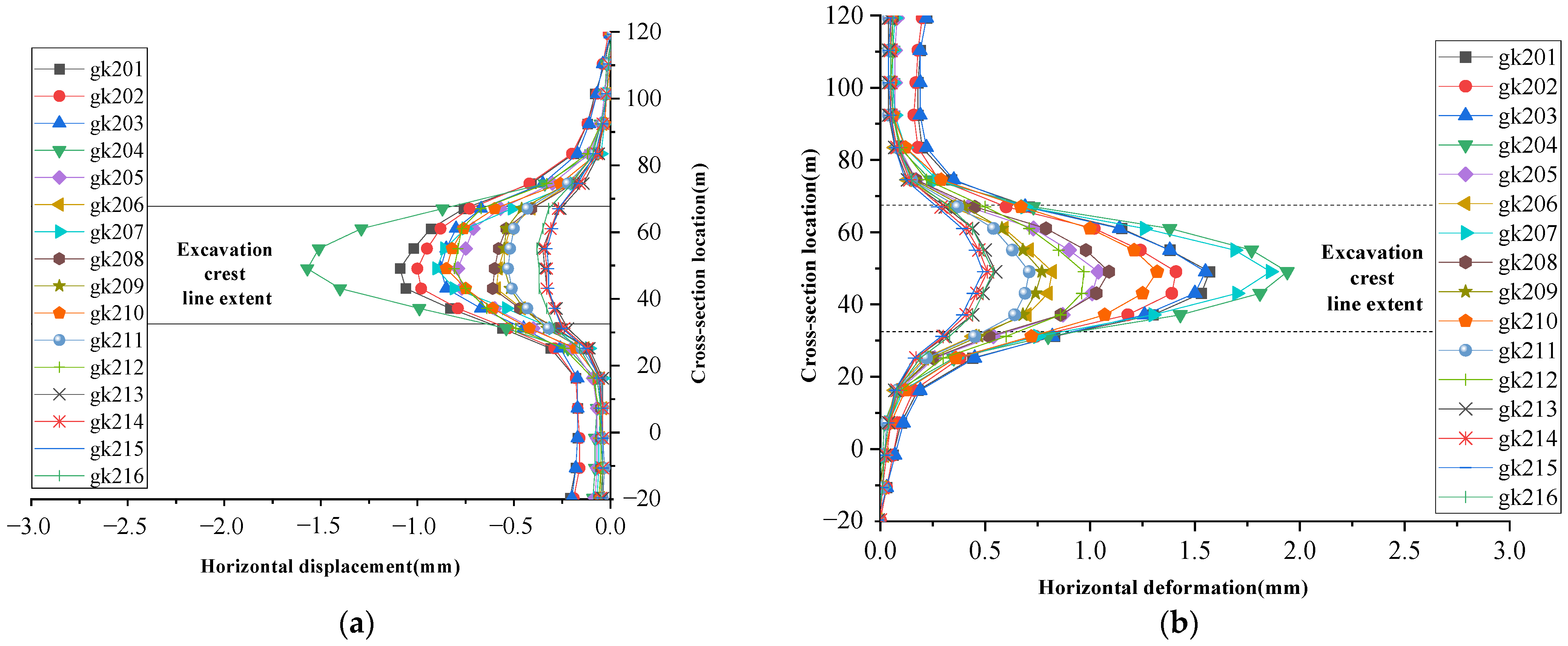

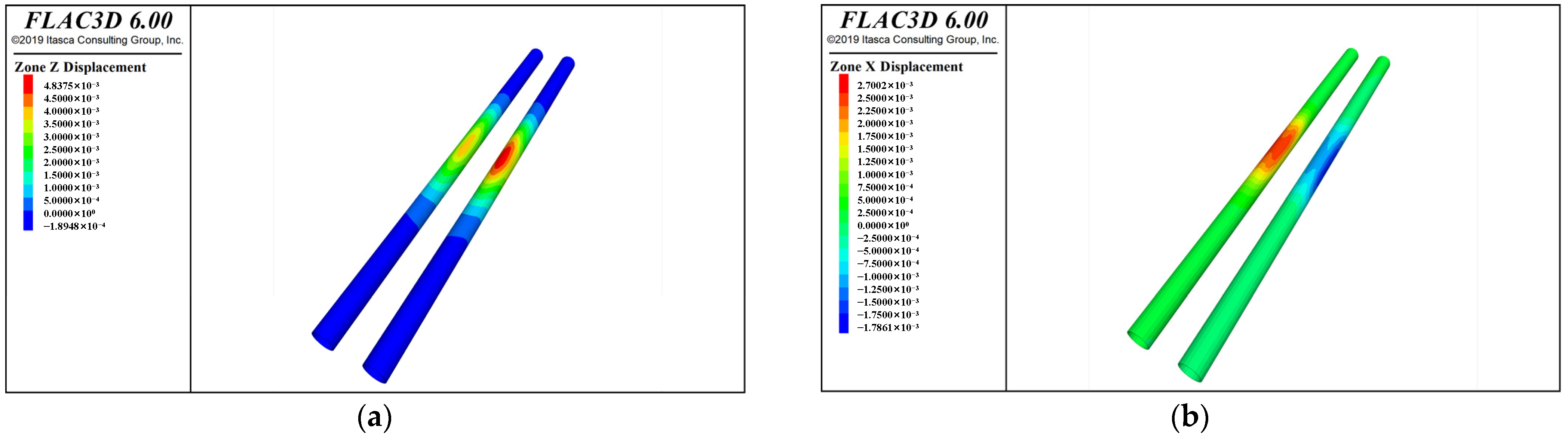

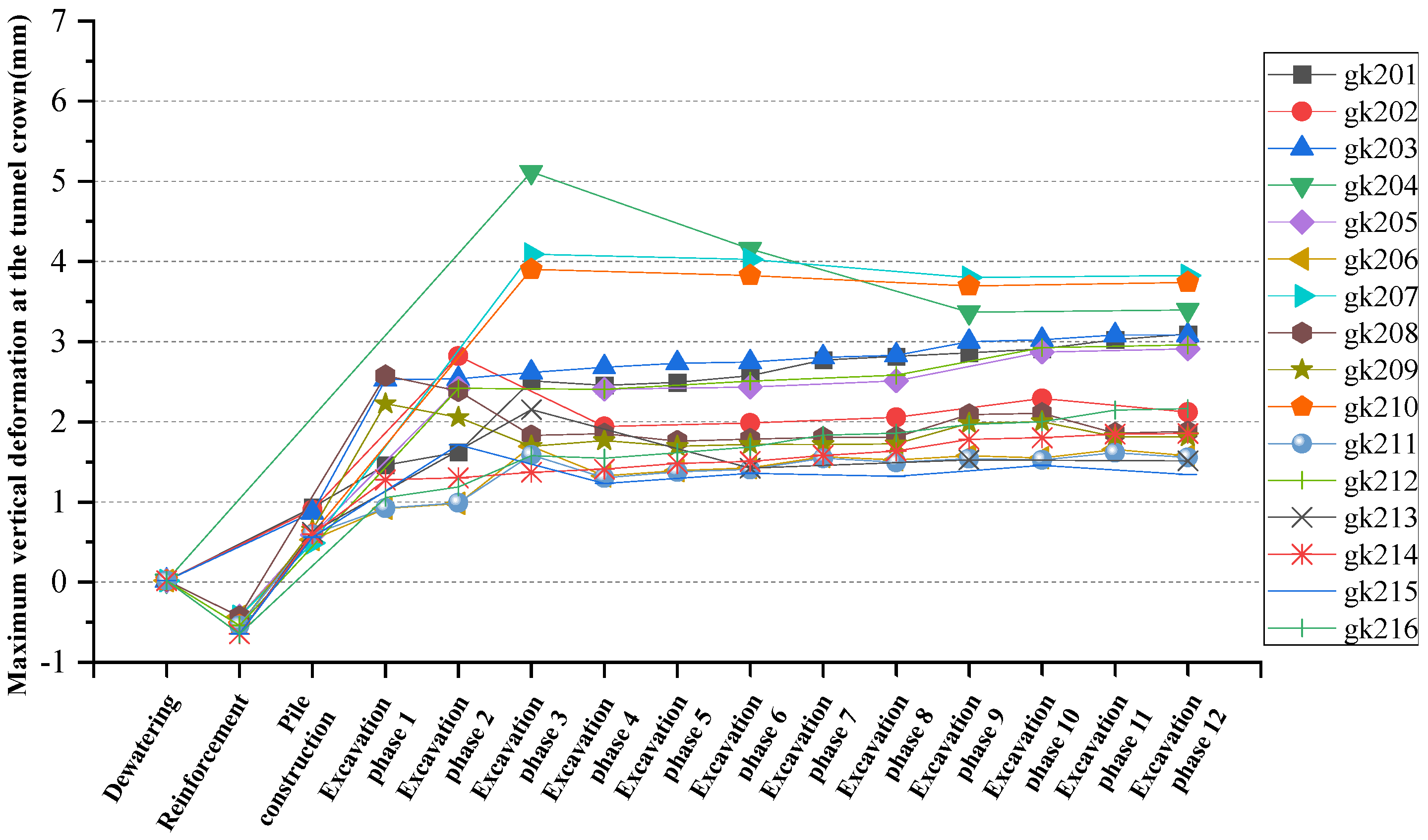
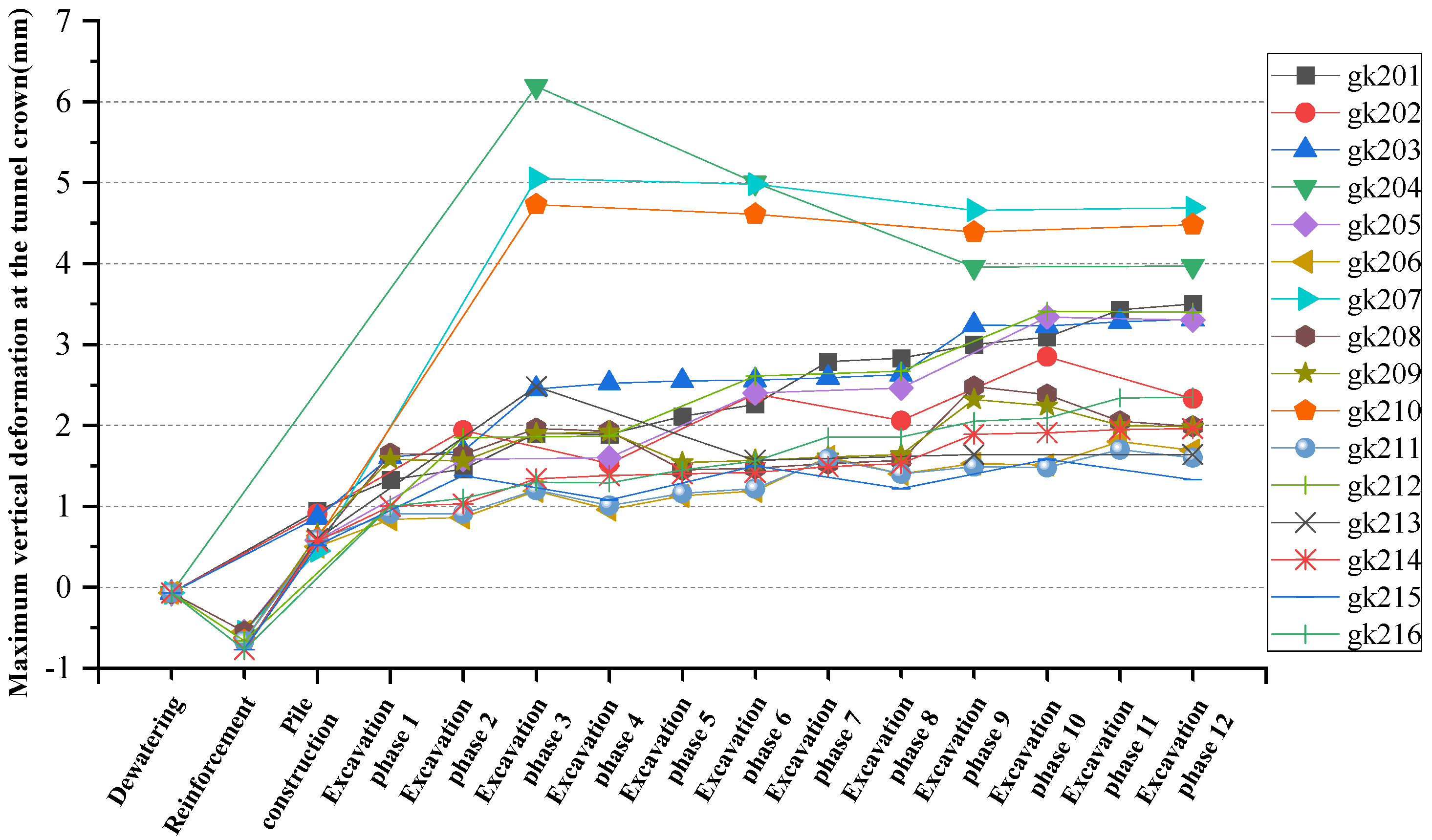

| No. | Existing Tunnel | Tunnel Burial Depth | Pit Depth | Unloading Ratio | Pile Length | Pile Diameter | Anti-Floating Slab Thickness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m | m | m | m | m | |||
| 1 | Line 5 | 11.10 | 7.80 | 0.70 | 19.00 | 1.20 | 0.60 |
| 2 | Line 1 | 12.33 | 4.73 | 0.38 | 18.17 | 1.20 | 0.60 |
| 3 | Line 5 | 13.85 | 8.00 | 0.58 | 20.00 | 1.00 | 0.60 |
| 4 | Line 11 | 15.05 | 8.55 | 0.57 | 20.00 | 1.00 | 0.60 |
| 5 | Line 3 | 13.70 | 8.00 | 0.58 | 24.45 | 1.00 | 3.00 |
| 6 | Line 9 west extension | 11.64 | 6.93 | 0.6 | 15.44 | 1.2/1.0 | 0.30 |
| 7 | Line 1 | 15.50 | 12.50 | 0.81 | 23.60 | 1.20 | 0.50 |
| 8 | Line 11 | 16.30 | 6.55 | 0.40 | 28.00 | 1.20 | 1.00 |
| 9 | Line 11 | 13.44 | 4.10 | 0.31 | 24.80 | 1.80 | 2.50 |
| 10 | Line 5 | 12.38 | 8.50 | 0.69 | 24.50 | 1.80 | 2.50 |
| 11 | Line 2 | 16.80 | 12.00 | 0.71 | 25.00 | 1.2/1.5 | 2.50 |
| 12 | Line 11 | 22.50 | 17.10 | 0.76 | 18.00 | 1.00 | 0.90 |
| 13 | 22.50 | 16.50 | 0.73 | 18.00 | 1.00 | 0.90 | |
| 14 | 20.00 | 14.90 | 0.75 | 18.00 | 1.00 | 0.90 | |
| 15 | Line 9 | 8.50 | 5.00 | 0.63 | 22.00 | 1.20 | 1.00 |
