Abstract
The classification, assessment, and estimation of the atmospheric corrosivity are fixed by the ISO 9223 standard. Its recent second edition introduced a new corrosivity category for extreme environments CX, and defined mathematical models that contain dose–response functions for normative corrosivity estimations. It is shown here that application of the ISO 9223 standard to archipelagic subtropical areas exhibits major shortcomings. Firstly, the corrosion rates of zinc and copper exceed the range employed to define the CX category. Secondly, normative corrosivity estimation would require the mathematical models to be redefined introducing the time of wetness and a new set of operation constants.
1. Introduction
Atmospheric corrosion is a process caused by the interaction of metals with the atmosphere causing their degradation. The relevance of atmospheric corrosion is often quantified in terms of the high costs caused by its action, because repairs and replacements due to corrosion amount ca. 5% of the gross domestic product (GDP) in Western countries, China, and India per year [1]. Even if this process was not producing the costs of material replacement, it would also account for production losses, energy-based costs, and the release of toxic substances to the environment. Given its impact, numerous studies on atmospheric corrosion are available in the scientific and technical literature [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10], often directed to the acquisition of atmospheric corrosivity maps for a given geographic region. The methodology required to perform these studies is established by a series of international standards (namely ISO 9223 to 9226) that were first published in 1992, and subjected to technical revision in 2012 [11,12,13,14]. In particular, the revised ISO 9223 contains substantial changes from its first edition [15]. Among them, the procedure to assign the corrosivity categories based on environmental data (i.e., SO2 and chloride dry depositions, temperature and time of wetness) was removed from the international standard, whereas dose–response functions were introduced for the normative corrosivity estimation based on environmental data. In addition, a new corrosivity category, CX, corresponding to extreme environments, was included for classifying the corrosion rates of standard metals (i.e., carbon steel, zinc, copper, and aluminum). Indeed, several reports in the literature had previously shown the shortcomings of the first edition of ISO 9223 to rank, determine, and estimate the corrosion of metals and alloys in subtropical and tropical regions [3,16,17,18,19,20,21,22], because category C5 failed to determine their actual aggressiveness, thus requiring higher corrosivity categories.
The Canary Islands are subject to the climatic dynamics of the subtropical latitudes, which, together with its proximity to the African continent and its abrupt orography, originate very specific climate conditions. The action of the trade winds determines the climate of the islands [23]. They are very humid winds of Northeast (NE) component with an annual frequency higher than 80% that bestow a very stable weather to the archipelago. The most eastern islands (i.e., Lanzarote and Fuerteventura) have desert-like climates, associated to a slightly rugged terrain with low mountains that are not able to retain the moisture of the trade winds. The remaining islands have a Mediterranean-type climate [23]. As they are more abrupt islands, the moisture of the trade winds is effectively sustained. The complex combination of climate and orography conditions may originate various climatic zones (e.g., microclimates) to develop on the same island, which supports the popular topic that the Canary Islands are a continent in miniature. These climatic zones have been determined and characterized in a recent project named CLIMCAN-010 [24]. The main objective of this project was to perform a complete climatological characterization of the Canary archipelago aimed for inclusion into the Technical Building Catalogue of Spain [25]. A major outcome of that work was probing several distinct climate zones to be present in all the islands, highlighting the islands of Tenerife and Gran Canaria with 6 and 5 zones, respectively. As a result, there is a complex distribution of Canarian atmospheres of varying aggressiveness, given that in a small geographical area there are large climatic variations. Another major project performed in the Canaries aimed to obtain the corrosion map of the Canary Islands by measuring the weight losses of carbon steel, copper, zinc, and aluminum from a large number of corrosion stations distributed along the seven main islands of the archipelago [21,26]. It was found that the ISO 9223:1992 failed to characterize the atmospheric corrosivities because the weight losses measured for the standard metals in a large number of the stations exceeded by far the highest C5 corrosivity category [21,26].
In this work, the atmospheric corrosivities of the atmospheres occurring in the Canary Islands have been reassessed in order to classify them using the revised ISO 9223:2012 standard [11], as well as to verify the validity of the proposed dose–response functions for the estimation of normative corrosivities from corrosion losses.
