Abstract
The influence of isothermal aging at 620 °C in combination with subsequent electrochemical hydrogen charging at room-temperature was studied on quenched-and-tempered T92/TP316H martensitic/austenitic weldments in terms of their room-temperature tensile properties and fracture behavior. Hydrogen charging of the weldments did not significantly affect their strength properties; however, it resulted in considerable deterioration of their plastic properties along with significant impact on their fracture characteristics and failure localization. The hydrogen embrittlement plays a dominant role in degradation of the plastic properties of the weldments already in their initial material state, i.e., before thermal aging. After thermal aging and subsequent hydrogen charging, mutual superposition of thermal and hydrogen embrittlement phenomena had led to clearly observable effects on the welds deformation and fracture processes. The measure of hydrogen embrittlement was clearly lowered for thermally aged material state, since the contribution of thermal embrittlement to overall degradation of the weldments has dominated. The majority of failures of the weldments after hydrogen charging occurred in the vicinity of T92 BM/Ni weld metal (WM) fusion zone; mostly along the Type-II boundary in Ni-based weld metal. Thus, regardless of aging exposure, the most critical failure regions of the investigated weldments after hydrogen charging and tensile straining at room temperature are the T92 BM/Ni WM fusion boundary and Type-II boundary acting like preferential microstructural sites for hydrogen embrittling effects accumulation.
1. Introduction
In several last decades, demands for higher efficiency and lower environmental pollution in electricity generation, have led to the development of so-called “ultra-supercritical” (USC) power plant boiler technology using as a working medium supercritically heated and pressurized steam with temperature of 620 °C and pressure of 25 MPa and above [1,2,3]. Specific constructional components with variable properties and design conditions often require the applications of dissimilar metals joints [4,5,6]. In the maximally thermally-loaded steam circuits of the USC boiler equipment, dissimilar weldments between tempered martensitic and austenitic heat resistant steels are being frequently employed, e.g., within superheater and reheater sections. Such dissimilar weldments are commonly produced by gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) using Ni-based weld metal (Ni WM), therefore, often referred to as Ni-based transition weldments [7,8]. A relatively great heat input of fusion welding technologies (including GTAW) leads to a formation of significant heat-affected zone (HAZ) within the regions of welded base materials located close to the weld fusion zone. In general, the HAZ region with its strongly heterogeneous microstructure, so-called “HAZ microstructural gradient”, is considered to be the critical region of welded joints because of its high propensity for several types of cracking and final failure occurrence [9,10]. The findings of our several former studies about dissimilar T92/TP316H weldments [11,12,13,14] have clearly indicated that the HAZ microstructural heterogeneity can be efficiently suppressed by the application of unconventional “quenching-and-tempering” post-welding heat treatment (QT PWHT). In contrast to microstructural characteristics obtained after conventional “tempering” PWHT (T PWHT), the microstructures of welded base materials after performing QT PWHT became coarser and homogenized with respect to the grain size and state of secondary phase precipitation. Moreover, the application of QT PWHT has led to considerable improvements of the welds’ toughness [13] and creep life performance [11].
Apart from thermal and mechanical loading, inner parts of power plant boiler tubing and/or piping may operate in hydrogen containing environments since the used working medium can be a source of free atomic hydrogen. It is well-known that mechanical properties of metallic materials can be significantly affected by absorbed hydrogen in their microstructures containing several specific microstructural constituents such as free dislocations, grain/subgrain boundaries, precipitates and inclusions which may act like either reversible or irreversible hydrogen traps [15,16,17,18]. By rule, free dislocations and grain/subgrain boundaries act like reversible hydrogen traps enhancing the effect of hydrogen embrittlement (HE). In contrast, the role of secondary phase precipitates can be varied. It has been reported [17] that very fine precipitate particles with their sizes in nanometer range can act like irreversible hydrogen traps and thus HE suppressors. On the contrary, pronounced coarsening of secondary precipitate particles may significantly contribute to HE enhancement due to highly increased local hydrogen concentration at precipitate/matrix interfaces, particularly if the coarse precipitates are located on grain boundaries [15]. The HE phenomenon of high-strength alloys including structural and creep-resistant steels and their weldments may also be an issue in power plant boiler equipment during its regular or accidental shut-down and cooling below 150 °C [19]. Thus hydrogen dissolved in microstructure may lead to hydrogen-induced cracking (HIC) or hydrogen-assisted cracking (HAC) in tensile stress conditions. In consideration of hydrogen interaction with microstructure, several HE mechanisms, e.g., hydrogen enhanced localized plasticity (HELP), hydrogen enhanced decohesion (HEDE), adsorption-induced dislocation emission (AIDE), and hydrogen enhanced strain induced vacancy formation (HESIV), have been suggested in literature [20,21,22,23,24]. However, the mentioned mechanisms describe specific cases of HE phenomena and cannot be considered universally. Therefore, each failure caused by hydrogen has to be studied individually, taking into account specific material characteristics, loading and environmental conditions.
In our previous studies [25,26,27,28], the effects of electrochemical hydrogen charging on the notch tensile properties and fracture characteristics of individual HAZ regions were investigated for several types of conventionally post-weld heat treated dissimilar weldments between different grades of creep-resistant steels. It has been revealed that higher density of fine carbide precipitates in T92 steel microstructure resulted in its higher resistance against HE, compared to T24 steel microstructure containing lower density of coarser precipitates [27,28]. The manifestation of combined effects of thermal exposure and hydrogen charging on tensile properties and fracture behavior of T91/TP316H weldment was more complex than in the case of the effect of pure thermal ageing [26]. The influence of hydrogen charging on the plasticity of thermally exposed weld regions has varied in dependence of their individual microstructural characteristics and thermal exposure duration. Although the HE effects were clearly manifested by gradual decrease of plastic properties, their differences between the hydrogen-free and hydrogen-charged material states were gradually decreasing with increasing thermal exposure [26,28]. This observation indicated that the influence of hydrogen charging on the plasticity was decreasing with increasing duration of thermal exposure and the dominance of thermal embrittlement was increasing. In addition, it has been concluded that the observed fracture characteristics of individual HAZ regions of T91/TP316H weldment after hydrogen charging corresponded well with their local microstructures and notch tensile properties [26].
