Drivers of Carbon Emissions in China’s Construction Industry: A Perspective from Interregional Carbon Transfer
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Status of Construction Carbon Emissions
1.2. Research Status on Carbon Transfer
1.3. Research Status on Factors Influencing Construction Carbon Emissions
1.4. Review of Research
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. InterRegional Carbon Emission Transfer Model for the Construction Industry
2.1.1. Carbon Emission Measurement Model of the Construction Industry
2.1.2. Interregional Construction Carbon Emission Transfer Measurement Model
- (1)
- Calculating Construction Carbon Emission Transfer Coefficients
- (2)
- Calculate the total amount of carbon transfer in the construction industry.
2.2. Carbon Emission Transfer Network Model of the National Construction Industry
2.3. Model of Carbon Emission Drivers in the Construction Industry
2.3.1. Construction of Panel Regression Model
2.3.2. The Selection of Dependent and Independent Variables
- Construction Carbon Emission Inflow and Outflow Intensity (INE, OUTE):
- Mediation Capacity (BC):
- Degree of Influence (EC):
2.3.3. The Selection of Control Variables
2.4. Data Sources and Process
3. Measurement of Interregional Construction Carbon Emission Transfers
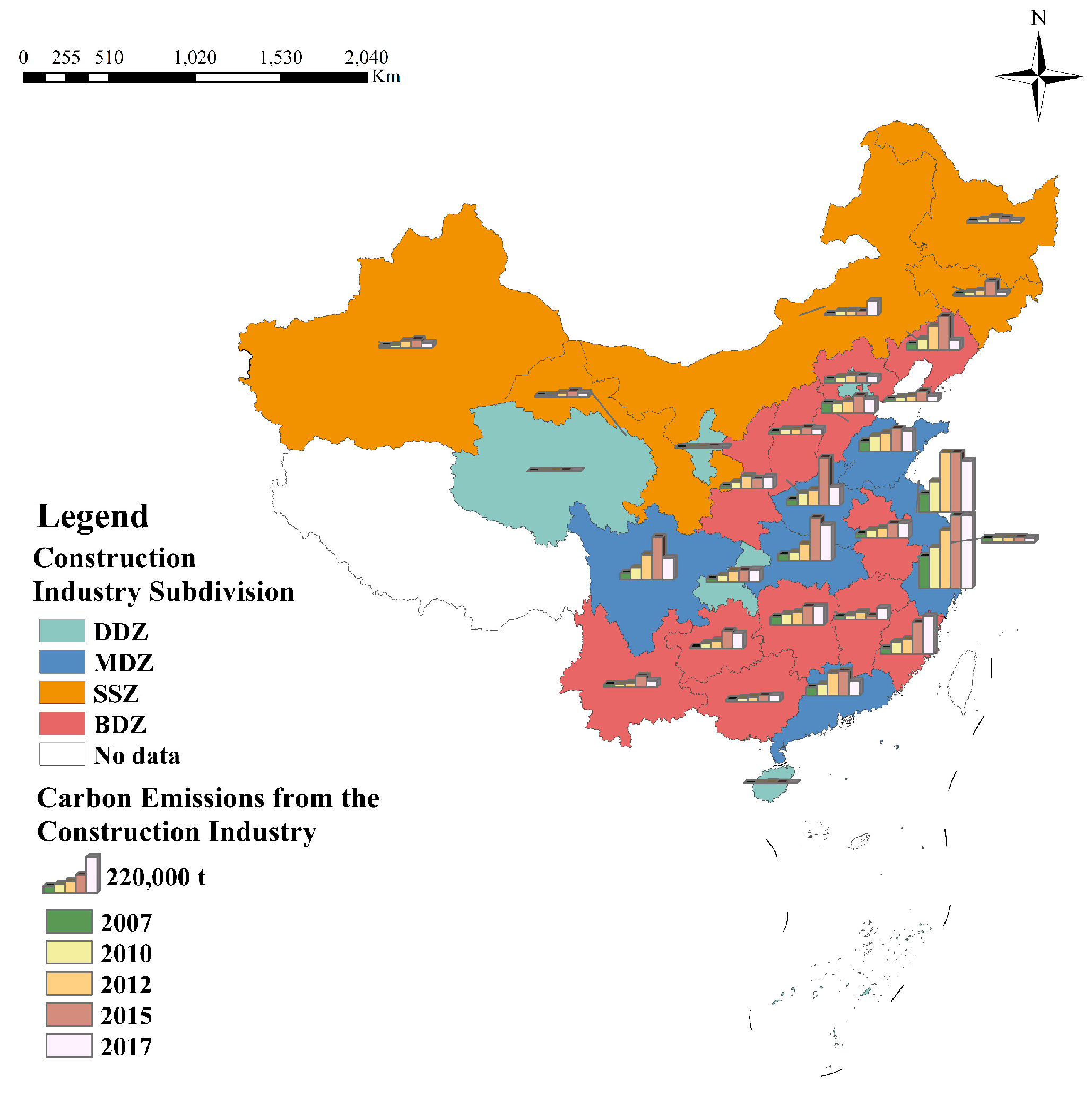
3.1. Analysis of Interregional Total Construction Carbon Emissions
3.2. Analysis of Interregional Construction Carbon Emission Transfer
4. Results