| Parameter | Unit | Fill Soil | Fill Stone | Cohesive Soil | Remnant Soil | Fully Weathered Granite | Strongly Weathered Granite |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| li | m | 2.0 | 2.0 | 3.5 | 12.0 | 15.0 | 15.5 |
| MPa | 4.9 | 6.4 | 5.7 | 5.2 | 5.4 | 12.8 | |
| MPa | 19.7 | 25.6 | 21.8 | 32.8 | 33.9 | 57.5 | |
| c | kPa | 13.5 | 5.0 | 23.8 | 23.0 | 25.0 | 35.0 |
| φ | ° | 16.1 | 30.9 | 18.0 | 20.2 | 25.0 | 33.0 |
| ψ | ° | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| m | - | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.76 | 0.85 | 0.80 |
| Rf | - | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.94 | 0.73 | 0.71 | 0.90 |
| MPa | 141.9 | 385.6 | 189.3 | 260.6 | 421.5 | 1204.0 | |
| γ0.7 | 10−4 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.2 | 1.7 | 1.4 | 2.0 |
| MPa | 3.5 | 6.4 | 4.7 | 5.2 | 5.4 | 12.8 | |
| n | - | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| e | - | 0.74 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 1.01 | 0.72 | 0.60 |
| γ | kN/m3 | 19.2 | 19.5 | 19.6 | 18.1 | 18.5 | 19.0 |
| pref | kPa | 100.0 | |||||
| Factor | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reinforcement Range | Anti-Pulling Pile Length | Excavation Method | Backfill Load | |
| Level 1 | None | 9 m | 1/4-section zoned excavation | None |
