Crystallization Kinetics of 50% W Particles/Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 Metallic Glass Matrix Composite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
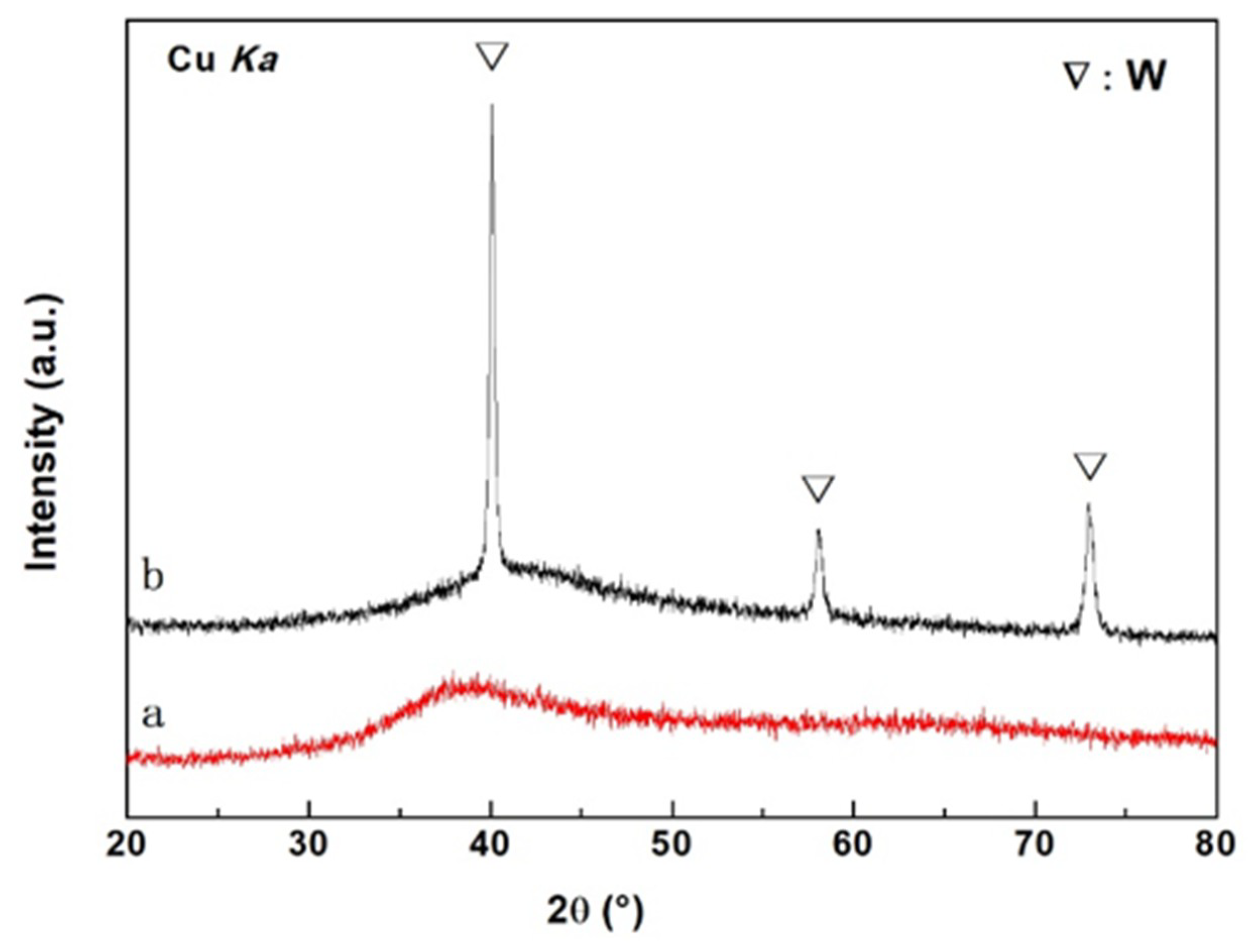
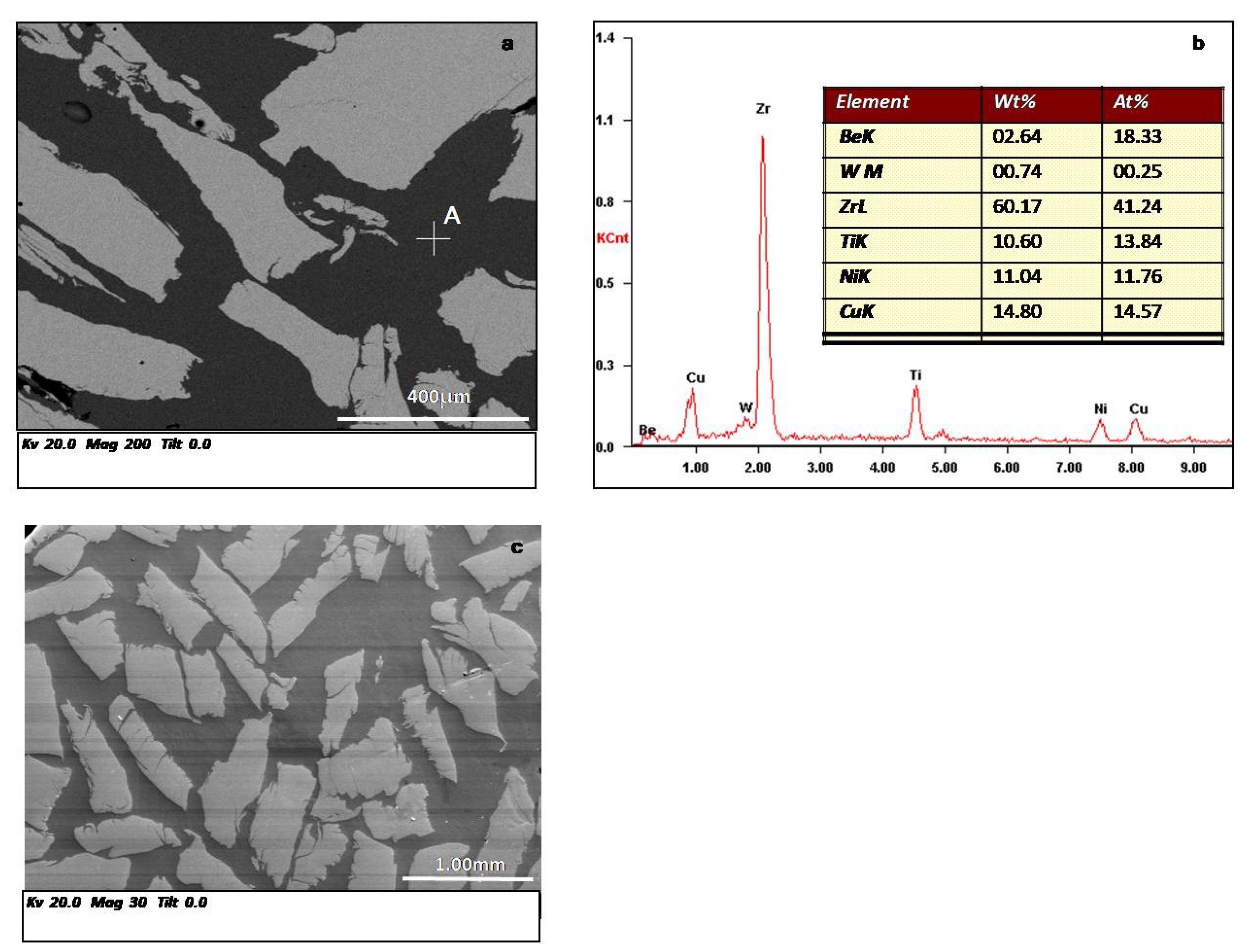
3.1. Structure
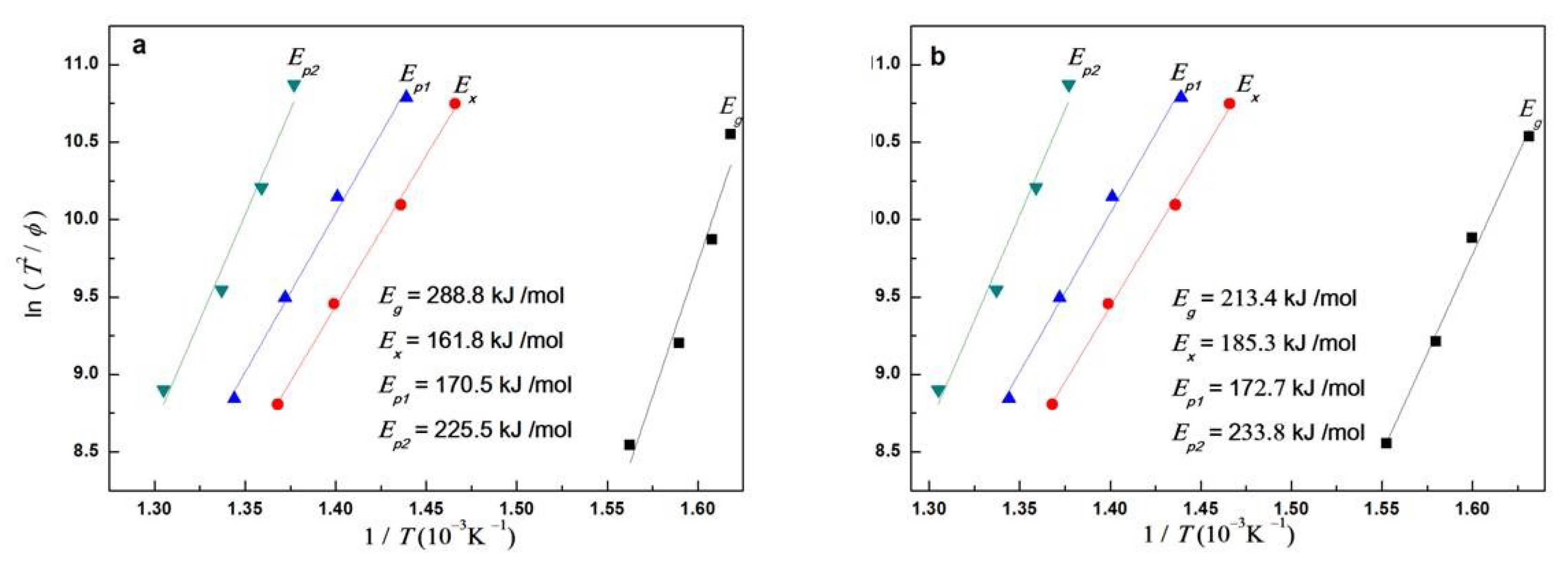
3.2. Crystallization Kinetics
3.3. Isothermal Crystallization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Inoue, A.; Zhang, T.; Masumoto, T. Zr-Al-Ni amorphous alloys with high glass transition temperature and significant supercooled liquid region. Mater. Trans. JIM 1990, 31, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhash, G.; Dowding, R.J.; Kecskes, L.J. Characterization of uniaxial compressive response of bulk amorphous Zr-Ti-Cu-Ni-Be alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 334, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Prakash, V.; Lewandowski, J.J. Spall strength and Hugoniot elastic limit of a Zirconium-based bulk metallic glass under planar shock compression. J. Mater. Res. 2007, 22, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Zhang, T.; Saida, J. High strength and good ductility of bulk quasicrystalline base alloys in Zr65Al7.5Ni10Cu17.5-xPdx system. Mater. Trans. JIM 1999, 40, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruck, H.A.; Christman, T.; Rosakis, A.J.; Johnson, W.L. Quasi-static constitutive behavior of Zr41.25Ti13.75Ni10Cu12.5Be22.5 bulk amorphous alloys. Scr. Metal. Mater. 