Filtration Performance of Ultrathin Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Filters Doped with TiO2 and Activated Charcoal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
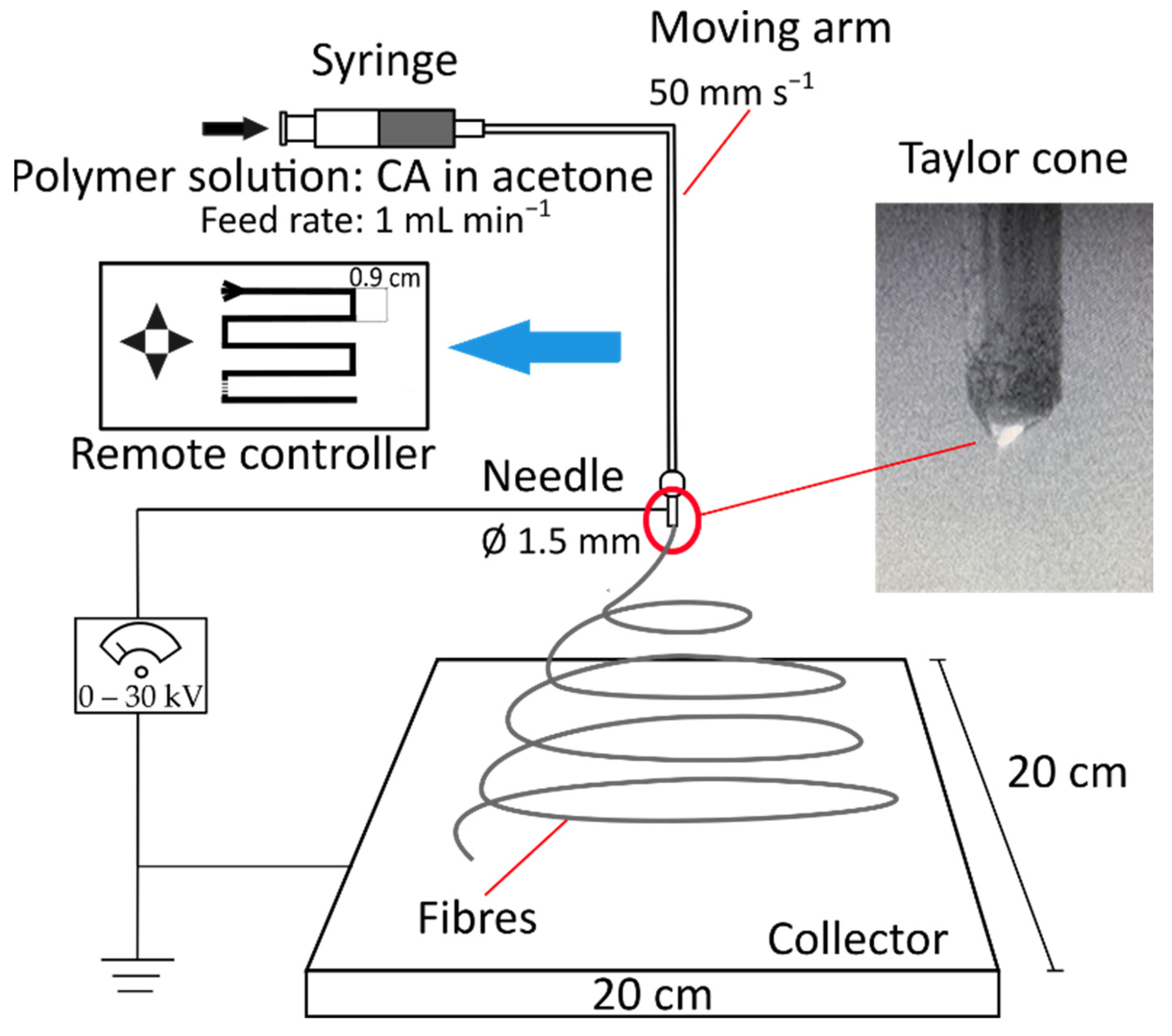
2.2. Fabrication of Electrospun Fibre Filters
2.2.1. Preparation of CA Solution
2.2.2. Preparation of TiO2 and AC Dispersions
2.2.3. Electrospinning Process
2.2.4. Preparation of the Doped Filters
2.3. Fibre Characterisation
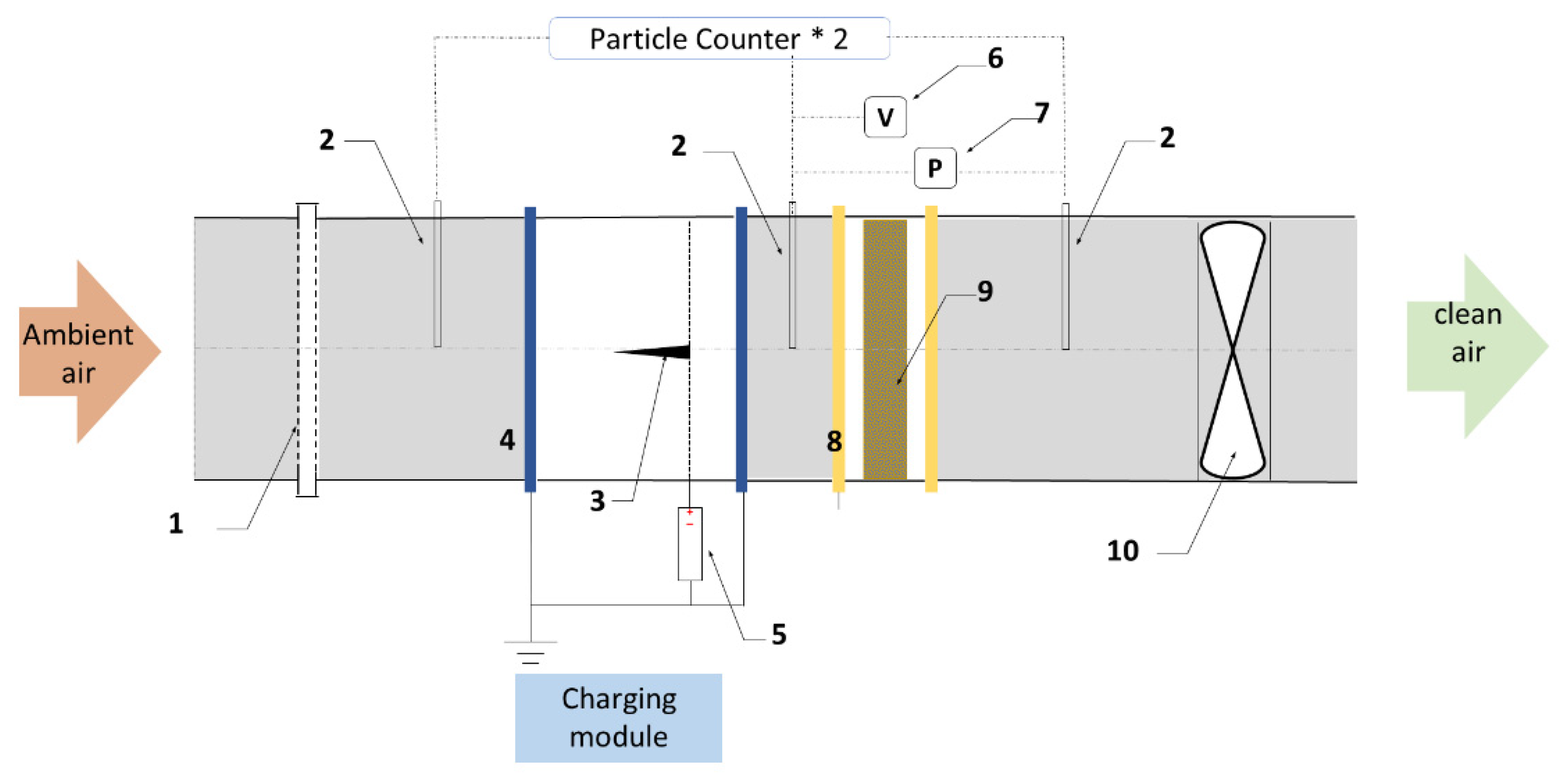
2.4. Investigation of Filtration Performance
3. Results and Discussion
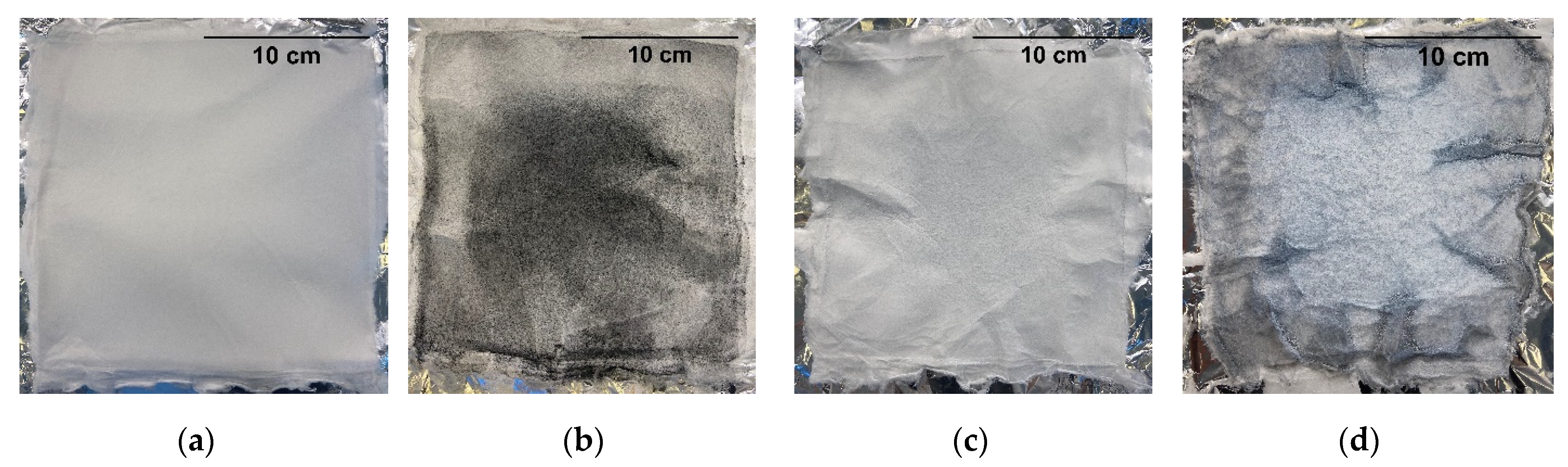
3.1. Preparation of Electrospun Fibre Filters
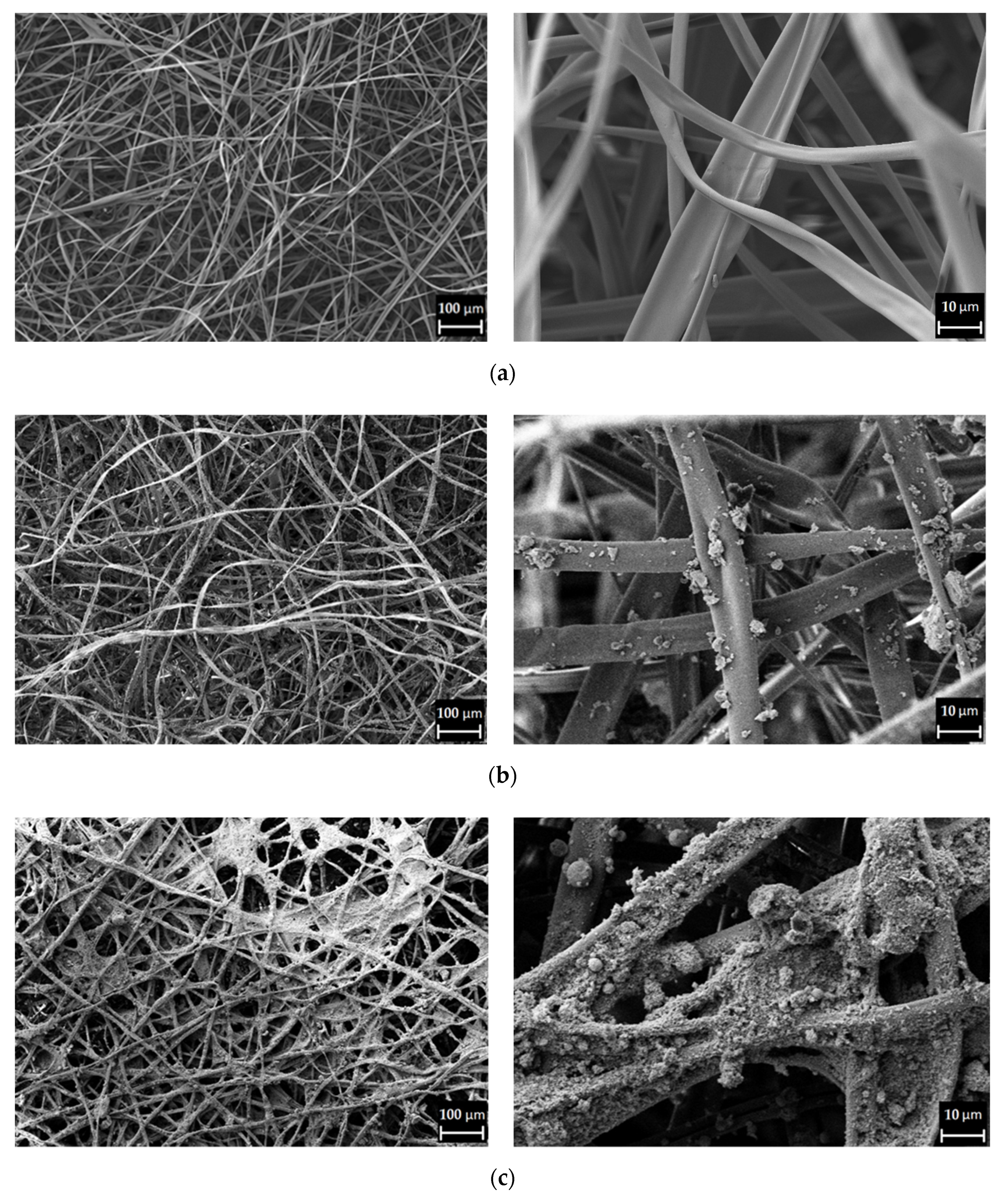
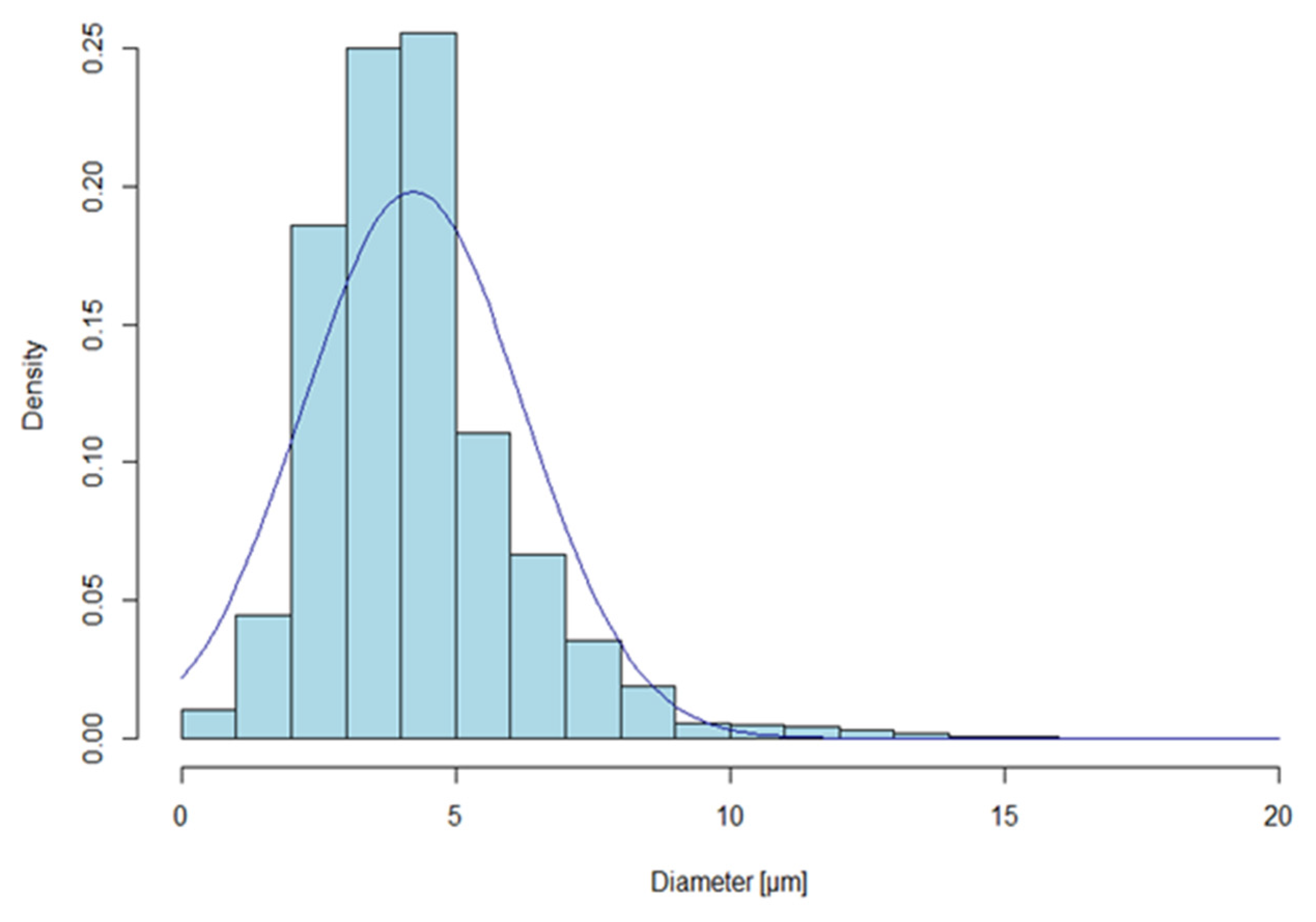
3.2. Fibre Characterisation
3.3. Filtration Performance
3.3.1. Pressure Drop
3.3.2. Particle Filtration Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mills, N.L.; Donaldson, K.; Hadoke, P.W.; Boon, N.A.; MacNee, W.; Cassee, F.R.; Sandström, T.; Blomberg, A.; Newby, D.E. Adverse cardiovascular effects of air pollution. Nat. Clin. Pr. Neurol. 2008, 6, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunekreef, B.; Holgate, S.T. Air pollution and health. Lancet 2002, 360, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A., 3rd; Dockery, D.W. Health Effects of Fine Particulate Air Pollution: Lines that Connect. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 709–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsouyanni, K.; Touloumi, G.; Samoli, E.; Gryparis, A.; Le Tertre, A.; Monopolis, Y.; Rossi, G.; Zmirou, D.; Ballester, F.; Boumghar, A.; et al. Confounding and Effect Modification in the Short-Term Effects of Ambient Particles on Total Mortality: Results from 29 European Cities within the APHEA2 Project. Epidemiology 2001, 12, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines. Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, T.; Chen, C. Differentiating between indoor exposure to PM2.5 of indoor and outdoor origin using time-resolved monitoring data. Build. Environ. 2019, 147, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, B. Review of relationship between indoor and outdoor particles: I/O ratio, infiltration factor and penetration factor. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazli, T.; Zeng, Y.; Stephens, B. Fine and ultrafine particle removal efficiency of new residential HVAC filters. Indoor Air 2019, 29, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brincat, J.-P.; Sardella, D.; Muscat, A.; Decelis, S.; Grima, J.; Valdramidis, V.; Gatt, R. A review of the state-of-the-art in air filtration technologies as may be applied to cold storage warehouses. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, B.; Siegel, J.A. Ultrafine particle removal by residential heating, ventilating, and air-conditioning filters. Indoor Air 2013, 23, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASME. Addenda to ASME AG-1–2003 Code on Nuclear Air and Gas Treatment; ASME: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bourrous, S.; Bouilloux, L.; Ouf, F.-X.; Lemaitre, P.; Nerisson, P.; Thomas, D.; Appert-Collin, J.-C. Measurement and modeling of pressure drop of HEPA filters clogged with ultrafine particles. Powder Technol. 2016, 289, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardkapan, S.R.; Johnson, M.S.; Yazdi, S.; Afshari, A.; Bergsøe, N.C. Filtration efficiency of an electrostatic fibrous filter: Studying filtration dependency on ultrafine particle exposure and composition. J. Aerosol Sci. 2014, 72, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COAG. Guide to Best Practice Maintenance & Operation of HVAC Systems for Energy Efficiency; COAG: Canberra, ACT, Australia, 2012.
