Microstructure and Properties of Bi-Sn, Bi-Sn-Sb, and Bi-Sn-Ag Solder Alloys for Electronic Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Bi–Sn binary alloy: Melting was performed in a resistance furnace stabilized at 300 °C. Pre-weighed Bi and Sn were introduced after thermal equilibrium was achieved;
- Bi–Sn–Sb alloy: The furnace was stabilized at 650 °C, and Sb was first introduced and melted, followed by the addition of Sn and Bi to complete the alloy composition;
- Bi–Sn–Ag alloy: Ag was initially melted at 980 °C (peak ~1000 °C), followed by the sequential addition of Bi and Sn.
3. Results and Discussion
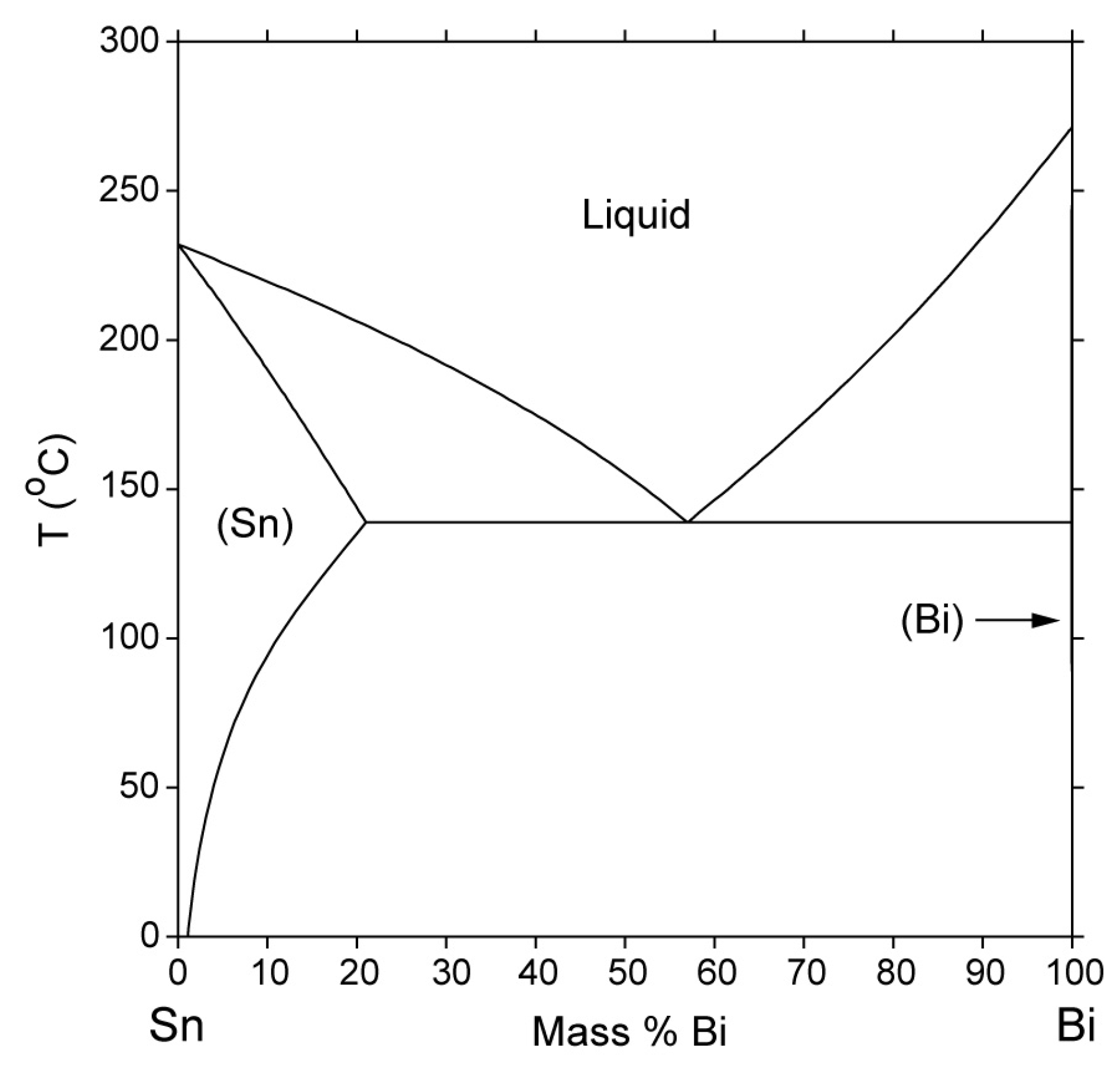
3.1. Characterization of Bi-Sn-Based Solder Alloys
3.1.1. Chemical Composition
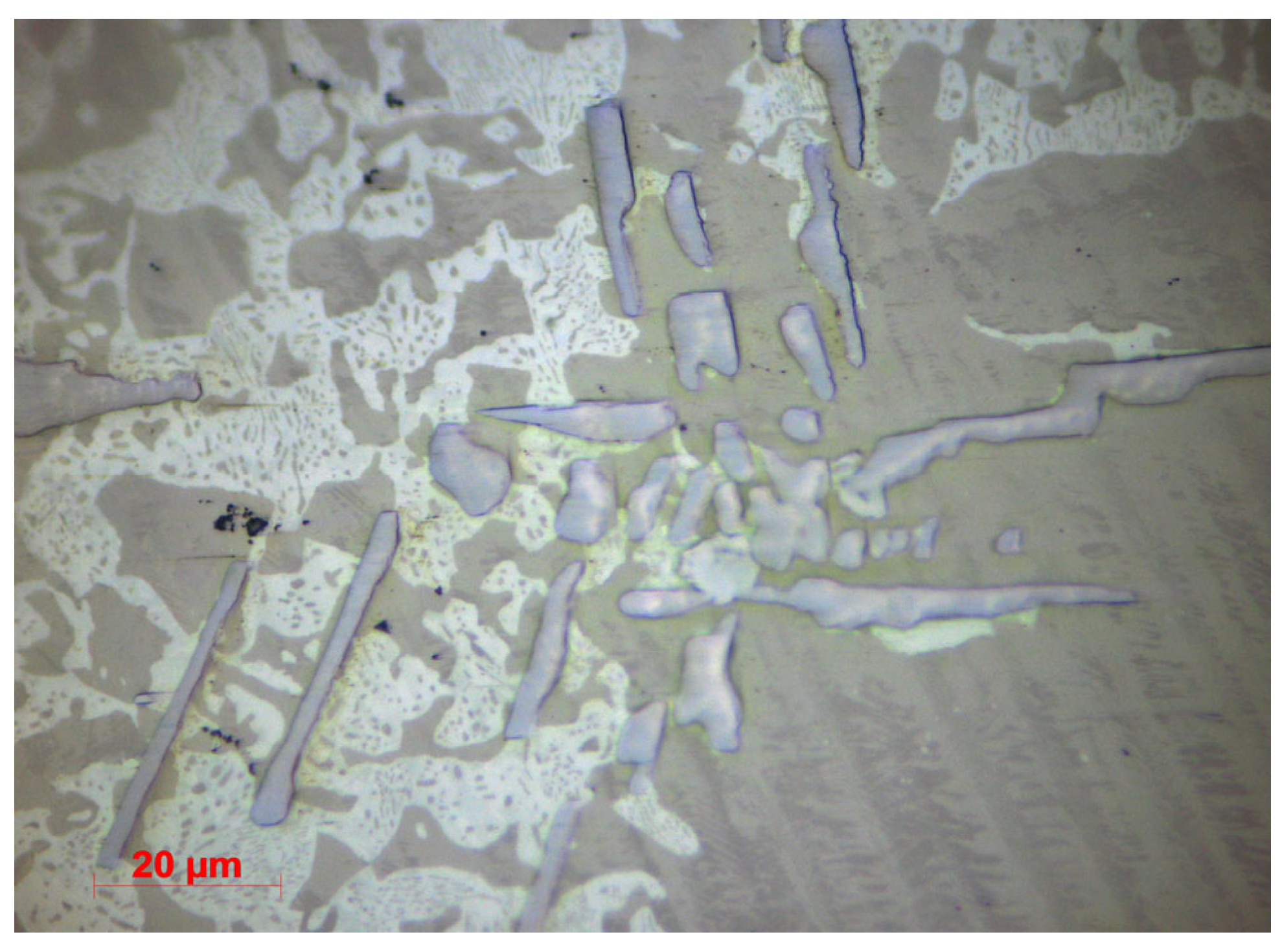
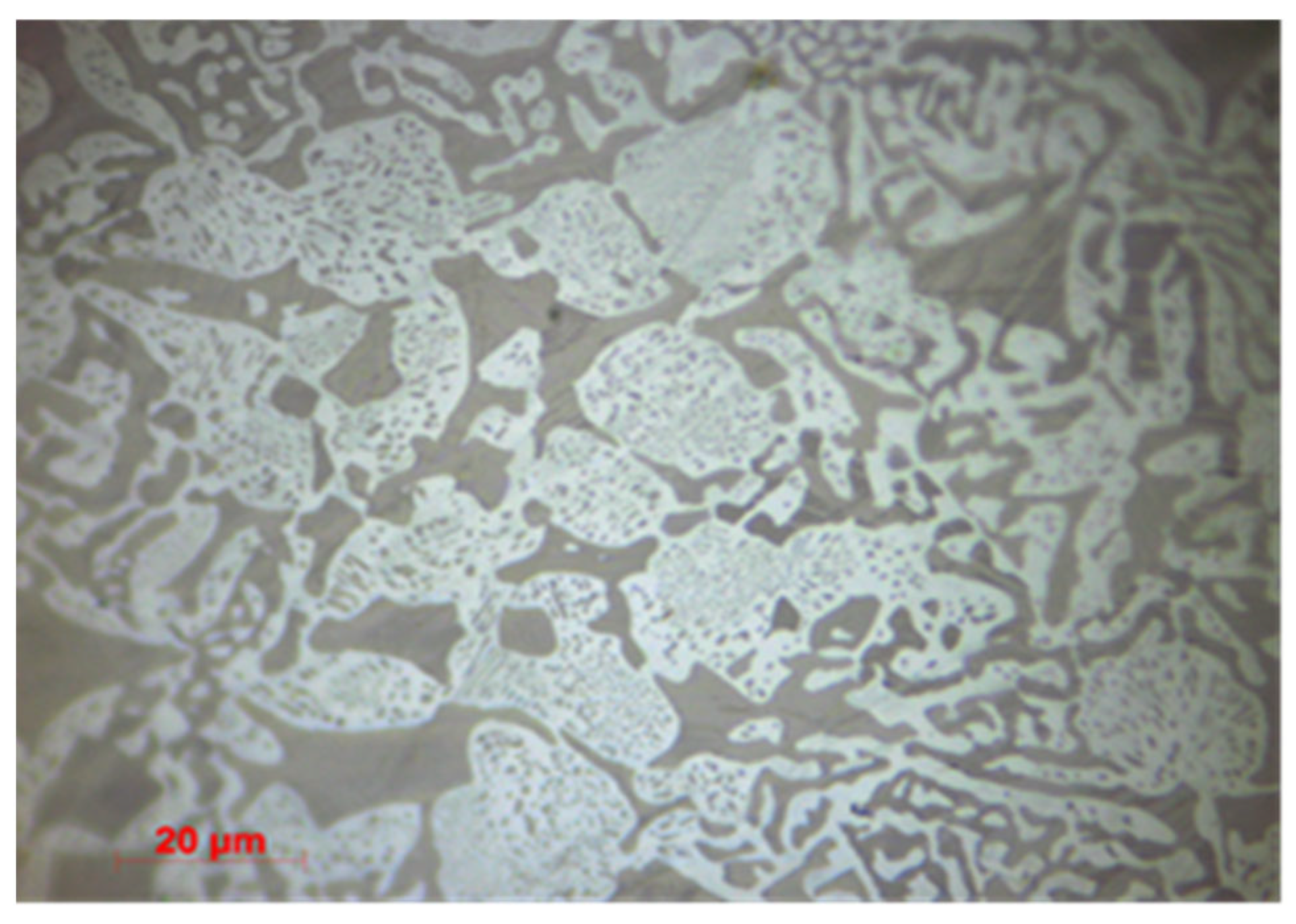
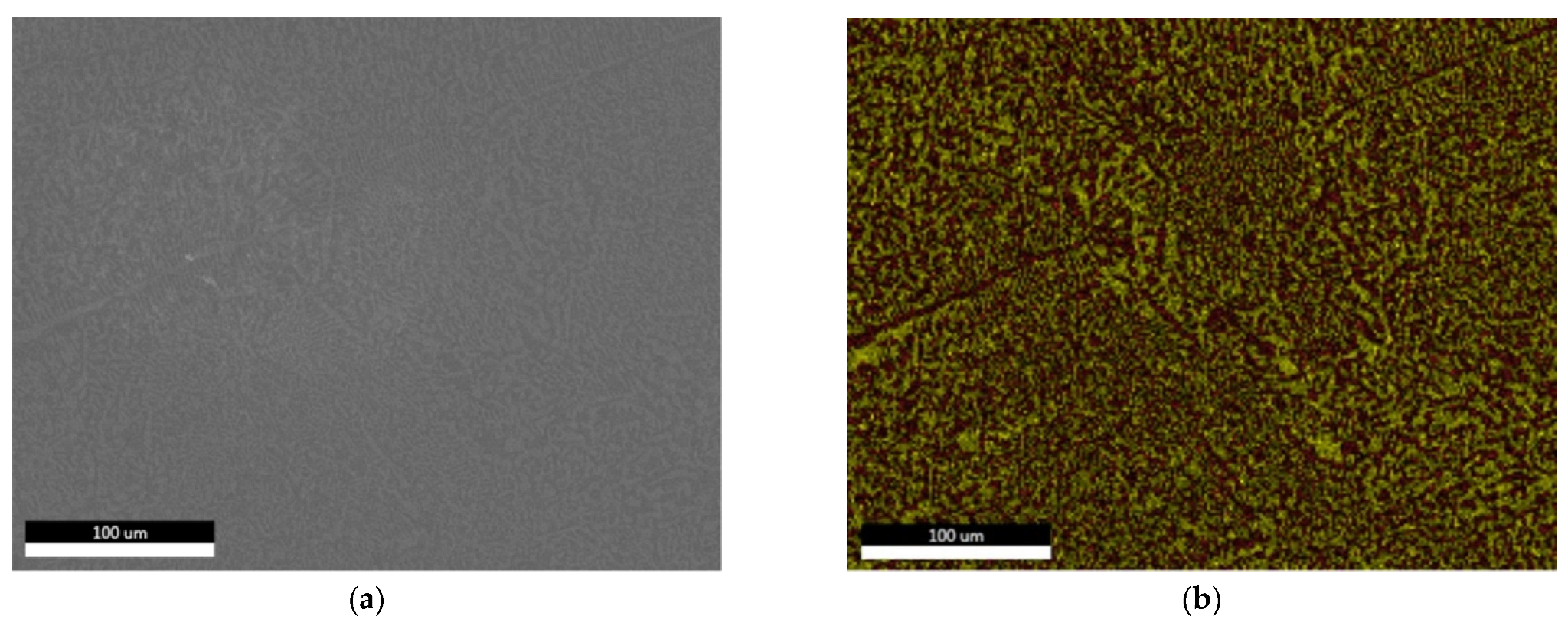
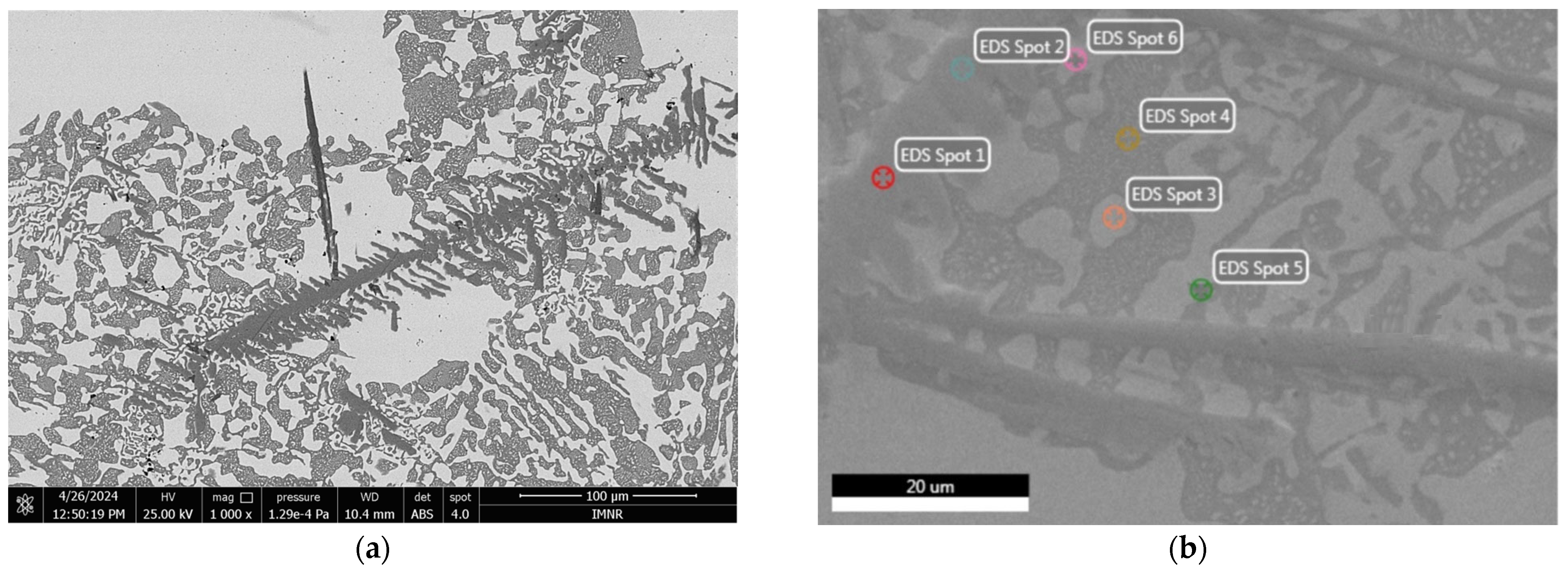
3.1.2. Microstructural Characterization
3.2. Microhardness Evaluation of Bi-Sn-Based Solder Alloys
3.3. Thermal and Electrical Conductivity of Bi-Sn-Based Solder Alloys
4. Conclusions
- Sb induces granular Sn-Sb intermetallics that may strengthen the structure but degrade thermal transport;
- Ag promotes fine, directional intermetallics (Ag3Sn), enhances electrical conductivity, and moderately reduces thermal conductivity;
- Both Ag and Sb raise electrical conductivity compared to the binary alloy, reflecting complex structural interactions;
- The binary Bi60Sn40 serves as a stable baseline, offering high thermal conductivity and a uniform eutectic structure suitable for low-temperature soldering.
