Moderating Effects of Internationalization between Corporate Social Responsibility and Financial Performance: The Case of Construction Firms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. The CSR–CFP Relationship
2.2. Moderating Role of Internationalization
3. Research Methods
3.1. Sample and Data Collection
3.2. Variables
3.3. Model
4. Results
5. Findings and Discussion
5.1. The CSR–CFP Relationship
5.2. The Moderating Effect of DOI
5.3. Managerial Implications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lubin, D.A.; Esty, D.C. Bridging the sustainability gap. Nutr. Today 2012, 47, 161–162. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.-L.; Ho, J.M.; Pidani, R.; Goveravaram, A.D. Doing good does you good? The financial impact of individual CSR dimensions: A Malaysian context. Soc. Responsib. J. 2021; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devie, D.; Liman, L.P.; Tarigan, J.; Jie, F. Corporate social responsibility, financial performance and risk in Indonesian natural resources industry. Soc. Responsib. J. 2019, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, M.L.; Salomon, R.M. Does it pay to be really good? Addressing the shape of the relationship between social and financial performance. Strateg. Manag. J. 2012, 33, 1304–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwanathan, P.; van Oosterhout, H.J.; Heugens, P.P.M.A.R.; Duran, P.; Essen, M.V. Strategic CSRA Concept Building Meta-Analysis. J. Manag. Stud. 2020, 57, 314–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kao, E.H.; Yeh, C.-C.; Wang, L.-H.; Fung, H.-G. The relationship between CSR and performance: Evidence in China. Pac. -Basin Financ. J. 2018, 51, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnea, A.; Rubin, A. Corporate Social Responsibility as a Conflict Between Shareholders. J. Bus. Ethics 2010, 97, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nollet, J.; Filis, G.; Mitrokostas, E. Corporate social responsibility and financial performance: A non-linear and disaggregated approach. Econ. Model. 2016, 52, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.-J.; Guo, R.-S.; Hsiao, Y.-C.; Chen, K.-L. How business strategy in non-financial firms moderates the curvilinear effects of corporate social responsibility and irresponsibility on corporate financial performance. J. Bus. Res. 2018, 92, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.L.; Law, S.H.; Ho, J.A.; Sambasivan, M. The causality direction of the corporate social responsibility—Corporate financial performance Nexus: Application of Panel Vector Autoregression approach. N. Am. J. Econ. Financ. 2019, 48, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, O.; Naccache, P.; Schier, G. Exploring the Curvature of the Relationship Between HRM–CSR and Corporate Financial Performance. J. Bus. Ethics 2019, 170, 857–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaghbari, W.; Al-Sakkaf, A.A.; Sultan, B. Factors affecting construction labour productivity in Yemen. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2017, 19, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Ye, M.; Flanagan, R.; Ye, K. Corporate Social Responsibility Disclosures in International Construction Business: Trends and Prospects. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2016, 04015053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ngowi, A.B.; Pienaar, E.; Talukhaba, A.; Mbachu, J. The globalisation of the construction industry—A review. Build. Environ. 2005, 40, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Lee, S.; Dalbor, M. The negative synergistic effect of internationalization and corporate social responsibility on US restaurant firms’ value performance. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2016, 28, 1759–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J. The relationship between corporate diversification and corporate social performance. Strateg. Manag. J. 2013, 34, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polonsky, M.; Chao, P.; Jevons, C. Global branding and strategic CSR: An overview of three types of complexity. Int. Mark. Rev. 2009, 26, 327–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attig, N.; Boubakri, N.; El Ghoul, S.; Guedhami, O. Firm Internationalization and Corporate Social Responsibility. J. Bus. Ethics 2016, 134, 171–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.T.; Eden, L.; Miller, S.R. Multinationals and corporate social responsibility in host countries: Does distance matter? J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2011, 43, 84–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, A.; Huang, C.-H.; Padmanabhan, P.; Wang, C.-H. The determinants of foreign giving: An exploratory empirical investigation of US manufacturing firms. Int. Bus. Rev. 2013, 22, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, H.; Song, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.-H. Does the restaurant type matter for investment in corporate social responsibility? Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2016, 58, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiandrino, S.; Devalle, A.; Cantino, V. Corporate governance and financial performance for engaging socially and environmentally responsible practices. Soc. Responsib. J. 2019, 15, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, P.; Cupertino, S. CSR Strategic Approach, Financial Resources and Corporate Social Performance: The Mediating Effect of Innovation. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Reimsbach, D.; Braam, G. Political embeddedness and the diffusion of corporate social responsibility practices in China: A trade-off between financial and CSR performance? J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rjiba, H.; Jahmane, A.; Abid, I. Corporate social responsibility and firm value: Guiding through economic policy uncertainty. Financ. Res. Lett. 2020, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Lu, W. The inverse U-shaped relationship between corporate social responsibility and competitiveness: Evidence from Chinese international construction companies. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Quan, B.-T.; Li, J.; Forrest, J. A supply chain coordination mechanism with cost sharing of corporate social responsibility. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheldon, O. The Philosophy of Management; 1923; Available online: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/mono/10.4324/9780203507827/philosophy-management-oliver-sheldon (accessed on 3 September 2021).
