Irregular Openings Identification at Construction Sites Based on Few-Shot Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
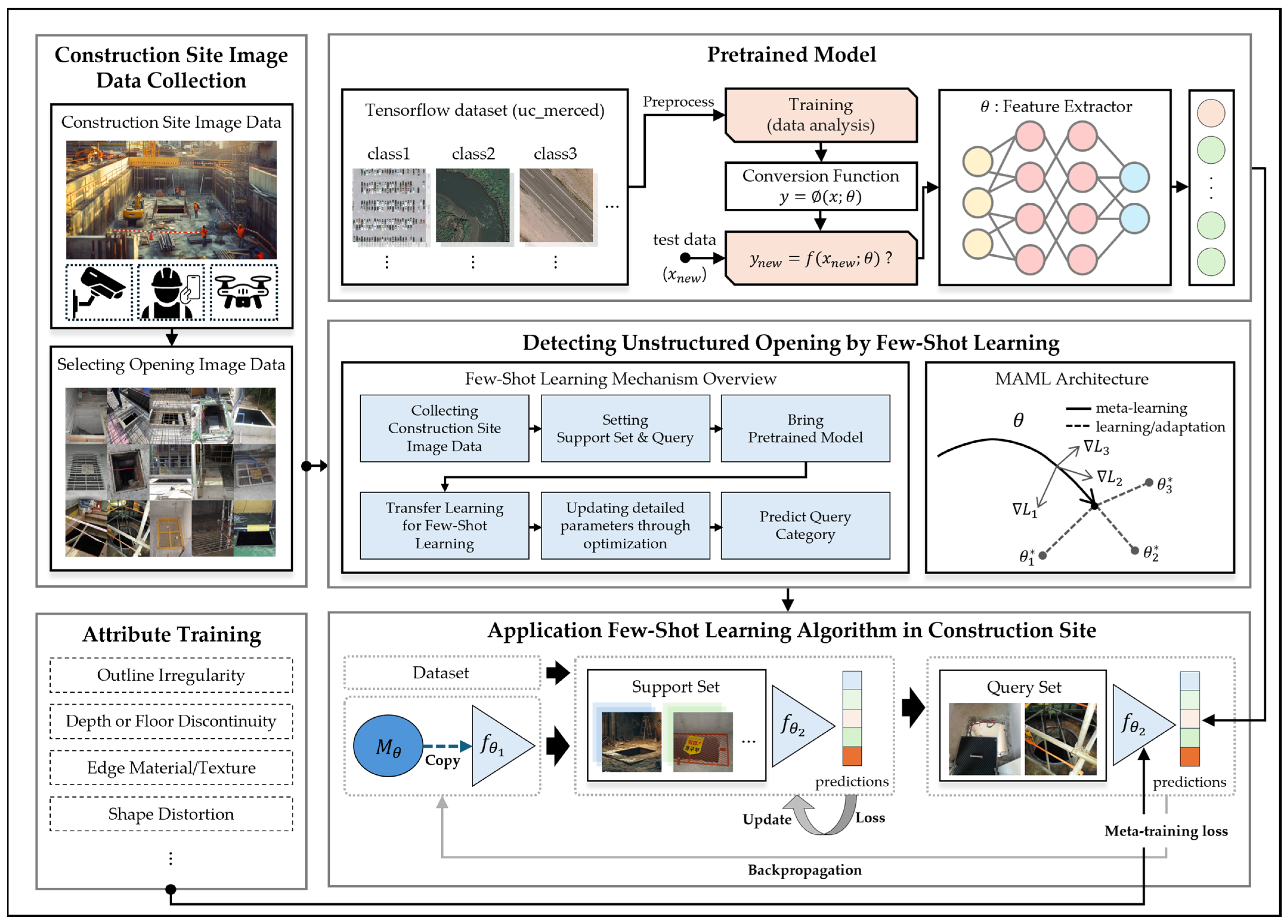
2.1. Framework for FSL in Construction
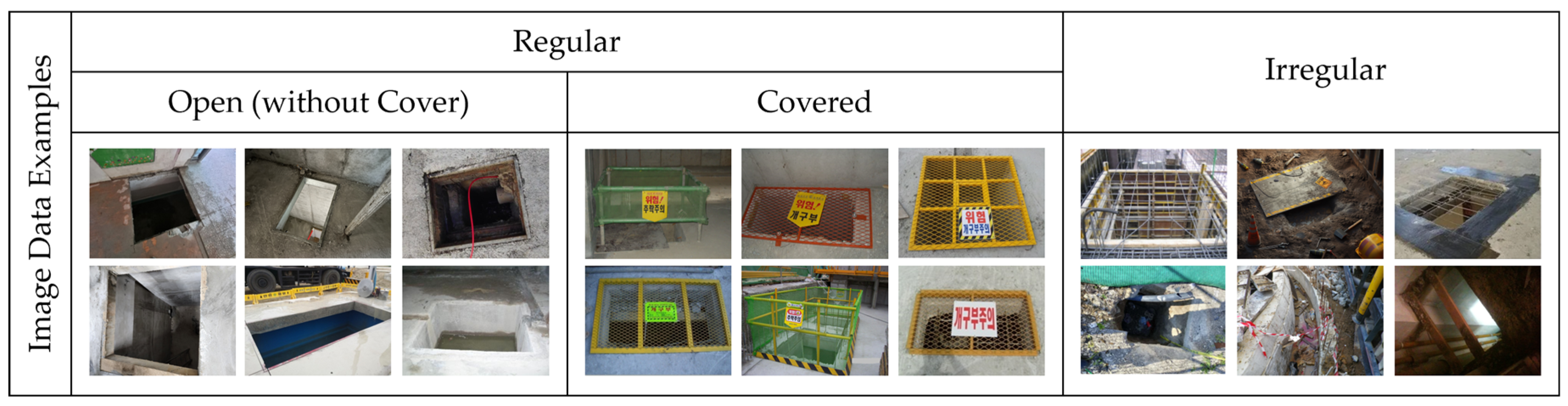
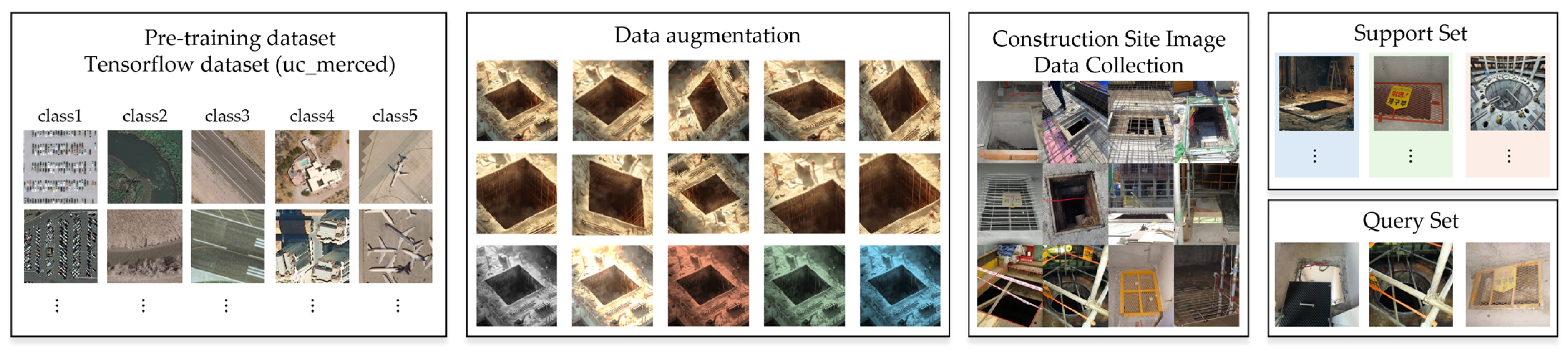
2.2. Dataset Development
2.3. FSL Model
2.3.1. Model Architecture
2.3.2. Meta Learning: MAML Algorithm
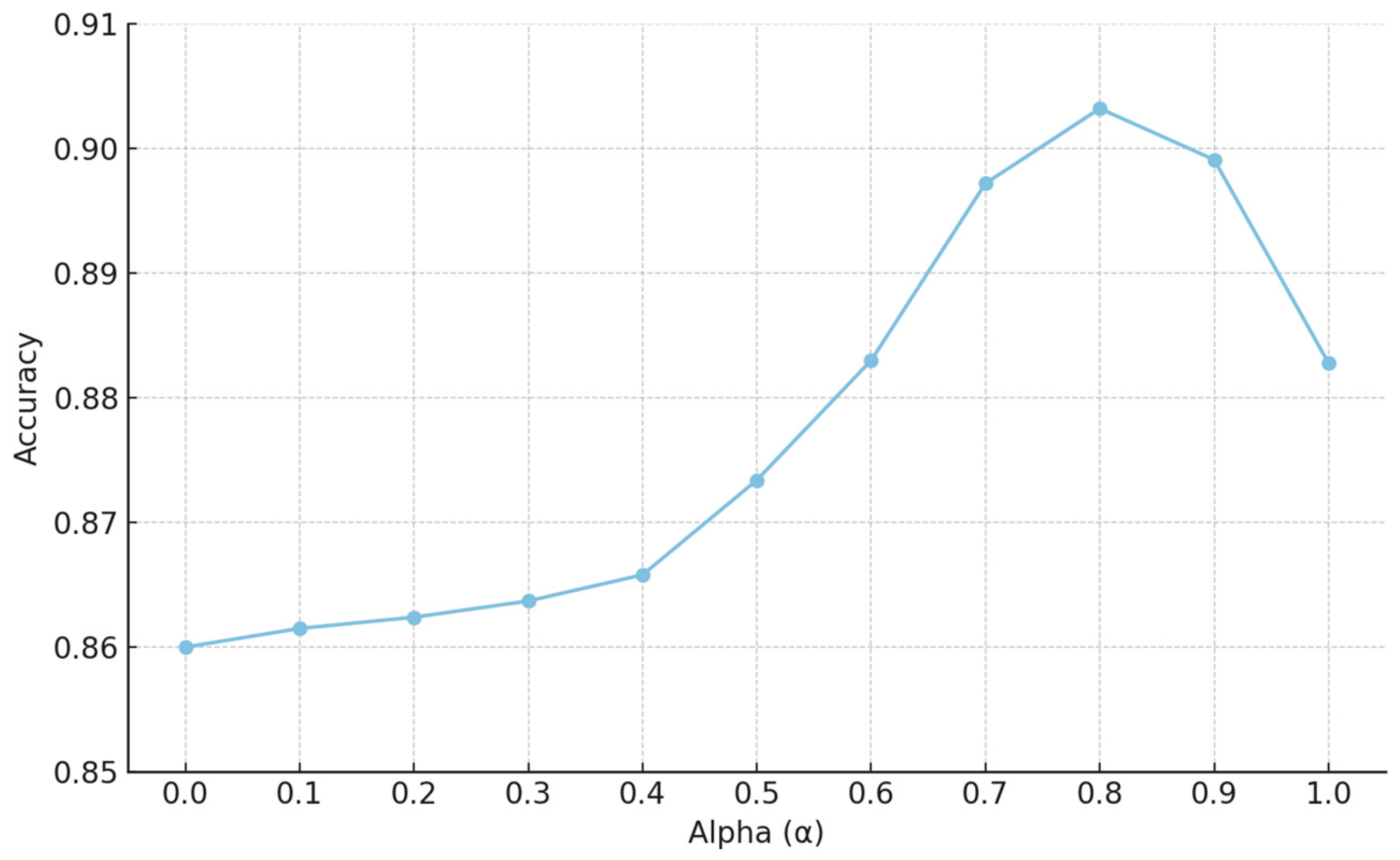
2.3.3. Attribute-Based Enhancement
2.4. Experimental Setup
2.4.1. Data Preparation and Splitting
2.4.2. Implementation and Hyperparameters
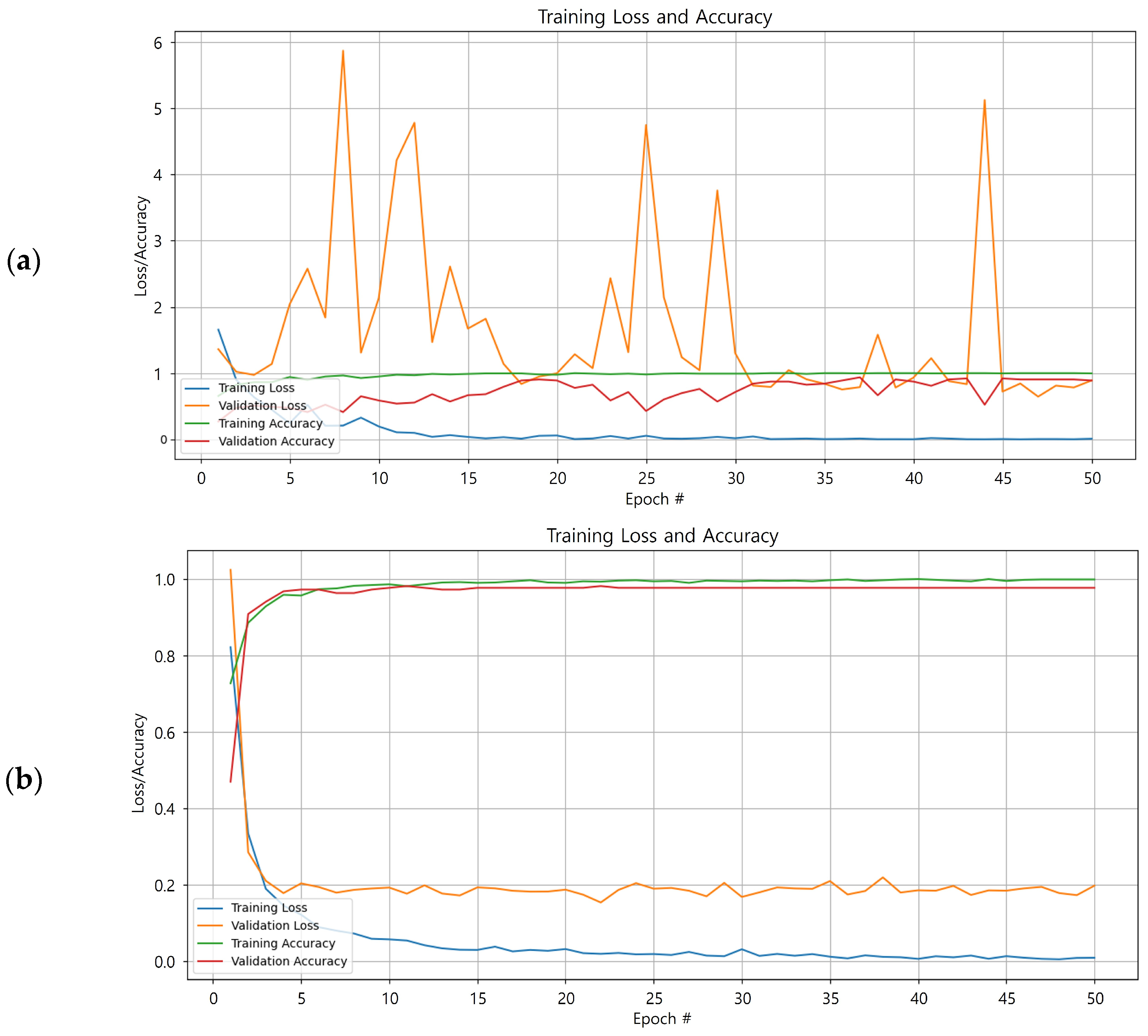
3. Results
3.1. Performance of the Proposed FSL Model
3.2. Comparison: FSL vs. Conventional Supervised Approach
3.3. Comparison Between the Base MAML and Advanced MAML Algorithms
4. Discussion
4.1. Potential Applications of FSL for Hazard Identification
4.2. Contributions
4.3. Limitations and Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Son, S.; Na, Y.; Han, B. Assessment of Risk Priorities by Cause of Construction Safety Accidents: A Case Study of Falling Accidents in South Korea. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.-G.; Ahn, C.R.; Yum, S.-G.; Oh, T.K. Establishment of Safety Management Measures for Major Construction Workers through the Association Rule Mining Analysis of the Data on Construction Accidents in Korea. Buildings 2024, 14, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-M.; Won, J.-H.; Jeong, H.-J.; Shin, S.-H. Identifying Critical Factors and Trends Leading to Fatal Accidents in Small-Scale Construction Sites in Korea. Buildings 2023, 13, 2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, D.; Kim, H. The Influence of Fatigue, Recovery, and Environmental Factors on the Body Stability of Construction Workers. Sensors 2024, 24, 3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Construction Site Fall Accidents to Be Gradually Reduced by 10% Each Year—Pressreleases—Report|Korea Occupational Safety and Health Agency (KOSHA). Available online: https://kosha.or.kr/kosha/report/pressreleases.do?mode=view&articleNo=454431&article.offset=0&articleLimit=10&srSearchVal=%EA%B1%B4%EC%84%A4&srSearchKey=article_title (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Dewlaney, K.S.; Hallowell, M. Prevention through Design and Construction Safety Management Strategies for High Performance Sustainable Building Construction. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2012, 30, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Hwang, S.; Kim, H. The Feasibility of Information-Entropy-Based Behavioral Analysis for Detecting Environmental Barriers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.S.; Park, M.; Hyun, H. Analysis of Safety Risk Factors of Modular Construction to Identify Accident Trends. