An Experimental Study on Tensile Characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V Thin Struts Made by Laser Powder-Bed Fusion: Effects of Strut Geometry and Linear Energy Density
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Design
2.2. Fabrication Process
2.3. Tensile Testing
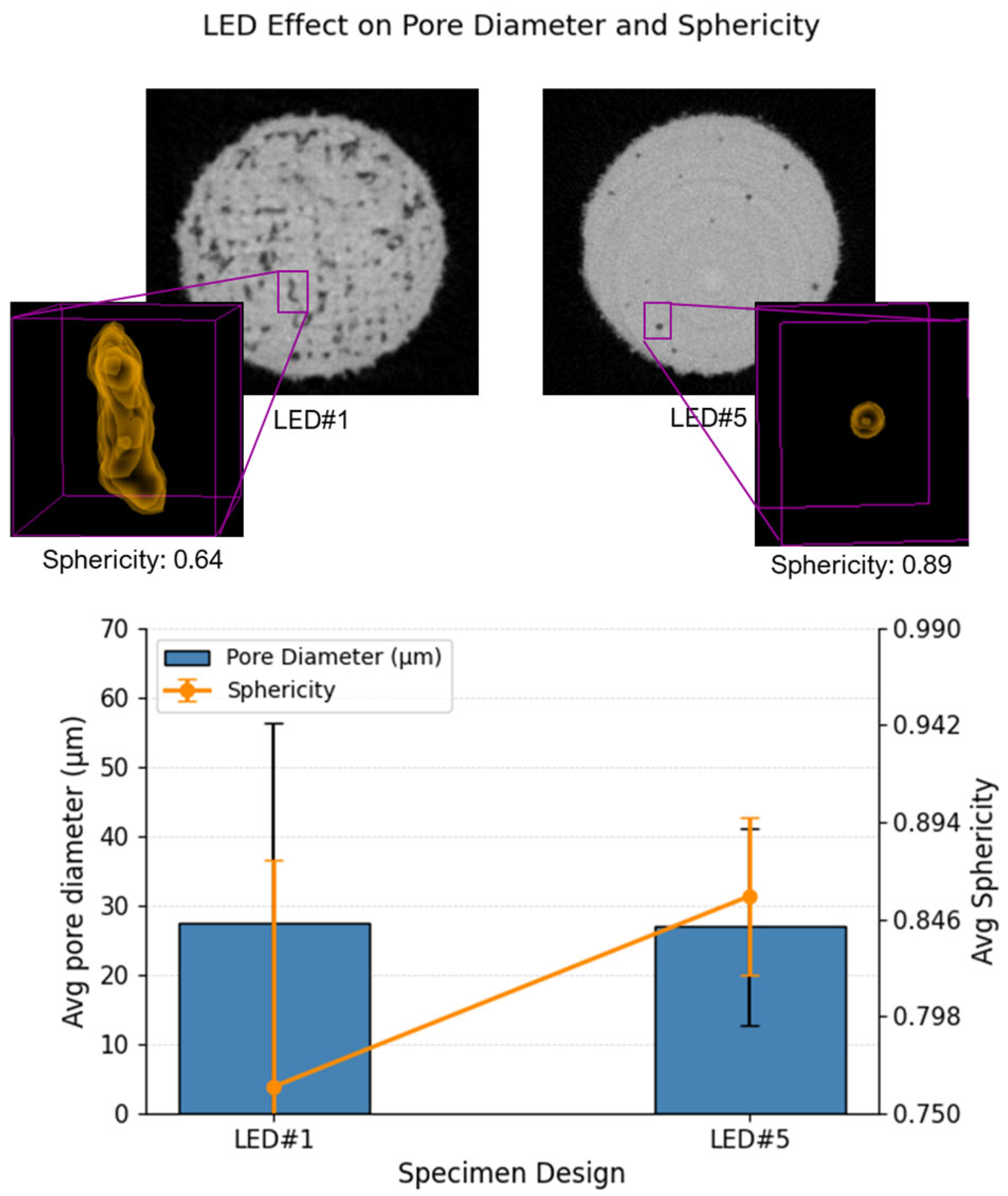
2.4. Micro-CT Scan
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Strut Geometry Effect