1994, 30, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, V.R.; Kuhn, U.; Wolff, U.; Schneider, F.; Eckert, J.; Reiche, R.; Gebert, A. Corrosion behavior of Zr-based bulk glass-forming alloys containing Nb or Ti. Mater. Lett. 2002, 57, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.Z.; Liu, R.P.; Xiao, Y.; Lou, D.C.; Liu, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, W.K. Wear resistance of Zr-based bulk metallic glass applied in bearing rollers. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 386, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Li, C.; Inoue, A. Deformation behavior of Zr-based bulk nanocrystalline amorphous alloys. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Inoue, A. Ductility of bulk nanocrystalline composites and metallic glasses at room temperature. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 77, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K. Phase transformation from an amorphous alloy into nanocrystalline materials. Acta Met. Sin. 1994, 30, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, D.K. High temperature homogeneous plastic flow behavior of a Zr based bulk metallic glass matrix composite. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 495, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Inoue, A. Ta-particulate reinforced Zr-based bulk metallic glass matrix composite with tensile plasticity. Scr. Mater. 2010, 62, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi-Yim, H.; Conner, R.D.; Szuecs, F.; Johnson, W.L. Processing, microstructure and properties of ductile metal particulate reinforced Zr57Nb5Cu15.4Ni12.6 bulk metal lie glass composites. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 2737–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandliker, R.B.; Conner, R.D.; Johnson, W.L. Melt infiltration casting of bulk metallic-glass matrix composites. J. Mater. Res. 1998, 13, 2896–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.Q.; Dmirei, V.L.L.; Kimura, H.; Inoue, A. Fabrication of ZrCuAlNi metallic glassy matrix composite containing ZrO2 particles by spark plasma sintering process. Mater. Trans. 2007, 48, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.L.; Wang, L.; Xue, Y.F.; Wang, Y. An in situ high-energy X-ray diffraction study of micromechanical behavior of Zr-based metallic glass reinforced porous W matrix composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 530, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi-Yim, H.; Conner, R.D.; Szuecs, F.; Johnson, W.L. Quasistatic and dynamic deformation of tungsten reinforced Zr57Nb5Al10Cu15.4Ni12.6 bulk metallic glass matrix composites. Scr. Mater. 