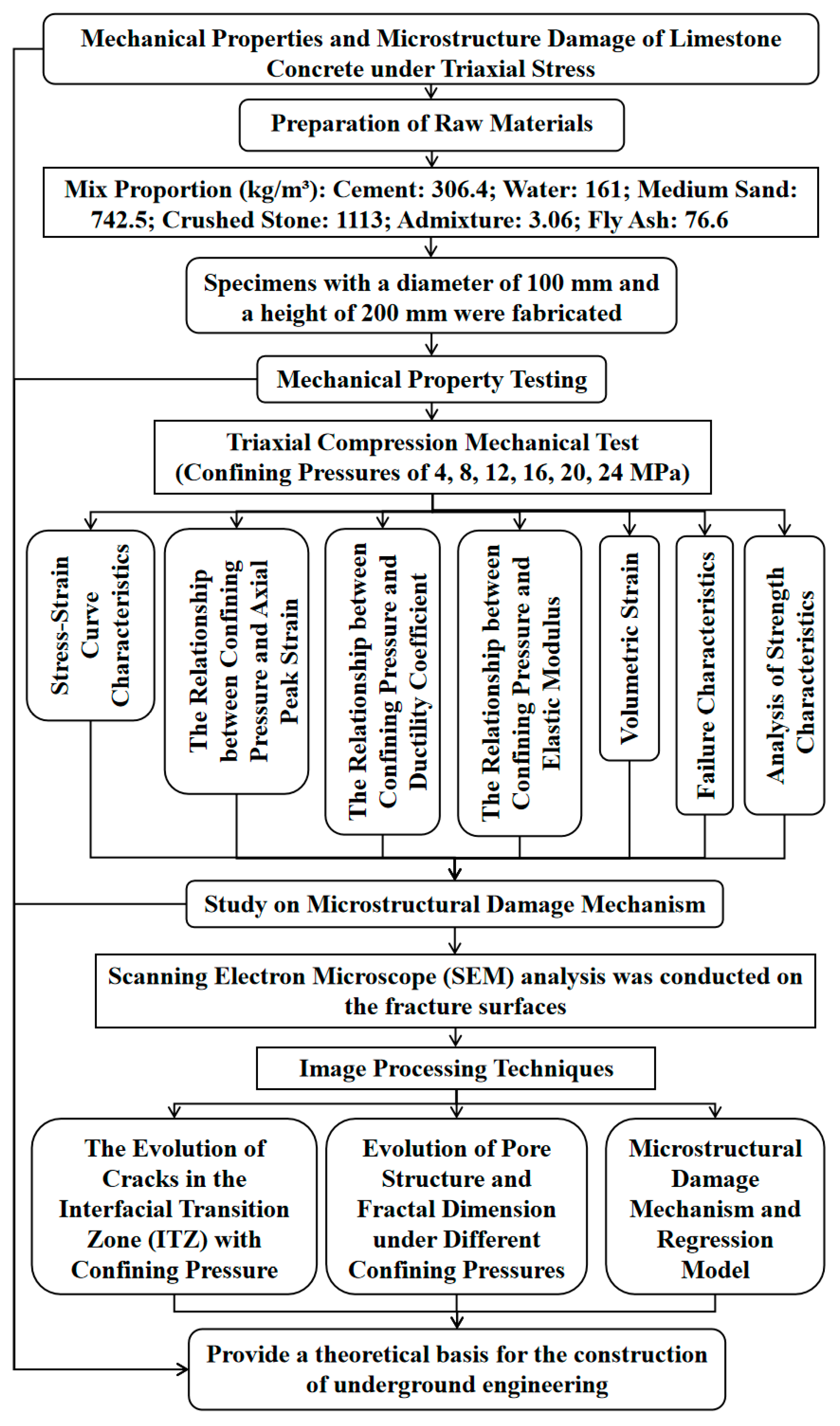
Mechanical Properties and Microstructure Damage of Limestone Concrete Under Triaxial Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Test Preparation
2.1. Raw Materials and Mix Proportion of Test Pieces
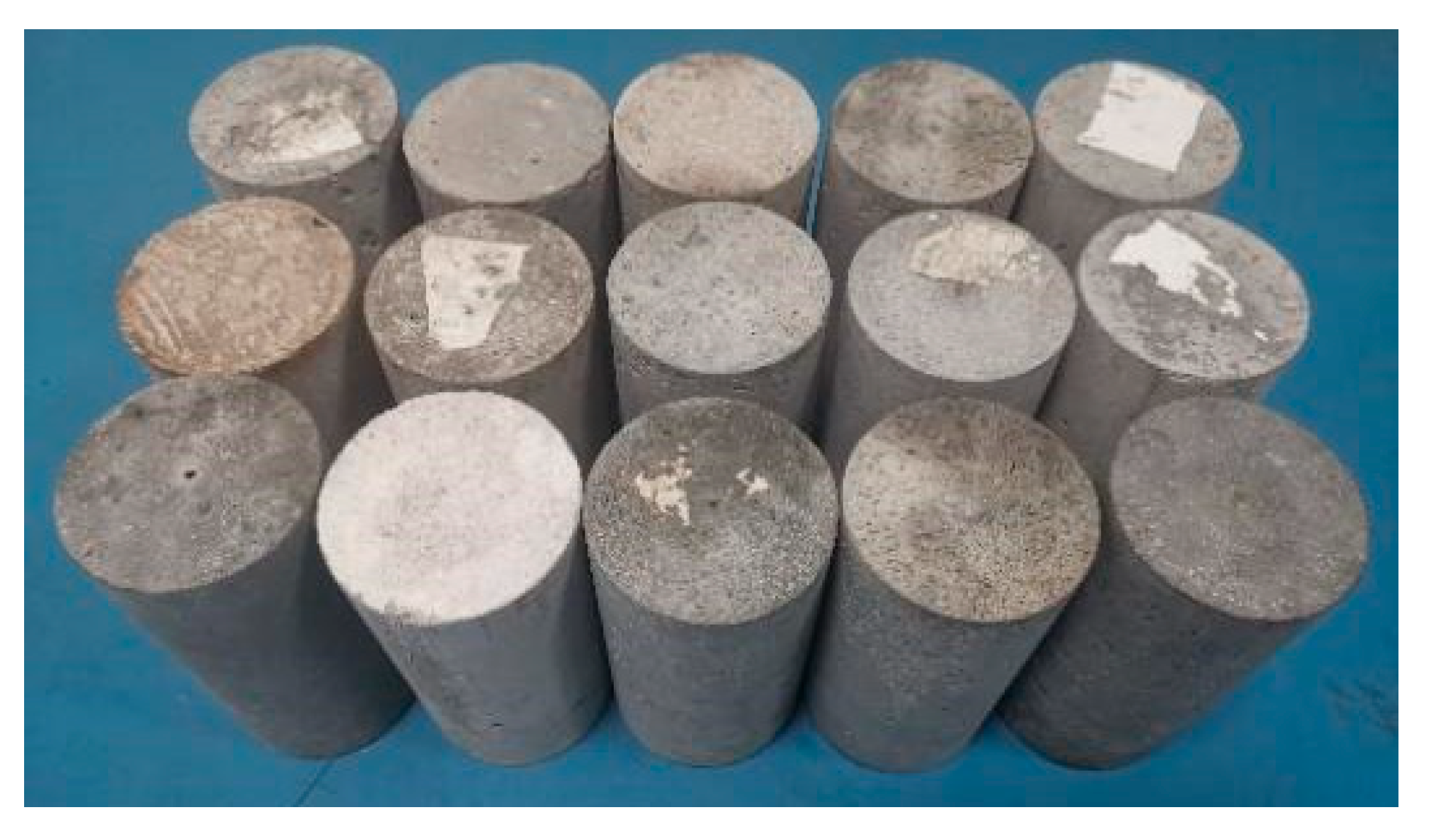
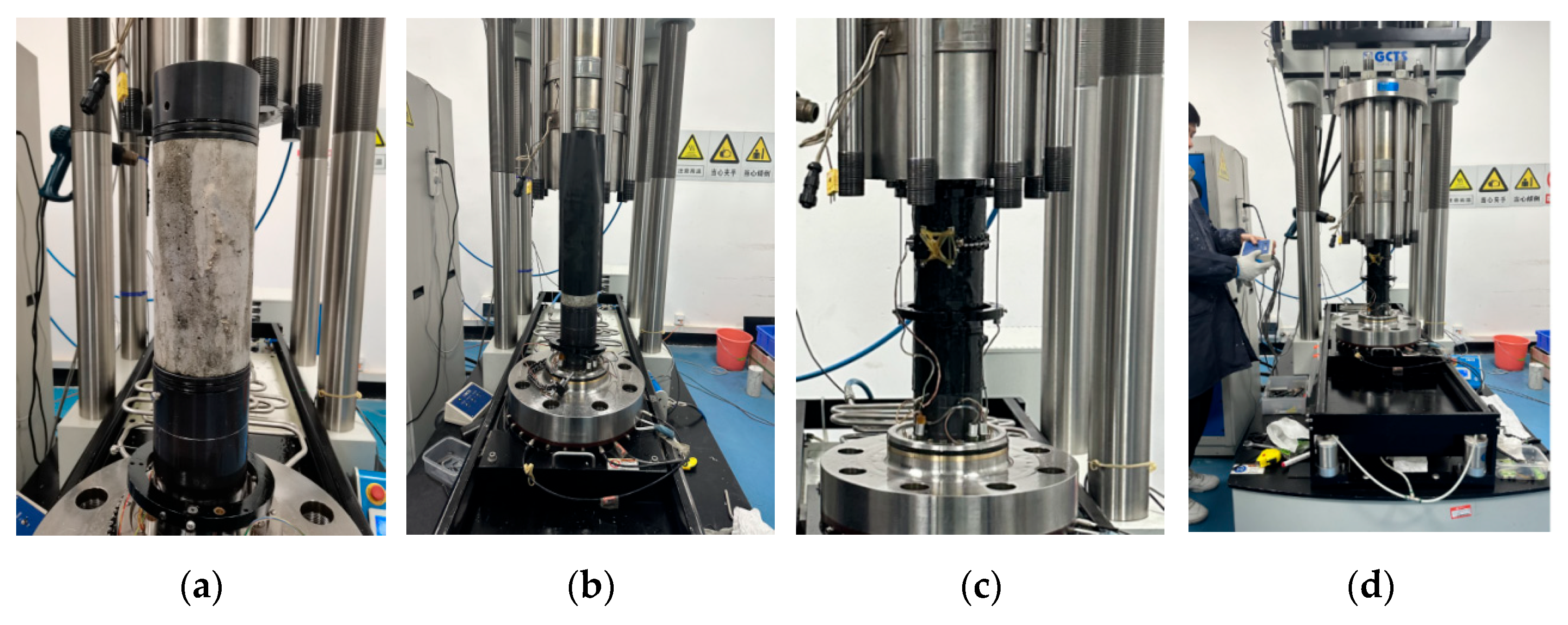
2.2. Sample Design and Fabrication
2.2.1. Triaxial Compression Test
2.2.2. Scanning Electron Microscope Test
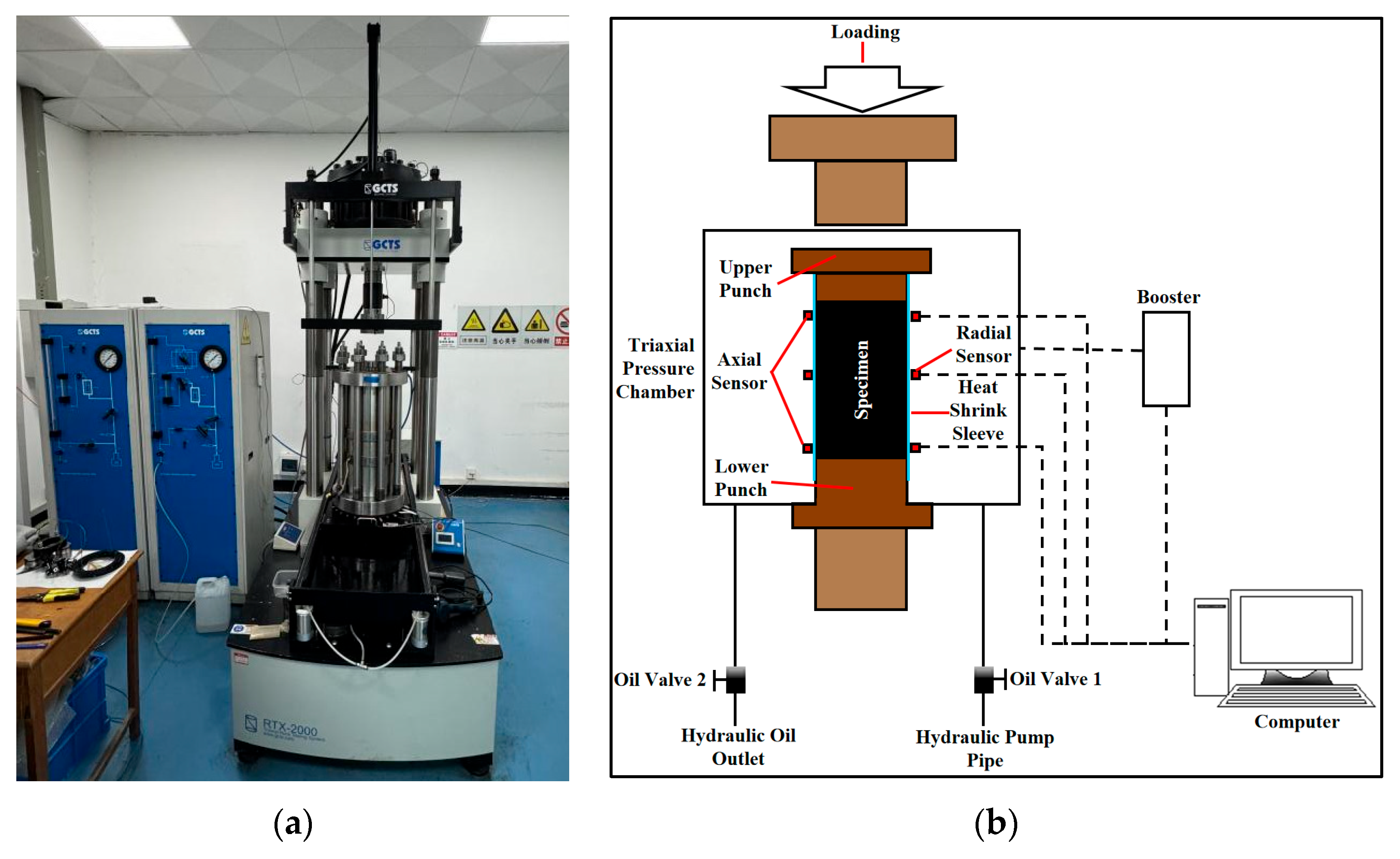
2.3. Test Device and Method
2.3.1. Triaxial Compression Test
2.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscope Test
3. Analysis of Mechanical Properties
3.1. Analysis of Deformation Characteristics
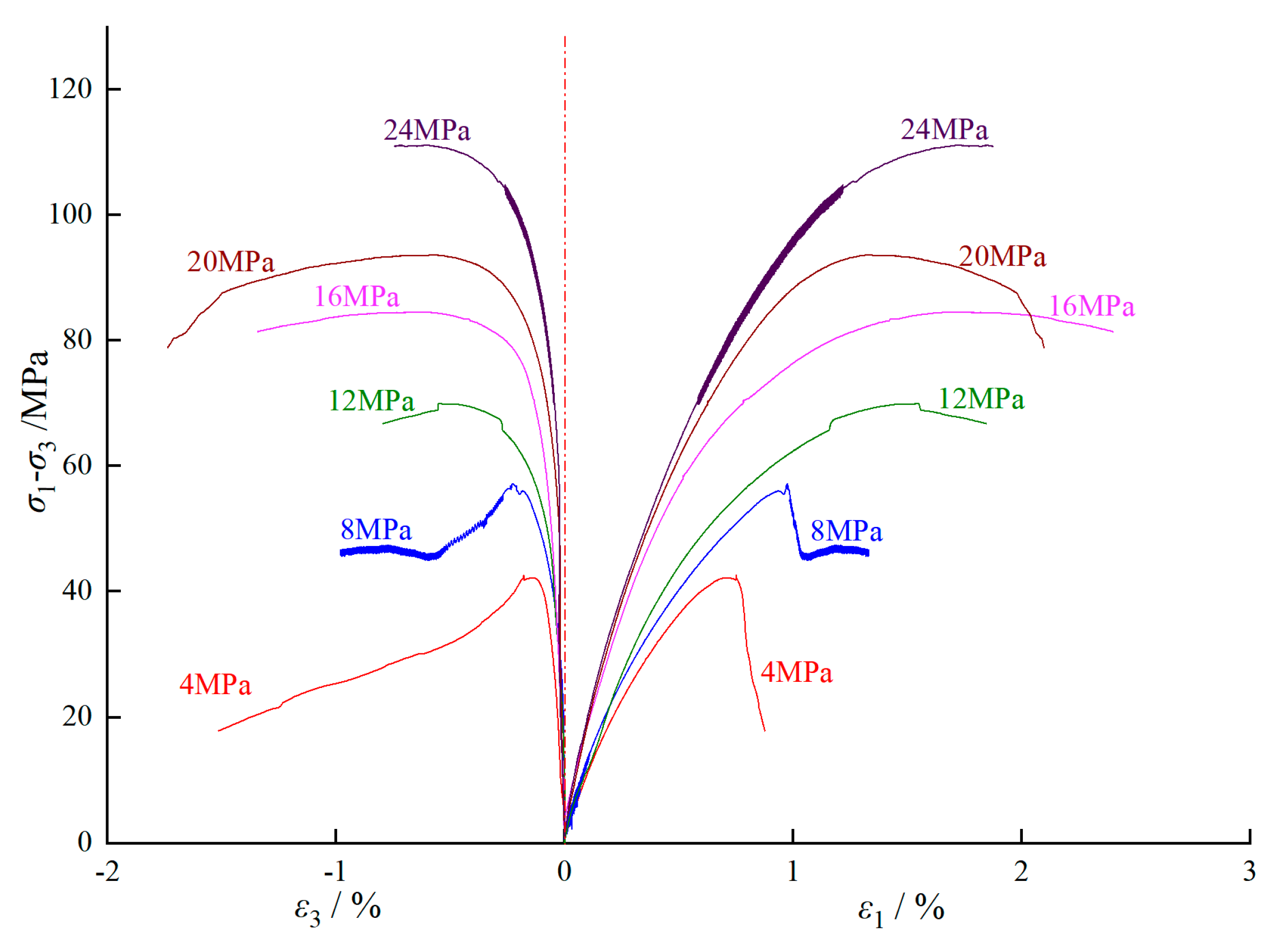
3.1.1. Characteristic Analysis of Deviatoric Stress–Strain Curve
3.1.2. Relationship Between Confining Pressure and Axial Peak Strain
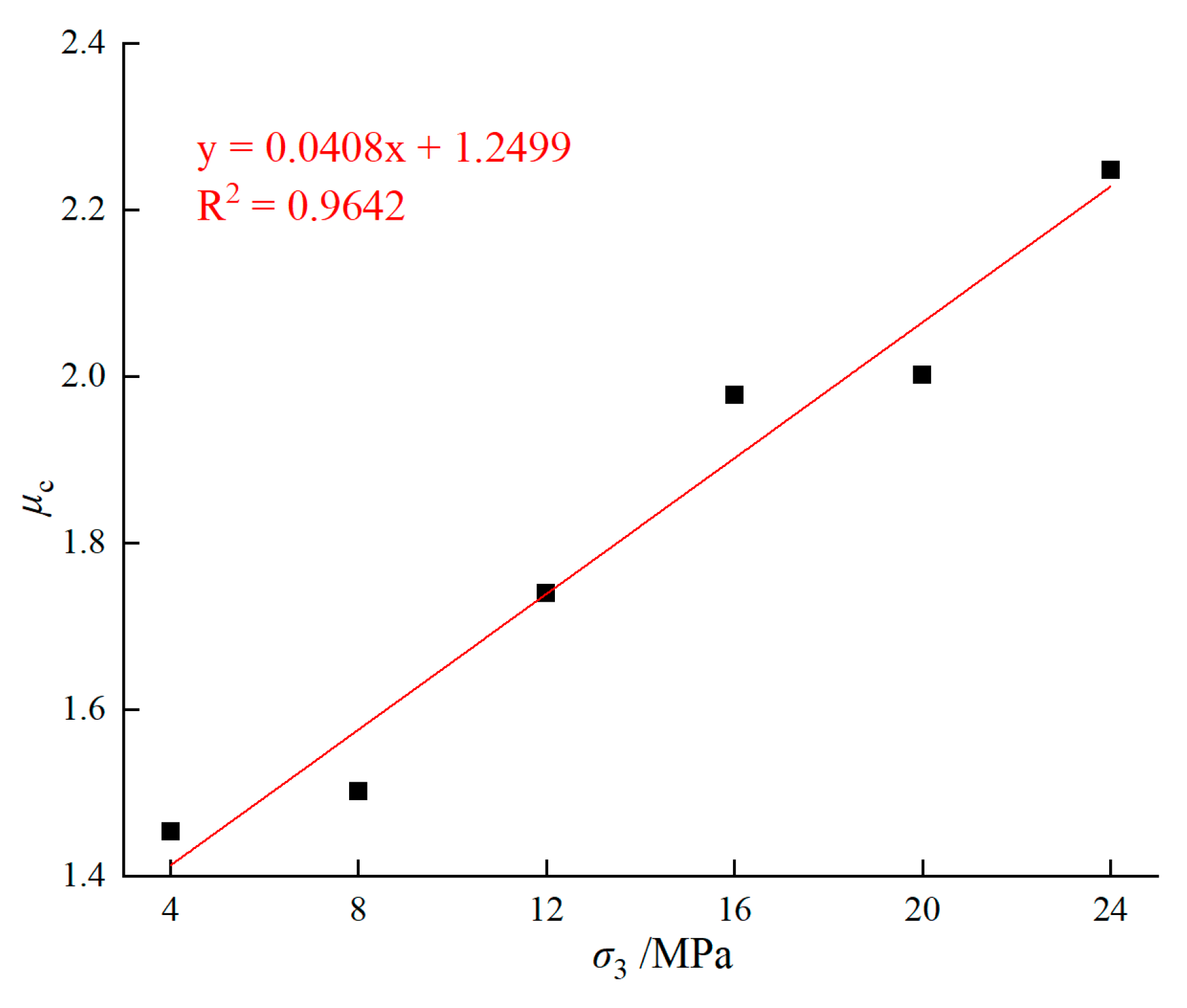
3.1.3. Relationship Between Confining Pressure and Ductility Coefficient
3.1.4. Relationship Between Confining Pressure and Elastic Modulus
3.1.5. Volumetric Strain
3.2. Analysis of Damage and Strength Characteristics of Limestone Crushed Stone Concrete
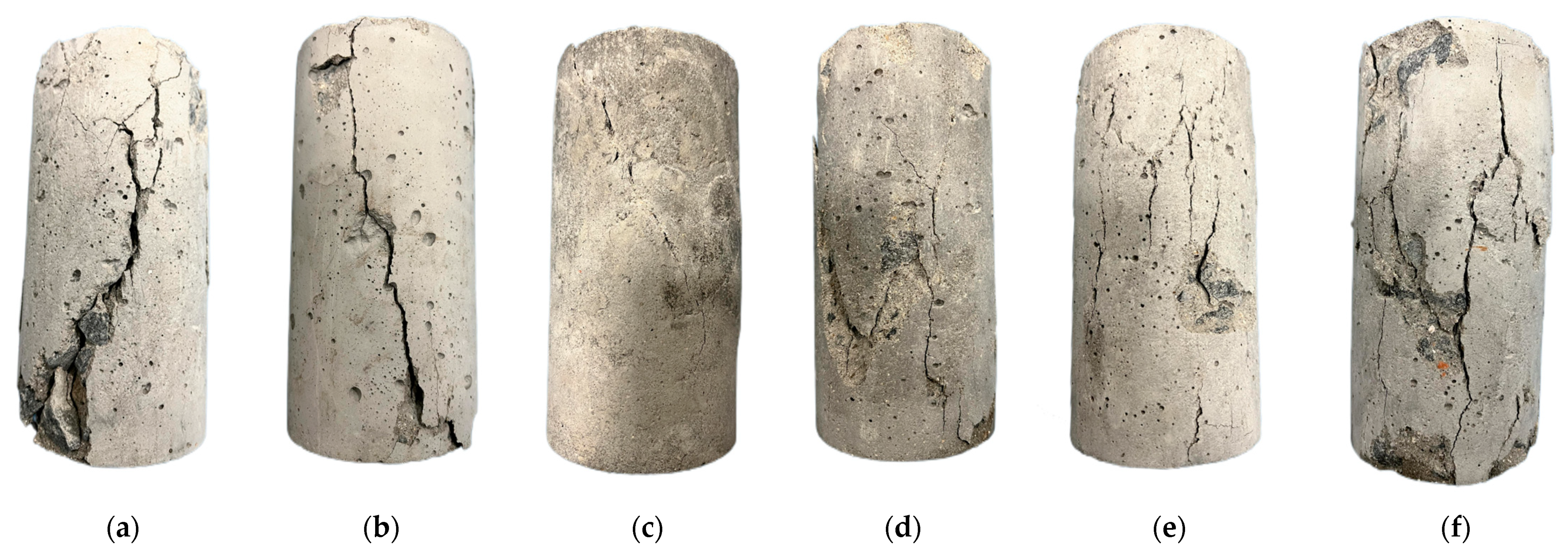
3.2.1. Damage Characteristics
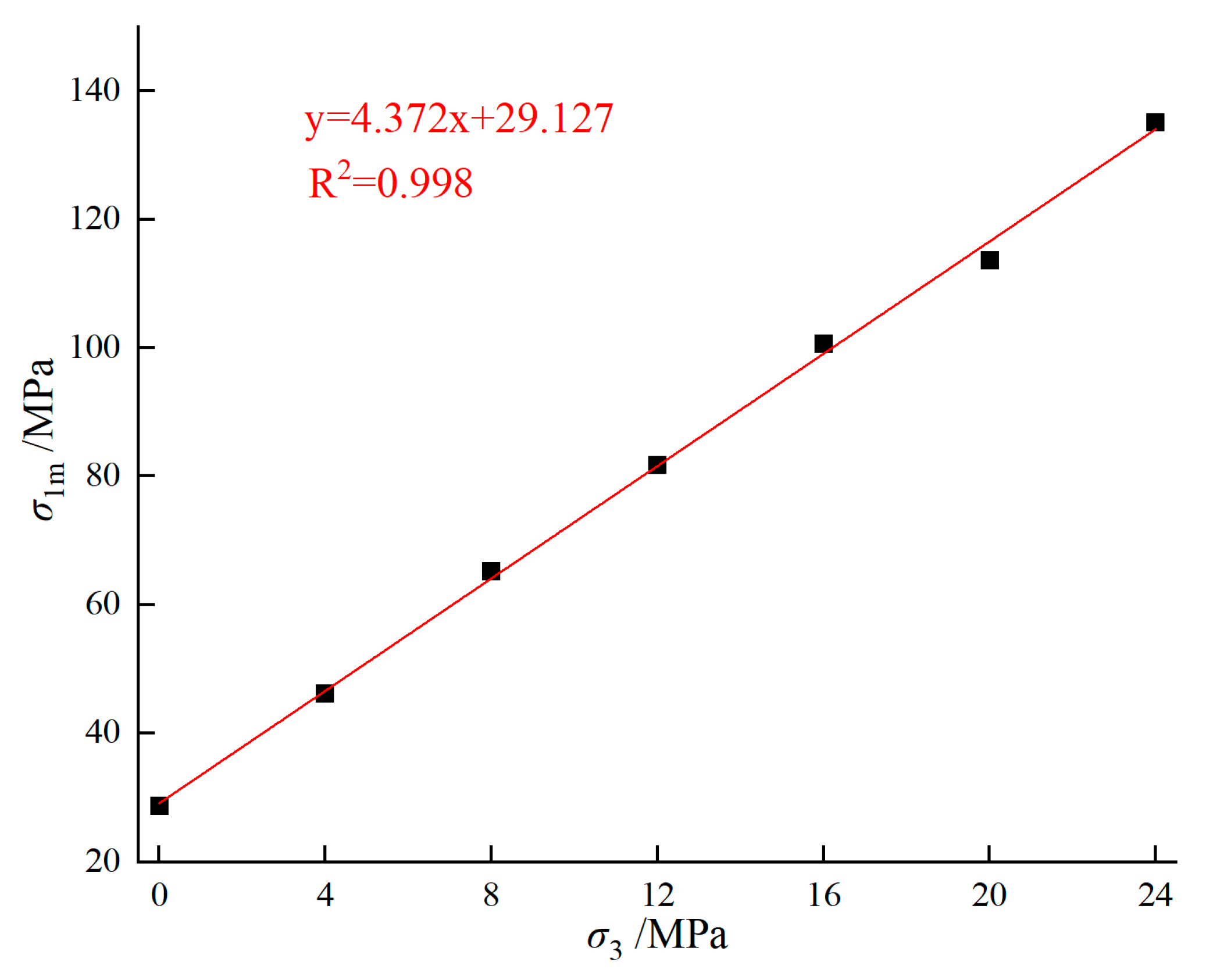
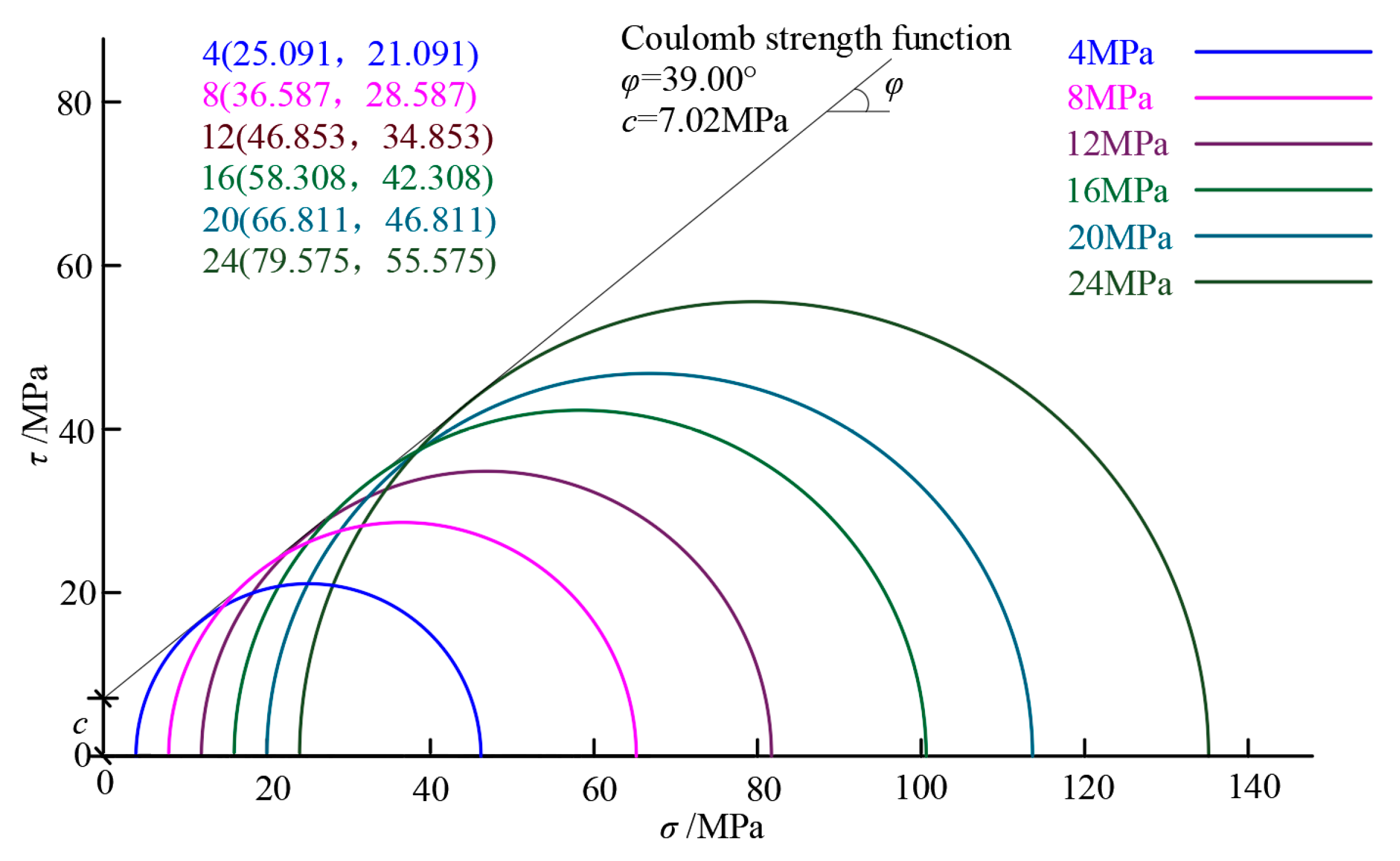
3.2.2. Analysis of Strength Characteristics of Limestone Crushed Stone Concrete
4. Research on Microstructural Damage Mechanism
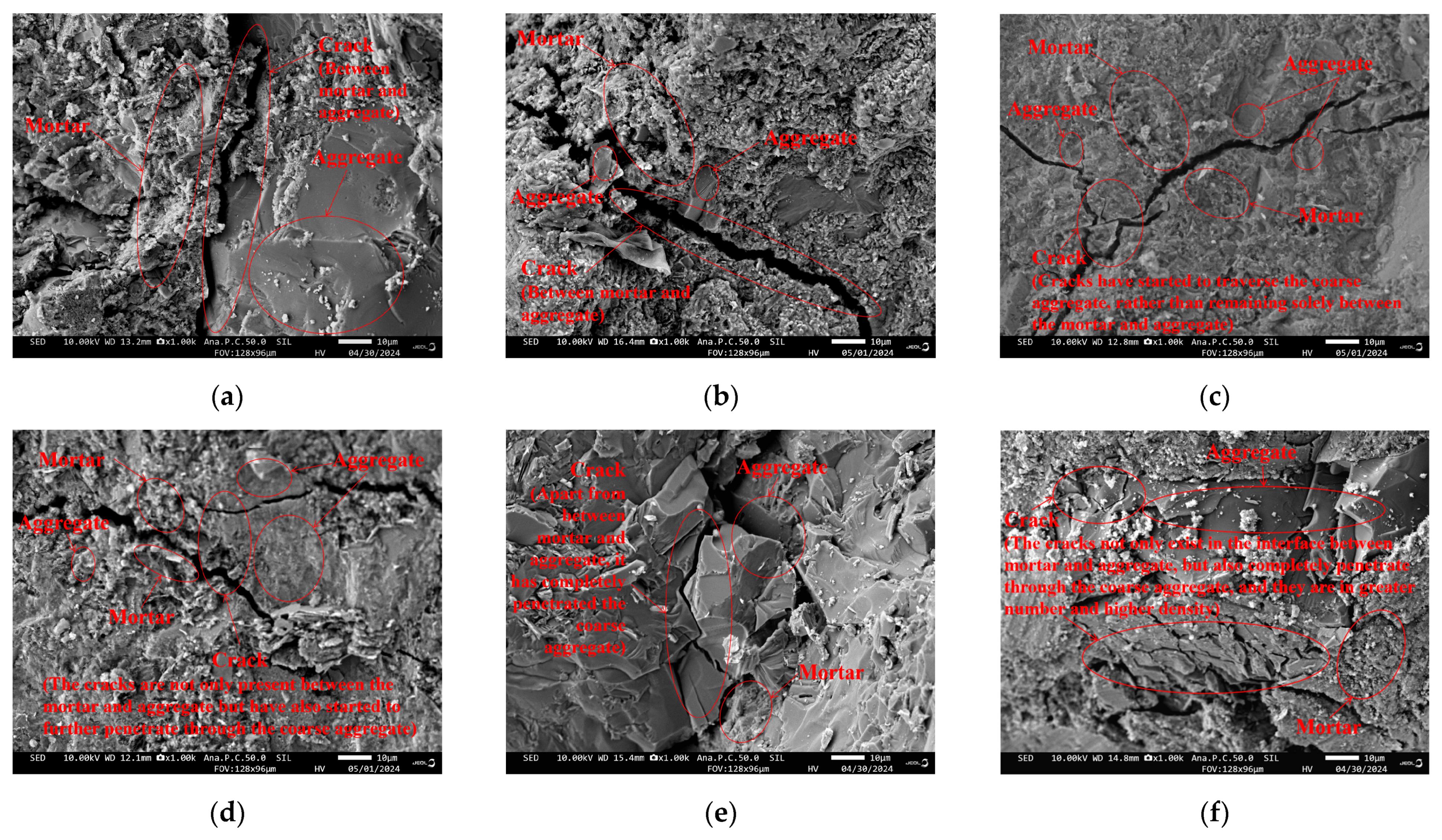
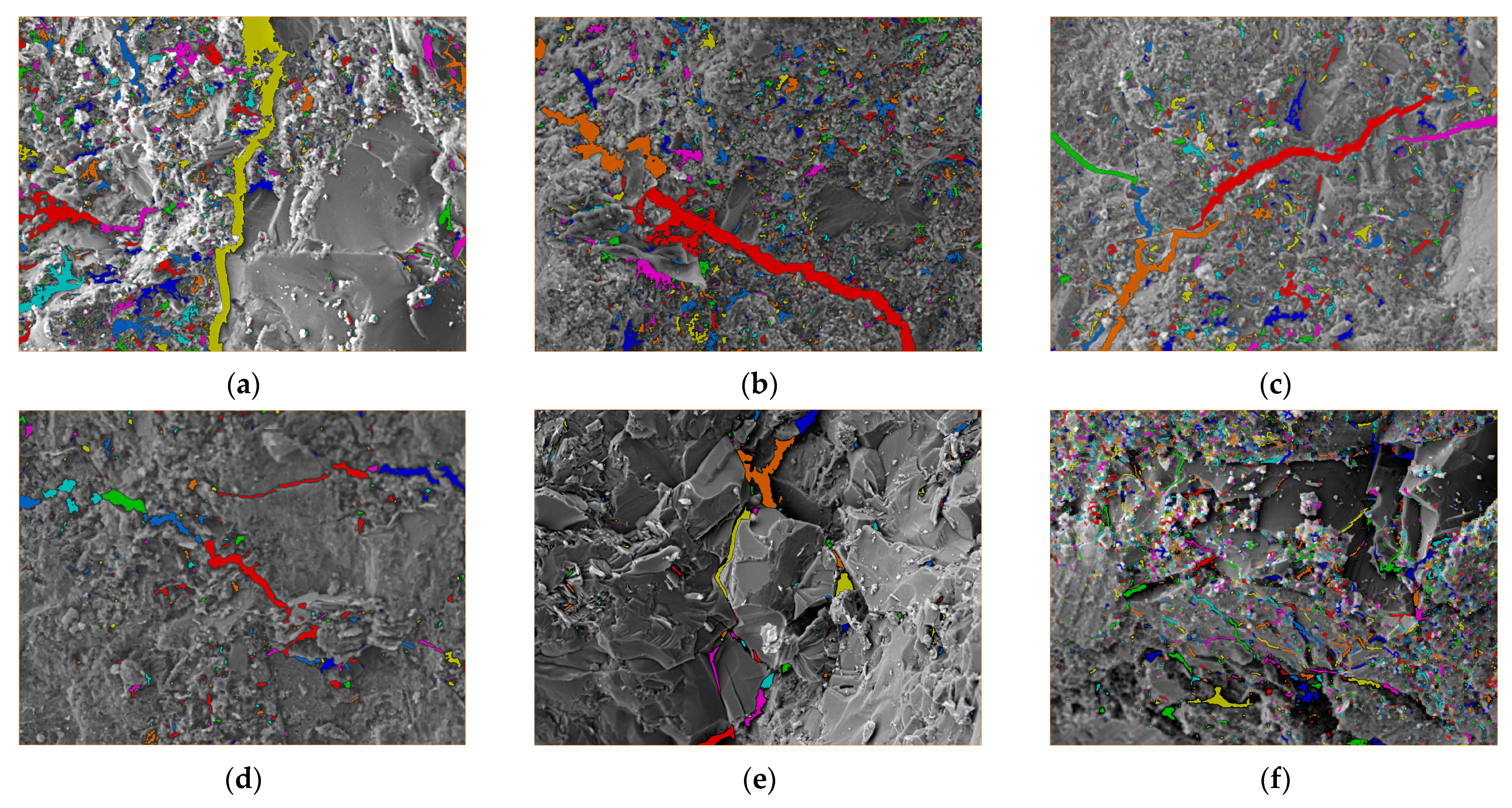
4.1. Evolution of Interface Transition Zone Cracks Under Different Confining Pressures
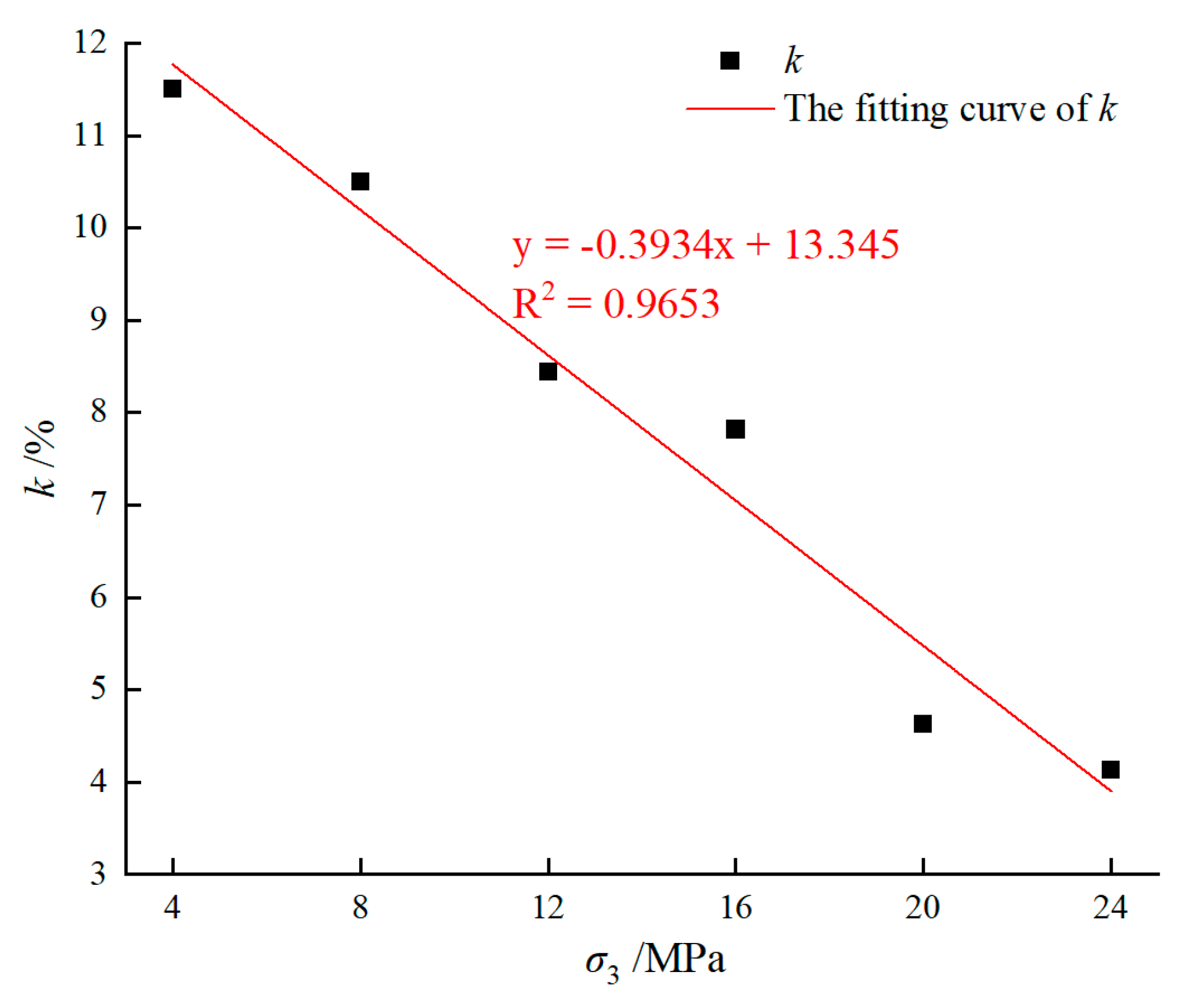
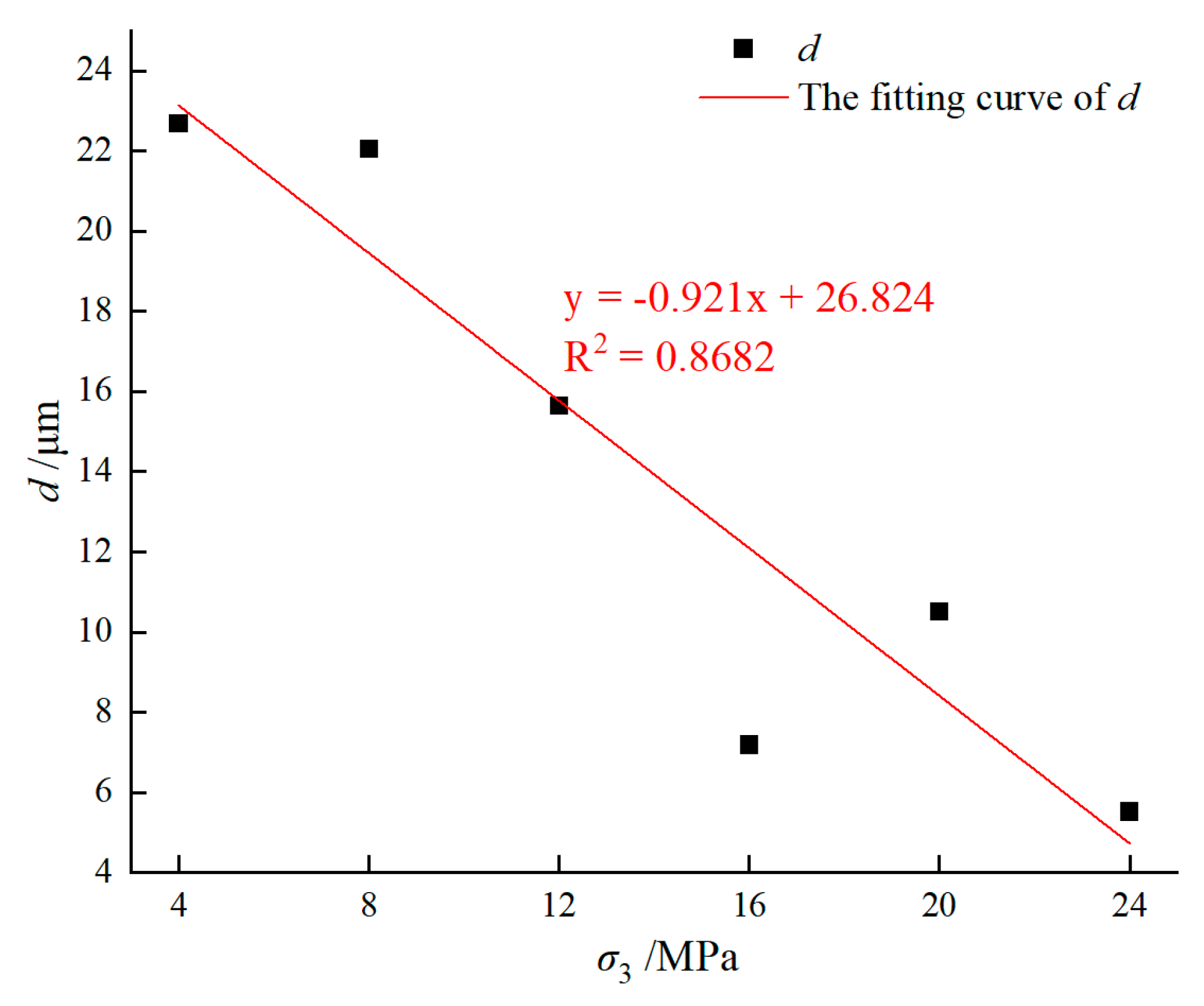
4.2. Evolution of Pore Structure and Fractal Dimension Under Different Confining Pressures
4.3. Microscopic Damage Mechanism and Regression Model
5. Discussion
5.1. Relationship Between Volumetric Strain and the Level of Micro-Cracking
5.2. Comparison and Analysis with Existing Research