2. Materials and Methods
The Canary Islands are located near the Northwest (NW) African coast, between 27°37’ and 29°27’ North (N) and 13°20’ and 18°20’ West (W) (see Figure 1). The main orographic characteristics of the archipelago together with the geographical coordinates of each island are shown in Figure 2. In addition, Figure 2 depicts the climatic zones defined by the CLIMCAN-010 project [24] as well as the distribution of the 74 corrosion exposure sites through the 7 islands. Table S1 in the Supplementary Material gives the localization and the elevation of the test sites, together with the type of atmosphere on the basis of classification criteria other than corrosivity according to ISO 9223:1992(E) [15] and ISO 9223:2012 standards [11].
Figure 1.
Location of the Canary Islands.
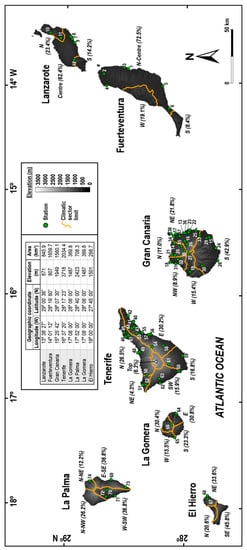
Figure 2.
Subdivision of Canary Islands into local climate sectors (adapted from [24]), and location of the 74 corrosion exposure sites (see Table S1 in Supplementary Material for codes and local orography details).
Metal samples of carbon steel, zinc, and copper of dimensions 10 cm × 4 cm × 2 mm were exposed at the corrosion exposure sites, and their chemical composition is given in Table 1. The specimens were cleaned according to ASTM G1-90 standard [27], weighed, and duly codified for identification. Subsequently, they were placed in a metal frame oriented towards the North-Northeast (NNE), with an inclination of 45 degrees with respect to the horizontal. Samples were collected every six months during the first year for copper and zinc, and with quarterly periodicity for carbon steel. In each collection, four specimens of each metal were taken. Three of these samples were cleaned according to ASTM G1-90 standard [27], and corrosivity categories were assigned from first-year weight losses according to ISO 9223:2012 standard [11].

Table 1.
Chemical composition of the carbon steel, zinc, and copper test samples.
The relative humidity level was quantified using a thermohygrometer, whereas chloride and SO2 dry deposition rates were determined monthly according to standard procedures. Namely, two methods were employed to determine SO2 pollution, namely the Husy method according to the ISO/TC 156 N 250 standard [28], and the lead dioxide candle according to the ASTM D 2010-85 standard [29]. The concentration of chloride was monitored by the wet candle method according to the ISO 9225 standard [13]. Finally, the ISO 9223:1992 standard [15] was employed to characterize the atmosphere of the localities in terms of pollution categories based on airborne salinity contamination (Sd) and with sulfur compounds based on sulfur dioxide (Pd), and of time of wetness (τ).
The effect of the environmental parameters on the average corrosion rates of metals for the first year of atmospheric exposure, rcorr, was analyzed using a multivariate variance analysis (ANOVA).
X-Ray Diffractometry (XRD) was performed using a Siemens D-5000 instrument (Bruker-Siemens, Billerica, MA, USA) provided with a copper anode (Cu Kα 5406 Å) and a scintillation detector.
3. Results
3.1. Classification of Corrosivity of the Atmosphere and General Corrosivity Estimation
The great variability of local environmental conditions occurring along the Canary archipelago is readily observable by inspecting Figure 3. This graph depicts time of wetness, and SO2 and Cl− deposition distributions measured during 3 years at the 74 corrosion exposure sites. Based on the local environmental conditions occurring at each location, corrosivity categories were assigned according to the ISO 9223:2012 standard [11], and they are listed in Table S1 in the Supplementary Material.