Our most recently published study [14] was dealing with isothermal ageing effects on room-temperature tensile properties and fracture behavior of “quenched-and-tempered” T92/TP316H dissimilar weldments with Ni-based weld metal (Ni WM). It has been revealed that the used thermal exposure at 620 °C for up to 2500 h resulted in gradual microstructural changes of individual weld regions. Consequently, thermally-induced microstructure degradation by precipitate coarsening has led to recognizable decrease of the weld plastic properties (total elongation “EL” and reduction of area at fracture “RA”), whereas its effect on the weld strength properties (yield stress “YS” and ultimate tensile strength “UTS”) was only small. Due to differing microstructural degradation of individual weld regions by applied thermal exposure, several variations in the welds failure locations were observed depending on the welds ageing duration. From the observations of necking-related strain-hardening peaks within cross-weld hardness profiles of fractured tensile specimens, it has been clearly indicated that the regions of TP316H austenitic steel base material (TP316H BM) and Ni WM exhibited mutually competitive tensile straining behavior. The role of locally evolved microstructural inhomogeneities was found to be crucial for affecting plastic deformation and fracture localization.
Our current work represents a direct research continuation of the above described investigation [14]. It is focused on electrochemical hydrogen charging effects on room-temperature mechanical properties of T92/TP316H dissimilar weldments without artificial stress concentrators in “quenched-and-tempered” and thermally-aged conditions. The homogenization effect of unconventional QT PWHT on the weldments hydrogen embrittlement resistance is examined. The observed hydrogen-induced changes in mechanical properties and fracture behavior of the investigated weldments are characterized and discussed.
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
In the present study the same type of T92/TP316H dissimilar weldment was investigated as was also studied in our preceding work [14] about the ageing effects on its room-temperature tensile properties and fracture behavior. The tubes (outer diameter 38 mm, wall thickness 5.6 mm) of T92 tempered martensitic and TP316H austenitic heat-resistant steels were circumferentially welded in the company SES a.s. Tlmače, Slovakia by gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) technique using “Inconel-type” filler metal Thermanit Nicro 82. The details concerning the weld preparation can be found in [14]. Chemical composition of individual base materials and Ni-based filler metal (Thermanit Nicro 82) is shown in Table 1. The produced weldments were subjected to unconventional QT PWHT (see Figure 1).

Table 1.
Chemical composition (wt%) of base materials and Ni-based weld metal (Ni WM) of T92/TP316H dissimilar weldment.
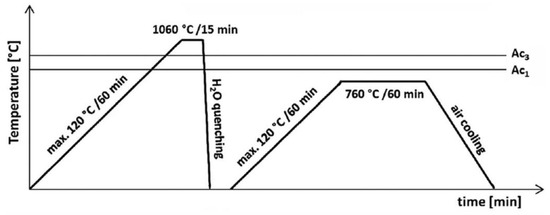
Figure 1.
Scheme of unconventional “quenching-and-tempering” post-welding heat treatment (QT PWHT).
In the present investigation, two heat-treated material states of the weldment were considered, namely the initial “QT PWHT” state and thermally-aged “QT PWHT + 620 °C/2500 h” state. Both these material states were separately investigated in hydrogen-free and hydrogen-charged conditions. Electrochemical (cathodic) hydrogen charging of prepared cylindrical cross-weld (c-w) tensile specimens (M6 head, 4 mm in body diameter, 40 mm gauge length) was realized during 24 h, at ambient temperature in electrolytic solution of 1 M HCl with 0.1 N N2H6SO4 at a current density of 300 A·m−2. At once, three tensile specimens were hydrogen charged (see Figure 2), prior to tensile testing at room temperature.
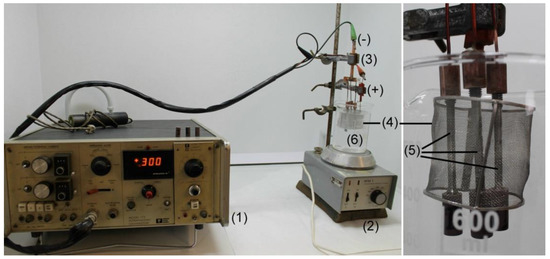
Figure 2.
Experimental apparatus for electrochemical hydrogen charging: (1) potentiostat, (2) solute mixer, (3) samples holder, (4) platinum mesh electrode, (5) tensile samples, (6) electrolytic solution.
The used experimental procedure has been optimized during our previous experience [25] which indicated full saturation of tensile specimens by hydrogen after 24 h of cathodic hydrogen charging. In the study of Nguyen et al. [29] it was observed that hydrogen concentration in 316L stainless steel reached its maximum after 24 h of cathodic charging. Experimental material in our study consists of joints of the two systems, T92 with bcc structure and the second one with fcc structure (Ni WM and TP316H). Because of the higher activation energy of diffusion in fcc structures, the diffusivity of hydrogen in fcc iron is lower than that in bcc iron [30]. Therefore, the selected time of electrochemical hydrogen charging in this study is quite reasonable.
Immediately after the hydrogen charging, room-temperature tensile tests of hydrogen charged tensile specimens (i.e., in “QT PWHT + H” and “QT PWHT + 620 °C/2500 h + H” material states) were performed by using TIRATEST 2300 universal testing machine (TIRA GmbH, Schalkau, Germany) at a cross-head speed of 0.05 mm/min. Three tensile test specimens were investigated for both hydrogen charged material states. Similarly, for both hydrogen-free material states (i.e., “QT PWHT” and “QT PWHT + 620 °C/2500 h”), also three tensile specimens were investigated. The evaluation of c-w tensile properties (i.e., yield stress “YS” estimated as 0.2% proof stress, ultimate tensile strength “UTS”, total elongation “EL”, and reduction of area at fracture “RA”) included the calculation of their standard deviations. In order to indicate local strain hardening effects in dissimilar weldments during the tensile tests, c-w hardness measurements using Vickers 432 SVD hardness tester (Wolpert Wilson Instruments, division of INSTRON DEUTSCHLAND GmbH, Aachen, Germany) were performed on plain surfaces of longitudinal sections of fractured tensile specimens after the tensile tests. The conditions of Vickers hardness measurements were: load 98 N, dwell time 10 s per measurement.
Microstructural and fractographic analyses of the investigated weldments were carried out using light optical microscope OLYMPUS GX71 (OLYMPUS Europa Holding GmbH, Hamburg, Germany), scanning electron microscope JEOL JSM-7000F (Jeol Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) with an energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) analyzer INCA X-sight model 7557 (Oxford Instruments, Abingdon, Oxfordshire, UK) and environmental scanning electron microscope EVO MA15 (Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH, Jena, Germany) with an EDX analyzer X-Max 50 model 51-XMX1003 (Oxford Instruments, Abingdon, Oxfordshire, UK).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure
The individual microstructural regions of investigated T92/TP316H dissimilar weldment, namely T92 tempered martensitic steel base material (T92 BM), Ni-based weld metal (Ni WM) Thermanit Nicro 82, and TP316H austenitic steel base material (TP316H BM) are documented in Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6.