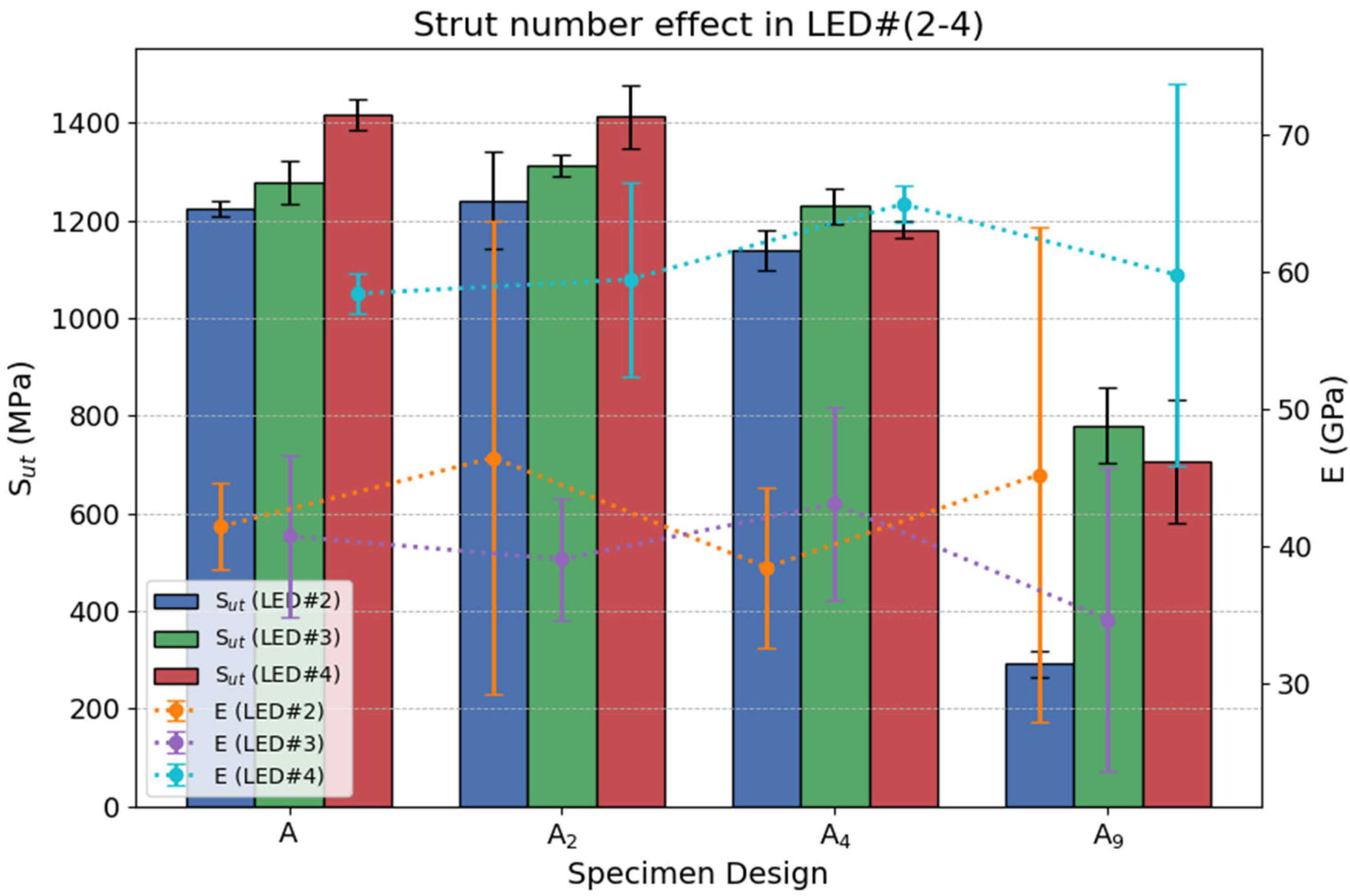
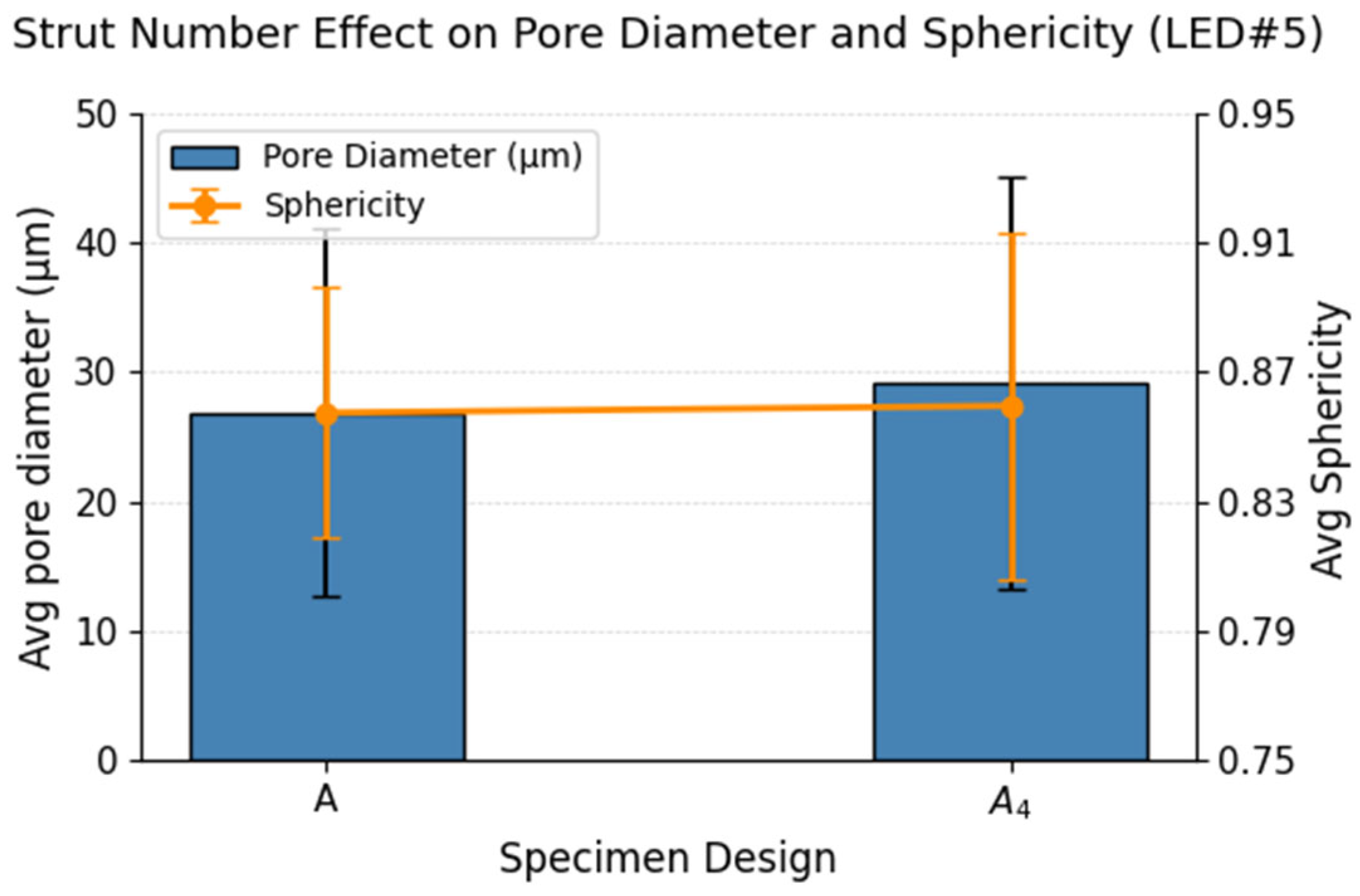
3.1.1. Strut Number Effect
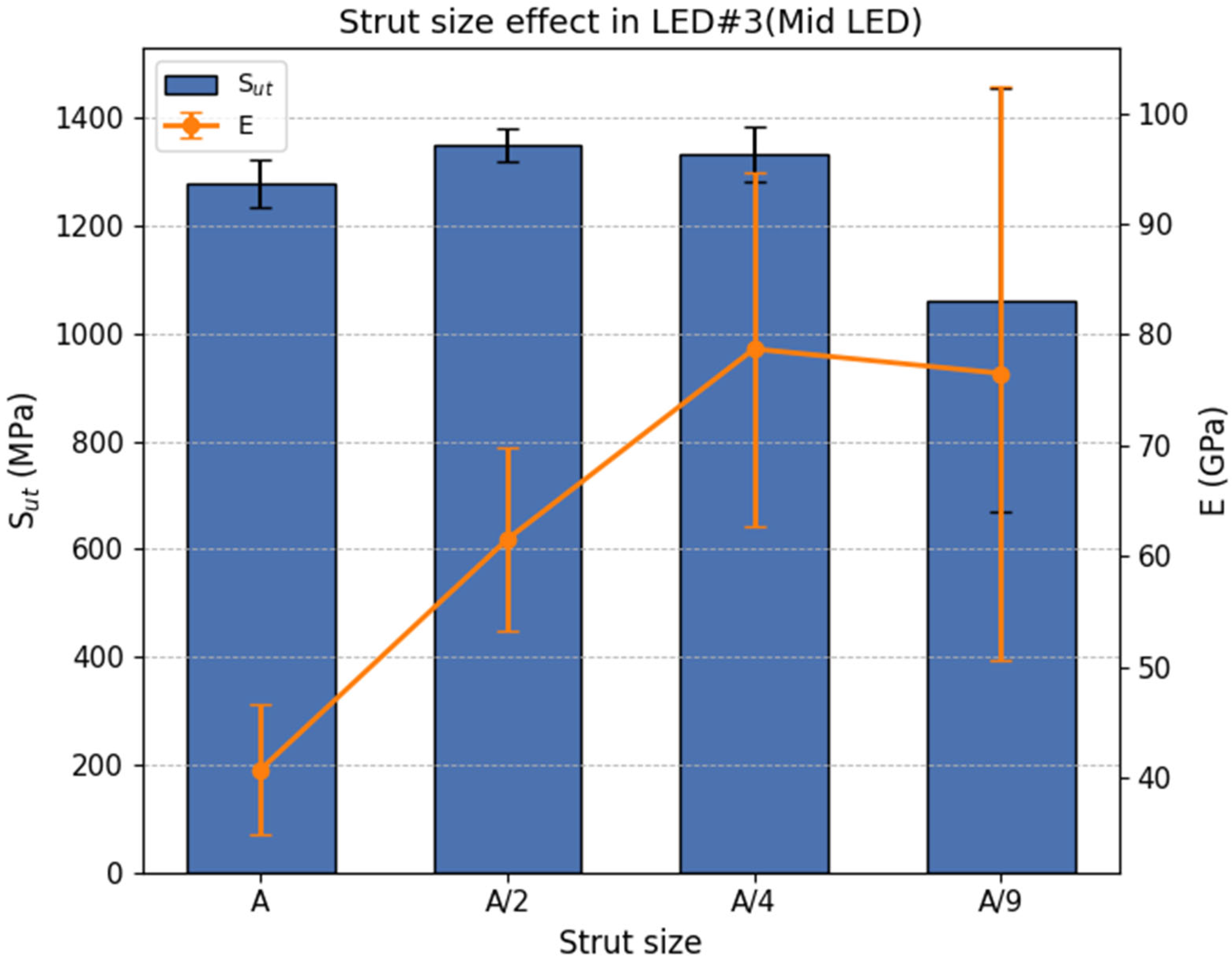
3.1.2. Strut Size Effect
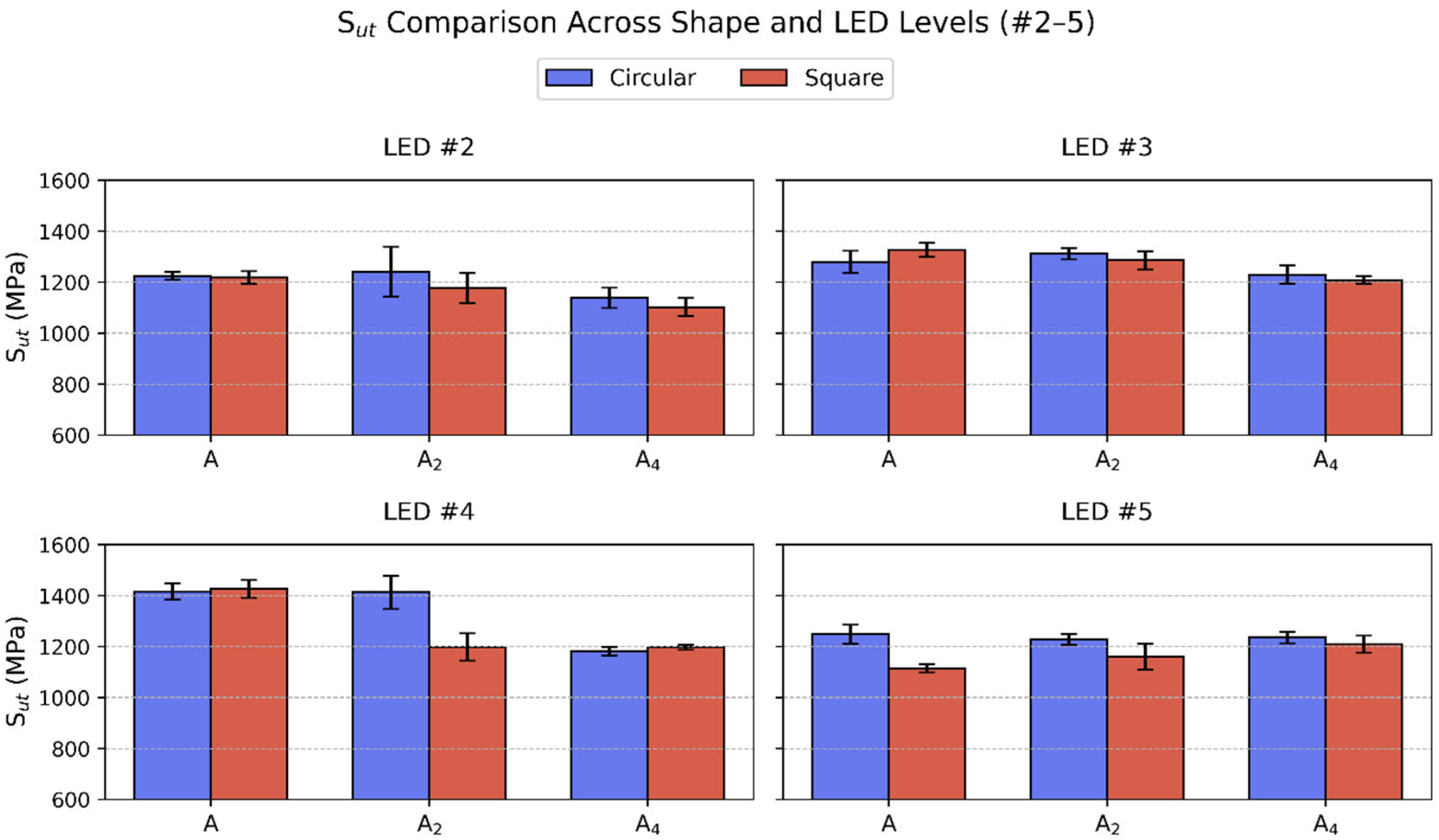
3.1.3. Strut Shape Effect
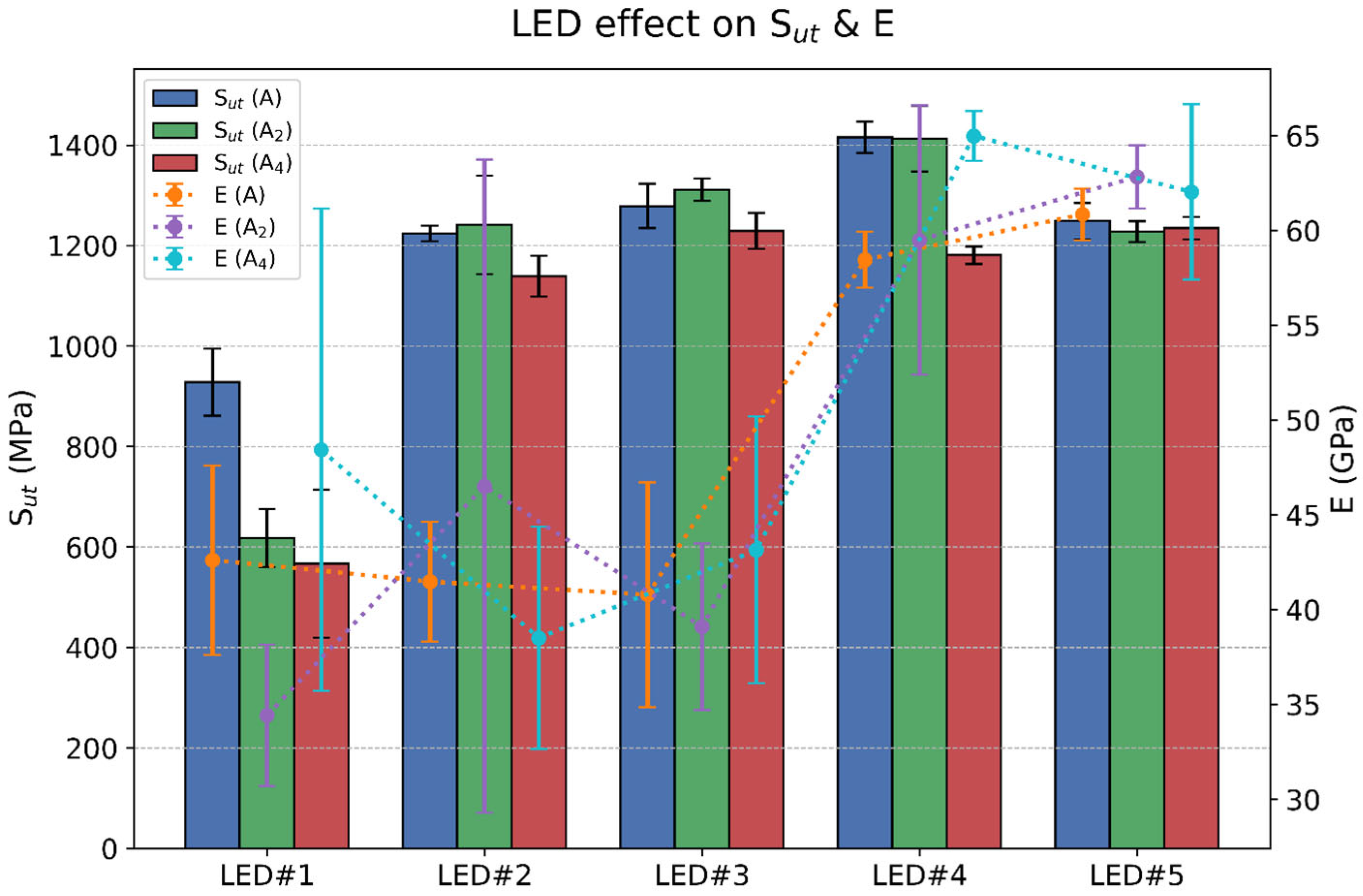
3.2. Process Parameter Effect
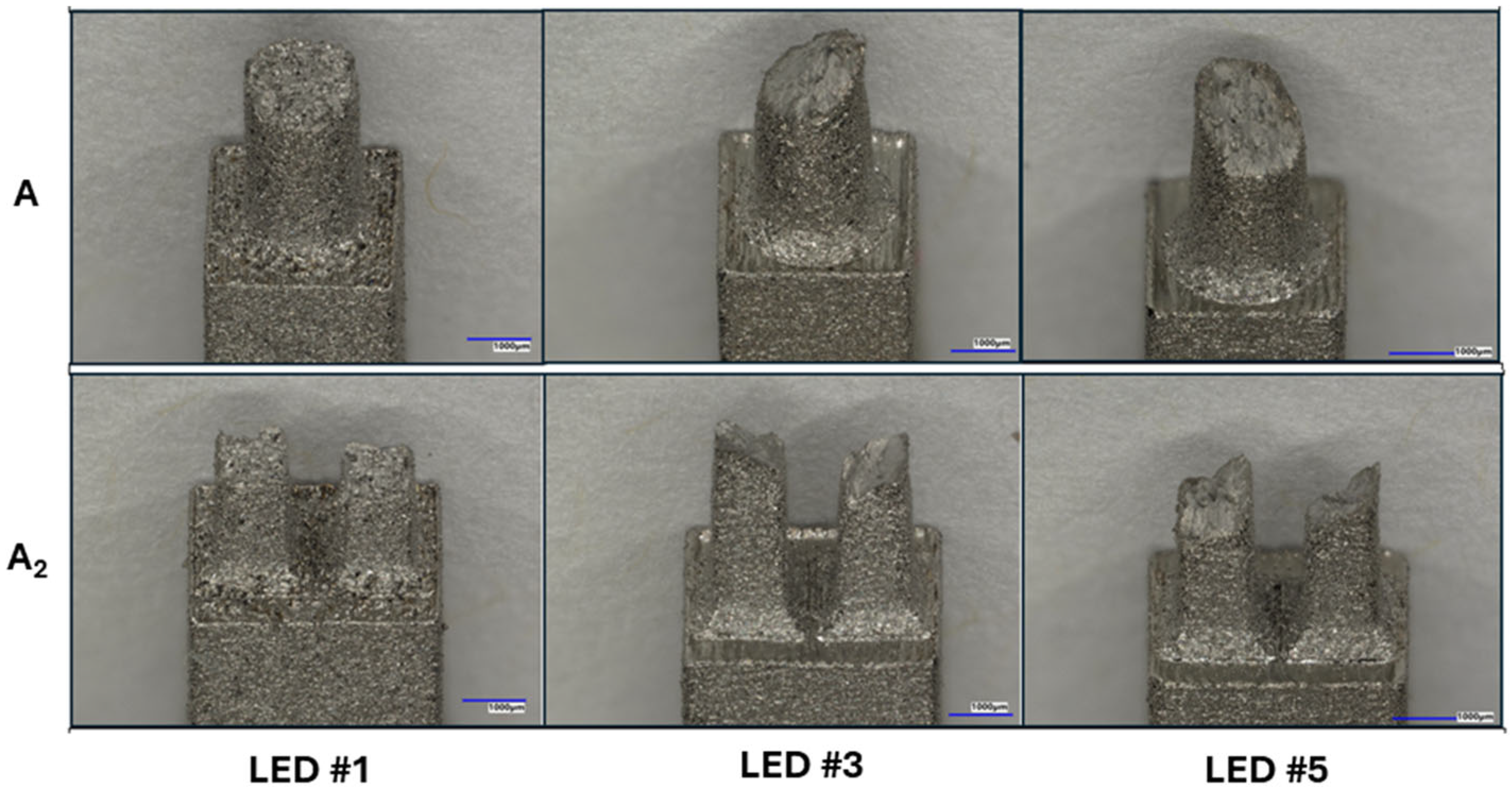
3.3. Fracture Location Along Strut Length
4. Conclusions
- Increasing the number of struts while maintaining a constant total cross-sectional area led to a reduction in tensile strength. Notably, the ultimate tensile strength (Sut) dropped sharply in nine-strut configurations (A9), with ~70% reduction in LED#2 specimens and ~35% reduction in LED#3 and LED#4 specimens. The combination of low energy input and high strut number produced a compounding negative effect on tensile strength.
