Rheological Properties and Structural Build-Up of Cement Based Materials with Addition of Nanoparticles: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Static and Dynamic Rheological Measurements
2.1. Fluidity Measurement
2.2. Rheological Measurements
2.2.1. Static Rheological Measurement
2.2.2. Dynamic Rheological Measurement
2.2.3. Small Amplitude Oscillatory Shear (SAOS) Test
3. Rheological Models Determined by Dynamic Rheological Test
4. Mechanism Analysis of Rheology
4.1. Packing Density
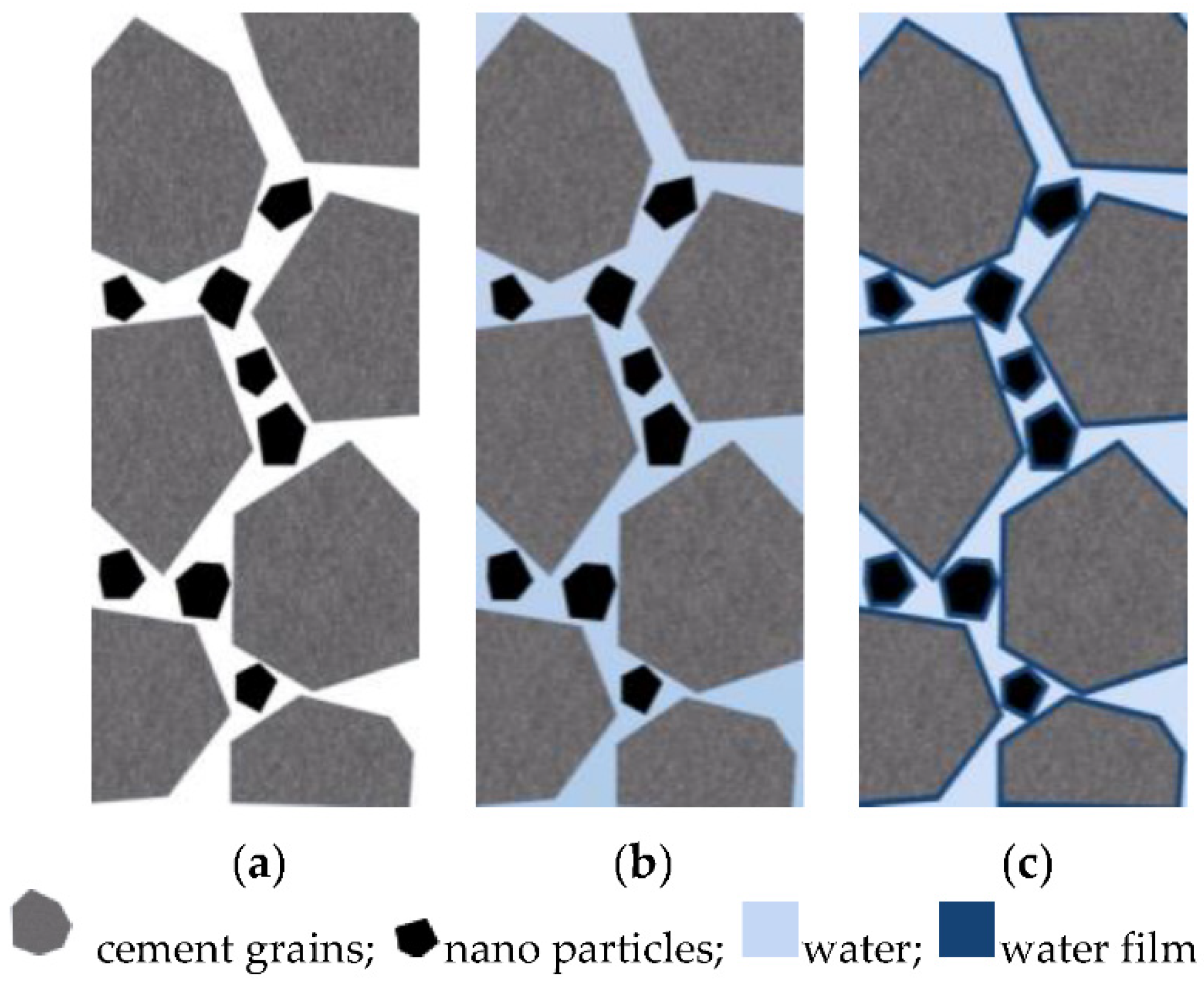
4.2. Water Film Thickness
4.3. Flocculation Structures
5. Analysis of Influencing Factors
5.1. Effect of Dispersion Method
5.2. Effect of Species and Contents of Nanoparticles
5.3. Effect of Superplasticizer
6. Structural Build-Up of Cement Paste in Early Hydration
7. Further Development
8. Conclusions
- (1)
- The Bingham model, modified Bingham model, and Herschel–Bulkley model are the commonly used models to describe the rheological characteristics of cement-based materials with nanoparticles. Nanoparticles affect rheological characteristics. The cement pastes with nano-SiO2, carbon nanotubes, nano-CaCO3, and nano-metakaolin show shear-thinning behavior, and nano-TiO2 yields shear-thickening for cement paste.
