Influence of the Mass Percentage of Bottom Ash and Its State of Maturation on the Mechanical Performance of a Bio-Composite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Bottom Ash
2.1.2. The Bio-Sourced Matrix
2.2. Experimental Techniques
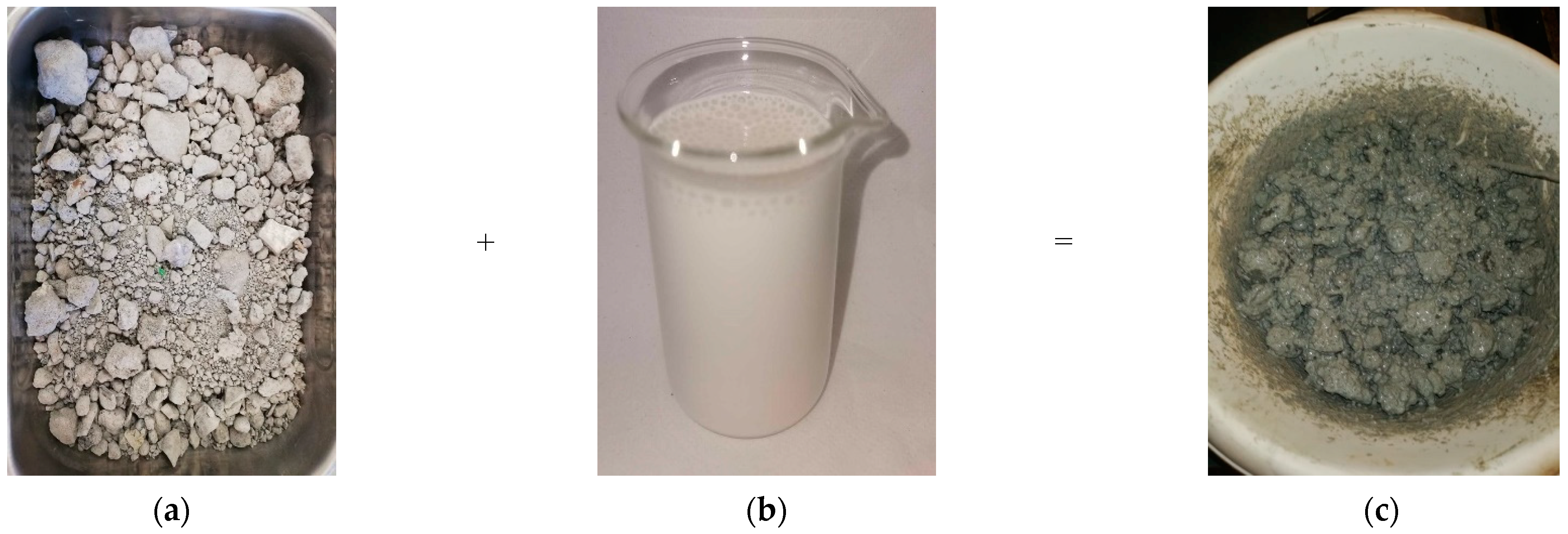
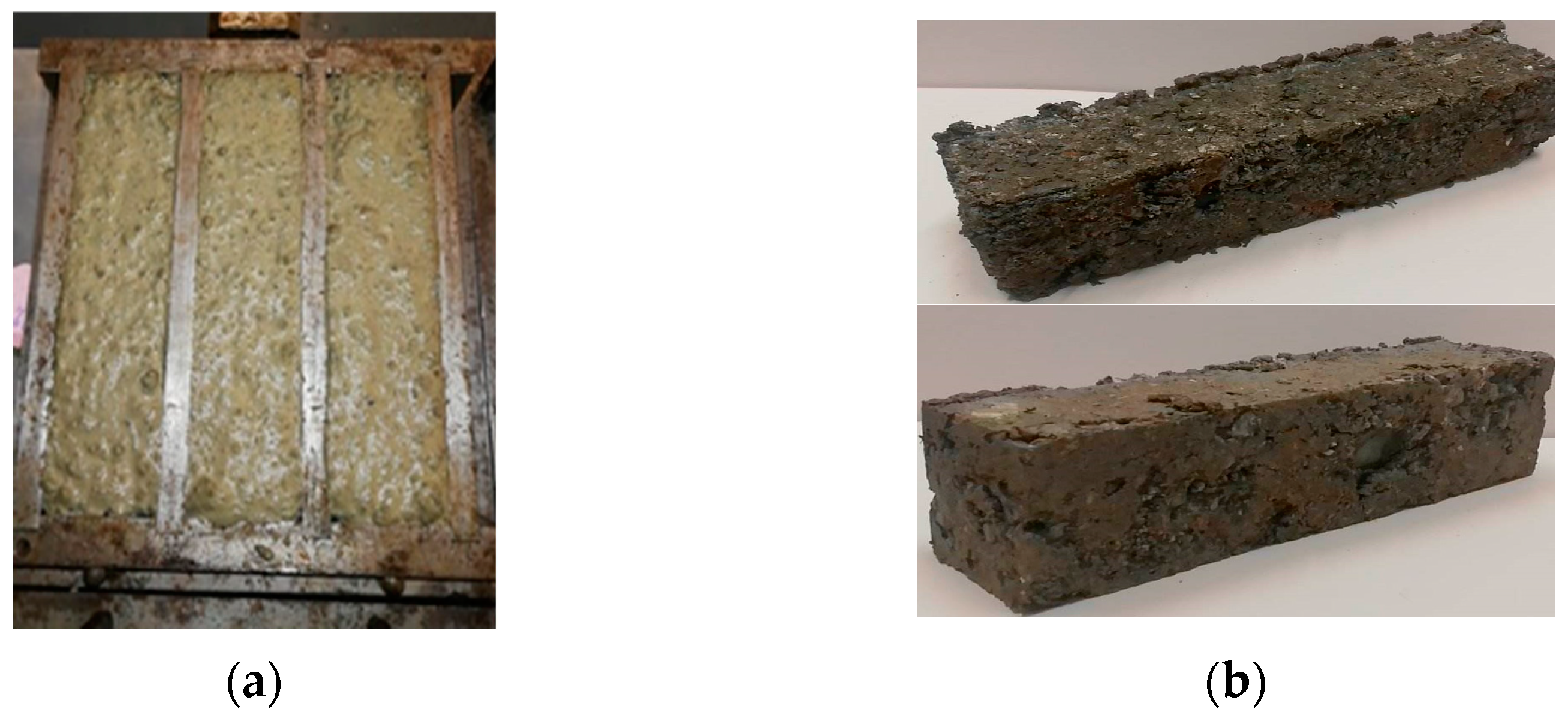
2.2.1. Production Techniques for Bottom Ash–Bio-Sourced Matrix Composites
2.2.2. Characterization Techniques
- Bottom ash characterization techniques
- Composite characterization techniques
3. Results and Analysis
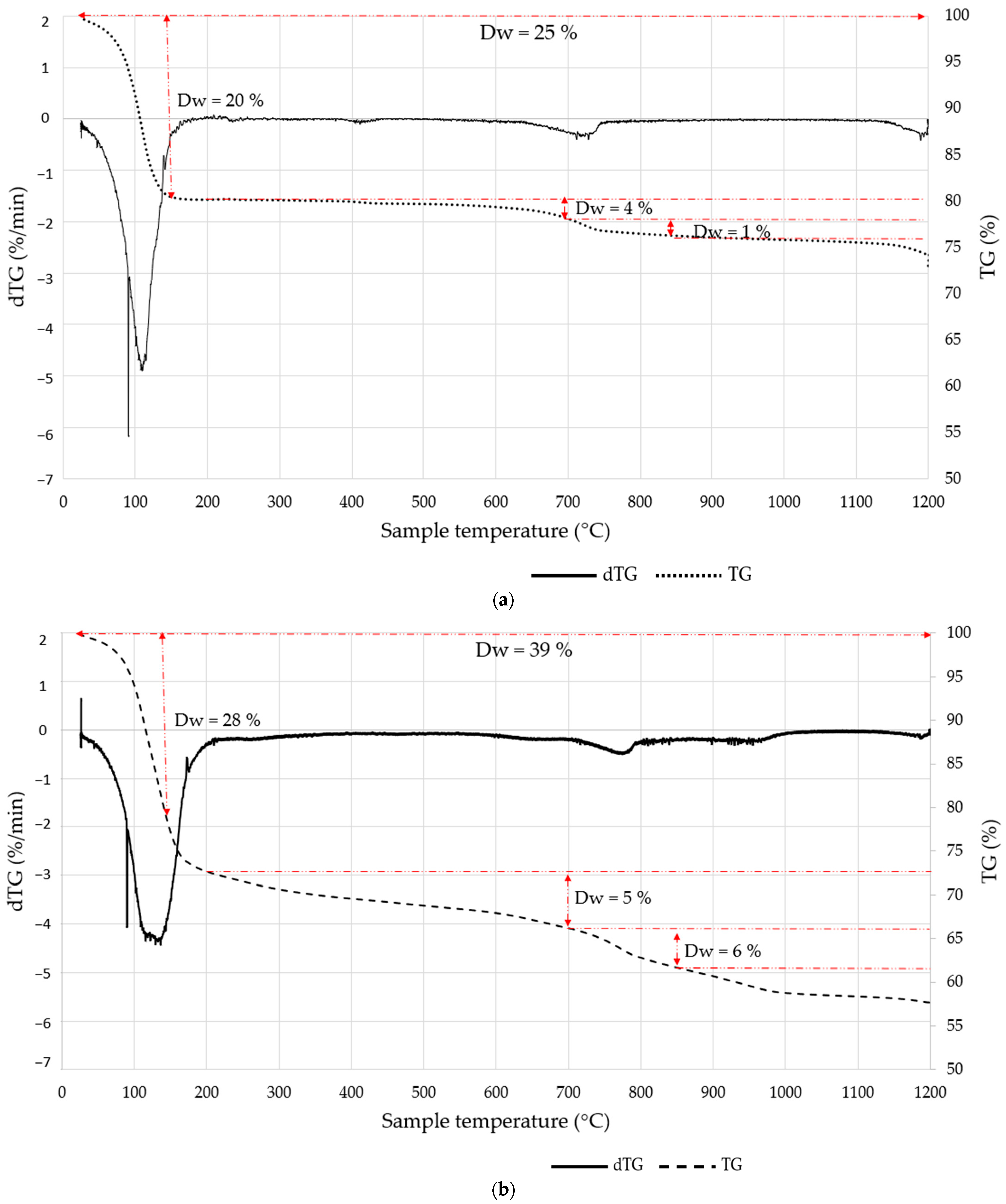
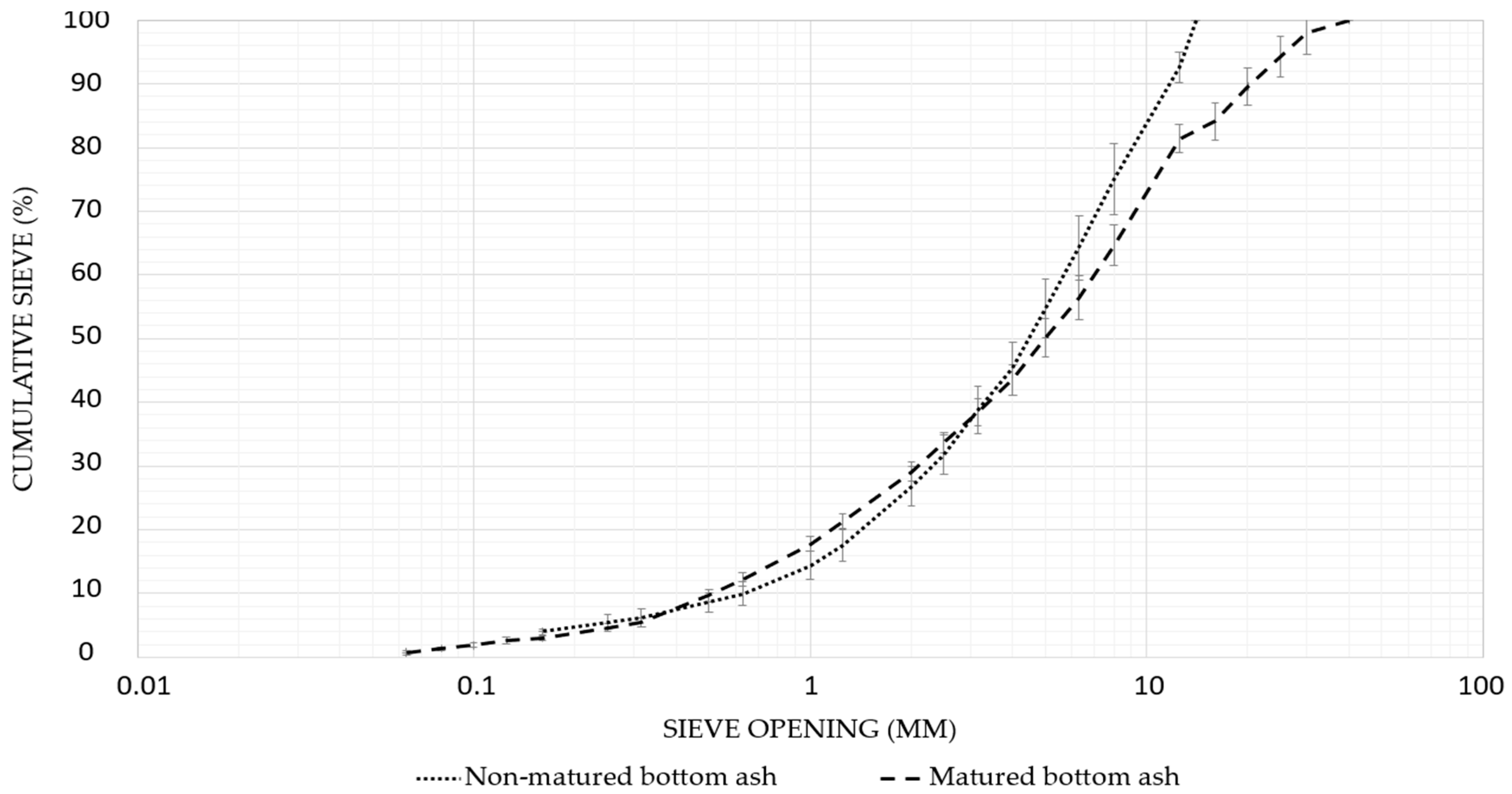
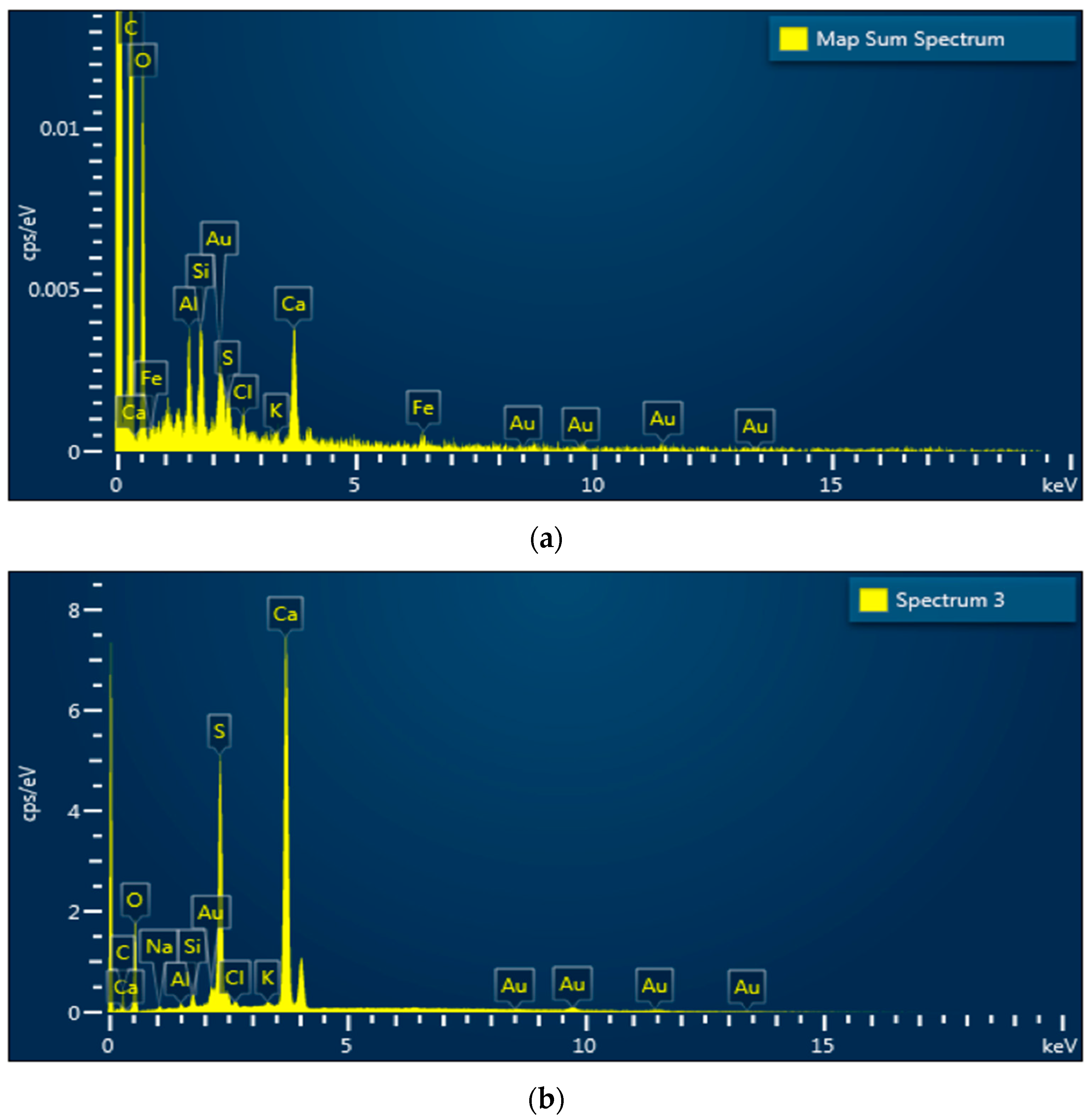
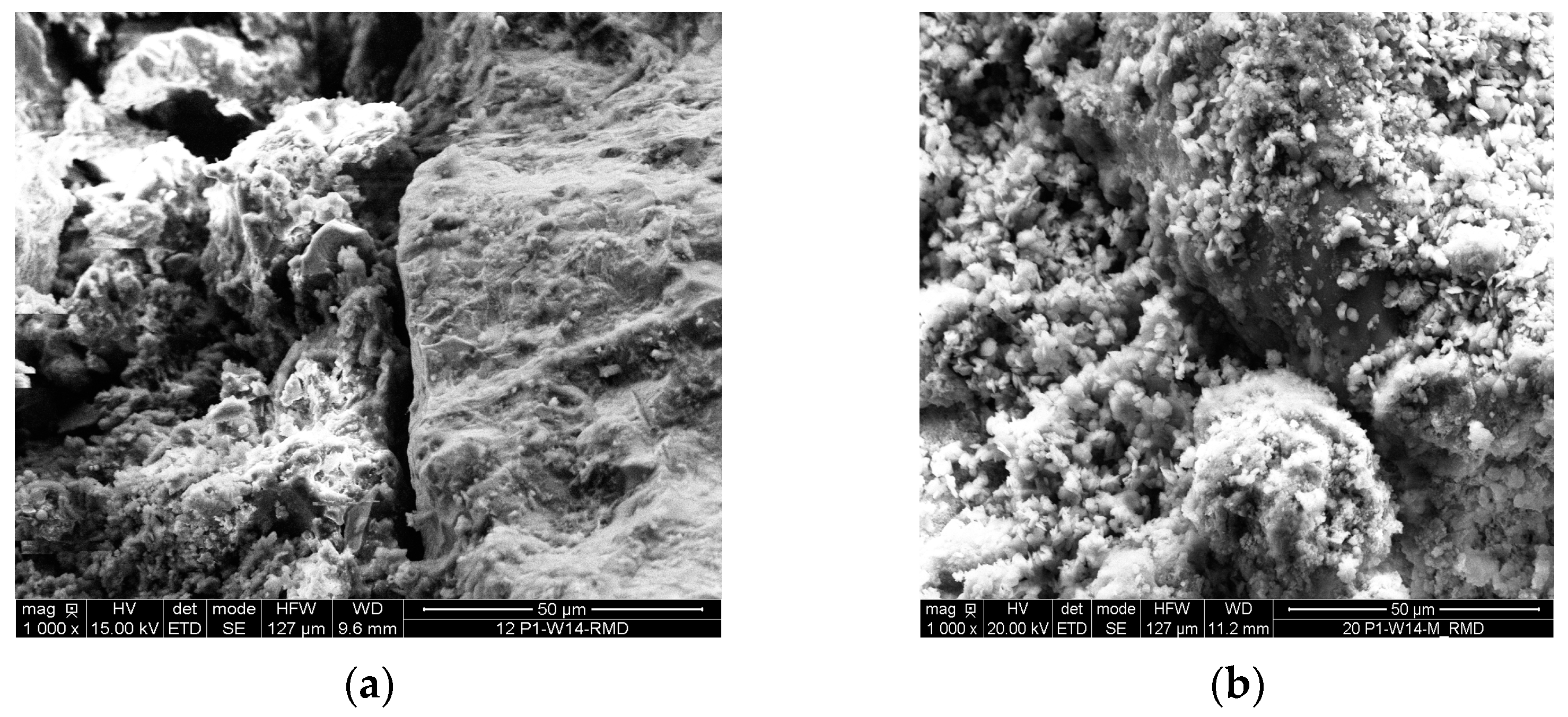
3.1. Effect of Bottom Ash Maturation on Its Properties
3.2. Influence of Bottom Ash Maturation on Composite Characteristics
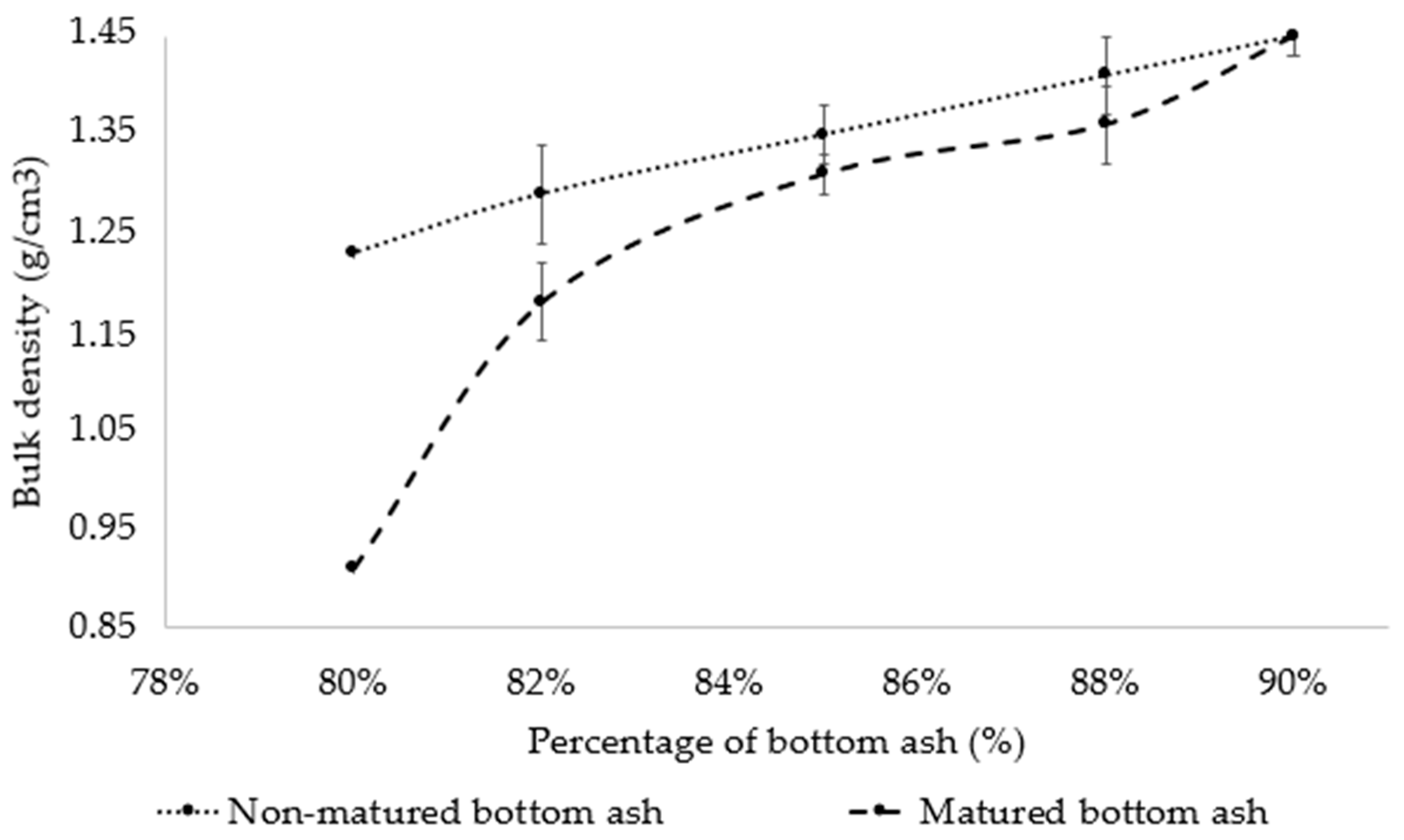
3.2.1. Influence on Bulk Density of Composites
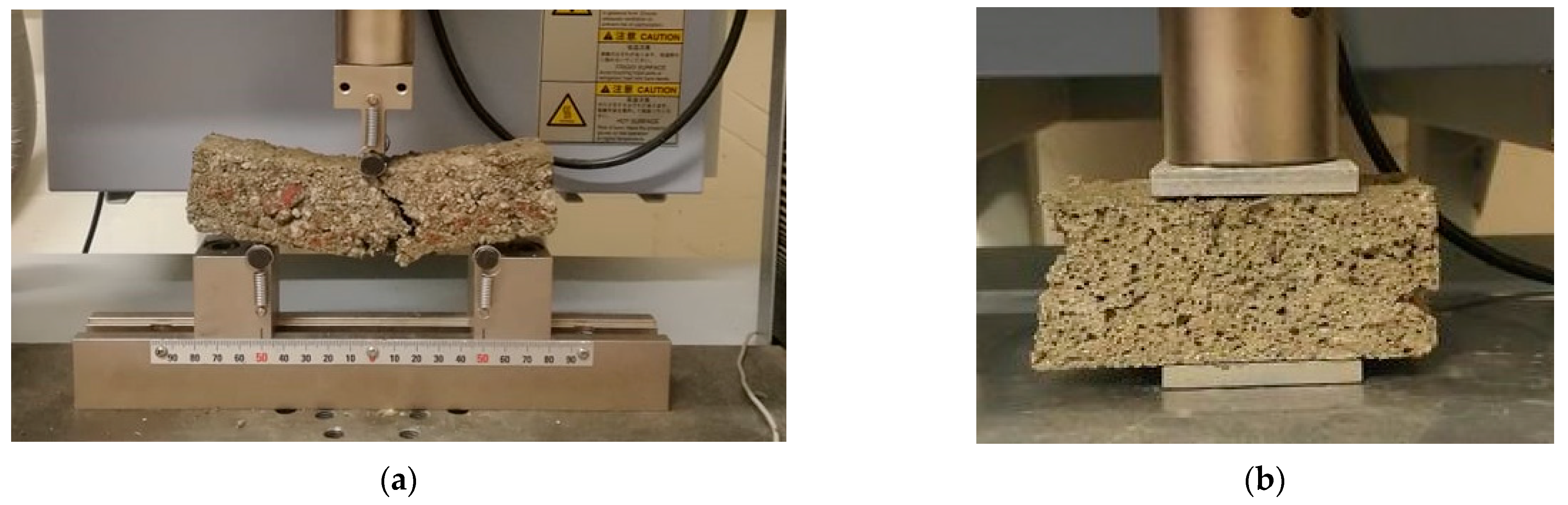
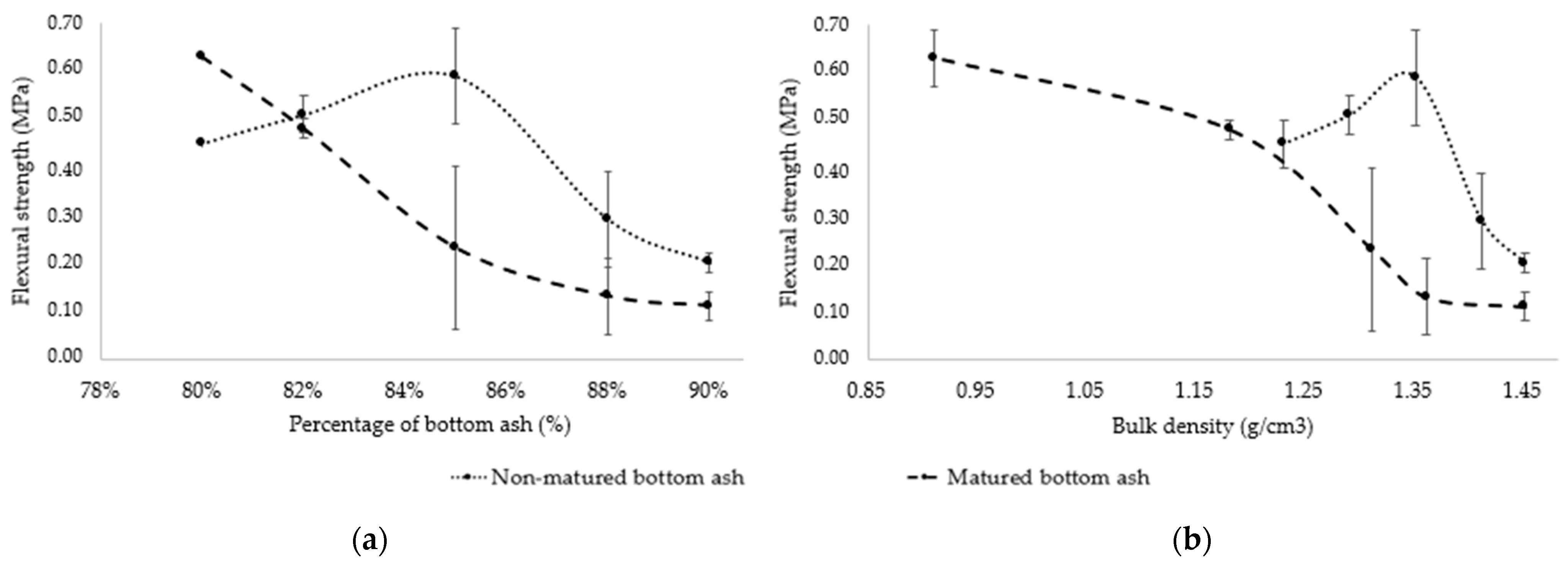
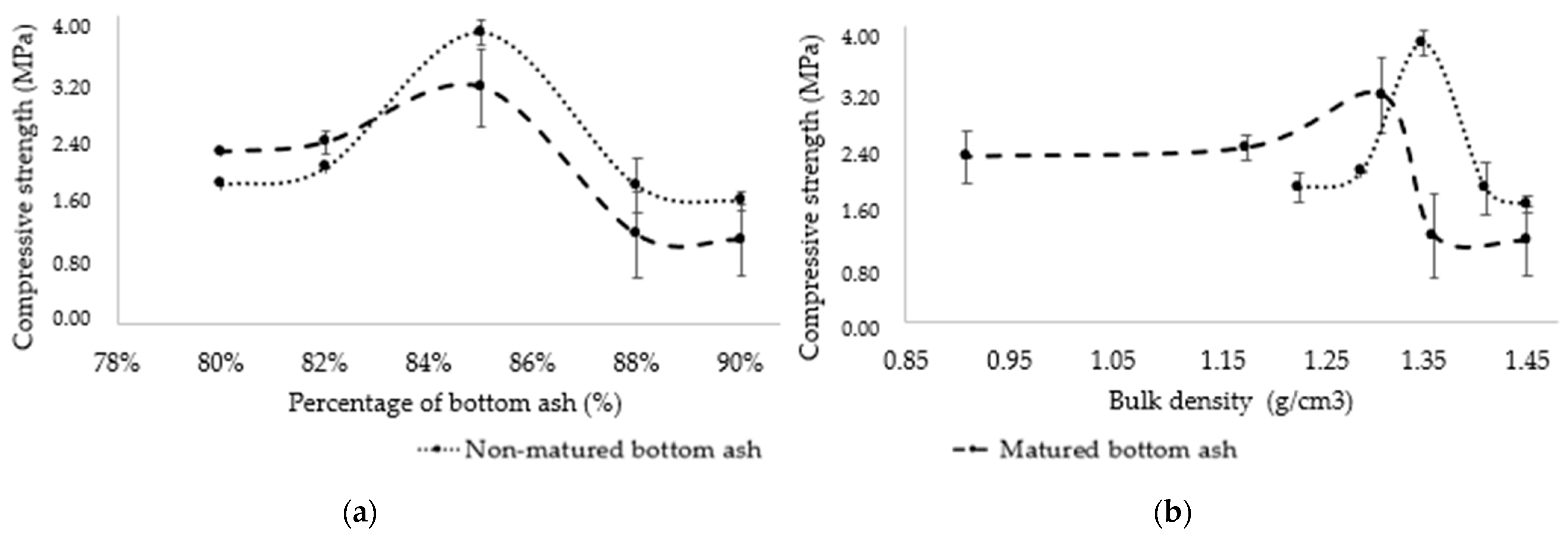
3.2.2. Influence on the Mechanical Strengths of Composites
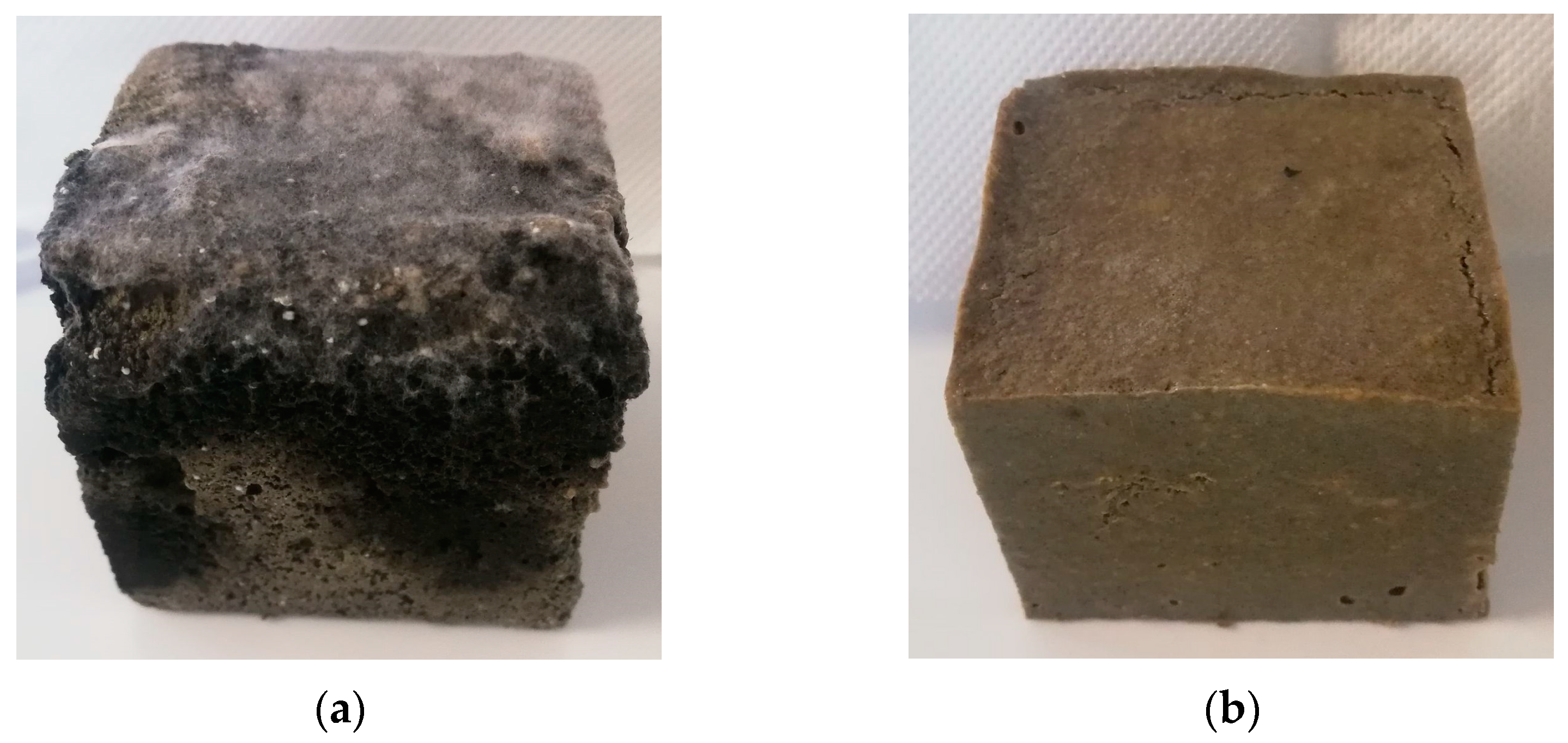
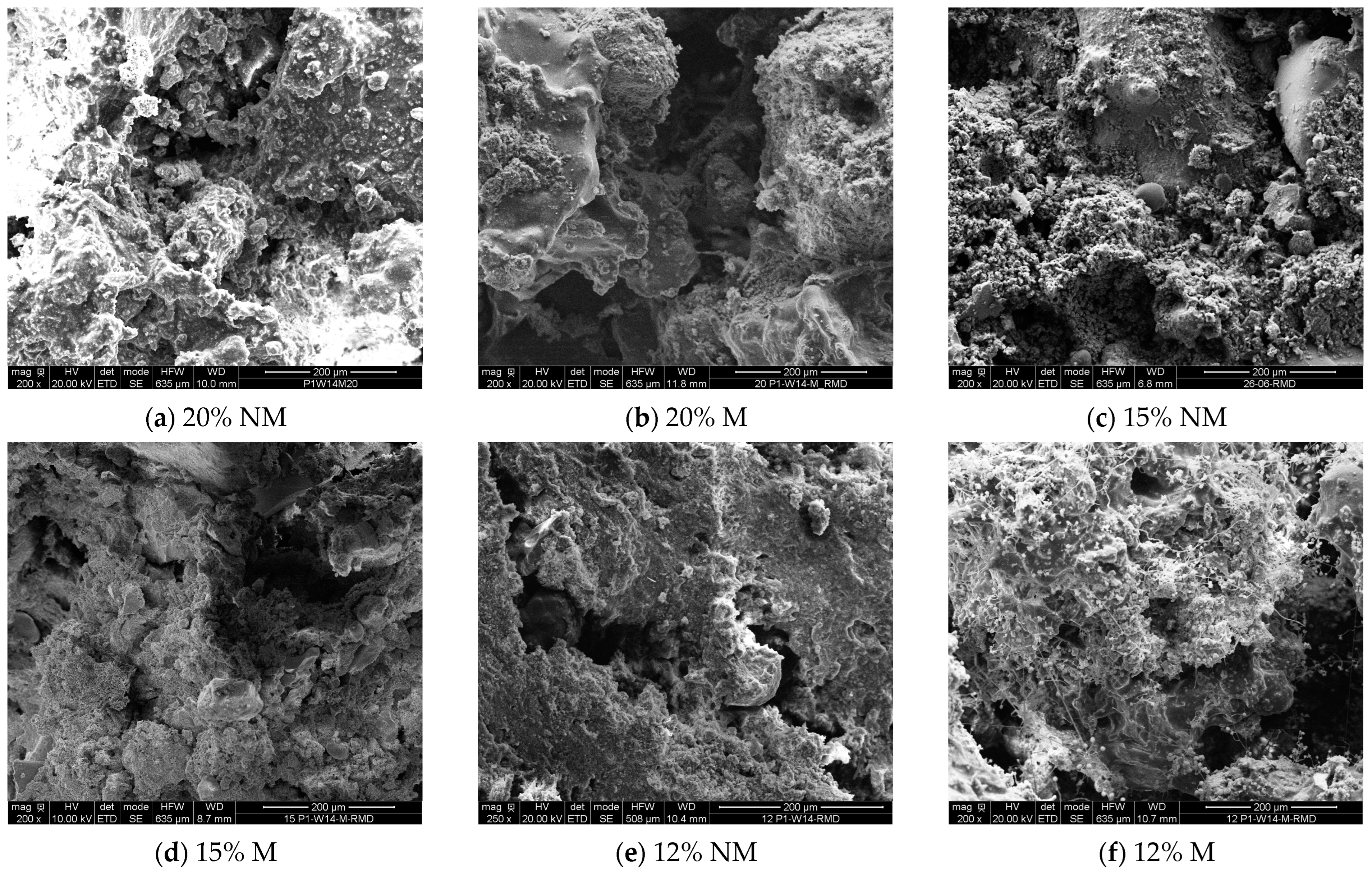