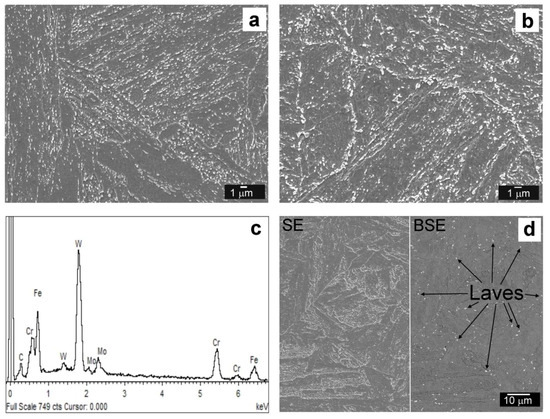
Figure 3.
Microstructural characterization of the T92 base material (BM) region in different material states: QT PWHT (a); QT PWHT + 620 °C/2500 h (b) with typical EDX spectrum of Fe2(W,Mo) based Laves phase precipitates (c) and distribution of coarse Laves phase particles visualized in secondary electrons (SE) mode and back-scattered electrons (BSE) mode (d).
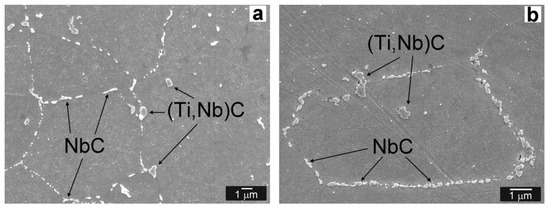
Figure 4.
Microstructure of the Ni weld metal (WM) (Thermanit Nicro 82) region, states: QT PWHT (a); QT PWHT + 620 °C/2500 h (b).
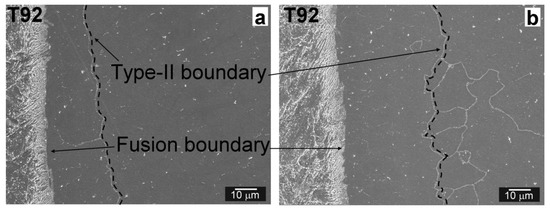
Figure 5.
Microstructure of the Ni WM near T92 BM/Ni WM interface: Type-II boundary in initial QT PWHT material state (a); and migrating Type-II boundary observed after 620 °C/2500 h of thermal aging (b).
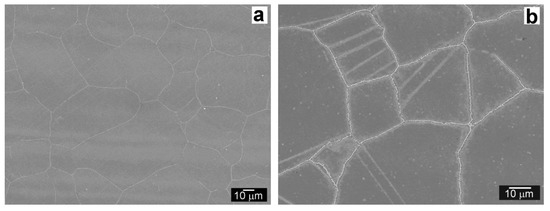
Figure 6.
Microstructure of TP316H BM region, states: QT PWHT (a); QT PWHT + 620 °C/2500 h (b).
The microstructure of the T92 BM region in QT PWHT state (Figure 3a) consists of tempered martensitic laths inside the blocks and packets structures within prior austenitic grains. In thermally-aged T92 BM microstructure (Figure 3b) typical features of microstructure recovery have been indicated such as lath widening and/or formation of new subgrains. As it was discussed in our previous paper [14], the phase composition of the T92 BM region in its initial condition consists of ferrite matrix and secondary phase precipitates M23C6 (M = Cr, Fe,…) and MX (M = V, Nb, X = C, N) carbo-nitrides. As indicated by EDX analysis (Figure 3c), thermal aging led to additional precipitation of Fe2(W,Mo) Laves phase and its rapid coarsening (Figure 3d). The results of microstructure and phase analyses are in agreement with the results of other studies about Grade 92 tempered martensitic steels published previously [31,32,33,34,35,36].
The Ni WM region in QT PWHT state (Figure 4a) consists of “nickel–austenite” matrix with primary (Ti,Nb)(C,N) and (Ti,Nb,B)(C,N) precipitate particles [14] and secondary precipitates of mostly NbC type [14]. In Ni WM region located close to the T92 BM/Ni WM interface, grain-boundary carbides of Cr23C6 type have also been detected [14]. The primary precipitates were distributed randomly within Ni WM microstructure, i.e., they were located on grain boundaries as well as in grain interiors. Regardless of slight precipitate coarsening and thermally-activated grain boundaries migration, the microstructure of thermally-aged Ni WM (Figure 4b) preserved its original heterogeneous features as observed in its initial QT PWHT state. Near the T92/Ni WM interface parallel to the fusion boundary, a so-called “Type-II boundary” was observed in initial Ni WM microstructure (Figure 5a). The Type-II boundary is a specific microstructural object typically observed in Ni WM interfacial microstructure of Ni-based transition weldments [37,38,39]. The Type-II boundary formation in such dissimilar welded joints is known to be related to the phase transition of δ-bcc crystal structure of the base metal to γ-fcc phase during welding. As it was shown by Nelson et al. [40] and Lippold et al. [41], during allotropic δ-to-γ-transformation in austenite temperature range, a δ/γ boundary becomes a γ/γ boundary and it migrates into the weld metal as a result of temperature and compositional gradient. During thermal aging, the Type-II boundary can migrate further away from the fusion boundary [42]. This behavior was observed also in the present work (Figure 5b).
The TP316H BM region in QT PWHT state (Figure 6a) is formed of polygonal recrystallized austenitic grains with secondary phase precipitates of M23C6 carbide on grain boundaries [14]. The same phase composition was also observed in other studies on similar types of AISI 316 grade austenitic steels [43,44]. An obvious consequence of thermal exposure of austenitic TP316H BM is related to a formation of annealing twin boundaries after performed ageing (Figure 6b).
3.2. Mechanical Properties
Figure 7 and Figure 8 show the effects of isothermal aging at 620 °C and subsequent electrochemical hydrogen charging at room-temperature on tensile properties of the investigated weld joints. Figure 7 shows a variation of strength properties (YS and UTS), whereas Figure 8 shows a variation of plastic properties (EL, RA). The results presented in Figure 7 show that applied thermal exposure of studied weldments resulted in negligible changes of their strength properties (YS and UTS). Such a behavior is commonly observed for 9-12Cr heat resistant steels, austenitic steels, and their weld joints [13,26,28,31,39,45]. After the application of hydrogen charging, the values of YS and UTS were only slightly affected. The individual values varied within the range of their standard deviations. Rosenberg and Sinaiová [46] reported that influence of hydrogen on mechanical properties depends on the used mechanical testing conditions. However, they showed that for aged smooth specimens of high strength steels, hydrogenation practically did not affect the values of YS and UTS which qualitatively agrees with the results of present investigation.