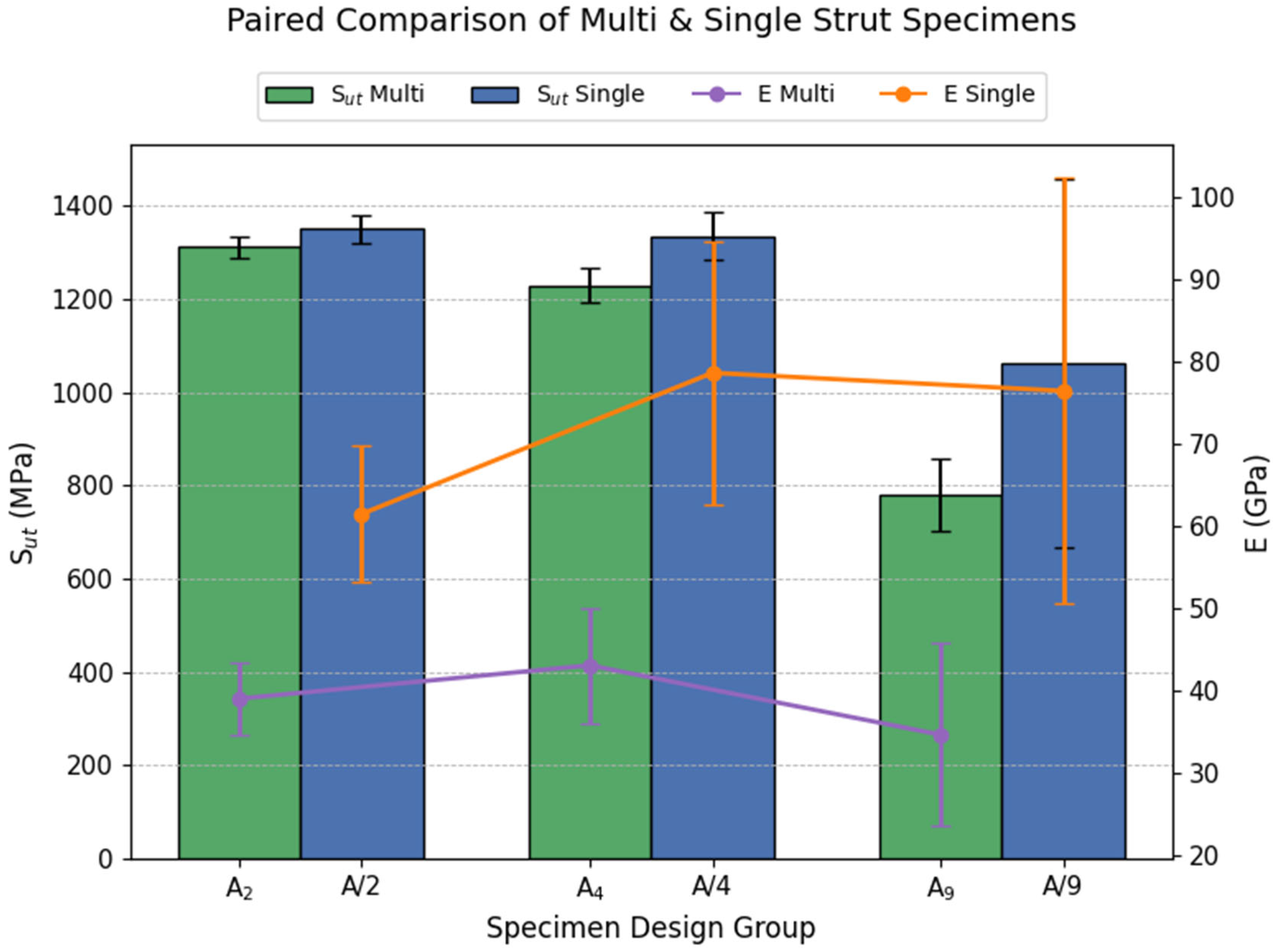
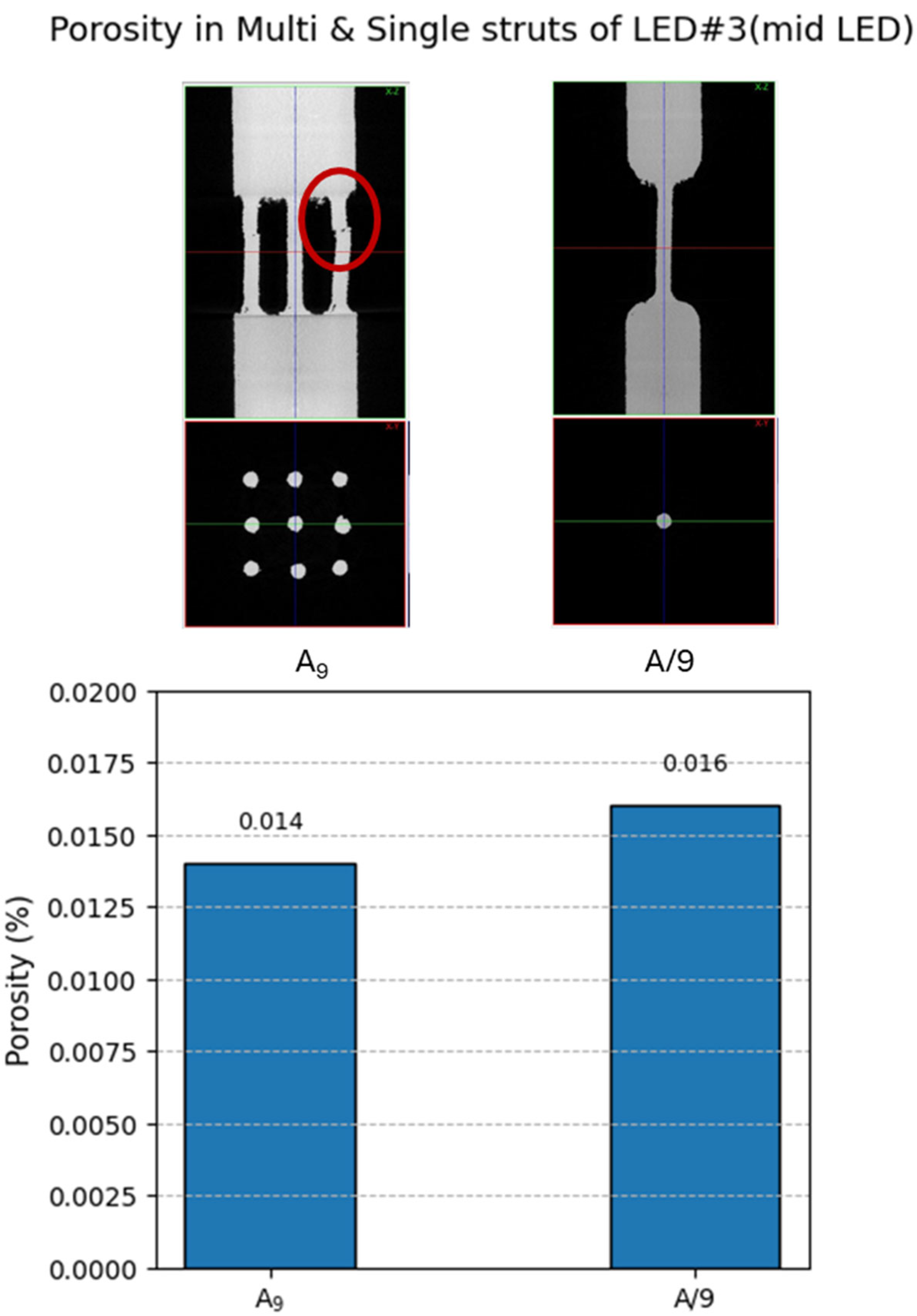
- Multi-strut configurations consistently performed 5–10% lower than equivalent single-strut arrangements. However, in the case of the nine-strut configuration (A9) versus its single-strut counterpart (A/9), the multi-strut specimen exhibited a 25–50% lower Sut.
- Sut remained relatively consistent across most strut sizes, with only minor deviations. However, at the smallest scale (A/9), ~20% reduction in strength was observed. This reduction is likely due to increased susceptibility to surface defects at smaller scales.
- Circular and square cross-sections demonstrated comparable tensile properties under high energy inputs, with only 1–5% variance in Sut. However, at low energy input (LED#1), square specimens performed noticeably worse, possibly due to stress concentrations at sharp corners that were exacerbated by lack-of-fusion defects and promoted early failure.
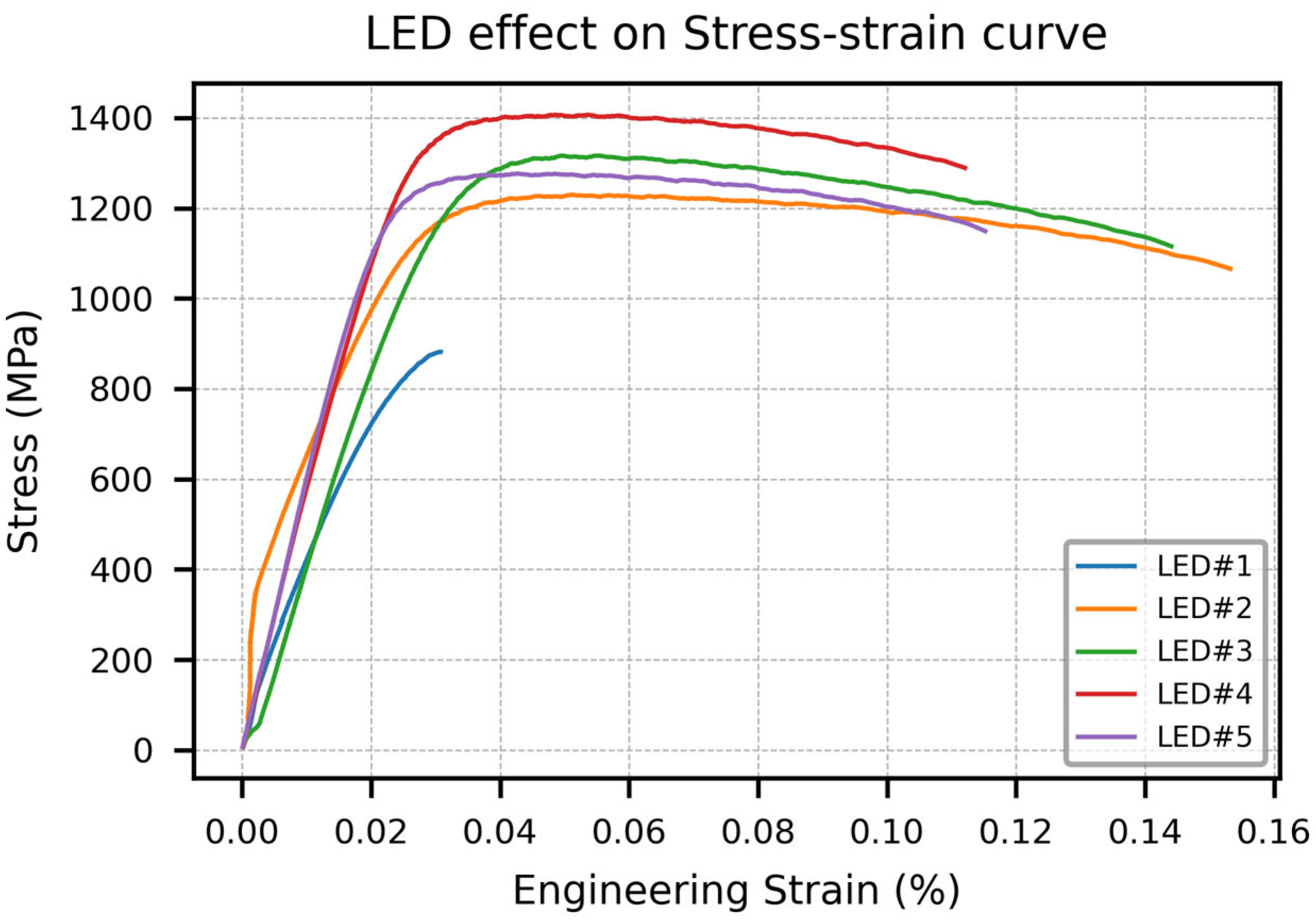
- Among all variables, LED exhibited the strongest influence on tensile behavior. As LED increased from 0.075 J/mm to approximately 0.2 J/mm, both strength and stiffness improved significantly, corresponding with reduced porosity and improved fusion. Beyond this optimal LED range (i.e., at LED#5), a slight decline in Sut was observed despite a sustained high E. This correlated with keyhole-induced porosity and thermal instability in the melt pool at excessive energy densities, consistent with prior literature on keyhole-induced defects.