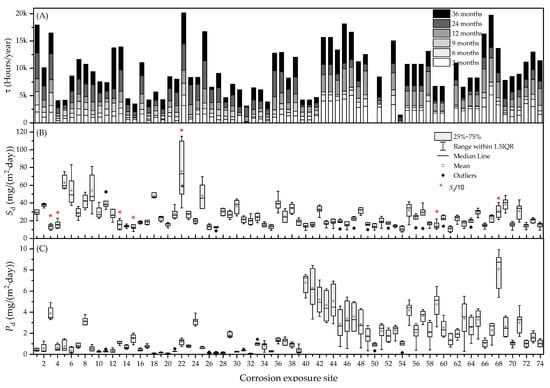
Figure 3.
Local environmental conditions at the 74 corrosion exposure sites determined during 3 years. (A) Time of wetness, (B) average Cl− deposition, and (C) average SO2 deposition.
Weight losses were measured for carbon steel, zinc, and copper after 1-year exposure, and they are given as first-year corrosion rates in Table S1 (Supplementary Material). Local atmosphere corrosivities were assigned for the three metals according to the ISO 9223:2012 standard [11], and they are also included in Table S1 (Supplementary Material). In addition, atmosphere corrosivity maps were drawn in Figure 4 together with the local climate sectors.
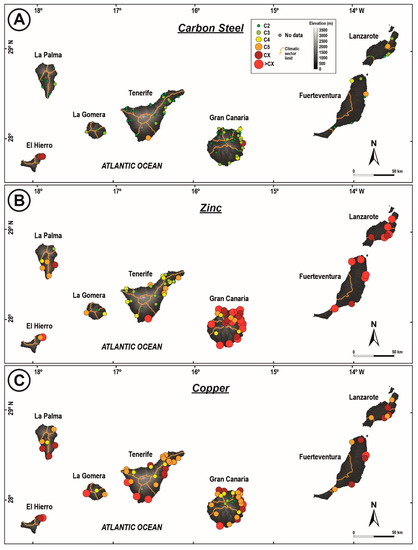
Figure 4.
Corrosion maps for (A) carbon steel, (B) zinc, (C) and copper according to ISO 9223:2012 [11].
Since the local environmental conditions influence the corrosion rates of metals, multivariate variance analysis (ANOVA) was performed in order to evaluate the effect of these parameters on the first-year corrosion rates. The following environmental parameters were considered: annual average air temperature (T), SO2 deposition rate (Pd), Cl− deposition rate (Sd), time of wetness (τ), and relative humidity (RH). To carry out this analysis, the values adopted by these environmental conditions were grouped into levels according to ISO 9223:2012 [11], and they are given in Table 2 together with the number of corrosion exposure sites included in each level. Levels were assigned to T and RH by establishing intervals of 2 °C and 10% allowance, respectively.

Table 2.
Environmental parameters and levels employed in the ANOVA analysis.
Next, the ANOVA variance analysis was performed to determine the corrosivity for the three metals based on the corrosion rates measured at each exposure site, and the results for carbon steel, zinc, and copper, are respectively listed in Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5. The analysis was done on the data from 64 corrosion exposure sites, because incomplete or not reproducible data were found at sites 13, 15, 18, 22, 50, 52, 54, 61, 67, and 68, and they were discarded for the rest of the study.

Table 3.
Statistical analysis of results for carbon steel.

Table 4.
Statistical analysis of results for zinc.

Table 5.
Statistical analysis of results for copper.
Next, the ANOVA variance analysis was performed to determine the corrosivity for the three metals based on the corrosion rates measured at each exposure site, and the results for carbon steel, zinc, and copper, are respectively listed in Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5. The analysis was done on the data from 64 corrosion exposure sites, because incomplete or not reproducible data were found at sites 13, 15, 18, 22, 50, 52, 54, 61, 67, and 68, and they were discarded for the rest of the study.
3.2. Normative Corrosivity Estimation
Corrosivity estimation was first attempted employing the dose–response functions of exposure proposed in ISO 9223:2012 (Section 8.2) [11]. Namely, the norm establishes both the function (given by Equation (1)) and the corresponding set of constants (see Table 6):

Table 6.