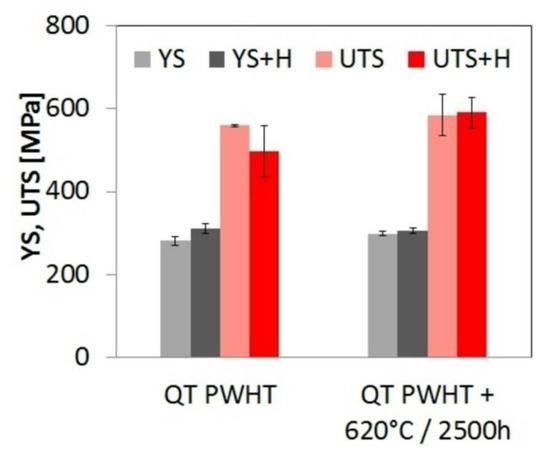
Figure 7.
Effects of isothermal aging at 620 °C and electrochemical hydrogen charging on the room-temperature strength properties of T92/TP316H dissimilar weldments (YS—yield stress, UTS—ultimate tensile strength).
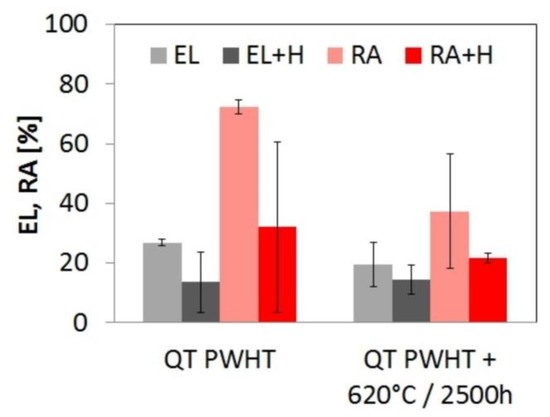
Figure 8.
Effects of isothermal aging at 620 °C and electrochemical hydrogen charging on the room-temperature plastic properties of T92/TP316H dissimilar weldments (EL—total elongation, RA—reduction of area at fracture).
On the other hand, Figure 8 shows that the studied weldments exhibit clearly observable degradation of the plastic properties (EL and RA) after thermal aging. In accordance with the results of our previous studies [13,14,28,45], the observed plasticity deterioration can be related to thermal embrittlement effects, such as coarsening of secondary phase precipitates, namely M23C6 carbides and additional precipitation and coarsening of intermetallic Fe2(W,Mo) Laves phase during thermal aging.
Figure 8 also indicates that hydrogen charging of the weldments resulted in further deterioration of the plastic properties. The mean values of EL and RA in hydrogenated material states drop almost to their half in comparison with the values obtained without hydrogen charging as a consequence of the hydrogen embrittlement [47]. The large scatter of plastic properties in Figure 8 is related to the weldments microstructural heterogeneity affecting the localization of plastic deformation and final failure occurrence, which will be discussed later. The corresponding engineering stress–strain curves are shown in Figure 9. It can be seen that the effects of both thermal exposure and hydrogen charging do strongly influence not only the course of individual stress–strain curves but also the final weld failure location. Moreover, it is clearly visible that deformation behavior of the welded joints in both QT PWHT and thermally aged (QT PWHT + 620 °C/2500 h) conditions is significantly deteriorated after hydrogen charging.
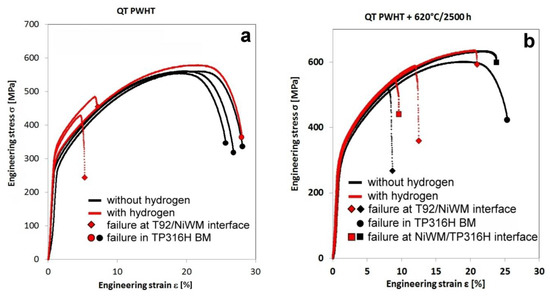
Figure 9.
Effects of isothermal aging at 620 °C and electrochemical hydrogen charging on the room-temperature tensile deformation behavior of T92/TP316H dissimilar weldments, states: QT PWHT (a); QT PWHT + 620 °C/2500 h (b).
The overview of room-temperature tensile properties and failure locations which occurred after tensile tests for individual material states is summarized in Table 2. Figure 10 represents the results of cross-weld hardness measurements after the tensile tests.

Table 2.
Room-temperature tensile properties and failure locations of T92/T316H dissimilar weldments with Ni-base weld metal for individual material states.
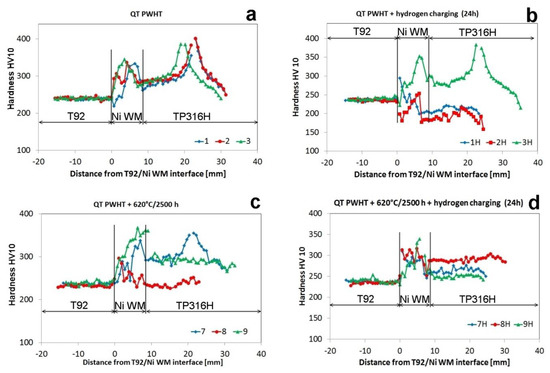
Figure 10.
Effects of isothermal aging at 620 °C and electrochemical hydrogen charging at room temperature on the cross-weld hardness profiles determined after room-temperature tensile tests of T92/TP316H dissimilar weldments, states: QT PWHT (a); QT PWHT + H (b); QT PWHT + 620 °C/2500 h (c); QT PWHT + 620 °C/2500 h + H (d).
The depicted interruptions in the graphs represent final failure locations, which according to our previous study [14], were found to be related to enhanced local microstructural degradation in specific weld regions by the applied thermal exposure. In the case of thermal ageing effects, it has been clearly indicated that the regions of TP316H BM and Ni WM exhibited mutually competitive tensile straining behavior. However, in the case of hydrogen effect on deformation and fracture behavior, the situation is even more complicated due to different hydrogen trapping capacity of specific microstructural constituents in individual microstructural regions. In hydrogen charged material states, it is reasonable to expect the occurrence of hydrogen-assisted failures in microstructural regions with increased local hydrogen concentration. In the present study, the most of hydrogen charged tensile specimens were fractured after the room-temperature tensile tests in the vicinity of T92/Ni WM interface. The highly brittle interfacial failures occurred in both QT PWHT and thermally aged, i.e., QT PWHT + 620 °C/2500 h material states which indicated that hydrogen embrittlement effects were not much depending on the application of thermal exposure.