| Level 2 | Upper | 15 m | Full-section zoned excavation | 60 kPa |
| Level 3 | Portal | 21 m | Half-section zoned excavation | - |
| Level 4 | Full-section | 0 m | Full half-section zoned excavation | - |
| Working Condition | Reinforcement Range | Pile Length | Excavation Method | Surcharge Loading |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gk201 | None | 9 m | 1/4-section zoned excavation | None |
| gk202 | None | 15 m | Full-section zoned excavation | 60 kPa |
| gk203 | None | 21 m | Half-section zoned excavation | None |
| gk204 | None | 0 m | Full half-section zoned excavation | 60 kPa |
| gk205 | Upper | 9 m | Full-section zoned excavation | None |
| gk206 | Upper | 15 m | 1/4-section zoned excavation | 60 kPa |
| gk207 | Upper | 21 m | Full half-section zoned excavation | None |
| gk208 | Upper | 0 m | Half-section zoned excavation | 60 kPa |
| gk209 | Portal | 9 m | Half-section zoned excavation | 60 kPa |
| gk210 | Portal | 15 m | Full half-section zoned excavation | None |
| gk211 | Portal | 21 m | 1/4-section zoned excavation | 60 kPa |
| gk212 | Portal | 0 m | Full-section zoned excavation | None |
| gk213 | Full-section | 9 m | Full half-section zoned excavation | 60 kPa |
| gk214 | Full-section | 15 m | Half-section zoned excavation | None |