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, Q.; Chang, J. Research Progress of Dark Matter Particle Explore. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, F.; Ding, Z.; Tang, J. Shanghai Jiao Tong University’s Institute of Advanced Technology Vice Director Liu Jianglai: Capturing dark matter 2,400 meters underground and repeatedly breaking international records. Everyday Econ. News 2024, 54. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, F.; Ding, Z.; Tang, J. Detecting dark matter in the world’s deepest and largest underground laboratory. Mil. Dig. 2024, 8, 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Ren, J.; Ding, Z.; Liu, Q. Failure mechanisms and stability control principles of high geostressed deep mining structures: Investigation by FDEM and field measurements. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2025, 169, 109233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gao, X.; Ding, Z.; Ma, H.; Ren, J.; Liu, Z. Fracture characteristic and support effect around deep lined tunnels using CGP-FDEM simulation and field investigation analysis. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2024, 161, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Wang, G.; Ge, T.; Bai, E.; Qin, L.; Zhao, J.; Liu, G. Dynamic compression mechanical behavior and strength prediction modeling of sulfate attacked concrete under triaxial static pre-loading. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 100, 111784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, F. Experimental study on mix proportion optimization of high performance concrete for tunnel secondary lining. Util. Fly. Ash 2021, 35, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Teng, M.; Song, Q.; Ding, X. Study on damage characteristics and impermeability of concrete under triaxial loading and unloading. Peoples Yangtze River 2024, 55, 195–202. [Google Scholar]
