Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti35421 Alloy: A Comparison Between Laser Directed Energy Deposition (L-DED) and Rolling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
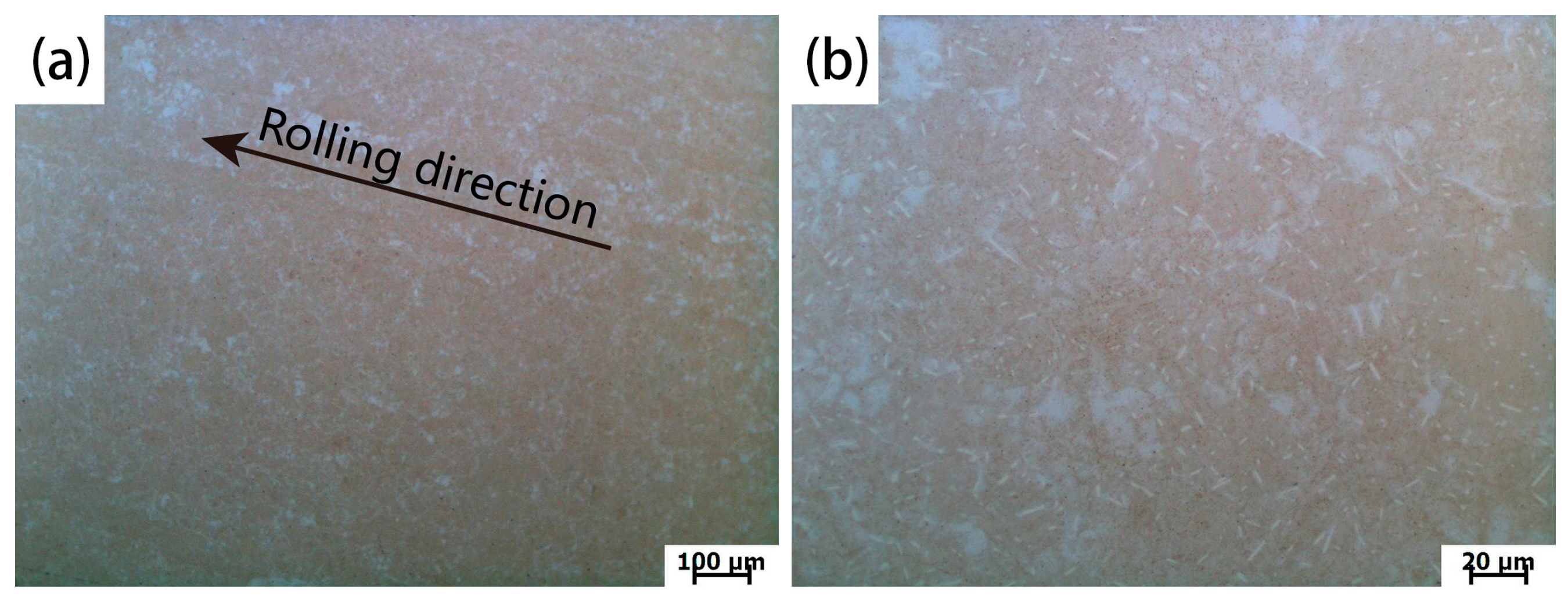
2.1. Material Preparation
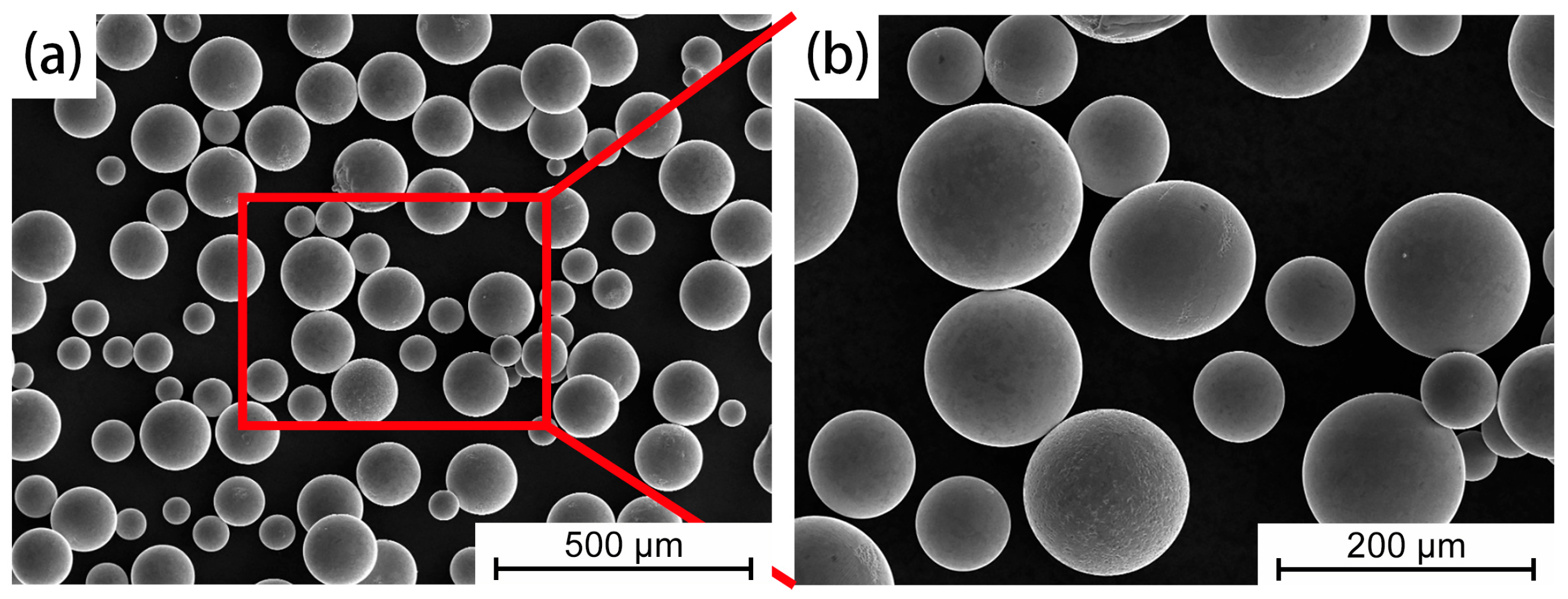
2.2. Laser Directed Energy Deposition
2.3. Heat Treatment
2.4. Microstructure Characterization
2.5. Mechanical Properties Testing
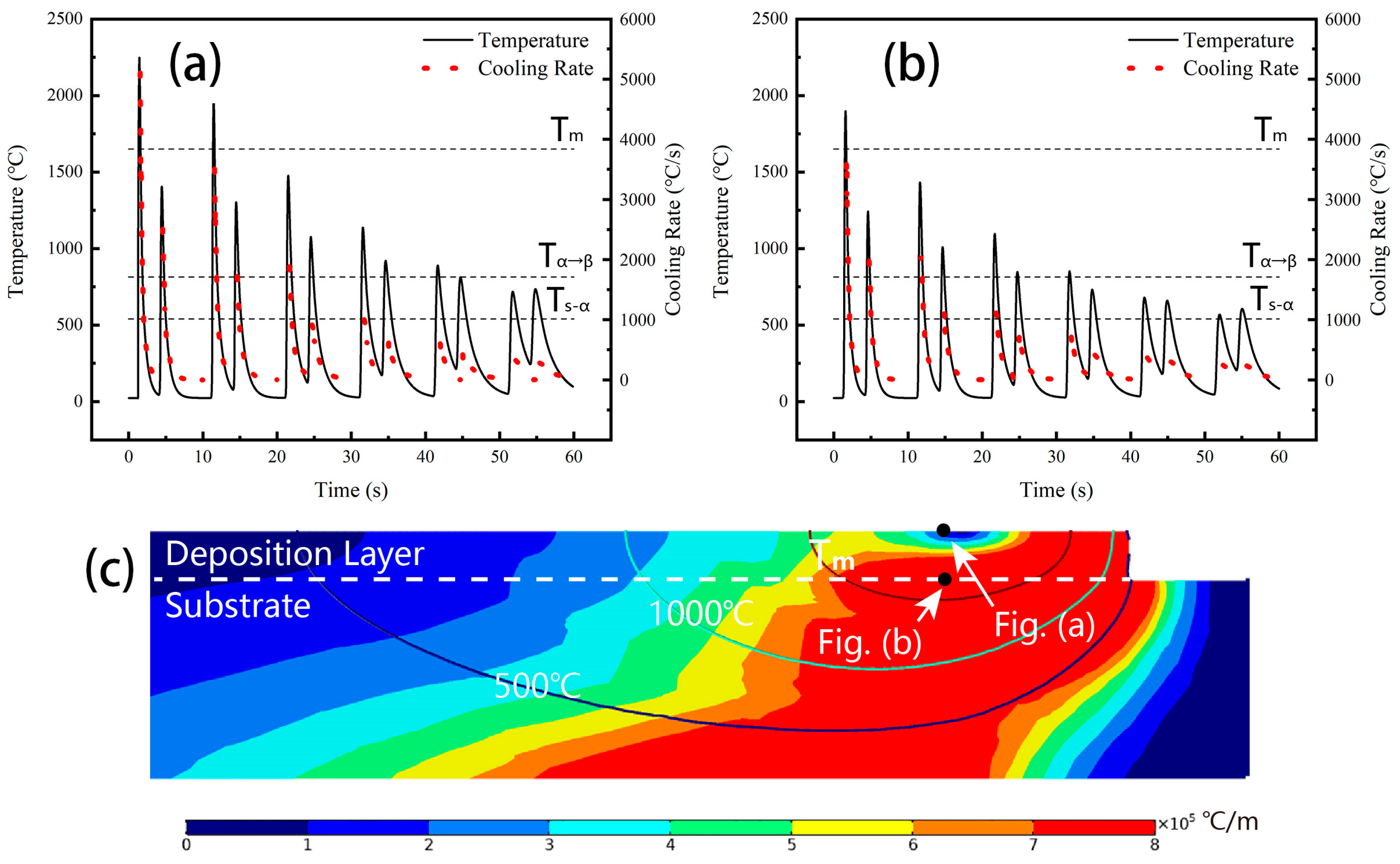
2.6. Computational Methods
3. Results and Discussion
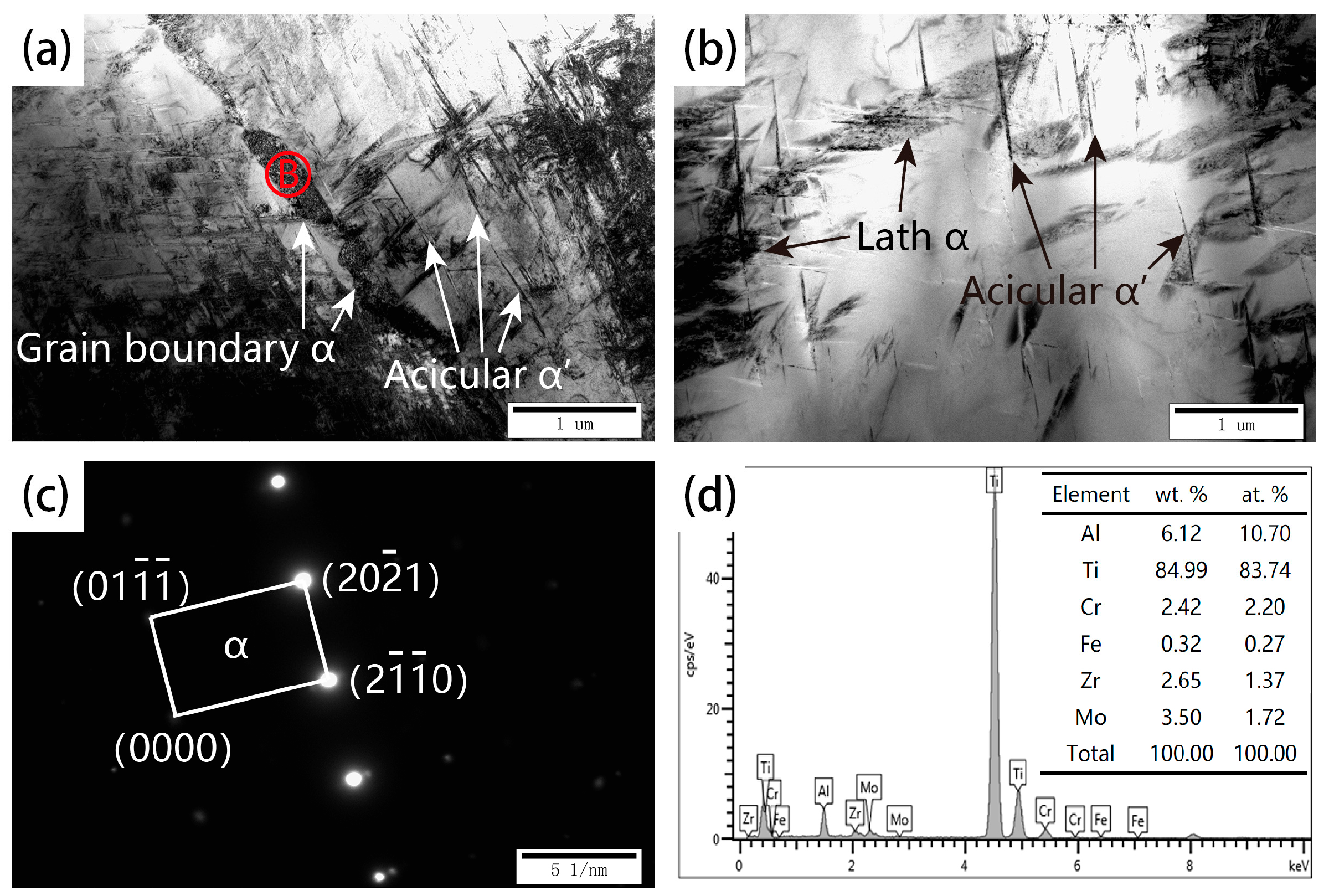
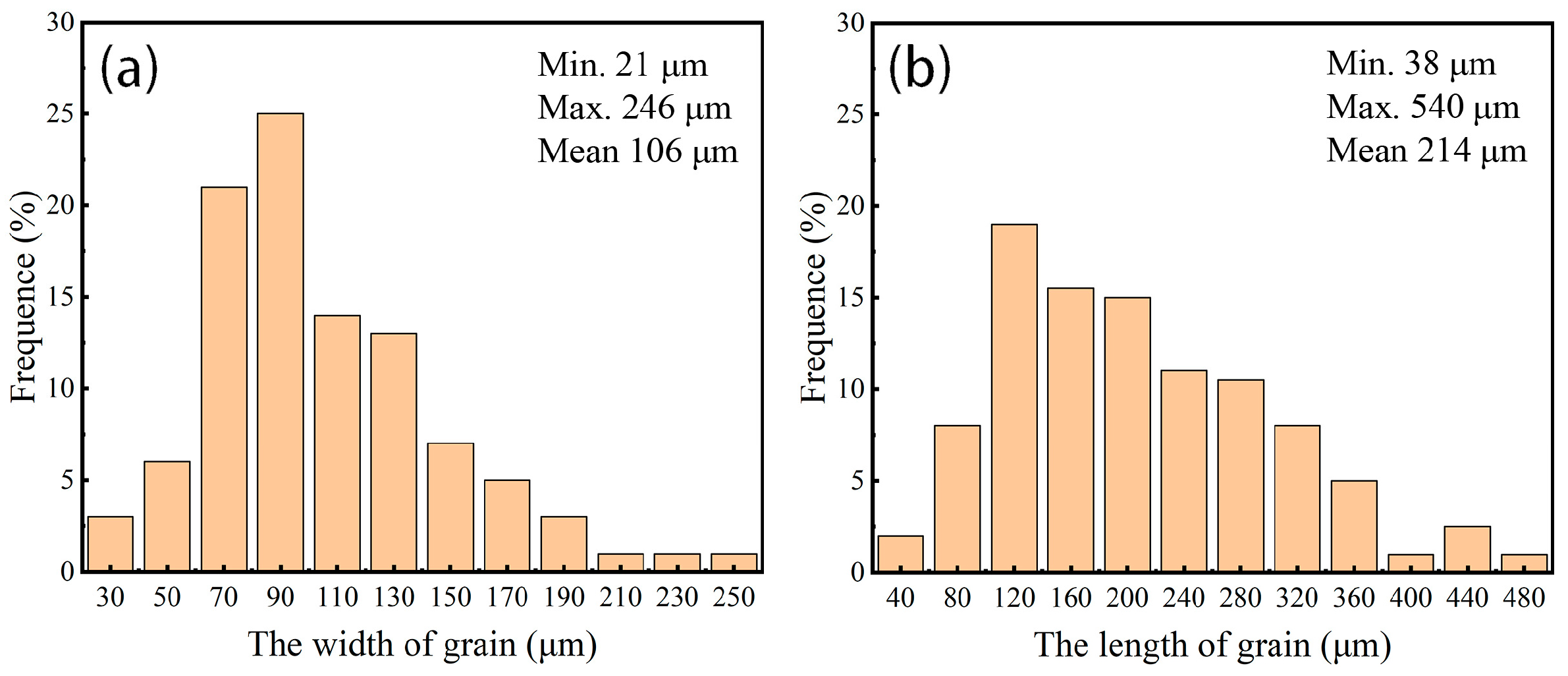
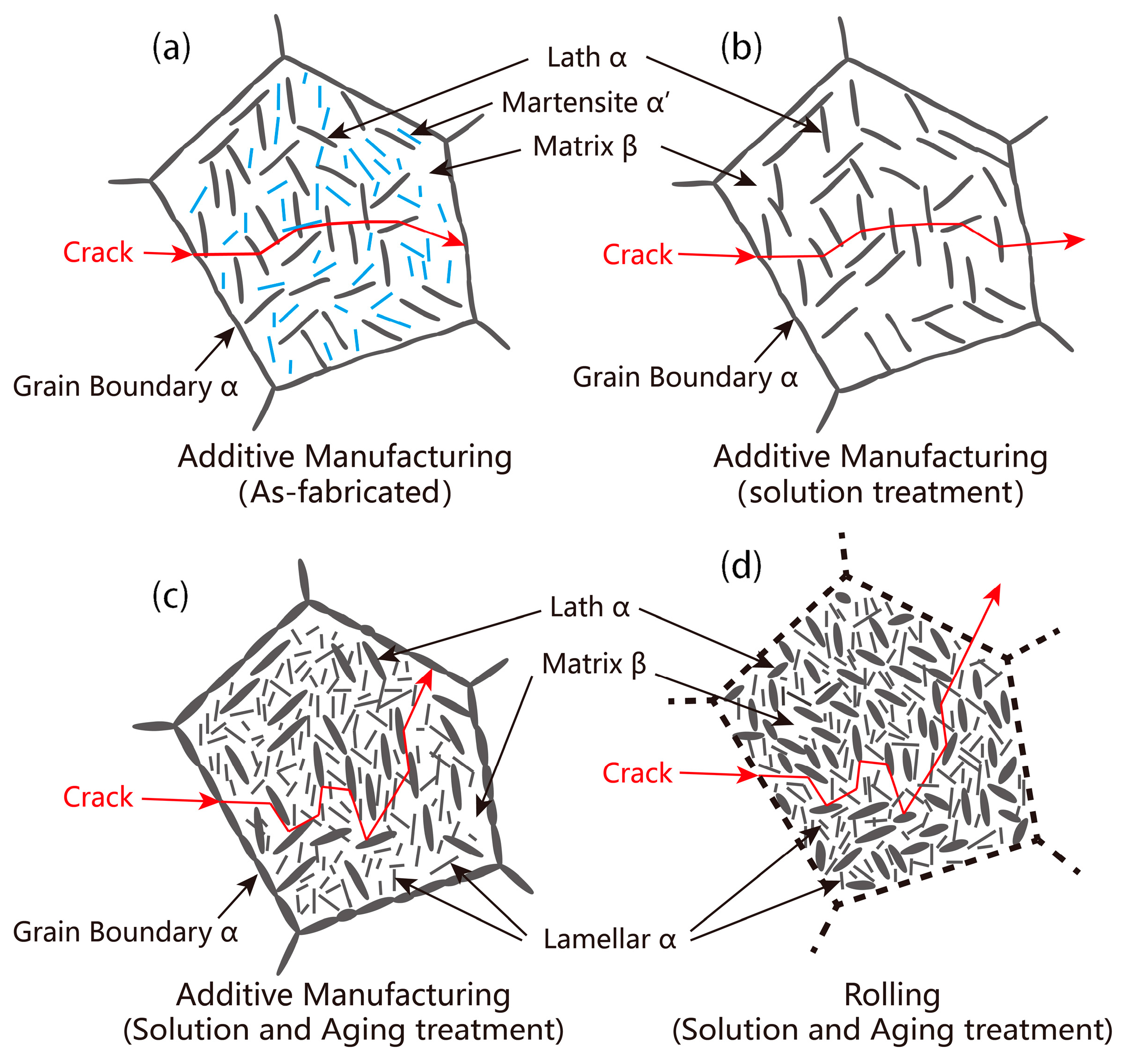
3.1. As-Fabricated Microstructure
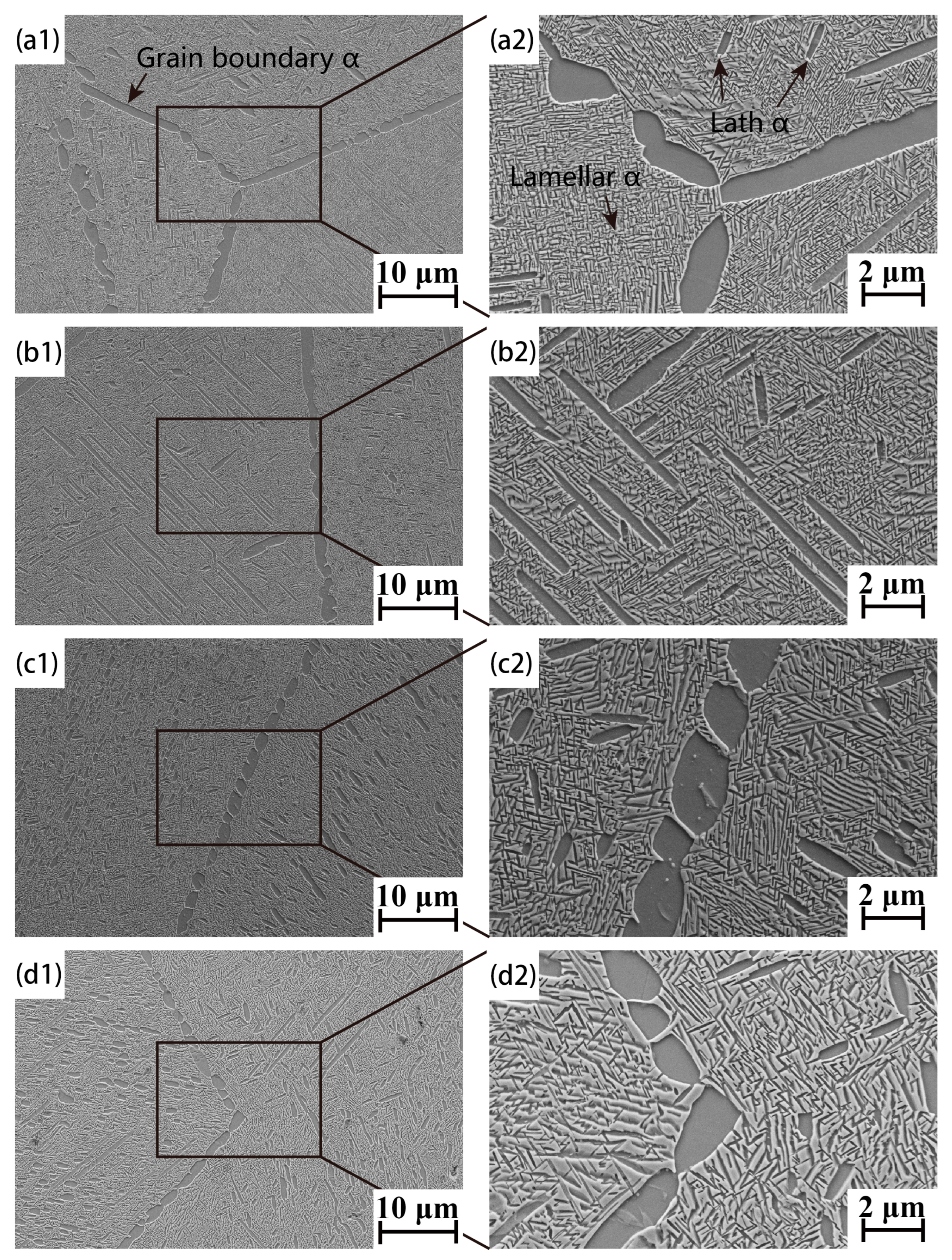
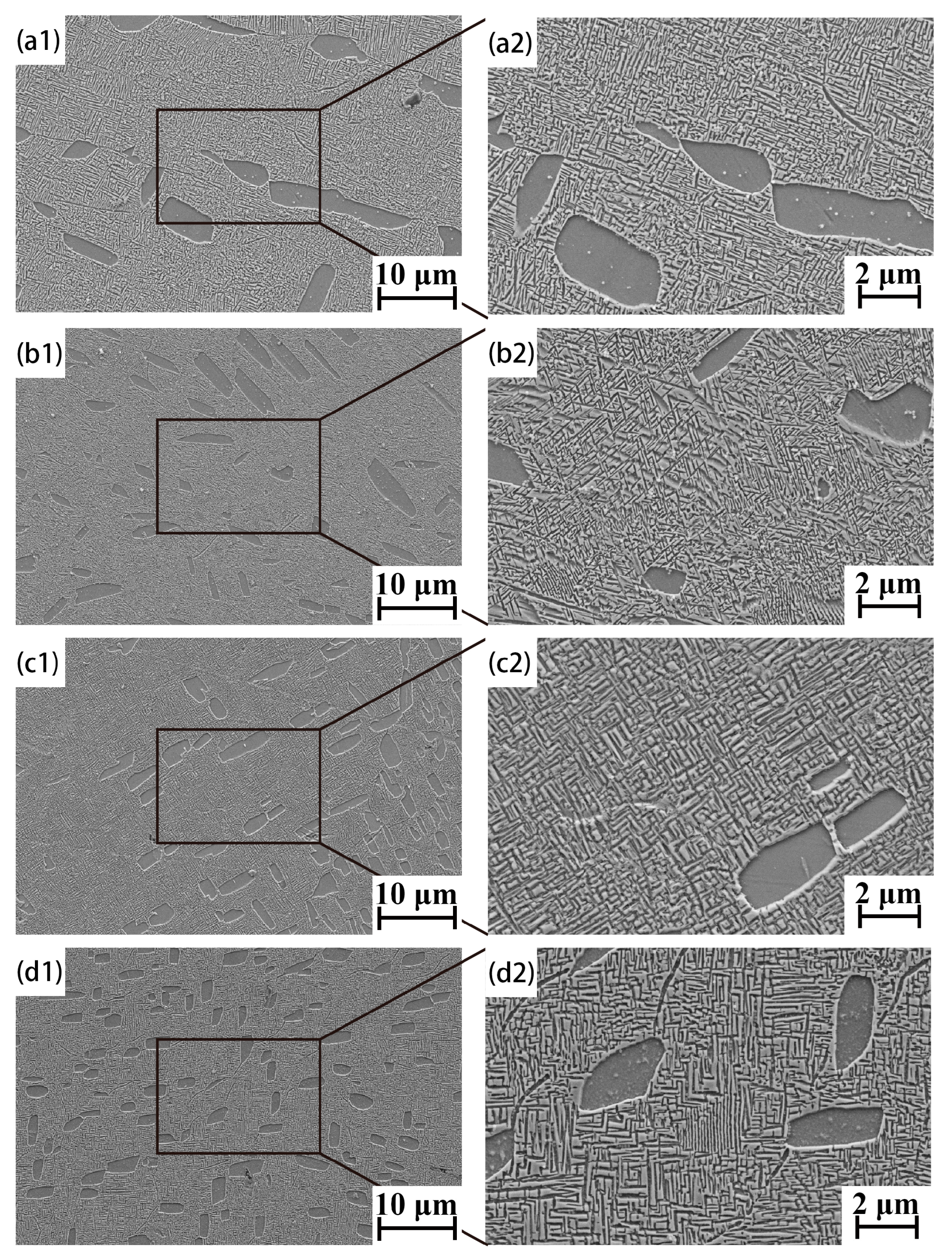
3.2. Heat-Treated Microstructure
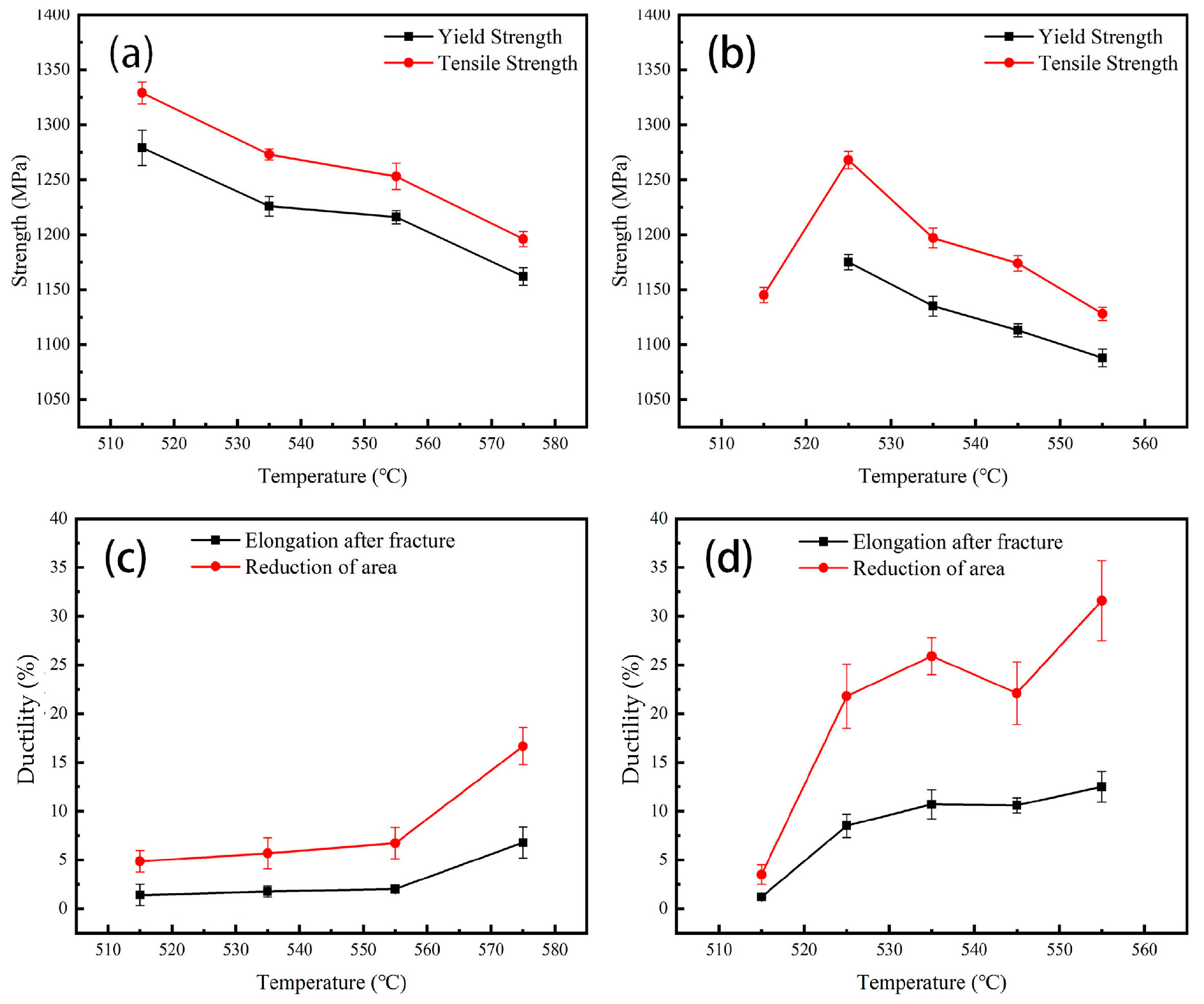
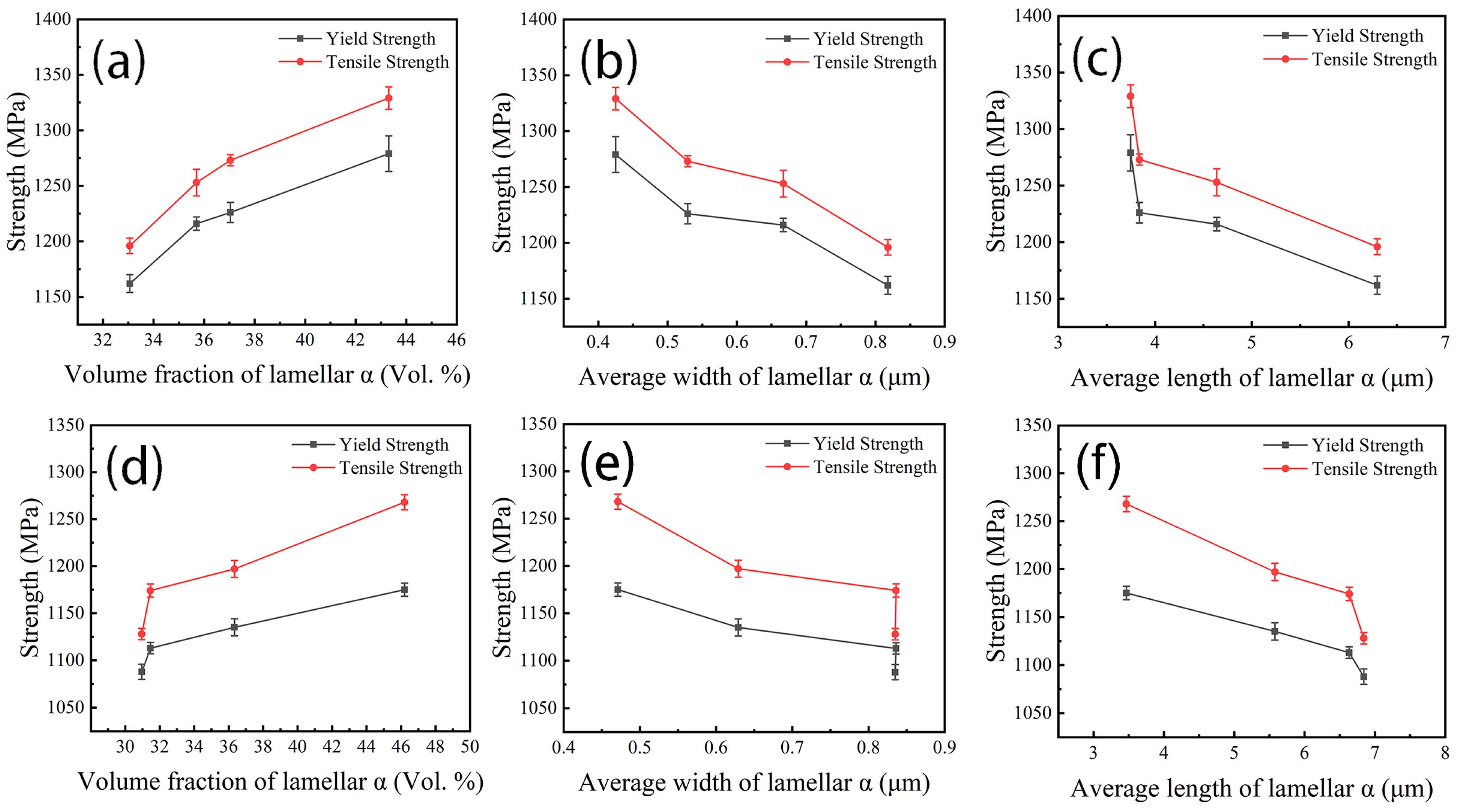
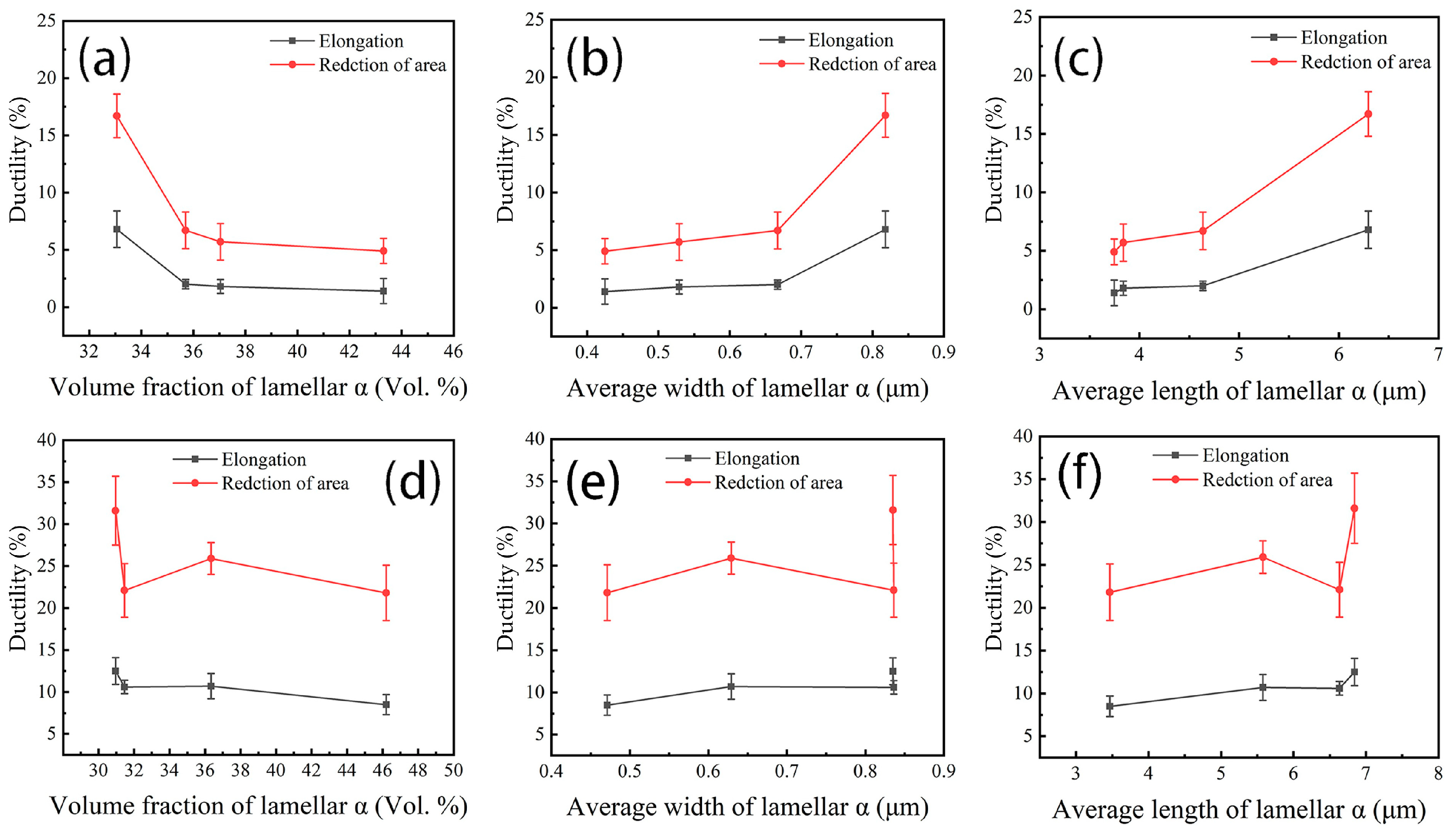
3.3. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Durai Murugan, P.; Vijayananth, S.; Natarajan, M.P.; Jayabalakrishnan, D.; Arul, K.; Jayaseelan, V.; Elanchezhian, J. A current state of metal additive manufacturing methods: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 59, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; Rathee, S.; Patel, V.; Kumar, A.; Koppad, P.G. A review of various materials for additive manufacturing: Recent trends and processing issues. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 2612–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liang, Y.; Ge, G.; Yang, G.; Yi, F.; Lin, J. Comparison of microstructure and mechanical properties of GH4099 superalloys manufactured by L-DED and L-PBF. Mater. Lett. 2025, 395, 138686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milošev, I.; Rodič, P.; Kapun, B.; Sačer, D.; Nair, A.; Kramar, D.; Jeromen, A.; Govekar, E. Composition, microstructure and corrosion resistance of DED-LB additively manufactured Ti–6Al–4V alloy: Comparison with wrought alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1033, 181280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Williams, S.; Colegove, P. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Wire and Arc Additive Manufactured Ti-6AI-4V. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, W.; Fisher, D.J. Fundamentals of Solidification; Trans Tech Publications, Ltd.: Bäch, Switzerland, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Brandt, M.; Sun, S.; Elambasseril, J.; Liu, Q.; Latham, K.; Xia, K.; Qian, M. Additive manufacturing of strong and ductile Ti–6Al–4V by selective laser melting via in situ martensite decomposition. Acta Mater. 2015, 85, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Sun, S.; Elambasseril, J.; Liu, Q.; Brandt, M.; Qian, M. Ti-6Al-4V Additively Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting with Superior Mechanical Properties. JOM 2015, 67, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobryn, P.A.; Moore, E.H.; Semiatin, S.L. The effect of laser power and traverse speed on microstructure, porosity, and build height in laser-deposited Ti-6Al-4V. Scr. Mater. 