Building Energy Efficiency Enhancement through Thermochromic Powder-Based Temperature-Adaptive Radiative Cooling Roofs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
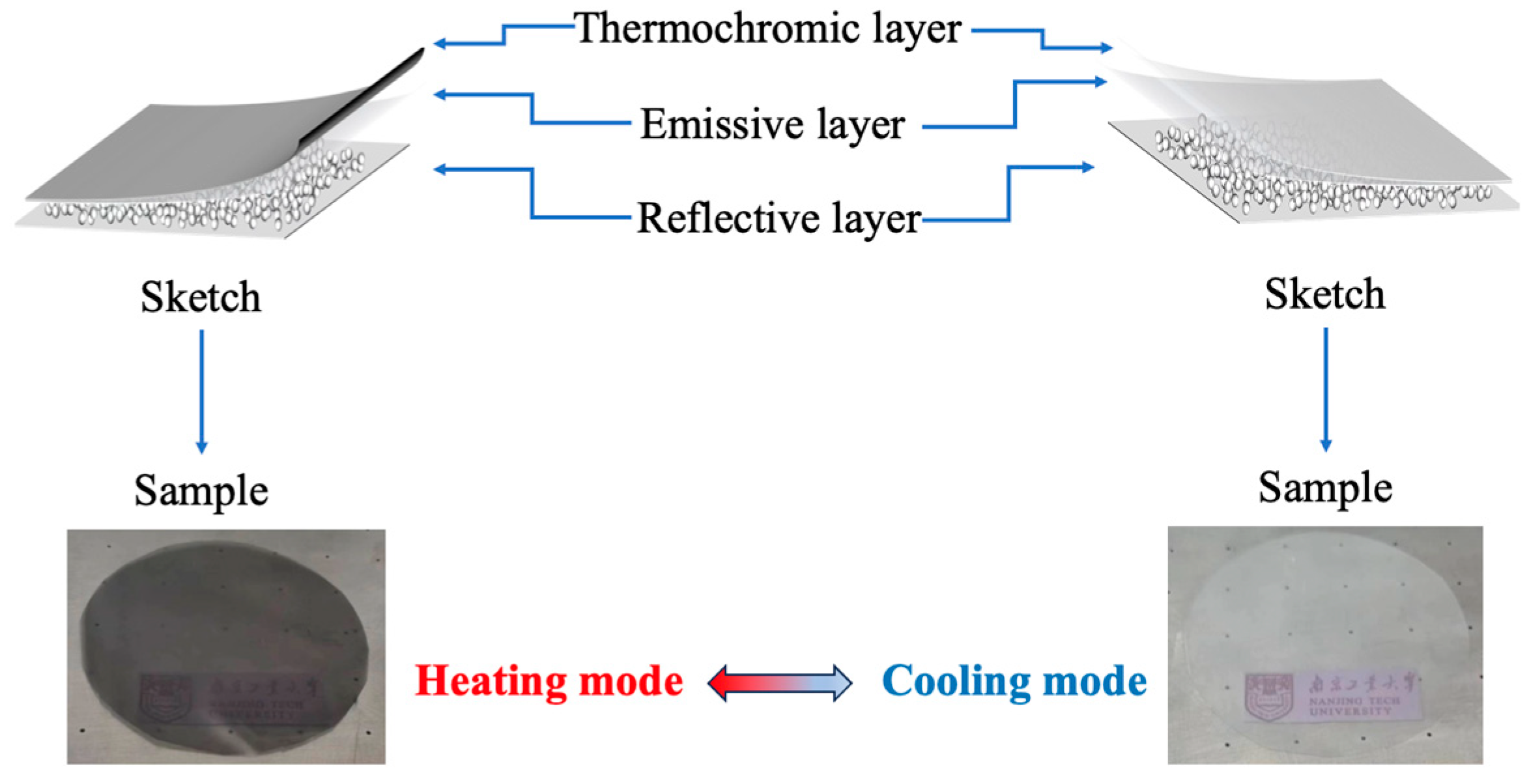
2.1. Preparation of the TARC Coating
2.2. Characterization of the TARC Coating
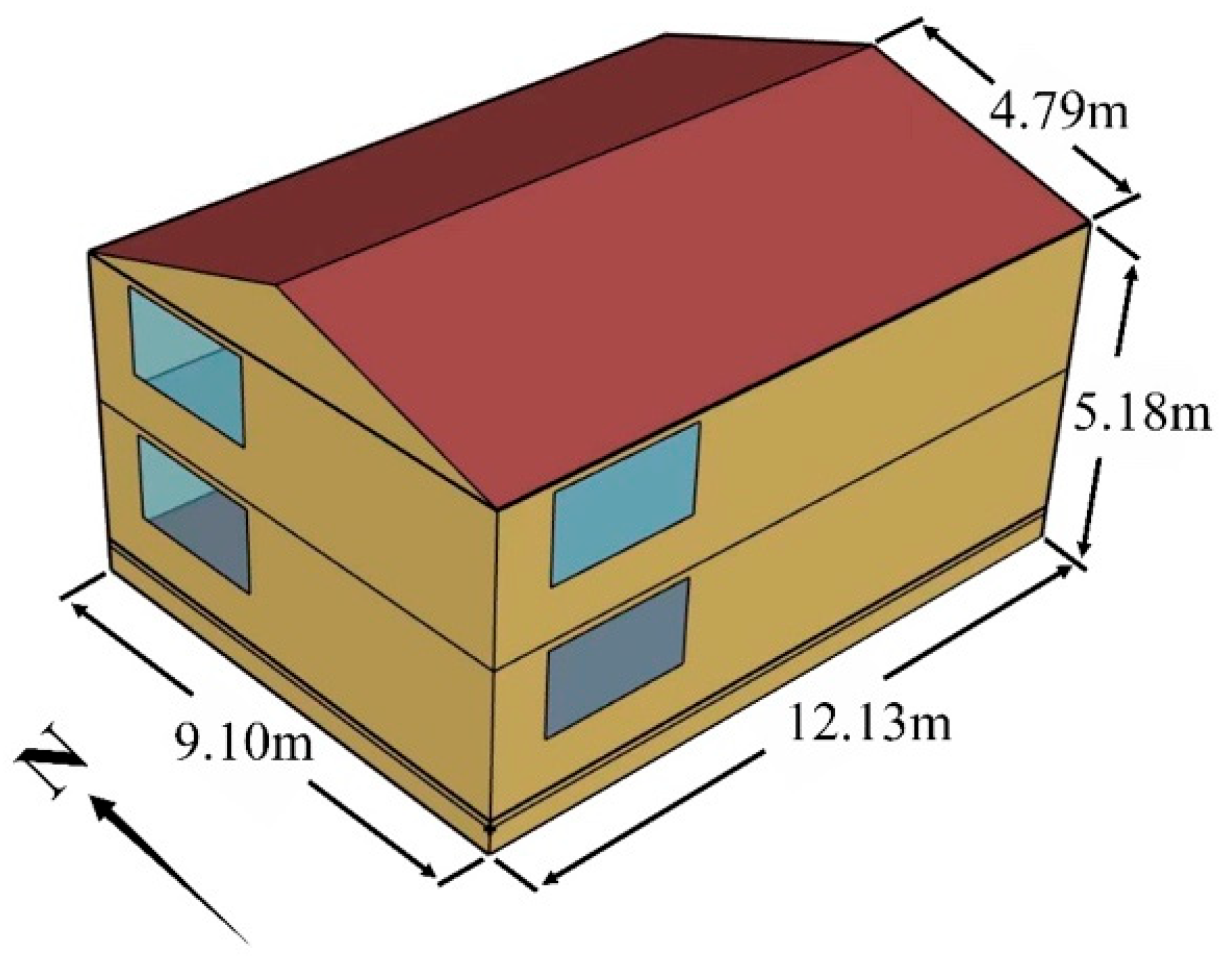
2.3. Modeling of the Building
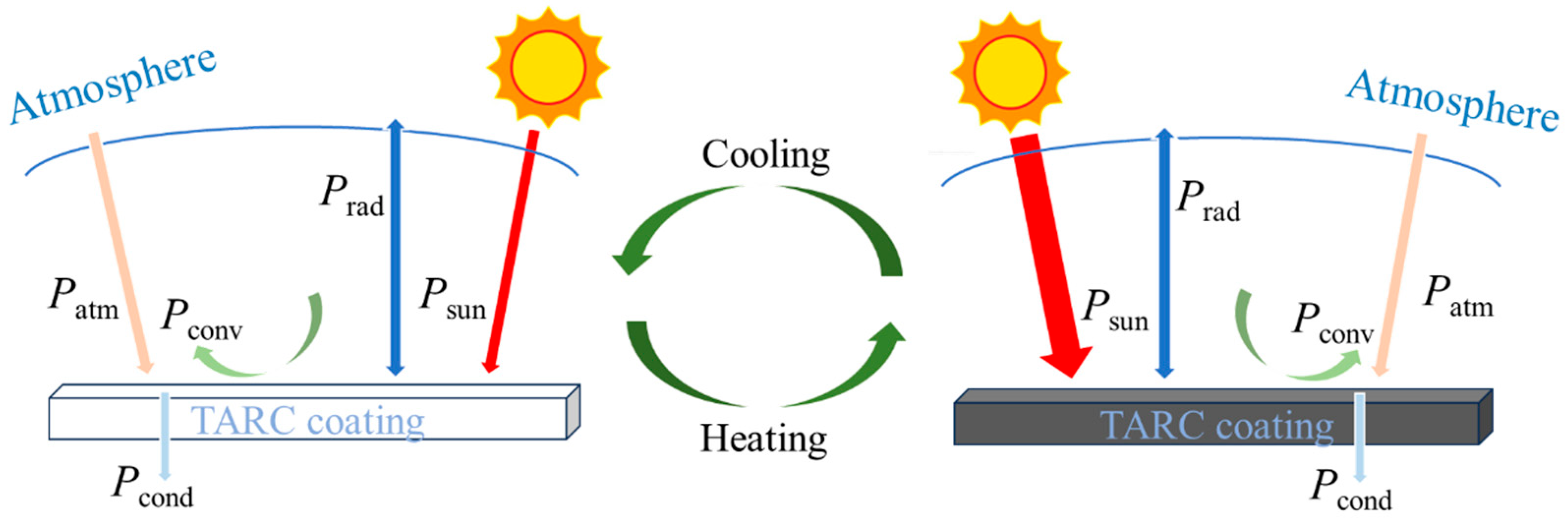
2.4. Heat transfer of the TARC Coating
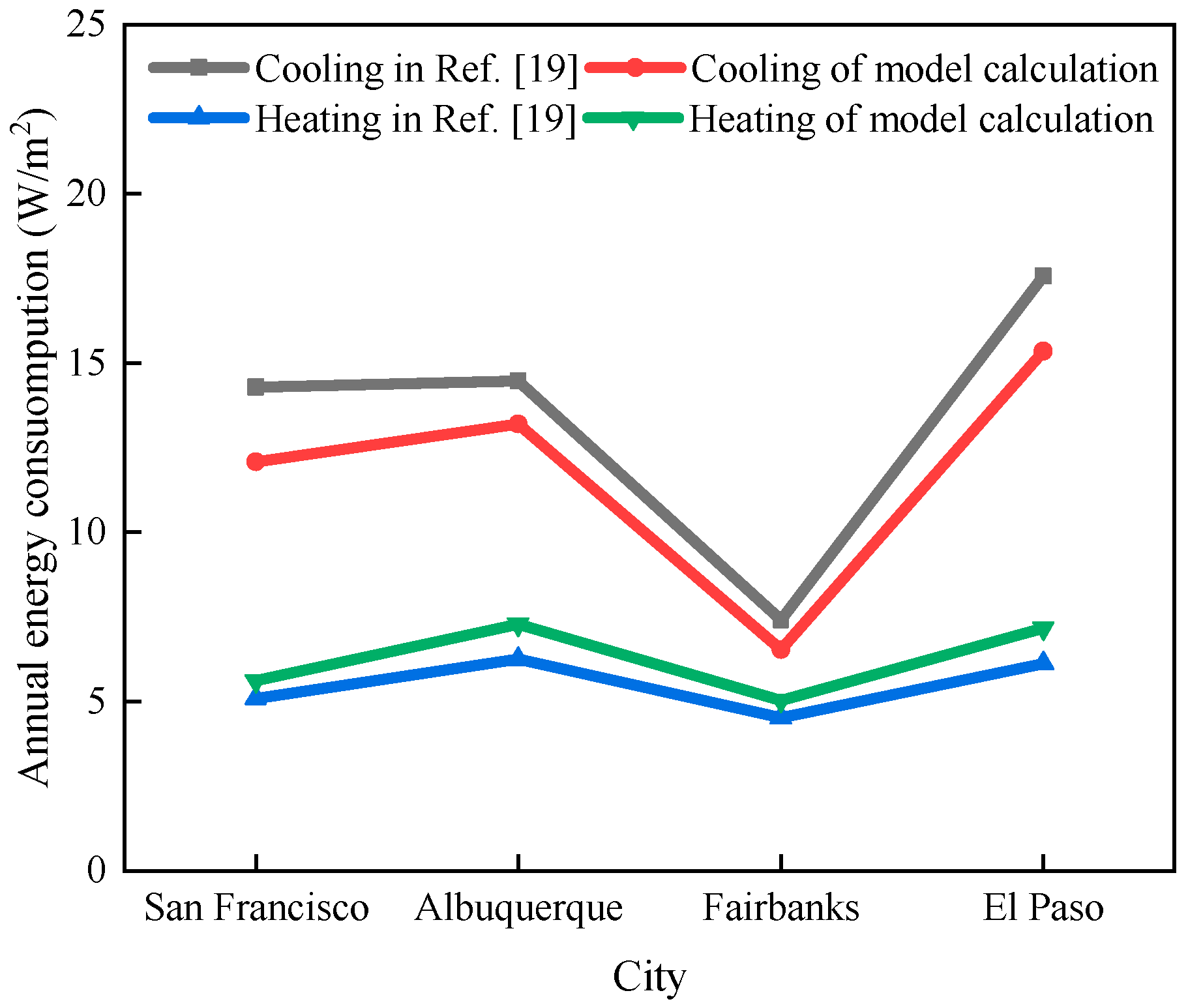
2.5. Model Validation
3. Results and Discussion
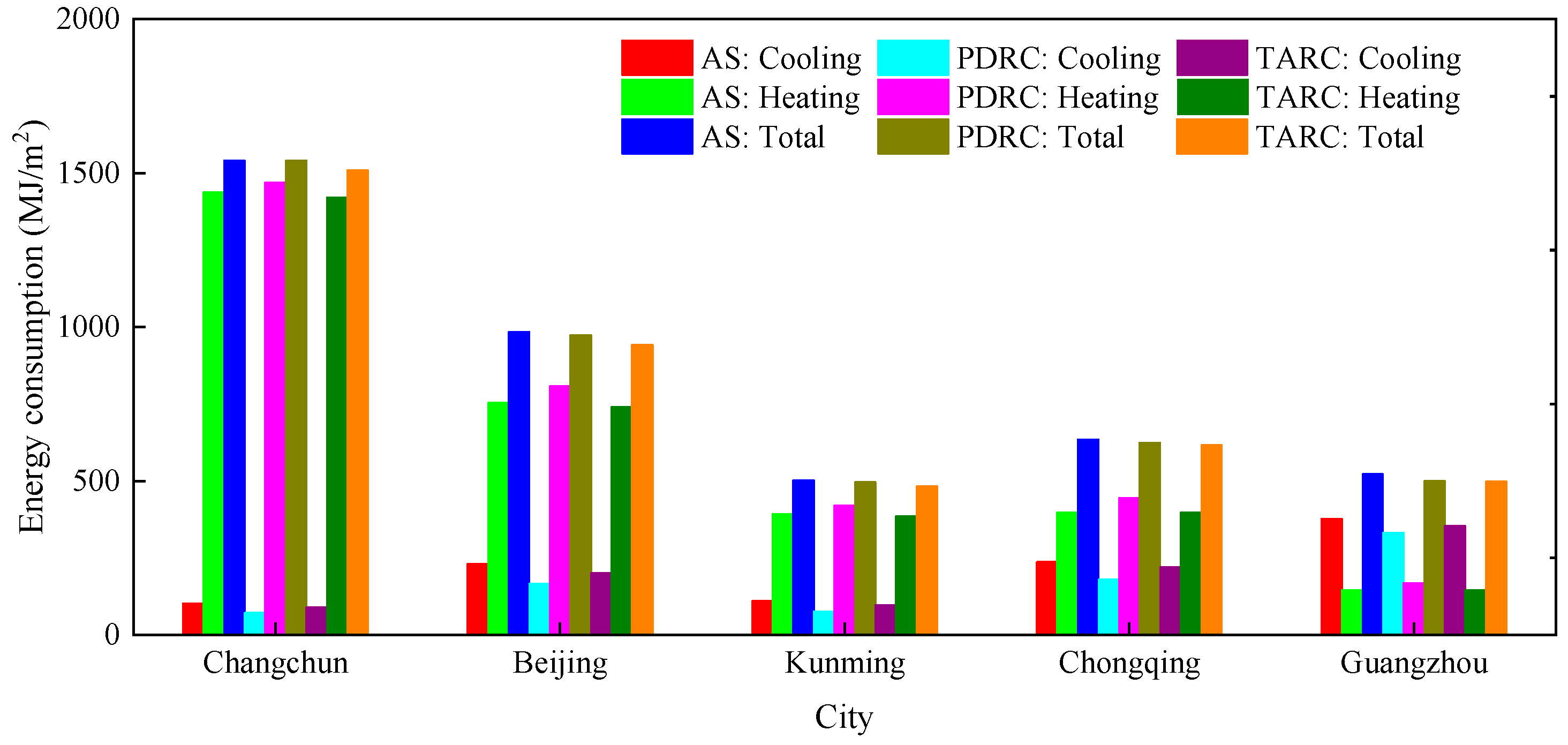
3.1. Effect of the TARC Roof on Annual Building Energy
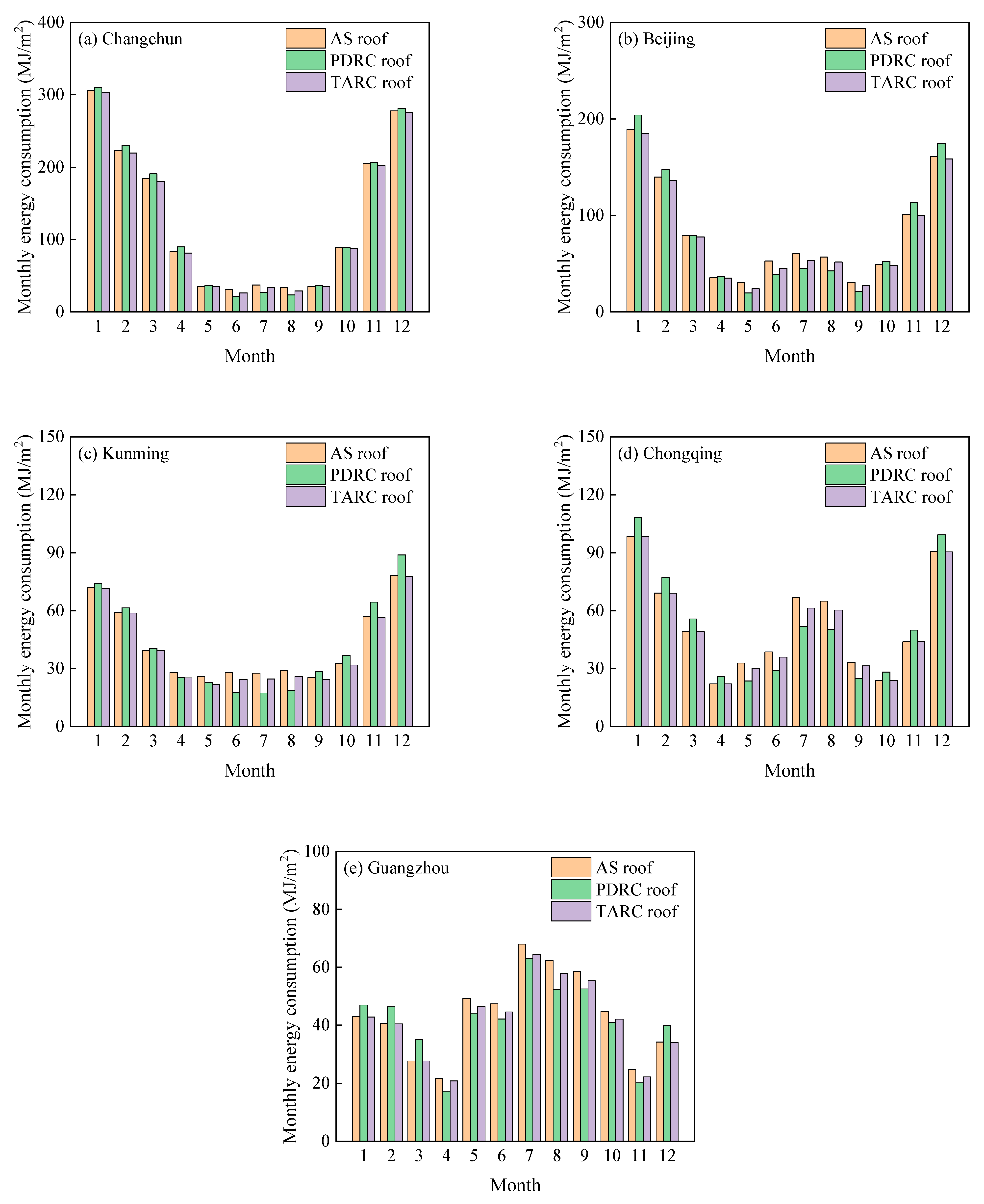
3.2. Monthly Energy Consumption of Buildings with TARC Roofs
3.3. Building Carbon Reduction of Applying TARC
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AS | Original roof | PDMS | Polydimethylsiloxane |
| PDRC | Passive daytime radiative cooling | PE | Polyethylene |
| TARC | Temperature-adaptive radiative cooling | TPX | Ploymethylpentene |
References
- Li, R.; You, K.R.; Cai, W.G.; Wang, J.B.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Y.H. Will the Southward Center of Gravity Migration of Population, Floor Area, and Building Energy Consumption Facilitate Building Carbon Emission Reduction in China. Build. Environ. 2023, 242, 110576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, K.Y.G.; Kim, J.; Chong, W.K.O.; Ariaratnam, S.T. Structuring a Comprehensive Carbon-Emission Framework for the Whole Lifecycle of Building, Operation, and Construction. J. Archit. Eng. 2016, 22, 04016006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutakki, T.U.K.; Kazim, K.W.U.; Alamara, K.; Salameh, T.; Abdelkareem, M.A. Experimental Investigation on Aging and Energy Savings Evaluation of High Solar Reflective Index (Sri) Paints: A Case Study on Residential Households in the GCC