Abstract
Urban floods research has been attracting extensive attention with the increasing threat of flood risk and environmental hazards due to global climate change and urbanization. However, there is rarely a comprehensive review of this field and it remains unclear how the research topics on urban floods have evolved. In this study, we analyzed the development of urban floods research and explored the hotspots and frontiers of this field by scientific knowledge mapping. In total, 3314 published articles from 2006 to 2021 were analyzed. The results suggest that the number of published articles in the field of urban floods generally has an upward trend year by year, and the research focus has shifted from exploring hydrological processes to adopting advanced management measures to solve urban flood problems. Moreover, urban stormwater management and low impact development in the context of climate change and urbanization have gradually become research hotspots. Future research directions based on the status and trends of the urban floods field were also discussed. This research can not only inspire other researchers and policymakers, but also demonstrates the effectiveness of scientific knowledge mapping analysis by the use of the software CiteSpace and VOSviewer.
1. Introduction
Global urbanization and the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events as a result of climate change are serious problems for urban floods [1,2,3,4]. Moreover, they have caused massive casualties and economic losses [5,6]. For example, a severe rainstorm occurred in Henan Province, China on 20 July 2020, with the maximum hourly rainfall of 201.9 mm and the maximum 24 h rainfall of 645.6 mm, which caused more than 300 people to lose their lives. In July 2018, a continuous rainstorm occurred in western Japan, which was the most serious rainstorm disaster in Japan since the Nagasaki flood in July 1982, causing more than 200 deaths [7].
The occurrence of urban floods is generally related to two main phenomena: the generation of runoff during precipitation events (flash flooding) and the overflow of watercourses (fluvial or overbank flooding) [8]. As for the reasons, on one hand, climate change increases the frequency and intensity of extreme weather, with more intermittent rainstorms, more severe droughts, and higher coastal storm surges [9,10], such as the rainstorms in Europe and northern China in July 2021. On the other hand, with the development of social productivity, the progress of science and technology, and the adjustment of industrial structure in a country or region, society has gradually transformed from a traditional rural one dominated by agriculture to a modern urban one dominated by non-agriculture such as industry (secondary) and service industry (tertiary). This caused the ongoing migration of people from rural areas to cities and the continuous increase of urban areas, and the urban phenomenon in the 21st century is much more extensive [11,12,13]. For example, China’s urbanization rate increased from 10.64% in 1949 to 63.89% in 2020 (see National Bureau of Statistics of China http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/#, accessed on 8 March 2021). Urbanization greatly reduces the permeable area of the urban underlying surface, causing a lot of urban rainwater to flow onto the ground or into the artificial drainage system, instead of naturally being infiltrated into the ground and absorbed by the soil [14,15]. When the rainfall exceeds the capacity of the drainage system, especially in some areas with deterioration and insufficiency of the capacity of urban drainage infrastructure and lack of excellent urban planning strategies [16,17], stormwater has no way to go, but must stay on the ground to form urban waterlogging [18,19]. In addition, rapid urban expansion exacerbates the urban heat island effect [20], leading to the formation of hot air flows over the city, which accumulate and thicken, and eventually form precipitation. This is called the urban rain island effect, which further aggravates the urban flood problem.
Many countries in the world have conducted a series of explorations on the management of urban floods and their related problems, mainly urban drainage and water pollution [21,22,23]. For instance, the United States promulgated and revised the Clean Water Act, Water Quality Act, and Federal Water Control Act, and gradually proposed the best management practices (BMPs) to handle the problems of urban water pollution in the 1940s to 1980s [24,25,26]. In the late 1970s, an integrated urban drainage system (IUDS) was started in Switzerland to develop the urban system [27]. Low impact development (LID) was gradually implemented in the 1990s [28], aiming at achieving “natural” hydrology, namely minimizing the impact on the environment when specialists develop and design systems, by use of site layout and integrated control measures [29]. LID is commonly adopted in New Zealand and North America. Sustainable urban drainage system (SUDS), most used in the UK, originated in the 1990s [30]. In 1992, water sensitive urban design (WSUD) was first proposed by Mouritz in Australia [31], and then was presented in a report for the Western Australian government to reduce the adverse effects of urban development on the surrounding hydrological environment [32]. The United States increasingly used the concept of green infrastructure (GI), emphasizing the comprehensive application of multiple disciplines in order to achieve multiple ecosystem benefits and further explore urban stormwater management after entering the 21st century [33,34,35,36]. Sponge city was firstly proposed in the “2012 Low Carbon Urban Development and Technology Forum”, held in Shenzhen, China in April 2012 [37]. This means that a city, designed to act like a sponge, has good resilience in adapting to environmental changes and dealing with natural disasters caused by rainstorms [38].
A growing number of studies on urban floods monitoring and prediction models have been carried out. As the input of real-time simulation models, monitoring data are of great importance, which not only affect the accuracy of prediction, but also are a vital reference for issuing early warnings before disasters [39]. Khalid and Alias [40] generated a 3D city by model geospatial tools and databases to monitor flood risks. Based on the visual image, Dhaya [41] and Zhao [42] used a convolutional neural network and deep neural network algorithms to monitor urban floods, respectively. Besides, the urban hydrological process simulation should be close to the actual situation as much as possible to minimize the discrepancies between simulated and observed runoff, achieving accurate prediction or other goals [43]. Examples of factors to consider include digital elevation model [44], different urban surfaces [45,46], meteorology [47], and others (e.g., hydraulic structures, soil type, precipitation) [48,49,50]. A large number of researchers focus on the prediction of urban floods, part of which aims at improving the model accuracy. The methods often used are deep learning (e.g., long short-term memory, artificial or ensemble neural networks) [51,52,53], hydrodynamic model [54], and other new proposed models [50].
Urban floods have negative impacts on people’s trips and traffic in cities due to road ponding and low visibility [55]. Su [56] developed an integrated simulation method that can analyze urban waterlogging and traffic congestion. Chen [57] assessed the trip difficulty for people of different ages walking in various depths of ponding by an experiment, and found that residents could not pass the areas when ground ponding depth is above 0.5 m moving at 1.5 m/s. To reduce these negativities and alleviate urban floods, building green structures, such as rain gardens [58], green roofs [59], green swales [60], and grey infrastructure are conducted. In addition, some scholars have studied the coupling of these two measures [61,62]. With the increasing popularity of the concept of rain as resource rather than risk [63], many methods to strengthen the utilization of urban rainwater have been proposed. For example, Zhang [64] proved that building above-ground cisterns to exploit rainwater harvesting from rooftops and other underlying surfaces has high potential. With the goal of sustainable rainwater utilization, Lu [65] considered the advantages of monitoring data, stakeholder preferences, and monetary-based techniques, and proposed a four-step method of cost-effectiveness-based multi-criteria optimization. However, when heavy rainfall comes, most of these measures will play limited roles in absorbing rainwater. Considering this circumstance, some studies focus on emergency response, including logistics preparation [66], community evacuation [67], physical assets management [68], citizen rescue [69], and other aspects, such as relief supplies demand and the spatial accessibility of the response [70,71].
Over the years, the studies of urban floods have advanced considerably. Although a large number of publications have touched on the theme of urban floods from different perspectives, there has not yet been any systematic review article that analyzes the development of the entire urban floods field, including the key advances of urban floods and what topic transformation has been experienced. This work aims to study the development of the entire urban floods field and to present a clearer development process for readers combined with visualization software. The remainder of this study is organized as follows: Section 2 introduces the data and methodology. The next section follows a literature overview, including the cooperative network description of the authors, institutions, countries, and the analysis of influential sources and documents of the urban floods field. Section 4 describes the research focus and frontiers on urban floods through scientometrics analysis. The last section summarizes the conclusions obtained from the study. Figure 1 shows the framework for this study.
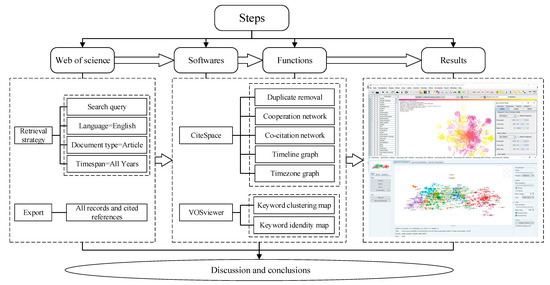
Figure 1.
The framework of the present study.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Screening
The data for analysis were retrieved from the Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI) and the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE) of Web of Science (WOS) Core Collection databases. We finally chose WOS as the data source after comparing the famous databases such as WOS, Scopus, and IEEE for the following reasons: firstly, WOS is the largest comprehensive academic database on a global scale, covering more than 8700 core academic journals and seven databases in the fields of natural sciences, engineering technology, social sciences, arts, and humanities [72,73]. It can retrieve more comprehensive literature compared with the others. A number of scholars use the WOS database as the data source for literature analysis [74,75]. Secondly, WOS provides a guarantee for the reliability of raw data in the visual analysis given its long time span and the quantity and quality of entries. It has been long considered to be the most authoritative scientific and technical literature indexing tool and is often recognized as the ideal data source for bibliometric investigations [76].
The searching methodology followed the procedures below to ensure no important published articles were duplicated or overlooked. Firstly, the search string, namely “((TS = (“urban waterlog *” or “urban storm *” or “urban flood *” or “urban rain *”)) or (TI = ((waterlog * or storm * or flood* or rain *) same city)))”, was identified, ensuring that the literature identified was relevant. Secondly, only data on original articles, which are peer-reviewed, representing original scientific development [77], were included. Therefore, the document type was set to “Article”. Besides, the language and the period were set to “English” and “All Years”, respectively. Thirdly, we eliminated repetitive articles and conference papers. In addition, the titles and abstracts of most of the retrieved articles and the full text of some manuscripts were examined to exclude irrelevant literature that was not focused on urban floods. After the screening, the final document storage of urban floods used in this study was formed and a total of 3314 articles, ranging from 2006 to 2021, were included.