- Bousleh, A.; El Euch Khay, S. Shrinkage performance and modelling of concretes incorporating crushed limestone sand with a high content of fillers for pavement slabs. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2024, 28, 1696–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J.; Cheng, W. Experimental analysis on pre-stress friction loss of crushed limestone sand concrete beams. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsène, M.I.L.; Frédéric, C.; Nathalie, F. Improvement of lifetime of compressed earth blocks by adding limestone, sandstone and porphyry aggregates. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 29, 101155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanijaya, J.; Tappi, S. The mechanical properties of limestone as an aggregate on high strength concrete. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1088, 12098. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, L.; Wang, F.; Wu, H.; Duan, X. Mechanical Properties and Cracking Characteristics of UHPC with Hybrid Steel Fibers at Early Age under Different Curing Conditions. J. Ceram. Soc. Chin. 2022, 50, 429–437. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Wong, H.S.; Buenfeld, N.R. Effect of confining pressure and microcracks on mass transport properties of concrete. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2014, 113, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Niu, L.; Zhang, N.; Gu, J.; Dong, H. Study on mechanical properties and fracture characteristics of single cracked concrete under uniaxial compression. Concrete 2019, 10, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, S. Experimental investigation on triaxial mechanical properties of coral coarse aggregate-sea sand seawater concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 134213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, K.; Liu, P.; Su, Y. Triaxial Compressive Behaviour of Ultra-high Performance Geopolymer Concrete (UHPGC) and Its Applications in Contact Explosion and Projectile Impact Analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 449, 138394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, L.; Li, B.; Liu, S.; Chi, Y. Mechanical behavior and stress-strain model of steel-polypropylene hybrid fiber reinforced ultra-high performance concrete under triaxial compression. