Machining Performance of TiAlN-Coated Cemented Carbide Tools with Chip Groove in Machining Titanium Alloy Ti-6Al-0.6Cr-0.4Fe-0.4Si-0.01B
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Works
2.1. Workpiece Material
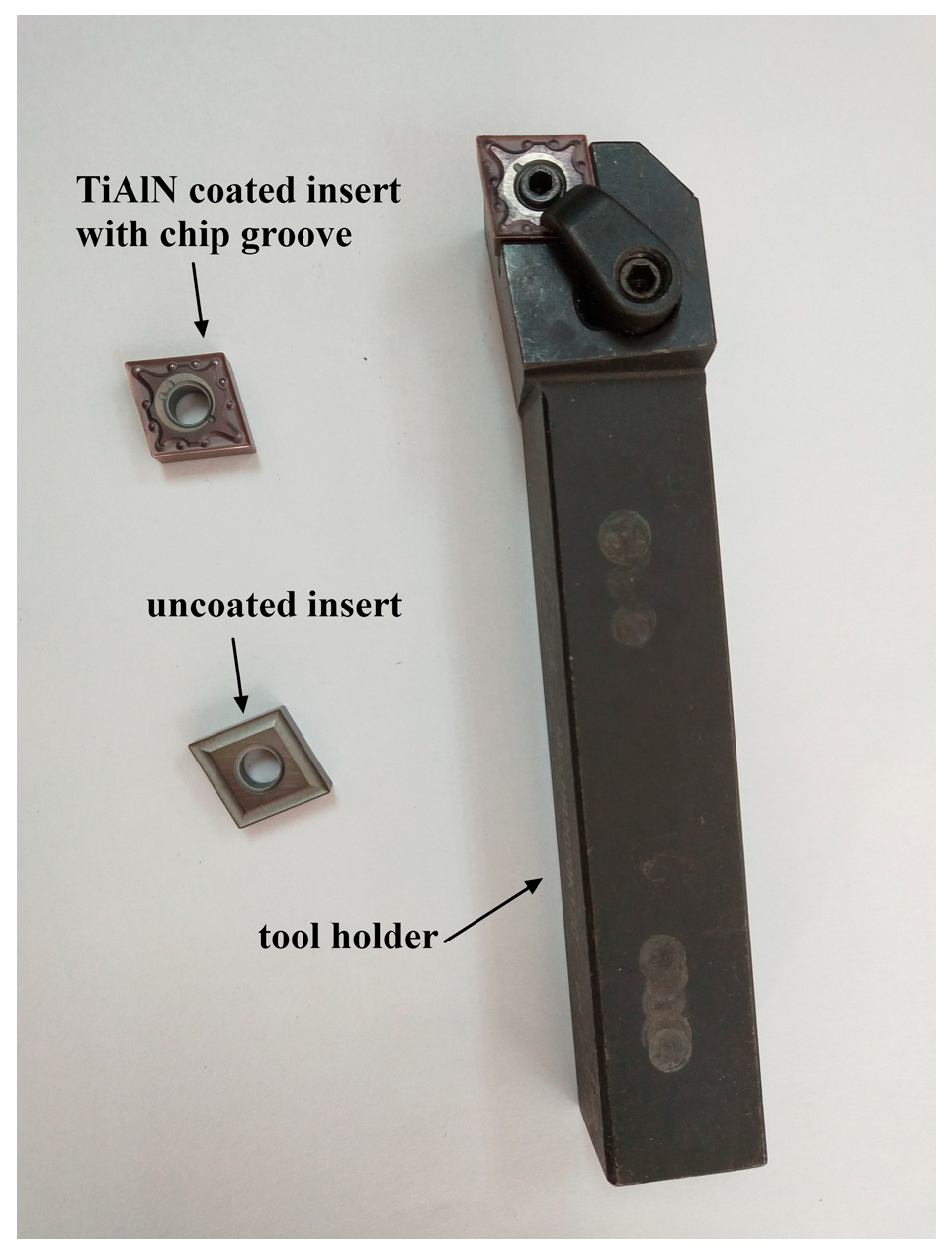
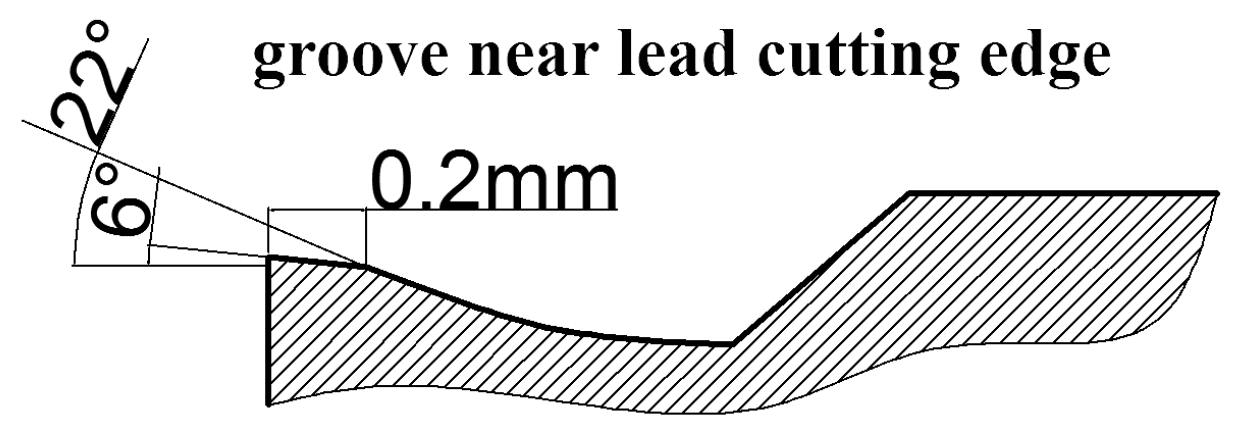
2.2. Cutting Tool
2.3. Machine Tool and Process Strategy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Wear Mechanisms of the Tool
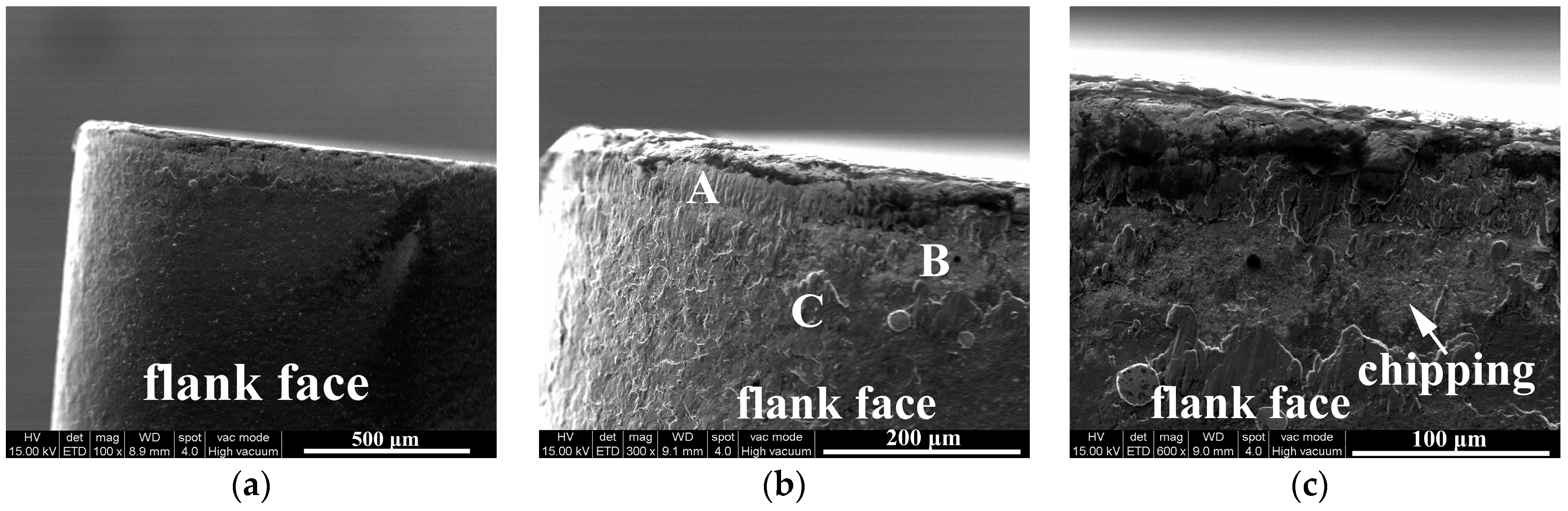
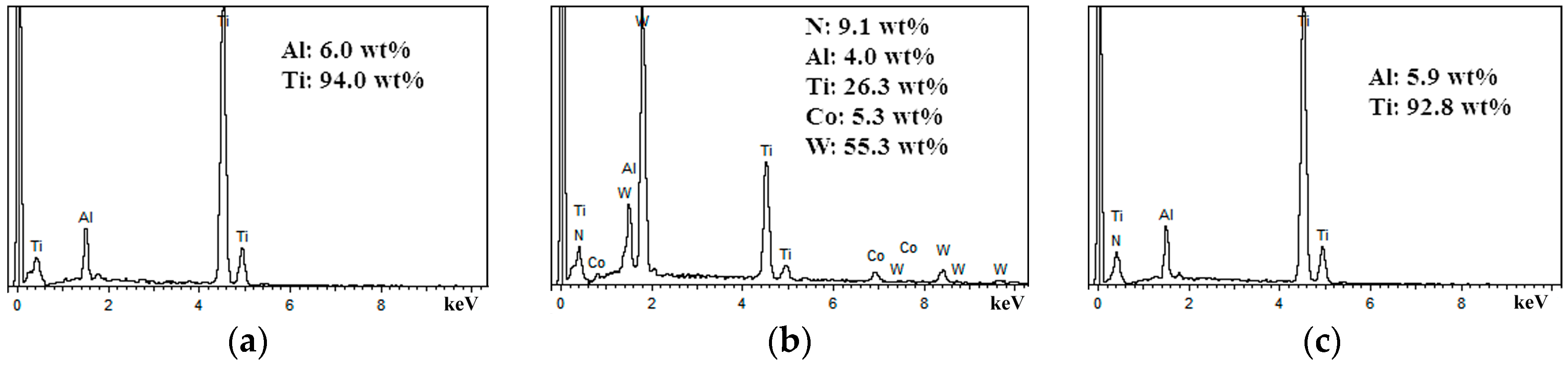
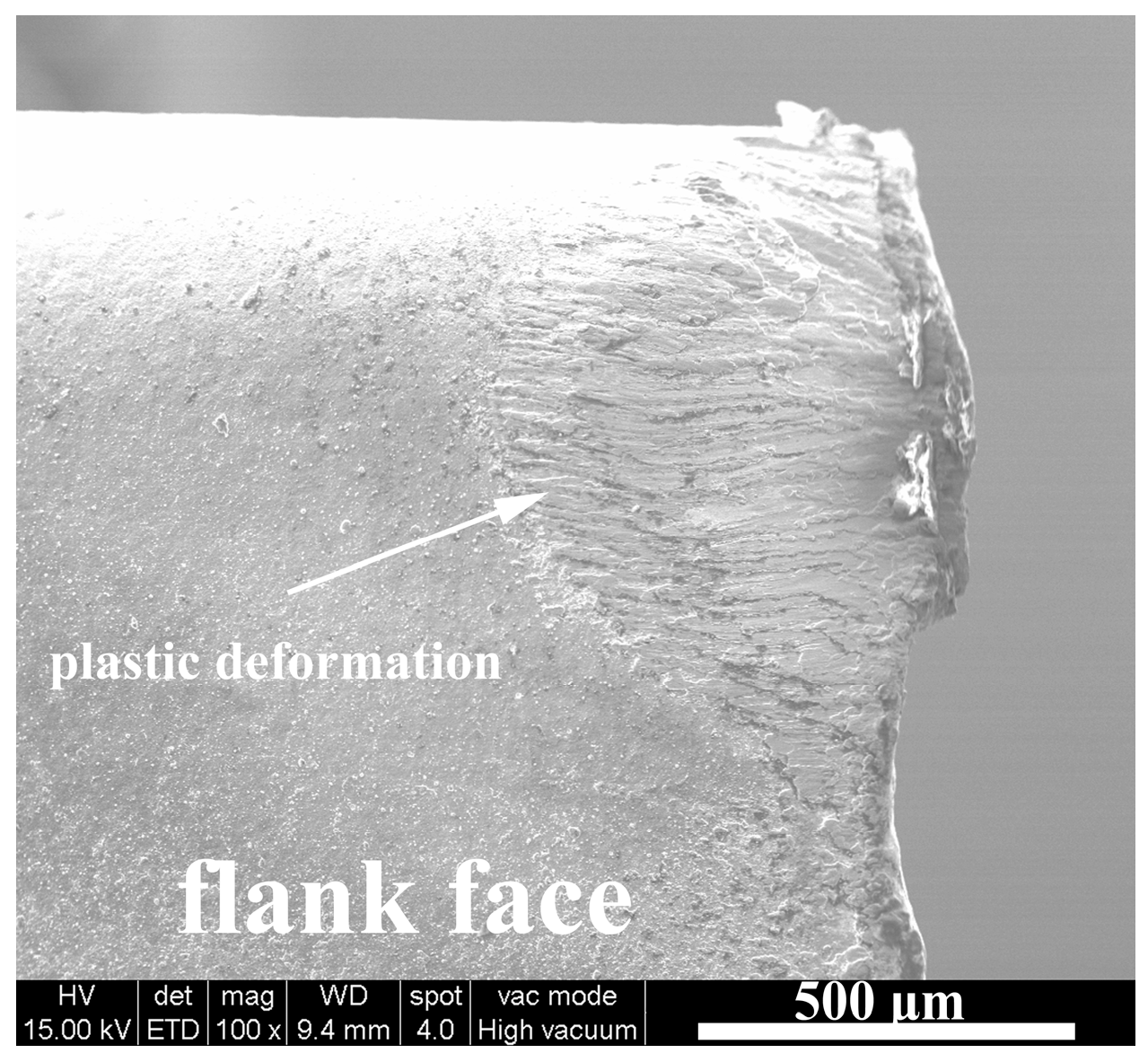
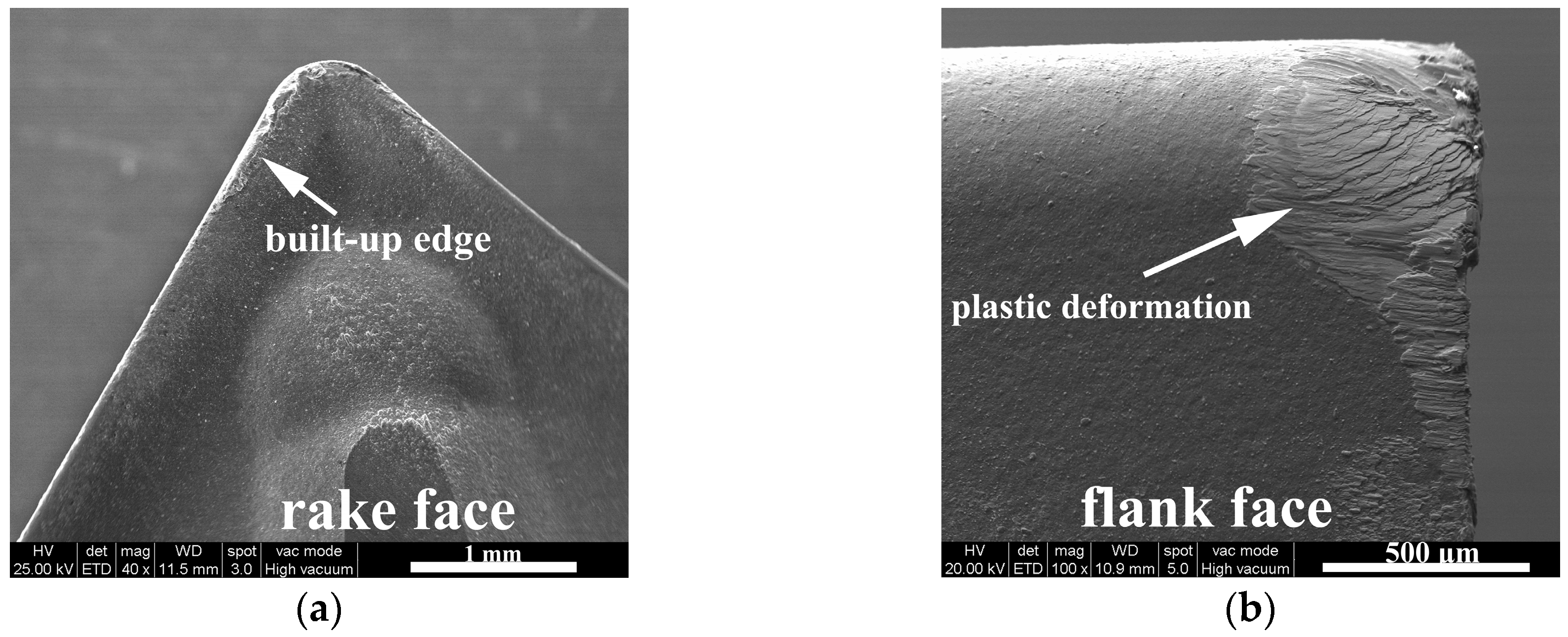
3.1.1. Flank Face Wear
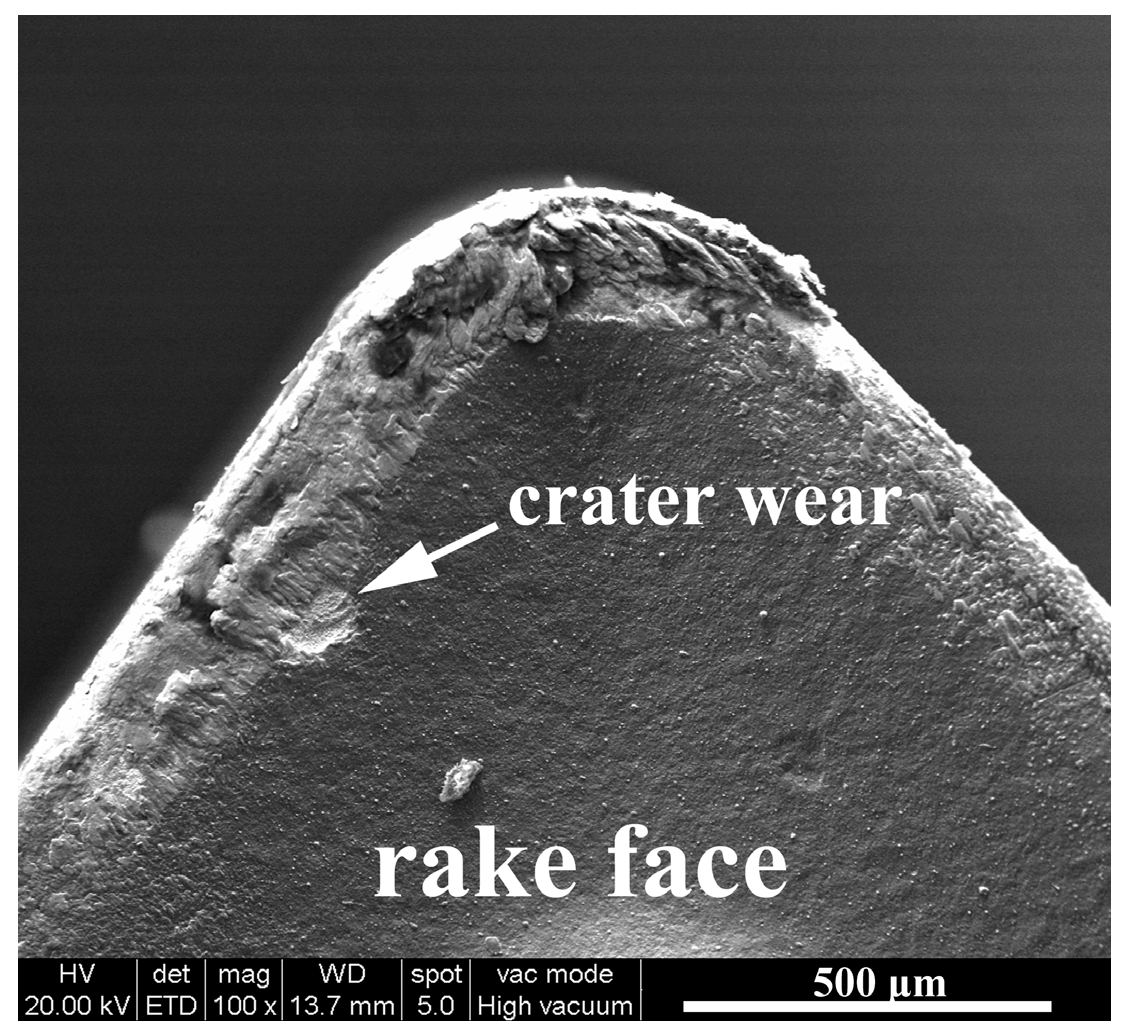
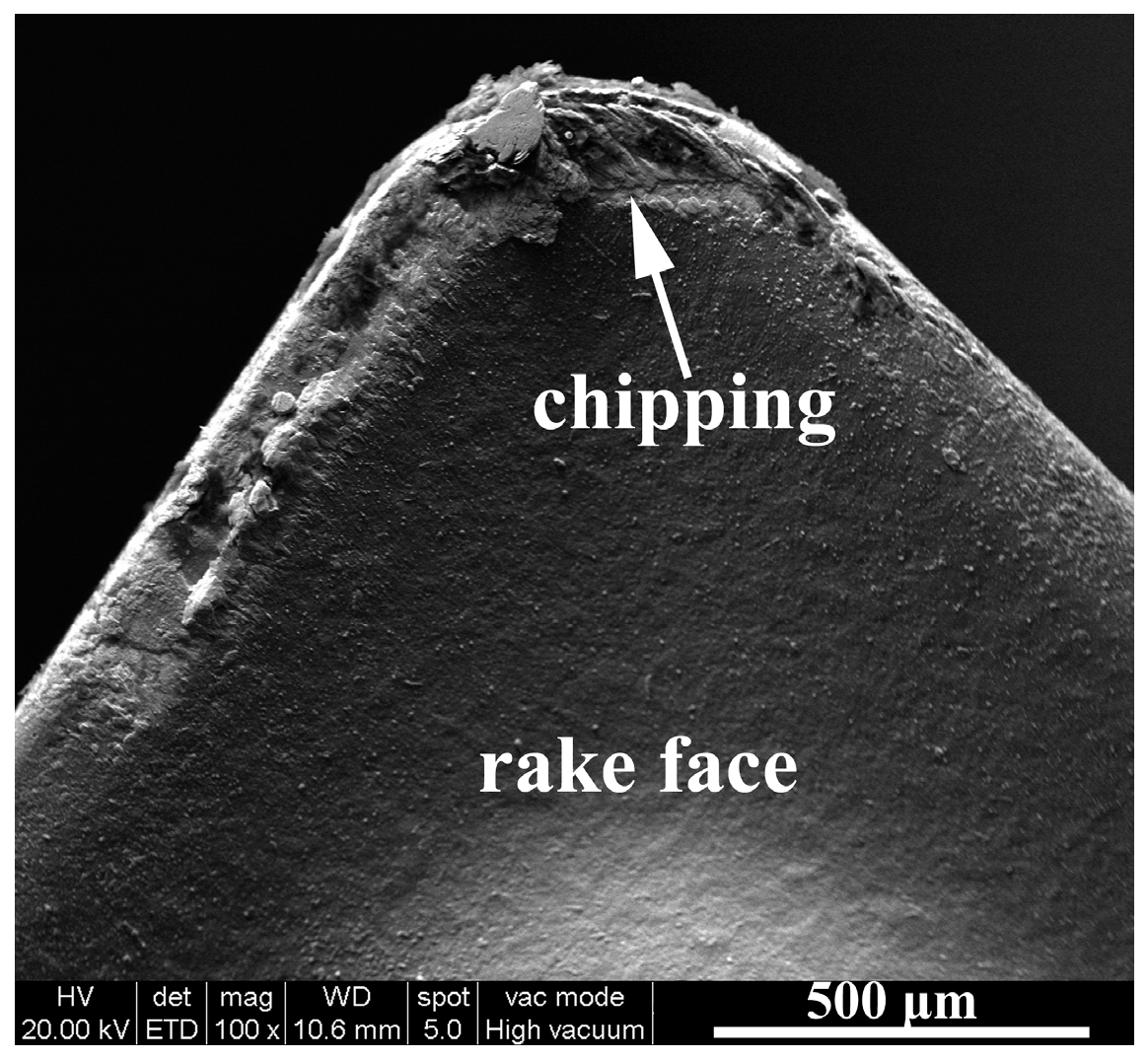
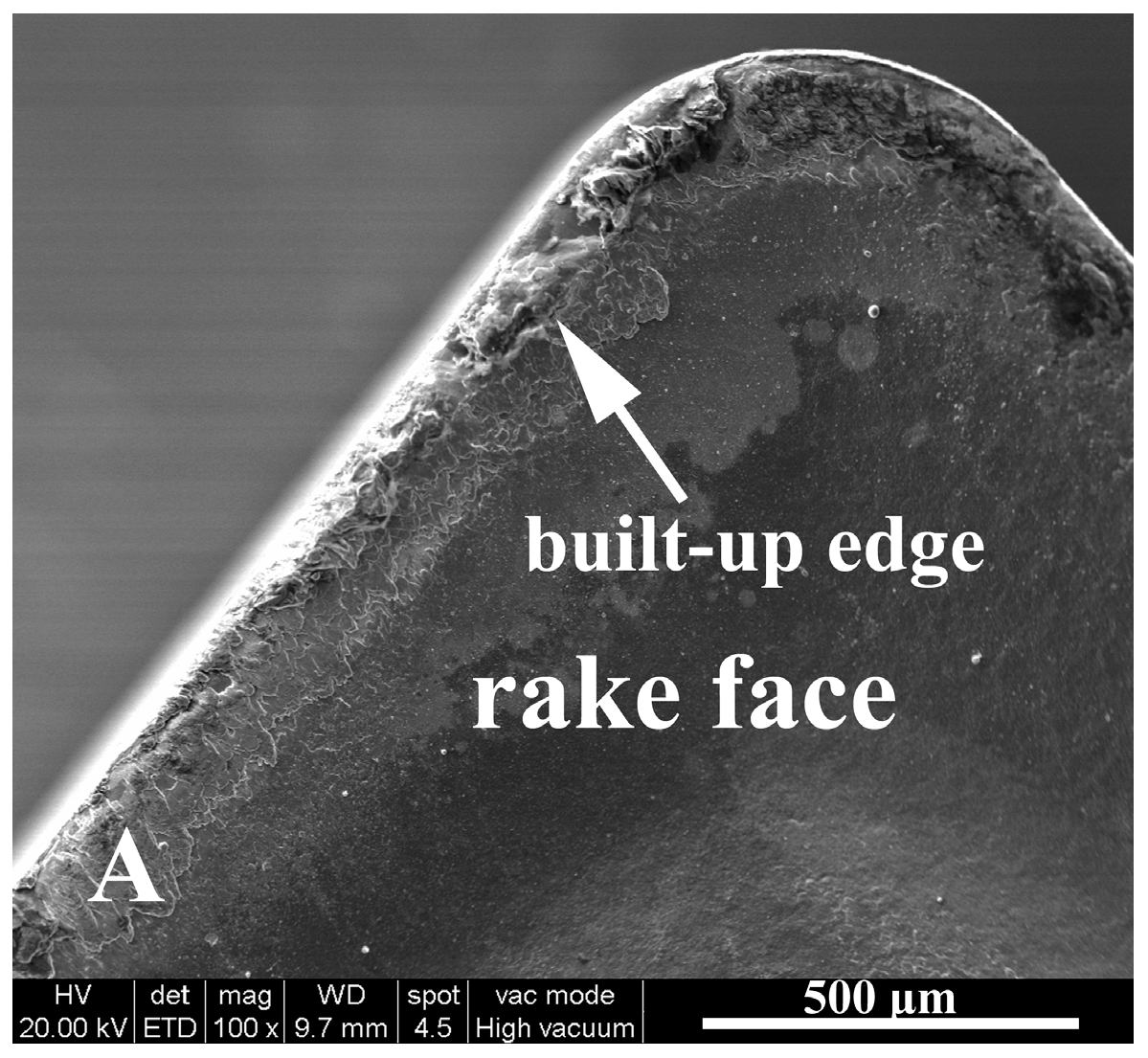
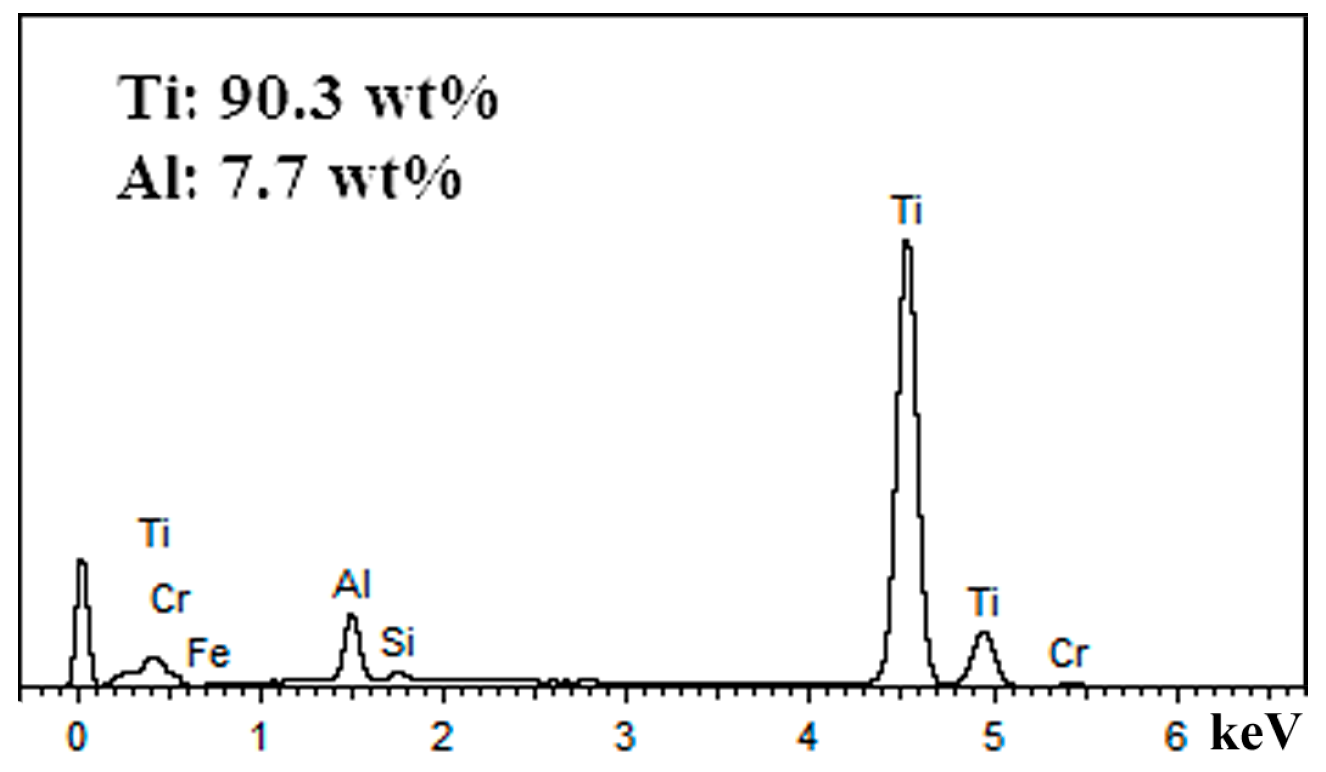
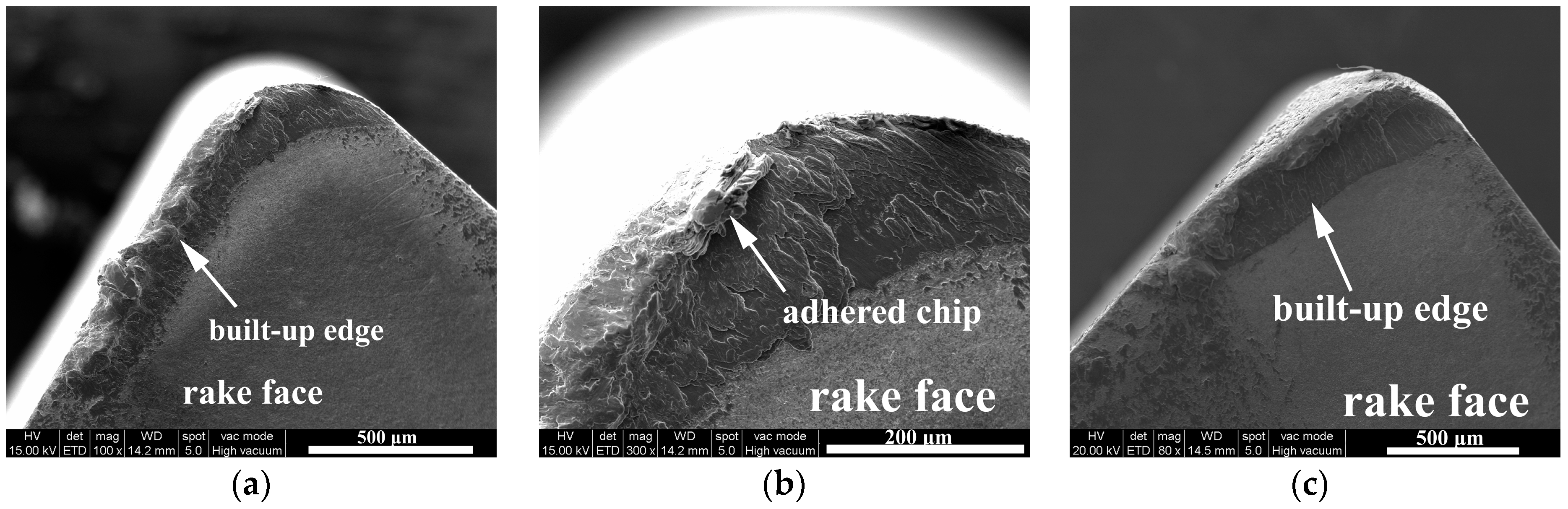
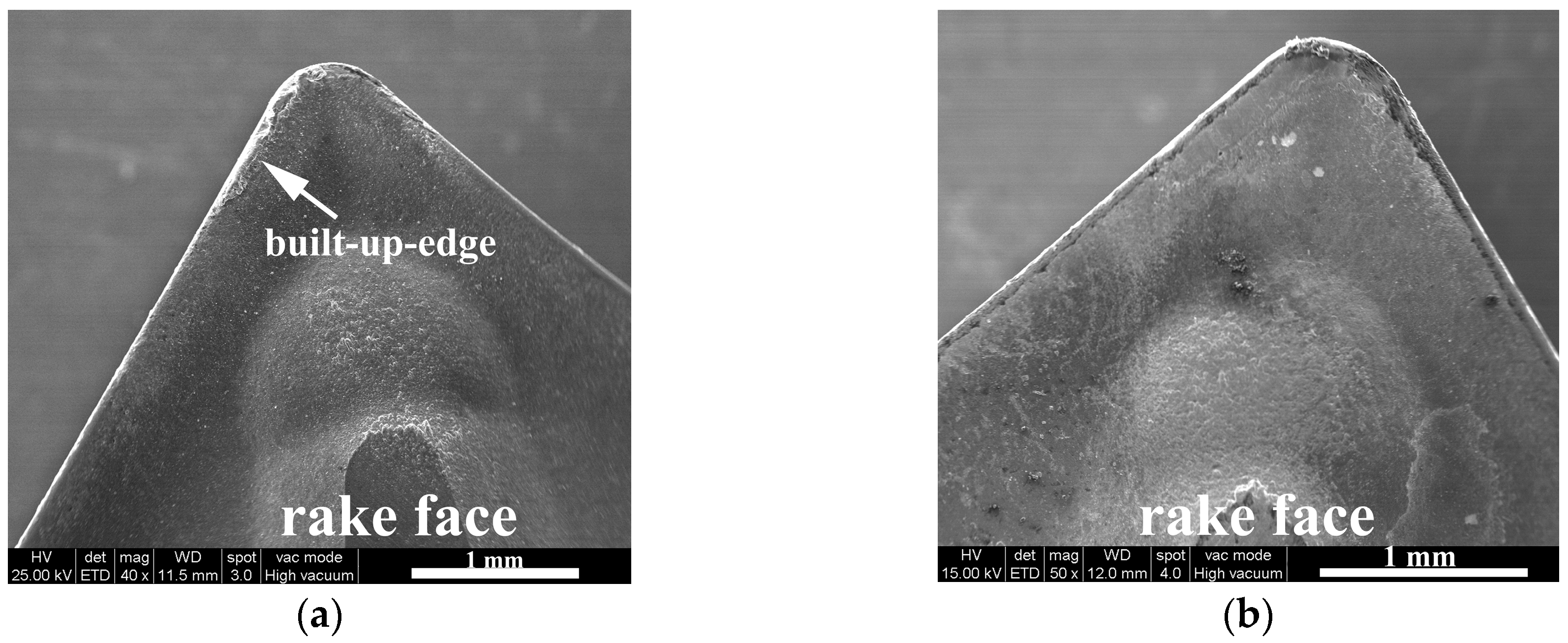
3.1.2. Rake Face Wear
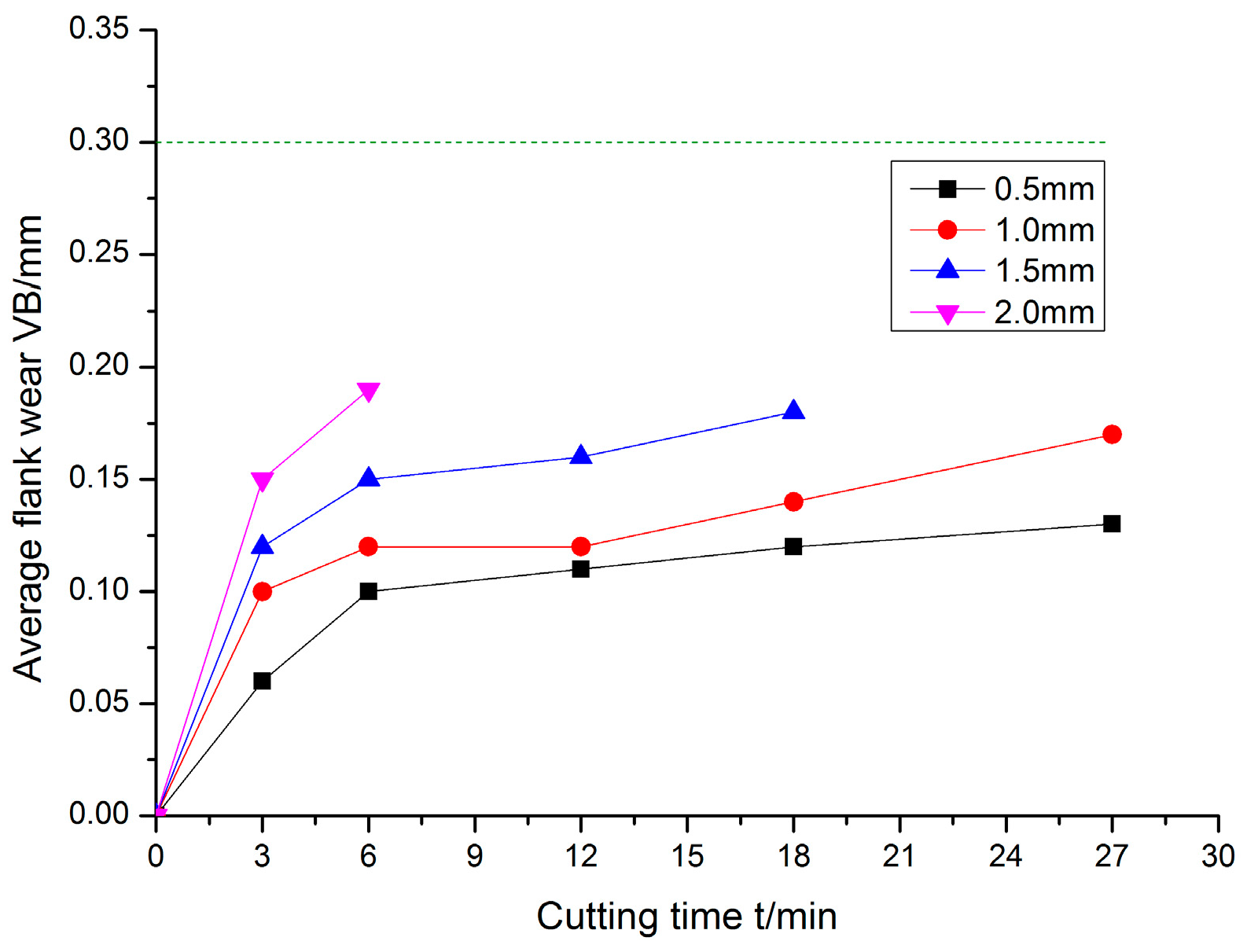
3.2. Influence of Cutting Parameters on Tool Life of TiAlN-Coated Cemented Carbide Tools
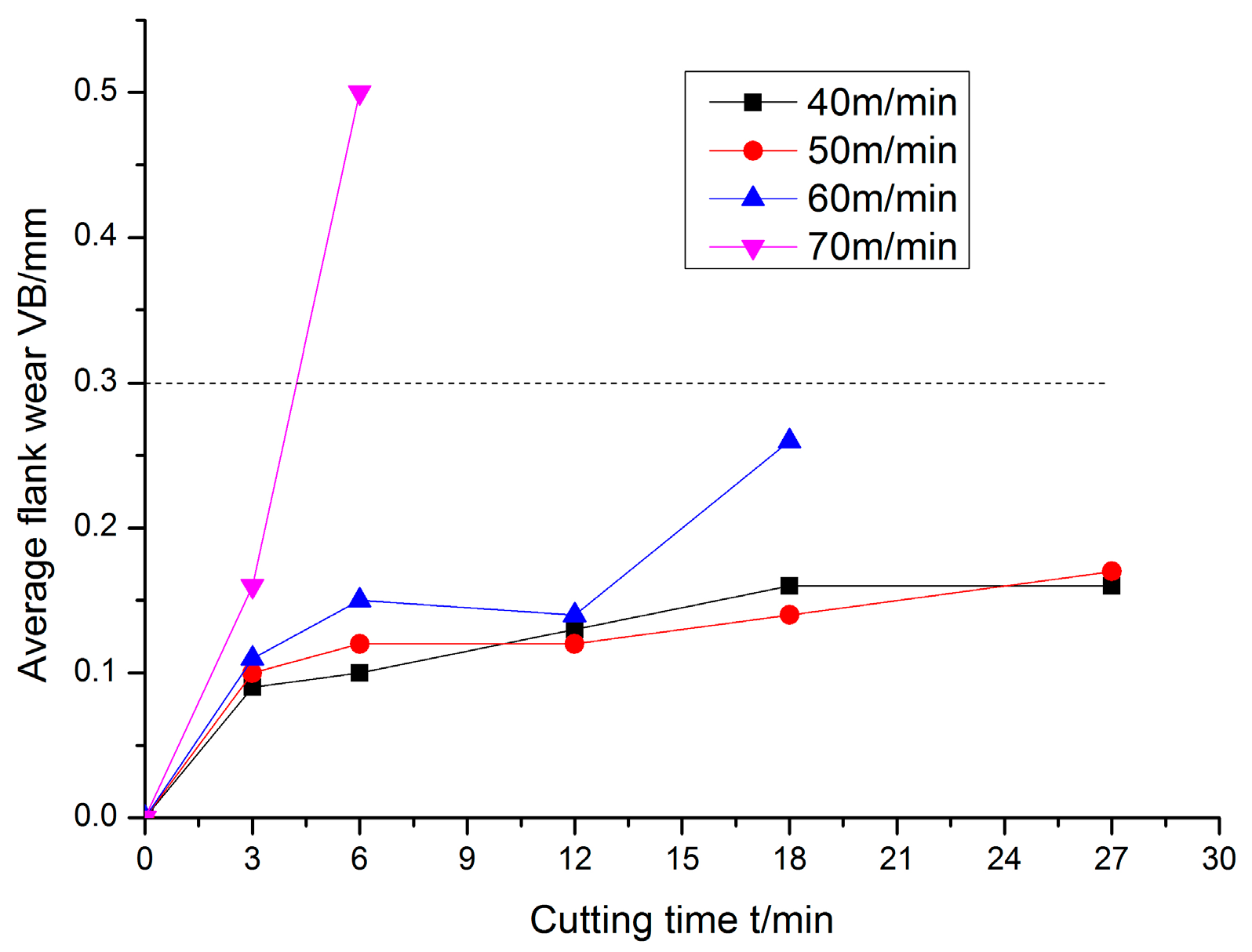
3.2.1. Influence of Cutting Speed
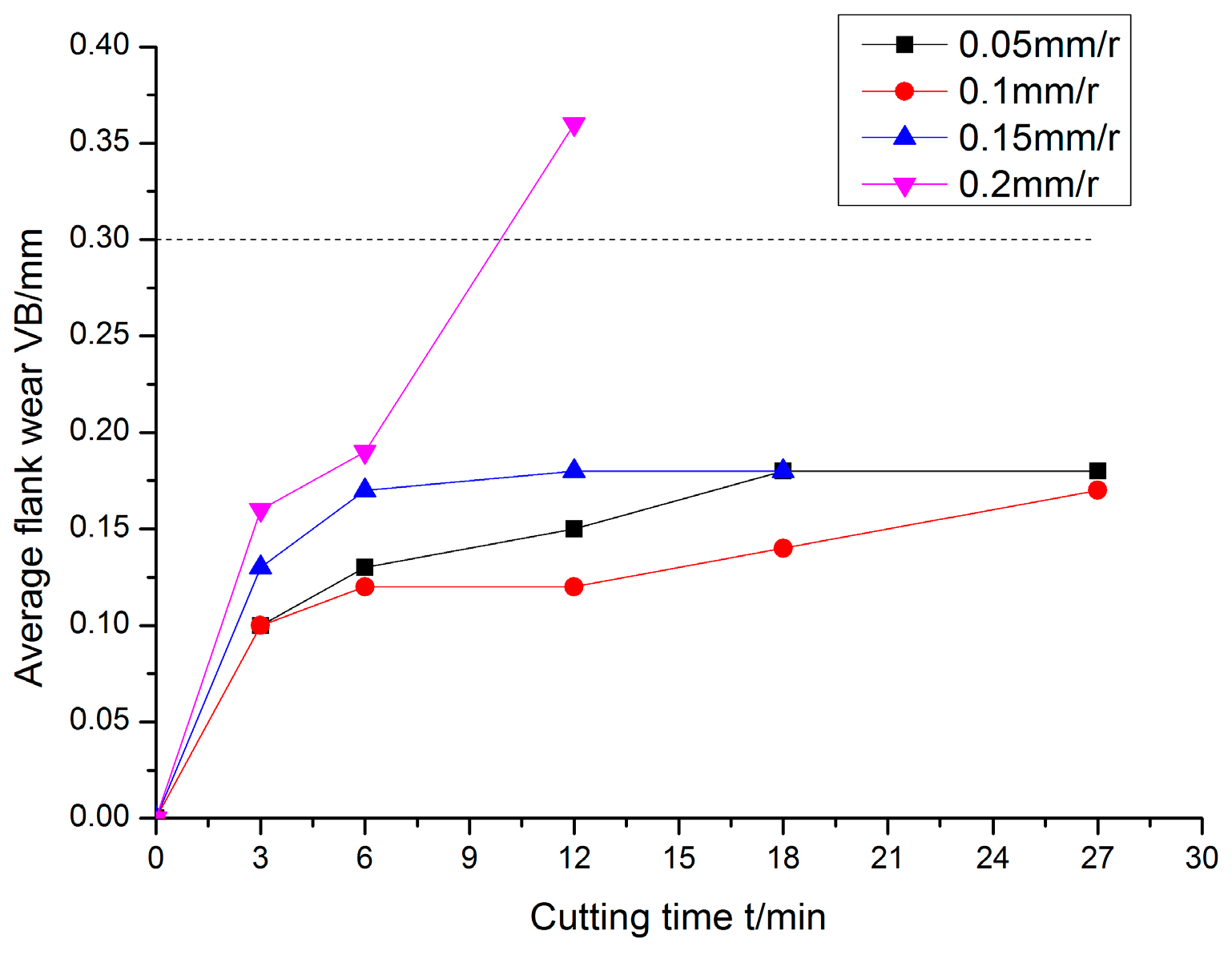
3.2.2. Influence of Feed Rate
3.2.3. Influence of the Depth of Cut
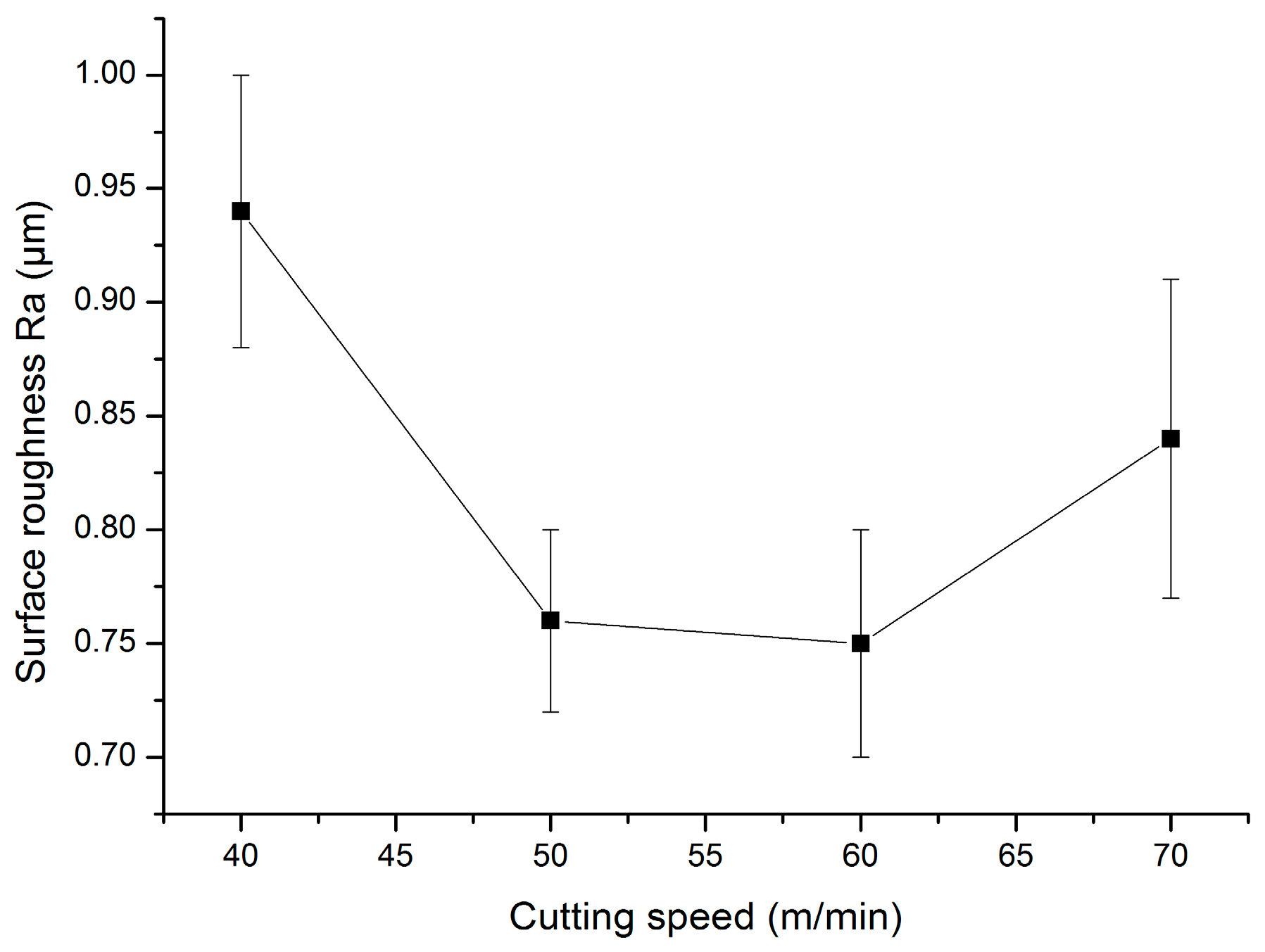
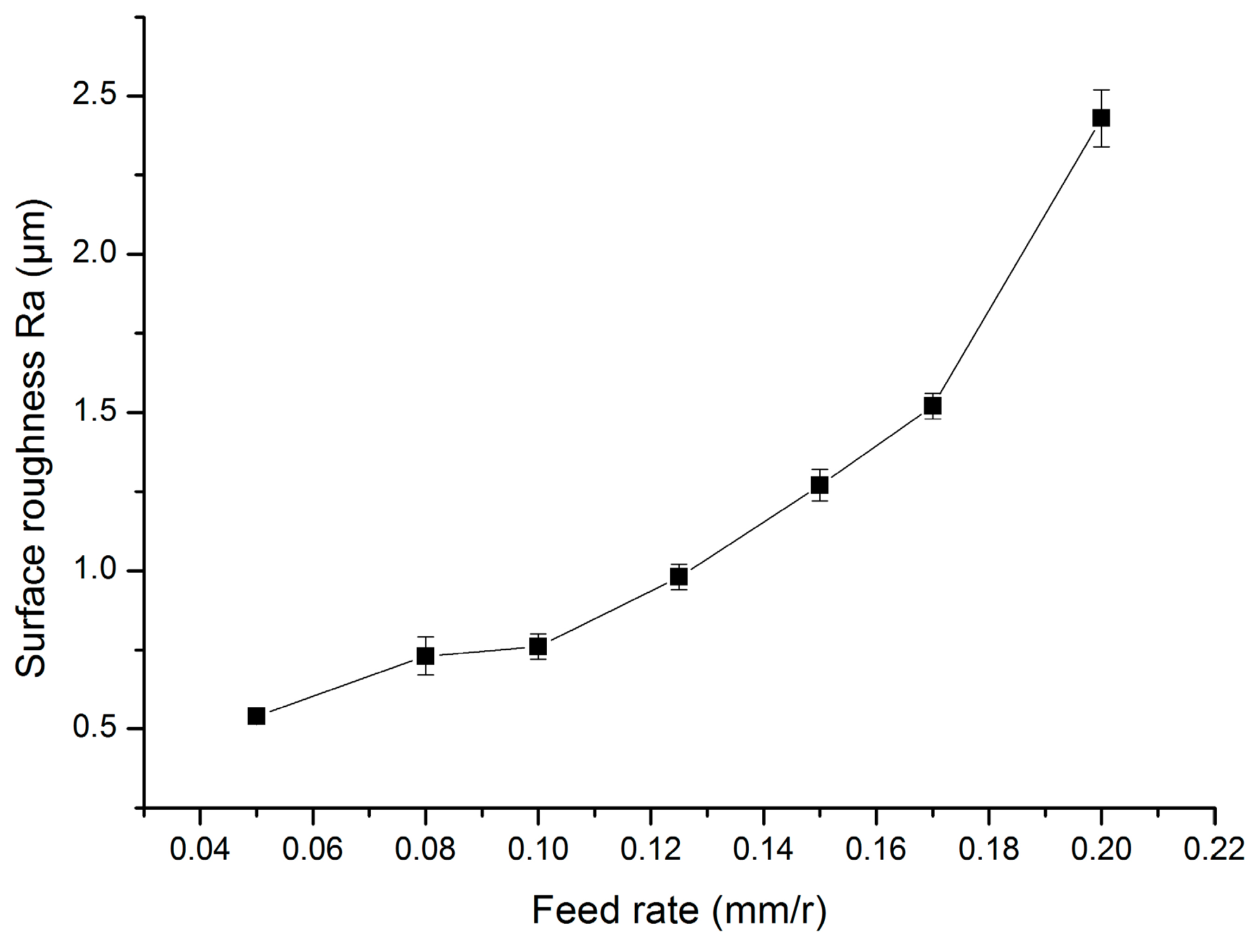
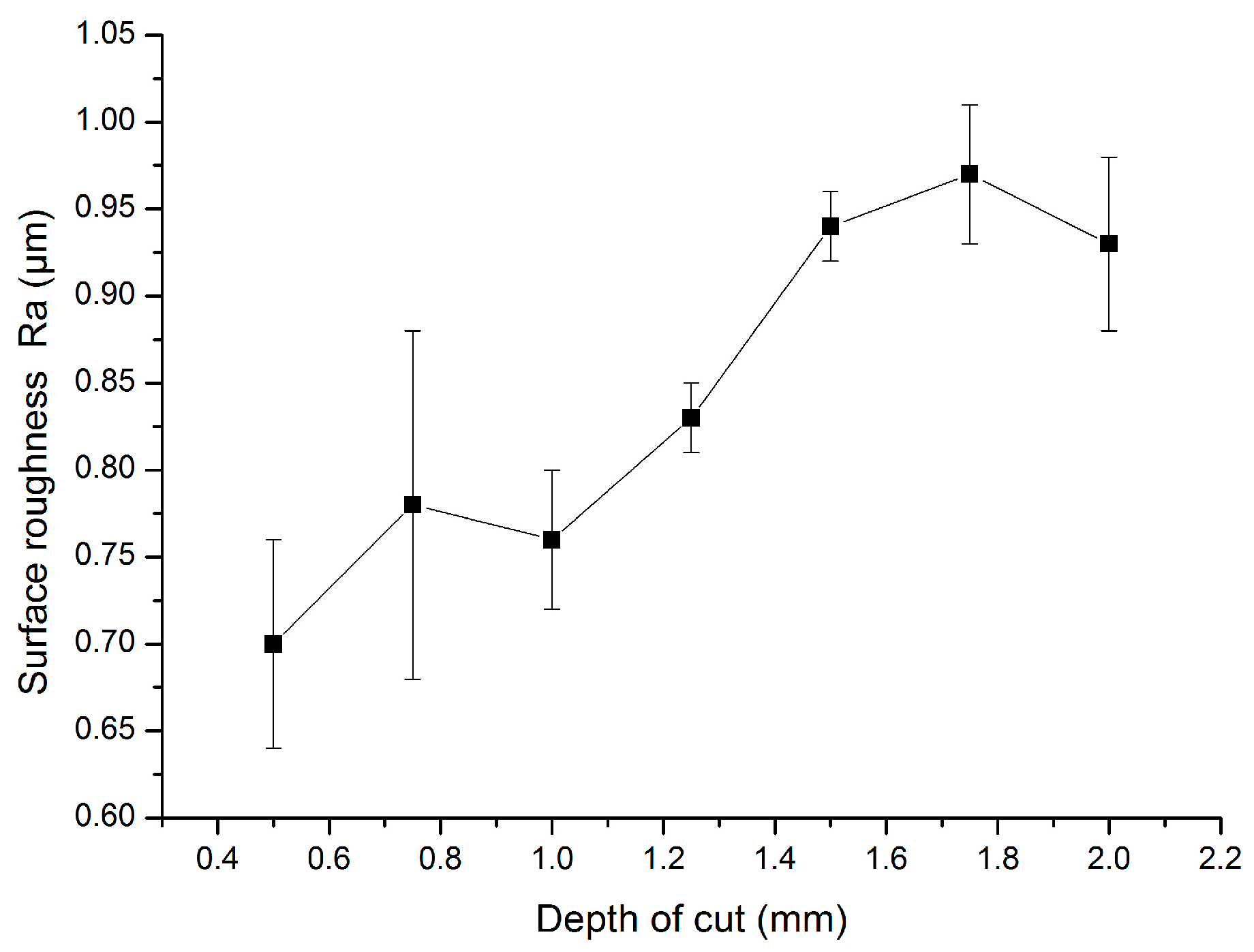
3.3. Influence of Cutting Parameters on Surface Roughness with TiAlN-Coated Cemented Carbide Tools
3.3.1. Influence of Cutting Speed
3.3.2. Influence of the Feed Rate
3.3.3. Influence of the Depth of Cut
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaffery, S.I.; Mativenga, P.T. Wear mechanisms analysis for turning Ti-6Al-4V—Towards the development of suitable tool coatings. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 58, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.X.; Li, Y.S.; Song, W.L. Diffusion wear in dry cutting of Ti-6Al-4V with WC/Co carbide tools. Wear 2008, 265, 1776–1783. [Google Scholar]