- (2)
- Nanoparticles affect the rheology of cement-based materials by changing the particle packing density, water film thickness, and flocculation structures of cement paste. Small particles fill the voids between cementitious particles and increase the packing density. The smaller size particles tend to trigger agglomeration, resulting in the increase of interparticle spaces and the decrease of the particle packing density of the cementitious system.
- (3)
- Nanoparticles have a high specific surface area, surface energy, and high surface activity, which cause the increase of flocculation structures in cement paste. Flocculation structures wrap free water, which causes the free water to reduce, and the paste’s flowability worsens. Nanoparticles increase the flocculation structures and the thixotropy of cement paste.
- (4)
- The nanoparticles’ dispersion mode affects cement-based materials’ rheology. Mechanical agitation, ultrasonic dispersion, and incorporating surfactant are effective methods to improve the dispersibility of nanoparticles in cement-based materials. When the surfactant is used to disperse nanoparticles, the viscosity decreases. For the mechanical agitation method, the higher the stirring rate, the lower the yield stress of cement paste; when ultrasonic dispersion of nanoparticles is used, the yield stress of nano-modified cement paste decreases.
- (5)
- The species and contents of nanoparticles and the amount of superplasticizer significantly affect the rheological properties of cement-based materials with nanoparticles. The yield stress of cement-based materials increases with the increase of nanoparticle content.
- (6)
- Nanoparticles promote structural build-up and accelerate cement hydration at an early age. Nanoparticles provide more nucleation sites and provide a seeding surface for hydrate deposition.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, C.L.; Cao, X.H.; Wu, X.J.; He, Q.Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.Z.; Zhao, W.; Han, S.K.; Nam, G.H.; et al. Recent advances in ultrathin two-dimensional nanomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6225–6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makwana, D.; Bellani, J.; Verma, K.H.; Khatri, D.; Shah, M. Emergence of nano silica for oil and gas well cementing: Application, challenges, and future scope. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 37110–37119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senff, L.; Hotza, D.; Lucas, S.; Ferreira, V.M.; Labrincha, J.A. Effect of nano-SiO2 and nano-TiO2 addition on the rheological behavior and the hardened properties of cement mortars. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 532, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, M.S.; Shoukry, H.; Mokhtar, M.M.; Ali, M.A.; El-Khodary, S.A. Facile production of nano-scale metakaolin: An investigation into its effect on compressive strength, pore structure and microstructural characteristics of mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 172, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guneyisi, E.; Gesoglu, M.; Al-Goody, A.; İpek, S. Fresh and rheological behavior of nano-silica and fly ash blended self-compacting concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 95, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.F.; Zhang, S.Y.; Wang, Q.; Shah, S.P. The effects of nano-calcined kaolinite clay on cement mortar exposed to acid deposits. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 102, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafari, E.; Ghahari, S.A.; Feng, Y.; Severgnini, F.; Luet, N. Effect of Zinc oxide and Al-Zinc oxide nanoparticles on the rheological properties of cement paste. Compos. Part. B Eng. 2016, 105, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Shan, B.H.; Ouyang, J.; Zhang, W.; Yu, X.; Li, P.G.; Han, B.G. Rheological properties of cementitious composites with nano/fiber fillers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 158, 786–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manawi, Y.M.; Ihsanullah; Samara, A.; Al-Ansari, T.; Atieh, T.A. A review of carbon nanomaterials’ synthesis via the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) method. Materials 2018, 11, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, X.J.; Li, Q.N.; Hu, Y.; Tan, Y.S.; Liu, C.F. Properties of cement-based materials incorporating nano-clay and calcined nano-clay: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 284, 122820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.C.; Fan, Y.F. Rheological evaluation of nano-metakaolin cement pastes based on the water film thickness. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 324, 126517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobon, J.I.; Mendoza, O.; Restrepo, O.J.; Borrachero, M.V.; Paya, J. Effect of different high surface area silicas on the rheology of cement paste. Mater. Constr. 2020, 70, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavergne, F.; Belhadi, R.; Carriat, J.; Fraj, B.A. Effect of nano-silica particles on the hydration, the rheology and the strength development of a blended cement paste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 95, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flores, Y.C.; Cordeiro, G.C.; Filho, R.D.T.; Tavares, L.M. Performance of Portland cement pastes containing nano-silica and different types of silica. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 146, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Ma, S.W.; Kawashima, S.; De Schutter, G. Rheological characterization of the viscoelastic solid-like properties of fresh cement pastes with nanoclay addition. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2019, 103, 102262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Beacraft, M.; Shah, S.P. Effect of mineral admixtures on formwork pressure of self-consolidating concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2010, 32, 665–671. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Kawashima, S. Use of creep recovery protocol to measure static yield stress and structural rebuilding of fresh cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 90, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, R.M.; Bombard, A.J.F. Rheology of fresh cement paste with superplasticizer and nanosilica admixtures studied by response surface methodology. Mater. Struct. 2012, 45, 905–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissanen, J.; Ohenoja, K.; Kinnunen, P.; Romagnoli, M.; Illikainen, M. Milling of peat-wood fly ash: Effect on water demand of mortar and rheology of cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 180, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damineli, B.L.; John, V.M.; Lagerblad, B.; Pileggi, R.G. Viscosity prediction of cement-filler suspensions using interference model: A route for binder efficiency enhancement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 84, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, C.J.; Jiao, D.W.; An, X.P. Rheological properties, model and measurements for fresh cementitious materials—A short review. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 45, 708–716. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Zhou, S.H.; Wang, D.F.; Peng, Y.X.; Fan, B. Rheological properties of cement-ground limestone paste with nano-CaCO3. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2018, 35, 2185–2190. [Google Scholar]
- Knop, Y.; Peled, A. Packing density modeling of blended cement with limestone having different particle sizes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 102, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, A.K.H.; Fung, W.W.S. Packing density measurement and modelling of fine aggregate and mortar. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Deng, G.H.; Shao, X.D. Review on dispersion methods of carbon nanotubes in cement-based composites. Mater. Rep. 2018, 32, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Nadiv, R.; Vasilyev, G.; Shtein, M.; Peled, A.; Zussman, E.; Regev, O. The multiple roles of a dispersant in nanocomposite systems. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 133, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejaeghere, I.; Sonebi, M.; De Schutter, G. Influence of nano-clay on rheology, fresh properties, heat of hydration and strength of cement-based mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 222, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, S.H.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, D.F. Effect of nano-SiO2 on rheological property of fresh cement pastes. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 38, 317–322. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Q.; Zhou, D.; Khayat, K.H.; Feys, D.; Shi, C. On the measurement of evolution of structural build-up of cement paste with time by static yield stress test vs. small amplitude oscillatory shear test. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 99, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Zhou, D.; Li, B.Y.; Huang, H.; Shi, C. Effect of mineral admixtures on the structural build-up of cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 160, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, A.K.H.; Li, Y. Effects of fly ash microsphere on rheology, adhesiveness and strength of mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 42, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douba, A.; Genedy, M.; Matteo, E.N.; Kandil, U.F.; Stormont, J.; Taha, M.M.R. The significance of nanoparticles on bond strength of polymer concrete to steel. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2017, 74, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.C.; Huang, Y.F. Modeling the simultaneous effects of particle size and porosity in simulating geo-materials. Materials 2022, 15, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, A.K.H.; Fung, W.W.S. Roles of water film thickness and SP dosage in rheology and cohesiveness of mortar. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.; Oliveira, P.M.; Coutinho, J.S.; Figueiras, J. Rheological characterization of SCC mortars and pastes with changes induced by cement delivery. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2011, 33, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjoudj, M.; Ezziane, K.; Kadri, E.H.; Soualhi, H. Study of the rheological behavior of mortar with silica fume and superplasticizer admixtures according to the water film thickness. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 22, 2480–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeini, M.A.; Hosseinpoor, M.; Yahia, A. Effectiveness of the rheometric methods to evaluate the build-up of cementitious mortars used for 3D printing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 257, 119551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, I.; Mechtcherine, V. Possibilities and challenges of constant shear rate test for evaluation of structural build-up rate of cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 130, 105974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Qian, Y.; Kawashima, S. Experimental and modeling study on the non-linear structural build-up of fresh cement pastes incorporating viscosity modifying superplasticizer. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 108, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.W.; De, S.R.; Shi, C.J.; De, S.G. Thixotropic structural build-up of cement-based materials: A state-of-the-art review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 122, 104152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.; El Cheikh, K.; Shi, C.; Lesage, K.; De Schutter, G. Structural build-up of cementitious paste with nano-Fe3O4 under time-varying magnetic fields. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 124, 105857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.M.; Yahia, A. New approach to assess build-up of cement-based suspensions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 85, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachbaur, L.; Mutin, J.C.; Nonat, A.; Choplin, L. Dynamic mode rheology of cement and tricalcium silicate pastes from mixing to setting. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.W.; Lesage, K.; Yardimci, M.Y.; Cheikh, K.E.; Shi, C.J.; Schutter, G.D. Rheological properties of cement paste with nano-Fe3O4 under magnetic field: Flow curve and nanoparticle agglomeration. Materials 2020, 13, 5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandipan, K.; Mohammed, S.; Giuseppina, A.; Arnaud, P.; Kumar, D.U. Influence of nanoclay on the fresh and rheological behaviour of 3D printing mortar. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 58, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar]
- Nehdi, M.; Rahman, M.A. Estimating rheological properties of cement pastes using various rheological models for different test geometry, gap and surface friction. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 1993–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feys, D.; Verhoeven, R.; De Schutter, G. Why is fresh self-compacting concrete shear thickening? Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 510–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallevik, O.H.; Feys, D.; Wallevik, J.E.; Khayat, K.H. Avoiding inaccurate interpretations of rheological measurements for cement-based materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 78, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.N.; De Sousa, S.R.G.; Bombard, A.J.F.; Vieira, S.L. Rheological study of cement paste with metakaolin and/or limestone filler using mixture design of experiments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 143, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Taengua, E.; Sonebi, M.; Hossain, K.M.A.; Lachemi, M.; Khatib, J. Effects of the addition of nanosilica on the rheology, hydration and development of the compressive strength of cement mortars. Compos. Part. B Eng. 2015, 81, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feys, D.; Verhoeven, R.; De Schutter, G. Fresh self compacting concrete, a shear thickening material. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 920–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Kwan, A.K.H. Superfine cement for improving packing density, rheology and strength of cement paste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tregger, N.A.; Pakula, M.E.; Shah, S.P. Influence of clays on the rheology of cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 40, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahia, A. Shear-thickening behavior of high-performance cement grouts-Influencing mix-design parameters. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiad, I. Influence of time addition of superplasticizers on the rheological properties of fresh cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.I.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, T.Y. Rheological model selection and a general model for evaluating the viscosity and microstructure of a highly-concentrated cement suspension. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 123, 105775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.N.; He, J.Y. Polymer Rheology and Its Applications; China Light Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 264–265. [Google Scholar]
- Seneff, L.; Labrincha, J.A.; Ferreira, V.M.; Hotza, D.; Repette, W.L. Effect of nano-silica on rheology and fresh properties of cement pastes and mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2487–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.F. The study on the measuring methods of rheological properties of HPC fresh concrete. Concrete. 2002, 10, 8–9. [Google Scholar]
