TMD-Inerter for Tall Building Damping: Approximate Closed-Form Solution, Performance and Conclusions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modelling
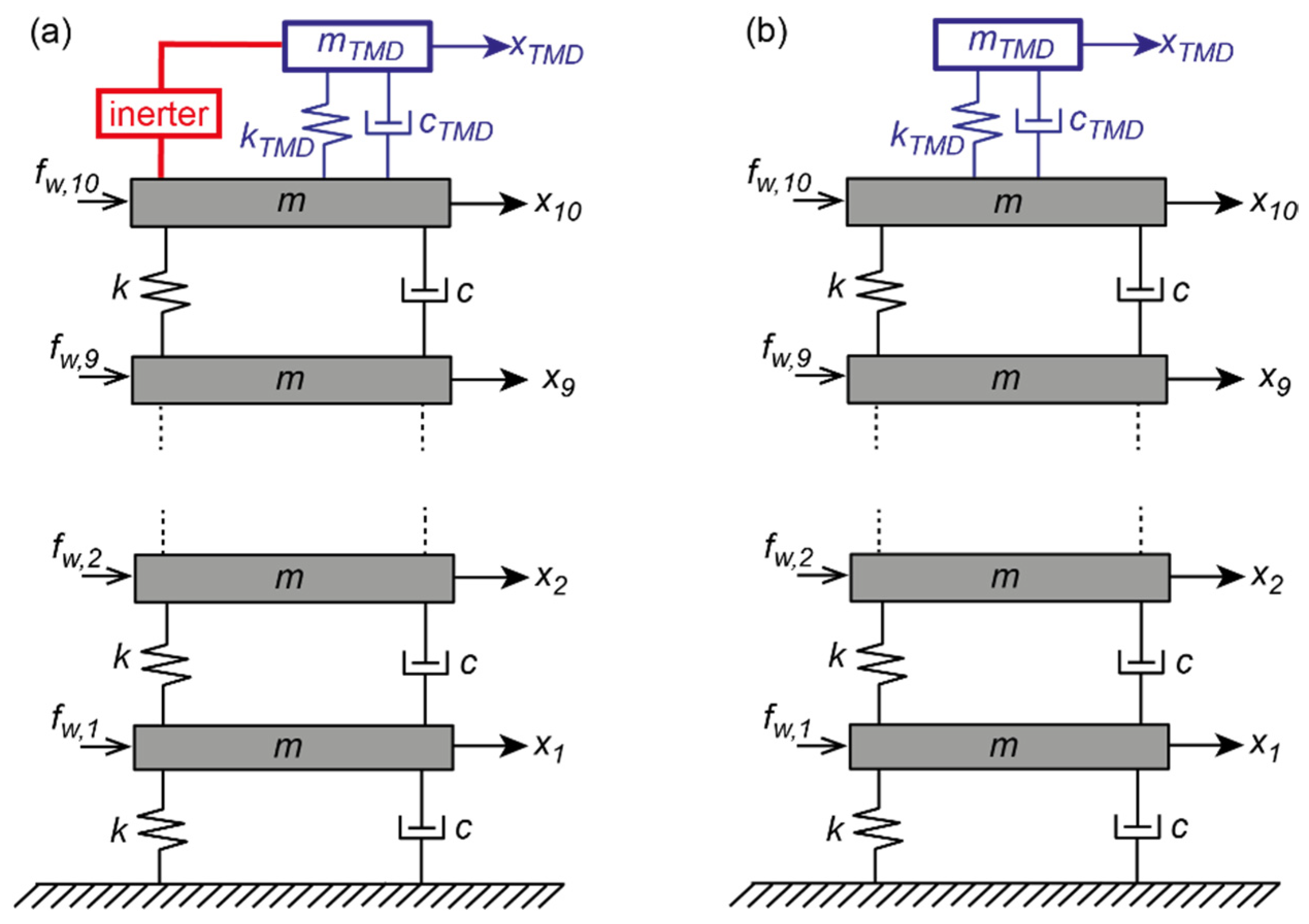
2.1. Model Structure of Tall Building with TMDI
2.2. Tall Building Model
2.3. Equations of Motion
2.4. Excitation
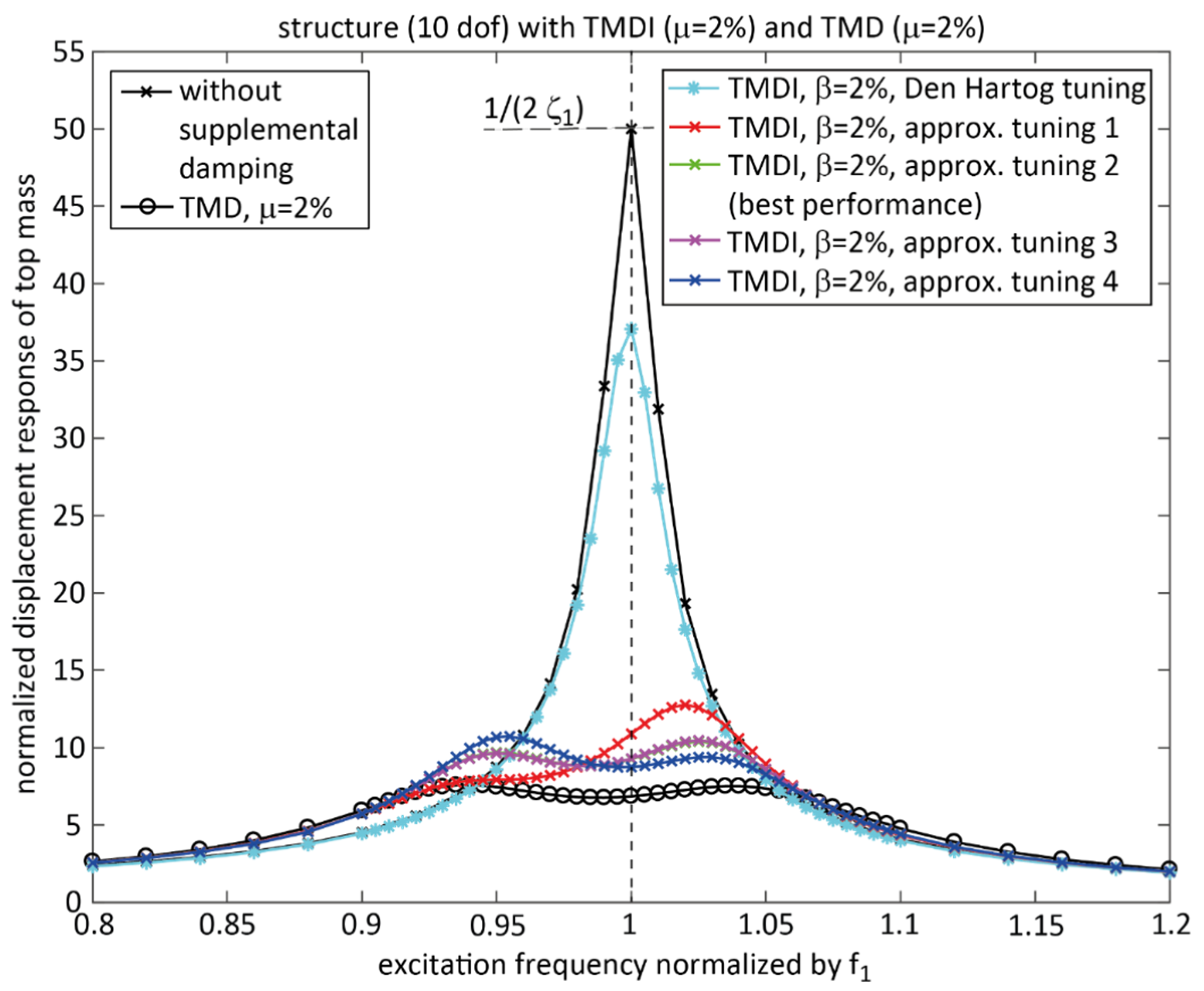
3. Approximate Tuning of TMDI and Resulting Performance
3.1. Den Hartog Tuning
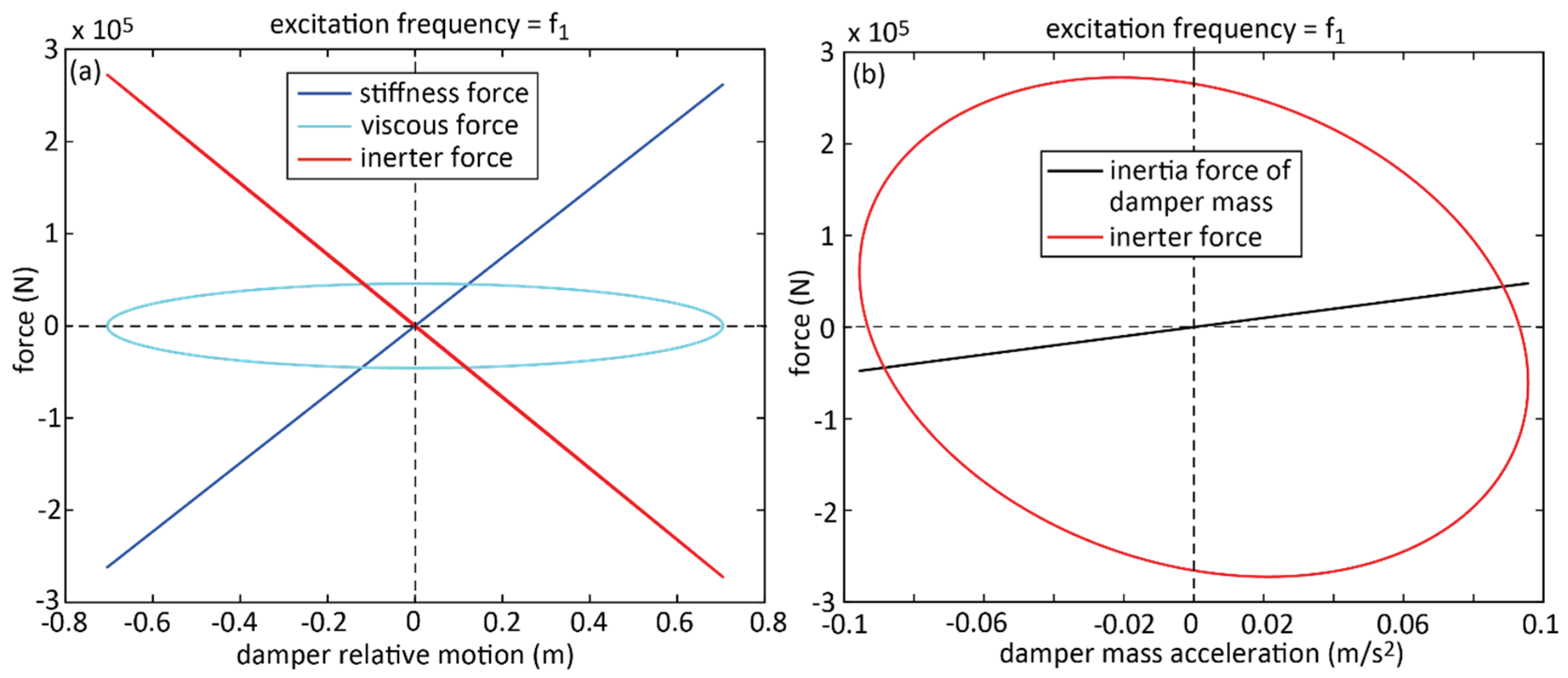
3.2. Inerter Force Characteristics
3.3. Approximate TMDI Tuning 1 (“Approximate Tuning 1”)
3.4. Approximate TMDI Tuning 2 (“Approximate Tuning 2”)
3.5. Approximate TMDI Tuning 3 (“Approximate Tuning 3”)
3.6. Approximate TMDI Tuning 4 (“Approximate Tuning 4”)
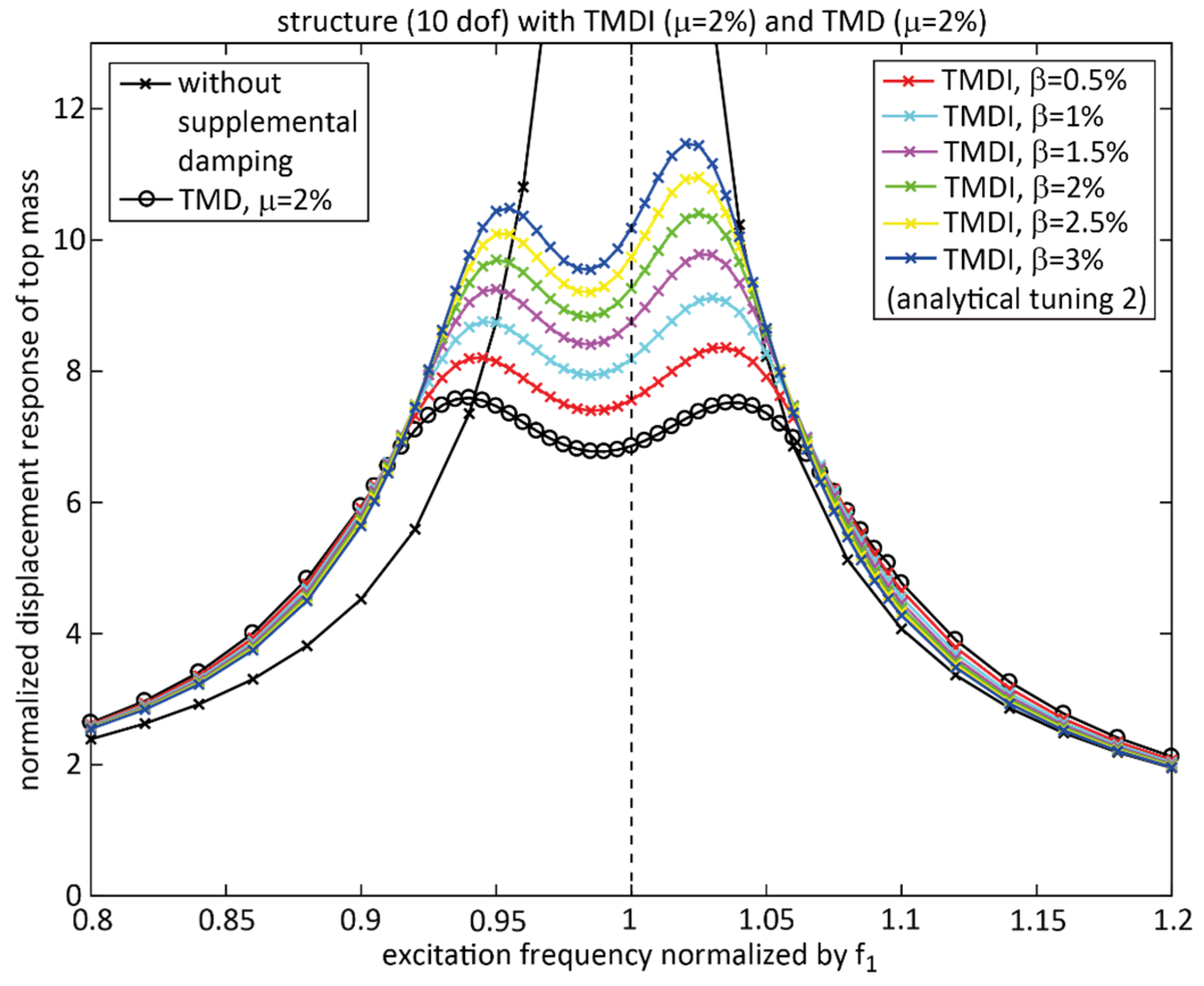
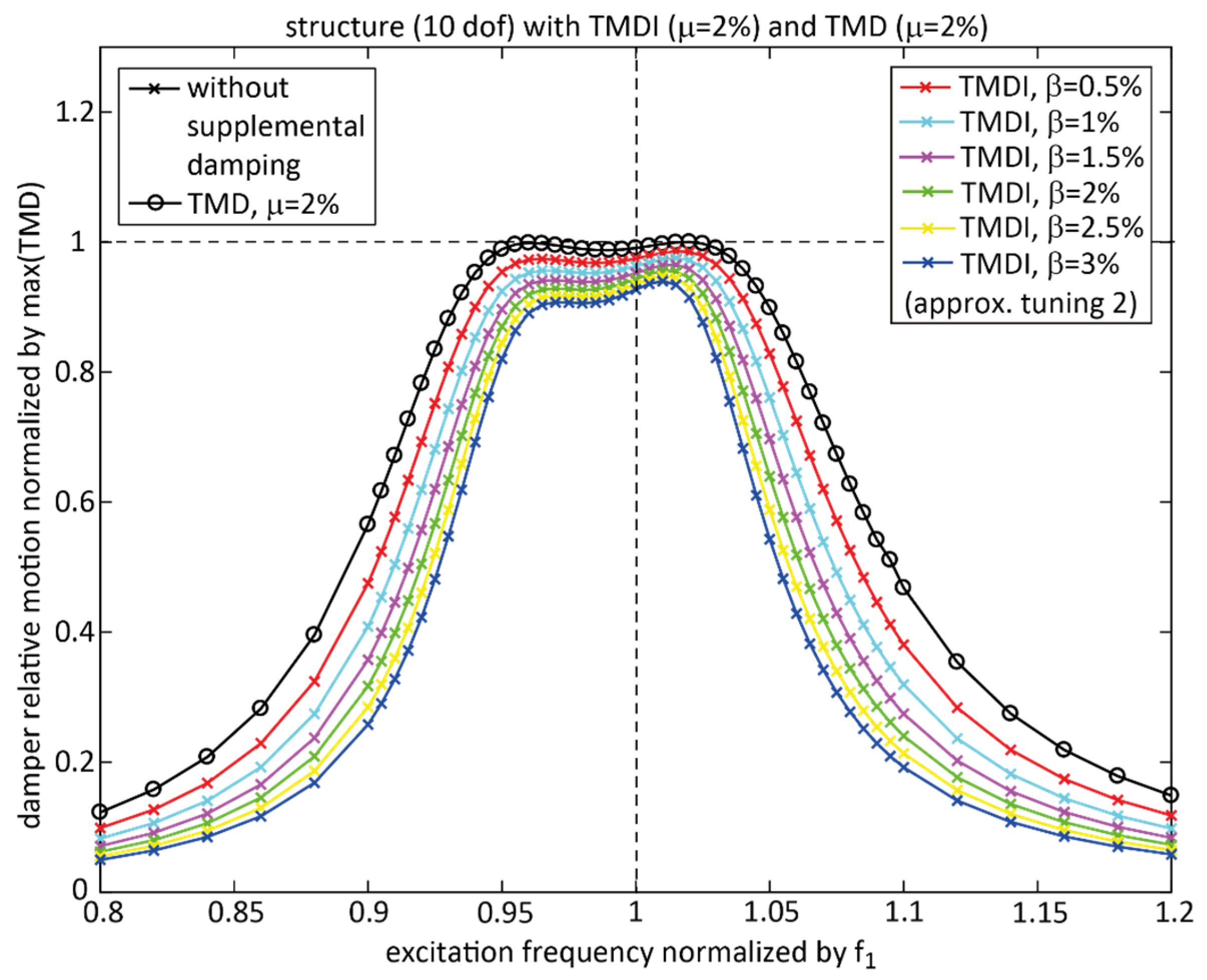
4. Performance for Various Inertance Ratios