It was observed by Čiripová et al. [14] that in initial QT PWHT state without tensile deformation, the T92 region exhibited notably higher hardness values, compared to both Ni WM and TP316H austenitic regions. However, after room-temperature tensile tests, both TP316H and Ni WM regions showed much higher hardness values compared to those of T92 region. The increased hardness values of both austenitic regions after tensile tests are related to their intensive strain hardening due to their higher strain hardening capacity [48], while the T92 region remained macroscopically unstrained thanks to its significantly higher yielding point. This behavior was also observed for the majority of hydrogen charged test specimens after their tensile straining as well (Figure 10). Although in two specific cases (Figure 10b), the hardness in TP316H austenitic region was lower than that in T92 region, it can confirm the previous statement about strain hardening effect which was here localized in Ni WM region. Both samples of this material state (QT PWHT + H) failed relatively quickly in a brittle manner (Figure 9a) and thus there was not enough time for strain hardening evolution. As it was mentioned above, the failure occurred in the vicinity of the T92/Ni WM boundary. This premature failure can be attributed to the consequence of increased hydrogen inherence at this boundary. It was shown in the previous section that the Type-II boundary arose near the T92/Ni WM fusion line (Figure 5). Yoo et al. [42] observed that narrow zone between the fusion line and Type-II boundary is more susceptible to material degradation than the rest weld metal. Wang et al. [49] showed that Type-II boundary in dissimilar ferrite/austenite weldment cracked first before weld metal necking under tensile strain. Similarly, also other authors [37,38,41] refer to the Type-II boundary as a potential path for crack propagation and failure. The Type-II boundary is a specific type of high angle grain boundary [39,46] and therefore it acts like a reversible hydrogen trap [50]. Since high angle boundaries have lower hydrogen binding energy than precipitates [16], hydrogen is released during tensile straining and it induces the embrittlement [51] and final failure along the Type-II boundary (Figure 11).
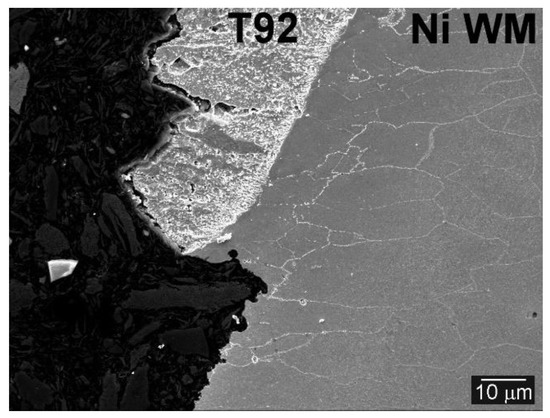
Figure 11.
Fracture path along the Type-II boundary and the T92 BM/Ni WM fusion zone, material state QT PWHT + 620 °C/2500 h + H.
The same interpretation can be applied to understanding of the brittle failure after thermal aging and hydrogen charging (Figure 10d).
To make some quantitative assessment of the thermal exposure and hydrogen influence on the failure of studied dissimilar weldment, the index of embrittlement EI can be calculated according to the following equation:
where RA0 and RAx are the values of reduction of area at fracture of two individual material states, the subscripts “0” and “x” refer to the states selected as initial and final, respectively. The values of index of embrittlement calculated according to the Equation (1) using mean RA values listed in Table 2 are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Index of embrittlement for individual material states.
From Table 3 it follows that after hydrogen charging and tensile straining, the initial state (Row 1) has higher index of embrittlement than the state after thermal ageing (Row 3). This indicates that the QT PWHT state is more sensitive to the hydrogen embrittlement than the state after thermal aging. The same can be considered after comparison of the thermally aged state (Row 2) and the state thermally aged and hydrogen charged (Row 3). The value of embrittlement index is higher in the former case than in the latter. These findings are consistent with the previous findings by Falat et al. [26,27,28]. In the initial state, the hydrogen embrittlement plays the dominant role. After thermal aging, the superposition of the both thermal and hydrogen embrittlement affects the final behavior of dissimilar weldment. Due to additional precipitation of carbides and/or their coarsening during thermal exposure, the number of irreversible hydrogen traps is increased and by this way the volume of free mobile hydrogen is decreased [17]. Because only diffusible hydrogen plays a role in the hydrogen embrittlement [52,53], the performed thermal aging has led to decreased measure of hydrogen embrittlement and the dominance of thermal embrittlement [26,27]. The details on the fracture behavior of the studied weldments will be discussed in the following section.
3.3. Fracture Behavior
As it follows from Figure 9a and Figure 10a and Table 2, all samples of the initial QT PWHT state failed during tensile straining in the austenitic TP316H region. Figure 12a represents the fracture surface of the QT PWHT state with ductile dimple areas and some tear ridges as a result of intensive local plastic deformation. After hydrogen charging (state QT PWHT + H), the failure became brittle with the transgranular cleavage character (Figure 12b) and typical signs of hydrogen embrittlement (“fish-eye”) on the fracture surface appears (Figure 12c). As it was already mentioned in previous sections, the samples fractured mostly in the fusion zone near the T92 BM/Ni WM interface (see, e.g., Figure 10b).
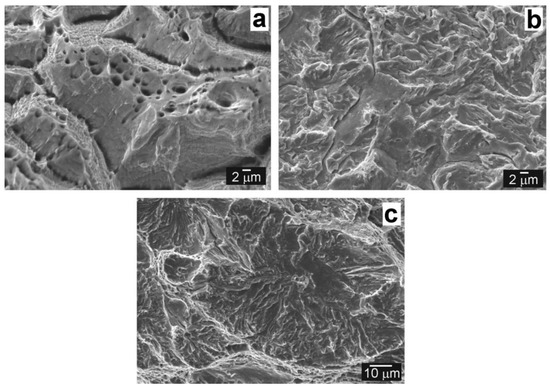
Figure 12.
Fracture surfaces of the samples failed after room-temperature tensile test of T92/TP316H dissimilar weldments: state QT PWHT with failure in T316H BM region (a); state QT PWHT + H with failure in interfacial region T92 BM/Ni WM (b); the view of the “fish-eye” fracture morphology (c).
Figure 13 documents the effect of isothermal aging at 620 °C/2500 h and electrochemical hydrogen charging on fracture characteristics of T92/TP316H dissimilar weldments after room-temperature tensile testing. Figure 13a shows the fracture surface of the state QT PWHT + 620 °C/2500 h. The failure of the aged sample can be characterized by ductile dimple tearing with the visible brittle cracked secondary phase particles at the bottom of some dimples (Figure 13a). After hydrogen charging of the aged samples, the signs of observed embrittlement include trangranular cleavage and intergranular decohesion fracture areas (Figure 13b,c). Similarly as in the case of hydrogenated samples without thermal exposure, the most of thermally aged and hydrogen charged samples fractured in the vicinity of T92 BM/Ni WM interface (see Figure 10d).
