Manufacturing and Characterization of NiTi Alloy with Functional Properties by Selective Laser Melting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
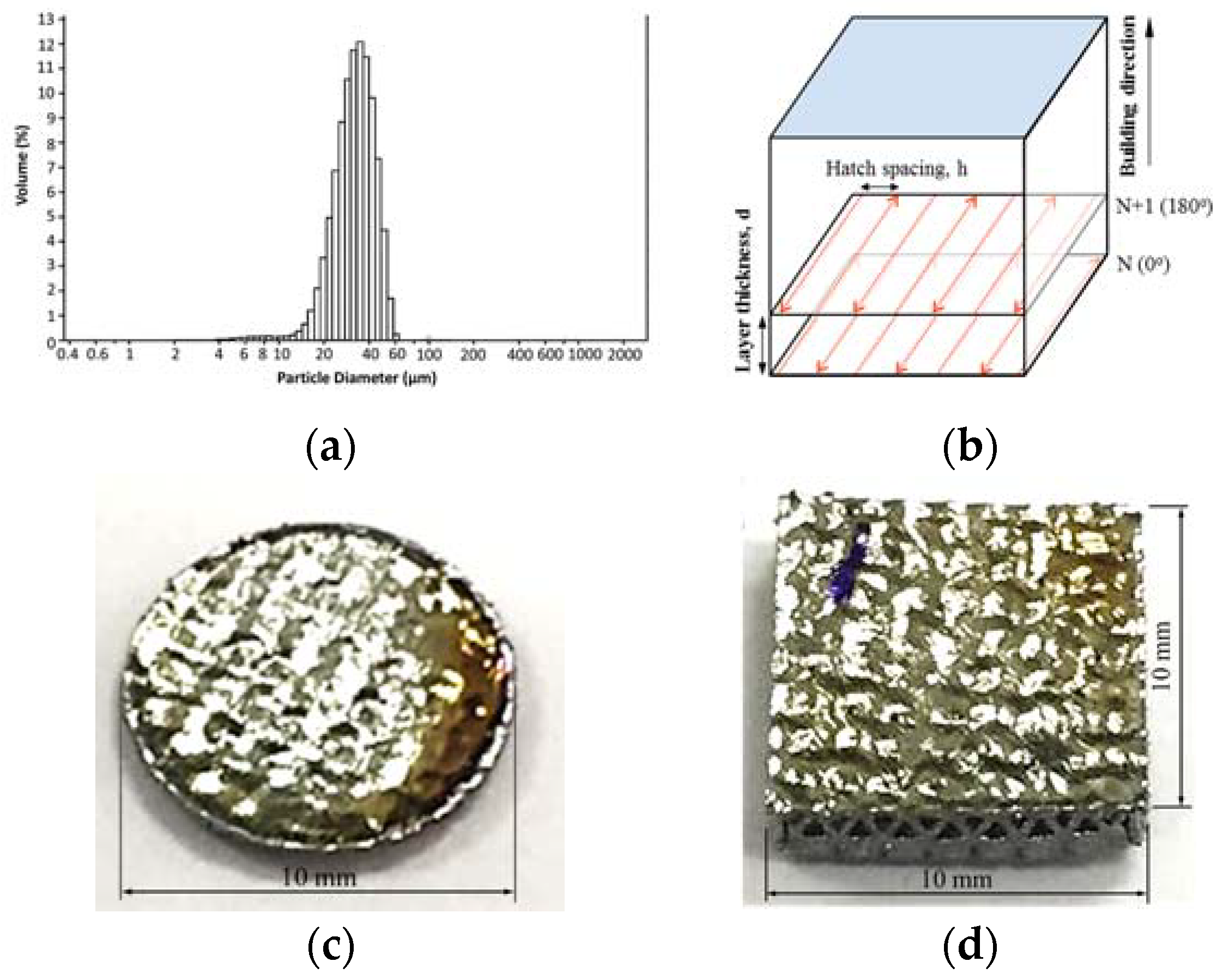
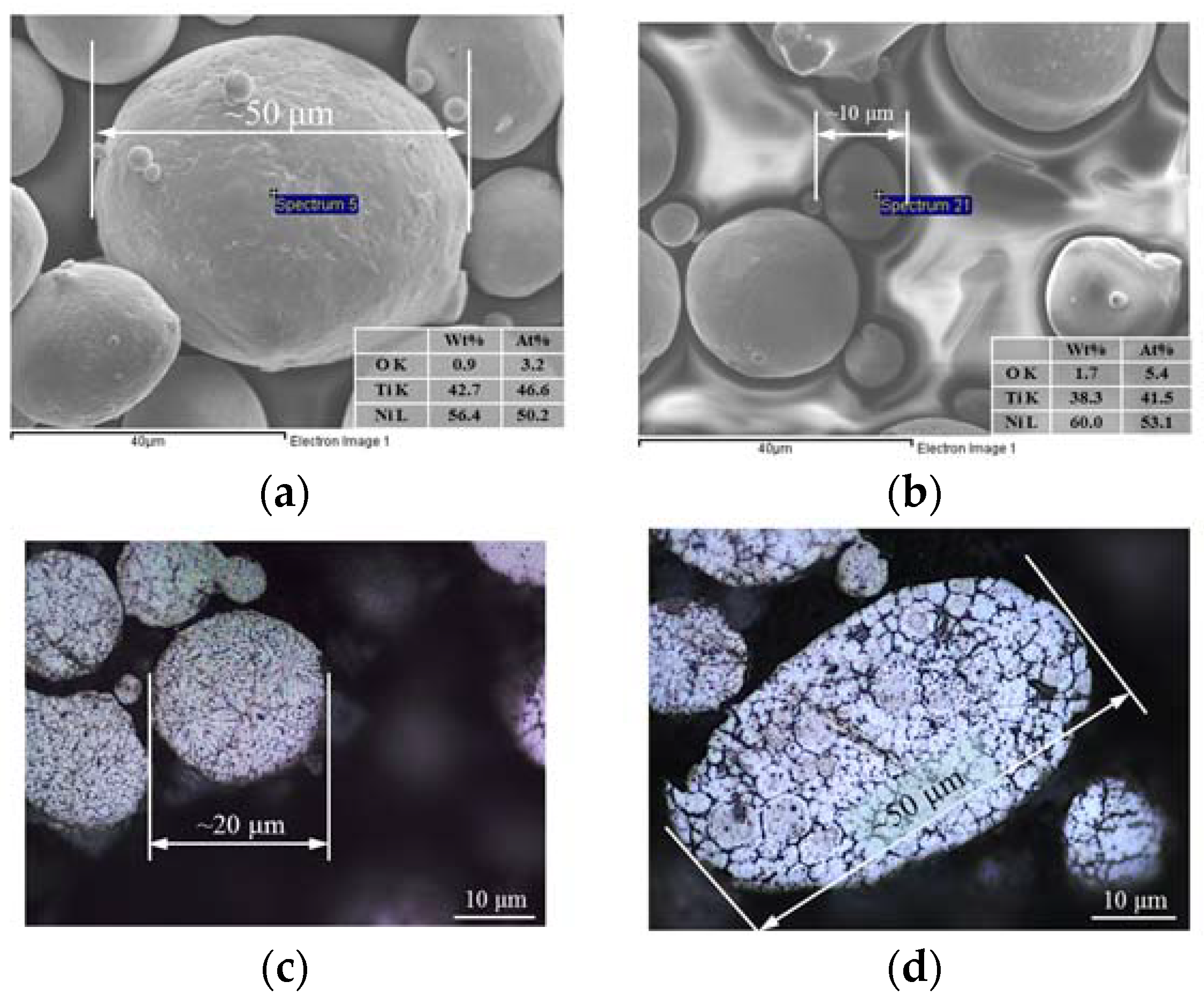
3.1. Composition and Microstructure of NiTi Powder
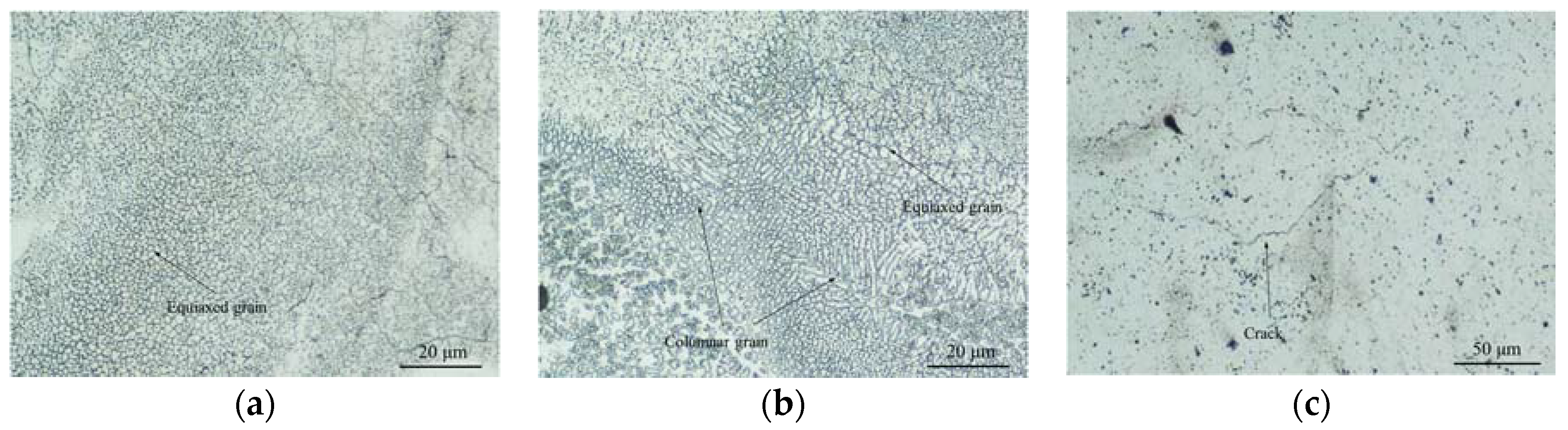