- Ag increases electrical conductivity but slightly lowers thermal conductivity at higher temperatures.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vianco, P.T.; Rejent, J.A. Properties of ternary Sn-Ag-Bi solder alloys: Part I—Thermal properties and microstructural analysis. J. Electron. Mater. 1999, 28, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtew, M.; Selvaduray, G. Lead-free Solders in Microelectronics. Mater. Sci. Eng. R. Rep. 2000, 27, 95–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.A.; Chen, F.Y.; Gao, R.; Ho, C.E.; Nishikawa, H.; Chen, C.M. Effect of Bi Addition on Melting Behavior, Solder Joint Strength, and Thermal Aging Resistance of Sn-3.5Ag/Cu Joints. JOM 2025, 77, 4206–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA—European Environment Agency. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/european-zero-pollution-dashboards/indicators/progress-in-regulating-lead-signal (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- Razak, N.R.A.; Salleh, M.A.A.M.; Saud, N.; Said, R.M.; Ramli, M.I.I. Influence of Bismuth in Sn-Based Lead-Free Solder—A Short Review. Solid State Phenom. 2018, 273, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koleňák, R.; Provazník, M.; Kostolný, I.; Kar, A. Soldering by the Active Lead-Free Tin and Bismuth-Based Solders. In Lead Free Solders; Kar, A., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattner, U. NIST Phase Diagrams and Computational Thermodynamics—Solder Systems—SRD 139, National Institute of Standards and Technology; 1990. Available online: https://www.metallurgy.nist.gov/phase/solder/bisn.html (accessed on 2 August 2025).
- Kang, H.; Rajendran, S.H.; Jung, J.P. Low Melting Temperature Sn-Bi Solder: Effect of Alloying and Nanoparticle Addition on the Microstructural, Thermal, Interfacial Bonding, and Mechanical Characteristics. Metals 2021, 11, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, M.S.; Osman, S.A.; Efzan, E. The Development of Low-Temperature Lead-Free Solders using Sn-Bi Solders Alloys. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2019, 8, 11956–11962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Collins, M.N. Improved Reliability and Mechanical Performance of Ag Microalloyed Sn58Bi Solder Alloys. Metals 2019, 9, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.A. Influence of Ag and Zn on the Microstructure and Properties of Sn-40 Bi Alloy for Improved Soldering Applications. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2024, 6, 8084–8093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.L.; Reinhart, G.; Nguyen-Thi, H.; Mangelinck-Noël, N.; Garcia, A.; Spinelli, J.E. Microstructural development and mechanical properties of a near-eutectic directionally solidified Sn–Bi solder alloy. Mater. Charact. 