2.2. Data Cleaning
Co-occurrence analysis and co-word analysis, the literature analysis methods mainly used in this paper, are based on the frequency statistics of target words. Traditional co-occurrence analysis assumes the independence of keywords and ignores the similarity in meaning between different words. Therefore, it is necessary to consider the phenomenon of “different words with the same meaning” and improve co-occurrence analysis. In this section, the different abbreviations of the same researchers’ names in different journals and the variety of expressions of the same meaning as keywords in the original data downloaded from the database are combined into one, respectively, to avoid missing terms and ambiguity, ensuring the validity of data analysis.
2.2.1. Authors
We took the following steps to solve the problem in which the abbreviations of the same authors’ names are different when their articles are published in different journals. For example, Deletic, Ana published an article under the name of “Ana Deletic” in Journal of Water Research [78] and another article under the name of “A. Deletic” in Journal of Hydrology [79]. Firstly, the functions of “analysis of search results” and “author statistics” in WOS were used to sort out the alternate names of the authors based on the different abbreviations. Then, a manual screening was implemented based on the fact that the similar name abbreviations may represent two or more researchers, instead of one. Finally, data processing was carried out according to the findings obtained in the previous step. All the authors’ alternate names were replaced with the same one in the initial data exported in Web of Science. This procedure avoids the inaccurate analysis of the author’s knowledge map and guarantees better performance of clustering and bursts identification.
2.2.2. Keywords
The various keywords needed to be unified in the following situations: first, different keywords may express the same meaning, such as “urban flood” and “urban flooding”; and second, there are singular or plural and abbreviated or unabbreviated keywords. For example, “model” and “models”, “LID” and “low impact development” refer to the same meaning, respectively. Third, some keywords in the original text documents have different formats, such as “heavy metal” and “heavy-metal”. All these lead to inaccuracy of the knowledge map. The combination of synonyms was conducted to obtain more comprehensive and accurate results.
2.3. Data Analysis Methods
Scientometrics is a branch of informatics that can quantitatively analyze bibliometric characteristics and objectively reflect the development history and trend of scientific research based on the published literature [80,81]. It has been widely used to assess scientific contributions, capture scientific developments, figure out map knowledge structures, and identify emerging trends [82,83,84,85,86]. Scientific knowledge mapping combines the theories and methods of applied mathematics, graphics, information science, and information visualization technology with citation analysis and co-occurrence analysis, visualizing the core structure, development history, and frontier fields of a given research field by the visual mapping [86,87].
Various scientific knowledge mapping tools have sprung up since the introduction of visualization in scientometrics analysis [88,89]. BibExcel, developed by Olle Person, is specialized document measurement software aimed at assisting a user in analyzing bibliographic data or any data of a textual nature formatted in a similar manner [90]. The generated data files can be imported to Excel or any program that takes tabbed data records, for further processing [91,92]. CiteSpace is a free available Java-based software package, jointly developed by the team of Dr. Chen Chaomei at Drexel University and specially used for mapping scientific knowledge, by which duplicate removal of data can be conducted [93,94]. Pajek can analyze the large complex network, used for analysis and visualization of large networks with thousands or even millions of nodes, which is a powerful tool for the study of various complex nonlinear networks [95]. Ucinet is a social network analysis tool including NetDraw which is responsible for network visualization. It is used to process a variety of relational data. The color, shape, and size of the nodes, namely the intersection points in the network, are changeable through their attributes [96]. VOSviewer is a visual analysis tool of literature developed by Leiden University in the Netherlands, by which the visualization of the knowledge unit is implemented based on VOS clustering technology [97,98,99]. HistCite is a free system for the link analysis of scientific literature and visualization, developed by Eugene Garfield et al. in 2001 [100], through which the citation data of SCI, SSCI, and SA & HCI databases of ISI can be quantitatively analyzed to generate a matrix and real-time dynamic chronology of literature, authors, and journals. Considering the large number of publications we selected, it would be prohibitively difficult to extract and directly analyze their information manually, so it is of great necessity to resort to software. In this study, CiteSpace and VOSviewer were selected as the main analysis tools because of their powerful and advanced functions, in order to provide a comprehensive analysis of the identified literature. CiteSpace is the most used knowledge mapping software in China, which can be used to track the hot spots and development trends and obtain knowledge of the research frontiers of the research field. It can directly reflect the citation relationship of publications we identified, the historical inheritance relationship of authors, and the development of scientific knowledge [95]. VOSviewer is suitable for large-scale sample data because of its strong visualization ability with four views, namely label view, cluster view, density view, and scatter view [101].
Besides, three bibliometric methods were mainly chosen to obtain a systematic and comprehensive analysis of publications in this study. Firstly, co-occurrence analysis was used to count the number of times the characteristic items of documents appeared together, including the external and the internal, such as title, author, keyword, and organization, revealing the content relevance and quantitative characteristics of documents. Secondly, co-word analysis is a kind of content analysis, whose principle is to count the number of times a group of words appears in the same document. On this basis, cluster analysis has been carried out on these words to generate co-word literature clusters, and then the structural changes of the disciplines and topics represented by these words were analyzed. Thirdly, co-citation analysis is a method of measuring the relationship between documents, which was put forward in 1973. The citation refers to the situation where two articles are cited by one or more articles at the same time, and the number of articles cited together is called co-citation intensity or co-citation frequency.
3. Literature Overview
3.1. Publication Trends
The trend of the number of annually published papers, as an important indicator of the current state of research, reflects the attention of researchers and the development of this field from a macro perspective [102]. We analyzed the number of publications, slicing the WOS data from January 2006 to December 2020 annually, and compiled them into a line chart (Figure 2) to gain a general view of urban floods research. It should be noted that the 2021 data are excluded when generating the line chart since the date of data collection for these publications ended in March 2021 and the data are not enough for the whole year.
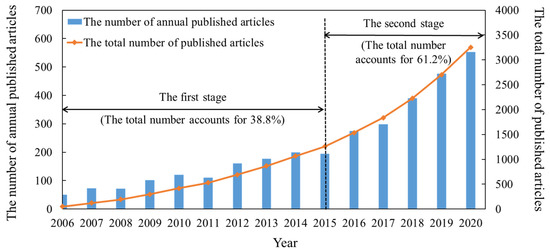
Figure 2.
The trends of published articles in the urban floods field during 2006–2021.
The number of articles exhibited an upward trend with the change of the year. We found that the number of publications in urban floods increased slowly from 2006 to 2015, and did not show a significant growth trend until 2016, revealing two stages, which can be seen from Figure 2. In the first stage (2006–2015), the average annual number of published articles is 126.1 and the average annual increase is 19.4. In the second stage (2016–present), the number of articles published each year is growing rapidly. During this period, it has increased by 71.8 articles per year, on average, from 275 in 2016 to 552 in 2020, by a factor of about three compared to the previous stage. In addition, in the last three years (2018–2020), 43.6% of the articles (1419 out of 3254) were published. This shows that the urban floods field is still at a vigorous development stage; as a result, the number of worldwide researchers will increase and new research hotspots will emerge continuously in the near future.
3.2. Cooperation Network Analysis
The research literature in a specific field is usually completed by many scholars, whose countries, institutions, and collaborators are different [103]. The cooperation relationship means that research scholars work together for the common purpose of producing new scientific knowledge, divided into national, institutional, and individual from macro, meso, and micro—three perspectives [104] to deeply analyze academic collaboration in the field of urban floods. In the network, the size of the nodes, which represent the information about authors or literature, is strictly proportional to the number of publications sent by authors, institutions, or countries, and the larger the nodes, the more articles were published. The links between different nodes reflect their intrinsic relationships, whose thickness directly indicates the close degree of the cooperative relationship [8,93,105,106,107].
3.2.1. Country
The cooperation network between countries is depicted in Figure 3. Generally, all nodes in the network are connected as a whole, indicating that each country cooperates with others, rather than researching alone. Although England ranks fourth in the number of publications, the betweenness centrality (0.26) which measures the importance of nodes in the network is more than other countries, reflecting the beneficial international influence of the research results in the field of urban floods. In addition to England, the United States, Australia, China, France, and the Netherlands have relatively high centrality, which is 0.21, 0.18, 0.17, 0.16, and 0.16, respectively.
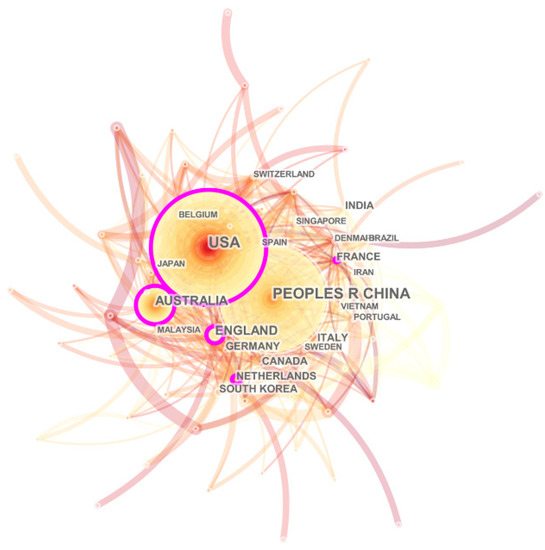
Figure 3.
Countries’ cooperation network.
Figure 4 shows the annual and total number of published articles from the United States and China, respectively, which are the two largest nodes in Figure 3, indicating that their numbers of published articles are much higher than those in other countries. The overall trend of these two countries is on the rise, of which China has a faster upward trend. The United States has published 837 papers, accounting for 25.3% of total studies, while China has published 739 articles, accounting for 22.3%. Comparing the number of articles published in the United States and China from 2006 to 2020, we found that the number of articles published in the United States increased steadily, while that in China grew slowly from 2006 to 2015, but rapidly after 2016, the growth trend of which is consistent with that of the overall increase.
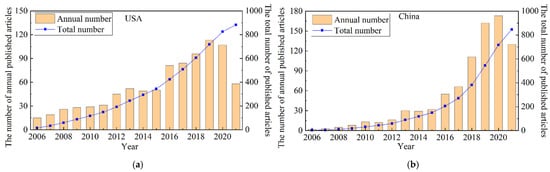
Figure 4.