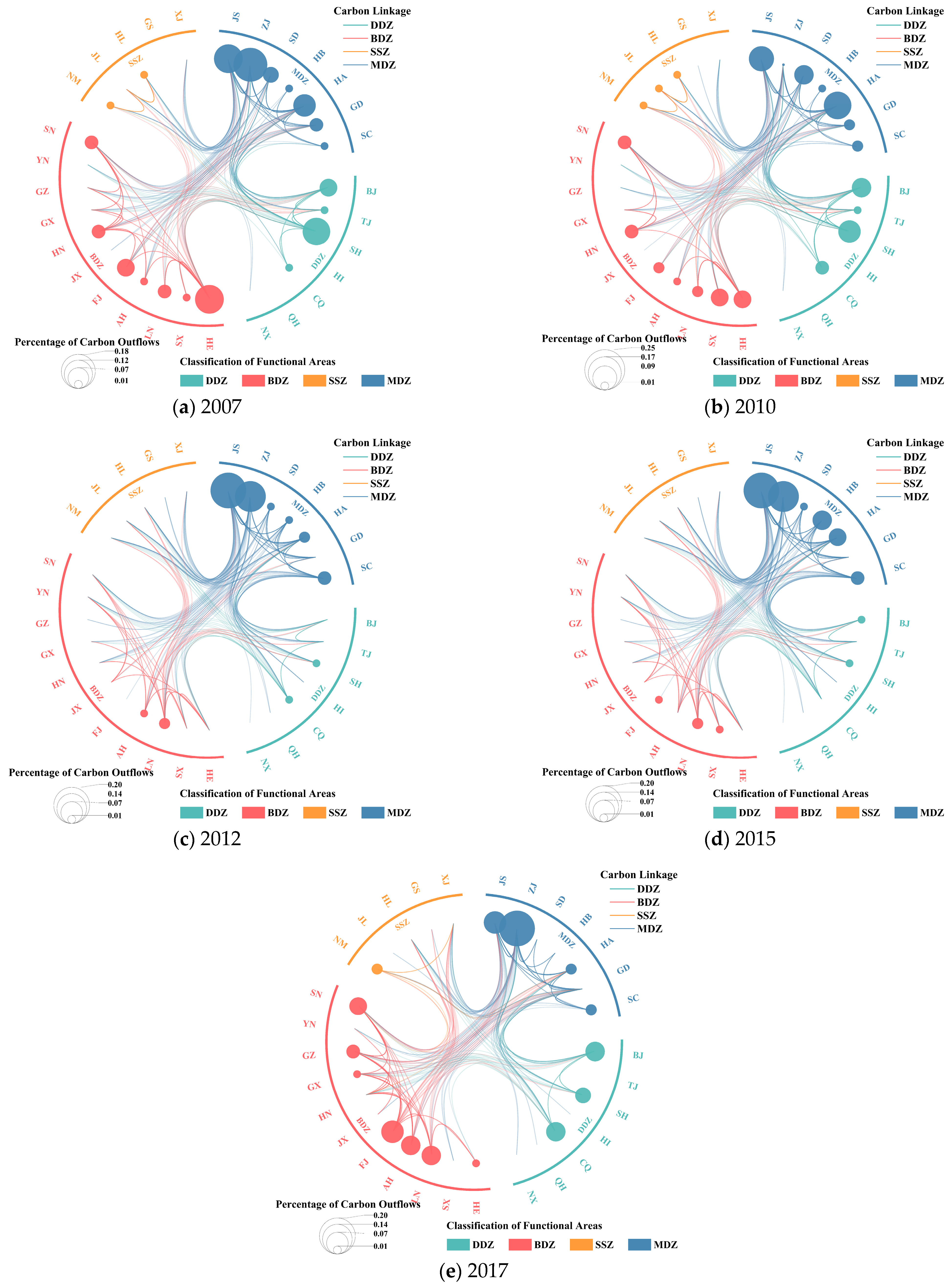
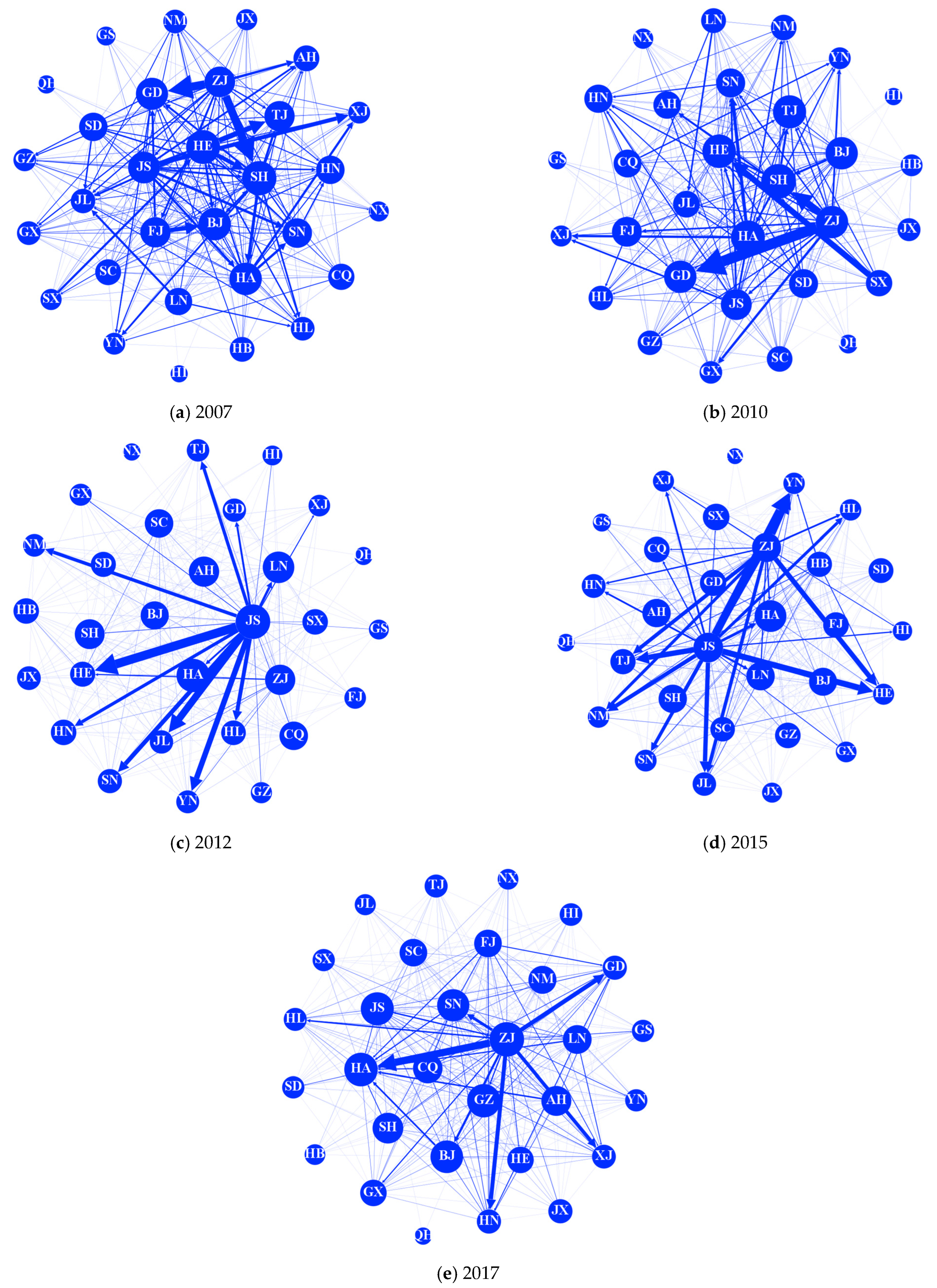
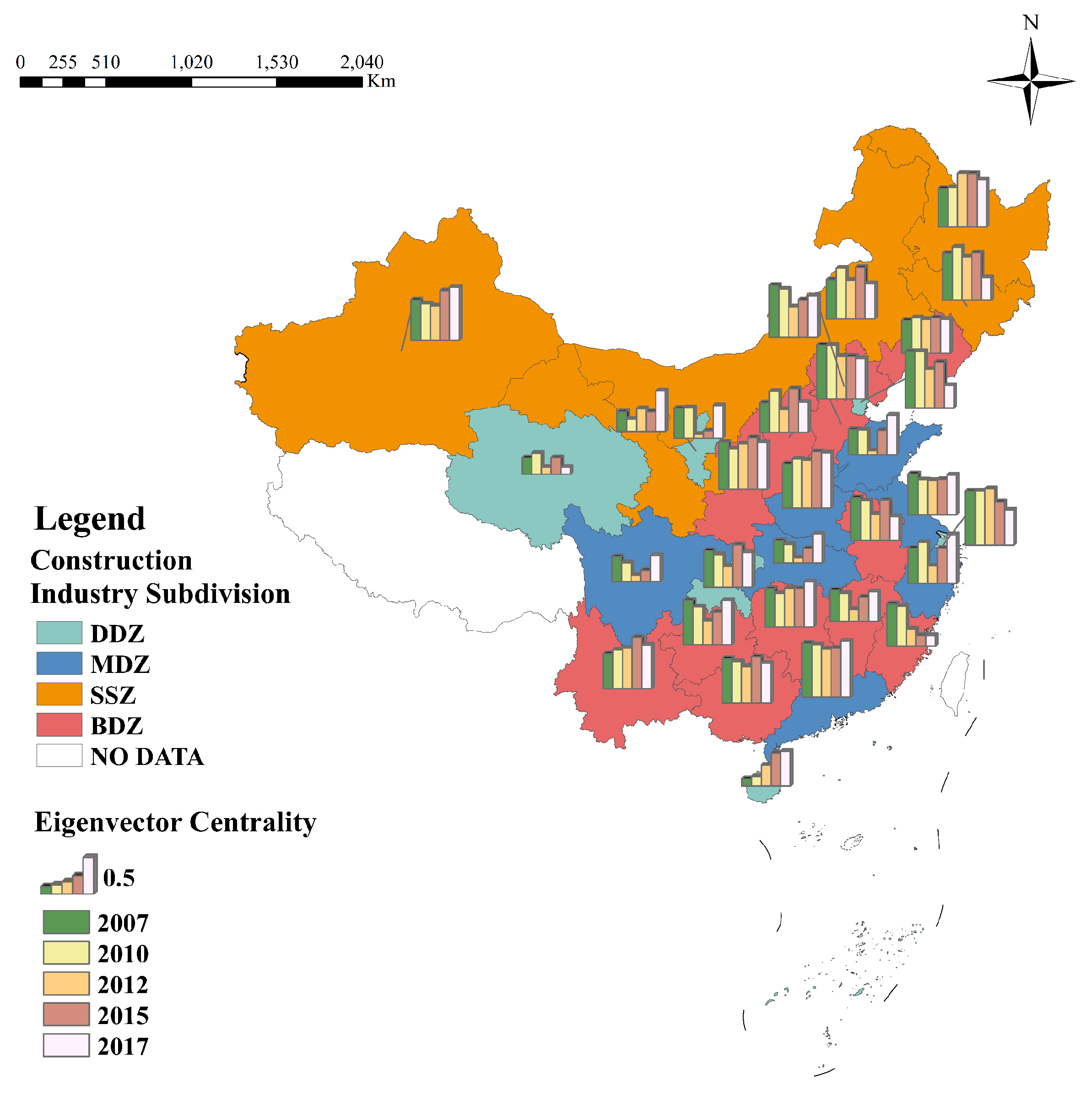
4.1. Analysis of China’s Construction Carbon Emission Transfer Network
4.1.1. Construction of the Complex Network for China’s Construction Carbon Emission Transfers
4.1.2. Analysis of Construction Carbon Emission Transfer Network Metrics
- Overall Network Characteristics
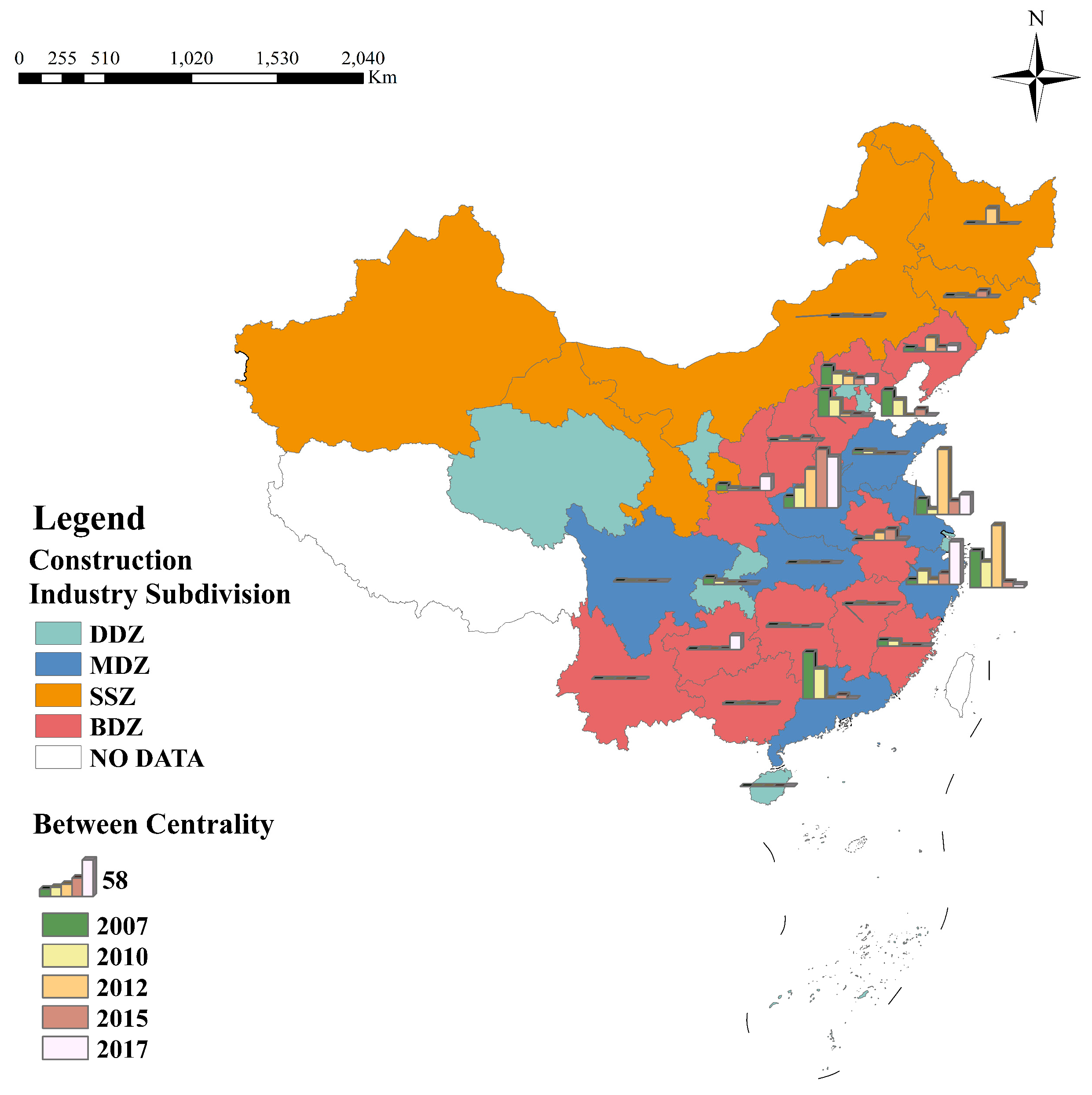
- Individual Network Characteristics
- Strength
- 2.