Normative corrosivity estimation based on calculated first-year corrosion losses. Set of constants and sum of the quadratic error for carbon steel, zinc, and copper using the dose–response functions given by Equations (1) and (3).
The criteria for establishing the quality of the dose–response function for the estimation of corrosion rates was made in terms of the sum of squared errors (SSE) between the experimental observations and those predicted by the model under consideration, as shown in Equation (2):
In this way, the applicability of the dose response function of exposure and the set of constants defined in ISO 9223:2012 for each metal is described by the SSE values included in the first set of rows of Table 6. Values in excess of 100 were found for carbon steel and zinc, whereas the errors for copper amounted ca. 41. A new attempt to improve the estimation of corrosion rates for carbon steel and zinc using the dose–response function given by Equation (1) consisted in the modification of the set of constants for each metal given by the norm as to better fit the experimental observations. The procedure consisted in introducing these constants as fitting parameters in the function, and using the algorithm of the simplex method of Nelder–Mead [30] to obtain the best set of parameters [31,32]. Accordingly, the new sets of constants for the dose–response function and the resulting fit qualities, expressed in terms of SSE values, are included in the second set of rows in Table 6 (i.e., labeled as Equation (1) *). It is observed that corrosivity estimation based on environmental information using the dose–response function defined in the ISO 9223:2012 [11] requires obtaining a new set of constants based on the first-year corrosion rates of the corresponding metal. The improvement of the fit quality was significant even for copper, even though the corrosion rates observed in this fragmented subtropical territory could still be assigned to the corrosivity categories included in the norm.
An alternate method for the estimation of corrosivity based on metal corrosion losses consisted in defining new dose–response functions for each metal using the time of wetness instead of the relative humidity. The resulting dose–response function is Equation (3):
The third set of rows in Table 6 gives the new set of constants that fit Equation (3), corresponding to the new proposal, as well as the values of the sums of quadratic errors SSE. A better agreement between the estimated corrosion rates and the experimental observations is also observed in this case.
Fit quality analysis was also performed by considering the residual error for each corrosion exposure site that was determined using Equation (4):
The residues are plotted in Figure 5 for each metal by comparing the estimations done using either the new set of constants (i.e., Equation (1) *, see Figure 5A–C) or the new dose–response function (i.e., Equation (3), cf. Figure 5D–F) with the estimates from ISO 9223:2012 [11]. In all cases, the worst results were obtained using the norm. This section may be divided by subheadings. It should provide a concise and precise description of the experimental results, their interpretation as well as the experimental conclusions that can be drawn.
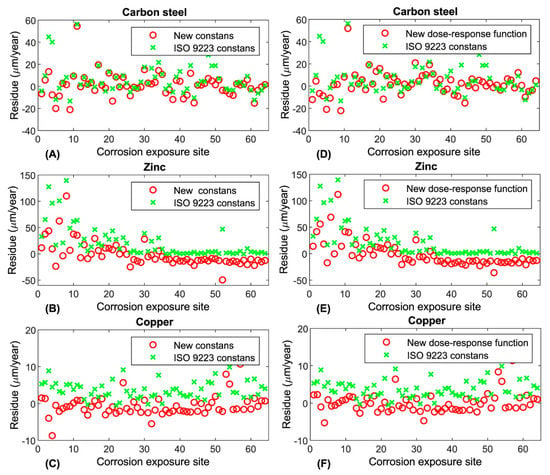
Figure 5.
Residue distributions from the application of dose–response functions for normative corrosivity estimation based on calculated first-year corrosion losses. (A–C) Application of Equation (1) using either the set of constants given by ISO 9223:2012 [11] or a new set of constants that best fit the results from corrosion exposure sites considered in this work; (D–F) application of the new dose–response function given by Equation (3). Metals: (A,D) carbon steel; (B,E) zinc; and (C,F) copper.