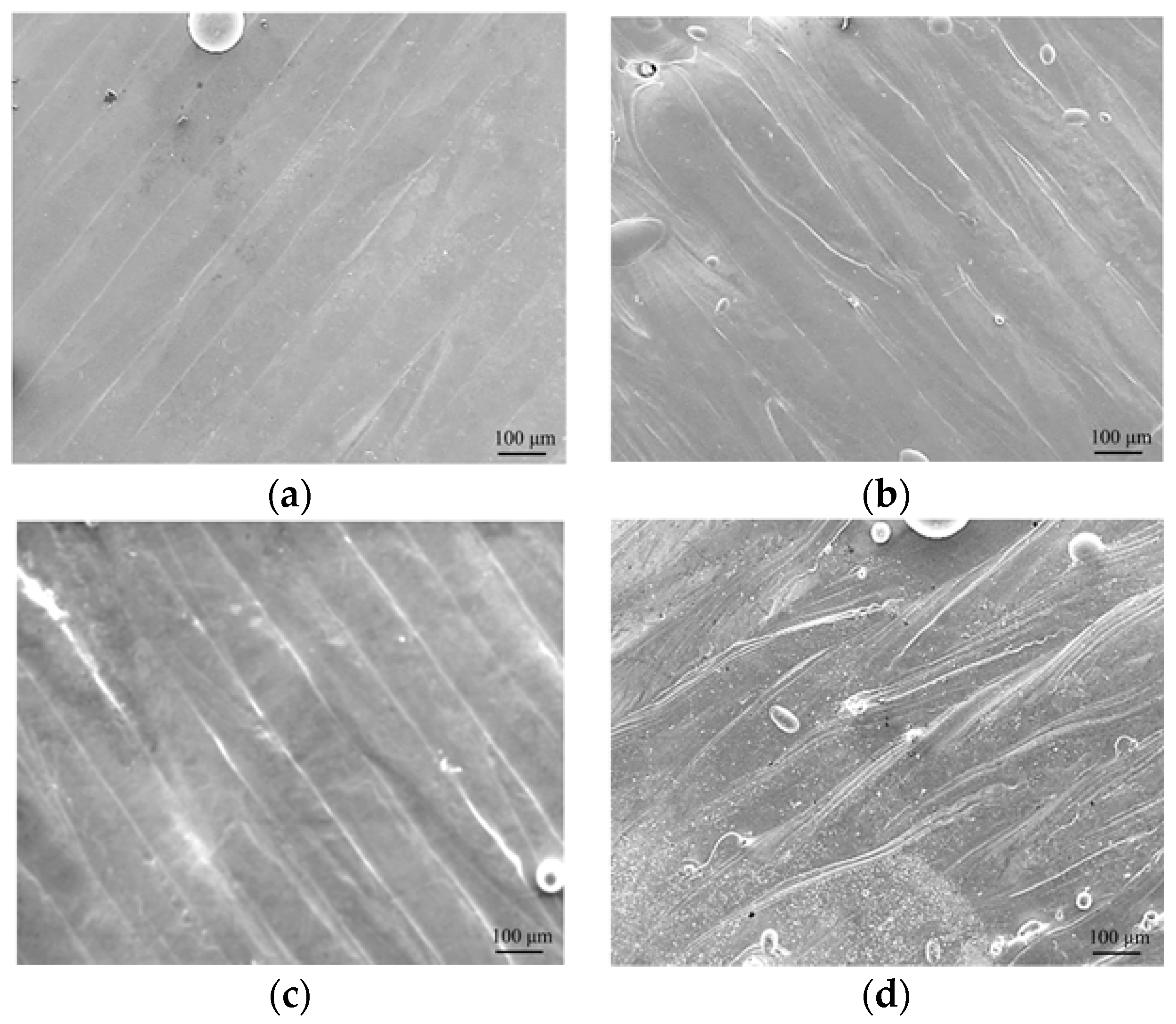
3.2. Composition and Microstructure of Thin-Wall Samples
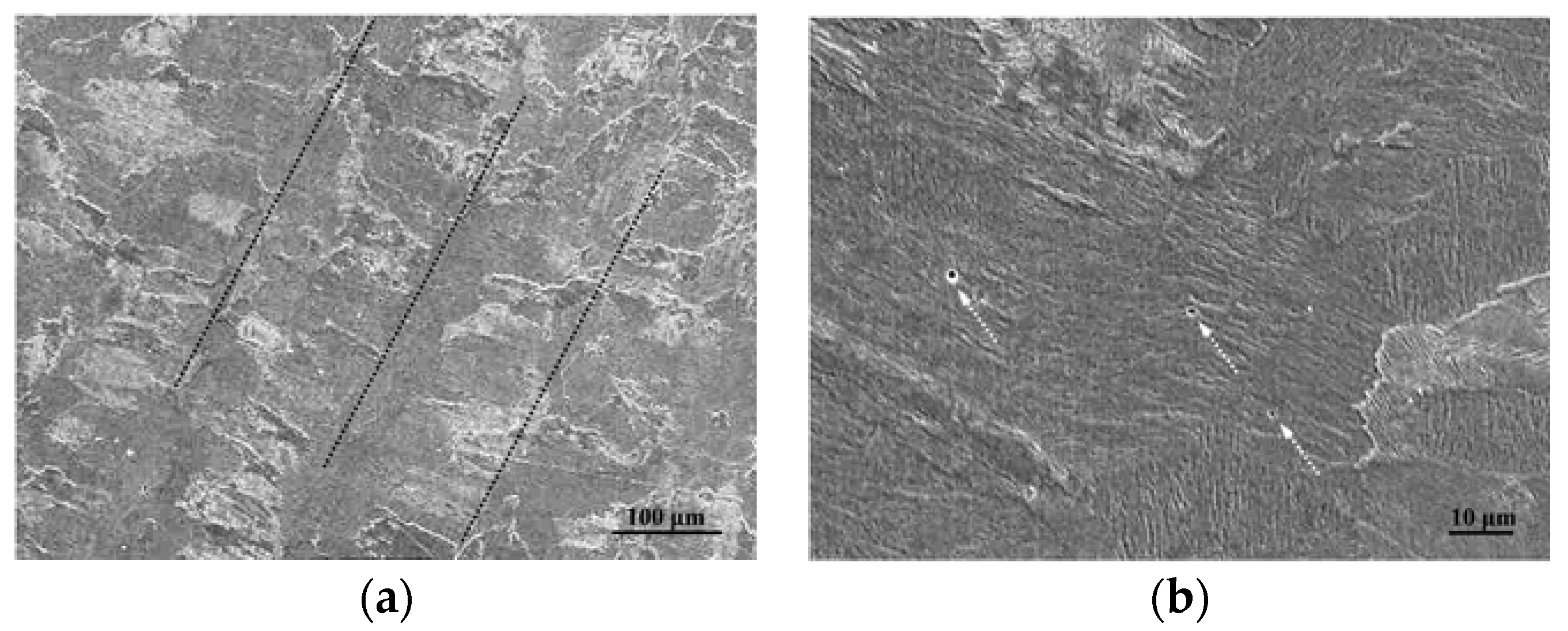