Region. Buildings 2023, 13, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.R.; Zhang, K.; Shi, Z.J.; Jiang, K.Y.; Wu, B.Y.; Ye, P.L. Cooling Benefit of Implementing Radiative Cooling on a City-Scale. Renew. Energy 2023, 212, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.Y.; Zhang, K.; Shi, Z.J.; Li, H.R.; Wu, B.Y.; Mahian, O.; Zhu, Y.T. Experimental and Numerical Study on the Potential of a New Radiative Cooling Paint Boosted by SiO2 Microparticles for Energy Saving. Energy 2023, 283, 128473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.Q.; Zhang, K.; Chen, L.F.; Tang, S.H. Analysis of the Impact of a Novel Cool Roof on Cooling Performance for a Low-Rise Prefabricated Building in China. Build. Serv. Eng. Res. Technol. 2020, 42, 26–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.Y.; Yang, X.B.; Xie, K.; Tang, M.Y.; Xu, Y.B.; Ben, X.Y. The Mathematical Modeling and Performance of Sky Radiative Coolers. Buildings 2023, 13, 2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.L.; Liao, Y.X.; Jia, Y.H.; Zhang, W.T.; Long, E.S. Summer Thermal Challenges in Emergency Tents: Insights into Thermal Characteristics of Tents with Air Conditioning. Buildings 2024, 14, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.X.; Du, Y.W.; Chen, S.R.; Chao, L.K.; Lee, H.H.; Ho, C.T.; Zhu, Y.H.; Zeng, Y.J.; Pan, A.Q.; Yan, T.C. Nanoparticle-Polymer Hybrid Dual-Layer Coating with Broadband Solar Reflection for High-Performance Daytime Passive Radiative Cooling. Energy Build. 2022, 276, 112507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.M.; Bu, X.H.; Liu, R.Q.; Feng, M.X.; Zhang, Z.W.; He, M.; Huang, M.J.; Zhou, Y.M. Construction of Robust Silica-Hybridized Cellulose Aerogels Integrating Passive Radiative Cooling and Thermal Insulation for Year-Round Building Energy Saving. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Lu, L.; Gong, Q.; Wang, B.X.; Jin, S.G.; Wang, M. Development of a New Spectral Selectivity-Based Passive Radiative Roof Cooling Model and Its Application in Hot and Humid Region. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.; Xuan, Q.D.; Fu, Y.; Ma, X.; Lei, D.Y.; Niu, J.L.; Dai, J.G. Phosphate Activated Geopolymer-Based Coating with High Temperature Resistance for Sub-Ambient Radiative Cooling. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 100, 104992. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, C.Y.; Chen, W.B.; Wei, Z.C.; Ding, C.X.; Sun, B.J.; Gerhard, C.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, K. Bioinspired “Aerogel Grating Metasurfaces Durable Daytime Radiat. Cool. Year-Round Energy Savings”. Nano Energy 2023, 114, 108625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.S.; Lei, S.; Wang, F.J.; Long, H.B.; Ou, J.F.; Amirfazli, A.; Baldelli, A. A Comprehensive Investigation of Zeolite/Polyurea Cooling Coating on Concrete for Building Energy Conservation. Prog. Org. Coat. 2024, 188, 108265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.S.; Lv, Y.Y.; Zhao, D.L.; Zhao, W.B.; Xu, J.T.; Yang, R.G. Performance Evaluation of Radiative Cooling for Commercial-Scale Warehouse. Mater. Today Energy 2022, 24, 100927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giulia, U.; Gianluca, R.; Kwok, W.S.; Jie, F.; Mattheos, S. On the Energy Modulation of Daytime Radiative Coolers: A Review on Infrared Emissivity Dynamic Switch Against Overcooling. Sol. Energy 2020, 209, 278–301. [Google Scholar]
- Michał, M.; Lech, L. The Impact of a Mobile Shading System and a Phase-Change Heat Store on the Thermal Functioning of a Transparent Building Partition. Materials 2021, 14, 14102512. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, L.F.; Song, G.; Niu, X.F.; Li, F. Passive Cooling/Heating Double-Effect Material. International Patent WO2021120706A1, 24 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, K.; Dong, K.C.; Li, J.C.; Gordon, M.P.; Reichertz, F.G.; Kim, H.; Rho, Y.; Wang, Q.J.; Lin, C.Y.; Grigoropoulos, C.P.; et al. Temperature-Adaptive Radiative Coating for All-Season Household Thermal Regulation. Science 2021, 374, 1504–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.C.; Jiang, T.Y.; Meng, Y.; Yang, R.G.; Tan, G.; Long, Y. Scalable Thermochromic Smart Windows with Passive Radiative Cooling Regulation. Science 2021, 374, 1501–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Li, R.Z.; Xu, P.; Zhong, W.H.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, F.; Xiang, B. Thermochromic Smart Window Utilizing Passive Radiative Cooling for Self-Adaptive Thermoregulation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.C.; Zhang, X.-k.; Yu, X.Y.; Tang, G.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Du, M. Scalable Self-Adaptive Radiative Cooling Film through VO2-Based Switchable Core–Shell Particles. Renew. Energy 2024, 224, 120208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Li, G.; Zhao, D.L. Multi-Objective Optimization of an Anti-Reflection AIN/VO2/AIN Thermochromic Window for Building Energy Saving. Energy 2024, 288, 129798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, X.Z.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, J.L.; Xu, N.; Du, X.R.; Zeng, M.Y.; Li, W.; Zhu, B.; Zhu, J. A Smart Thermal-Gated Bilayer Membrane for Temperature-Adaptive Radiative Cooling and Solar Heating. Sci. Bull. 2023, 18, 2054–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, N.; Liu, S.Q.; Chen, C.X.; Song, C.X.; Mo, S.H.; Yan, H.J.; Chen, M.J. Outdoor Adaptive Temperature Control Based on a Thermochromic Hydrogel by Regulating Solar Heating. Sol. Energy 2024, 270, 112405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Chen, S.M.; Wang, J.T.; He, C.Y.; Fang, K.; Yin, H.L.; Liu, Y.T.; Li, Y.; Yu, D. Smart Thermally Responsive Perovskite Materials: Thermo-Chromic Application and Density Function Theory Calculation. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.W.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Z.W.; Lee, H.H.; Ho, T.C.; Feng, S.-P.; Tso, C.Y. Study on the Halide Effect of MA4PbX6·2H2O Hybrid Perovskites–from Thermochromic Properties to Practical Deployment for Smart Windows. Mater. Today Phys. 2022, 23, 100624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.Q.; Li, A.K.; Wu, H.L.; Tong, Z.P.; Qu, J.H.; Sun, W.; Yang, Z.W. Scalable and All-Season Passive Thermal Modulation Enabled by Radiative Cooling, Selective Solar Absorption, and Thermal Retention. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 221, 119707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarevich, A.M.; Sobol, A.G.; Sadykov, L.; Sharovarov, D.I.; Amelichev, V.A.; Tsymbarenko, D.M.; Boytsova, O.V.; Kaul, A.R. Delicate Tuning of Epitaxial VO2 Films for Ultra-Sharp Electrical and Intense IR Optical Switching Properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 853, 157214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.Y.M.; Tso, C.Y.; Chao, C.Y.H.; Huang, B.; Wan, M.P. Ultra-Broadband Asymmetric Transmission Metallic Gratings for Subtropical Passive Daytime Radiative Cooling. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2018, 186, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.H.; Akkurt, N.; Zhang, K.; Chen, L.F.; Ma, M.Q. Effect of Roof and Ceiling Configuration on Energy Performance of a Metamaterial-based Cool Roof for Low-rise Office Building in China. Indoor Built Environ. 