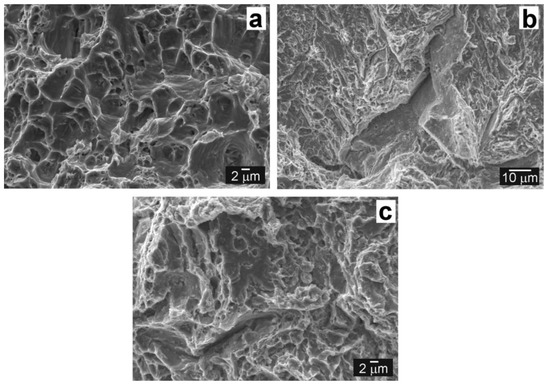
Figure 13.
Fracture surfaces of the aged samples failed after room-temperature tensile test of T92/TP316H dissimilar weldments in fusion zone T92 BM/Ni WM: state QT PWHT + 620 °C/2500 h (a); state QT PWHT + 620 °C/2500 h + H (b); and its detailed view (c).
In our previous study [14] it was observed that the effects of strain hardening and plasticity exhaustion play a significant role in the final failure occurrence and the regions of TP316H BM and Ni WM compete mutually during tensile straining. As a consequence, the position of the failure changed from TP316H BM region to T92 BM/Ni WM interface zone after aging of the weldments (Figure 10a,c). As it was also observed by Čiripová et al. [14], the failure of the samples ran partly through T92 BM and largely through precipitation depleted zone of Ni WM near the Type-II boundary. Moreover, it has been revealed that the observed fracture mechanisms were mostly related to the cracking of secondary phase particles and decohesion at precipitate/matrix interfaces during tensile straining.
In our present work, the failure of the weldments in both the QT PWHT and QT PWHT + 620 °C/2500 h material states became strongly influenced by hydrogen charging. The fracture surfaces exhibited typical signs of hydrogen embrittlement (Figure 12b and Figure 13b). The failure position of the welds in both material states was located mostly in the vicinity of T92/Ni WM interface. Although one sample of the state QT PWHT + H failed in the TP316H BM region, it may likely be a consequence of local microstructural inhomogeneities in the TP316H BM. It was shown in the previous Section 3.2 that the most of failures of hydrogenated tensile specimens ran along the Type-II boundary (Figure 11) as a consequence of the hydrogen embrittlement localization at this type of boundary in Ni WM [37,38,41]. In these cases, the fracture path ran partly also through the T92 BM (Figure 11). The sub-fracture microstructure of the T92 BM region, which failed near the T92 BM/Ni WM boundary, is presented in Figure 14.
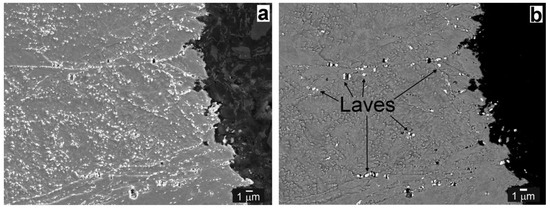
Figure 14.
Microstructure and fracture path of the T92 BM region beneath the failure in the vicinity of T92 BM/Ni WM interface, state QT PWHT + 620 °C/2500 h + H: distribution of secondary phase particles in SE mode (a) and visualization of Laves phase particles in BSE mode (b).
The fracture path indicates the presence of both transgranular cleavage and intergranular decohesion fracture mechanisms. Obviously, during tensile straining, the voids arose along the grain boundaries (Figure 14a). Moreover, the cracked secondary phase particles at the grain boundaries can be clearly visible. The preferential secondary phase precipitation and coarsening of the Laves phase particles on grain boundaries is considered the critical factor influencing premature failure of T92 steel in creep loading conditions [7]. In our study it has been confirmed that the highly coarsened secondary phase particles on grain boundaries are mostly the Fe2(W,Mo) Laves phase particles (see the bright appearing particles in Figure 14b). Similarly, in the microstructure just beneath the fracture surface of Ni WM, the cracked NbC particles and voids formation were observed (Figure 15). Thus, the major mechanism of the plastic properties degradation by hydrogen can be related to the microvoid coalescence, secondary phase particles cracking and final decohesion at matrix/particles interfaces or grain boundaries.
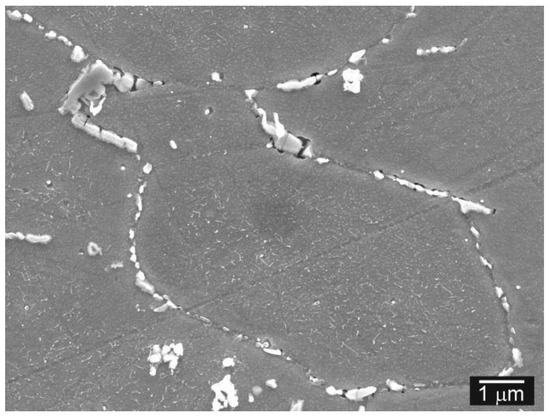
Figure 15.
SEM micrograph of Ni WM—detailed view on detached and/or cracked NbC precipitates at grain boundaries.
The complementary analyses of the results obtained from the tensile tests stress–strain data (Figure 9), cross-weld hardness measurements (Figure 10) and fractography (this section) of investigated T92/TP316H dissimilar weldments with Ni-based weld metal after hydrogen charging and tensile straining indicate the competitive behavior between individual weldment regions. Such a behavior between the austenitic TP316H BM and Ni WM regions was also observed by Čiripová et al. [14] for the same type of weldment during tensile deformation of thermally aged material states. It has been shown that the most critical zone of the weldment after thermal aging is the interfacial region T92 BM/Ni WM [14]. There are many studies on the creep behavior of martensitic/austenitic dissimilar weld joints between T92 steel and austenitic heat resistant steels (e.g., AISI 304 or 347 grades) [7,54,55,56]. It has been frequently observed that the final fracture location after creep exposure was located mainly at the T92 weld part within its fine grained heat-affected zone [7,54,55,56]. As it was observed by Falat et al. [11,12,13], the quenching-and-tempering post weld treatment (QT PWHT) of the investigated T92/TP316H dissimilar weldments led to microstructural homogenization of welded base materials. The results of our present investigation about the effect of hydrogen charging on room-temperature tensile behavior of T92/TP316H dissimilar weldment demonstrate that even the used homogenization QT PWHT regime is not efficient to suppress the as-cast microstructure heterogeneity of Ni-based weld metal. Thus, the fusion boundary at T92 BM/Ni WM interface and Type-II boundary in Ni WM still represent the most critical regions of T92/TP316H dissimilar weldment with respect to the occurrence of hydrogen-assisted failures.