4. Discussion
4.1. Corrosivity of the Atmospheres
Table 7 lists the changes introduced in the second edition of the ISO 9223 standard with respect to the corrosivity categories based on the deposition rate of SO2, as well as the definition of a new corrosivity category CX. Only the ranges that affect the levels of SO2 have been modified, effectively decreasing the amounts of pollutant assigned to the categories of rural atmosphere (namely down from 10 to 4 mg/(m2 day)), urban atmosphere (the ranges are modified from 10–35 to 4–24 mg/(m2 day), and industrial atmosphere (modifying only the lower limit that changes from 35 to 24 mg/(m2 day). These changes have a very small effect on the classification of the Canary atmospheres in terms of SO2 deposition. That is, they only affect the corrosion exposure sites 23, 25, and 38 in the island of Gran Canaria, as well as sites 40 to 46, 55, 57, 59, and 63 in the island of Tenerife, and site 68 in the island of El Hierro. In general, they are moved from category P0 to category P1, although they all remain near the lower limit of the interval. As result, the ratio of corrosion exposure sites with level P0 changes from 94.4% to 74% by applying the modifications in the new edition of the standard with respect to the reports made using its first edition [18,19]. In this way, most of the territory in the archipelago apparently would exhibit urban atmosphere corrosivity, although it must be noticed that SO2 deposition in most corrosion exposure sites originates from marine contributions as sulphate ion, and therefore most of the atmospheres in the Canaries are predominantly rural. In addition, the ISO 9223:1992 [15] specifies that SO2 deposition rates corresponding to the P0 category must be considered as background concentration and would not affect the corrosion process.

Table 7.
Changes made between the first and the second editions of the ISO 9223 norm.
Conversely, the classification based on the rate of chloride deposition did not undergo any change by applying the revised norm. About 87.8% of the stations belong to category S1, 9.5% to category S2, and 2.7% to category S3, a fact that reveals the relevance of this pollutant in the atmospheres of the archipelago. Indeed, category S0 could not be assigned anywhere, not even for corrosion exposure sites located either far from the coast or in high elevation. Although the second edition of the ISO 9223 standard states that atmospheres with high levels of chloride pollutant are outside its scope, this should not be the case of the Canary Islands, where even two corrosion exposure sites are classified into category S3 (namely, sites 22 and 68), with 933.7 and 334.7 mg/(m2 day), thus being far from the upper range of the interval that is established at 1500 mg/(m2 day).
Regarding the time of wetness (TOW), the classification established in the first edition experienced no changes by applying the revised standard. Therefore, for the Canary archipelago, all islands exhibit atmosphere classes higher than τ2, distributed as 37.8% with class τ3, 45.9% with class τ4, and 16.2% with class τ5. This feature evidences the high humidity atmospheres occurring in the archipelago due to the action of the trade winds.
When the corrosivity categories were re-evaluated using the new ranges established by ISO 9223:2012, the distribution of categories exceeding the ranges of the category C5 as established in the first edition are listed in Table 8. Thus, for the entire archipelago, the introduction of a new CX category should account for all the cases found. However, this does not happen as much for zinc as for copper, where it is observed that 32.4% of cases exceed CX category for zinc and 11.0% for copper. It is observed for these two metals, Zn and Cu, that more than 44.4% and 38.4% of cases, respectively, have the highest category in the norm or higher, this effect being even more noticeable for the eastern islands. XRD analyses carried out for zinc samples reveal the absence of the protective layer of zinc hydroxosulphate (Zn4SO4(OH)6·H2O), being the majority compound a basic chloride Zn5Cl2(OH)8·H2O, typical of marine atmospheres and of a less protective nature. This fact justifies the high corrosion rate values found for zinc in the complete Canary archipelago. A special mention is deserved by corrosion exposure sites 15, 22, 59, 68, and 69, that were located in very windy areas with high salinity values. The corrosion rates exceed by far those determined in the remaining exposure sites, due to the combined effect of erosion that breaks the passive layer of corrosion products. On the other hand, the corrosion products found in copper were mostly a patina composed of cuprite (Cu2O), hydroxyl-chloride dimorphs, atacamite and paratacamite (CuCl2·3Cu(OH)2), and malachite (Cu2CO3(OH)2). The presence of atacamite in most exposure sites throughout the islands must be highlighted. Finally, in those exposure sites where the chlorides deposition rate exceeded 30 mg/(m2 day) (namely, stations 3, 4, 5, 8, 13, 15, 22, 59, 65, 68, 69, and 71), atmospheric aggressiveness hindered the formation of a passive layer even after three years of exposure.