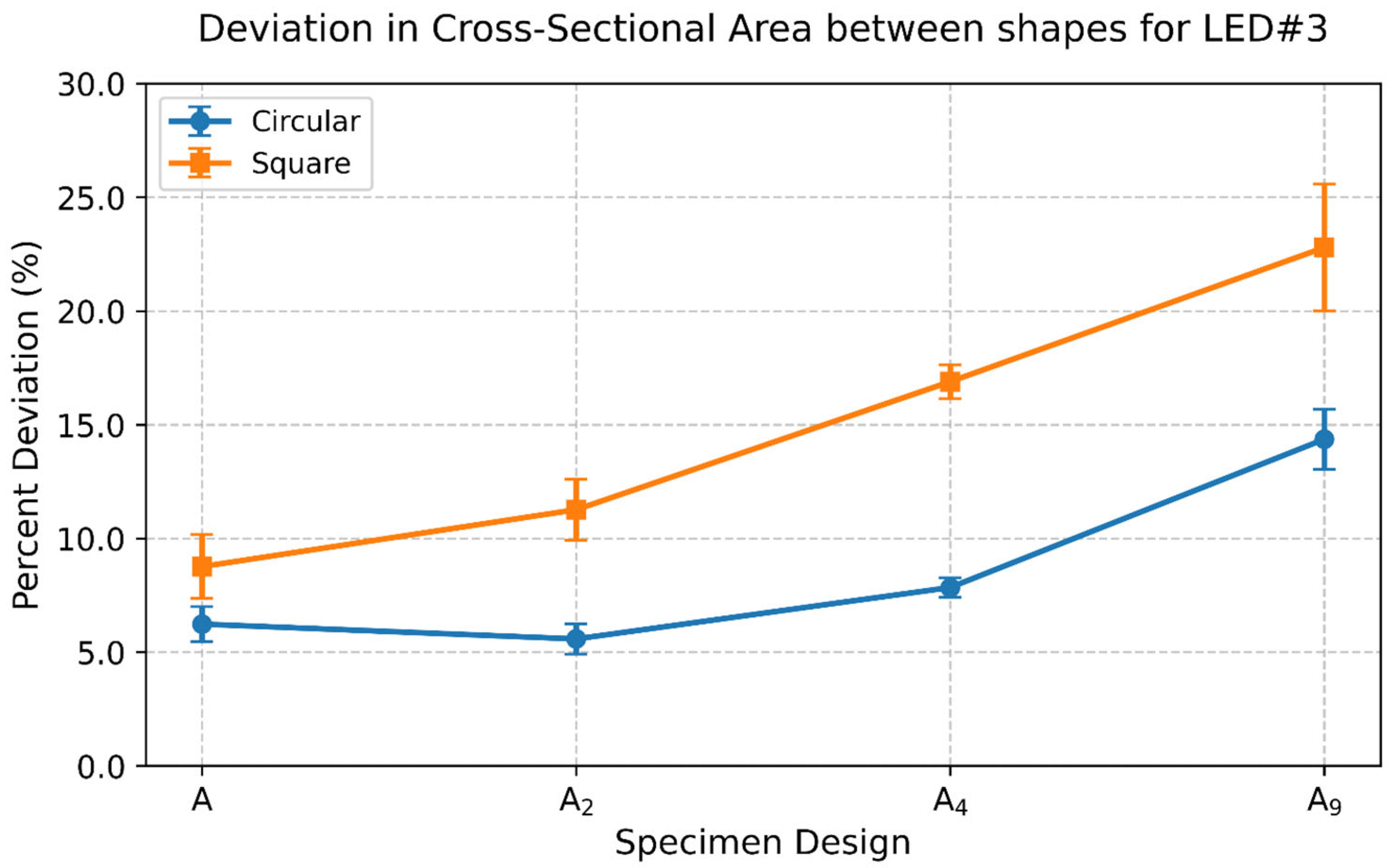
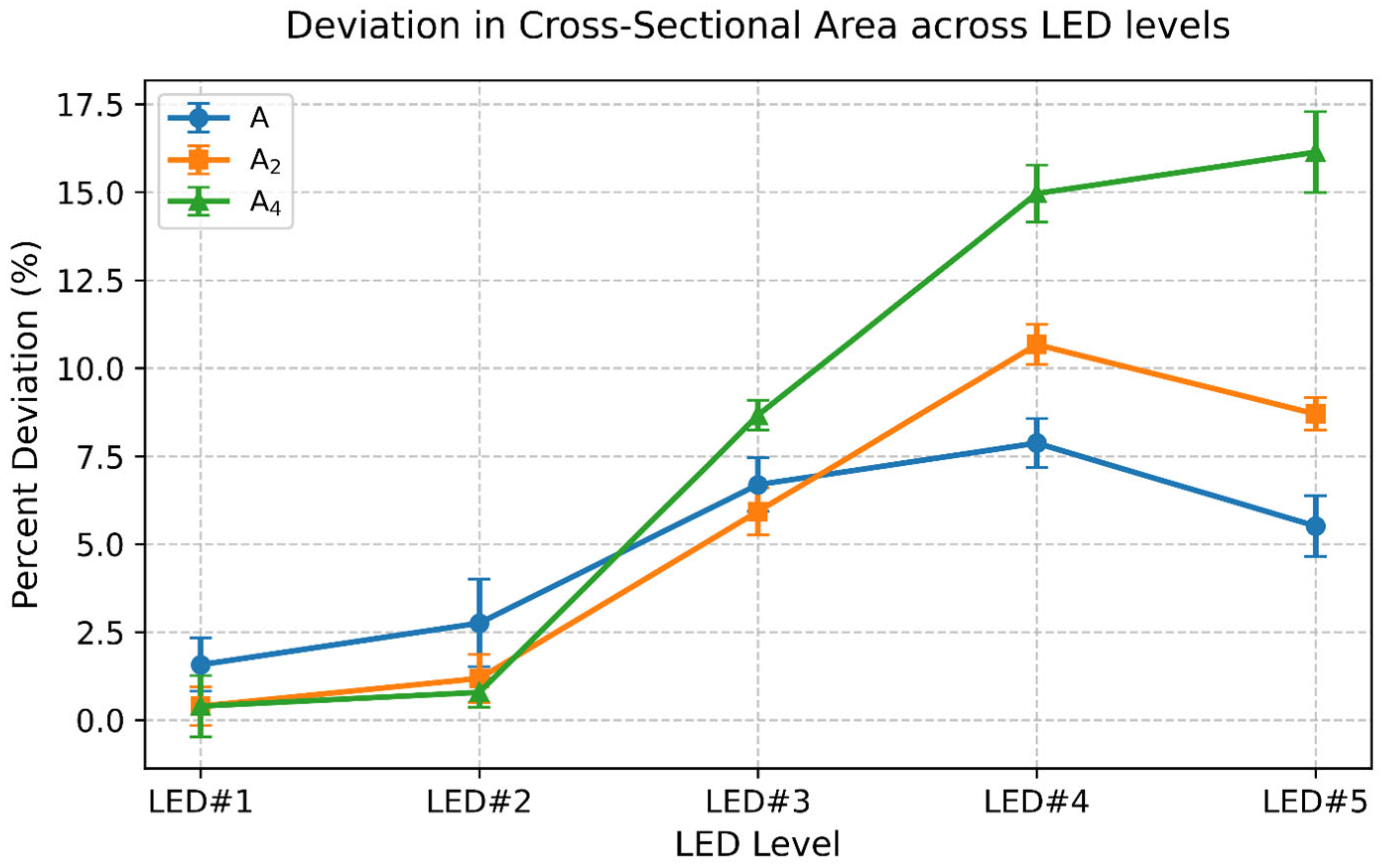
- Dimensional deviations increased with LED level, reaching 15–20% at LED#5. Square cross-sections showed 5–15% higher deviation than circular ones. Furthermore, deviations were 5–10% more for multi-strut configurations compared to single struts.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AM | Additive manufacturing |
| L-PBF | Laser powder bed fusion |
| DIC | Digital image correlation |
| XCT | X-ray computed tomography |
| LoF | Lack of fusion |
| ASTM | American Society for Testing and Materials |
| VED | Volumetric energy density |
| LED | Linear energy density |
| EDM | Electrical discharge machine |
References
- Gibson, I.; Rosen, D.W.; Stucker, B. Additive Manufacturing Technologies: Rapid Prototyping to Direct Digital Manufacturing; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orquéra, M.; Campocasso, S.; Millet, D. Design for Additive Manufacturing Method for a Mechanical System Downsizing. Procedia CIRP 2017, 60, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, D.; Elbestawi, M.A. Lattice Structures and Functionally Graded Materials Applications in Additive Manufacturing of Orthopedic Implants: A Review. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2017, 1, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabort, E.; Barba, D.; Reed, R.C. Design of metallic bone by additive manufacturing. Scr. Mater. 2019, 164, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, M.E.; Gupta, M.K.; Robak, G.; Moj, K.; Krolczyk, G.M.; Kuntoğlu, M. Development of lattice structure with selective laser melting process: A state of the art on properties, future trends and challenges. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 81, 1040–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, L.; Stamp, R.C.; Brooks, W.K.; Jones, E.; Sutcliffe, C.J. Selective Laser Melting: A regular unit cell approach for the manufacture of porous, titanium, bone in-growth constructs, suitable for orthopedic applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 89B, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Pramanik, A.; Basak, A.K.; Dong, Y.; Prakash, C.; Debnath, S.; Shankar, S.; Jawahir, I.S.; Dixit, S.; Buddhi, D. A critical review on additive manufacturing of Ti-6Al-4V alloy: Microstructure and mechanical properties. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 4641–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shin, Y.C. Additive manufacturing of Ti6Al4V alloy: A review. Mater. Des. 2019, 164, 107552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, C.; Davim, J.P.; Loureiro, A.J.R. Properties and Applications of Titanium Alloys: A Brief Review. J. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2012, 32, 14–34. [Google Scholar]
- Sing, S.L.; Wiria, F.E.; Yeong, W.Y. Selective laser melting of lattice structures: A statistical approach to manufacturability and mechanical behavior. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2018, 49, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsalla, H.; Hao, L.; Smith, C. Fracture toughness and tensile strength of 316L stainless steel cellular lattice structures manufactured using the selective laser melting technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 669, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wang, J.; Jia, L.; Yang, G.; Tang, H.; Li, Y. Additive manufacturing of Ti-6Al-4V lattice structures with high structural integrity under large compressive deformation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhnen, P.; Haase, C.; Bültmann, J.; Ziegler, S.; Schleifenbaum, J.H.; Bleck, W. Mechanical properties and deformation behavior of additively manufactured lattice structures of stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2018, 145, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, M.; Mazur, M.; Elambasseril, J.; McMillan, M.; Chirent, T.; Sun, Y.; Qian, M.; Easton, M.; Brandt, M. Selective laser melting (SLM) of AlSi12Mg lattice structures. Mater. Des. 2016, 98, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dressler, A.D.; Jost, E.W.; Miers, J.C.; Moore, D.G.; Seepersad, C.C.; Boyce, B.L. Heterogeneities dominate mechanical performance of additively manufactured metal lattice struts. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 28, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiza, I.; Baldi, C.; de la Vega, F.M.; Sebastiani, S.; Veronese, N.E.; Yousefi, M.; Mosallanejad, M.H.; Maleki, E.; Guagliano, M.; Iuliano, L.; et al. Effects of build orientation and inclined features on physical, microstructural and mechanical properties of powder bed fusion additively manufactured metallic parts. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2025, 147, 101357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murchio, S.; Dallago, M.; Zanini, F.; Carmignato, S.; Zappini, G.; Berto, F.; Maniglio, D.; Benedetti, M. Additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V thin struts via laser powder bed fusion: Effect of building orientation on geometrical accuracy and mechanical properties. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 119, 104495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, U.; Ghouse, S.; Nai, K.; Jeffers, J.R.T. Mechanical and morphological properties of additively manufactured SS316L and Ti6Al4V micro-struts as a function of build angle. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 46, 102050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bültmann, J.; Merkt, S.; Hammer, C.; Hinke, C.; Prahl, U. Scalability of the mechanical properties of selective laser melting produced micro-struts. J. Laser Appl. 2015, 27, S29206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskery, I.; Aboulkhair, N.T.; Corfield, M.R.; Tuck, C.; Clare, A.T.; Leach, R.K.; Wildman, R.D.; Ashcroft, I.A.; Hague, R.J.M. Quantification and characterisation of porosity in selectively laser melted Al–Si10–Mg using X-ray computed tomography. Mater. Charact. 2016, 111, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Qu, S.; Ma, J.; London, G.; Shen, Z.; Liu, W. 3D-imaging of selective laser melting defects in a Co–Cr–Mo alloy by synchrotron radiation micro-CT. Acta Mater. 2015, 98, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, S.; Abel, A.; Gumpinger, J.; Brandão, A.D.; Beretta, S. Quality control of AlSi10Mg produced by SLM: Metallography versus CT scans for critical defect size assessment. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 28, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voisin, T.; Calta, N.P.; Khairallah, S.A.; Forien, J.-B.; Balogh, L.; Cunningham, R.W.; Rollett, A.D.; Wang, Y.M. Defects-dictated tensile properties of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V. Mater. Des. 2018, 158, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, W.H.; Gao, M.; Zhang, X.; Liang, E.; Chiu, N.S.L.; Lim, C.V.S.; Huang, A. The influence of porosity on Ti-6Al-4V parts fabricated by laser powder bed fusion in the pursuit of process efficiency. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 119, 5417–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, K.; Promoppatum, P.; Quek, S.S.; Raghavan, S.; Johan, N.S.; Shukla, S.; Samudrala, S.; Van Der Veen, S.; Jhon, M.H. Effect of porosity distribution on the strength and strain-to-failure of Laser-Powder Bed Fusion printed Ti-6Al-4V. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 75, 103738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Chou, K. Formation of keyhole and lack of fusion pores during the laser powder bed fusion process. Manuf. Lett. 2022, 32, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Starr, T.; Chou, K. A Study of Keyhole Porosity in Selective Laser Melting: Single-Track Scanning With Micro-CT Analysis. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2019, 141, 071004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskery, I.; Aremu, A.O.; Simonelli, M.; Tuck, C.; Wildman, R.D.; Ashcroft, I.A.; Hague, R.J.M. Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Selectively Laser Melted Parts with Body-Centred-Cubic Lattices of Varying cell size. Exp. Mech. 2015, 55, 1261–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyre, P.; Da Silva, J.R.; Hamouche, Z.; Helbert, A.-L.; Daligault, J.; Dal, M.; Coste, F.; Baudin, T. Size and build strategy effects for the L-PBF process applied to Inconel 625 vertical struts: A combined numerical and experimental approach. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 132, 5063–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Fernández, M.A.; Mumtaz, K.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J.; Galindo-Nava, E.I.; Ghadbeigi, H. A microstructure sensitive model for deformation of Ti-6Al-4V describing Cast-and-Wrought and Additive Manufacturing morphologies. Mater. Des. 2018, 160, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, D.; Alabort, C.; Tang, Y.T.; Viscasillas, M.J.; Reed, R.C.; Alabort, E. On the size and orientation effect in additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V. Mater. Des. 2020, 186, 108235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Sercombe, T.B.; Wang, S.; Hao, Y.; Yang, R.; Murr, L.E. Comparison of the microstructures and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V fabricated by selective laser melting and electron beam melting. Mater. Des. 2016, 95, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promoppatum, P.; Taprachareon, K.; Chayasombat, B.; Tanprayoon, D. Understanding size-dependent thermal, microstructural, mechanical behaviors of additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V from experiments and thermo-metallurgical simulation. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 75, 1162–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narra, S.P.; Rollett, A.D.; Ngo, A.; Scannapieco, D.; Shahabi, M.; Reddy, T.; Pauza, J.; Taylor, H.; Gobert, C.; Diewald, E.; et al. Process qualification of laser powder bed fusion based on processing-defect structure-fatigue properties in Ti-6Al-4V. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2023, 311, 117775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.V.; Narra, S.P.; Cunningham, R.W.; Liu, H.; Chen, H.; Suter, R.M.; Beuth, J.L.; Rollett, A.D. Defect structure process maps for laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, C.; Shuai, S.; Zhao, R.