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2022, 21, 1040–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Kulinan, A.S.; Tran, D.Q.; Bak, J.; Park, S. Preventing Falls from Floor Openings Using Quadrilateral Detection and Construction Worker Pose-Estimation. Autom. Constr. 2024, 165, 105536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Nnaji, C.; Khan, M.S.; Ibrahim, A.; Lee, D.; Park, C. Risk Factors and Emerging Technologies for Preventing Falls from Heights at Construction Sites. Autom. Constr. 2023, 153, 104955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.-F.; Chang, T.-C.; Ting, H.-I. Accident Patterns and Prevention Measures for Fatal Occupational Falls in the Construction Industry. Appl. Ergon. 2005, 36, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadhim, E.A.; Hon, C.; Xia, B.; Stewart, I.; Fang, D. Falls from Height in the Construction Industry: A Critical Review of the Scientific Literature. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Hinze, J. Analysis of Construction Worker Fall Accidents. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2003, 129, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fall Protection in Construction: Protecting Floor Openings. Available online: https://www.onlinesafetytrainer.com/fall-protection-in-construction-protecting-floor-openings/ (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Chi, C.-F. Accident Causes and Prevention Measures for Fatal Occupational Falls in the Construction Industry. In Fall Prevention and Protection; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1-315-37374-4. [Google Scholar]
- Winge, S.; Albrechtsen, E. Accident Types and Barrier Failures in the Construction Industry. Saf. Sci. 2018, 105, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobick, T.G.; McKenzie, E.A.; Kau, T.-Y. Evaluation of Guardrail Systems for Preventing Falls through Roof and Floor Holes. J. Saf. Res. 2010, 41, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liy, C.H.; Ibrahim, S.H.; Affandi, R.; Rosli, N.A.; Nawi, M.N.M. Causes of Fall Hazards in Construction Site Management. Int. Rev. Manag. Mark. 2016, 6, 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Navon, R.; Kolton, O. Algorithms for Automated Monitoring and Control of Fall Hazards. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2007, 21, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvi Newaz, M.; Ershadi, M.; Carothers, L.; Jefferies, M.; Davis, P. A Review and Assessment of Technologies for Addressing the Risk of Falling from Height on Construction Sites. Saf. Sci. 2022, 147, 105618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskutas, V.; Dale, A.M.; Nolan, J.; Patterson, D.; Lipscomb, H.J.; Evanoff, B. Fall Hazard Control Observed on Residential Construction Sites. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2009, 52, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaskati, D.; Kermanshachi, S.; Pamidimukkala, A.; Loganathan, K.; Yin, Z. A Review on Construction Safety: Hazards, Mitigation Strategies, and Impacted Sectors. Buildings 2024, 14, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellappa, V.; Salve, U.R. Fall Risk Assessment for Vertical Formwork Activities in Construction. ASCE-ASME J. Risk Uncertain. Eng. Syst. Part A Civ. Eng. 2023, 9, 04023027. Available online: https://ascelibrary.org/doi/abs/10.1061/AJRUA6.RUENG-958 (accessed on 1 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Shi, R.; Yang, Z. A Critical Review of Vision-Based Occupational Health and Safety Monitoring of Construction Site Workers. Saf. Sci. 2020, 126, 104658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Gambatese, J. Development of a Cost-Effective Proximity Warning System for Fall Protection. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2024, 2023, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Hwang, B.-G. Development of a Sensor-Based Safety Performance Analytic Mobile System to Detect, Alert, and Analyze Workers’ Unsafe Behaviors. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2024, 2023, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.M.; Alrasheed, K.A.; Waqar, A.; Almujibah, H.; Benjeddou, O. Internet of Things (IoT) for Safety and Efficiency in Construction Building Site Operations. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Luo, X.; Zheng, Z.; Ke, J. A Proactive Workers’ Safety Risk Evaluation Framework Based on Position and Posture Data Fusion. Autom. Constr. 2019, 98, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lu, M.; Hsu, S.-C.; Gray, M.; Huang, T. Proactive Behavior-Based Safety Management for Construction Safety Improvement. Saf. Sci. 2015, 75, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maali, O.; Ko, C.-H.; Nguyen, P.H.D. Applications of Existing and Emerging Construction Safety Technologies. Autom. Constr. 2024, 158, 105231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OSHA’s Fall Prevention Campaign—Educational Materials and Resources for Workers and Employers|Occupational Safety and Health Administration. Available online: https://www.osha.gov/stop-falls/educational-resources (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Choo, H.; Lee, B.; Kim, H.; Choi, B. Automated Detection of Construction Work at Heights and Deployment of Safety Hooks Using IMU with a Barometer. Autom. Constr. 