Trends comparison of the number of publications between the United States and China: (a) the United States; (b) China.
3.2.2. Institution
CiteSpace was used to establish a cooperation network and visualize the research distribution in different institutions in the research field of urban floods [108]. The institutional cooperation network is depicted in Figure 5, which consists of 801 institutional nodes with 1226 connections. Monash University is the most significant core institution, which has published 99 articles in different journals between 2006 and 2021, followed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (count = 81), The University of Melbourne (count = 57), Tsinghua University (count = 51), The University of Exeter (count = 50), and Delft University of Technology (count = 50), which play an intermediary and leading role. In addition, the global distribution of urban floods research institutions was uneven. The top 20 institutions with the largest number of papers published are mainly located in China (count = 6), Australia (count = 4), and the USA (count = 4). There are 36 institutions with more than 20 papers published.
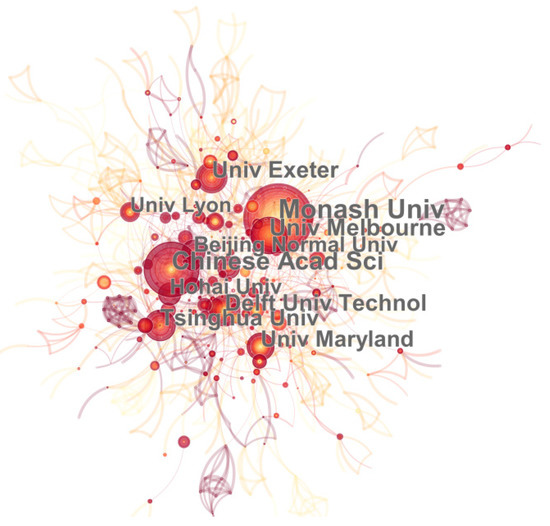
Figure 5.
Institutional cooperation network.
Generally, nodes in the institution cooperation network gather together, illustrating the frequent exchanges and close cooperation between institutions on the research of urban floods. Monash University not only published the highest number of papers, but also has the highest intermediary centrality, which is 0.17, located in the center of the cooperation network. Then follow the Delft University of Technology and Hohai University with an intermediary centrality of 0.09, which have published 50 and 40 papers, respectively. The research institutions are mainly universities, with a small number of scientific research institutions and government agencies from the perspective of the nature of institutions.
3.2.3. Author
A core author group and its cooperative relationship can be determined by analyzing the structural characteristics of the authors and their cooperative network in the field of urban floods. The authors with outstanding performance in publishing documents are Deletic and Fletcher. As of 8 March 2021, Deletic published the most articles related to urban floods, namely 57 articles, as the first author and co-author from 2007 to 2021. The second is Fletcher, with 50 articles. They are the most important scholars, laying the academic foundation in the field of urban floods. The number of articles published by other authors is relatively small compared with the first two authors.
Co-authorship network analysis not only facilitates the discovery of scholars and institutions worthy of attention, but also provides references for evaluating academic influence [109]. An authors’ cooperation network is generated as in Figure 6. There are 3359 nodes and 7262 links and the network density is 0.0013. Deletic and Fletcher occupy the largest node position, which is consistent with the number of published papers. As can be seen from the graph, several clusters have been formed according to the close cooperation between the authors. Cluster A has a large number of researchers, including Ana Deletic, Fletcher Tim, McCarthy David, William Hunt, Maria Viklander, and so on. The number of articles published by the members is ranked first, second, fourth, seventh, and ninth, respectively, and the number of articles published is 57, 50, 33, 25, and 24, respectively. Among the top 10 authors in the number of published articles, the number of authors in cluster A accounts for 50%, indicating that this cluster is one of the most important research teams in the urban floods field. The number of authors in cluster B, represented by Ashantha Goonetilleke, Prasanna Egodawatta, and An Liu, is lower than that of cluster A, and the cooperation network is relatively small and simple. The number of articles published by the top two representative authors is within the top ten of all authors. In cluster C, Slobodan Djordjevic is the core researcher, whose number of articles ranks sixth among all authors in the urban floods field, and who cooperates with Zoran Vojinovic, Albert Chen, and other scholars. The different researchers have a small amount of cooperation, but with low aggregation. In particular, cluster D only contains one author, namely Allen Davis, in the cooperation network diagram, indicating that the author has less cooperation with others.
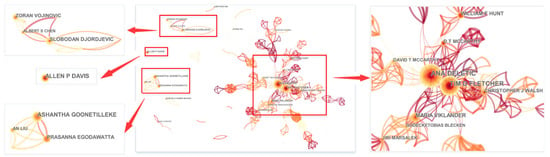
Figure 6.
Authors’ cooperation network.
3.3. Influential Sources and Documents
The number of articles being downloaded and cited can reflect the academic influence and quality of journals to a large extent [110]. The citation of articles generally has a certain lag from the perspective of bibliometrics; that is, the number of citations gradually increases with the accumulation of time [111]. The quantity of download and citation of 3314 articles was analyzed, which showed that as of 8 March 2021, 63 articles were cited more than 100 times, accounting for 1.90% of the total number of articles; the number of articles cited less than 10 times was 1982, accounting for 59.81%, while 38.29% of the total was cited between 10 and 100 times.
The distribution and characteristics of highly cited articles were statistically analyzed to discover the research trends and research hotspots in the urban floods field. The top 10 highly cited papers, according to the statistics of citation times of academic papers in the WOS database, were selected for statistical analysis, as shown in Table 1. The total number of citations of 10 highly cited papers was 3752, accounting for 6.57% of the total citations of 3314 articles. The highest number of citations was 817, while the lowest was 242, and the average number of citations was 357.2. From the perspective of authors, 10 highly cited papers involved 57 authors, in which one author, namely Fletcher, Tim D., has participated in the works of two articles, while others only participated in one. To a certain extent, the change of core authors reflects the change of research hotspots, and plays a leading role in various periods, constantly pushing the research of urban floods to a new level. From the perspective of research content, five articles focus on the evaluation methods and solutions for urban floods, such as vulnerability index [112], hydrological prediction [113], green roofs [114], and flood emergency logistics preparation [68]; three articles, respectively, lay out statistics and predictions for the change of urban floods risk [115], annual flood peak records [116], and future flood loss [117] from a macro point of view, so as to provide a reference for urban stormwater management in the future. Two articles are concerned with the water pollution of heavy metals in urban stormwater runoff [118,119].

Table 1.
Details of the top 10 highly cited papers.
4. Research Hotspots and Frontiers
4.1. Research Hotspots Analysis
Research hotspots refer to one or more core research topics in a specific research field [120], which represent the most important theoretical knowledge and technology application of researchers. Researchers can ascertain the mainstream research direction by grasping the research hotspots in the field of urban floods.
Keywords are the theme generalization of the paper. There are some associations among the keywords given in a paper, which can be expressed by the frequency of co-occurrence. It is generally believed that the more frequently two keywords appear in the same document, the closer the relationship between the two topics is. The co-word characteristics of keywords in literature can reflect the research hotspots, and the co-occurrence frequency determines the intensity of hotspots. Co-word analysis entails obtaining statistics on the frequency of a group of words in the same groups of literature and measuring the degree of closeness by the number of co-occurrence cases; a co-word network composed of these words can be formed by counting the frequency of subject words appearing in the same document. Researchers can analyze the topics of the research field directly through the results of the co-word analysis [121].
4.1.1. Keywords Co-Occurrence Analysis
The keyword density map and clustering map were generated by VOSviewer whose co-occurrence frequency was set more than 20 times, based on the literature from 2006 to 2020. In the keyword density map in Figure 7, the color blue means low density, while yellow means high density. The deeper the yellow, the higher the density; that is, the higher the co-occurrence frequency. Table 2 shows the occurrence frequency and total link strength of the top 20 keywords. We can see that the research hotspots mainly focus on urban flood, urban stormwater, runoff, and climate change from the density map, whose co-occurrence times are 541, 469, 424, and 386, respectively, representing that the research of ontology theory and technology in urban floods is the most popular. Compared with “urban flood” and “urban stormwater”, although the frequency of other hot words, such as “climate change”, “management”, “urbanization”, and “model” is relatively high, there is still a gap compared with the former. This may be related to the research topic of this study, and “urban flood” is directly included in the retrieval formula, as well as “urban stormwater”. It is noteworthy that the keyword “management” has the highest centrality, surpassing the keyword “urban flood”, which ranks first in frequency.
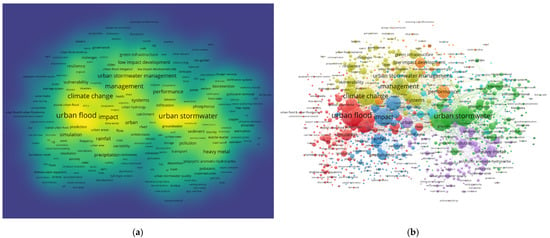
Figure 7.
Density and clustering map of co-occurrence keywords in the urban floods field: (a) the keyword density map; (b) the keyword clustering map.

Table 2.
The occurrence frequency and total link strength of the top 20 keywords.
In the keyword clustering map, different colors represent different clusters. The larger the nodes on the map, the more times keywords appear, indicating that their contribution to the urban floods field is greater. Closely related nodes are connected by lines, and the greater the link strength is, the stronger the internal relationship is. The node group is composed of many nodes.