| gk215 | Full-section | 21 m | Full-section zoned excavation | 60 kPa |
| gk216 | Full-section | 0 m | 1/4-section zoned excavation | None |
| Excavation Phase | 1/4-Section Zoned Excavation | Full-Section Zoned Excavation | Half-Section Zoned Excavation | Full Half-Section Zoned Excavation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | No. 1 pit backfill | No. 1 pit excavation | ||
| 2 | No. 2 pit backfill | No. 1 pit excavation | No. 1 pit backfill | |
| 3 | No. 3 pit backfill | No. 2 pit excavation | No. 1 pit excavation | |
| 4 | No. 4 pit backfill | No. 1 pit backfill | No. 2 pit backfill | |
| 5 | No. 5 pit backfill | No. 3 pit excavation | ||
| 6 | No. 6 pit backfill | No. 2 pit excavation | No. 3 pit backfill | No. 1 pit backfill |
| 7 | No. 7 pit backfill | No. 4 pit excavation | ||
| 8 | No. 8 pit backfill | No. 2 pit backfill | No. 4 pit backfill | |
| 9 | No. 9 pit backfill | No. 5 pit excavation | No. 2 pit excavation | |
| 10 | No. 10 pit backfill | No. 3 pit excavation | No. 5 pit backfill | |
| 11 | No. 11 pit backfill | No. 6 pit excavation | ||
| 12 | No. 12 pit backfill | No. 3 pit backfill | No. 6 pit backfill | No. 2 pit backfill |
| Working Condition | Left Line Arch Vertical Deformation (mm) | Right Line Arch Vertical Deformation (mm) | The Largest Arch Vertical Deformation (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| gk201 | 3.5 | 3.66 | 3.66 |