2001, 45, 1039–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, R.D.; Dandliker, R.B.; Johnson, W.L. Mechanical properties of tungsten and steel fiber reinforced Zr41.25Ti13.75Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 metallic glass matrix composites. Acta. Mater. 1998, 46, 6089–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Xue, Y.F.; Zhang, H.F. Thermal residual stresses in W fibers/Zr-based metallic glass composites by high-energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, G.; Huang, D.W.; Yang, M.C. Penetrating behaviors of Zr-based metallic glass composite rods reinforced by tungsten fibers. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2012, 58, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.F.; Cai, H.N.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.C.; Zhang, H.F. Dynamic compressive deformation and failure behavior of Zr-based metallic glass reinforced porous tungsten composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 275, 445–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi-Yim, H.; Schroers, J.; Johnson, W.L. Microstructures and mechanical properties of tungsten wire/particle reinforced ZrNbAlCuNi metallic glass matrix composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K.Q.; Ren, Y.L. Tungsten particulate reinforced Zr based bulk metallic glass composites. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2006, 35, 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Subhash, G.; Kecskes, L.J.; Dowding, R.J. Mechanical behavior of tungsten perform reinforced bulk metallic glass composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 403, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peker, A.; Johnson, W.L. A highly process able metallic glass: Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10.0Be22.5. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1993, 63, 2342–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi-Yim, H.; Busch, R.; Köster, U.; Johnson, W.L. Synthesis and characterization of particulate reinforced Zr57Nb5Al10Cu15.4Ni12.6 bulk metallic glass composites. Acta. Mater. 1999, 47, 2455–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Inoue, A. High glass-forming ability and good mechanical properties of new bulk glassy alloys in Cu–Zr–Ag ternary system. J. Mater. Res. 2006, 21, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.P.; Liu, C.T. Glass formation criterion for various glass-forming systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 115505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasocka, M. The effect of scanning rate on glass transition temperature of splat-cooled Te85Ge15. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1976, 23, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.S. A method for evaluating viscosities of metallic glasses from the rates of thermal transformations. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1978, 27, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasstone, S.; Laidler, K.J.; Eyring, H. The Theory of Rate Process; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.C.; Wang, Y.R.; Wei, B.C.; Li, W.; Sun, Y. Kinetics of glass transition and crystallization of carbon nanotube reinforced Mg-Cu-Gd bulk metallic glass. J. Chin. Rare Earth Soc. 2006, 24, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.A.; Al-Kotb, M.S.; Kotkata, M.F. Model-free transformation kinetics for ZnS quantum dots synthesized via colloidal reaction. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2014, 433, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, B.; Gregorys, A.; Michel, A. Direct observation of the thickness-induced crystallization and stress build-up during sputter-deposition of nanoscale silicide films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 34888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calka, A.; Radliński, A.P. Decoupled bulk and surface crystallization in Pd85Si15 glassy metallic alloys: Description of isothermal crystallization by a local value of the Avrami exponent. J. Mater. Res. 1988, 3, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

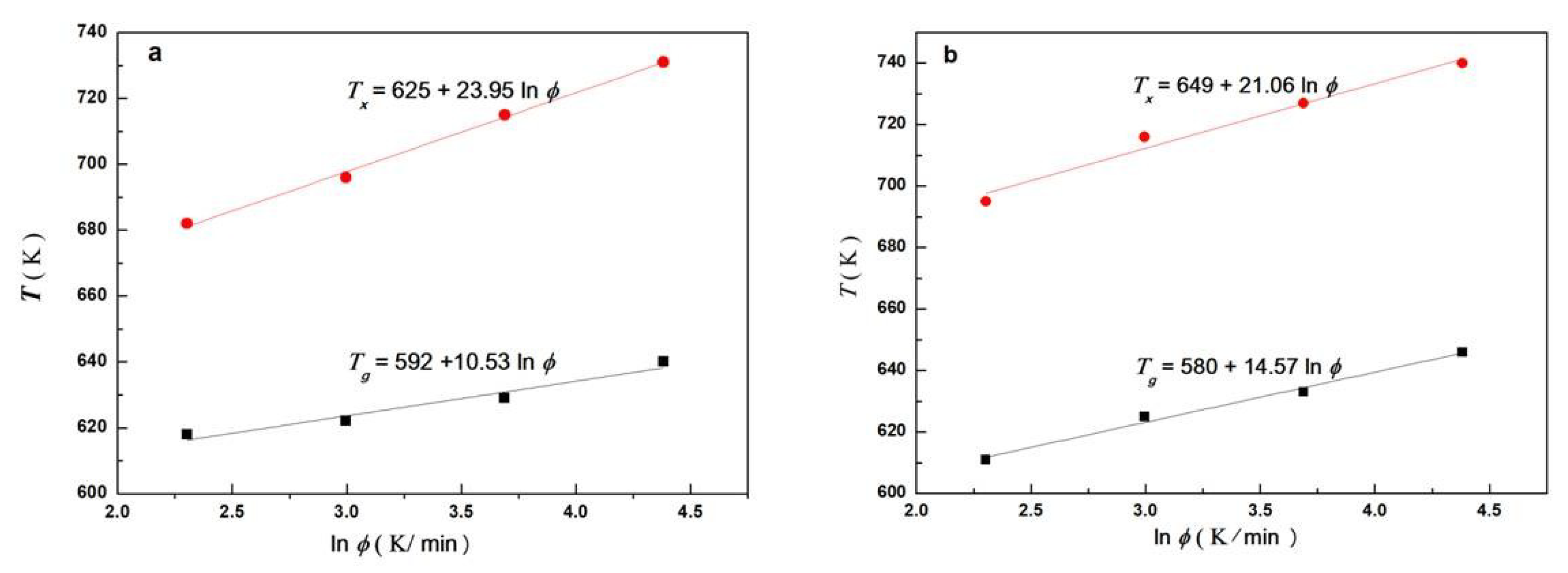
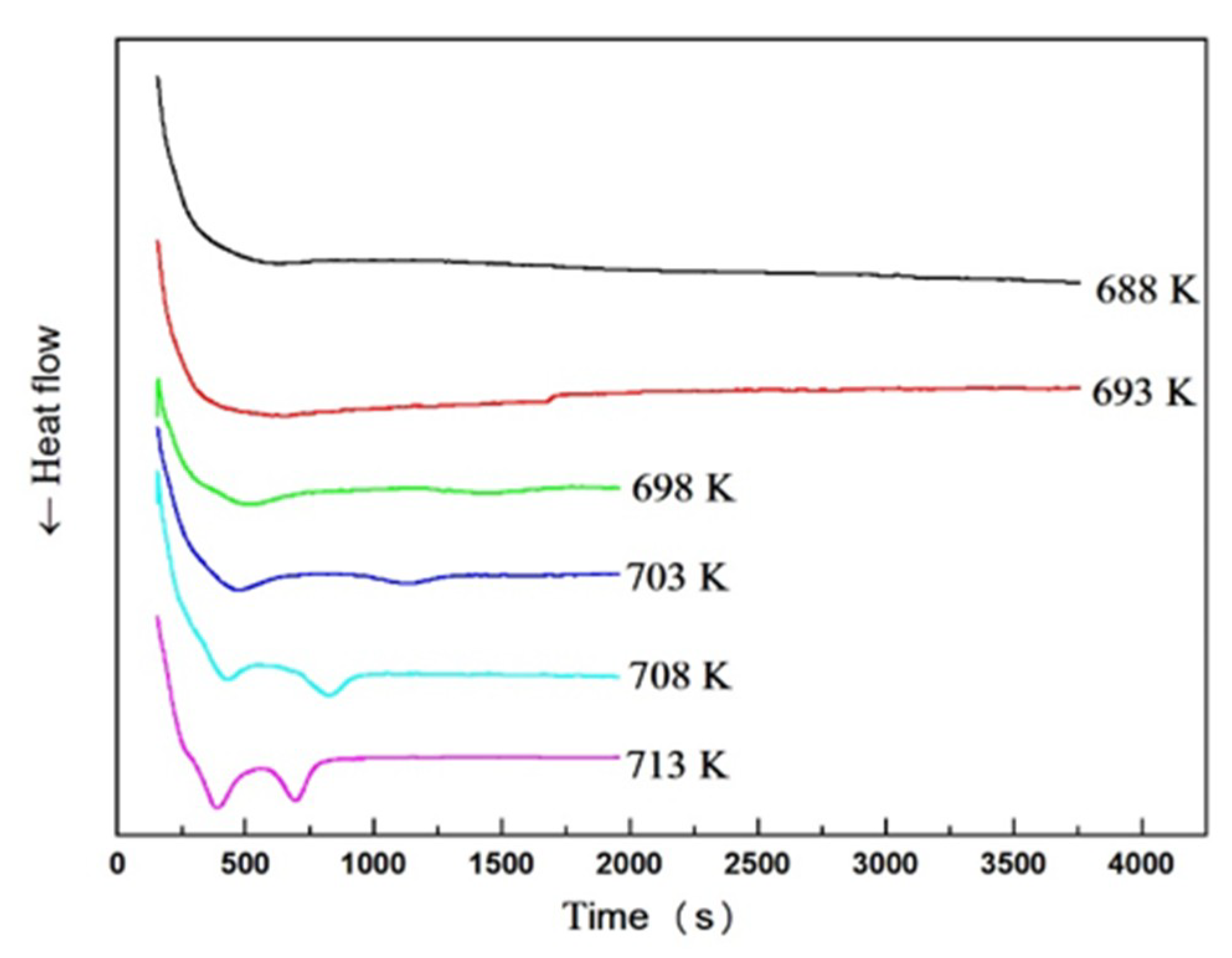


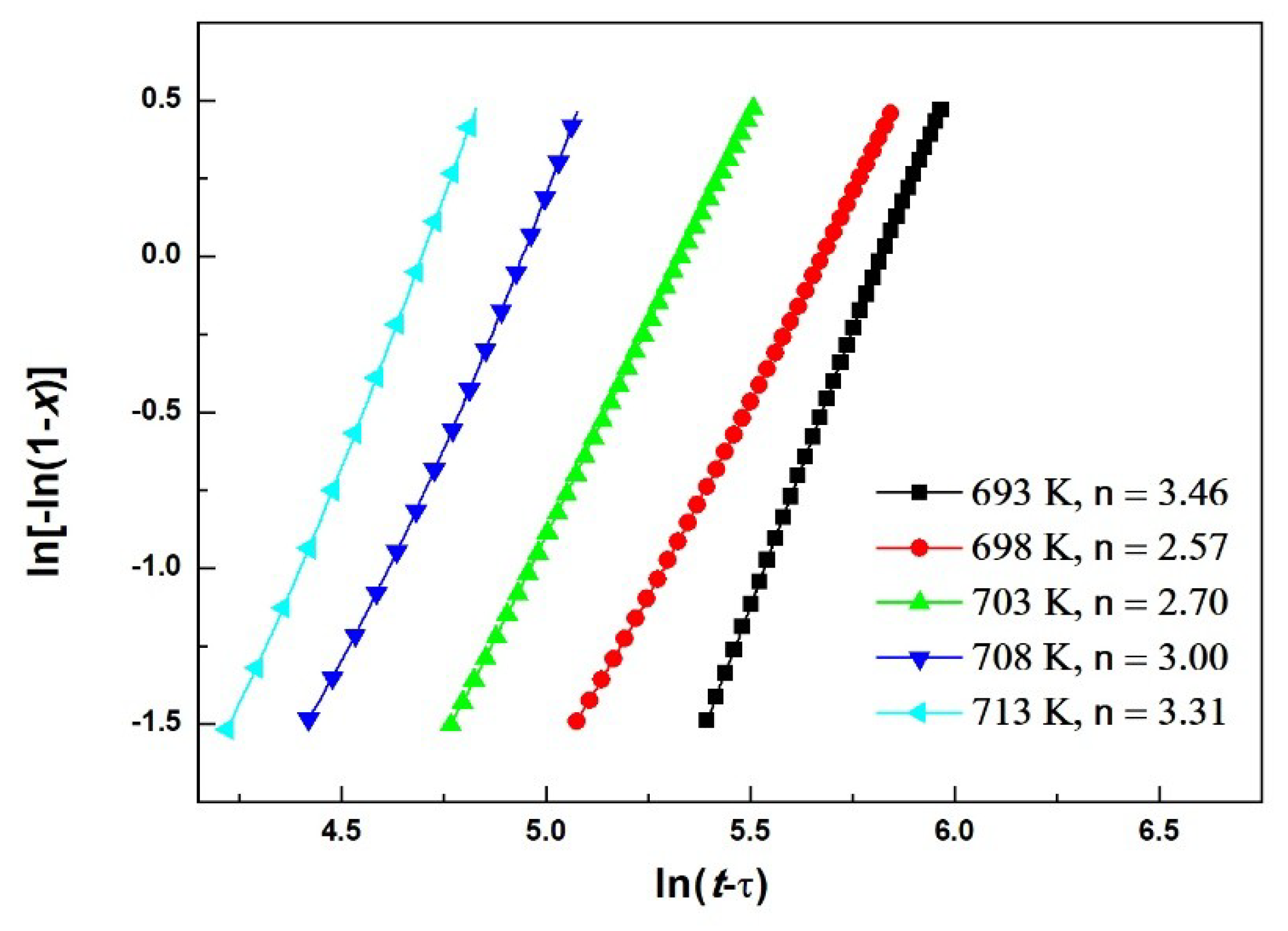
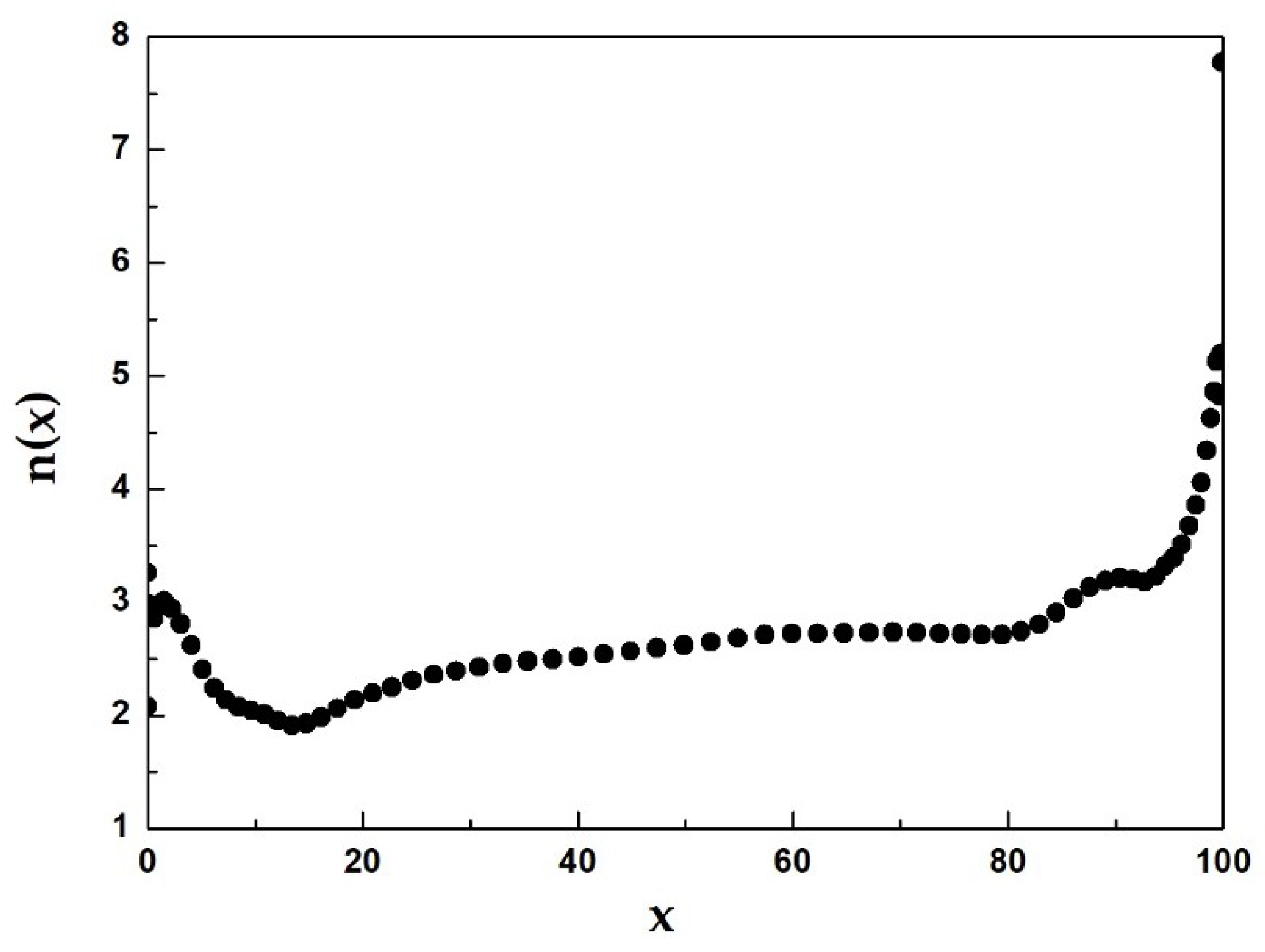
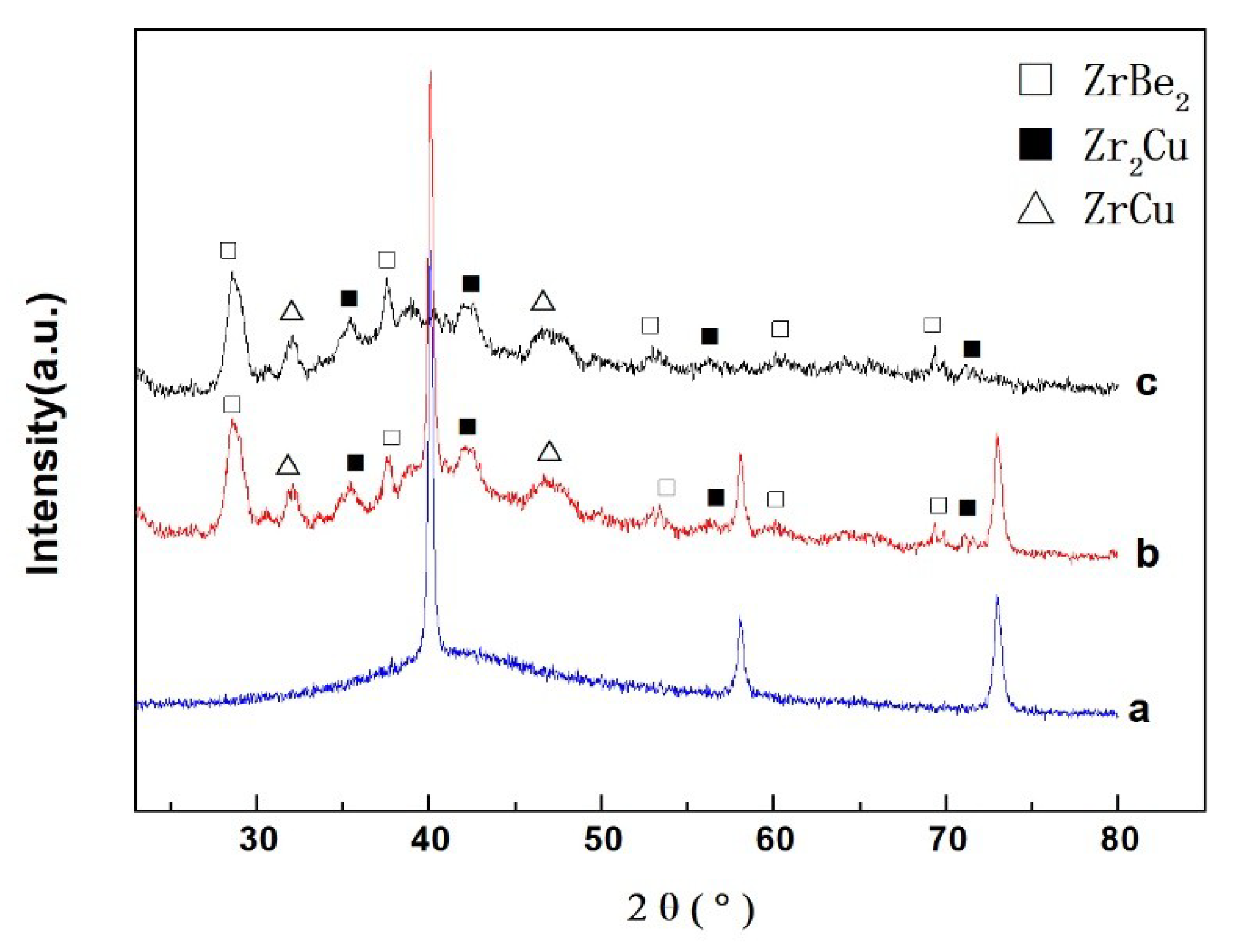
| Material | Heating Rates | Tg (K) | Tx (K) | ΔT (K) | Tp1 (K) | Tp2 (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic glass Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 | 10 K/min | 618 ± 0.5 | 682 ± 0.5 | 64 | 695 ± 0.5 | 726 ± 0.5 |
| 20 K/min | 622 ± 0.5 | 696 ± 0.5 | 74 | 714 ± 0.5 | 736 ± 0.5 | |
| 40 K/min | 629 ± 0.5 | 715 ± 0.5 | 86 | 729 ± 0.5 | 748 ± 0.5 | |
| 80 K/min | 640 ± 0.5 | 731 ± 0.5 | 91 | 744 ± 0.5 | 766 ± 0.5 | |
| W particles/Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 metallic glass matrix composite | 10 K/min | 613 ± 0.5 | 695 ± 0.5 | 82 | 712 ± 0.5 | 738 ± 0.5 |
| 20 K/min | 625 ± 0.5 | 716 ± 0.5 | 91 | 726 ± 0.5 | 750 ± 0.5 | |
| 40 K/min | 633 ± 0.5 | 727 ± 0.5 | 94 | 740 ± 0.5 | 761 ± 0.5 | |
| 80 K/min | 644 ± 0.5 | 740 ± 0.5 | 96 | 760 ± 0.5 | 779 ± 0.5 |
| Material | Eg (kJ/mol) | Ex (kJ/mol) | Ep1 (kJ/mol) | Ep2 (kJ/mol) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | Error | Value | Error | Value | Error | Value | Error | |
| Metallic glass Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 | 288.8 | 5.28% | 161.8 | 0.60% | 170.5 | 1.15% | 225.5 | 2.71% |
| W particles/Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 metallic glass matrix composite | 213.4 | 1.51% | 185.3 | 0.61% | 172.7 | 1.17% | 233.8 | 2.60% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, X.; Hu, H.; Kong, X.; Lu, Z. Crystallization Kinetics of 50% W Particles/Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 Metallic Glass Matrix Composite. Metals 2018, 8, 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8121011
Su X, Hu H, Kong X, Lu Z. Crystallization Kinetics of 50% W Particles/Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 Metallic Glass Matrix Composite. Metals. 2018; 8(12):1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8121011
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Xiaohong, Huie Hu, Xiaodong Kong, and Zhou Lu. 2018. "Crystallization Kinetics of 50% W Particles/Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 Metallic Glass Matrix Composite" Metals 8, no. 12: 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8121011
APA StyleSu, X., Hu, H., Kong, X., & Lu, Z. (2018). Crystallization Kinetics of 50% W Particles/Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 Metallic Glass Matrix Composite. Metals, 8(12), 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8121011