2000, 43, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, B.; Shiva, S.; Nath, T. A review on wire arc additive manufacturing: Processing parameters, defects, quality improvement and recent advances. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liang, J.; Mei, J.; Mitchell, C.; Goodwin, P.S.; Voice, W. Microstructures of laser-deposited Ti–6Al–4V. Mater. Eng. 2004, 25, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooke, R.; Zhang, D.; Qiu, D.; Gibson, M.A.; Easton, M. Compositional criteria to predict columnar to equiaxed transitions in metal additive manufacturing. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Ning, F.; Wang, H.; Cong, W. In-situ ultrafine three-dimensional quasi-continuous network microstructural TiB reinforced titanium matrix composites fabrication using laser engineered net shaping. Mater. Lett. 2017, 195, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Qiu, D.; Gibson, M.A.; Zheng, Y.; Fraser, H.L.; StJohn, D.H.; Easton, M.A. Additive manufacturing of ultrafine-grained high-strength titanium alloys. Nature 2019, 576, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonelli, M.; McCartney, D.G.; Barriobero-Vila, P.; Aboulkhair, N.T.; Tse, Y.Y.; Clare, A.; Hague, R. The Influence of Iron in Minimizing the Microstructural Anisotropy of Ti-6Al-4V Produced by Laser Powder-Bed Fusion. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 2444–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Ning, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Long, J.; Ma, W. Fe element promotes the transformation from columnar to equiaxed grains and the formation of ultrafine microstructure of Ti-6Al-4V alloy by laser wire deposition. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 48, 102442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Dai, G.; Niu, J.; Guo, Y.; Sun, Z.; Chang, H.; Zhang, Q. Fe nanoparticles modified pure Ti alloy on microstructure evolution and fine crystallization mechanism fabricated by additive manufacturing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 5860–5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Xia, J.; Dai, G.; Guo, Y.; Sun, Z.; Chang, H.; Zhang, Q. Enhanced mechanical properties and refined microstructure induced by micron Fe for additive manufactured Ti-Fe alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1033, 181144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermingham, M.J.; McDonald, S.D.; StJohn, D.H.; Dargusch, M.S. Segregation and grain refinement in cast titanium alloys. J. Mater. Res. 2009, 24, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Dan, Z.; Li, T.; Dai, G.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, K.; Yi, D.; Chang, H.; Zhou, L. Flow softening and microstructural evolution of near β titanium alloy Ti-35421 during hot compression deformation in the α+β region. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 2257–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6892-1:2009; Metallic Materials—Tensile Testing—Part 1: Method of Test at Room Temperature. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Ahmed, T.; Rack, H.J. Phase transformations during cooling in α+β titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 243, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Ghadbeigi, H.; Mumtaz, K. Effect of scanning strategies on residual stress and mechanical properties of Selective Laser Melted Ti6Al4V. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 712, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wu, S.; Chang, H. The effect of heat treatment on microstructure evolution and tensile properties of selective laser melted Ti6Al4V alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 782, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Xu, G.; Cui, Y.; Chang, H. Optimization of Low-Cost Ti-35421 Titanium Alloy: Phase Transformation, Bimodal Microstructure, and Combinatorial Mechanical Properties. Materials 2019, 12, 2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Li, X.; Zhu, H.; Chen, F.; Li, F.; Chang, H. Microstructure evolution and phase transformation kinetics of low cost Ti-35421 titanium alloy during continuous heating. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shin, Y.C. Additive manufacturing of Ti6Al4V alloy: A review. Mater. Des. 2019, 164, 107552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Dai, G.; Guo, Y.; Sun, Z.; Dan, Z.; Dong, Y.; Chang, H.; Alexandrov, I.V.; Zhou, L. Microstructure and mechanical properties of B modified Ti–Fe alloy manufactured by casting, forging and laser melting deposition. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 216, 108854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanning, J.C. Properties of TIMETAL 555 (Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-3Cr-0.6Fe). J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2005, 14, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasu, G.; Natraj, Y.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Nandy, T.K.; Nageswara Rao, G.V.S. Tensile and fracture toughness of high strength β Titanium alloy, Ti–10V–2Fe–3Al, as a function of rolling and solution treatment temperatures. Mater. Des. 2013, 47, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Luo, H.; Deng, H.; Chen, L.; Qiu, W. Thermomechanical processing of near-β Ti–5Al–5Mo–5V–1Cr–1Fe alloys: Effect of deformation reduction on microstructures and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 853, 143786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Du, Z.; Xiao, S.; Xu, L.; Tian, J. Effect of aging heat treatment on microstructure and tensile properties of a new β high strength titanium alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 586, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Mi, X.; Ye, W.; Hui, S.; Yu, Y.; Wang, W. A study on the microstructures and tensile properties of new beta high strength titanium alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 550, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Ti | Al | Mo | Cr | Zr | Fe | O | N | H | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bal. | 3.29 | 5.26 | 3.82 | 1.98 | 1.34 | 0.045 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.008 |
| Chemical Composition (wt.%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | Al | Mo | Cr | Zr | Fe | O | N | H | C |
| Bal. | 3.24 | 5.23 | 3.85 | 1.96 | 1.29 | 0.063 | 0.012 | 0.002 | 0.007 |
| Particle size | Flowability | Apparent density | Particle shape | ||||||