- Ruggiero, A.; D’Amato, R.; Gómez, E.; Merola, M. Experimental comparison on tribological pairs UHMWPE/TIAL6V4 alloy, UHMWPE/AISI316L austenitic stainless and UHMWPE/Al2O3 ceramic, under dry and lubricated conditions. Tribol. Int. 2016, 96, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, A.; D’Amato, R.; Gómez, E. Experimental analysis of tribological behavior of UHMWPE against AISI420C and against TiAl6V4 alloy under dry and lubricated conditions. Tribol. Int. 2015, 92, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.S.; Sun, J.F.; Chen, W.Y.; Wang, T.M. Wear mechanisms of WC/Co tools when machining high-strength titanium alloy TB6 (Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al). Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 90, 2863–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, M.D.; Sehgal, R. Experimental Study of Machining Characteristics of Titanium Alloy (Ti–6Al–4V). Arabian J. Sci. Eng. 2012, 38, 3201–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, S.; Moro, L.; Ghiotti, A.; Bruschi, S. On the tool wear mechanisms in dry and cryogenic turning Additive Manufactured titanium alloys. Tribol. Int. 2017, 105, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, A. Problems and solutions in machining of titanium alloys. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 70, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, J.F.; Deng, J.X.; Li, Y.S. Investigation on diffusion wear during high-speed machining Ti-6Al-4V alloy with straight tungsten carbide tools. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2008, 44, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; An, Q.; Xu, J.; Chen, M.; Han, S. Wear performance of (nc-AlTiN)/(a-Si3N4) coating and (nc-AlCrN)/(a-Si3N4) coating in high-speed machining of titanium alloys under dry and minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) conditions. Wear 2013, 305, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginting, A.; Nouari, M. Surface integrity of dry machined titanium alloys. Int. J. Mach. Tool Manuf. 