- Bowen, H.R.; Gond, J.P.; Bowen, P.G. Social Responsibilities of the Businessman; Harper & Brothers: New York, NY, USA, 1953; p. 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, K. Can Business Afford to Ignore Social Responsibilities? Calif. Manag. Rev. 1960, 2, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.M. Corporate Social Responsibility Revisited, Redefined. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1980, 22, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manne, H.; Wallich, H.C. The Modern Corporation and Social Responsibility; American Enterprise Institute for Public Policy Research: Washington, DC, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlsrud, A. How corporate social responsibility is defined: An analysis of 37 definitions. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2008, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, C.; Jennings, M. The role of purchasing in corporate social responsibility: A structural equation analysis. J. Bus. Logist. 2004, 25, 145–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S. Coordination of a socially responsible supply chain using revenue sharing contract. Transp. Res. Part E 2014, 67, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.E. Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Approach; Pitman: Boston, MA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Saeidi, S.P.; Sofian, S.; Saeidi, P.; Saeidi, S.P.; Saaeidi, S.A. How does corporate social responsibility contribute to firm financial performance? The mediating role of competitive advantage, reputation, and customer satisfaction. J. Bus. Res. 2015, 68, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliams, A.; Siegel, D. Corporate social responsibility and financial performance: Correlation or misspecification. Strat. Manag. 2000, 21, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, D.R.; Handfield, R.B.; Scannell, T.V. An empirical investigation of supplier development: Reactive and strategic processes. J. Oper. Manag. 1998, 17, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Zhang, J. Performance of green supply chain management: A systematic review and meta analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 183, 1064–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhardt, K.M. Agency theory: An assessment and review. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1989, 14, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wnuczak, P. The business case for corporate social responsibility: A literature overview and integrative framework. J. Manag. Bus. Adm. Cent. Eur. 2018, 26, 100–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, M.; Testa, F.; Bianchi, L.; Iraldo, F.; Frey, M. Corporate Social Responsibility and Competitiveness within SMEs of the Fashion Industry: Evidence from Italy and France. Sustainability 2014, 6, 872–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brammer, S.J.; Brooks, C.; Pavelin, S. Corporate Social Performance and Stock Returns: UK Evidence from Disaggregate Measures. Read. Teach. 2007, 69, 427–428. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Choi, J.; Li, J. Too little or too much? untangling the relationship between corporate philanthropy and firm financial performance. Organ. Sci. 2008, 19, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jensen, M.C.; Meckling, W.H. Theory of the firm: Managerial behavior, agency costs and ownership structure. J. Financ. Econ. 1976, 3, 305–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, B.; Morris, S.A.; Bartkus, B.R. Having, Giving, and Getting: Slack Resources, Corporate Philanthropy, and Firm Financial Performance. Bus. Soc. 2004, 43, 135–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aastha, B.; Shazi, S.J. Corporate Social Responsibility Practices in Small and Medium Enterprises. Pol. J. Manag. Stud. 2019, 19, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaol, F.A.L.; Harjanto, K. Impact of Selected Factors Towards Corporate Social Responsibility (Csr) Disclosure: Evidence from Indonesia. Pol. J. Manag. Stud. 2019, 20, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.X.; Ma, H.Y.; Lin, H.; Zeng, R.C.; Tam, V.W.Y. Social responsibility of major infrastructure projects in China. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2015, 33, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, L.; Guo, F.; Yang, G. Does corporate internationalization affect corporate social responsibility? Evidence from China. Emerg. Mark. Rev. 2021, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, M.L.; Salomon, R.M. Beyond dichotomy: The curvilinear relationship between social responsibility and financial performance. Strateg. Manag. J. 2006, 27, 1101–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Sun, M.; Ma, L.; Li, X.; Shi, L. Estimating carbon emissions from the pulp and paper industry: A case study. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewatsch, S.; Kleindienst, I. When Does It Pay to be Good? Moderators and Mediators in the Corporate Sustainability–Corporate Financial Performance Relationship: A Critical Review. J. Bus. Ethics 2017, 145, 383–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal Joshi, P.; Gao, S.S. Multinational corporations’ corporate social and environmental disclosures (CSED) on web sites. Int. J. Commer. Manag. 2009, 19, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Kyu, Y.; Park, L.B. Institutional legitimacy and norms-based CSR marketing practices. Int. Mark. Rev. 2015, 32, 463–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharfman, M.P.; Shaft, T.M.; Tihanyi, L. A Model of the Global and Institutional Antecedents of High-Level Corporate Environmental Performance. Bus. Soc. 2016, 43, 6–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostova, T.; Zaheer, S. Organizational Legitimacy Under Conditions of Complexity: The Case of the Multinational Enterprise. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1999, 24, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contractor, F.J.; Kumar, V.; Kundu, S.K. Nature of the relationship between international expansion and performance: The case of emerging market firms. J. World Bus. 2007, 42, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steurer, R. The Role of Government in Corporate Social Responsibility: Characterizing Public Policies on CSR in Europe. Policy Sci. 2010, 43, 49–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, G.K.; Tung, R.L.; Kostova, T.; Zellmer-Bruhn, M. Widening the lens: Rethinking distance, diversity, and foreignness in international business research through positive organizational scholarship. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2016, 47, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mezias, J.M. Identifying liabilities of foreignness and strategies to minimize their effects: The case of labor lawsuit judgments in the United States. Strateg. Manag. J. 2002, 23, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doh, J.P.; Littell, B.; Quigley, N.R. CSR and sustainability in emerging markets: Societal, institutional, and organizational influences. Organ. Dyn. 2015, 44, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, D.; Judge, W. Reappraising liabilities of foreignness within an integrated perspective of the costs and benefits of doing business abroad. Int. Bus. Rev. 2009, 18, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Shen, X. CSR in China Research: Salience, Focus and Nature. J. Bus. Ethics 2010, 94, 613–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaitzoglou, I.; Pan, H.; Niklewski, J. Corporate social responsibility: How much is enough? A higher dimension perspective of the relationship between financial and social performance. Ann. Oper. Res. 2020, 306, 209–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Chau, K.W.; Wang, H.; Pan, W. A decade’s debate on the nexus between corporate social and corporate financial performance: A critical review of empirical studies 2002–2011. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 79, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carroll, A.B. The pyramid of corporate social responsibility: Toward the moral management of organizational stakeholders. Bus. Horiz. 1991, 34, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Qiu, J.; Wan, C. Corporate globalization and bank lending. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2011, 42, 1016–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M. Corporate social performance, corporate financial performance, and firm size: A meta-analysis. J. Am. Acad. Bus. 2006, 8, 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Andrikopoulos, A.; Kriklani, N. Environmental disclosure and financial characteristics of the firm: The case of Denmark. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2013, 20, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.H.; Lee, S.; Huh, C. Impacts of positive and negative corporate social responsibility activities on company performance in the hospitality industry. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2010, 29, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, S.; Caroli, M.G.; Cappa, F.; Del Chiappa, G. Are you good enough? CSR, quality management and corporate financial performance in the hospitality industry. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 88, 102395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Lee, S. Effects of different dimensions of corporate social responsibility on corporate financial performance in tourism-related industries. Tour. Manag. 2011, 32, 790–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haans, R.F.J.; Pieters, C.; He, Z.