3.2.3. Influence on the Preservation of Composites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sétra. Acceptabilité Environnementale de Matériaux Alternatifs en Technique Routière. Les Mâchefers D’incinération de Déchets non Dangereux (MIDND); Service D’études sur les Transports, les Routes et leurs Aménagements: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.M.; Kim, K.; Le, T.H.M. Advancing Sustainability and Performance with Crushed Bottom Ash as Filler in Polymer-Modified Asphalt Concrete Mixtures. Polymers 2024, 16, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudelin, P. Conséquences de l’exploitation des granulats dans la Garonne. Rev. Geogr. Pyren. Sud-Ouest 1989, 60, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksel, İ.; Bilir, T.; Özkan, Ö. Durability of concrete incorporating non-ground blast furnace slag and bottom ash as fine aggregate. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 2651–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilir, T. Effects of unground slag and bottom ash as fine aggregates on the permeability properties of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 26, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, Y.; Siddique, R. Microstructure and properties of concrete using bottom ash and waste foundry sand as partial replacement of fine aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 54, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Siddique, R. Properties of concrete containing high volumes of coal bottom ash as fine aggregate. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 91, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, S.; Menda, S.; Useldinger-Hoefs, J.; Guteta, L.E.; Dockter, B.; Gedafa, D.S. The Use of Ground Coal Bottom Ash/Slag as a Cement Replacement for Sustainable Concrete Infrastructure. Materials 2024, 17, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pera, J.; Coutaz, L.; Ambroise, J.; Chababbet, M. Use of incinerator bottom ash in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 27, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecqueur, G.; Crignon, C.; Quénée, B. Behaviour of cement-treated MSWI bottom ash. Waste Manag. 2001, 21, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Onaizi, A.M.; Onaizi, S.A.; Sajjad, U.; Liu, Y. Integrated Use of Furnace Bottom Ash as Fine Aggregate and Cement Replacement for Sustainable Mortar Production. Materials 2024, 17, 3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, U.; Rübner, K. The microstructure of concrete made with municipal waste incinerator bottom ash as an aggregate component. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 1434–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.; Courard, L. Comportement des Mâchefers D’incinérateur D’ordures Ménagères dans les Bétons. Master’s Thesis, University of Liège—Faculty of Sciences Appliques, Liège, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Filipponi, P.; Polettini, A.; Pomi, R.; Sirini. Physical and mechanical properties of cement-based products containing incineration bottom ash. Waste Manag. 2003, 23, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkahal, Z. Co-valorisation des Matériaux Alternatifs en Technique Routière: Faisabilité Technique et Environnementale des Usages en Remblais et Liants Hydrauliques Routiers. Doctoral Dissertation, Ecole Nationale Superieure Mines-Télécom Lille Douai, Douai, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dabo, D. Impact Environnemental des Mâchefers D’incinération D’ordures Ménagères (MIOM) Valorisés en Technique Routière: Caractérisation, Expérimentations Multi-Échelles et Modélisation Hydro-Géochimique. Doctoral Dissertation, École Nationale Supérieure des Mines de Paris, Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- De Windt, L.; Dabo, D.; Lidelöw, S.; Badreddine, R.; Lagerkvist, A. MSWI bottom ash used as basement at two pilot-scale roads: Comparison of leachate chemistry and reactive transport modeling. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.V.; de Brito, J.; Lynn, C.J.; Dhir, R.K. Environmental impacts of the use of bottom ashes from municipal solid waste incineration: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 140, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valvez, S.; Maceiras, A.; Santos, P.; Reis, P.N. Olive stones as filler for polymer-based composites: A review. Materials 2021, 14, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Mantia, F.P.; Morreale, M. Green composites: A brief review. Compos. Part A 2011, 42, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.K.; Michaud, P.; Mathias, J.D. Polysaccharides as adhesives: A critical review. Rev. Adhes. Adhes. 2013, 1, 312–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhiram, Y.; Das, A.; Sharma, K.K. Green composites for structural and non-structural applications: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 2658–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, C. Composites à Fibres Longues de lin: Évaluation des Procédés par Infiltration. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Havre, Havre, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Saravanakumar, R.; Elango, K.S.; Revathi, V.; Balaji, D. Influence of aggressive environment in macro and microstructural properties of bottom ash geopolymer concrete. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Gunasekaran, S. Cow blood adhesive: Characterisation of physicochemical and adhesion properties. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2010, 30, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patent (No. 20 12870) Entitled “Process for Preparing Bio Sourced Elastomer Polymers”. (ref FR3117118A1 (B1) 2022-06-10 UNIV PICARDIE FR. Espacenet. Available online: https://worldwide.espacenet.com/publicationDetails/biblio?II=0&ND=3&adjacent=true&locale=fr_EP&FT=D&date=20220610&CC=FR&NR=3117118A1&KC=A1 (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- AFNOR NF 933-1; Tests for Geometrical Properties of Aggregates—Part 1: Determination of Particle Size Distribution—Sieving Method. Normes et Normalisation Européenne: Brussels, Belgium, 2012.
- AFNOR NF EN 1097-3; Tests for Mechanical and Physical Properties of Aggregates—Part 3: Determination of Loose Bulk Density and Voids. Normes et Normalisation Européenne: Brussels, Belgium, 1998.
- AFNOR NF EN 1097-5; Tests for Mechanical and Physical Properties of Aggregates—Part 5: Determination of the Water Content by Drying in a Ventilated Oven. Normes et Normalisation Européenne: Brussels, Belgium, 2008.
- AFNOR NF EN 196-1; Methods of Testing Cement—Part 1: Determination of Strength. Normes et Normalisation Européenne: Brussels, Belgium, 2016.