| D10/μm | D50/μm | D90/μm | s/50 g | g/cm3 | % | ||||
| 97.3 | 130.5 | 165.6 | 22.5 | 2.76 | 0.97 | ||||
| Aging Temperature /°C | Lath α | Lamellar α | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volume Fraction /vol.% | Volume Fraction /vol.% | Average Length /μm | Average Width /μm | |
| 515 | 14.1 ± 1.5 | 43.3 ± 2.7 | 0.43 ± 0.04 | 3.75 ± 0.62 |
| 535 | 13.5 ± 0.6 | 37.0 ± 2.8 | 0.51 ± 0.05 | 3.84 ± 0.02 |
| 555 | 14.1 ± 1.3 | 35.7 ± 1.3 | 0.67 ± 0.04 | 4.64 ± 1.15 |
| 575 | 13.8 ± 3.2 | 33.1 ± 2.1 | 0.82 ± 0.02 | 6.30 ± 0.35 |
| Temperature /°C | Lath α | Lamellar α | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volume Fraction /vol.% | Volume Fraction /vol.% | Average Length /μm | Average Width /μm | |
| 525 | 13.3 ± 1.3 | 46.2 ± 4.1 | 0.47 ± 0.02 | 3.47 ± 0.69 |
| 535 | 12.2 ± 1.9 | 36.3 ± 1.9 | 0.63 ± 0.01 | 5.58 ± 0.63 |
| 545 | 14.6 ± 1.3 | 31.5 ± 5.8 | 0.84 ± 0.04 | 6.64 ± 0.39 |
| 555 | 12.4 ± 1.0 | 31.0 ± 4.1 | 0.84 ± 0.05 | 6.84 ± 0.47 |
| Aging Temperature /°C | Strength | Ductility | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength /MPa | Yield Strength /MPa | Elongation /% | Reduction in Area /% | |
| As-fabricated | 1446 ± 46 | 1377 ± 52 | 1.7 ± 0.3 | / |
| 515 | 1329 ± 10 | 1279 ± 16 | 1.4 ± 1.1 | 4.9 ± 1.1 |
| 535 | 1273 ± 5 | 1226 ± 9 | 1.8 ± 0.6 | 5.7 ± 1.6 |
| 555 | 1253 ± 12 | 1216 ± 6 | 2.0 ± 0.4 | 6.7 ± 1.6 |
| 575 | 1196 ± 7 | 1162 ± 8 | 6.8 ± 1.6 | 16.7 ± 1.9 |
| Aging Temperature /°C | Strength | Ductility | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength /MPa | Yield Strength /MPa | Elongation /% | Reduction in Area /% | |