- Mediation Capacity
- 3.
- Degree of Influence
4.2. Analysis of Drivers of Construction Carbon Emissions
4.2.1. Benchmark Model Selection
4.2.2. Multicollinearity Test
4.2.3. Heteroscedasticity Test
4.2.4. Panel Regression Results
4.2.5. Robustness Test
4.2.6. Endogeneity Test
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
6.1. Conclusions
6.2. Recommendations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DDZ | Demand-Driven Zones |
| BDZ | Balanced Development Zones |
| SSZ | Specialized Supplementary Zones |
| MDZ | Major Development Zones |
References
- Ma, X.J.; Wang, C.X.; Dong, B.Y.; Gu, G.C.; Chen, R.M.; Li, Y.F.; Zou, H.F.; Zhang, W.F.; Li, Q.N. Carbon emissions from energy consumption in China: Its measurement and driving factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallapaty, S. How China Could Be Carbon Neutral by Mid-Century. Nature 2020, 586, 482–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Normile, D. China’s bold climate pledge earns praise-but is it feasible? Science 2020, 370, 17–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.T.; Zhai, P.M. Achieving Paris Agreement temperature goals requires carbon neutrality by middle century with far-reaching transitions in the whole society. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2021, 12, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.W.; Fu, X.S.; Song, W.H.; Wang, L.L. Complex network analysis of embodied carbon emission transfer in China’s construction industry. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1409539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Hu, J.; Zhao, K.X.; Chen, H.; Zhao, S.D.; Li, W.W. Dynamics and Decoupling Analysis of Carbon Emissions from Construction Industry in China. Buildings 2022, 12, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Ma, M.D.; Xiang, X.W.; Feng, W.; Ma, Z.L.; Cai, W.G.; Ma, X. Carbon reduction in commercial building operations: A provincial retrospection in China. Appl. Energy 2022, 306, 118098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.X.; Ma, M.D.; Lin, Y.C.; Ma, Z.L.; Li, K. Carbon Kuznets curve in China’s building operations: Retrospective and prospective trajectories. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 150104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.D.; Ma, X.; Cai, W.; Cai, W.G. Low carbon roadmap of residential building sector in China: Historical mitigation and prospective peak. Appl. Energy 2020, 273, 115247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onat, N.C.; Kucukvar, M. Carbon footprint of construction industry: A global review and supply chain analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 124, 109783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.X.; Qu, M.; Li, Q.; Umer, M. Analysis of the non-equilibrium and evolutionary driving forces of carbon emissions in China’s construction industry. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 97, 110834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hu, D.; Wang, T.; Tian, H.; Gan, L. Decoupling effect and spatial-temporal characteristics of carbon emissions from construction industry in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 419, 138243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.N.; Al-duais, Z.A.M.; Zhu, X.Q.; Lin, S.Y. Digital economy’s role in shaping carbon emissions in the construction field: Insights from Chinese cities. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 365, 121548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y.N.; Yu, M. An approach for measuring and analyzing embodied carbon in the construction industry chain based on energy accounting. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.S.; Zhou, Y.X.; Wang, T.; Zhao, N. Efficiency of construction waste and carbon reduction in the construction industry: Based on improved three stage SBM-DEA model in China. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.C.; Li, S.Y.; Meng, X.X.; Peng, Y.Z.; Tang, W.Z. Study on Regional Differences of Carbon Emission Efficiency: Evidence from Chinese Construction Industry. Energies 2023, 16, 6882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.B.; Yuan, X.Y.; Lee, C.C. Prediction of carbon emissions in China’s construction industry using an improved grey prediction model. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 938, 173351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Gao, Y.Y.; Jiang, Y.D.; Zhao, C.W.; Ge, H.J. Predictive modeling of carbon emissions in Jiangsu Province’s construction industry: An MEA-BP approach. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 86, 108903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Wu, J.J.; Lin, C.X. Decarbonizing provincial construction industry under the “dual carbon” goals: Assessing reduction capacities and charting optimal pathways. Build. Environ. 