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 450, 138595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, P.; Sun, S.; Liu, M. Dynamic mechanical properties and failure criteria of concrete under biaxial compression. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2019, 5, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, N.; Chen, D.; Peng, G.; Xiao, J.; Xu, T. Mechanical properties of concrete under confining pressure after cyclic loading. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2017, 4, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Tugrul Tunc, E. Relationship Between Schmidt Hammer Rebound Hardness Test and Concrete Strength Tests for Limestone Aggregate Concrete Based on Experimental and Statistical Study. Materials 2025, 18, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yao, H.; Zhu, D.; Li, Y. Research on the conventional triaxial compressive properties of saturated concrete. Concrete 2015, 3, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Lin, H.; Chen, W.; Liang, S.; Huang, L. A numerical study on the tensile splitting of concrete with digital image processing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 1626–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Huang, S.; Ding, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Han, G.; Dai, Z. Mechanical behavior and failure characteristics of limestone-concrete specimens with different prefabricated fracture angles under compressive-shear loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 476, 141284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Y. Synergistic application of weathered granite and recycled coarse aggregate in concrete: Mechanical properties and microstructural mechanisms. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 482, 141695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Abdelaziz, M.; Farid, A.; Osman, K. Nano-Zeolite-Modified Concrete: A Comprehensive Study of Mechanical Properties, Corrosion Resistance, and Microstructural of Concrete under Varied Exposure Conditions. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2025, 25, 100900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buettner, N.; Iyacu, G.; Dal Poggetto, G.; Akono, A.T. The Effect of Carbon Nanofibers on the Microstructure, Chemistry, and Pore Structure of Concrete Made with Fine Recycled Concrete Aggregates. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Liu, Y.; Gao, R.; Li, C.; Chen, J.; Ye, C. Study on the influence mechanism of interfacial inclination angle on the mechanical behavior of coal and concrete specimens. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 443, 137787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Wan, Y.; Liu, W.J.; Huang, S.; Qin, Q. Influence of different porosity on concrete strength under high stress level. Hunan Transp. Sci. Technol. 2021, 47, 27–30+59. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, K.; Lu, W.; Zhou, C.; Chen, B.; Dong, C. Effect of carbonation on mesostructures and mechanical properties of dam concrete. Adv. Sci. Technol. Hydr. Eng. 2025, 45, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Li, H.; Huang, F.; Li, L.; Dong, H.; Yang, Z. Study on uniaxial compressive properties and microfracture toughness of interface transition zones in recycled sand concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 477, 141365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Xie, F.; Yang, T.; Han, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y. Fractal dimension analysis of concrete specimens under different strain rates. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 76, 107044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JGJ 55-2019; Code for Mix Proportion Design of Ordinary Concrete. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- GB/T 50081-2019; Standards for Test Methods of Physical and Mechanical Properties of Concrete. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- GB/T 17361-2013; Microbeam Analysis - Identification of Authigenic Clay Mineral in Sedimentary Rock by Scanning Electron Microscope and Energy Dispersive Spectrometer. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- ASTM D7012-14e1; Standard Test Methods for Determination of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Nitrogen in Petroleum Products and Lubricants. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, H.; Wang, X. Energy evolution law and failure criterion of high strength concrete under conventional triaxial compression. J. Jilin Univ. 2025, 55, 974–985. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, M.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Qin, L.; Liang, Y.; Chen, Z. Investigation on triaxial compressive mechanical properties of glass fiber coral seawater concrete. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2023, 40, 3459–3472. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, K.; Zhu, J.; Lu, X. Study of mechanical properties of raw coal under high stress with triaxial compression. Chin. J. Rock. Mech. Eng. 2014, 33, 24–34. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, M.F. Rock Mechanics and Engineering; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 219–228. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.F.; Salop, A.F. Elasticity and Plasticity; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 281–301. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xiao, T.; Wang, B.; Xu, P. Experimental study of Jinping II hydropower station marble under loading and unloading stress paths. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2012, 31, 882–889. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, D.; Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.; Han, Z.; Liu, Y. Quantitative analysis of pore structure’s impact on early mechanical properties and durability of foam concrete: Macroscopic and mesoscopic insights. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 459, 139775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M. Fracal Theory and Its Applications to Porous Media, Rough Surface Ard Thermal Contact Conductance; Huazhong University of Science and Technology: Wuhan, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, W.; Qi, Q.; Zhang, L. Study on fissure development rule of overlying strata influenced by mining based on fractal theory. J. Chin. Coal Soc. 2014, 39, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, H.; Kang, X.; Hu, J.; Ren, J. Study on fractal characteristics of overburden fracture evolution in coal seam mining under the influence of double faults. Min. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 25, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C. Quantitative Analysis of the Spatial Pattern of Ding Village Settlement in Xiangfen County Based on the Integration of Urban Form and Geographic Information; Beijing Jiaotong University: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. Study on the Influence of Pre-Existing Microcracks on Rock Crushing Performance; Jilin University: Changchun, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Ma, Y.; Peng, N. Study on the correlation between fractal dimension values of Dongting Lake drainage system based on DEM and geological disasters. Earth Sci. Front. 2025. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.3370.p.20250423.0946.002 (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Qin, B. Experimental study on strength and deformation feature of hybrid-fiber high-strength concrete under conventional triaxial compression. J. Henan Polytech. Univ. 2013, 32, 225–229. [Google Scholar]














| Material | Cement | Water | Medium Sand | Crushed Stone | Admixture | Fly Ash |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volume mass/kg/m3 | 306.40 | 161.00 | 742.50 | 1113.00 | 3.06 | 76.60 |