2021, 30, 1739–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weather Date. Available online: https://energyplus.net/weather-region (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- GB 55015-2021; Code for Building Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Utilization. Ministry of Housing: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Yang, Y.; Long, L.S.; Meng, S.; Denisuk, N.; Chen, G.Z.; Zhu, L.P. Bulk Material Based Selective Infrared Emitter for Sub-Ambient Daytime Radiative Cooling. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2020, 211, 110548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Fan, D. Core-Shell Microspheres Hybridized Membrane for Light Emitting and Radiative Cooling. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 924, 166480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.W.; Zhang, D.B.; Jiao, S.F.; Zhou, Z.H.; Zhang, Z.F.; Gao, F. Preliminary Study of Radiative Cooling in Cooling Season of the Humid Coastal Area. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2020, 208, 110412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoleon, K.J.; Eumorfopoulou, E.A. The Influence of Wall Orientation and Exterior Surface Solar Absorptivity on Time Lag and Decrement Factor in the Greek Region. Renew. Energy 2008, 7, 1652–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.Y.; Zhang, K.; Ye, P.L.; Niu, Z.Y.; Song, G. Effect of Electronic and Phonon Properties on Polar Dielectric Embedded Polymer-Based Radiative Cooling Materials. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2018, 224, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, N.N.; Shafique, M. Embodied Carbon Emissions of Buildings: Taking a Step Towards Net Zero Buildings. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 260, 112473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Dong, M.Y.; Wang, C.H. Passive Interfacial Photothermal Evaporation and Sky Radiative Cooling Assisted All-Day Freshwater Harvesting: System Design, Experiment Study, and Performance Evaluation. Appl. Energy 2023, 475, 146431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Item | Details | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Window–wall ratio | 12.78% | ||