2009, 49, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goindi, G.S.; Sarkar, P. Dry machining: A step towards sustainable machining–challenges and future directions. J. Clean Prod. 2017, 165, 1557–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, K.A.; Paul, S.; Chattopadhyay, A.B. Tool wear in cryogenic turning of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Cryogenics 2007, 47, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.Y.; Lai, H.M. Wear behavior and cutting performance of CrAlSiN and TiAlSiN hard coatings on cemented carbide cutting tools for Ti alloys. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 259, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaynak, Y.; Karaca, H.E.; Noebe, R.D.; Jawahir, I.S. Tool-wear analysis in cryogenic machining of NiTi shape memory alloys: A comparison of tool-wear performance with dry and MQL machining. Wear 2013, 306, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Meng, Q.S.; Zhuang, L.; Chen, S.P.; Dai, J.J. Oxidation behavior of AlMgB14-TiB2 composite at elevated temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 347, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B.A.; Harringa, J.L.; Anderegg, J.; Russell, A.M.; Qu, J.; Blau, P.J.; Higdon, C.; Elmoursi, A.A. Analysis of wear mechanisms in low-friction AlMgB14-TiB2 coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, 2296–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouari, M.; Makich, H. Experimental investigation on the effect of the material microstructure on tool wear when machining hard titanium alloys: Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-555. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2013, 41, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, Y.H.; Kilickap, E.; Güney, M. Investigation of cutting parameters affecting on tool wear and surface roughness in dry turning of Ti-6Al-4V using CVD and PVD coated tools. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2016, 39, 2085–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.Y.; Liu, G.J.; Li, G.H. Experimental study on adhesive wear of milling insert with complex groove. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2009, 44, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanigarathne, P.C.; Kardekar, A.D.; Dillon, O.W.; Poulachon, G.; Jawahir, I.S. Progressive tool-wear in machining with coated grooved tools and its correlation with cutting temperature. Wear 2005, 259, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawahir, I.S.; Ghosh, R.; Fang, X.D.; Li, P.X. An investigation of the effects of chip flow on tool-wear in machining with complex grooved tools. Wear 1995, 184, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawahir, I.S.; Li, P.X.; Gosh, R.; Exner, E.L. A New parametric approach for the assessment of comprehensive tool wear in coated grooved tools. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 1995, 44, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ee, K.C.; Balaji, A.K.; Li, P.X.; Jawahir, I.S. Force decomposition model for tool-wear in turningwith grooved cutting tools. Wear 2002, 249, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.B.D.; Braga, D.U.; Nevez, F.O.; Da Silva, A.S.C. Analysis of surface roughness and cutting force when turning AISI 1045 steel with grooved tools through Scott–Knott method. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 69, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayed, Y.; Germain, G.; Ammar, A.; Furet, B. Degradation modes and tool wear mechanisms in finish and rough machining of Ti17 Titanium alloy under high-pressure water jet assistance. Wear 2013, 305, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, K.A.; Paul, S.; Chattopadhyay, A.B. Growth