As can be seen from Figure 7b, the clustering network is a complex co-occurrence relation, from which we detected seven main clusters that reflect the knowledge base for urban floods research. The red cluster, including one of the keywords as a retrieval theme, namely “urban flood”, formed the largest cluster and contained the most cited publications. In this cluster, models are used by researchers for numerical simulation on the issues of runoff. Besides, the hazards and risks of urban floods are also studied. The green cluster represented by “urban stormwater” and the purple one by “heavy metal” tend to focus on the pollution of urban stormwater. The keywords involved in these two clusters include “pollution”, “phosphorus”, “bioretention”, “pollutant removal”, “sediment”, “nitrogen removal”, and “Escherichia coli”. The yellow cluster reveals the research based on climate change and urban stormwater management in the urban floods field. On the one hand, with the change of global climate, cities’ vulnerability and resilience are studied [122,123]; on the other hand, a portion of researchers, with thoughts of the system, focus on urban stormwater management around green infrastructure and put forward policy suggestions from the perspective of the government. Climate change and urbanization are generally regarded as the two main causes of urban floods [124,125,126]. Aside from the climate change focus in the yellow cluster, other researchers emphasized urbanization and its impact, as in the dark blue cluster.
4.1.2. Co-Citation Analysis of Literature
Co-citation of references refers to the phenomenon in which two or more references are cited by the same document. The analysis of literature co-citation in CiteSpace reveals the theoretical knowledge foundation of relevant research by analyzing the high frequency of co-citation literature and the knowledge structure of a research field is revealed by analyzing the key nodes and clusters in the co-citation network [127]. The schematic of literature co-citation was obtained as shown in Figure 8. The nodes represent the cited literature, whose sizes denote the citation frequency. The color of the nodes depicts the citation time corresponding with the time bar above, and the labels on the nodes are the first author and publication year of the article.
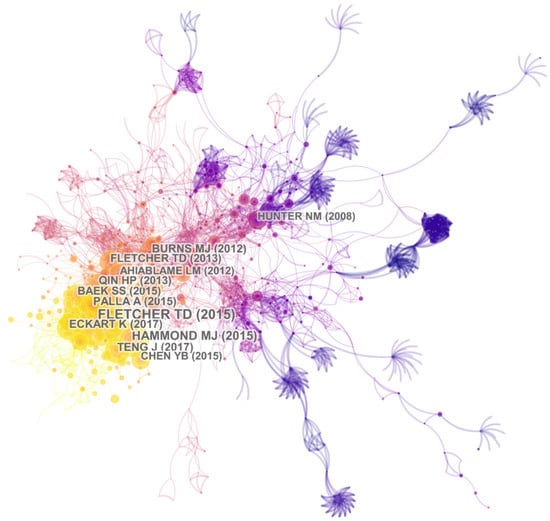
Figure 8.
Co-citation network of references.
The co-citation network in the urban floods field was composed of 978 nodes and 2725 connections. Fifteen key articles with important academic influence, corresponding to the largest 15 nodes in Figure 8, were selected in this study, as shown in Table 3. As can be seen, only one article was published earlier than 2010, and had no direct connection with the other 14 articles, while the connection between the latter was very strong. Among the 15 articles, there were 9 reviews or summaries, indicating that reviews are relatively more often cited due to their nature in all article types.

Table 3.
Details of the top 15 highly co-cited articles.
Fletcher Tim et al. published “SUDS, LID, BMPs, WSUD and more—The evolution and application of terminology surrounding urban drainage” in Urban Water Journal in 2015, which ranks first in citation frequency [128]. As of 8 March 2021, this article has been co-cited 88 times. In this article, the history, application, and underlying principles of terms used in urban drainage were documented, such as low impact development (LID), water sensitive urban design (WSUD), and best management practices (BMPs), making it a summary classic. What ranks second is a review, named “Urban flood impact assessment: A state-of-the-art review”, published in 2015 by Hammond MJ et al., revealing the tangible and intangible damage of urban floods [129]. Burns Matthew et al. [130] systematically discussed the hydrologic shortcomings of conventional urban stormwater management by contrasting the hydrologic effects of two conventional approaches, namely drainage-efficiency-focused and pollutant-load-reduction-focused, and proposed a new approach, ranking third. Teng J. et al. [131] summarized the advantages and limitations of the flood inundation model. The article entitled “Performance and implementation of low impact development—A review” was published by Eckart Kyle et al. in Science of the Total Environment in 2017 [132]. This article provides a summary of the knowledge of low impact development (LID), as well as the current state of research. Palla Anna and Ilaria Gnecco [133] used a hydrologic model to confirm the effectiveness of LID solutions in several scenarios. Qin Huapeng et al. [134] analyzed the effects of three LID techniques, namely swales, permeable pavements, and green roofs, by simulation experiment. In 2013, the state of art regarding stormwater management was summarized by Fletcher Tim et al. [113], whose cited position ranks tenth, making it the only article that ranks not only in the top 10 of the total number of citations, but also in the top of co-cited articles. Ahiablame Laurent et al. [135] discussed and evaluated the effectiveness of low impact development practices by field and laboratory studies. In addition, Hunter et al. [136] compared the ability of six two-dimensional (2D) hydraulic models to simulate surface flows in a densely urbanized area through the simulation of a happened flood event.
4.2. Research Frontiers Analysis
The research frontier mainly discusses the emerging topics in a scientific field. It is a group of prominent concepts and potential research points. Many research frontiers may not only become research hotspots in the future under the tide of science and technology, but may also fade out of the research field after a short rise in a certain historical stage [137,138]. Therefore, timely identification of research frontiers in a specific field is bound to vigorously promote the development of this field. Research frontier, based on the latest academic work, refers to the collection of recently published and often cited literature in a scientific citation network from the perspective of scientometrics. Besides, concepts such as potential knowledge, emerging trends, and new research fields can also be classified as research frontiers.
In general, research frontiers represent the most advanced, innovative, and potentially important academic topics, which can be obtained from the highly cited collection of the latest literature in the scientific literature citation network. This study mainly analyzed the research frontier of the urban floods field according to the literature co-citation network relationship and drew the research frontier knowledge map of urban floods at the present stage through CiteSpace and VOSviewer, which can directly show the research frontier dynamics of the urban floods field evolving.
4.2.1. Overall Change Trend of Keywords
Research trend analysis is helpful to grasp the development of research and excavate the laws and driving forces behind the changes of research hotspots, providing direction for future research. The keywords are clustered and sorted according to time to obtain Figure 9.
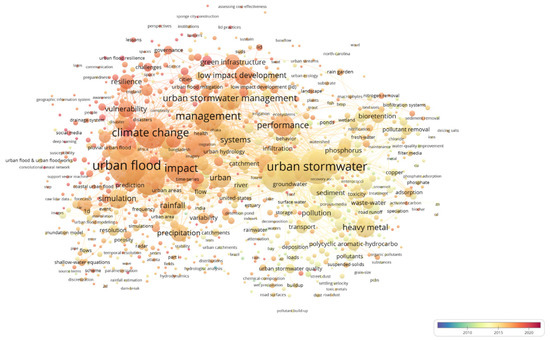
Figure 9.
Overlay visualization of keywords in VOSviewer.
In this figure, it should be noted that the color of nodes is determined by the average time of each keyword year, and the bluer the node is, the earlier the research year is, while the redder the node, the more recent the research year. We found that researchers paid more attention to the problem of urban floods pollution before 2015. Then, the methods of model and numerical simulation were used to research urban stormwater management, low impact development, and so on. The current studies mainly consider cities and urban vulnerability and resilience under the background of climate change and urbanization.
4.2.2. Timeline Graph Analysis
The timeline graph clearly shows the historical research results, trends, and internal relationships of each cluster unit [139,140]. The keywords timeline analysis of the documents from 2006 to 2021 on urban floods was carried out by CiteSpace, whose slicing time and clustering algorithm were set as one year and LLR, respectively; the keywords appearing more than 55 times in each period were extracted and clustered. As shown in Figure 10, the horizontal axis is the time span and the vertical axis is the clustering partition. The size of the arc in the graph represents the span time of the keywords, and the number of nodes represents the internal connection degree of each keyword. In CiteSpace, different settings lead to different clustering results. Under the above settings, 48 clusters are generated. This study analyzed the first 12 clusters in order to receive acquaintance with the evolution laws of the keywords on the time axis.

Figure 10.
A timeline view of keywords in CiteSpace.
The clusters with the longest duration are “urban flood”, “urban stormwater”, “urban stormwater management”, “particulate matters”, and “urban hydrology”, which existed throughout the whole study period. In addition, “best management practices”, “probability distribution”, and “diffuse pollution” existed only in the early stage of the study period, while the study of “groundwater” continued until the middle of the study period. The cross and time span between the clusters of “urban flood” and “urban stormwater” are the largest, which indicates that the relationship between them is the closest because they are the names that have been chosen for the overall field of research. In the cluster of “urban flood”, there is the largest number of bursting keywords.
4.2.3. Time Zone Chart Analysis of Keywords
The time zone graph reflects the evolution of knowledge based on the transmission relationship of research hotspots expressed by two-dimensional time location and links [93,141]. Figure 11 shows the time zone graph of keywords by frequency, from which we can find that most of the research topics in the field of urban floods, such as urban stormwater management, water quality, runoff, and so on, were carried out from 2006 to 2008. There was almost no major research hotspot in the field of urban floods research in the later stage. However, some new research focuses still exist from the relatively micro perspective. For example, urban floods risk was studied in 2011 and low impact development (LID) was adopted by a large number of scholars for research around 2014, while in 2018, the resilience of urban floods and cities became the research hotspot.
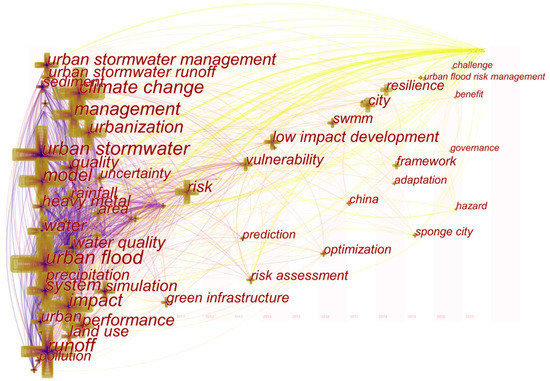
Figure 11.
The evolution of subjects in the field of urban floods.