2023, 147, 104714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, Y.; Kaneta, T.; Nishino, S. A Review of Monitoring Construction Equipment in Support of Construction Project Management. Front. Built Environ. 2022, 7, 632593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulinan, A.S.; Park, M.; Aung, P.P.W.; Cha, G.; Park, S. Advancing Construction Site Workforce Safety Monitoring through BIM and Computer Vision Integration. Autom. Constr. 2024, 158, 105227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Guo, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, R.; Hu, X.; Yang, R.; Wang, G. Multi-Task Intelligent Monitoring of Construction Safety Based on Computer Vision. Buildings 2024, 14, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Hong, S.; Choi, B.; Ham, Y.; Kim, H. Integrating Text Parsing and Object Detection for Automated Monitoring of Finishing Works in Construction Projects. Autom. Constr. 2025, 174, 106139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H. Feasibility of DRNN for Identifying Built Environment Barriers to Walkability Using Wearable Sensor Data from Pedestrians’ Gait. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Kim, H. Two-Step k-Means Clustering Based Information Entropy for Detecting Environmental Barriers Using Wearable Sensor. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wei, H.; Han, Z.; Jiang, N.; Wang, W.; Huang, J. Computer Vision-Based Hazard Identification of Construction Site Using Visual Relationship Detection and Ontology. Buildings 2022, 12, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Na, S.; Heo, S. Integrating Drone Imagery and AI for Improved Construction Site Management through Building Information Modeling. Buildings 2024, 14, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, S. Construction Site Safety Management: A Computer Vision and Deep Learning Approach. Sensors 2023, 23, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paneru, S.; Jeelani, I. Computer Vision Applications in Construction: Current State, Opportunities & Challenges. Autom. Constr. 2021, 132, 103940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Shaqib, S.M.; Ramit, S.S.; Khushbu, S.A.; Sattar, A.; Noori, S.R.H. A Deep Learning Approach to Detect Complete Safety Equipment For Construction Workers Based On YOLOv7. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.07707. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.; Kim, H. Occlusion-Aware Worker Detection in Masonry Work: Performance Evaluation of YOLOv8 and SAMURAI. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Ahn, C.R.; Kim, H. Deep Learning-Based Classification of Work-Related Physical Load Levels in Construction. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2020, 45, 101104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Cho, G.Y.; Kim, H. Performance Analysis of Wearable Robotic Exoskeleton in Construction Tasks: Productivity and Motion Stability Assessment. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Banna, V.; Vivek, N.; Goel, A.; Synovic, N.; Thiruvathukal, G.K.; Davis, J.C. Challenges and Practices of Deep Learning Model Reengineering: A Case Study on Computer Vision. Empir. Softw. Eng. 2024, 29, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Choi, B.; Ham, Y.; Jeon, J.; Kim, H. Massive-Scale Construction Dataset Synthesis through Stable Diffusion for Machine Learning Training. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2024, 62, 102866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Pan, W. Deep Learning-Based Object Detection for Dynamic Construction Site Management. Autom. Constr. 2024, 165, 105494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Lin, P.; Fan, Q.; Qiang, M. Real-Time Safety Risk Assessment Based on a Real-Time Location System for Hydropower Construction Sites. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 235970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Hwang, S. Pedestrian Visual Satisfaction and Dissatisfaction toward Physical Components of the Walking Environment Based on Types, Characteristics, and Combinations. Build. Environ. 2023, 244, 110776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbi, A.B.K.; Jeelani, I. AI Integration in Construction Safety: Current State, Challenges, and Future Opportunities in Text, Vision, and Audio Based Applications. Autom. Constr. 2024, 164, 105443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagabandi, A.; Clavera, I.; Liu, S.; Fearing, R.S.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S.; Finn, C. Learning to Adapt in Dynamic, Real-World Environments Through Meta-Reinforcement Learning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1803.11347. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Chi, S. A Few-Shot Learning Approach for Database-Free Vision-Based Monitoring on Construction Sites. Autom. Constr. 2021, 124, 103566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; El-Gohary, N. Few-Shot Object Detection and Attribute Recognition from Construction Site Images for Improved Field Compliance. Autom. Constr. 