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Hu, T.; Xuan, W.; Li, C.; Yu, J.; et al. Study of pore defect and mechanical properties in selective laser melted Ti6Al4V alloy based on X-ray computed tomography. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 797, 139981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbano, T.; Briggs, B.N.; Waterman, J.L.; Nimer, S.; Peitsch, C.; Sopcisak, J.; Trigg, D.; Storck, S. Uncovering the coupled impact of defect morphology and microstructure on the tensile behavior of Ti-6Al-4V fabricated via laser powder bed fusion. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2021, 294, 117113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaschel, F.R.; Celikin, M.; Dowling, D.P. Effects of laser power on geometry, microstructure and mechanical properties of printed Ti-6Al-4V parts. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 278, 116539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
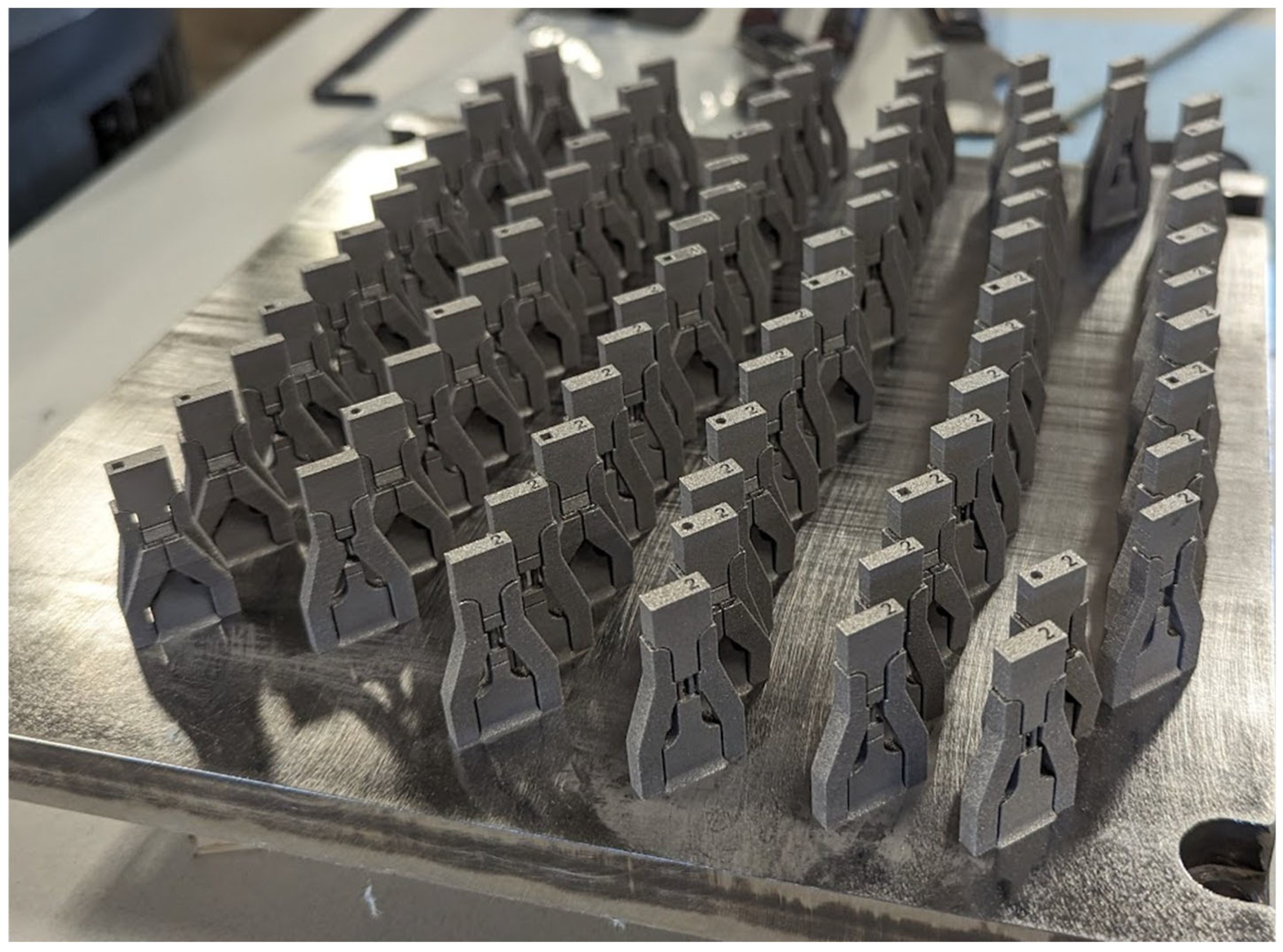
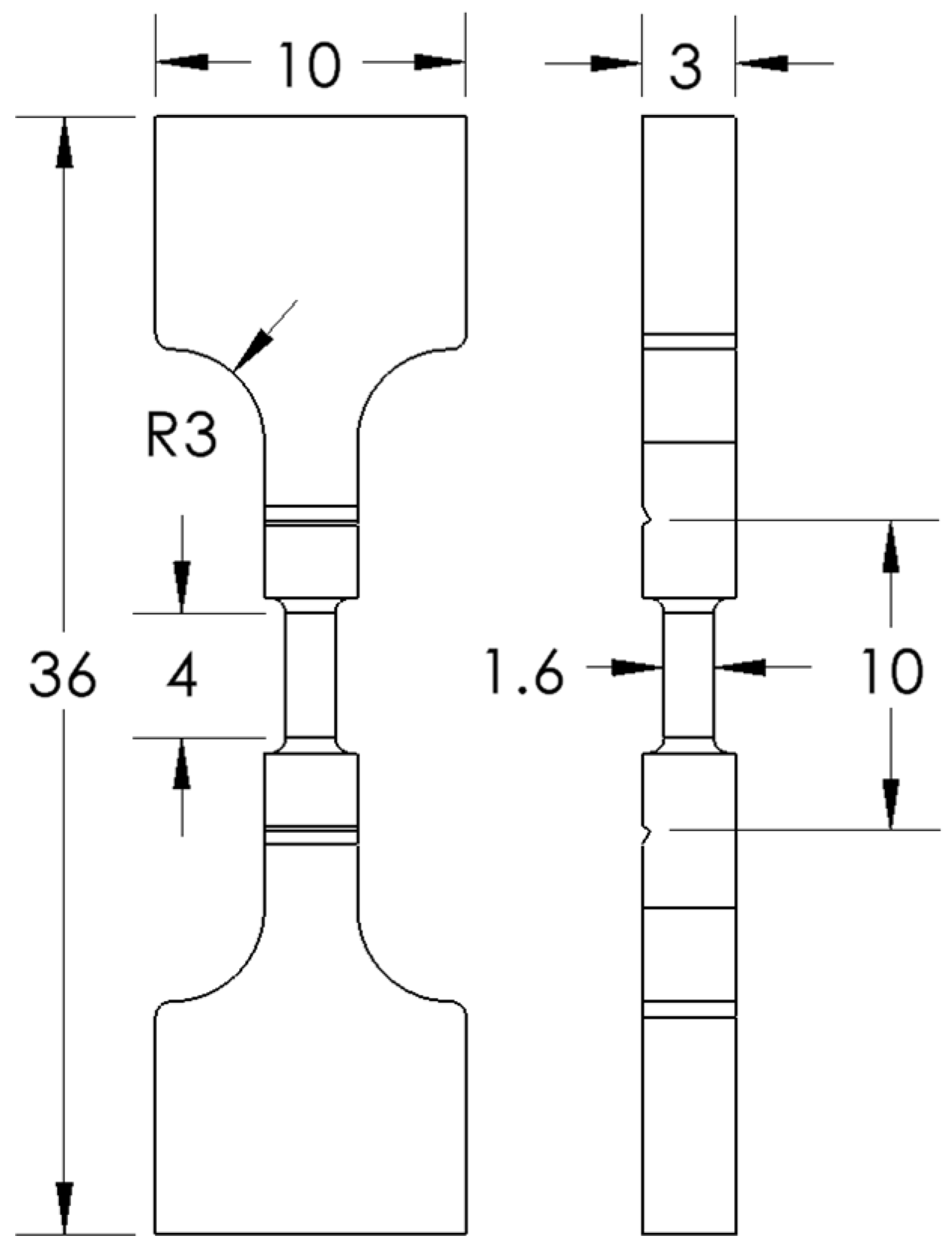


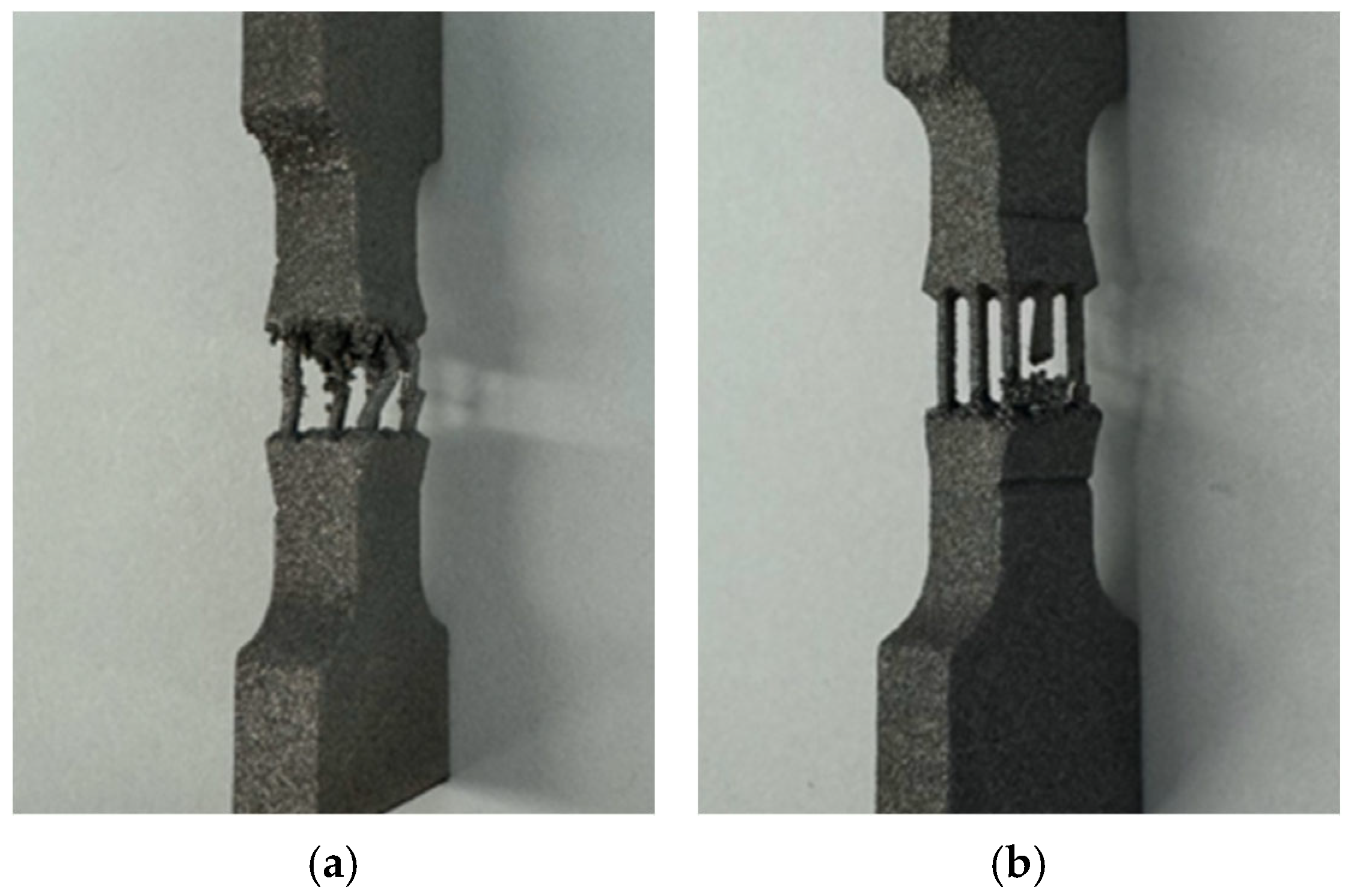
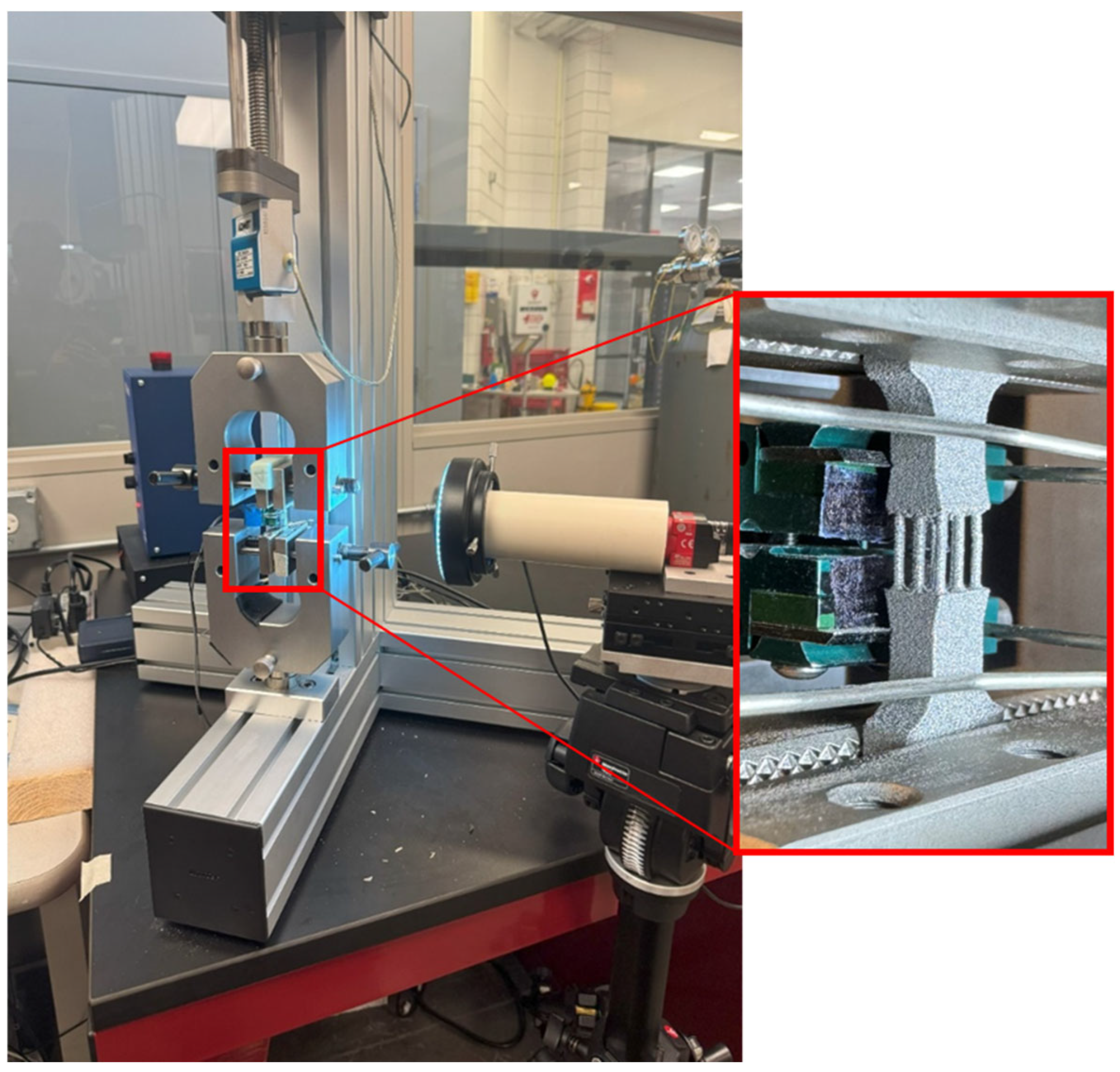
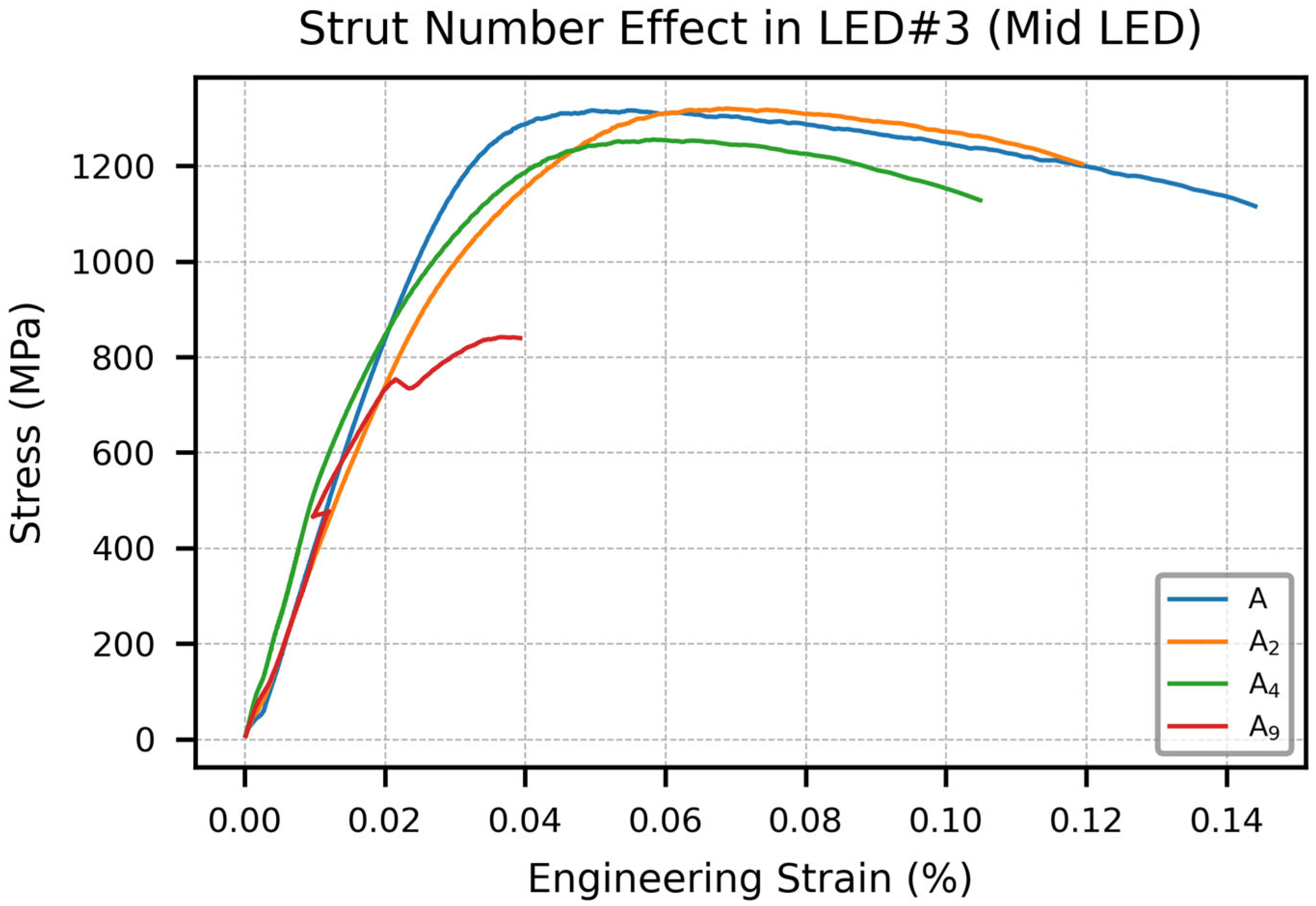




| Specimen | A | A2 | A4 | A9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Circular | 1.8 mm | 1.27 mm | 0.9 mm | 0.6 mm |
| Square | 1.6 mm | 1.13 mm | 0.8 mm | 0.53 mm |
| A | A2 | A4 | A9 |
|---|---|---|---|
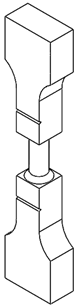 | 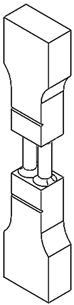 | 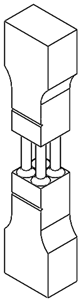 | 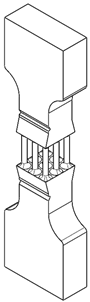 |
| A | A/2 | A/4 | A/9 |
|---|---|---|---|
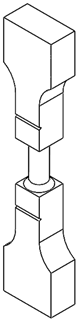 | 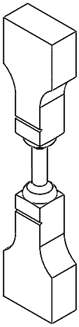 |  | 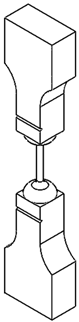 |
| Parameter | P (W) | V (mm/s) | LED (J/mm) | Abv. | Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 60 | 800 | 0.075 | LED#1 | Lowest |
| 2 | 120 | 1200 | 0.100 | LED#2 | Low |
| 3 | 120 | 800 | 0.150 | LED#3 | Mid |
| 4 | 120 | 600 | 0.200 | LED#4 | High |
| 5 | 190 | 800 | 0.238 | LED#5 | Highest |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, R.; Aydogan, B.; Chou, K. An Experimental Study on Tensile Characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V Thin Struts Made by Laser Powder-Bed Fusion: Effects of Strut Geometry and Linear Energy Density. Metals 2025, 15, 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15091009
Islam R, Aydogan B, Chou K. An Experimental Study on Tensile Characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V Thin Struts Made by Laser Powder-Bed Fusion: Effects of Strut Geometry and Linear Energy Density. Metals. 2025; 15(9):1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15091009
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Rabiul, Beytullah Aydogan, and Kevin Chou. 2025. "An Experimental Study on Tensile Characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V Thin Struts Made by Laser Powder-Bed Fusion: Effects of Strut Geometry and Linear Energy Density" Metals 15, no. 9: 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15091009
APA StyleIslam, R., Aydogan, B., & Chou, K. (2025). An Experimental Study on Tensile Characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V Thin Struts Made by Laser Powder-Bed Fusion: Effects of Strut Geometry and Linear Energy Density. Metals, 15(9), 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15091009