- Gervais, C. Evaluation Environmentale des Perspectives de Valorisation en BTP des Scories de Première Fusion de plomb et de zinc. Ph.D. Thesis, Institut National des Sciences Appliquées de Lyon, Lyon, France, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Verrecchia, E.P. Géodynamique du Carbonate de Calcium à la Surface des Continents. Géologie de la Préhistoire: Méthodes, Techniques, Applications; Géopré Editions: Paris, France, 2002; pp. 233–276. [Google Scholar]
- Sow, L.C.; Toh, N.Z.Y.; Wong, C.W.; Yang, H. Combination of sodium alginate with tilapia fish gelatin for improved texture properties and nanostructure modification. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, J.L.; Compbell, D. Functional classification of lightweight concrete. Mater. Struct. 1972, 5, 171–172. [Google Scholar]






| Bio-Composite Names | Bottom Ash | Bio-Sourced Matrix | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | g | % | g | |
| 80 | 80 | 1354.2 | 20 | 338.6 |
| 82 | 82 | 1388 | 18 | 304.7 |
| 85 | 85 | 1438.8 | 15 | 253.9 |
| 88 | 88 | 1489.6 | 12 | 203.2 |
| 90 | 90 | 1523.5 | 10 | 169.3 |
| Bottom Ash | Particle Size Class (mm) | Bulk Density (g/cm3) | Water Content (%) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-matured | 0/14 | 0.98 | 24.2 | 12 |