2024, 167, 105539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losada del Olmo, J.J.; Perales Gómez, Á.L.; López-de-Teruel, P.E.; Ruiz, A. A Few-Shot Learning Methodology for Improving Safety in Industrial Scenarios through Universal Self-Supervised Visual Features and Dense Optical Flow. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 167, 112375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, Q.; Kwok, J.T.; Ni, L.M. Generalizing from a Few Examples: A Survey on Few-Shot Learning. ACM Comput. Surv. 2020, 53, 63:1–63:34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, P.; Xie, W.; Zisserman, A. Label, Verify, Correct: A Simple Few Shot Object Detection Method. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 14237–14247. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Qiu, X.; Ren, B.; Fu, Y.; Timofte, R.; Sebe, N.; Yang, M.-H.; Gool, L.V.; Zhang, K.; Nong, Q.; et al. NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Cross-Domain Few-Shot Object Detection: Methods and Results. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.10685. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Hong, Y.; Mi, R.; Zhang, L.-J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y. A Survey on Anomaly Detection with Few-Shot Learning. In Proceedings of the Cognitive Computing—ICCC 2024, Bangkok, Thailand, 16–19 November 2024; Xu, R., Chen, H., Wu, Y., Zhang, L.-J., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 34–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Min, W.; Jiang, S. Attribute-Guided Feature Learning for Few-Shot Image Recognition. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 23, 1200–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Chang, X.; Liu, J.; Ge, Z.; Zheng, Q. Auto-FSL: Searching the Attribute Consistent Network for Few-Shot Learning. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porikli, F. Challenges of Computer Vision Research from an Industry Perspective. In Computer Vision; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; ISBN 978-1-00-332895-7. [Google Scholar]
- Madan, S.; Chaudhury, S.; Gandhi, T.K. Explainable Few-Shot Learning with Visual Explanations on a Low Resource Pneumonia Dataset. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2023, 176, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Shu, K.; Liu, C.; Liu, H. Graph Prototypical Networks for Few-Shot Learning on Attributed Networks. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, Virtual, 19–23 October 2020; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 295–304. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Xian, Y.; Wang, J.; Schiele, B.; Akata, Z. Attribute Prototype Network for Any-Shot Learning. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2022, 130, 1735–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Chang, H.; Guo, Z.; Ma, B.; Shan, S.; Chen, X. Understanding Few-Shot Learning: Measuring Task Relatedness and Adaptation Difficulty via Attributes. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 19397–19409. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Bao, Y.; Li, H. Few-Shot Learning for Structural Health Diagnosis of Civil Infrastructure. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2024, 62, 102650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, C.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S. Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning for Fast Adaptation of Deep Networks. In International Conference on Machine Learning; PMLR: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nichol, A.; Achiam, J.; Schulman, J. On First-Order Meta-Learning Algorithms. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.02999. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, F.; Chen, F.; Li, H. Meta-SGD: Learning to Learn Quickly for Few-Shot Learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.09835. [Google Scholar]
- Jamal, M.A.; Qi, G.-J. Task Agnostic Meta-Learning for Few-Shot Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 11719–11727. [Google Scholar]
- Zintgraf, L.; Shiarli, K.; Kurin, V.; Hofmann, K.; Whiteson, S. Fast Context Adaptation via Meta-Learning. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; PMLR: London, UK, 2019; pp. 7693–7702. [Google Scholar]
- Oreshkin, B.; Rodríguez López, P.; Lacoste, A. TADAM: Task Dependent Adaptive Metric for Improved Few-Shot Learning. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, H.-J.; Hu, H.; Zhan, D.-C.; Sha, F. Few-Shot Learning via Embedding Adaptation with Set-to-Set Functions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 8808–8817. [Google Scholar]
- Bertinetto, L.; Henriques, J.F.; Torr, P.H.S.; Vedaldi, A. Meta-Learning with Differentiable Closed-Form Solvers. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1805.08136. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Zou, S.; Zhou, W.; Huang, Y.; Shao, L.; Yuan, J.; Gou, X.; Jin, W.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; et al. Clinically Applicable Histopathological Diagnosis System for Gastric Cancer Detection Using Deep Learning. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, H.; Wu, J.; Dahal, S.; Joo, T.; Garg, N. Automated Estimation of Cementitious Sorptivity via Computer Vision. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.0 | |
| 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | |
| Accuracy | 0.8600 | 0.8615 | 0.8624 | 0.8637 | 0.8658 | 0.8734 | 0.8830 | 0.8972 | 0.9032 | 0.8991 | 0.8828 |
| K-Way N-Shot | Validation Accuracy | Recall | Precision | F1 Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K-Way | N-Shot | ||||
| Two-way | 1 | 0.8680 | 0.7525 | 0.6624 | 0.6916 |
| 2 | 0.9086 | 0.7998 | 0.7327 | 0.7601 | |
| 3 | 0.9343 | 0.8747 | 0.8084 | 0.8370 | |
| 5 | 0.9495 | 0.9222 | 0.8276 | 0.8668 | |
| 10 | 0.9596 | 0.9278 | 0.8580 | 0.8888 | |
| Three-way | 1 | 0.8255 | 0.6827 | 0.6494 | 0.6441 |
| 2 | 0.8440 | 0.7394 | 0.6956 | 0.7000 | |
| 3 | 0.8761 | 0.7999 | 0.7520 | 0.7570 | |
| 5 | 0.9054 | 0.8558 | 0.8018 | 0.8204 | |
| 10 | 0.9134 | 0.8832 | 0.8443 | 0.8598 | |
| Seed No. | Accuracy | Recall | Precision | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seed 1 (42) | 0.9054 | 0.8558 | 0.8018 | 0.8204 |
| Seed 2 (106) | 0.8967 | 0.8413 | 0.7922 | 0.8131 |
| Seed 3 (2024) | 0.9112 | 0.8625 | 0.8076 | 0.8322 |
| Seed 4 (77) | 0.9031 | 0.8504 | 0.7940 | 0.8187 |
| Seed 5 (9) | 0.9079 | 0.8612 | 0.7998 | 0.8284 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.9049 ± 0.0050 | 0.8542 ± 0.0086 | 0.7991 ± 0.0055 | 0.8226 ± 0.0074 |
| Model | Dataset | Accuracy | Recall | Precision | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet-50 | 15images | 0.4933 | 0.4867 | 0.5837 | 0.4606 |
| EfficientNetB0 | 15images | 0.6905 | 0.6771 | 0.6902 | 0.6629 |
| FSL model | 3way, 5shot | 0.9054 | 0.8558 | 0.8018 | 0.8204 |
| Model | Dataset | Accuracy | Recall | Precision | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base MAML | 3way, 5shot | 0.9054 | 0.8558 | 0.8018 | 0.8204 |
| CAVIA | 3way, 5shot | 0.9336 | 0.8774 | 0.8302 | 0.8516 |
| Meta-SGD | 3way, 5shot | 0.9268 | 0.8699 | 0.8196 | 0.8403 |
| Reptile | 3way, 5shot | 0.9221 | 0.8645 | 0.8133 | 0.8312 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, M.; Kim, H. Irregular Openings Identification at Construction Sites Based on Few-Shot Learning. Buildings 2025, 15, 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15111834
Seo M, Kim H. Irregular Openings Identification at Construction Sites Based on Few-Shot Learning. Buildings. 2025; 15(11):1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15111834
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Minjo, and Hyunsoo Kim. 2025. "Irregular Openings Identification at Construction Sites Based on Few-Shot Learning" Buildings 15, no. 11: 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15111834
APA StyleSeo, M., & Kim, H. (2025). Irregular Openings Identification at Construction Sites Based on Few-Shot Learning. Buildings, 15(11), 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15111834