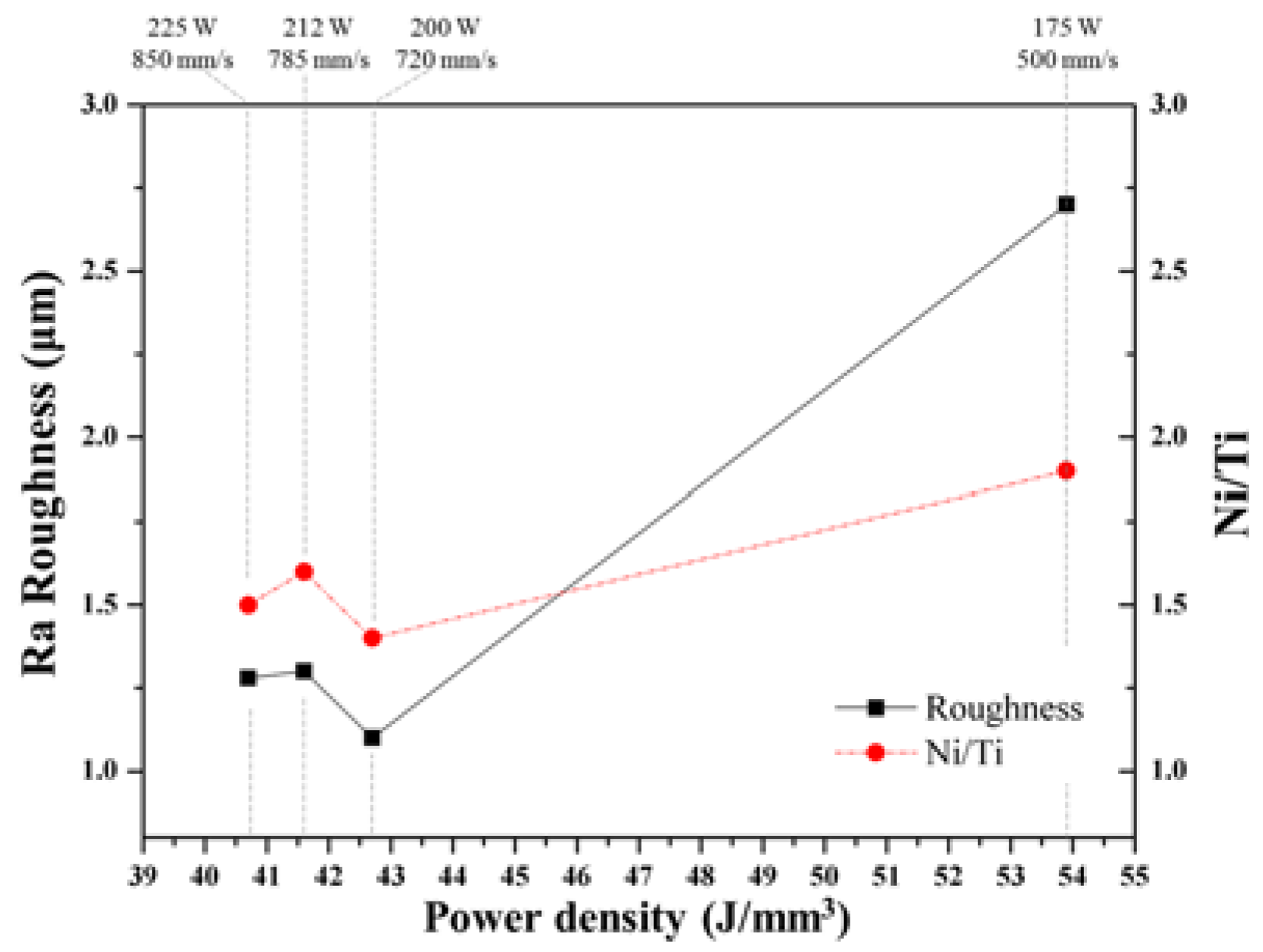
3.3. Effect of Laser Energy Density on Composition and Microstructure of Cuboid Samples
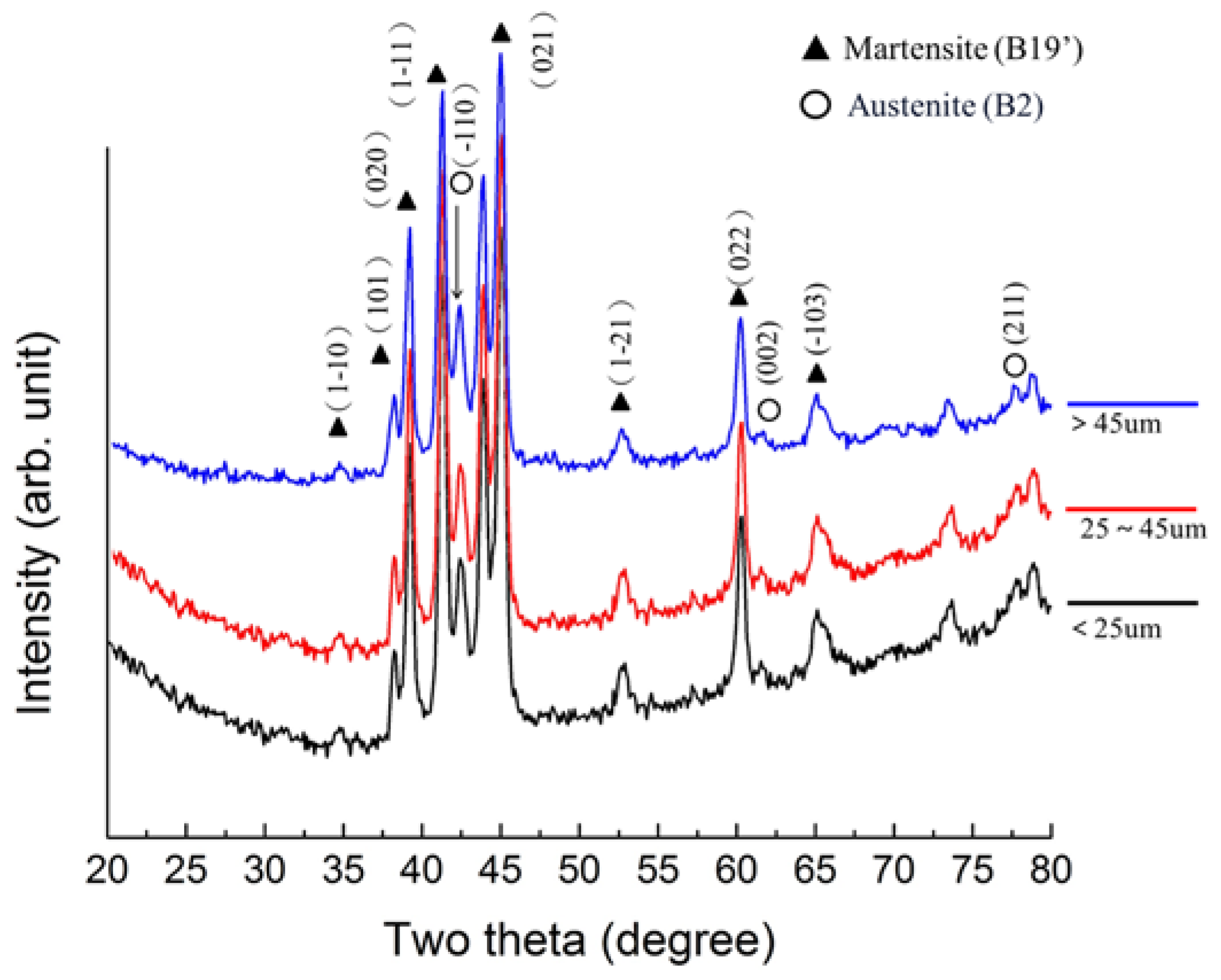