- Stephens, B.; Siegel, J.A.; Novoselac, A. Energy implications of filtration in residential and light-commercial buildings. Ashrae Trans. 2010, 116, 346–357. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning of Nanofibers: Reinventing the Wheel? Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1151–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Slip-Effect Functional Air Filter for Efficient Purification of PM2.5. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shou, D.; Ye, L.; Fan, J. Gas transport properties of electrospun polymer nanofibers. Polymer 2014, 55, 3149–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Electrospun nanofibers for high-performance air filtration. Compos. Commun. 2019, 15, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Han, J.; Wang, F.; Shao, W.; Xiong, R.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, H.; Yang, Y.; Samal, S.K.; Zhang, F.; et al. Electrospun Nanofibers Membranes for Effective Air Filtration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Wang, R.; Ting, S.H.; Chen, C.; Zhang, L. Electrospun SF/PVA Nanofiber Filters for Highly Efficient PM2.5 Capture. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2018, 17, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Bian, Y.; Xia, T.; Zhang, L.; Chen, C. An optimization approach for fabricating electrospun nanofiber air filters with minimized pressure drop for indoor PM2.5 control. Build. Environ. 2021, 188, 107449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, F.; Abdulhamid, M.A.; Hardian, R.; Holtzl, T.; Szekely, G. Nanofibrous membranes comprising intrinsically microporous polyimides with embedded metal–organic frameworks for capturing volatile organic compounds. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 424, 127347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Jang, J.; Oh, H.; Jung, B.J.; Lee, Y.; Park, H.; Yang, K.H.; Seong, Y.C.; Lee, J.