Table 8.
Percentage distribution of atmosphere corrosivity categories in the Canary archipelago.
4.2. ANOVA Analysis
The following observations were made with respect to the analysis of the ANOVA variance, for a significance level of 5%, and taking as reference the information indicated by the p-values in the last column of Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5:
- The corrosion rates, rcorr, showed a strong dependence with Sd for the three metals studied (carbon steel, zinc, and copper), since the p-values were below the level of significance of the study.
- The relative humidity (RH) only had an influence on the corrosion rate of zinc, because this was the only metal with p-value smaller than 5%.
- The deposition of sulfur dioxide (Pd) only showed a weak influence with the corrosion rate of steel, since its p-value slightly exceeded the level of significance 5.8%, being unable to associate such an influence in the cases of zinc and copper.
- Regarding the temperature (T) data, no influence was observed on the corrosion rates for any of the three metal systems.
- The wetting time (τ) exhibited a major effect on the corrosion rate for zinc, whereas its influence was small for steel, and almost negligible for copper.
4.3. Normative Corrosivity Estimation Based on Calculated First-Year Corrosion Losses
Regarding the estimation of corrosion rates using dose–response functions, Table 6 evidences that the results obtained using the functions given in ISO 9223:2012 [11], represented by Equation (1), delivered the worst fitting values to the experimental data. Conversely, when constants estimated especially for the experimental data were used, better fits were obtained, as indicated by the smaller values of the sum of the squared errors (SSE), which were listed in Table 6 under the label of Equation (1) *. Even better results were obtained in the case of the newly proposed Equation (3). In addition, the best behavior in terms of the plots of the residuals shown in Figure 5, corresponded again to the fits made using the new determined constants, for most of sampling exposure sites. These improvements were indicated in Table 6 under the labels for Equations (1) * and (3) for the estimation of the corrosion rates, and resulted mainly from the fact that the constants provided by ISO 9223:2012 have been determined in atmospheres with characteristics considerably different from those occurring in the Canary Islands. Altogether, it can be inferred that it would be desirable to establish a new set of models that adequately consider the parameters showing a greater influence on the corrosion rates, these being determined by means of analysis of influence, such as the variance analysis.
5. Conclusions
Due to the big microclimatic variability existing in the Canary Islands and the subtropical conditions determined by the trade winds, the corrosion rates for carbon steel, copper, and zinc from 74 corrosion exposure sites exceeded the ranges contained in the ISO 9223:2012 standard.
In the case of carbon steel, corrosivity categories were observed to range between C2 and CX. For this metal, the second edition of the ISO 9223 standard satisfactorily described all the situations found in the archipelago.
In the case of zinc and copper, the high salinity and TOW caused high corrosion rates in many locations. In the case of zinc, the CX corrosivity category was assigned to 14.9% of the exposure sites distributed throughout the archipelago, whereas 32.4% exhibited corrosion rates higher than those corresponding to the category CX. Copper exhibited a general behavior similar to that described for zinc. Thus, 27.4% of the total number of exposure sites exhibited a CX corrosivity category, and 11.0% were higher than CX. These results show that either it would be necessary to readjust the upper limit of the category CX for metals such as Zn and Cu, or even to introduce a new corrosivity category to describe the greater aggressivity of subtropical climatologies.
With respect to the analysis of the variance for the three metals, it was found that the most influential environmental parameter affecting the corrosion rates was the chloride deposition rate (Sd), with a p-value of 0.49% in the worst case (i.e., copper), well below the level of significance of the study, namely 5%. On the contrary, the environmental temperature (T) showed the smallest influence, with a p-value of 8.9% in the best case (copper), which was clearly above the level of significance of the study, 5%.