4.3. Comparative Analysis of Keywords Density Map
We divided the research on the urban floods field into two stages according to the number of papers published each year in Section 3.1. The first stage refers to the period from 2006 to 2015 and the second stage from 2016 to the present. Combined with the stage divisions, this study analyzed the changes of research hotspots in five years, that is, the first part referred to 2006–2010, the second to 2011–2015, and the third to 2016–2021. Finally, all published literature in the past three years was clustered by year, and the changes of research hotspots in each year were analyzed.
4.3.1. Comparison of Three Time Stages
The co-occurrence frequency of keywords was set to 5 times and the keywords hotspot maps of 2006–2010, 2011–2015, and 2016–2021, respectively, were obtained from VOSviewer. In Figure 12, the yellow areas indicate the research hotspots, and the more yellow the area is, the higher the co-occurrence frequency of keywords is.
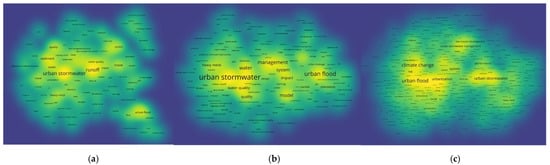
Figure 12.
The density maps of the three stages’ keywords: (a) 2006–2010; (b) 2011–2015; (c) 2016–present.
It can be seen from Figure 12 and Table 4, from the perspective of the number of keywords, the total number of articles published from 2006 to 2010 is the least; correspondingly, the number of keywords is the least, and the total frequency of 5 times or more is 109. The total number of published papers is the highest in 2016–2021, namely 723. From the perspective of research hotspots, the overall high-density areas in Figure 12a are relatively small, as well as scattered, indicating that the research focus in the early research stage of the urban floods field is low and the correlation between hot spots is not so strong compared to the latter. The number of research hotspots increased and the concentration became stronger in Figure 12b. In Figure 12c, the research focuses are further concentrated, which is shown in the expansion of yellow areas in the figure, and different yellow areas begin to overlap to form a new bigger yellow area. This is because more and more scholars have joined in the research of the urban floods field over time, and the number of published articles gradually increased, leading to the rise of keyword co-occurrence frequency.

Table 4.
Comparison of the top 10 keywords in the three stages.
From the perspective of research content, the research mainly focused on “urban stormwater” and “runoff” from 2006 to 2010, and the latter covered a wide range, including “urban runoff”, “road runoff”, “urban stormwater runoff”, etc. At the same time, water quality attracted a lot of attention, such as the keywords “sediment”, “water quality”, “waste water”, etc. From 2011 to 2015, in addition to the research topic “urban storm water” and “urban flood”, the importance of management began to attract attention. Scholars used more models for simulation research, and the pollution of urban stormwater was still a hot topic, such as the keywords “pollution”, “heavy metal”, and “water quality”. Between 2016 and 2021, the second stage of the research on the whole urban floods field, we found that the frequency of the keywords “climate change” and “urbanization” rose rapidly, becoming prevalent in this research period, representing that researchers in the field of urban floods had been paying more and more attention to global climate change and urbanization. Moreover, “urban stormwater management” and “low impact development” have become new research hotspots. In addition, the rapid development of “resilience” and “vulnerability” is also noteworthy.
4.3.2. Comparison of the Last Three Years
The top 10 keywords of co-occurrence frequency in 2019–2021 (as of 15 June 2021, the same applies to 2021 mentioned below) are similar to those in 2016–2021. Figure 13 shows that the top four keywords in 2019, 2020, and 2021 are all “urban flood”, “climate change”, “model”, and “impact”, while “urbanization” is likely to occupy the fifth place for a long time. Although the research on runoff is not as prevalent as that in the previous 10 years, there are still a large number of scholars studying it, which was indicated by the fact that the frequency of the keyword “runoff” in the past three years was 8, 10, and 7, respectively. Significantly, “Management”, which has been extensively studied from 2011 to 2015, still had a place in the recent three years, ranking 7, 6, and 12, respectively, in 2019, 2020, and 2021. It is worth noting that the published articles in 2021 show that the research popularity of “land use” and “SWMM (stormwater management model)” has increased sharply.
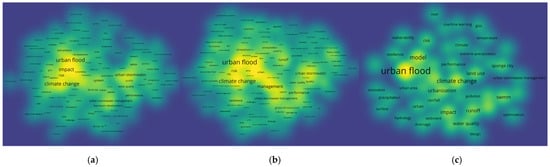
Figure 13.
The density maps of the last three year’s keywords: (a) 2019; (b) 2020; (c) 2021.
In summary, we can deduce that the research on urban floods will continue to flourish, the number of keywords will continue to increase, and the research focus will further expand in a certain period in the future based on the existing literature data. In terms of research content, based on the background of climate change and urbanization, SWMM and other models are used for simulation research, and the concepts of low impact development and sponge city have been put forward to carry out risk analysis, exploring the impact of urban floods and optimizing and even proposing new solutions. Meanwhile, the research on the vulnerability and resilience of flood and city are also worthy of attention.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we analyzed 3314 published articles in the Web of Science core database from the beginning of the field of urban floods research to the present and used CiteSpace and VOSviewer to quantitatively review the academic achievements and progress in this field. Based on the analyses of co-authorship, keywords co-occurrence, and co-citation in the preceding part of the text, the conclusions are as follows:
- (1)
- Two stages were identified for the field by a comprehensive analysis of the literature, namely the first stage (2006–2015) and the second stage (2016—present). The number of publications in the urban floods field was low until 2015, but since then it has progressively increased. In total, 61.24% of the articles were published over the past five years (2016–2020).
- (2)
- Seven main clusters of keywords were found through the clustering map generated by VOSviewer. The dominant one is mainly focused on the methods of model building and simulation to research the hazard and risk of urban floods. Another major cluster pays attention to the pollution of urban stormwater, with a clear emphasis on heavy metal, phosphorus, and nitrogen. The third one focuses on vulnerability and resilience under climate change and urbanization. Besides, other clusters also research the management of urban stormwater, low impact development, and green infrastructure.
- (3)
- The research focus has gradually shifted from water quality and urban stormwater management to urban flood vulnerability and resilience with the development of urbanization and climate change, and the sustainability of urban development has become an enduring topic. A more macro and ecological perspective was taken by a number of researchers who call for permeable grounds, such as parks, rather than concrete underlying surfaces in the process of urban planning as the solution to urban flood problems, reducing the loss of life and property.
In addition to identifying overall publication trends, research hotspots, and frontiers, this study also focuses on authors, institutions, countries, and their cooperative network that lay the foundation of the field of urban floods. Furthermore, CiteSpace provides bursts analysis, through which the strength, beginning, and ending times of bursts are calculated. For example, the change of research focuses will inevitably lead to bursts of new keywords in a short period. This can be used by interested groups as a point of reference to gain better knowledge about the thematic evolution of urban floods research by focusing on the keywords with high strength.
The present study represents a more holistic analysis of the entire development history of the urban floods field, and provides support for more scientific and accurate predictions of changes in the field of urban floods. It solves an important problem of previous reviews in this field, which rarely provided a comprehensive analysis of urban floods research from perspectives of literature statistical analysis and did not fully reveal the changes of this field over time. Therefore, this provides guidance for policymakers and insights into the future development of the urban floods field.