| Number | / MPa | H/ mm | D/ mm | / MPa | / 10–2 | / 10–2 | / 10–2 | E/ GPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC-04-1 | 4.00 | 200 | 100 | 46.18 | 0.71 | −0.14 | 0.42 | 6.15 |
| LC-08-2 | 8.00 | 200 | 100 | 65.17 | 0.97 | −0.23 | 0.52 | 7.03 |
| LC-12-1 | 12.00 | 200 | 100 | 81.71 | 1.51 | −0.52 | 0.47 | 9.12 |
| LC-16-1 | 16.00 | 200 | 100 | 100.62 | 1.73 | −0.65 | 0.43 | 11.84 |
| LC-20-2 | 20.00 | 200 | 100 | 113.62 | 1.36 | −0.61 | 0.14 | 13.80 |
| LC-24-2 | 24.00 | 200 | 100 | 135.15 | 1.73 | −0.62 | 0.51 | 14.39 |
| σ3/MPa | 4 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 20 | 24 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k/% | 11.5 | 10.5 | 8.4 | 7.8 | 4.6 | 4.1 |
| d/μm | 22.681 | 22.049 | 15.653 | 7.182 | 10.503 | 5.515 |
| D | 1.442 | 1.427 | 1.401 | 1.303 | 1.233 | 1.160 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, K.; Zhao, S.; Wang, D.; Yue, W.; Sun, C.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Q. Mechanical Properties and Microstructure Damage of Limestone Concrete Under Triaxial Stress. Buildings 2025, 15, 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15111924
Liu K, Zhao S, Wang D, Yue W, Sun C, Xia Y, Wang Q. Mechanical Properties and Microstructure Damage of Limestone Concrete Under Triaxial Stress. Buildings. 2025; 15(11):1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15111924
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Kaide, Songxin Zhao, Dingbo Wang, Wenping Yue, Chaowei Sun, Yu Xia, and Qiyu Wang. 2025. "Mechanical Properties and Microstructure Damage of Limestone Concrete Under Triaxial Stress" Buildings 15, no. 11: 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15111924
APA StyleLiu, K., Zhao, S., Wang, D., Yue, W., Sun, C., Xia, Y., & Wang, Q. (2025). Mechanical Properties and Microstructure Damage of Limestone Concrete Under Triaxial Stress. Buildings, 15(11), 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15111924