Regarding the dose–response functions associated with the corrosion rates, for the three metals, it was found that the proposed modifications of these functions, given in the form of new sets of constants, delivered better fits than those sets of constants given by the ISO 9223 standard. In the worst case, a decrease in the sum of squared errors, SEE, of approximately 25% was observed, with respect to the standard function for carbon steel, whereas in the best case, a decrease in the SEE of approximately 48% occurred with respect to the ISO 9223 standard function for copper.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2075-4701/9/10/1105/s1. Table S1 lists the location, characteristics, and corrosivity categories according to ISO 9223:2012 Norm [11] of the 74 corrosion exposure sites considered in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.J.S. and R.M.S.; Data curation, J.J.S., A.R., A.R.-G., V.M. and B.M.F.-P.; Formal analysis, J.J.S., A.R. and R.M.S.; Funding acquisition, J.J.S. and R.M.S.; Investigation, J.J.S. and R.M.S.; Methodology, J.J.S., H.C.V. and R.M.S.; Project administration, J.J.S., A.R. and R.M.S.; Resources, J.J.S. and R.M.S.; Software, J.J.S., A.R., A.R.-G., V.M. and B.M.F.-P.; Supervision, J.J.S. and .M.S.; Validation, J.J.S., H.C.V. and R.M.S.; Visualization, J.J.S. and R.M.S.; Writing—original draft, J.J.S., A.R., A.R.-G. and H.C.V.; Writing—review & editing, J.J.S., A.R., A.R.-G. and R.M.S.
Funding
This research was funded by UNELCO-ENDESA (Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain) and by the Canarian Agency for Research, Innovation and Information Society (Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain) and the European Social Fund (Brussels, Belgium) under grant ProID2017010042. V.F.M. is grateful to Universidad de La Laguna and Obra Social “La Caixa” for a research contract.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gramberg, U. Korrosionsschutz-Antworten auf eine Herausforderung. Zur Gründung der Gesellschaft für Korrosionsschutz GfKORR. Mater. Corros. 1996, 47, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, S.W.; Hernández-Duque Delgadillo, G.; Bushman, J.B. Marine Corrosion in Tropical Environments, 1st ed.; ASTM Stock Number STP 1399; American Society for Testing Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2000; pp. 1–305. [Google Scholar]
- Leygraf, C.; Odnevall Wallinder, I.; Tidblad, J.; Graedel, T. Atmospheric Corrosion, 2nd ed.; The Electrochemical Society, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Pennington, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–397. [Google Scholar]
- Lopesino, P.; Alcántara, J.; de la Fuente, D.; Chico, B.; Jiménez, J.A.; Morcillo, M. Corrosion of copper in unpolluted chloride-rich atmospheres. Metals 2018, 8, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, I.; Cano, H.; Lopesino, P.; de la Fuente, D.; Chico, B.; Jiménez, J.A.; Medina, S.F.; Morcillo, M. Five-year atmospheric corrosion of Cu, Cr and Ni weathering steels in a wide range of environments. Corros. Sci. 2018, 141, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, I.; Cano, H.; Crespo, D.; Chico, B.; de la Fuente, D.; Morcillo, M. Atmospheric corrosion of ASTM A-242 and ASTM A-588 weathering steels in different types of atmosphere. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBozec, N.; Thierry, D.; Persson, D.; Riener, C.K.; Luckeneder, G. Influence of microstructure of zinc-aluminium-magnesium alloy coated Steel on the corrosion behavior in outdoor marine atmosphere. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 374, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcillo, M.; Díaz, I.; Cano, H.; Chico, B.; de la Fuente, D. Atmospheric corrosion of weathering steels. Overview for engineers. Part I: Basic concepts. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 213, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcillo, M.; Díaz, I.; Cano, H.; Chico, B.; de la Fuente, D. Atmospheric corrosion of weathering steels. Overview for engineers. Part II: Testing, inspection, maintenance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 222, 750–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cao, F.; Song, G.