| Occupants | 3 | ||
| Fresh air volume | 30 m3/h per person | ||
| Lighting density | 8.5 W/m2 | ||
| Equipment power density | 6.0 W/m2 | ||
| Interior design temperatures | Winter: | 20 °C | |
| Summer: | 27 °C | ||
| Roof | TARC | Cooling mode | |
| Reflectivity: | 0.65 | ||
| Emissivity: | 0.92 | ||
| Heating mode | |||
| Reflectivity: | 0.73 | ||
| Emissivity: | 0.93 | ||
| PDRC [5] | Reflectivity: | 0.92 | |
| Emissivity: | 0.91 | ||
| AS [6] | Reflectivity: | 0.25 | |
| Emissivity: | 0.90 | ||
| City | Climatic Zone | Heat Transfer Coefficient (W/m2∙K) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exterior Wall | Roof | ||
| Changchun | Severe cold zone | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Beijing | Cold zone | 0.25 | 0.2 |
| Kunming | Moderate zone | 0.4 | 0.25 |
| Chongqing | Hot summer and cold winter zone | 0.4 | 0.25 |
| Guangzhou | Hot summer and warm winter zone | 0.45 | 0.3 |
| City | Compared to AS Roof (kWh/m2) | Compared to PDRC Roof (kWh/m2) |
|---|---|---|
| Changchun | 8.6 | 8.9 |
| Beijing | 12.0 | 9.1 |
| Kunming | 5.7 | 4.0 |
| Chongqing | 5.0 | 2.2 |
| Guangzhou | 6.6 | 0.6 |
| City | Energy Reduction (MJ/m2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compared to AS Roof | Compared to PDRC Roof | |||
| Cooling Season | Heating Season | Cooling Season | Heating Season | |
| Changchun | 12.6 | 18.0 | −17.3 | 49.1 |
| Beijing | 29.8 | 13.2 | −34.1 | 66.8 |
| Kunming | 13.9 | 6.5 | −20.1 | 34.5 |
| Chongqing | 17.3 | 0.5 | −40.0 | 47.8 |
| Guangzhou | 23.2 | 0.5 | −21.3 | 23.3 |
| City | Emission Factors (kg CO2/kWh) |
|---|---|
| Changchun | 0.7769 |
| Beijing | 0.8843 |
| Kunming | 0.5271 |