2025, 272, 112639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.C.; Merkert, R. “Door-to-door” carbon emission calculation for airlines—Its decarbonization potential and impact. Transp. Res. Part D-Transp. Environ. 2023, 121, 103849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, J.A.; de Castro, A.; Brasil, G.H.; de Souza, P.A.; Mendiburu, A.Z. CO2 Emission Factors and Carbon Losses for Off-Road Mining Trucks. Energies 2022, 15, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperow, M. Updated potential soil carbon sequestration rates on US agricultural land based on the 2019 IPCC guidelines. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 204, 104719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenbo, A.; O’Toole, A.; Astrup, R.; Rasse, D. Biochar mitigation potential in Norway estimated by IPCC Tier 1 and Tier 2 methods. Carbon Manag. 2024, 15, 2410823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, C.; Fiore, A.; Hagemann, U.; Nendel, C.; Xiloyannis, C. Improving the accounting of field emissions in the carbon footprint of agricultural products: A comparison of default IPCC methods with readily available medium-effort modeling approaches. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2016, 21, 791–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boguski, T.K. Life cycle carbon footprint of the National Geographic magazine. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2010, 15, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foteinis, S.; Andresen, J.; Campo, F.; Caserini, S.; Renforth, P. Life cycle assessment of ocean liming for carbon dioxide removal from the atmosphere. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 370, 133309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Ruocco, G.; Gaita, A. Life Cycle Assessment from Cradle-to-Handover Approach to Greenhouse Gas Emissions Mitigation: Carbon Storage in Timber Buildings. Buildings 2023, 13, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavsson, L.; Joelsson, A.; Sathre, R. Life cycle primary energy use and carbon emission of an eight-storey wood-framed apartment building. Energy Build. 2010, 42, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneifel, J. Life-cycle carbon and cost analysis of energy efficiency measures in new commercial buildings. Energy Build. 2010, 42, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Wenk, R.; Brandao, M. Climatic impact of land use in LCA-carbon transfers between vegetation/soil and air. International J. Life Cycle Assess. 2010, 15, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrowski, M.; Kanz, E.; Wolgast, K. ABC LCA-booklet: Life cycle assessment of structures using an example. Bautechnik 2025, 102, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Y.; Teng, Y.; Pan, W.; Zhang, Y. BIM-integrated LCA to automate embodied carbon assessment of prefabricated buildings. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 374, 133894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Vu, D.; Perera, S.C.; Wang, G.F.; Xiong, R. Nexus between water-energy-carbon footprint network: Multiregional input-output and coupling coordination degree analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 430, 139639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.Q.; Shao, L.; Geng, Z.H.; Guo, M.L.; Wei, Z.J.; Wu, Z. Consumption-Based Carbon Emissions of Tianjin Based on Multi-Scale Input-Output Analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Liu, Q.L.; Zhang, H.R.; Wang, S.Q.; Fang, K. Comparison of city-level carbon footprint evaluation by applying single- and multi-regional input-output tables. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 110108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Huang, C.Y.; Wang, H.M.; Liao, F.W. Impact Factors in Chinese Construction Enterprises’ Carbon Emission-Reduction Intentions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Song, X.J.; Chen, K.K. Which Influencing Factors Cause CO2 Emissions Differences in China’s Provincial Construction Industry: Empirical Analysis from a Quantile Regression Model. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, X. Research on High-Quality Development Evaluation, Space-Time Characteristics and Driving Factors of China’s Construction Industry under Carbon Emission Constraints. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Pang, Q.Y.; Bao, T.N.; Guo, X.Q.; Deng, Y.G. Critical factors influencing carbon emissions of prefabricated building supply chains in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, H.Y. Research on factors influencing total carbon emissions of construction based on structural equation modeling: A case study from China. Build. Environ. 2025, 275, 112396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.D.; Lu, C.; Liu, J.X. A synthesized factor analysis on energy consumption, economy growth, and carbon emission of construction industry in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 13896–13905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.W.; Song, W.H.; Pei, X.M.; Wang, L.L. Measurement of Carbon Emission Transfer in China’s Construction Industry and Analysis of Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Carbon Emissions. Glob. Chall. 