-L. Thinking about U: Theorizing and testing U- and inverted U-shaped relationships in strategy research. Strateg. Manag. J. 2016, 37, 1177–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mela, C.F.; Kopalle, P.K. The impact of collinearity on regression analysis: The asymmetric effect of negative and positive correlations. Appl. Econ. 2002, 34, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappa, F.; Cetrini, G.; Oriani, R. The impact of corporate strategy on capital structure: Evidence from Italian listed firms. Q. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2020, 76, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooltridge, J.M. Econometrics Analysis of Cross-Section and Panel Data. Mit Press Books 2001, 1, 206–209. [Google Scholar]
- Lind, J.T.; Mehlum, H. With or without u? the appropriate test for a U-shaped relationship. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Stat. 2010, 72, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heckman, J.J. Sample specification bias as a selection error (with an application to the estimation of labor supply functions). NBER Work. Pap. 1977, 172, 153–162. [Google Scholar]
- Certo, S.T.; Withers, M.C.; Semadeni, M. A tale of two effects: Using longitudinal data to compare within- and between-firm effects. Strateg. Manag. J. 2015, 38, 1536–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maon, F.; Swaen, V.; Lindgreen, A. One Vision, Different Paths: An Investigation of Corporate Social Responsibility Initiatives in Europe. J. Bus. Ethics 2017, 143, 405–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ratajczak, P. The mediating role of natural and social resources in the corporate social responsibility—Corporate financialperformance relationship. Manag. Decis. Econ. 2021, 42, 100–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wong, J.K.W. Key activity areas of corporate social responsibility (CSR) in the construction industry: A study of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlitzky, M.; Shen, J. Corporate social responsibility, industry, and strategy. Ind. Organ. Psychol. 2013, 6, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salancik, G.R.; Pfeffer, J. A social information processing approach to job attitudes and task design. Adm. Sci. Q. 1978, 23, 224–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valor, C. Corporate social responsibility and corporate citizenship: Towards corporate accountability. Bus. Soc. Rev. 2005, 110, 191–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crilly, D.; Ni, N.; Jiang, Y. Do-no-harm versus do-good social responsibility: Attributional thinking and the liability of foreignness. Strateg. Manag. J. 2016, 37, 1316–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contractor, F.J.; Kundu, S.K.; Hsu, C.-C. A three-stage theory of international expansion: The link between multinationality and performance in the service sector. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2003, 34, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.C. Agency costs of free cash flow, corporate finance, and takeovers. Am. Econ. Rev. 1986, 76, 323–329. [Google Scholar]