of tool wear in turning of Ti-6Al-4V alloy under cryogenic cooling. Wear 2007, 262, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, V.; Baili, M.; Dessein, G. The relationship between the cutting speed, tool wear, and chip formation during Ti-5553 dry cutting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 76, 893–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawaid, A.; Sharif, S.; Koksal, S. Evaluation of wear mechanisms of coated carbide tools when face milling titanium alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2000, 99, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareena, A.R.; Veldhuis, S.C. Tool wear mechanisms and tool life enhancement in ultra-precision machining of titanium. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.J.; Qu, S.; Pan, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, C. Machining performance of a grooved tool in dry machining Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 73, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramana, M.V.; Aditya, Y.S. Optimization and influence of process parameters on surface roughness in turning of titanium alloy. Mate. Today Proceed. 2017, 4, 1843–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, R.R.; Da Silva, M.B.; Machado, Á.R.; Sales, W.F. The effect of application of cutting fluid with solid lubricant in suspension during cutting of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Wear 2015, 332, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phapale, K.; Patil, S.; Kekade, S.; Jadhav, S.; Powar, A.; Supare, A.; Singh, R.K.P. Tool wear investigation in dry and high pressure coolant assisted machining of titanium alloy Ti6Al4V with variable α and β volume fraction. Procedia Manuf. 2016, 6, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffery, S.I.; Mativenga, P.T. Assessment of the machinability of Ti-6Al-4V alloy using the wear map approach. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2008, 40, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman Rashid, R.A.; Palanisamy, S.; Sun, S.; Dargusch, M.S. Tool wear mechanisms involved in crater formation on uncoated carbide tool when machining Ti6Al4V alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 83, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetan; Behera, B.C.; Ghosh, S.; Rao, P.V. Wear behavior of PVD TiN coated carbide inserts during machining of Nimonic 90 and Ti6Al4V superalloys under dry and MQL conditions. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 14873–14885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.J.; Brandt, M.; Palanisamy, S.; Dargusch, M.S. Effect of cryogenic compressed air on the evolution of cutting force and tool wear during machining of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 221, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliaei, S.N.B.; Karpat, Y. Investigating the influence of built-up edge on forces and surface roughness in micro scale orthogonal machining of titanium alloy Ti6Al4V. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 235, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatt, O.; Crawforth, P.; Jackson, M. On the mechanism of tool crater wear during titanium alloy machining. Wear 2017, 374, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetan; Narasimhulu, A.; Ghosh, S.; Rao, P.V. Study of tool wear mechanisms and mathematical modeling of flank wear during machining of Ti alloy (Ti6Al4V). J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. C 2014, 96, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, X.T.; Mayer, J.R.R.; Balazinski, M. Initial tool wear behavior during machining of titanium metal matrix composite (TiMMCs). Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2016, 60, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che-Haron, C.H. Tool life and surface integrity in turning titanium alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2001, 118, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawaid, A.; Che-Haron, C.H.; Abdullah, A. Tool wear characteristics in turning of titanium alloy Ti-6246. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1999, 92, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astakhov, V.P. Effects of the cutting feed, depth of cut, and workpiece (bore) diameter on the tool wear rate. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2006, 34, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ee, K.C.; Li, P.X.; Balaji, A.K.; Jawahir, I.S.; Stevenson, R. Performance-based predictive models and optimization methods for turning operations and applications: Part 1-Tool wear/tool life in turning with coated grooved tools. J. Manuf. Process. 2006, 8, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.W.; Pervaiz, S.; Deiab, I. Tool wear patterns when turning of titanium alloy using sustainable lubrication strategies. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2014, 15, 1979–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithyanandam, J.; LalDas, S.; Palanikumar, K. Surface roughness analysis in turning of titanium alloy by nanocoated carbide insert. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 5, 2159–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helu, M.; Behmann, B.; Meier, H.; Dornfeld, D.; Lanza, G.; Schulze, V. Impact of green machining strategies on achieved surface quality. CIRP Annals Manuf. Technol. 2012, 61, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.; Karunamoorthy, L.; Palanikumar, K. Measurement and analysis of surface roughness in turning of aerospace titanium alloy (gr5). Measurement 2012, 45, 1266–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.F.; Lin, J.N.; Wu, D.X.; Ren, J.X. Surface integrity and fatigue behavior when turning γ-TiAl alloy with optimized PVD-coated carbide inserts. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2018, 31, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Element | Al | Ti | Cr | Fe | Si | B | C | H | O | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | 5.29 | 89.28 | 0.60 | 0.38 | 0.31 | 0.011 | 0.005 | <0.001 | 0.053 | 0.006 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Reduction of Cross-section Area (%) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio | Micro Hardness (HV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 810 | 910 | 12.8 | 30 | 113.7 | 0.296 | 360 |
| Relief Angle | Cutting Edge Angle | Minor Cutting Edge Angle | Nose Radius |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5° | 95° | 5° | 0.4 mm |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, Z.; Qu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, C. Machining Performance of TiAlN-Coated Cemented Carbide Tools with Chip Groove in Machining Titanium Alloy Ti-6Al-0.6Cr-0.4Fe-0.4Si-0.01B. Metals 2018, 8, 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8100850
Ren Z, Qu S, Zhang Y, Li X, Yang C. Machining Performance of TiAlN-Coated Cemented Carbide Tools with Chip Groove in Machining Titanium Alloy Ti-6Al-0.6Cr-0.4Fe-0.4Si-0.01B. Metals. 2018; 8(10):850. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8100850
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Zhaojun, Shengguan Qu, Yalong Zhang, Xiaoqiang Li, and Chao Yang. 2018. "Machining Performance of TiAlN-Coated Cemented Carbide Tools with Chip Groove in Machining Titanium Alloy Ti-6Al-0.6Cr-0.4Fe-0.4Si-0.01B" Metals 8, no. 10: 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8100850
APA StyleRen, Z., Qu, S., Zhang, Y., Li, X., & Yang, C. (2018). Machining Performance of TiAlN-Coated Cemented Carbide Tools with Chip Groove in Machining Titanium Alloy Ti-6Al-0.6Cr-0.4Fe-0.4Si-0.01B. Metals, 8(10), 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8100850