2025, 9, 2400368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.M.; Wu, S.M.; Lei, Y.L.; Li, S.T. Study on embodied CO2 transfer between the Jing-Jin-Ji region and other regions in China: A quantification using an interregional input-output model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 14068–14082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.D. Theory and Practice of Interregional Input-Output Table Compilation of 30 Provinces, Autonomous Regions and Cities in China in 2007, 1st ed.; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.D. Theory and Practice of Interregional Input-Output Table Compilation of 30 Provinces, Autonomous Regions and Cities in China in 2010, 1st ed.; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.R.; Zhang, Z.K.; Wei, W.D.; Song, M.L.; Dietzenbacher, E.; Wang, X.Y.; Meng, J.; Shan, Y.L.; Ou, J.M.; Guan, D.B. Regional determinants of China’s consumption-based emissions in the economic transition. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 074001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, P.C.B.; Moon, H.R. Nonstationary panel data analysis: An overview of some recent developments. Econom. Rev. 2000, 19, 263–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltagi, B.H. Econometric Analysis of Panel Data, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; p. 458. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.H.; An, H.Z.; Gao, X.Y.; Liu, S.Y.; Xi, X. Factors driving global carbon emissions: A complex network perspective. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 146, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.W.; Luo, B.L. Good Agents or Bad Collaborators: How Do Clans Influence Farmland Adjustment? Manag. World 2019, 35, 97–109+191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.Q.; Wei, Y.B.; Wang, W.G.; Liu, D.H. Empirical Analysis of the Impact of the International Financial Crisis on the Output of China’s Construction Industry. Sci. Technol. Manag. Res. 2010, 30, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.B.; Hu, K.C.; Yu, Q. Analysis of the Threshold Effect of Financial Deepening on Green Development. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2017, 27, 205–211. [Google Scholar]

| Energy | Coal | Crude Oil | Petroleum | Coke | Petrol | Diesel | Diesel Oil | Fuel Oil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon emission factor | 2.69 Kg CO2/Kg | 2.76 Kg CO2/L | 2.09 Kg CO2/m3 | 3.14 Kg CO2/Kg | 3.14 Kg CO2/L | 2.56 Kg CO2/L | 2.73 Kg CO2/L | 3.14 Kg CO2/L |
| Building Material | Clinker | Nylon | Steels | Aluminum | Lumber |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon emission factors | 0.815 kg/kg | 0.9655 kg/kg | 1.789 kg/kg | 2.6 kg/kg | −842.8 kg/m3 |
| Recovery factor | — | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.85 | 0.2 |
| Abbreviations of Province | Province | Abbreviations of Provinces | Province |
|---|---|---|---|
| BJ | Beijing | QH | Qinghai |
| TJ | Tianjin | NX | Ningxia |
| HE | Hebei | NM | Inner Mongolia |
| SX | Shanxi | LN | Liaoning |
| SH | Shanghai | JL | Jilin |
| JS | Jiangsu | HL | Heilongjiang |
| ZJ | Zhejiang | AH | Anhui |
| FJ | Fujian | SD | Shandong |
| JX | Jiangxi | SC | Sichuan |
| HA | Henan | SN | Shaanxi |
| HB | Hubei | GS | Gansu |
| GX | Guangxi | XJ | Xinjiang |
| HI | Hainan | GD | Guangdong |
| CQ | Chongqing | YN | Yunnan |
| GZ | Guizhou | HN | Hunan |
| Year | 2007 | 2010 | 2012 | 2015 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Node | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Edge | 399 | 414 | 283 | 382 | 382 |
| Density | 0.459 | 0.436 | 0.325 | 0.439 | 0.441 |
| Average path length | 1.505 | 1.417 | 1.684 | 1.423 | 1.444 |
| Dependent Variable | F-Test | Hausman-Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDCE | F-statistic | p-value | p-value | |
| 5.61 | Prob > F = 0.0000 | 17.77 | Prob > F = 0.0068 | |
| Variable | VIF | 1/VIF |
|---|---|---|
| CCL | 3.350 | 0.299 |
| UL | 2.720 | 0.367 |
| CE | 2.500 | 0.401 |
| EC | 1.440 | 0.692 |
| BC | 1.350 | 0.742 |
| OUTE | 1.310 | 0.765 |
| MES | 1.310 | 0.766 |
| SP | 1.280 | 0.778 |
| INE | 1.030 | 0.967 |
| Mean VIF | 1.810 | |
| BP Test Statistic | p-Value |
|---|---|
| 43.35 | 0.0000 |
| Variables Type | Variables Name | Variable | Unit | Mean | Standard Deviation | Maximum | Minimum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variable | Construction Carbon Emissions | CDCE | t | 7.38 × 107 | 8.81 × 107 | 4.46 × 108 | 1.39 × 106 |
| Independent Variables | Carbon Emission Inflow Intensity | INE | t | 16,843.352 | 37,498.199 | 2.15 × 105 | 39.394 |