- Buckley, P.J.; Casson, M. The Future of the Multinational Enterprise; Macmillan: London, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Eden, L.; Miller, S. Opening the Black Box: Multinationals and the Costs of Doing Business Abroad. Acad. Manag. Proc. 2001, 2001, C1–C6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.-C.; Shih, Y.-N.; Wu, C.-L.; Zhang, X.-L.; Wang, Y. Does corporate social performance pay back quickly? A longitudinal content analysis on international contractors. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthorpe, S.; James, R.; Taylor, S. Corporate social responsibility: An imperative or imposition upon the UK constructionindustry. In Proceedings of the CIB World Congress, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2–7 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.L.; Law, S.H.; Azman-Saini, W.N.W. Market differentiation threshold and the relationship between corporate social responsibility and corporate financial performance. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2019, 27, 1279–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J. The Handbook of Project Based Management. International Journal of Project Management. 1993, 11, 185–186. [Google Scholar]
- Werther, W.B., Jr.; Chandler, D. Corporate Social Responsibility-Stakeholders in a Global Environment; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Du, S.; Bhattacharya, C.B.; Sankar, S. Maximizing business returns to corporate social responsibility (csr): The role of csr communication. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2010, 12, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.F. The Current Conditions of Csr Implementation in Construction Industry: A Lesson from Taiwan. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2017, 15, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Obs | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSR | 501 | 25.515 | 16.501 | −7.17 | 77.92 |
| DOI | 501 | 0.148 | 0.202 | 0 | 0.983 |
| lnTotalAssets | 501 | 23.6160 | 1.8463 | 19.5852 | 28.6365 |
| NetDebt | 501 | 14,570,000,000 | 44,470,000,000 | −22,730,000,000 | 343,600,000,000 |
| Age | 501 | 17.303 | 6.919 | 2 | 38 |
| ROE | 501 | 0.088 | 0.108 | −0.678 | 0.568 |
| Employees | 501 | 43,343.323 | 101,298.53 | 147 | 552,810 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) ROE | 1.000 | ||||||
| (2) CSR | 0.381 *** | 1.000 | |||||
| (0.000) | |||||||
| (3) lnTotalAssets | 0.095 | 0.264 *** | 1.000 | ||||
| (0.033) ** | (0.000) | ||||||
| (4) NetDebt | 0.015 | 0.101 ** | 0.649 *** | 1.000 | |||
| (0.735) | (0.024) | (0.000) | |||||
| (5) Age | −0.156 *** | −0.311 *** | −0.331 *** | −0.280 *** | 1.000 | ||
| (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.000) | ||||
| (6) Employees | 0.051 | 0.174 *** | 0.582 *** | 0.487 *** | −0.330 *** | 1.000 | |
| (0.256) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.000) | |||
| (7) DOI | 0.095 * | 0.102 ** | −0.057 | −0.003 | 0.044 | 0.026 | 1.000 |
| (0.034) | (0.022) | (0.199) | (0.946) | (0.326) | (0.556) |
| ROE | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSR | 0.0018 ***(0) | 0.0062 ***(0) | 0.0017 ***(0) | 0.0062 ***(0) | |
| CSR2 | −0.0002 ***(0) | −0.0002 ***(0) | |||
| Interact1 | 0.0016(0.243) | −0.0032(0.167) | |||