4.1. Considered Tuning, Mass Ratio and Inertance Ratios
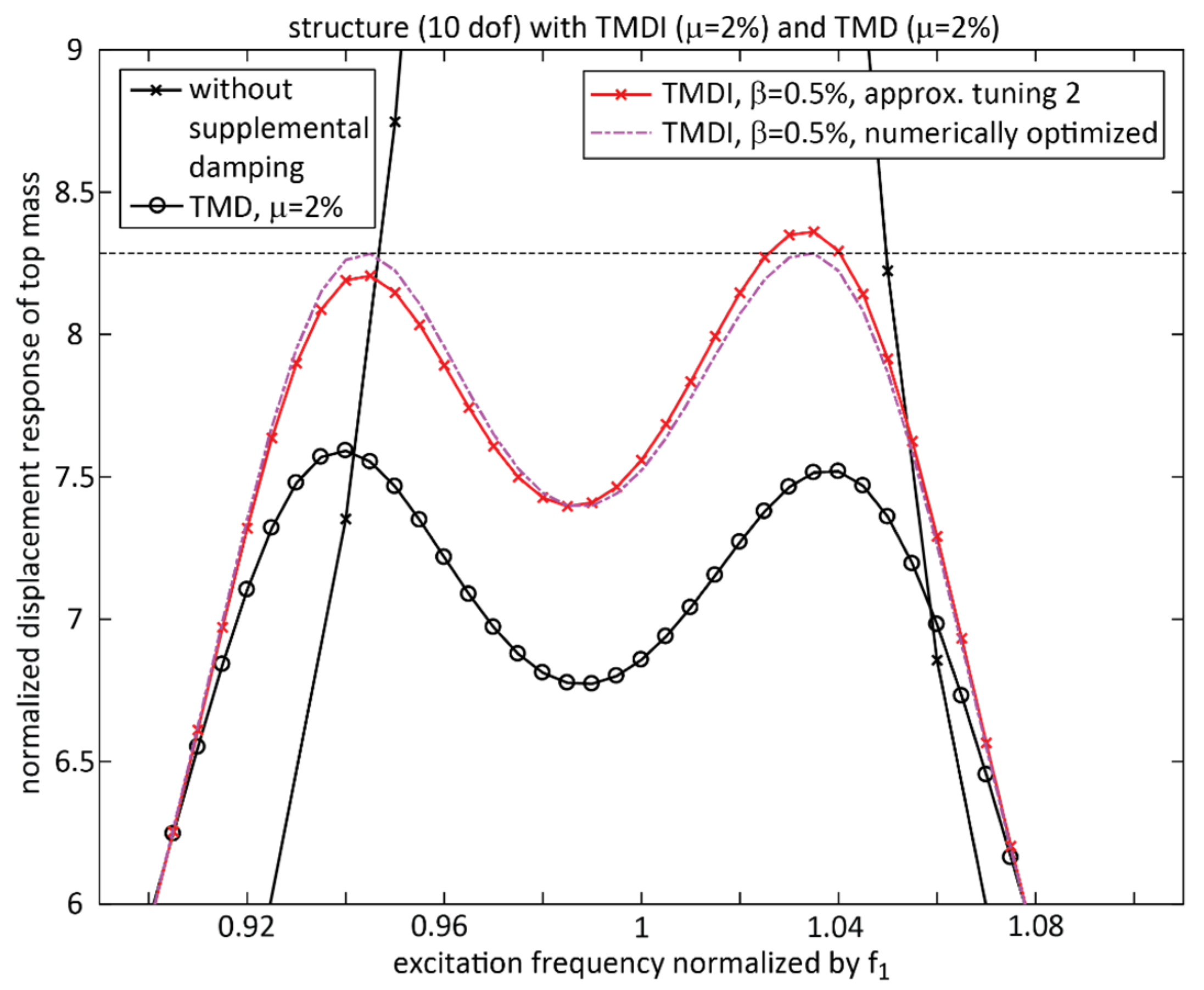
4.2. Double-Check of Approximate Tuning with Numerical Optimization
4.3. Performance Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Den Hartog, J.P. Mechanical Vibrations, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Zucca, M.; Longarini, N.; Simoncelli, M.; Aly, A.M. Tuned Mass Damper Design for Slender Masonry Structures: A Framework for Linear and Nonlinear Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asami, T.; Nishihara, O.; Baz, A.M. Analytical solutions to H∞ and H2 optimization of dynamic vibration absorber attached to damped linear systems. J. Vib. Acoust. ASME 2002, 124, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Wang, S.; Brennan, M.J. Optimal and robust modal control of a flexible structure using an active dynamic vibration absorber. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 045003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F.; Yalniz, F.; Kerner, D.; Huber, P. Performance of Adaptive TMD for Tall Building Damping. Int. J. High-Rise Build. 2021, 10, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaralis, A.; Petrini, F. Wind-induced vibration mitigation in tall buildings using the tuned mass-damper-inerter (TMDI). J. Struct. Eng. 2017, 143, 04017127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrosanti, D.; De Angelis, M.; Basili, M. Optimal design and performance evaluation of systems with Tuned Mass Damper Inerter (TMDI). Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2017, 46, 1367–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Xu, Z.D.; Gai, P.P. Tuned mass-damper-inerter control of wind-induced vibration of flexible structures based on inerter location. Eng. Struct. 2019, 199, 109585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrini, F.; Giaralis, A.; Wang, Z. Optimal tuned mass-damper-inerter (TMDI) design in wind-excited tall buildings for occupants’ comfort serviceability performance and energy harvesting. Eng. Struct. 2020, 204, 109904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Qiao, H.; Li, W.; You, Y.; Fan, Z.; Tiwari, N. Parametric optimization of an inerter-based vibration absorber for wind induced vibration mitigation of a tall building. Wind Struct. 2020, 31, 241–253. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, F.; Huber, P.; Borchsenius, F.; Braun, C. Performance of TMDI for Tall Building Damping. Actuators 2020, 9, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barredo, E.; Larios, M.; Mayén, J.; Flores-Hernández, A.A.; Colín, J.; Arias-Montiel, M. Optimal design for high-performance passive dynamic vibration absorbers under random excitation. Eng. Struct. 