-S. Antibacterial Polymeric Nanofibers from Zwitterionic Terpolymers by Electrospinning for Air Filtration. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 2375–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Bian, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, C. Relationship between pressure drop and face velocity for electrospun nanofiber filters. Energy Build. 2018, 158, 987–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Wang, N.; Yang, J.; Si, Y.; Chen, K.; Ding, B.; Sun, G.; El-Newehy, M.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Yu, J. Hierarchically structured polysulfone/titania fibrous membranes with enhanced air filtration performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 417, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, M.-J.; Liao, F.; Ke, Q.-F.; Guo, Y.-P. Synergetic effect of titanium dioxide ultralong nanofibers and activated carbon fibers on adsorption and photodegradation of toluene. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 962–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, C.; Lee, S.-C. Indoor air purification by photocatalyst TiO2 immobilized on an activated carbon filter installed in an air cleaner. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.-H.; Hong, G.-B.; Chang, C.-T. Study on particulates and volatile organic compounds removal with TiO2 nonwoven filter prepared by electrospinning. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2014, 64, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Ekberg, L. Ionizer Assisted Air Filtration for Collection of Submicron and Ultrafine Particles—Evaluation of Long-Term Performance and Influencing Factors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6891–6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Yoon, K.Y.; Hwang, J. Removal of submicron particles using a carbon fiber ionizer-assisted medium air filter in a heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning (HVAC) system. Build. Environ. 