3.4. Phase and Phase Transformation of SLM-NiTi
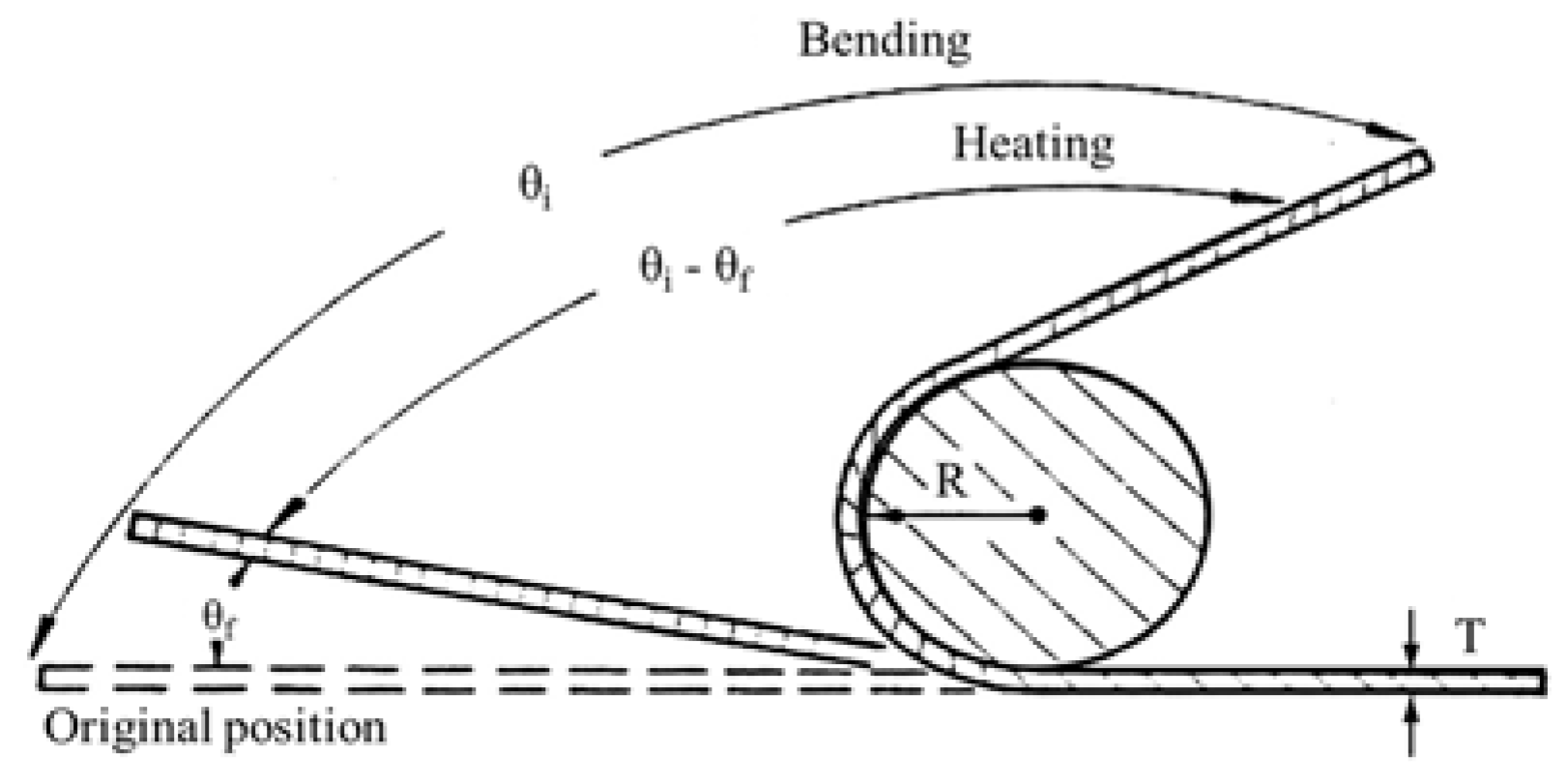
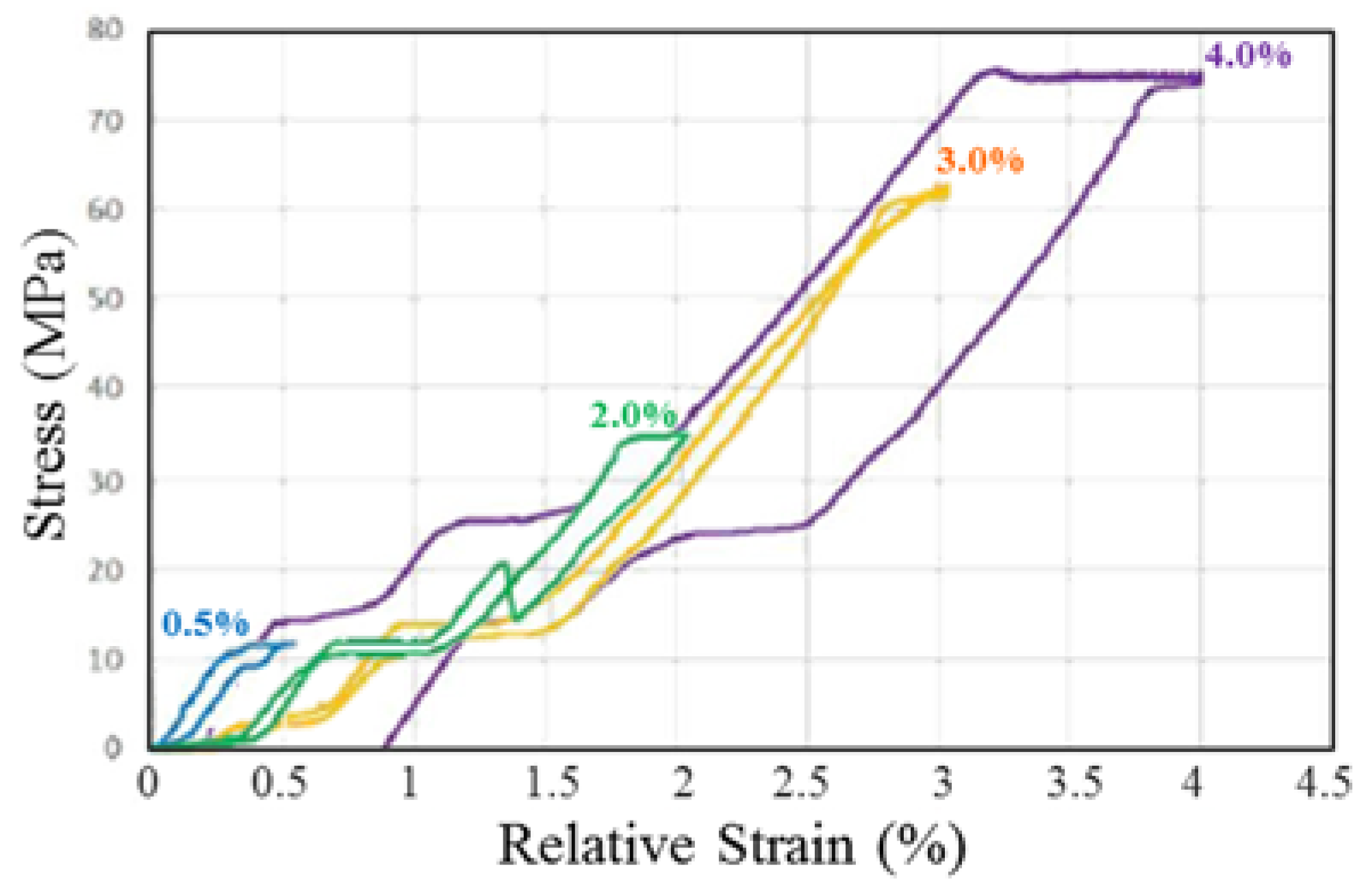
3.5. Shape Memory Capability and Pseudoelasticity of SLM-NiTi
4. Conclusions
- NiTi powder with larger particles exhibited lower oxygen content than that with smaller particles.