| Carbon Emission Outflow Intensity | OUTE | t | 19,847.692 | 95,051.726 | 8.81 × 105 | 0.000 | |
| Mediation Capacity | BC | - | 10.693 | 21.956 | 115.985 | 0.000 | |
| Degree of Influence | EC | - | 0.625 | 0.238 | 1.000 | 0.074 | |
| Control Variables | Population Size | SP | capita | 4505.100 | 2752.086 | 12,141.000 | 552.000 |
| Urbanization Rate | UL | % | 0.544 | 0.136 | 0.916 | 0.282 | |
| Construction Economic Output | CCL | CNY/capita | 1.015 | 0.898 | 4.438 | 0.096 | |
| Per Capita Net Income in Construction | CE | 37,814.173 | 16,392.943 | 99,718.000 | 13,102.000 | ||
| Machinery/Equipment Intensity | MES | Kw/m2 | 0.091 | 0.04 | 0.546 | 0.018 |
| Variable | Model(1) | Model(2) | Model(3) | Model(4) | Model(5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDCE | CDCE | CDCE | CDCE | CDCE | |
| SP | 42,783.230 *** (3.089) | 41,510.669 *** (3.007) | 36,567.397 *** (3.327) | 42,358.354 *** (2.933) | 42,746.289 *** (3.022) |
| UL | 3.93 × 108 ** (2.378) | 3.76 × 108 ** (2.282) | 3.69 × 108 ** (2.749) | 3.91 × 108 ** (2.270) | 3.93 × 108 ** (2.340) |
| CCL | 6.59 × 107 *** (3.815) | 6.55 × 107 *** (3.688) | 4.98 × 107 *** (3.376) | 6.58 × 107 *** (3.750) | 6.60 × 107 *** (3.884) |
| CE | −1504.405 ** (−2.102) | −1487.036 * (−2.040) | −1076.856 * (−1.929) | −1483.795 * (−1.936) | −1504.980 ** (−2.110) |
| MES | 5.77 × 108 ** (2.323) | 5.42 × 108 ** (2.093) | 4.27 × 108 * (1.966) | 5.81 × 108 ** (2.337) | 5.79 × 108 ** (2.346) |
| INE | 87.307 (1.214) | ||||
| OUTE | 246.655 *** (7.391) | ||||
| BC | 32,452.000 (0.227) | ||||
| EC | 1.45 × 106 (0.061) | ||||
| _cons | −3.47 × 108 *** (−2.965) | −3.34 × 108 *** (−2.866) | −3.09 × 108 *** (−3.330) | −3.45 × 108 *** (−2.810) | −3.48 × 108 *** (−3.070) |
| R2 | 0.498 | 0.501 | 0.639 | 0.498 | 0.498 |
| N | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 |
| Variable | Model (1) CDCE | Model (2) CDCE | Model (3) CDCE | Model (4) CDCE | Model (5) CDCE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP | 39,511.201 *** (3.269) | 38,098.861 *** (3.139) | 33,650.401 *** (3.321) | 40,060.276 *** (3.127) | 39,690.650 *** (3.165) |
| UL | 4.73 × 108 *** (2.959) | 4.62 × 108 *** (2.886) | 4.15 × 108 *** (3.235) | 4.77 × 108 *** (2.828) | 4.75 × 108 *** (2.881) |
| CCL | 6.47 × 107 *** (4.001) | 6.40 × 107 *** (3.835) | 5.08 × 107 *** (3.640) | 6.50 × 107 *** (3.847) | 6.44 × 107 *** (4.019) |
| CE | −1827.381 ** (−2.424) | −1800.270 ** (−2.354) | −1308.195 ** (−2.304) | −1859.672 ** (−2.239) | −1826.209 ** (−2.421) |
| MES | 4.06 × 108 (1.160) | 4.23 × 108 (1.269) | 3.51 × 108 (1.106) | 3.93 × 108 (1.089) | 4.07 × 108 (1.144) |
| INE | 93.975 (1.257) | ||||
| OUTE | 241.448 *** (7.429) | ||||
| BC | −3.72 × 104 (−0.215) | ||||
| EC | −4.97 × 106 (−0.205) | ||||
| _cons | −3.59 × 108 *** (−3.305) | −3.49 × 108 *** (−3.206) | −3.12 × 108 *** (−3.597) | −3.62 × 108 *** (−3.149) | −3.57 × 108 *** (−3.378) |
| R2 | 0.486 | 0.489 | 0.622 | 0.486 | 0.486 |
| N | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| Variable | Model(1) |
|---|---|
| CDCE | |
| SP | 33,571.057 *** (3.055) |
| UL | 3.40 × 108 ** (2.455) |
| CCL | 4.89 × 107 *** (3.258) |
| CE | −990.928 * (−1.705) |
| MES | 4.07 × 108 * (1.777) |
| INE | 100.186 (1.521) |
| OUTE | 250.229 *** (7.296) |
| BC | 98,119.868 (0.817) |
| EC | 6.33 × 106 (0.285) |
| _cons | −2.89 × 108 *** (−3.151) |
| R2 | 0.645 |
| N | 150 |
| Variables | (1) |
|---|---|
| GMM | |
| L.CDCE | −0.206 |
| (0.177) | |
| INE | −68.240 |
| (268.431) | |
| OUTE | 217.470 *** |
| (58.461) | |
| BC | 874,647.945 |
| (663,335.705) | |
| EC | −5.599 × 107 |
| (51,537,095.262) | |
| SP | 25,445.321 |
| (46,455.130) | |
| UL | 2.347 × 108 |
| (6.652 × 108) | |
| CCL | 71,846,623.447 ** |
| (30,406,021.534) | |
| CE | −241.031 |
| (3632.386) | |
| MES | 9.972 × 108 |
| (4.658 × 109) | |
| N | 120 |
| AR (1) | 0.0545 |
| AR (2) | 0.183 |
| Hansen | 0.190 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, W.; Song, W.; Pei, X.; Wang, L. Drivers of Carbon Emissions in China’s Construction Industry: A Perspective from Interregional Carbon Transfer. Buildings 2025, 15, 1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15101667
Xiao W, Song W, Pei X, Wang L. Drivers of Carbon Emissions in China’s Construction Industry: A Perspective from Interregional Carbon Transfer. Buildings. 2025; 15(10):1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15101667
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Wenwen, Wenhao Song, Xuemei Pei, and Lili Wang. 2025. "Drivers of Carbon Emissions in China’s Construction Industry: A Perspective from Interregional Carbon Transfer" Buildings 15, no. 10: 1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15101667
APA StyleXiao, W., Song, W., Pei, X., & Wang, L. (2025). Drivers of Carbon Emissions in China’s Construction Industry: A Perspective from Interregional Carbon Transfer. Buildings, 15(10), 1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15101667