| 515 | 1145 ± 7 | -- | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 3.5 ± 1.0 |
| 525 | 1268 ± 8 | 1175 ± 7 | 8.5 ± 1.2 | 21.8 ± 3.3 |
| 535 | 1197 ± 9 | 1135 ± 9 | 10.7 ± 1.5 | 25.9 ± 1.9 |
| 545 | 1174 ± 7 | 1113 ± 6 | 10.6 ± 0.8 | 22.1 ± 3.2 |
| 555 | 1128 ± 6 | 1088 ± 8 | 12.5 ± 1.6 | 31.6 ± 4.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Z.; Li, B.; Jiang, J.; Gu, H.; Sun, Z.; Lu, X. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti35421 Alloy: A Comparison Between Laser Directed Energy Deposition (L-DED) and Rolling. Metals 2025, 15, 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15091033
Liang Z, Li B, Jiang J, Gu H, Sun Z, Lu X. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti35421 Alloy: A Comparison Between Laser Directed Energy Deposition (L-DED) and Rolling. Metals. 2025; 15(9):1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15091033
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Zulei, Bin Li, Jie Jiang, Hai Gu, Zhonggang Sun, and Xianxiang Lu. 2025. "Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti35421 Alloy: A Comparison Between Laser Directed Energy Deposition (L-DED) and Rolling" Metals 15, no. 9: 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15091033
APA StyleLiang, Z., Li, B., Jiang, J., Gu, H., Sun, Z., & Lu, X. (2025). Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti35421 Alloy: A Comparison Between Laser Directed Energy Deposition (L-DED) and Rolling. Metals, 15(9), 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15091033