- Khayat, K.H.; Meng, W.N.; Vallurupalli, K.; Teng, L. Rheological properties of ultra-high-performance concrete—An overview. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 124, 105828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.W.; Shi, C.J.; Yuan, Q.; An, X.P.; Liu, Y.; Li, H. Effect of constituents on rheological properties of fresh concrete—A review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 83, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateja, S.; Maldenovic, A.; Maurizio, B.; Vesna, J.; Lina, Z. Particle packing and rheology of cement pastes at different replacement levels of cement by α-Al2O3 submicron particles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 139, 256–266. [Google Scholar]
- Knop, Y.; Peled, A.; Cohen, R. Influences of limestone particle size distributions and contents on blended cement properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 71, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.H.C.; Kwan, A.K.H. Packing density of cementitious materials: Part 1-measurement using a wet packing method. Mater. Struct. 2008, 41, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecomte, A.; Mechling, J.M.; Diliberto, C. Compaction index of cement paste of normal consistency. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 3279–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sun, X.; Du, H.; Lu, H.; Ma, Y.S.; Shen, W.K.; Tian, Z.H. Effects and threshold of water film thickness on multi-mineral cement paste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 112, 103677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, A.K.H.; Chen, J.J. Roles of packing density and water film thickness in rheology and strength of cement paste. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2012, 10, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, Z.D.; Han, K.D.; Tian, C.Y. Study on relationship between particle characteristics and rheological properties of cement-limestone power pastes. J. Build. Mater. 2021, 24, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Song, G.Z.; Wang, L.J.; Zhang, Y.R.; Guo, Y.; Cao, Y.P. Rheological and hydration properties of polymer-cementitious grouting material at early stage. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2018, 50, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.R.; Wang, D.M.; Zhang, W.L. Multi-level flocculation structures of fresh cement paste by confocal laser scanning microscope. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Sci. Ed. 2014, 29, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.; Lesage, K.; Yardimci, M.Y.; El Cheikh, K.; Shi, C.J.; De Schutter, G. Quantitative assessment of the influence of external magnetic field on clustering of nano-Fe3O4 particles in cementitious paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 142, 106345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.T.; Zhang, C.Y.; Pei, Y.; Chen, M.J.; Liu, H.J.; Li, X.H. Influence of flocculation effect on the apparent viscosity of cement slurry and analysis of different influencing factors. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 281, 122602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.M.; Zhang, L.R.; Zhang, W.L.; Hao, B. Effect of Effects of Superplasticizers on multi-level flocculation structure of fresh cement paste. J. Build. Mater. 2012, 15, 755–759. [Google Scholar]
- Roussel, N.; Ovarlez, G.; Garrauly, S.; Brumaud, C. The origins of thixotropy of fresh cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 42, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Kawashima, S. Distinguishing dynamic and static yield stress of fresh cement mortars through thixotropy. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 86, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Kong, X.M.; Gao, L.; Lu, Z.C.; Zhou, S.M.; Dong, B.Q.; Xing, F. In-situ measurement of viscoelastic properties of fresh cement paste by a microrheology analyzer. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 79, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.K.; Muzenda, T.R.; Li, Q.F.; Chen, H.; Kawashima, S.; Sui, T.B.; Yong, H.Y.; Xie, N.; Cheng, X. Mechanisms dominating thixotropy in limestone calcined clay cement (LC3). Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 140, 106316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Fan, Y.F.; Luan, H.Y.; Chen, Y. Effect of disperse condition of nano-clay on behavior of cement paste. J. Build. Mater. 2013, 16, 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Song, W.L.; Lu, Z.; Zeng, D.W.; Xie, C.S. Research progress on the stability of nanometer titanium dioxide dispersion. Mater. Rep. 2019, 33, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Horszczaruk, E.; Mijowska, E.; Cendrowski, K.; Mijowska, S.; Sikora, P. Effect of incorporation route on dispersion of mesoporous silica nanospheres in cement mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.M.; Yang, B.J.; Cho, K.J.; Kim, E.M.; Lee, H.K. Influences of CNT dispersion and pore characteristics on the electrical performance of cementitious composites. Compos. Struct. 2017, 164, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Ruan, P.Z.; Tang, Y.X.; Wang, W.N.; Li, Q.L. Research progress on influencing factors on electrical conductive properties of carbon nanotubes-reinforced cement based composite materials. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 49, 411–419. [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima, S.; Wang, K.J.; Ferron, R.D.; Kim, J.H.; Tregger, N.; Shah, S. A review of the effect of nanoclays on the fresh and hardened properties of cement-based materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 147, 106502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgun, Y.M.; Atahan, N.H. Rheological and fresh properties of reduced fine content self-compacting concretes produced with different particle sizes of nano SiO2. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 142, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Schutter, D.Y. Enhancing thixotropy of fresh cement pastes with nanoclay in presence of polycarboxylate ether superplasticizer (PCE). Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 111, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.C.; Fan, Y.F. Effect of nano-metakaolin on the thixotropy of fresh cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 353, 129062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhang, H.; Duan, L.; Yang, Y.Z.; Yan, J.; Shan, D.D.; Liu, X.L.; Pang, J.J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Li, X.; et al. Effect of nano metakaolin on compressive strength of recycled concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 256, 119393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, L.; Sun, Z.; Yang, H.; Yang, X.; Ji, Y.; Luo, Q. Experimental evidence for a possible dispersion mechanism of polycarboxylate-type superplasticisers. Adv. Cem. Res. 2016, 28, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, L.L.; Yang, H.J.; Sun, Z.P.; He, Y.; Zeng, W.B. Research progress on working mechanism of polycarboxylate superplasticizer. J. Build. Mater. 2020, 23, 64–79. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Wang, L. Research progress on clay tolerance of polycarboxylate superplasticizer. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 48, 1852–1858. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, S.S.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Z.M.; Cui, S.P.; Liu, X.; Zheng, C.Y. Preparation and mechanism of superplasticizer for reducing the viscosity of high strengh concrete. Mater. Rep. 2021, 35, 2046–2051. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.F.; Zhang, J.L.; Li, Q.C. Expertmental study on the effect of nano-metakaolin on the fracture behavior of cement mortar. J. Southeast Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2020, 50, 637–644. [Google Scholar]
- Sonebi, M.; Bassuoni, T.M.; Kwasny, J.; Amanuddin, A.K. Effect of nanosilica on rheology, fresh properties, and strength of cement-based grouts. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27, 04014145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Cui, X.Y.; Wang, J.; Lv, C.; Dong, Y. Effect of fly ash on rheological properties of graphene oxide cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 138, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.; Lesage, K.; Yardimci, M.Y.; El Cheikh, K.; Shi, C.J.; De Schutter, G. Structural evolution of cement paste with nano-Fe3O4 under magnetic field—Effect of concentration and particle size of nano-Fe3O4. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 120, 104036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.; Shi, C.; De Schutter, G. Magneto-responsive structural build-up of highly flowable cementitious paste in the presence of PCE superplasticizer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 327, 126925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, Z. Early-age properties evaluation of nano-metakaolin cement paste based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Buildings 2022, 12, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reches, Y. Nanoparticles as concrete additives: Review and perspectives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 175, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N. A thixotropy model for fresh fluid concretes: Theory, validation and applications. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Fan, Y.; Shah, S.P. Rheological Properties and Structural Build-Up of Cement Based Materials with Addition of Nanoparticles: A Review. Buildings 2022, 12, 2219. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12122219
Li Q, Fan Y, Shah SP. Rheological Properties and Structural Build-Up of Cement Based Materials with Addition of Nanoparticles: A Review. Buildings. 2022; 12(12):2219. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12122219
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qiuchao, Yingfang Fan, and Surendra P. Shah. 2022. "Rheological Properties and Structural Build-Up of Cement Based Materials with Addition of Nanoparticles: A Review" Buildings 12, no. 12: 2219. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12122219
APA StyleLi, Q., Fan, Y., & Shah, S. P. (2022). Rheological Properties and Structural Build-Up of Cement Based Materials with Addition of Nanoparticles: A Review. Buildings, 12(12), 2219. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12122219