| gk202 | 2.85 | 3.08 | 3.08 |
| gk203 | 3.26 | 3.28 | 3.28 |
| gk204 | 6.19 | 4.94 | 6.19 |
| gk205 | 3.34 | 3.61 | 3.61 |
| gk206 | 1.80 | 1.82 | 1.82 |
| gk207 | 5.00 | 3.73 | 5.00 |
| gk208 | 2.48 | 2.54 | 2.54 |
| gk209 | 2.32 | 2.38 | 2.38 |
| gk210 | 4.73 | 3.94 | 4.73 |
| gk211 | 1.65 | 1.67 | 1.67 |
| gk212 | 3.41 | 3.70 | 3.70 |
| gk213 | 2.48 | 2.57 | 2.57 |
| gk214 | 1.96 | 2.22 | 2.22 |
| gk215 | 1.53 | 1.74 | 1.74 |
| gk216 | 2.35 | 2.62 | 2.62 |
| m | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d | 0.71 | 0.52 | 0.45 | 0.4 | 0.37 | 0.35 | 0.34 | 0.32 | 0.31 |
| Num | Level | Reinforcement Range | Uplift-Resisting Pile Length | Excavation Method | Backfill Load |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | 1 | 16.26 | 12.22 | 9.82 | 28.92 |
| 2 | 13.02 | 11.85 | 12.18 | 22.09 | |
| 3 | 12.53 | 11.84 | 10.47 | - | |
| 4 | 9.2 | 15.05 | 18.54 | - | |
| Kavg | 1 | 4.07 | 3.05 | 2.46 | 3.61 |
| 2 | 3.25 | 2.96 | 3.04 | 2.76 | |
| 3 | 3.13 | 2.92 | 2.62 | - | |
| 4 | 2.3 | 3.76 | 4.63 | - | |
| The best level | 4 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| R | −1.77 | −0.84 | −2.18 | −0.85 | |
| Level quantity | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 | |
| r | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | |
| d | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.71 | |
| −1.59 | −0.76 | −1.96 | −1.71 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Ou, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, S.; Huang, K.; Zhang, X. Upper Shallow Foundation Pit Engineering: Utilization and Evaluation of Portal Frame Anti-Heave Structures. Buildings 2025, 15, 1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15111943
He J, Ou J, Chen X, Liu S, Huang K, Zhang X. Upper Shallow Foundation Pit Engineering: Utilization and Evaluation of Portal Frame Anti-Heave Structures. Buildings. 2025; 15(11):1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15111943
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jun, Jinping Ou, Xiangsheng Chen, Shuya Liu, Kewen Huang, and Xu Zhang. 2025. "Upper Shallow Foundation Pit Engineering: Utilization and Evaluation of Portal Frame Anti-Heave Structures" Buildings 15, no. 11: 1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15111943
APA StyleHe, J., Ou, J., Chen, X., Liu, S., Huang, K., & Zhang, X. (2025). Upper Shallow Foundation Pit Engineering: Utilization and Evaluation of Portal Frame Anti-Heave Structures. Buildings, 15(11), 1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15111943