| Interact2 | 0.0002 **(0.017) | ||||
| DOI | 0.0490(0.273) | 0.0744 *(0.089) | 0.0511(0.189) | 0.0645(0.147) | 0.0071(0.865) |
| lnTotalAssets | 0.0797 ***(0) | 0.0693 ***(0) | 0.0509 ***(0) | 0.0681 ***(0) | 0.0512 ***(0) |
| NetDebt | 0.0000(0.131) | 0.0000(0.261) | 0.0000(0.184) | 0.0000(0.293) | 0.0000(0.237) |
| Year | −0.0153 ***(0) | −0.0101 ***(0) | −0.0079 ***(0.001) | −0.0101 ***(0) | −0.0080 ***(0.001) |
| Employees | 0.0000(0.63) | 0.0000(0.298) | 0.0000(0.894) | 0.0000(0.357) | 0.0000(0.81) |
| Constant | −1.5391 ***(0) | −1.4419 ***(0) | −1.0969 ***(0) | −1.4090 ***(0) | −1.0925 ***(0) |
| Effect | Fixed | Fixed | Fixed | Fixed | Fixed |
| R-squared | 0.0851 | 0.1386 | 0.3222 | 0.1414 | 0.3340 |
| F-test | 7.846 | 11.293 | 28.516 | 9.884 | 23.293 |
| Prob > F | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0003 | 0.0000 | 0.0004 |
| Rho | 0.8220 | 0.8052 | 0.6997 | 0.7970 | 0.6830 |
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |
|---|---|---|
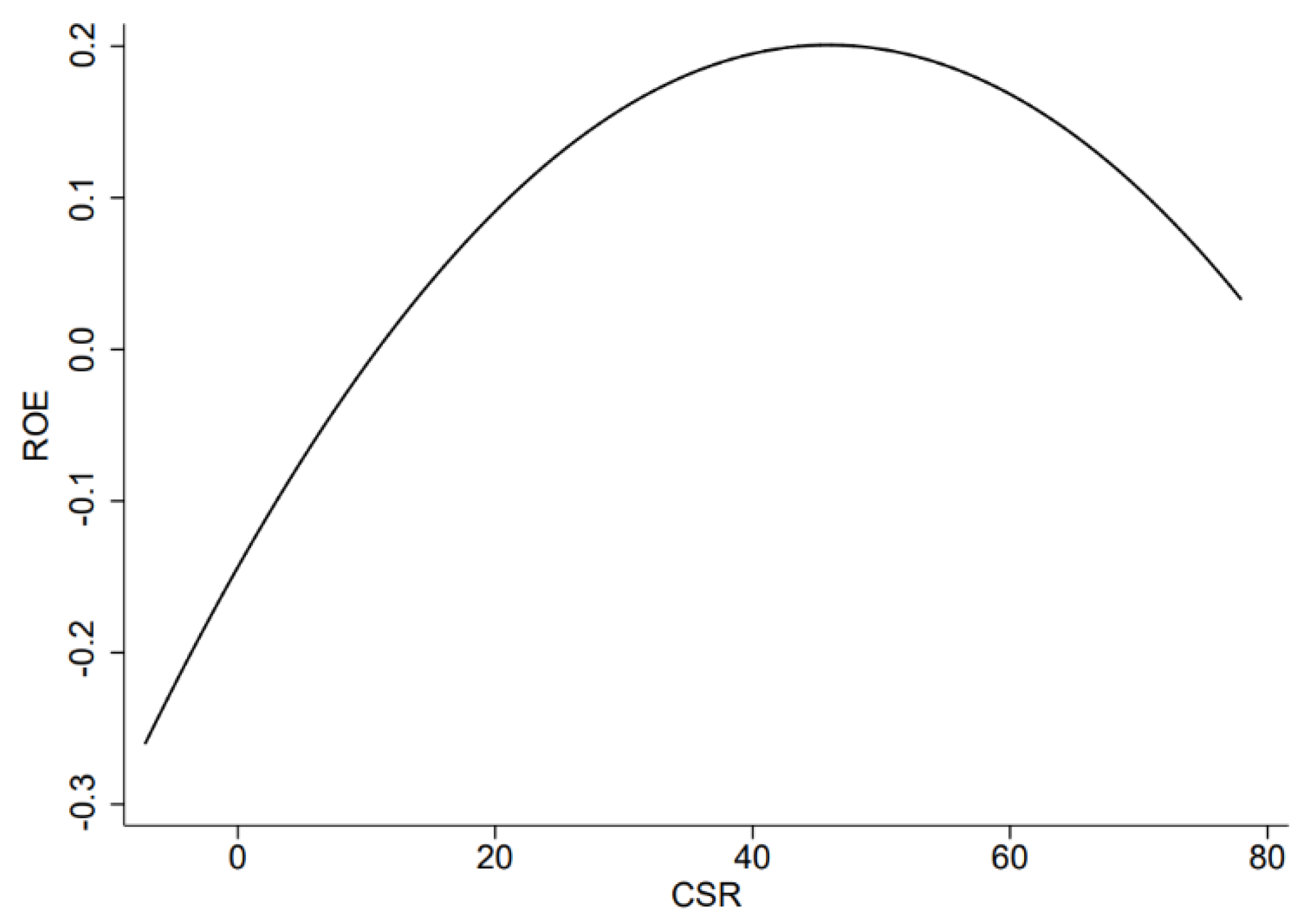
| Interval | −7.170 | 77.920 |
| Slope | 0.009 *** | −0.019 *** |
| (17.072) | (−12.812) | |
| t-value | P-value | |
| Overall test | 12.81 | 0.0000 |
| Extreme point: 19.70382 |
| Group | Observations | Mean | Std. Dev. |
|---|---|---|---|
| obs1 | 501 | 0.0959 | 0.0958 |
| obs2 | 498 | 0.0884 | 0.1083 |
| Combined | 999 | 0.0921 | 0.1023 |
| Ha: diff < 0 | Ha: diff! = 0 | Ha: diff > 0 | |
| Pr(T < t) = 0.8766 | Pr(|T| > |t|) = 0.2469 | Pr(T > t) = 0.1234 |
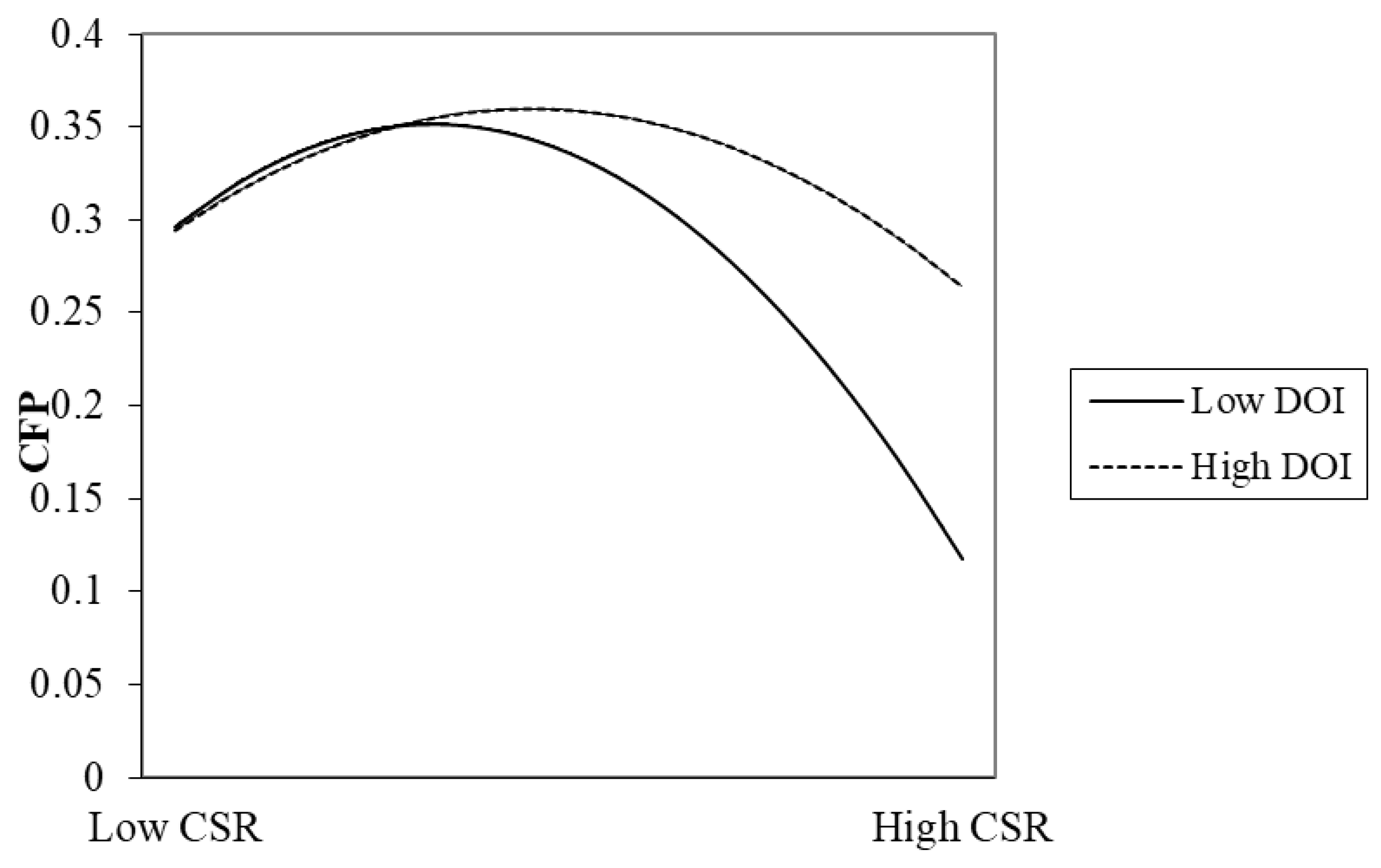
| ROE | Model (3) | Model (5) |
|---|---|---|
| CSR | 0.0069 ***(0) | 0.0070 ***(0) |
| CSR2 | −0.0002 ***(0) | −0.0002 ***(0) |
| Interact1 | −0.0028(0.193) | |
| Interact2 | 0.0002 ***(0.009) | |
| DOI | 0.0334 *(0.079) | −0.0032(0.887) |
| lnTotalAssets | 0.0010(0.734) | 0.0016(0.593) |
| NetDebt | 0.0012(0.152) | 0.0000(0.132) |
| Year | −0.0012 *(0.051) | −0.0012 **(0.043) |
| Employees | 0.0000(0.411) | 0.0000(0.437) |
| Wald chi2 | 339.970 | 356.390 |
| Prob > chi2 | 0.0003 | 0.0000 |
| Rho | 0.27743 | 0.27639 |
| lambda | 0.0237 *(0.057) | 0.0233*(0.059) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, K.; Jiang, W. Moderating Effects of Internationalization between Corporate Social Responsibility and Financial Performance: The Case of Construction Firms. Buildings 2022, 12, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12020185
Sang M, Zhang Y, Ye K, Jiang W. Moderating Effects of Internationalization between Corporate Social Responsibility and Financial Performance: The Case of Construction Firms. Buildings. 2022; 12(2):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12020185
Chicago/Turabian StyleSang, Meiyue, Yuqing Zhang, Kunhui Ye, and Weiyan Jiang. 2022. "Moderating Effects of Internationalization between Corporate Social Responsibility and Financial Performance: The Case of Construction Firms" Buildings 12, no. 2: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12020185
APA StyleSang, M., Zhang, Y., Ye, K., & Jiang, W. (2022). Moderating Effects of Internationalization between Corporate Social Responsibility and Financial Performance: The Case of Construction Firms. Buildings, 12(2), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12020185