| Chongqing | 0.5257 |
| Guangzhou | 0.5271 |
| City | Annual Carbon Emission (kgCO2/m2) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS Roof | PDRC Roof | TARC Roof | |||||||
| Cooling | Heating | Total | Cooling | Heating | Total | Cooling | Heating | Total | |
| Changchun | 79.0 | 1117.8 | 1196.8 | 55.8 | 1141.9 | 1197.7 | 69.3 | 1103.8 | 1173.0 |
| Beijing | 204.0 | 666.7 | 870.7 | 147.5 | 714.0 | 861.6 | 177.7 | 655.0 | 832.7 |
| Kunming | 58.3 | 206.8 | 265.0 | 40.4 | 221.5 | 261.9 | 51.0 | 203.4 | 254.3 |
| Chongqing | 124.5 | 209.0 | 333.6 | 94.4 | 233.9 | 328.3 | 115.4 | 208.8 | 324.2 |
| Guangzhou | 198.5 | 76.5 | 275.1 | 175.0 | 88.6 | 263.6 | 262.6 | 76.3 | 262.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, G.; Zhang, K.; Xiao, F.; Zhang, Z.; Jiao, S.; Gong, Y. Building Energy Efficiency Enhancement through Thermochromic Powder-Based Temperature-Adaptive Radiative Cooling Roofs. Buildings 2024, 14, 1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14061745
Song G, Zhang K, Xiao F, Zhang Z, Jiao S, Gong Y. Building Energy Efficiency Enhancement through Thermochromic Powder-Based Temperature-Adaptive Radiative Cooling Roofs. Buildings. 2024; 14(6):1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14061745
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Ge, Kai Zhang, Fei Xiao, Zihao Zhang, Siying Jiao, and Yanfeng Gong. 2024. "Building Energy Efficiency Enhancement through Thermochromic Powder-Based Temperature-Adaptive Radiative Cooling Roofs" Buildings 14, no. 6: 1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14061745
APA StyleSong, G., Zhang, K., Xiao, F., Zhang, Z., Jiao, S., & Gong, Y. (2024). Building Energy Efficiency Enhancement through Thermochromic Powder-Based Temperature-Adaptive Radiative Cooling Roofs. Buildings, 14(6), 1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14061745