| Matured | 0/40 | 1.25 | 14.29 | 7.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taleb-Ahmed, A.; Montrelay, N.; Houessou, K.J.; Quéneudec-t’Kint, M.; Sebaibi, N.; Dheilly, R.-M. Influence of the Mass Percentage of Bottom Ash and Its State of Maturation on the Mechanical Performance of a Bio-Composite. Buildings 2024, 14, 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14082586
Taleb-Ahmed A, Montrelay N, Houessou KJ, Quéneudec-t’Kint M, Sebaibi N, Dheilly R-M. Influence of the Mass Percentage of Bottom Ash and Its State of Maturation on the Mechanical Performance of a Bio-Composite. Buildings. 2024; 14(8):2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14082586
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaleb-Ahmed, Asmahan, Nicolas Montrelay, Koffi Justin Houessou, Michèle Quéneudec-t’Kint, Nassim Sebaibi, and Rose-Marie Dheilly. 2024. "Influence of the Mass Percentage of Bottom Ash and Its State of Maturation on the Mechanical Performance of a Bio-Composite" Buildings 14, no. 8: 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14082586
APA StyleTaleb-Ahmed, A., Montrelay, N., Houessou, K. J., Quéneudec-t’Kint, M., Sebaibi, N., & Dheilly, R.-M. (2024). Influence of the Mass Percentage of Bottom Ash and Its State of Maturation on the Mechanical Performance of a Bio-Composite. Buildings, 14(8), 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14082586