2011, 46, 1699–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agranovski, I.E.; Huang, R.; Pyankov, O.V.; Altman, I.S.; Grinshpun, S.A. Enhancement of the Performance of Low-Efficiency HVAC Filters Due to Continuous Unipolar Ion Emission. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, E.; Mo, J. Toward energy saving and high efficiency through an optimized use of a PET coarse filter: The development of a new electrostatically assisted air filter. Energy Build. 2019, 186, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, E.; Yu, Q.; Gao, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Zhu, M.; Mo, J.; Xu, G.; et al. Ultralow Resistance Two-Stage Electrostatically Assisted Air Filtration by Polydopamine Coated PET Coarse Filter. Small 2021, 17, 2102051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Gao, Y.; Tian, E.; Afshari, A.; Mo, J. Fast fabricating cross-linked nanofibers into flameproof metal foam by air-drawn electrospinning for electrostatically assisted particle removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 274, 119076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Tian, E.; Mo, J. Electrically Responsive Coarse Filters Endowed by High-Dielectric-Constant Surface Coatings toward Efficient Removal of Ultrafine Particles and Ozone. ACS ES&T Eng. 2021, 1, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entcheva, E.; Bien, H.; Yin, L.; Chung, C.Y.; Farrell, M.; Kostov, Y. Functional cardiac cell constructs on cellulose-based scaffolding. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5753–5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.; Kim, J.; Kim, J. Photocatalytic activity and filtration performance of hybrid TiO2-cellulose acetate nanofibers for air filter applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoforou, T.; Doumanidis, C. Biodegradable cellulose acetate nanofiber fabrication via electrospinning. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 6226–6233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Yang, G.; Cheng, C.; Huang, C.; Xu, H.; Ke, Q. Hierarchically structured TiO2/PAN nanofibrous membranes for high-efficiency air filtration and toluene degradation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 507, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.-H.; Wang, S.-Y. Electrospun nanofibers from crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) and its filtration efficiency. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibo, Y.; Qing, Z.; Yahong, Z.; Yin, Y.; Yumin, Y. The electrospun polyamide 6 nanofiber membranes used as high efficiency filter materials: Filtration potential, thermal treatment, and their continuous production. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, C.; Hsu, P.-C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, N.; Zhang, J.; Lee, H.R.; Lu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Chu, S.; et al. Nanofiber Air Filters with High-Temperature Stability for Efficient PM2.5 Removal from the Pollution Sources. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 3642–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Hua, D.; Pan, H.; Wang, F.; Manshian, B.; Soenen, S.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Green electrospun and crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol)/poly(acrylic acid) composite membranes for antibacterial effective air filtration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 511, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Tang, N.; Cao, L.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Highly Integrated Polysulfone/Polyacrylonitrile/Polyamide-6 Air Filter for Multilevel Physical Sieving Airborne Particles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 29062–29072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.T.; Ahn, Y.C.; Lee, J.K. Characteristics of Nylon 6 nanofilter for removing ultra fine particles. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2008, 25, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Si, Y.; Wang, N.; Sun, G.; El-Newehy, M.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Ding, B. Multilevel structured polyacrylonitrile/silica nanofibrous membranes for high-performance air filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 126, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Solution Parameters | Process Parameters | Environmental Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA Concentration | Solvent | Tip-to-Collector Distance | Voltage | Feed Rate | Needle Inner Ø | Temperature | Relative Humidity |
| 12.5 w/v% | Acetone | 9 cm | 14.8 kV | 1 mL min−1 | 1.5 mm | 21 °C ± 0.5 °C | 37% ± 3% |
| CA | CA/AC | CA/TiO2 | Composite | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface porosity (%) | 42.0 ± 5.4 | 38.5 ± 2.6 | 32.5 ± 5.1 | 34.4 ± 4.5 |
| Thickness (mm) | 0.11 ± 0.016 | 0.14 ± 0.012 | 0.15 ± 0.005 | 0.18 ± 0.007 |
| Filter | 0.035 m s−1 | 0.053 m s−1 | 0.069 m s−1 | 0.087 m s−1 | 0.8 m s−1 | 1 m s−1 | QF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA | 3 Pa | 3.5 Pa | 4.7 Pa | 6.6 Pa | 63.0 Pa | 74.1 Pa | 73.3% ± 3.1% | 0.020 Pa−1 |
| CA/AC | 3.2 Pa | 3.7 Pa | 4.9 Pa | 6.8 Pa | 63.3 Pa | 74.7 Pa | 80% ± 3.2% | 0.023 Pa−1 |
| CA/TiO2 | 3.2 Pa | 3.7 Pa | 4.9 Pa | 7.0 Pa | 63.4 Pa | 74.8 Pa | 76.8% ± 3.1% | 0.022 Pa−1 |
| Composite | 3.3 Pa | 3.8 Pa | 5.1 Pa | 7.0 Pa | 63.8 Pa | 75.3 Pa | 85.3% ± 5.9% | 0.027 Pa−1 |