2015, 107, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Xue, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Tatsumi, H.; Nishikawa, H. Influence of Isothermal Aging on Microstructure and Shear Property of Novel Epoxy Composite SAC305 Solder Joints. Polymers 2023, 15, 4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Sharma, A.; Jung, J.P. Low-melting and thermal-conducting Sn-Bi-Ag solder enhanced with SnO2 nanoparticles for reliable mini-LED microsystems. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2025, 36, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, A.; Nowottnick, M. Composite Soldering Materials Based on BiSnAg for High-Temperature Stable Solder Joints. J. Microelectron. Packag. 2022, 19, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavan, J.S.; Pazhani, A.; Amer, M.; Patel, N.; Tg, U. Microstructural Evolution and Phase Transformation on Sn–Ag Solder Alloys under High-Temperature Conditions Focusing on Ag3Sn Phase. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2024, 26, 2400660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavan, J.S.; Kadavath, G.; Honecker, D.; Pazhani, A. Small-angle neutron scattering analysis in Sn-Ag Lead-free solder alloys: A focus on the Ag3Sn intermetallic phase. Mater. Charact. 2024, 217, 114385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, K.S.; Hwang, C.W.; Suganuma, K. Effect of composition and cooling rate on microstructure and tensile properties of Sn–Zn–Bi alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2003, 352, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tu, K.N. Low melting point solders based on Sn, Bi, and In elements. Mater. Today Adv. 2020, 8, 100115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Tan, X.F.; McDonald, S.D.; Nogita, K. Phase Transformations and Mechanical Properties in In–Bi–Sn Alloys as a Result of Low-Temperature Storage. Materials 2024, 17, 3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, S.M.; Yow, H.K.; Yeoh, K.H. Lead-Free BiSnAg Soldering Process for Voidless Semiconductor Packaging. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 13, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xue, S.B.; Gao, L.L.; Sheng, Z.; Ye, H.; Xiao, Z.X.; Zeng, G.; Chen, Y.; Yu, S.L. Development of Sn–Zn lead-free solders bearing alloying elements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2009, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Hou, Z.; Xie, X.; Lin, P.; Huo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X. Mechanical properties and microstructure evolution of Sn–Bi-based solder joints by microalloying regulation mechanism. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 31, 3226–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Tan, X.F.; McDonald, S.D.; Nogita, K. Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Binary In-Sn Alloys for Flexible Low Temperature Electronic Joints. Materials 2022, 15, 8321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, J.R.d.S.; Reyes, R.A.V.; Gouveia, G.L.d.; Coury, F.G.; Spinelli, J.E. Evaluation of Solidification and Interfacial Reaction of Sn-Bi and Sn-Bi-In Solder Alloys in Copper and Nickel Interfaces. Metals 2024, 14, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacob, G.; Ghica, V.G.; Petrescu, M.I.; Niculescu, F.; Butu, M.; Stancel, C.D.; Stanescu, M.M.; Ilie, A.A. Research on the development and characterization of Bi-Sn, Bi-Sn-Sb and Bi-Sn-Ag solder alloys. UPB Sci. Bull. B Chem. Mater. Sci. 2024, 86, 187–198. [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi, A.; Kurose, M. Effect of Sb and Zn Addition on the Microstructures and Tensile Properties of Sn-Bi-Based Alloys. Materials 2022, 15, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, H.N.; Tay, S.X.; Blendell, J.; Handwerker, C.A. Microalloying effects of Sb and Ag on the microstructural evolution of eutectic Sn–Bi alloys. MRS Adv. 2023, 8, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, N.; Xian, J.W.; Sugiyama, A.; Yasuda, H.; Gourlay, C.M. Ag3Sn Morphology Transitions During Eutectic Growth in Sn–Ag Alloys. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2023, 54, 909–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šebo, P.; Švec, P.; Janičkovič, D.; Illeková, E.; Zemánková, M.; Sidorov, V.; Švec, P.; Plevachuk, Y. The influence of silver content on structure and properties of Sn–Bi–Ag solder and Cu/solder/Cu joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 571, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Septiwerdani, P.; Chen, Z. Elastic modulus, hardness and creep performance of SnBi alloys using nanoindentation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 558, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Chen, Y.; You, K.; Dong, Z.; Jia, Y.; Wang, G.; Peng, J.; Cai, S.; Luo, X.; Liu, C.; et al. Effect of Bi, Sb, and Ti on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of SAC105 Alloys. Materials 2022, 15, 4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, N. Interfacial Microstructure and Shear Strength Improvements of Babbitt–Steel Bimetal Composites Using Sn–Bi Interlayer via Liquid–Solid Casting. Sustainability 2023, 15, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
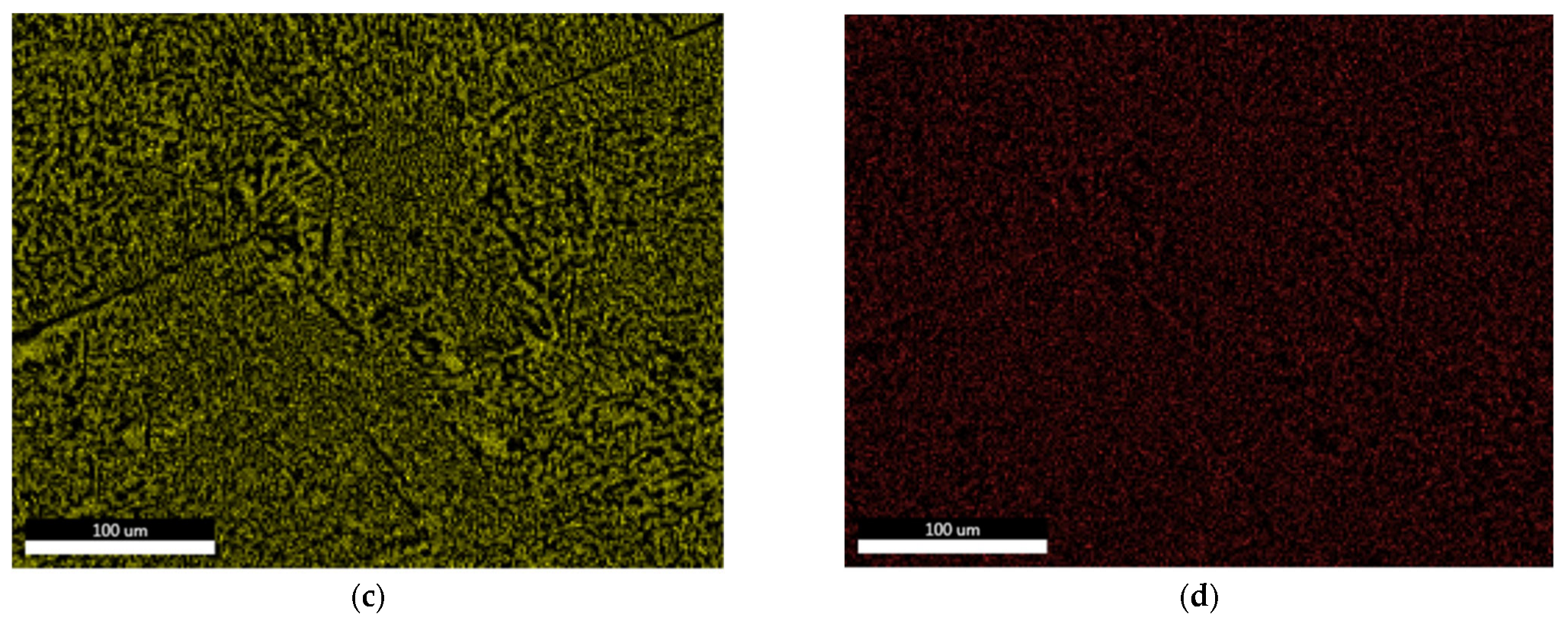




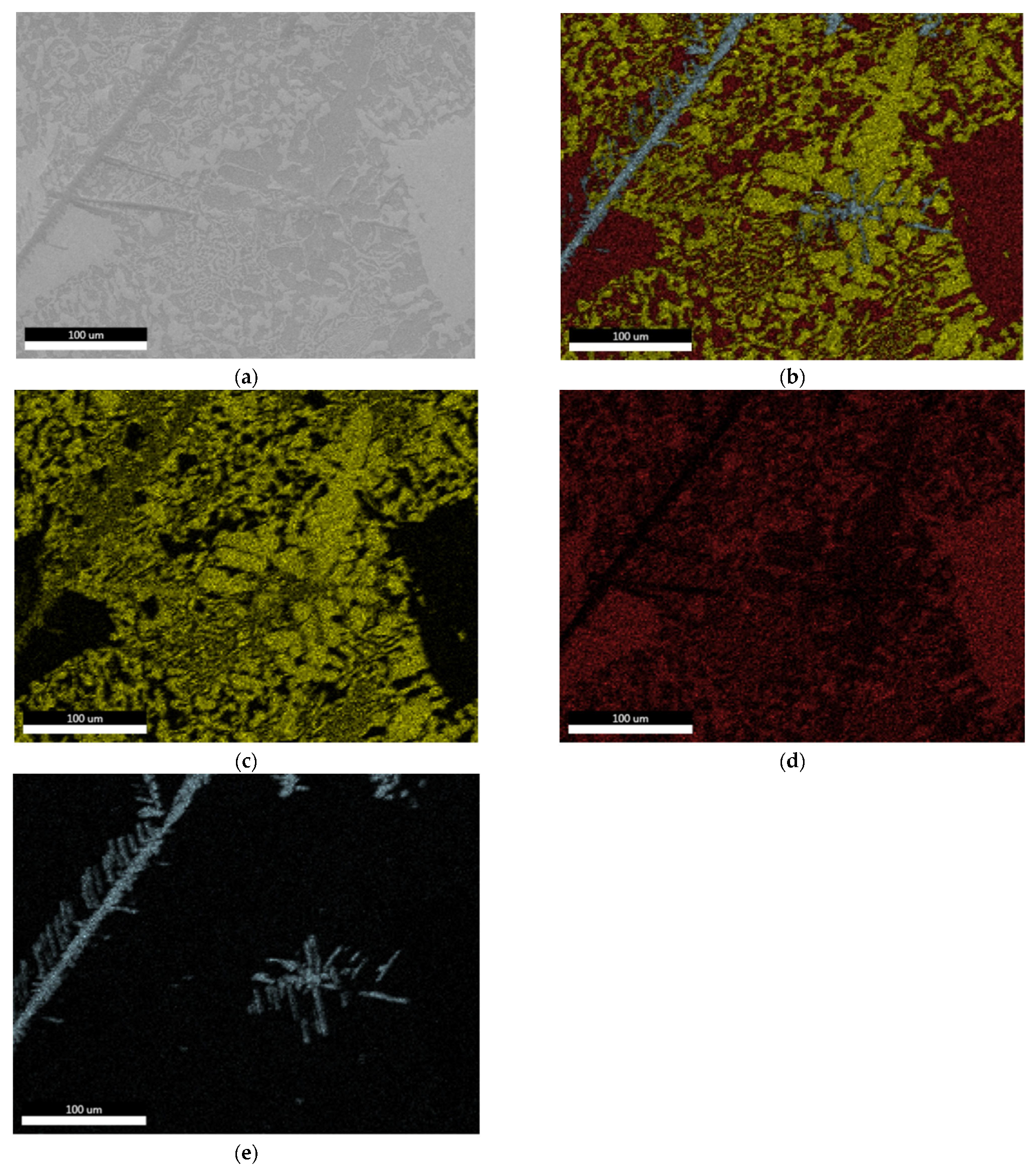
| Chemical Composition (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Element | Bi60Sn40 | Bi60Sn35Sb5 | Bi60Sn35Ag5 |
| Bi | 59.437 | 59.411 | 58.804 |
| Sn | 39.475 | 34.533 | 34.271 |
| Sb | 0.0167 | 4.88 | 0.0177 |
| Ag | 0 | 0 | 4.93 |
| Cu | 0.122 | 0.182 | 1.63 |
| Fe | 0.018 | 0.029 | 0.024 |
| O.E. * | rem. | rem. | rem. |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 |
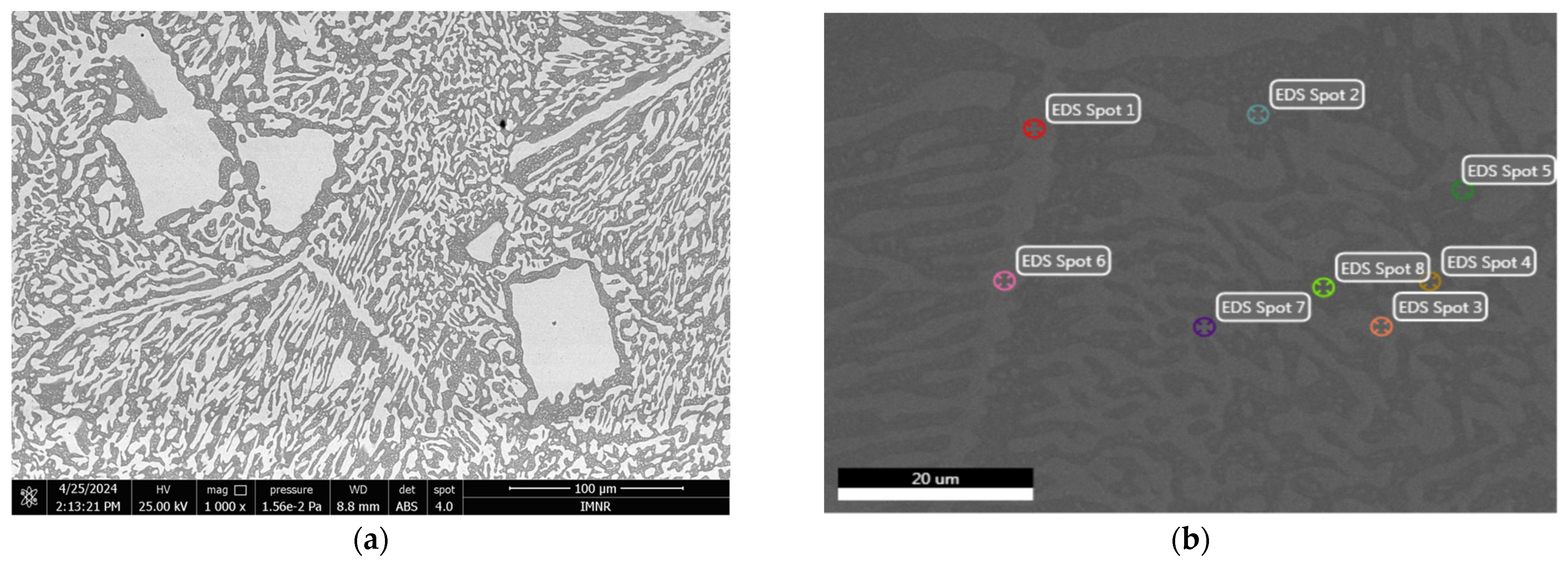
| EDS Analysis | Element | Weight % | Atomic % | Net Int. | Error % | Peak-to-Background (P/B) Ratio | Resolution, R | Fluorescence, F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spot 1 | BiL | 100.00 | 100.00 | 349.38 | 12.34 | 205.5412 | 1.1256 | 1.0445 |
| Spot 2 | SnL | 31.51 | 44.75 | 411.53 | 7.86 | 167.6377 | 1.0575 | 1.0067 |
| BiL | 68.49 | 55.25 | 280.07 | 12.92 | 182.9532 | 1.1144 | 1.0457 | |