2019, 195, 469–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barredo, E.; Larios, M.; Colín, J.; Mayén, J.; Flores-Hernández, A.A.; Arias-Montiel, M. A novel high-performance passive non-traditional inerter-based dynamic vibration absorber. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 485, 115583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotta, G.; Failla, G. Improved inerter-based vibration absorbers. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 192, 106087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F.; Borchsenius, F.; Distl, J.; Braun, C. Performance of numerically optimized Tuned Mass Damper with Inerter (TMDI). Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.C. The Inerter: A Retrospective. Annu. Rev. Control. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2020, 3, 361–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Modal Mass of First Bending Mode (t) | Eigenfrequency of First Bending Mode (Hz) | Damping Ratio of First Bending Mode (%) | Considered Inertance Ratios (%) | Mass Ratio (%) | Pendulum Mass (t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25,000 t | 0.14 Hz | 1% | 0.5%, 1%, 1.5%, 2%, 2.5%, 3% | 2% | 500 t |
| Influence on Frequency Tuning of Damper | Influence on Inertia of Damper |
|---|---|
| The presence of the inerter force influences the frequency tuning of the TMDI because the frequency tuning is determined by the positive slope of the stiffness force and the negative slope of the inerter force. | The inerter force is not an inertia force but it acts rather as an additional damping force on the oscillating damper mass. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weber, F. TMD-Inerter for Tall Building Damping: Approximate Closed-Form Solution, Performance and Conclusions. Buildings 2025, 15, 1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15111829
Weber F. TMD-Inerter for Tall Building Damping: Approximate Closed-Form Solution, Performance and Conclusions. Buildings. 2025; 15(11):1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15111829
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeber, Felix. 2025. "TMD-Inerter for Tall Building Damping: Approximate Closed-Form Solution, Performance and Conclusions" Buildings 15, no. 11: 1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15111829
APA StyleWeber, F. (2025). TMD-Inerter for Tall Building Damping: Approximate Closed-Form Solution, Performance and Conclusions. Buildings, 15(11), 1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15111829