| Case | Particle Filtration Efficiency (0.3–0.5 μm) (%) | Pressure Drop (Pa) | QF (Pa−1) | Material | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 99.98 | 243 | 0.0351 | Polyimide nanofibres | [43] |
| 2 | 98 | 1997 | 0.0019 | Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Poly(acrylic acid) + silica and silver nanoparticles | [44] |
| 3 | 99.992 | 1781 | 0.0053 | Polysulfone/Polyacrylonitrile/Polyamide 6 | [45] |
| 4 | 99.997 | 725 | 0.0143 | Polysulfone/TiO2 fibrous membrane | [26] |
| 5 | 99.99 | 4315 | 0.0021 | Nylon 6 nanofibre | [46] |
| 6 | 99.989 | 659 | 0.0138 | Polyacrylonitrile/silica nanoparticles | [47] |
| 7 | 82.3 | 63.8 | 0.0271 | Composite filter CA/AC/CA/TiO2 | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orlando, R.; Gao, Y.; Fojan, P.; Mo, J.; Afshari, A. Filtration Performance of Ultrathin Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Filters Doped with TiO2 and Activated Charcoal. Buildings 2021, 11, 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings11110557
Orlando R, Gao Y, Fojan P, Mo J, Afshari A. Filtration Performance of Ultrathin Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Filters Doped with TiO2 and Activated Charcoal. Buildings. 2021; 11(11):557. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings11110557
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrlando, Roberta, Yilun Gao, Peter Fojan, Jinhan Mo, and Alireza Afshari. 2021. "Filtration Performance of Ultrathin Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Filters Doped with TiO2 and Activated Charcoal" Buildings 11, no. 11: 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings11110557
APA StyleOrlando, R., Gao, Y., Fojan, P., Mo, J., & Afshari, A. (2021). Filtration Performance of Ultrathin Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Filters Doped with TiO2 and Activated Charcoal. Buildings, 11(11), 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings11110557