| Spot 3 | SnL | 2.31 | 3.99 | 18.93 | 45.62 | 9.9665 | 1.0628 | 1.0074 |
| BiL | 97.69 | 96.01 | 353.42 | 13.37 | 200.5332 | 1.1248 | 1.0446 | |
| Spot 4 | SnL | 82.19 | 89.04 | 1038.78 | 6.83 | 317.0775 | 1.0479 | 1.0056 |
| BiL | 17.81 | 10.96 | 44.85 | 32.78 | 38.6640 | 1.0952 | 1.0527 | |
| Spot 5 | SnL | 70.26 | 80.62 | 999.99 | 6.77 | 341.4499 | 1.0502 | 1.0058 |
| BiL | 29.74 | 19.38 | 89.68 | 21.60 | 78.9456 | 1.0999 | 1.0501 | |
| Spot 6 | SnL | 2.15 | 3.72 | 14.42 | 56.01 | 8.6900 | 1.0628 | 1.0074 |
| BiL | 97.85 | 96.28 | 342.71 | 11.76 | 188.3782 | 1.1248 | 1.0446 | |
| Spot 7 | SnL | 7.63 | 12.69 | 82.10 | 17.49 | 35.3432 | 1.0618 | 1.0072 |
| BiL | 92.37 | 87.31 | 368.21 | 13.08 | 205.4512 | 1.1229 | 1.0447 | |
| Spot 8 | SnL | 82.20 | 89.05 | 1386.51 | 6.45 | 414.2416 | 1.0479 | 1.0056 |
| BiL | 17.80 | 10.95 | 53.73 | 33.55 | 50.5040 | 1.0952 | 1.0527 |
| EDS Analysis | Element | Weight % | Atomic % | Net Int. | Error % | Peak-to-Background (P/B) Ratio | Resolution, R | Fluorescence, F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spot 1 | SnL | 2.74 | 4.73 | 14.75 | 41.77 | 11.3363 | 1.0627 | 1.0074 |
| BiL | 97.26 | 95.27 | 436.83 | 11.37 | 191.4222 | 1.1246 | 1.0446 | |
| Spot 2 | SnL | 20.20 | 29.05 | 371.86 | 8.01 | 101.1552 | 1.0578 | 1.0071 |
| SbL | 9.87 | 13.84 | 185.19 | 11.58 | 49.3374 | 1.0601 | 1.0073 | |
| BiL | 69.93 | 57.12 | 351.90 | 13.20 | 175.2969 | 1.1150 | 1.0456 | |
| Spot 3 | SnL | 19.99 | 27.99 | 329.99 | 8.73 | 97.1621 | 1.0570 | 1.0072 |
| SbL | 14.67 | 20.04 | 235.10 | 11.48 | 71.2188 | 1.0593 | 1.0072 | |
| BiL | 65.34 | 51.97 | 291.36 | 13.36 | 160.3760 | 1.1134 | 1.0458 | |
| Spot 4 | SnL | 49.87 | 53.12 | 966.44 | 6.79 | 263.7330 | 1.0469 | 1.0074 |
| SbL | 38.16 | 39.63 | 701.72 | 7.45 | 202.0403 | 1.0488 | 1.0060 | |
| BiL | 11.97 | 7.24 | 43.93 | 39.87 | 36.0446 | 1.0934 | 1.0538 |
| EDS Analysis | Element | Weight % | Atomic % | Net Int. | Error % | Peak-to-Background (P/B) Ratio | Resolution, R | Fluorescence, F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spot 1 | AgL | 72.18 | 74.06 | 1356.90 | 7.08 | 332.8965 | 1.0376 | 1.0065 |
| SnL | 27.82 | 25.94 | 328.80 | 10.20 | 125.1740 | 1.0429 | 1.0036 | |
| Spot 2 | AgL | 68.09 | 71.90 | 1394.17 | 6.89 | 329.1566 | 1.0388 | 1.0063 |
| SnL | 25.82 | 24.78 | 340.73 | 9.98 | 121.4951 | 1.0443 | 1.0038 | |
| BiL | 6.09 | 3.32 | 11.19 | 63.37 | 16.6575 | 1.0880 | 1.0600 | |
| Spot 3 | BiL | 100.00 | 100.00 | 385.37 | 12.23 | 182.3931 | 1.1256 | 1.0445 |
| Spot 4 | SnL | 74.24 | 83.54 | 1141.59 | 6.40 | 341.7386 | 1.0494 | 1.0057 |
| BiL | 25.76 | 16.46 | 87.96 | 24.13 | 65.6165 | 1.0983 | 1.0509 | |
| Spot 5 | SnL | 46.27 | 41.83 | 719.74 | 6.34 | 217.5642 | 1.0465 | 1.0076 |
| CuK | 26.03 | 43.95 | 490.31 | 8.35 | 155.4725 | 1.0806 | 1.1170 | |
| BiL | 27.69 | 14.22 | 95.13 | 21.38 | 72.2014 | 1.0926 | 1.0415 | |
| Spot 6 | SnL | 60.06 | 47.82 | 870.31 | 6.21 | 271.5037 | 1.0414 | 1.0078 |