- The thin-walled NiTi sample that wsa fabricated by SLM exhibited a marginally inhomogeneous microstructure between layers. In this sample, cracks and pores were frequently observed on the face of the sample in contact with the substrate.
- High energy density (53.9 J/mm3) resulted in the sample exhibiting a high surface roughness and a Ni/Ti ratio that was varying significantly from that of the original NiTi powder.
- SLM-NiTi exhibited a lower phase-transformation temperature and broader transformation range than the original NiTi. The transformation range can be reduced by annealing at 850 °C for 1 h.
- SLM-NiTi exhibited pseudoelasticity under 3.0% strain. The shape-recovery rate of the SLM-NiTi wire was 100% under 2% bending strain, which was equivalent to that of the NiTi wire that was formed by vacuum arc-melting.
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoneyama, T.; Doi, H.; Hamanaka, H.; Okamoto, Y.; Mogi, M.; Miura, F. Super-elasticity and thermal behavior of Ni–Ti alloy orthodontic arch wires. Dent. Mater. J. 1992, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xiang, H. Apparent modulus of elasticity of near-equiatomic NiTi. J. Alloys Compd. 1998, 270, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wever, D.J.; Veldhuizen, A.G.; de Vries, J.; Busscher, H.J.; Uges, D.R.A.; van Horn, J.R. Electrochemical and surface characterization of a nickel–titanium alloy. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duerig, T.; Pelton, A.; Stockel, D. An overview of nitinol medical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 273, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinert, K.; Petzoldt, V. Machining of NiTi based shape memory alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 378, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.H. Fabrication of NiTi materials and components. Mater. Sci. Forum 2002, 394–395, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.C.; Lin, K.M.; Cheng, I.S. The Electro-discharge machining characteristics of TiNi shape memory alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igharo, M.; Wood, J.V. Compaction and Sintering Phenomena in Titanium—Nickel Shape Memory Alloys. Powder Metall. 1985, 28, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbroucke, B.; Kruth, J.P. Selective laser melting of biocompatible metals for rapid manufacturing of medical parts. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2006, 13, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calleja, A.; Tabernero, I.; Fernández, A.; Celaya, A.; Lamikiz, A.; López de Lacalle, L.N. Improvement of strategies and parameters for multi-axis laser cladding operations. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2014, 56, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calleja, A.; Tabernero, I.; Ealo, J.A.; Campa, F.J.; Lamikiz, A.; López de Lacalle, L.N. Feed rate calculation algorithm for the homogeneous material deposition of blisk blades by 5-axis laser cladding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 74, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, B.; Mognol, P.; Hascoët, J.Y. Laser polishing of additive laser manufacturing surfaces. J. Laser Appl. 2015, 27, S29102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadbakhsh, S.; Speirs, M.; Kruth, J.P.; van Humbeeck, J. Influence of SLM on shape memory and compression behaviour of NiTi scaffolds. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Tech. 2015, 64, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andani, M.T.; Saedi, S.; Turabi, A.S.; Karamooz, M.R.; Haberland, C.; Karaca, H.E.; Elahinia, M. Mechanical and shape memory properties of porous Ni50.1Ti49.9 alloys manufactured by selective laser melting. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 68, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habijan, T.; Haberland, C.; Meier, H.; Frenzel, J.; Wittsiepe, J.; Wuwer, C.; Greulich, C.; Schildhauer, T.A.; Köller, M. The biocompatibility of dense and porous Nickel–Titanium produced by selective laser melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, R.; Senturker, S.; Shi, X.; Bal, W.; Dizdaroglu, M.; Kasprzak, K.S. Effects of Ni(II) and Cu(II) on DNA interaction with the N-terminal sequence of human protamine P2: Enhancement of binding and mediation of oxidative DNA strand scission and base damage. Carcinogenesis 1999, 20, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliades, T.; Zinelis, S.; Papadopoulos, M.A.; Eliades, G.; Athanasiou, A.E. Nickel content of as-received and retrieved NiTi and stainless steel archwires: Assessing the nickel release hypothesis. Angle Orthod. 2004, 74, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shishkovsky, I.V.; Yadroitsev, I.A.; Smurov, I.Y. Direct selective laser melting of nitinol powder. Phys. Procedia 2012, 39, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishkovsky, I.V.; Yadroitsev, I.A.; Smurov, I.Y. Manufacturing three dimensional nickel titanium articles using layer by layer laser melting technology. Technol. Phys. Lett. 2013, 39, 1081–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormann, T.; Schumacher, R.; Müller, R.B.; Mertmann, M.; de Wild, M. Tailoring selective laser melting process parameters for NiTi implants. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2012, 21, 2519–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.C.; Wu, S.K. Strengthening effect on shape recovery characteristic of the equiatomic TiNi alloy. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1992, 26, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, T.L.; Werschmoeller, D.; Duffie, N.A.; Li, X.; Pfefferkorn, F.E. Examination of selective pulsed laser micropolishing on microfabricated nickel samples using spatial frequency analysis. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2009, 131, 021002–021011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadali, M.; Ma, C.; Duffie, N.A.; Li, X.; Pfefferkorn, F.E. Pulsed laser micro polishing: Surface prediction model. J. Manuf. Process. 2012, 14, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfefferkorn, F.E.; Duffie, N.A.; Li, X.; Vadali, M.; Ma, C. Improving surface finish in pulsed laser micro polishing using thermocapillary flow. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 62, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Vadali, M.; Duffie, N.A.; Pfefferkorn, F.E.; Li, X. Melt Pool flow and surface evolution during pulsed laser micro polishing of Ti6Al4V. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2013, 135, 061023–061031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Vadali, M.; Li, X.; Duffie, N.A.; Pfefferkorn, F.E. Analytical and experimental investigation of thermocapillary flow in pulsed laser micropolishing. J. Micro Nano Manuf. 2014, 2, 021010–021018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, H.; Haberland, C.; Frenzel, J. Structural and functional properties of NiTi shape memory alloys produced by selective laser melting. In Innovative Developments in Design and Manufacturing: Advanced Research in Virtual and Rapid Prototyping; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2011; pp. 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil-Allafi, J.; Dlouhy, A.; Eggeler, G. Ni4Ti3-Precipitation During aging of NiTi shape memory alloys and its influence on martensitic phase transformations. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 4255–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenzel, J.; George, E.P.; Dlouhy, A.; Somsen, C.; Wagner, M.F.X.; Eggeler, G. Influence of Ni on martensitic phase transformations in NiTi shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 3444–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olier, P.; Barcelo, F.; Bechade, J.L.; Brachet, J.C.; Lefevre, E.; Guenin, G. Effects of impurities content (oxygen, carbon, nitrogen) on microstructure and phase transformation temperatures of near equiatomic TiNi shape memory alloys. J. Phys. IV 1997, 7, C5-143–C5-148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, H.; Haberland, C.; Frenzel, J.; Zarnetta, R. Selective laser melting of NiTi shape memory components. In Innovative Developments in Design and Manufacturing: Advanced Research in Virtual and Rapid Prototyping; CRC Press-Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 233–238. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna, B.V.; Bose, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Laser processing of net-shape NiTi shape memory alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2007, 38, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falvo, A.; Furgiuele, F.M.; Maletta, C. Laser welding of a NiTi alloy: Mechanical and shape memory behavior. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 412, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuissi, A.; Besseghini, S.; Ranucci, T.; Squatrito, F.; Pozzi, M. Effect of Nd-YAG laser welding on the functional properties of the Ni–49.6at.%Ti. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 273–275, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormann, T.; Müller, B.; Schinhammer, M.; Kessler, A.; Thalmann, P.; de Wild, M. Microstructure of selective laser melted nickel-titanium. Mater. Charact. 2014, 94, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Element | Ti | Ni | O | C | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition (wt %) | 45.52 | 54.34 | 0.101 | 0.033 | 0.006 |
| Front Surface | Back Surface | NiTi Powder | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti (wt %) | 34.3 ± 1.7 | 40.9 ± 4.7 | 45.5 |
| Ni (wt %) | 64.5 ± 1.9 | 53.9 ± 2.6 | 54.4 |
| O (wt %) | 1.2 ± 0.8 | 5.2 ± 2.3 | 0.1 |
| Phase | B2 | B19′ + B2 | B19′ + B2 |
| Ra Roughness (μm) | 3.44 | 7.16 | - |
| SLM-TiNi | SLM-TiNi after Annealing at 850 °C for 1 h | |
|---|---|---|
| M* (°C) | −10.18 | 4.71 |
| A* (°C) | 71.66 | 60.1 |
| Phase (25 °C) | B19′ + B2 | B19′ + B2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ou, S.-F.; Peng, B.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Tsai, M.-H. Manufacturing and Characterization of NiTi Alloy with Functional Properties by Selective Laser Melting. Metals 2018, 8, 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8050342
Ou S-F, Peng B-Y, Chen Y-C, Tsai M-H. Manufacturing and Characterization of NiTi Alloy with Functional Properties by Selective Laser Melting. Metals. 2018; 8(5):342. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8050342
Chicago/Turabian StyleOu, Shih-Fu, Bou-Yue Peng, Yi-Cheng Chen, and Meng-Hsiu Tsai. 2018. "Manufacturing and Characterization of NiTi Alloy with Functional Properties by Selective Laser Melting" Metals 8, no. 5: 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8050342
APA StyleOu, S.-F., Peng, B.-Y., Chen, Y.-C., & Tsai, M.-H. (2018). Manufacturing and Characterization of NiTi Alloy with Functional Properties by Selective Laser Melting. Metals, 8(5), 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8050342