4. Conclusions
Quenched-and-tempered T92/TP316H martensitic/austenitic dissimilar weldments with Ni-based weld metal (Thermanit Nicro 82) were isothermally aged at 620 °C for 2500 h and electrochemically hydrogen charged in order to investigate the effects of hydrogen charging on room-temperature tensile properties. The obtained results of the investigation can be summarized as follows:
1. Type-II boundary was observed in the microstructure of Ni-based weld metal parallel to the T92 BM/Ni WM fusion boundary at a distance of about 10–20 μm from the fusion boundary. The occurrence of Type-II boundary migration has been indicated after performed thermal exposure;
2. Electrochemical hydrogen charging of the weldments did not affect the strength properties significantly, but it resulted in considerable deterioration of the plastic properties of the weldments along with significant impact on their fracture behavior and final failure localization;
3. Electrochemical hydrogen charging of the weldments caused the interfacial failure of the weldments in the vicinity of T92 BM/Ni WM fusion boundary. A minor portion of fracture path was situated in T92 BM adjacent to the fusion boundary and the major part of the fracture passed through Type-II boundary in Ni WM;
4. It was observed that in the initial (unaged) state the hydrogen embrittlement plays a dominant role in deterioration of the weldments. Thermal aging of the weldments prior to hydrogen charging led to the superposition of thermal and hydrogen embrittlement effects during subsequent tensile deformation. The dominance of thermal embrittlement and the lowered measure of hydrogen embrittlement have been indicated;
5. The results of the present investigation about electrochemical hydrogen charging effects on room-temperature tensile behavior of the studied weldments show that with respect to the failure occurrence after combined effect of thermal exposure, hydrogen charging and tensile deformation, their most critical regions are the T92 BM/Ni WM fusion boundary and Type-II boundary.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.Š. and L.F.; Methodology, P.Š., L.F. and M.D.; Formal Analysis, P.Š., L.F., L.Č. and M.D.; Investigation, P.Š., L.F., L.Č., M.D. and M.V.; Data Curation, L.Č.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, P.Š. and L.F.; Writing—Review and Editing, P.Š. and L.F.; Visualization, L.Č.; Supervision, P.Š., L.F.; Project Administration, L.F. and P.Š.; Funding Acquisition, L.F.
Funding
This research was funded by “Vedecká Grantová Agentúra MŠVVaŠ SR a SAV” (Grant No.: VEGA 2/0062/19).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yin, Y.; Faulkner, R.; Starr, F. Austenitic steels and alloys for power plants. In Structural Alloys for Power Plants—Operational Challenges and High-Temperature Materials; Shirzadi, A., Jackson, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 105–152. [Google Scholar]
- Ennis, P.J. Ferritic and martensitic steels for power plants. In Structural Alloys for Power Plants—Operational Challenges and High-Temperature Materials; Shirzadi, A., Jackson, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 188–220. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, F. Research and development of heat-resistant materials for advanced USC power plants with steam temperatures of 700 °C and above. Engineering 2015, 1, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Han, J.M.; Lee, K.W.; Kong, B.O.; Hong, H.U. Transition of creep damage region in dissimilar welds between Inconel 740H Ni-based superalloy and P92 ferritic/martensitic steel. Mater. Charact. 2018, 139, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H. A hot cracking on dissimilar metal weld between A106Gr.B and A312 TP316L with buttering ERNiCr-3. Metals 2019, 9, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, P.; Schlacher, C.; Siefert, J.A.; Parker, J.D. Microstructural features, mechanical properties and high temperature failures of ferritic to ferritic dissimilar welds. Int. Mater. Rev. 2019, 64, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.Y.; Kwak, S.C.; Choi, I.S.; Lee, Y.K.; Suh, J.Y.; Fleury, E.; Jung, W.S.; Son, T.H. High-temperature tensile and creep deformation of cross-weld specimens of weld joint between T92 martensitic and Super304H austenitic steels. Mater. Charact. 2014, 97, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, R.; Sidhu, B.S. Microstructures and mechanical properties of dissimilar T91/347H steel weldments. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 220, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, P. Evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties of the heat-affected zone in 9Cr steels. Weld. World 2010, 54, R1–R11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Kannan, R. Transition from Type IV to Type I cracking in heat-treated grade 91 steel weldments. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 714, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falat, L.; Výrostková, A.; Svoboda, M.; Milkovič, O. The influence of PWHT regime on microstructure and creep rupture behaviour of dissimilar T92/TP316H ferritic/austenitic welded joints with Ni-based filler metal. Kov. Mater. 2011, 49, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falat, L.; Čiripová, L.; Kepič, J.; Buršík, J.; Podstranská, I. Correlation between microstructure and creep performance of martensitic/austenitic transition weldment in dependence of its post-weld heat treatment. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2014, 40, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falat, L.; Kepič, J.; Čiripová, L.; Ševc, P.; Dlouhý, I. The effects of postweld heat treatment and isothermal aging on T92 steel heat-affected zone mechanical properties of T92/TP316H dissimilar weldments. J. Mater. Res. 2016, 31, 1532–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čiripová, L.; Falat, L.; Ševc, P.; Vojtko, M.; Džupon, M. Ageing effects on room-temperature tensile properties and fracture behavior of quenched and tempered T92/TP316H dissimilar welded joints with Ni-based weld metal. Metals 2018, 8, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michler, T.; Balogh, M.P. Hydrogen environment embrittlement of an ODS RAF steel—Role of irreversible hydrogen trap sites. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 9746–9754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Nava, E.I.; Basha, B.I.Y.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J. Hydrogen transport in metals: Integration of permeation, thermal desorption and degassing. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 1433–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.Y.; Li, H.; Cheng, X.B. Carbides and possible hydrogen irreversible trapping sites in ultrahigh strength round steel. Micron 2017, 103, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Eeckhout, E.; Depover, T.; Verbeken, K. The effect of microstructural characteristics on the hydrogen permeation transient in quenched and tempered martensitic alloys. Metals 2018, 8, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manimozhi, S.; Suresh, S.; Muthupandi, V. HAZ hydrogen cracking of 9Cr-0.5 Mo-1.7W steels. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 51, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, S.P. Environmentally assisted cracking: Overview of evidence for an adsorption-induced localised-slip process. Acta Metall. 1988, 36, 2639–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, H.K.; Sofronis, P. Hydrogen-enhanced localized plasticity—a mechanism for hydrogen-related fracture. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1994, 176, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, M.; Fujinami, M.; Arai, K.; Fujii, H.; Nagumo, M. Hydrogen embrittlement of austenitic stainless steels revealed by deformation microstructures and strain-induced creation of vacancies. Acta Mater. 2014, 67, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, M.; Tasan, C.C.; Akiyama, E.; Tsuzaki, K.; Raabe, D. Hydrogen-assisted decohesion and localized plasticity in dual-phase steel. Acta Mater. 2014, 70, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toribio, J. HELP versus HEDE in progressively cold-drawn pearlitic steels: Between Donatello and Michelangelo. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2018, 94, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blach, J.; Falat, L.; Ševc, P. The influence of hydrogen charging on the notch tensile properties and fracture behaviour of dissimilar weld joints of advanced Cr–Mo–V and Cr–Ni–Mo creep-resistant steels. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2011, 18, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blach, J.; Falat, L. The influence of thermal exposure and hydrogen charging on the notch tensile properties and fracture behaviour of dissimilar T91/TP316H weldments. High Temp. Mater. Proc. 2014, 33, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falat, L.; Čiripová, L.; Homolová, V.; Futáš, P.; Ševc, P. Hydrogen pre-charging effects on the notch tensile properties and fracture behaviour of heat-affected zones of thermally aged welds between T24 and T92 creep-resistant steels. Kov. Mater. 2016, 54, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falat, L.; Čiripová, L.; Homolová, V.; Kroupa, A. The influence of isothermal ageing and subsequent hydrogen charging at room temperature on local mechanical properties and fracture characteristics of martensitic-bainitic weldments for power engineering. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B-Metall. 2017, 53, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.H.; Hwang, J.S.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, H.H.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, J.M. Charpy impact properties of hydrogen-exposed 316L stainless steel at ambient and cryogenic temperatures. Metals 2019, 9, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Völkl, J.; Alefeld, G. Diffusion of hydrogen in metals. Top. Appl. Phys. 1978, 28, 321–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yan, W.; Sha, W.; Shan, Y.Y.; Yang, K. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of short-term thermally exposed 9/12Cr heat-resistant steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 4113–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, A.; Golański, G.; Sroka, M. Assessment of microstructure stability and mechanical properties of X10CrWMoVNb9-2 (P92) steel after long-term thermal ageing for high-temperature applications. Kov. Mater. 2016, 54, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Du, B.S.; Li, X.M.; Qin, G.L.; Zou, Y. Microstructure evolution of P92 steel weld metal after service for 8000 h. Kov. Mater. 2017, 55, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklenička, V.; Kuchařová, K.; Svoboda, M. Creep behaviour and microstructure evolution of advanced creep-resistant 9% Cr martensitic steels under cyclic thermal loading. Kov. Mater. 2018, 56, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, C.; Mahapatra, M.M.; Kumar, P.; Saini, N. Comparative study of autogenous tungsten inert gas welding and tungsten arc welding with filler wire for dissimilar P91 and P92 steel weld joint. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 712, 720–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, C.; Mahapatra, M.M.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, P.; Saini, N.; Thakare, J.G.; Kumar, S. Study on effect of double austenitization treatment on fracture morphology tensile tested nuclear grade P92 steel. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2019, 96, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, F.; Nakagawa, H. Simulation test of disbonding between 2¼Cr-1Mo steel and overlaid austenitic stainless steel by electrolytic hydrogen charging technique. Trans. JWRI 1984, 13, 159–161. [Google Scholar]
- Morishige, N.; Kume, R.; Okabayashi, H. Influence of low-temperature hydrogen degassing on hydrogen-induced disbonding of cladding. Trans. Jpn. Weld. Soc. 1985, 16, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Karthick, K.; Malarvizhi, S.; Balasubramanian, V.; Krishnan, S.A.; Sasikala, G.; Albert, S.K. Tensile and impact toughness properties of various regions of dissimilar joints of nuclear grade steels. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2018, 50, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, T.W.; Lippold, J.C.; Mills, M.J. Nature and evolution of the fusion boundary in ferritic-austenitic dissimilar metal welds—Part 2: On-cooling transformations. Weld. J. 2000, 79, 267–277. [Google Scholar]
- Lippold, J.C.; Kotecki, D.J. Dissimilar welding of stainless steels. In Welding Metallurgy and Weldability of Stainless Steels; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 287–308. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, S.C.; Choi, K.J.; Bahn, C.B.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.H. Effects of thermal aging on the microstructure of Type-II boundaries in dissimilar metal weld joints. J. Nucl. Mater. 2015, 459, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Záhumenský, P.; Ševc, P.; Janovec, J. Kinetics of growth of M23C6 intergranular precipitates in 18Cr-12Ni-2.5Mo austenitic stainless steel. Kov. Mater. 1999, 37, 108–119. [Google Scholar]
- Janovec, J.; Grman, D.; Országhová, J.; Ševc, P.; Záhumenský, P.; Patscheider, J.; Tuleja, S.; Pecha, J.; Bogyó, M.; Blach, J.; et al. Role of M23C6 carbide precipitation and phosphorus grain boundary segregation in intergranular fracture and corrosion of 18Cr-12Ni austenitic stainless steel. Can. Metall. Quart. 2002, 41, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blach, J.; Falat, L.; Ševc, P. Fracture characteristics of thermally exposed 9Cr–1Mo steel after tensile and impact testing at room temperature. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2009, 16, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, G.; Sinaiová, I. Evaluation of hydrogen induced damage of steels by different test methods. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 682, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S.K.; Vishwakarma, M. Hydrogen embrittlement in different materials: A review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 21603–21616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiente, A.; Toribio, J.; Cortes, R.; Caballero, L. Tensile failure of stainless-steel notched bars under hydrogen charging. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 1996, 118, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Liu, W.; Wei, X.; Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Lu, H.; Yu, C. Study of type-II boundary behavior during SA508-3/EQ309L overlay weld interfacial failure process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 247, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pressouyre, G.M.; Bernstein, I.M. An example of the effect of hydrogen trapping on hydrogen embrittlement. Metall. Trans. A 1981, 12, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.L.; Somerday, B.P.; Ritchie, R.O.; Sofronis, P.; Robertson, I.M. Hydrogen-induced intergranular failure in nickel revisited. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 2739–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabke, H.J.; Riecke, E.M. Absorption and diffusion of hydrogen in steels. Mater. Tehnol. 2000, 34, 331–342. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, C.; Mahapatra, M.M.; Kumar, P.; Saini, N.; Srivastava, A. Microstructure and mechanical property relationship for different heat treatment and hydrogen level in multi-pass welded P91 steel joint. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 28, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Yu, X.; Hua, J.; Bai, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.; Tang, W. High-temperature short-term tensile test and creep rupture strength prediction of the T92/TP347H dissimilar steel weld joints. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2012, 26, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Jing, H.; Zhao, L.; Han, Y. Deformation mechanism and microstructure evolution of T92/S30432 dissimilar welded joint during creep. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 3960–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Du, J.; Li, L.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Z. Creep behavior and damage evolution of T92/Super304H dissimilar weld joints. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2019, 26, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).