-L.; Zheng, D.; Shi, Z.; Dargusch, M.S.; Atrens, A. Review of the atmospheric corrosion of magnesium alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 2003–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 9223:2012. Corrosion of Metals and Alloys—Corrosivity of Atmospheres—Clasification, Determination and Estimation, 2nd ed.; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 9224:2012. Corrosion of Metals and Alloys—Corrosivity of Atmospheres—Guiding Values for the Corrosivity Categories, 2nd ed.; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 9225:2012. Corrosion of Metals and Alloys—Corrosivity of Atmospheres—Measurement of Environmental Parameters Affecting Corrosivity of Atmospheres, 2nd ed.; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 9226:2012. Corrosion of Metals and Alloys—Corrosivity of Atmospheres—Determination of Corrosion Rate of Standard Specimens for the Evaluation of Corrosivity, 2nd ed.; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 9223:1992(E). Corrosion of Metals and Alloys—Corrosivity of Atmospheres—Classification, 1st ed.; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanauskas, R.; Muleshkova, L.; Maldonado, L.; Dobrovolskis, P. Characterization of the corrosion behaviour of Zn and Zn alloy electrodeposits: Atmospheric and accelerated tests. Corros. Sci. 1998, 40, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, A.R.; Corvo, F. Outdoor and indoor atmospheric corrosion of carbon steel. Corros. Sci. 1999, 41, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, J.J.; Santana, J.; González, J.E.; de la Fuente, D.; Chico, B.; Morcillo, M. Atmospheric corrosivity map for steel in Canary Isles. Br. Corros. J. 2001, 36, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veleva, L.; Kane, R. Atmospheric corrosion. In Corrosion, Fundamentals, Testing and Applications, ASM Handbook Series, 1st ed.; Cramer, S.D., Covino, B.S., Jr., Eds.; American Society for Testing Materials International: Columbus, OH, USA, 2003; Volume 13A, pp. 196–209. [Google Scholar]
- Mikhailov, A.A.; Tidblad, J.; Lucera, V. The classification system of ISO 9223 Standard and the dose-response functions assessing the corrosivity of outdoor atmospheres. Prot. Met. 2004, 40, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.; Martín-Krijer, S.; Díaz, F.; Hernández-Borges, J.; González, S. Atmospheric corrosion in subtropical areas: Influences of time of wetness and deficiency of the ISO 9223 norm. Corros. Sci. 2005, 47, 2005–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veleva, L.; Acosta, M.; Meraz, E. Atmospheric corrosion of zinc induced by runoff. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 2055–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, N.F.; Washington, R.; Whittaker, R.J. Future climate change of the subtropical North Atlantic: Implications for the cloud forests of Tenerife. Clim. Change 2004, 65, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caracterización Climática de las Islas Canarias para la Aplicación del Código Técnico de la Edificaci; CLIMCAN-010 y de su Aplicación Informática, prCTE-DR/CC.AA-008/10; Gobierno de Canarias: Las Palmas, Spain, 2010.
- Real Decreto 314/2006; BOE No. 74; Ministry of Housing of Spain: Madrid, Spain, 2006; pp. 11816–11831.
- Santana Rodríguez, J.J.; Santana Hernández, F.J.; González González, J.E. The effect of environmental and meteorological variables on atmospheric corrosion of carbon Steel, zinc and aluminium in a limited geographic zone with different types of environment. Corros. Sci. 2003, 45, 799–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G1-90. Standard Practice for Preparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Corrosion Test Specimens; American Society for Testing Materials: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- ISO/TC 156 N 250: Corrosion of Metals and Alloys. Aggressivity of Atmospheres. Methods of Measurement of Pollution Data; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D 2010-85: Standard Method for Evaluation of Total Sulfation Activity in the Atmosphere by the Lead Dioxide Candle; American Society for Testing Materials: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1985.
- Nelder, J.A.; Mead, R. A Simplex method for function minimization. Comput. J. 1965, 7, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanelas, I.; Collazo, A.; Izquierdo, M.; Nóvoa, X.R.; Pérez, C. Influence of galvanised surface state on the duplex systems behavior. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 1816–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, R.; Ackermann, H.; Lucka, K. Predicting the depletion of chromium in two high temperature Ni alloys. Corros. Sci. 2013, 69, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).