Although we conducted an effective scientometric analysis of the urban floods field, there were still some limitations in the current research. Firstly, WOS core database was only used as the foundation and language was set to English, resulting in neglect of other data sources and a linguistic bias against articles in other languages. Secondly, with the constant improvement of scientometric tools in function and methods, more detailed and valuable conclusions will be drawn in the future. Besides, it is noteworthy that different initial settings in CiteSpace will lead to numerical differences in analysis results. With the update of research and the development of technology, future researchers can carry out increasingly in-depth relevant analyses considering more keywords and databases in searching strategy, digging out more data information, and conducting detailed data analyses.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.Y.; validation, L.J. and X.Z.; resources, B.S.; data curation, B.S.; software, Y.C.; supervision, X.L.; visualization, Y.C.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.Y. and L.J.; writing—review and editing, Q.Y., X.Z. and X.L.; funding acquisition, X.Z. and L.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number 51878385), and Open Fund of Hubei Key Laboratory of Construction and Management in Hydropower Engineering (Grant number 2019KSD05).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://www.webofscience.com/wos/woscc/advanced-search (accessed on 6 December 2021).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhou, Q.; Leng, G.; Su, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Leng, G.; Su, J.; Ren, Y. Comparison of urbanization and climate change impacts on urban flood volumes: Importance of urban planning and drainage adaptation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivers, E.; McMillan, S.; Bell, C.; Clinton, S.; Rivers, E.; McMillan, S.; Bell, C.; Clinton, S. Effects of Urban Stormwater Control Measures on Denitrification in Receiving Streams. Water 2018, 10, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, D.; Ke, X.; Li, S.; Huang, S.; Yang, Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, D.; Ke, X.; et al. Flood vulnerability and resilience assessment in China based on super-efficiency DEA and SBM-DEA methods. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Olesen, K.B.; Borregaard, A.R.; Vollertsen, J.; Liu, F.; Olesen, K.B.; Borregaard, A.R.; Vollertsen, J. Microplastics in urban and highway stormwater retention ponds. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ng, S.T.; Dao, J.; Zhou, S.; Xu, F.J.; Xu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ng, S.T.; Dao, J.; et al. BIM-GIS-DCEs enabled vulnerability assessment of interdependent infrastructures—A case of stormwater drainage-building-road transport Nexus in urban flooding. Automat. Constr. 2021, 125, 103626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Feng, W.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Feng, W.; Huang, H. Short Term Real-Time Rolling Forecast of Urban River Water Levels Based on LSTM: A Case Study in Fuzhou City, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Ma, C.; Xu, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, K.; Han, H.; Qi, W.; Ma, C.; Xu, H.; Chen, Z.; et al. A review on applications of urban flood models in flood mitigation strategies. Nat. Hazards 2021, 108, 31–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, Y.; Chen, F.; Chen, Y. Urban climate research and planning applications in China: A scientometric and long-term review (1963–2018) based on CiteSpace. Clim. Res. 2020, 81, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zheng, H.; Huang, B.; Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Li, R.; Zheng, H.; Huang, B.; Xu, H.; Li, Y. Dynamic Impacts of Climate and Land-Use Changes on Surface Runoff in the Mountainous Region of the Haihe River Basin, China. Adv. Meteorol. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Wang, C.C.; Shen, X.; Zlatanova, S.; Xu, H.; Wang, C.C.; Shen, X.; Zlatanova, S. 3D Tree Reconstruction in Support of Urban Microclimate Simulation: A Comprehensive Literature Review. Buildings 2021, 11, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salata, S.; Salata, S. The Utilization of Supervised Classification Sampling for Environmental Monitoring in Turin (Italy). Sustainability 2021, 13, 2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jia, L.; Wu, W.; Yan, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Jia, L.; Wu, W.; Yan, J.; Liu, Y. Urbanization for rural sustainability—Rethinking China’s urbanization strategy. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, W.; Tao, X.; Chen, M.; Liu, W.; Tao, X. Evolution and assessment on China’s urbanization 1960–2010: Under-urbanization or over-urbanization? Habitat Int. 2013, 38, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salata, S.; Ronchi, S.; Giaimo, C.; Arcidiacono, A.; Pantaloni, G.G.; Salata, S.; Ronchi, S.; Giaimo, C.; Arcidiacono, A.; Pantaloni, G.G. Performance-Based Planning to Reduce Flooding Vulnerability Insights from the Case of Turin (North-West Italy). Sustainability 2021, 13, 5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nillesen, A.L.; Nillesen, A.L. Integrated design for flood risk and spatial quality—examples from the dutch delta programme. J. Green Build. 2018, 13, 157–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Fang, Y.; Sweetapple, C.; Wang, M.; Fang, Y.; Sweetapple, C. Assessing flood resilience of urban drainage system based on a ‘do-nothing’ benchmark. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Liu, C. Exploring the Influence of an Urban Water System on Housing Prices: Case Study of Zhengzhou. Buildings 2020, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, C. A GIS-based procedure for measuring the efects of the built environment on urban flash floods. J. Green Build. 2016, 11, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Xu, M.; Wang, Z.; Lai, C.; Zhang, M.; Xu, M.; Wang, Z.; Lai, C. Assessment of the vulnerability of road networks to urban waterlogging based on a coupled hydrodynamic model. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronchi, S.; Salata, S.; Arcidiacono, A.; Ronchi, S.; Salata, S.; Arcidiacono, A. Which urban design parameters provide climate-proof cities? An application of the Urban Cooling InVEST Model in the city of Milan comparing historical planning morphologies. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 63, 102459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez-Maranges, M.; Breuste, J.; Hof, A.; Gimenez-Maranges, M.; Breuste, J.; Hof, A. Sustainable Drainage Systems for transitioning to sustainable urban flood management in the European Union: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, M.P.; Mudgil, S.; Karmakar, S.; Mohanty, M.P.; Mudgil, S.; Karmakar, S. Flood management in India: A focussed review on the current status and future challenges. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 49, 101660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andenæs, E.; Time, B.; Muthanna, T.; Asphaug, S.; Kvande, T.; Andenæs, E.; Time, B.; Muthanna, T.; Asphaug, S.; Kvande, T. Risk Reduction Framework for Blue-Green Roofs. Buildings 2021, 11, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, G.; Chen, X.; Yang, Z.; Huang, H.; Shao, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; et al. Data Integration and its Application in the Sponge City Construction of CHINA. Procedia Eng. 2016, 154, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fesenmyer, K.A.; Wenger, S.J.; Leigh, D.S.; Neville, H.M.; Fesenmyer, K.A.; Wenger, S.J.; Leigh, D.S.; Neville, H.M. Large portion of USA streams lose protection with new interpretation of Clean Water Act. Freshw. Sci. 2021, 40, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamouz, M.; Heydari, Z.; Karamouz, M.; Heydari, Z. Conceptual Design Framework for Coastal Flood Best Management Practices. J. Water Res. Plan. Man. 2020, 146, 4020041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujer, W.; Krejci, V.; Schwarzenbach, R.; Zobrist, J.; Gujer, W.; Krejci, V.; Schwarzenbach, R.; Zobrist, J. Von der Kanalisation ins Grundwasser—Charakterisierung eines Regenereignisses im Glattal. Gas Wasserfach Wasser Abwasser 1982, 62, 298–311. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y. Dynamic water balance of infiltration-based stormwater best management practices. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.; Ligaray, M.; Pyo, J.; Park, J.; Kang, J.; Pachepsky, Y.; Chun, J.A.; Cho, K.H.; Baek, S.; Ligaray, M.; et al. A novel water quality module of the SWMM model for assessing low impact development (LID) in urban watersheds. J. Hydrol. 2020, 586, 124886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrans, P.; Torres, M.N.; Temprano, J.; Rodríguez Sánchez, J.P.; Ferrans, P.; Torres, M.N.; Temprano, J.; Rodríguez Sánchez, J.P. Sustainable Urban Drainage System (SUDS) modeling supporting decision-making: A systematic quantitative review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouritz, M.J. Sustainable Urban Water Systems: Policy and Professional Praxis. Ph.D. Thesis, Murdoch University, Perth, Australia, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Xu, S.; Yao, L.; Li, Z.; Xu, S.; Yao, L. A Systematic Literature Mining of Sponge City: Trends, Foci and Challenges Standing Ahead. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Peng, C.; Chiang, P.; Cai, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Li, C.; Peng, C.; Chiang, P.; Cai, Y.; et al. Mechanisms and applications of green infrastructure practices for stormwater control: A review. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raei, E.; Reza Alizadeh, M.; Reza Nikoo, M.; Adamowski, J.; Raei, E.; Reza Alizadeh, M.; Reza Nikoo, M.; Adamowski, J. Multi-objective decision-making for green infrastructure planning (LID-BMPs) in urban storm water management under uncertainty. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andenæs, E.; Engebø, A.; Time, B.; Lohne, J.; Torp, O.; Kvande, T.; Andenæs, E.; Engebø, A.; Time, B.; Lohne, J.; et al. Perspectives on Quality Risk in the Building Process of Blue-Green Roofs in Norway. Buildings 2020, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronchi, S.; Arcidiacono, A.; Pogliani, L.; Ronchi, S.; Arcidiacono, A.; Pogliani, L. Integrating green infrastructure into spatial planning regulations to improve the performance of urban ecosystems. Insights from an Italian case study. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 53, 101907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Han, Y.; Jiang, M.; Li, H. The review of Sponge City. In Proceedings of the 2016 5th International Conference on Sustainable Energy and Environment Engineering (ICSEEE 2016), Zhuhai, China, 12–13 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Zhang, J. A review of the progress in Chinese Sponge City programme: Challenges and opportunities for urban stormwater management. Water Supply 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falck, A.S.; Maggioni, V.; Tomasella, J.; Diniz, F.L.R.; Mei, Y.; Beneti, C.A.; Herdies, D.L.; Neundorf, R.; Caram, R.O.; Rodriguez, D.A.; et al. Improving the use of ground-based radar rainfall data for monitoring and predicting floods in the Iguaçu river basin. J. Hydrol. 2018, 567, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Kalbani, K.; Rahman, A.A. 3D city model for monitoring flash flood risks in Salalah, Oman. Int. J. Eng. Geosci. 2021, 7, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaya, R.; Kanthavel, R.; Dhaya, R.; Kanthavel, R. Video Surveillance-Based Urban Flood Monitoring System Using a Convolutional Neural Network. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2022, 32, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H. A localization method for stagnant water in city road traffic image. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ma, C.; Xu, K.; Lian, J.; Long, Y.; Xu, H.; Ma, C.; Xu, K.; Lian, J.; Long, Y. Staged optimization of urban drainage systems considering climate change and hydrological model uncertainty. J. Hydrol. 2020, 587, 124959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Fang, J.; Fang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wu, C.; Liu, M.; Xu, K.; Fang, J.; Fang, Y.; Sun, Q.; et al. The Importance of Digital Elevation Model Selection in Flood Simulation and a Proposed Method to Reduce DEM Errors: A Case Study in Shanghai. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Xia, J.; She, D.; Song, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, S.; Hu, C.; Xia, J.; She, D.; Song, Z.; et al. A new urban hydrological model considering various land covers for flood simulation. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shao, W.; Xiang, C.; Mei, C.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Shao, W.; Xiang, C.; Mei, C.; Li, Z. Uncertainties of urban flood modeling: Influence of parameters for different underlying surfaces. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 108929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Lei, Y.; Gong, X.; Ju, W.; Qin, Y.; Lei, Y.; Gong, X.; Ju, W. A model involving meteorological factors for short- to medium-term, water-level predictions of small- and medium-sized urban rivers. Nat. Hazards 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldshleger, N.; Maor, A.; Garzuzi, J.; Asaf, L.; Goldshleger, N.; Maor, A.; Garzuzi, J.; Asaf, L. Influence of land use on the quality of runoff along Israel′s coastal strip (demonstrated in the cities of Herzliya and Ra′anana). Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Liang, Q.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Xia, X.; Cui, Y.; Liang, Q.; Wang, G.; et al. Simulation of Hydraulic Structures in 2D High-Resolution Urban Flood Modeling. Water 2019, 11, 2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Kinsland, G.; Poudel, D.; Fenech, A.; Wang, X.; Kinsland, G.; Poudel, D.; Fenech, A. Urban flood prediction under heavy precipitation. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 123984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, D.B.; Sivakumar, M.; May, D.B.; Sivakumar, M. Prediction of urban stormwater quality using artificial neural networks. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2009, 24, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkhahn, S.; Fuchs, L.; Neuweiler, I.; Berkhahn, S.; Fuchs, L.; Neuweiler, I. An ensemble neural network model for real-time prediction of urban floods. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Z. Depth prediction of urban flood under different rainfall return periods based on deep learning and data warehouse. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timbadiya, P.V.; Patel, P.L.; Porey, P.D.; Timbadiya, P.V.; Patel, P.L.; Porey, P.D. A 1D–2D Coupled Hydrodynamic Model for River Flood Prediction in a Coastal Urban Floodplain. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2015, 20, 5014017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Ng, T.L.; Yang, P.; Ng, T.L. Gauging Through the Crowd: A Crowd-Sourcing Approach to Urban Rainfall Measurement and Storm Water Modeling Implications. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 9462–9478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Su, B.; Huang, H.; Li, Y. Integrated simulation method for waterlogging and traffic congestion under urban rainstorms. Nat. Hazards 2016, 81, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, X.; Liu, X.; Bao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, X.; Liu, X.; et al. Scenario Simulation-Based Assessment of Trip Difficulty for Urban Residents under Rainstorm Waterlogging. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 2057–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, R.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Xia, J.; Gao, X.; Han, R.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Xia, J.; Gao, X. Comprehensive benefits of different application scales of sponge facilities in urban built areas of northwest China. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2021, 21, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Lin, R.; Wei, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Shangguan, H.; Song, Y.; Fan, G.; Lin, R.; Wei, Z.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Effects of low impact development on the stormwater runoff and pollution control. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Jinyan, K.; Wenbin, P.; Xin, Z.; Yuanbin, C.; Peng, Z.; Jinyan, K.; Wenbin, P.; Xin, Z.; Yuanbin, C. Effects of Low-Impact Development on UrbanRainfall Runoff under Different Rainfall Characteristics. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtis, I.M.; Bellos, V.; Kopsiaftis, G.; Psiloglou, B.; Tsihrintzis, V.A.; Kourtis, I.M.; Bellos, V.; Kopsiaftis, G.; Psiloglou, B.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Methodology for holistic assessment of grey-green flood mitigation measures for climate change adaptation in urban basins. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, Y.; Li, S.; Tan, S.K.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Life-cycle cost analysis and resilience consideration for coupled grey infrastructure and low-impact development practices. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 75, 103358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meilvang, M.L.; Meilvang, M.L. From rain as risk to rain as resource: Professional and organizational changes in urban rainwater management. Curr. Sociol. 2021, 69, 1034–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, M.; Chen, G.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, M.; Chen, G.; Xu, Y. Urban Rainwater Utilization and its Role in Mitigating Urban Waterlogging Problems—A Case Study in Nanjing, China. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 3757–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, Y.P.; Yang, K.; Che, Y.; Shang, Z.Y.; Zhu, H.F.; Jian, Y.; Lü, Y.P.; Yang, K.; Che, Y.; Shang, Z.Y.; et al. Cost-effectiveness-based multi-criteria optimization for sustainable rainwater utilization: A case study in Shanghai. Urban Water J. 2013, 10, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Tseng, Y.; Chen, J.; Chang, M.; Tseng, Y.; Chen, J. A scenario planning approach for the flood emergency logistics preparation problem under uncertainty. Trans. Res. Part E Logist. Trans. Rev. 2007, 43, 737–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, J. MAS-Based Evacuation Simulation of an Urban Community during an Urban Rainstorm Disaster in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, G.; Huang, G.Q.; Fang, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, G.; Huang, G.Q.; Fang, J.; Chen, J. Cloud-based smart asset management for urban flood control. Enterp. Inf. Syst. 2015, 11, 719–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y. Research on Emergency Rescue of Urban Flood Disaster Based on Wargame Simulation. J. Indian Soc. Remote 2018, 46, 1677–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Wen, J.; Xi, J.; Xu, H.; Shan, X.; Yao, Q.; Shi, Y.; Wen, J.; Xi, J.; Xu, H.; et al. A Study on Spatial Accessibility of the Urban Tourism Attraction Emergency Response under the Flood Disaster Scenario. Complexity 2020, 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Wu, H.; Liang, G.; Cardenas-Tristan, A.; Wu, X.; Zhao, C.; Li, D.; Lin, A.; Wu, H.; Liang, G.; et al. A big data-driven dynamic estimation model of relief supplies demand in urban flood disaster. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 49, 101682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Singh, P.; Karmakar, M.; Leta, J.; Mayr, P.; Singh, V.K.; Singh, P.; Karmakar, M.; Leta, J.; Mayr, P. The journal coverage of Web of Science, Scopus and Dimensions: A comparative analysis. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 5113–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, H.; Shi, J.; Wu, G.; Chen, J.; Zhao, X.; Si, H.; Shi, J.; Wu, G.; Chen, J.; Zhao, X. Mapping the bike sharing research published from 2010 to 2018: A scientometric review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 213, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhou, M.; Lv, J.; Chen, K.; Huang, L.; Zhou, M.; Lv, J.; Chen, K. Trends in global research in forest carbon sequestration: A bibliometric analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulucak, R.; Sari, R.; Erdogan, S.; Alexandre Castanho, R.; Ulucak, R.; Sari, R.; Erdogan, S.; Alexandre Castanho, R. Bibliometric Literature Analysis of a Multi-Dimensional Sustainable Development Issue: Energy Poverty. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoa, F.K.H.; Lai, H.; Chang, L.L.; Honda, K.; Phoa, F.K.H.; Lai, H.; Chang, L.L.; Honda, K. A two-step deep learning approach to data classification and modeling and a demonstration on subject type relationship analysis in the Web of Science. Scientometrics 2020, 125, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schappert, M.; von Hauff, M.; Schappert, M.; von Hauff, M. Sustainable consumption in the smart grid: From key points to eco-routine. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 121585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, B.; Bach, P.M.; Deletic, A.; Jamali, B.; Bach, P.M.; Deletic, A. Rainwater harvesting for urban flood management—An integrated modelling framework. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lintern, A.; Leahy, P.; Deletic, A.; Heijnis, H.; Zawadzki, A.; Gadd, P.; McCarthy, D.; Lintern, A.; Leahy, P.; Deletic, A.; et al. Uncertainties in historical pollution data from sedimentary records from an Australian urban floodplain lake. J. Hydrol. 2018, 560, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, D.C.; Whitman, W.B.; Coleman, D.C.; Whitman, W.B. Linking species richness, biodiversity and ecosystem function in soil systems. Pedobiologia 2005, 49, 479–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganasegeran, K.; Hor, C.P.; Jamil, M.F.A.; Suppiah, P.D.; Noor, J.M.; Hamid, N.A.; Chuan, D.R.; Manaf, M.R.A.; Ch Ng, A.S.H.; Looi, I.; et al. Mapping the Scientific Landscape of Diabetes Research in Malaysia (2000–2018): A Systematic Scientometrics Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Yuan, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, Q.; Zheng, C.; Yuan, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, Q. From digital to sustainable: A scientometric review of smart city literature between 1990 and 2019. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, S.; Sengoku, S.; Miyashita, S.; Sengoku, S. Scientometrics for management of science: Collaboration and knowledge structures and complexities in an interdisciplinary research project. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 7419–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blümel, C.; Schniedermann, A.; Blümel, C.; Schniedermann, A. Studying review articles in scientometrics and beyond: A research agenda. Scientometrics 2020, 124, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Meng, G.; Yang, Y.; Meng, G. A bibliometric analysis of comparative research on the evolution of international and Chinese ecological footprint research hotspots and frontiers since 2000. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 650–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguntona, O.A.; Aigbavboa, C.O.; Thwala, W.D. A scientometric analysis and visualization of green building research in Africa. J. Green Build. 2021, 16, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, D.; Pang, R.; Xie, F.; Zhang, J.; Sun, D.; Wang, Z.; Ma, D.; Pang, R.; Xie, F.; et al. Research Progress and Development Trend of Social Media Big Data (SMBD): Knowledge Mapping Analysis Based on CiteSpace. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Tan, Y.; Huang, Z.; Liu, G.; Tan, Y.; Huang, Z. Knowledge Mapping of Homeowners’ Retrofit Behaviors: An Integrative Exploration. Buildings 2021, 11, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Glänzel, W.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Y.; Glänzel, W.; Zhang, L. Tracing the development of mapping knowledge domains. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 6201–6224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragán Martín, A.B.; Molero Jurado, M.D.M.; Pérez-Fuentes, M.D.C.; Simón Márquez, M.D.M.; Martos Martínez, Á.; Sisto, M.; Gázquez Linares, J.J.; Barragán Martín, A.B.; Molero Jurado, M.D.M.; Pérez-Fuentes, M.D.C.; et al. Study of Cyberbullying among Adolescents in Recent Years: A Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Robles, J.R.; Cobo, M.J.; Gutiérrez-Salcedo, M.; Martínez-Sánchez, M.A.; Gamboa-Rosales, N.K.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; López-Robles, J.R.; Cobo, M.J.; Gutiérrez-Salcedo, M.; Martínez-Sánchez, M.A.; et al. 30th Anniversary of Applied Intelligence: A combination of bibliometrics and thematic analysis using SciMAT. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 6547–6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Duan, X.; Zhang, W.; Dai, S.; Duan, X.; Zhang, W. Knowledge map of environmental crisis management based on keywords network and co-word analysis, 2005–2018. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, C. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2006, 57, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, T.; Han, D.; Song, X. Past, present, and future of global seawater intrusion research: A bibliometric analysis. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambeke, B.W.; Liu, M.; Hsiang, S.M.; Wambeke, B.W.; Liu, M.; Hsiang, S.M. Using Pajek and Centrality Analysis to Identify a Social Network of Construction Trades. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2012, 138, 1192–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Li, H.; Ali, R.; Rehman, R.U.; Xue, W.; Li, H.; Ali, R.; Rehman, R.U. Knowledge Mapping of Corporate Financial Performance Research: A Visual Analysis Using Cite Space and Ucinet. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orduña-Malea, E.; Costas, R.; Orduña-Malea, E.; Costas, R. Link-based approach to study scientific software usage: The case of VOSviewer. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 8153–8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, S.K.; Kumar, N.; Saini, M.; Sood, S.K.; Kumar, N.; Saini, M. Scientometric analysis of literature on distributed vehicular networks: VOSViewer visualization techniques. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çevikbaş, M.; Işık, Z.; Çevikbaş, M.; Işık, Z. An Overarching Review on Delay Analyses in Construction Projects. Buildings 2021, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.H.H.; Lei, S.; Ali, M.; Doronin, D.; Hussain, S.T.; Shah, S.H.H.; Lei, S.; Ali, M.; Doronin, D.; Hussain, S.T. Prosumption: Bibliometric analysis using HistCite and VOSviewer. Kybernetes 2019. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuni, I.Y.; Shen, G.Q.; Osei-Kyei, R.; Wuni, I.Y.; Shen, G.Q.; Osei-Kyei, R. sustainability of off-site construction: A bibliometric review and visualized analysis of trending topics and themes. J. Green Build. 2020, 15, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsolakis, N.; Anthopoulos, L.; Tsolakis, N.; Anthopoulos, L. Eco-cities: An integrated system dynamics framework and a concise research taxonomy. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2015, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, A.; Ahmed, A.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Azam, A.; Ahmed, A.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Knowledge structure and research progress in wind power generation (WPG) from 2005 to 2020 using CiteSpace based scientometric analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y. Visualization analysis of high-speed railway research based on CiteSpace. Transp. Policy 2020, 85, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fu, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fu, C.; Zhang, X. Progress in urban metabolism research and hotspot analysis based on CiteSpace analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 281, 125224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Zhu, Y.; Ao, T.; Chen, T.; Qin, F.; Zhu, Y.; Ao, T.; Chen, T. The Development Trend and Research Frontiers of Distributed Hydrological Models—Visual Bibliometric Analysis Based on Citespace. Water 2021, 13, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ibekwe-SanJuan, F.; Hou, J.; Chen, C.; Ibekwe-SanJuan, F.; Hou, J. The structure and dynamics of cocitation clusters: A multiple-perspective cocitation analysis. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 1386–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, N.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, N.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, X. Social Media Meets Big Urban Data: A Case Study of Urban Waterlogging Analysis. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2016, 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bu, Y.; Wang, B.; Chinchilla-Rodríguez, Z.; Sugimoto, C.R.; Huang, Y.; Huang, W.; Bu, Y.; Wang, B.; Chinchilla-Rodríguez, Z.; Sugimoto, C.R.; et al. Considering author sequence in all-author co-citation analysis. Inform. Process. Manag. 2020, 57, 102300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Pruñonosa, J.; Plaza-Navas, M.A.; Díez-Martín, F.; Prado-Roman, C.; Torres-Pruñonosa, J.; Plaza-Navas, M.A.; Díez-Martín, F.; Prado-Roman, C. The Sources of Knowledge of the Economic and Social Value in Sport Industry Research: A Co-citation Analysis. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- First systematic review on PM-bound water: Exploring the existing knowledge domain using the CiteSpace software. Scientometrics 2020, 124, 1945–2008. [CrossRef]
- Balica, S.F.; Wright, N.G.; van der Meulen, F.; Balica, S.F.; Wright, N.G.; van der Meulen, F. A flood vulnerability index for coastal cities and its use in assessing climate change impacts. Nat. Hazards 2012, 64, 73–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fletcher, T.D.; Andrieu, H.; Hamel, P.; Fletcher, T.D.; Andrieu, H.; Hamel, P. Understanding, management and modelling of urban hydrology and its consequences for receiving waters: A state of the art. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentens, J.; Raes, D.; Hermy, M.; Mentens, J.; Raes, D.; Hermy, M. Green roofs as a tool for solving the rainwater runoff problem in the urbanized 21st century? Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 77, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Kanae, S.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Handmer, J.; Nicholls, N.; Peduzzi, P.; Mechler, R.; Bouwer, L.M.; Arnell, N.; Mach, K.; et al. Flood risk and climate change: Global and regional perspectives. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 59, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villarini, G.; Smith, J.A.; Serinaldi, F.; Bales, J.; Bates, P.D.; Krajewski, W.F.; Villarini, G.; Smith, J.A.; Serinaldi, F.; Bales, J.; et al. Flood frequency analysis for nonstationary annual peak records in an urban drainage basin. Adv. Water Resour. 2009, 32, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegatte, S.; Green, C.; Nicholls, R.J.; Corfee-Morlot, J.; Hallegatte, S.; Green, C.; Nicholls, R.J.; Corfee-Morlot, J. Future flood losses in major coastal cities. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaegi, R.; Sinnet, B.; Zuleeg, S.; Hagendorfer, H.; Mueller, E.; Vonbank, R.; Boller, M.; Burkhardt, M.; Kaegi, R.; Sinnet, B.; et al. Release of silver nanoparticles from outdoor facades. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2900–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.N.; Peake, B.M.; Brown, J.N.; Peake, B.M. Sources of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban stormwater runoff. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 359, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fath, B.D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fath, B.D. Research progress and hotspot analysis for reactive nitrogen flows in macroscopic systems based on a CiteSpace analysis. Ecol. Model. 2021, 443, 109456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Hu, M. A review of life cycle research of the built environment at difference scales: A citation analysis using big data. J. Green Build. 2019, 14, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetta, G.; Salata, S.; Brunetta, G.; Salata, S. Mapping Urban Resilience for Spatial Planning—A First Attempt to Measure the Vulnerability of the System. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronchi, S.; Arcidiacono, A.; Ronchi, S.; Arcidiacono, A. Adopting an Ecosystem Services-Based Approach for Flood Resilient Strategies: The Case of Rocinha Favela (Brazil). Sustainability 2019, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, K.; Hettiarachchi, S.; Ou, Y.; Sharma, A.; Alexander, K.; Hettiarachchi, S.; Ou, Y.; Sharma, A. Can integrated green spaces and storage facilities absorb the increased risk of flooding due to climate change in developed urban environments? J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspersen, P.S.; Ravn, N.H.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; Madsen, H.; Drews, M.; Kaspersen, P.S.; Ravn, N.H.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; Madsen, H.; Drews, M. Comparison of the impacts of urban development and climate change on exposing European cities to pluvial flooding. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Soc. 2017, 21, 4131–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pour, S.H.; Wahab, A.K.A.; Shahid, S.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Dewan, A.; Pour, S.H.; Wahab, A.K.A.; Shahid, S.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Dewan, A. Low impact development techniques to mitigate the impacts of climate-change-induced urban floods: Current trends, issues and challenges. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 62, 102373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.K.F.; Köseoglu, M.A.; Kim, S.S.; Wong, A.K.F.; Köseoglu, M.A.; Kim, S.S. The intellectual structure of corporate social responsibility research in tourism and hospitality: A citation/co-citation analysis. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2021, 49, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, T.D.; Shuster, W.; Hunt, W.F.; Ashley, R.; Butler, D.; Arthur, S.; Trowsdale, S.; Barraud, S.; Semadeni-Davies, A.; Bertrand-Krajewski, J.; et al. SUDS, LID, BMPs, WSUD and more—The evolution and application of terminology surrounding urban drainage. Urban Water J. 2014, 12, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, M.J.; Chen, A.S.; Djordjević, S.; Butler, D.; Mark, O.; Hammond, M.J.; Chen, A.S.; Djordjević, S.; Butler, D.; Mark, O. Urban flood impact assessment: A state-of-the-art review. Urban Water J. 2013, 12, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burns, M.J.; Fletcher, T.D.; Walsh, C.J.; Ladson, A.R.; Hatt, B.E.; Burns, M.J.; Fletcher, T.D.; Walsh, C.J.; Ladson, A.R.; Hatt, B.E. Hydrologic shortcomings of conventional urban stormwater management and opportunities for reform. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 105, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Jakeman, A.J.; Vaze, J.; Croke, B.F.W.; Dutta, D.; Kim, S.; Teng, J.; Jakeman, A.J.; Vaze, J.; Croke, B.F.W.; et al. Flood inundation modelling: A review of methods, recent advances and uncertainty analysis. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2017, 90, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckart, K.; McPhee, Z.; Bolisetti, T.; Eckart, K.; McPhee, Z.; Bolisetti, T. Performance and implementation of low impact development—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 413–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palla, A.; Gnecco, I.; Palla, A.; Gnecco, I. Hydrologic modeling of Low Impact Development systems at the urban catchment scale. J. Hydrol. 2015, 528, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Li, Z.; Fu, G.; Qin, H.; Li, Z.; Fu, G. The effects of low impact development on urban flooding under different rainfall characteristics. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 129, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahiablame, L.M.; Engel, B.A.; Chaubey, I.; Ahiablame, L.M.; Engel, B.A.; Chaubey, I. Effectiveness of Low Impact Development Practices: Literature Review and Suggestions for Future Research. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 4253–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, N.M.; Bates, P.D.; Neelz, S.; Pender, G.; Villanueva, I.; Wright, N.G.; Liang, D.; Falconer, R.A.; Lin, B.; Waller, S.; et al. Benchmarking 2D hydraulic models for urban flooding. Proc. Inst. Civil Eng.—Water Manag. 2008, 161, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, M.; Long, R.; Bai, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, M.; Long, R.; Bai, Y.; Chen, H. Knowledge mapping analysis of international research on environmental communication using bibliometrics. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 298, 113475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malczewski, J.; Jankowski, P.; Malczewski, J.; Jankowski, P. Emerging trends and research frontiers in spatial multicriteria analysis. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2020, 34, 1257–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, S.; Qian, S.; Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, S.; Qian, S. Exploring Research Trends and Building a Multidisciplinary Framework Related to Brownfield: A Visual Analysis Using CiteSpace. Complexity 2021, 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; He, S.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, D.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Study on sustainable urbanization literature based on Web of Science, scopus, and China national knowledge infrastructure: A scientometric analysis in CiteSpace. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Hou, Y.; Ding, L.; Li, P.; He, C.; Hou, Y.; Ding, L.; Li, P. Visualized literature review on sustainable building renovation. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 102622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).