| CuK | 32.97 | 49.03 | 605.53 | 6.40 | 190.4063 | 1.0717 | 1.0779 | |
| BiL | 6.97 | 3.15 | 12.27 | 65.61 | 18.4796 | 1.0823 | 1.0416 |
| Alloys | Microhardness HV15 (Mean ± SD) |
|---|---|
| Bi60Sn40 | 14.59 ± 1.69 |
| Bi60Sn35Sb5 | 16.36 ± 3.42 |
| Bi60Sn35Ag5 | 17.33 ± 2.79 |
| Solder Alloy | Temperature (°C) | Thermal Diffusivity α (m2/s) | Thermal Conductivity λ (W/m·K) | Resistivity ρₑ (Ω·m) | Electrical Conductivity σ (S/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi60Sn40 | 25 | 10.75·10−6 | 16.93 | 3.80·10−7 | 2.63·106 |
| 50 | 11.85·10−6 | 18.94 | 4.45·10−7 | 2.25·106 | |
| 75 | 12.90·10−6 | 20.93 | 5.10·10−7 | 1.96·106 | |
| 100 | 13.93·10−6 | 22.93 | 6.35·10−7 | 1.57·106 | |
| 125 | 14.93·10−6 | 24.93 | 7.60·10−7 | 1.32·106 | |
| 140 | 16.06·10−6 | 26.93 | 8.35·10−7 | 1.20·106 | |
| ± s = 21.93 ± 3.74 | |||||
| Bi60Sn35Sb5 | 25 | 9.71·10−6 | 13.90 | 1.53·10−7 | 6.52·106 |
| 50 | 9.11·10−6 | 13.59 | 1.63·10−7 | 6.12·106 | |
| 75 | 8.66·10−6 | 13.43 | 1.76·10−7 | 5.67·106 | |
| 100 | 7.23·10−6 | 11.65 | 1.88·10−7 | 5.30·106 | |
| 125 | 6.81·10−6 | 11.38 | 2.00·10−7 | 4.86·106 | |
| 140 | 6.22·10−6 | 10.66 | 2.08·10−7 | 4.79·106 | |
| ± s = 12.44 ± 1.37 | |||||
| Bi60Sn35Ag5 | 25 | 11.91·10−6 | 18.28 | 1.52·10−7 | 6.54·106 |
| 50 | 11.56·10−6 | 18.25 | 1.66·10−7 | 6.15·106 | |
| 75 | 10.80·10−6 | 17.52 | 1.77·10−7 | 5.69·106 | |
| 100 | 10.46·10−6 | 17.43 | 1.89·10−7 | 5.33·106 | |
| 125 | 9.89·10−6 | 16.91 | 2.01·10−7 | 4.98·106 | |
| 140 | 9.56·10−6 | 16.77 | 2.08·10−7 | 4.81·106 | |
| ± s = 17.53 ± 0.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ilie, A.-A.; Niculescu, F.; Iacob, G.; Pencea, I.; Miculescu, F.; Bololoi, R.; Drăguț, D.-V.; Matei, A.-C.; Ghiţă, M.; Priceputu, A.; et al. Microstructure and Properties of Bi-Sn, Bi-Sn-Sb, and Bi-Sn-Ag Solder Alloys for Electronic Applications. Metals 2025, 15, 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080915
Ilie A-A, Niculescu F, Iacob G, Pencea I, Miculescu F, Bololoi R, Drăguț D-V, Matei A-C, Ghiţă M, Priceputu A, et al. Microstructure and Properties of Bi-Sn, Bi-Sn-Sb, and Bi-Sn-Ag Solder Alloys for Electronic Applications. Metals. 2025; 15(8):915. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080915
Chicago/Turabian StyleIlie, Andrei-Alexandru, Florentina Niculescu, Gheorghe Iacob, Ion Pencea, Florin Miculescu, Robert Bololoi, Dumitru-Valentin Drăguț, Alexandru-Cristian Matei, Mihai Ghiţă, Adrian Priceputu, and et al. 2025. "Microstructure and Properties of Bi-Sn, Bi-Sn-Sb, and Bi-Sn-Ag Solder Alloys for Electronic Applications" Metals 15, no. 8: 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080915
APA StyleIlie, A.-A., Niculescu, F., Iacob, G., Pencea, I., Miculescu, F., Bololoi, R., Drăguț, D.-V., Matei, A.-C., Ghiţă, M., Priceputu, A., & Ungureanu, C. (2025). Microstructure and Properties of Bi-Sn, Bi-Sn-Sb, and Bi-Sn-Ag Solder Alloys for Electronic Applications. Metals, 15(8), 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080915







