Synergistic Optimization of High-Temperature Mechanical Properties and Thermal Conductivity in B4C/Al Composites Through Nano-Al2O3 Phase Transformation and Process Engineering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
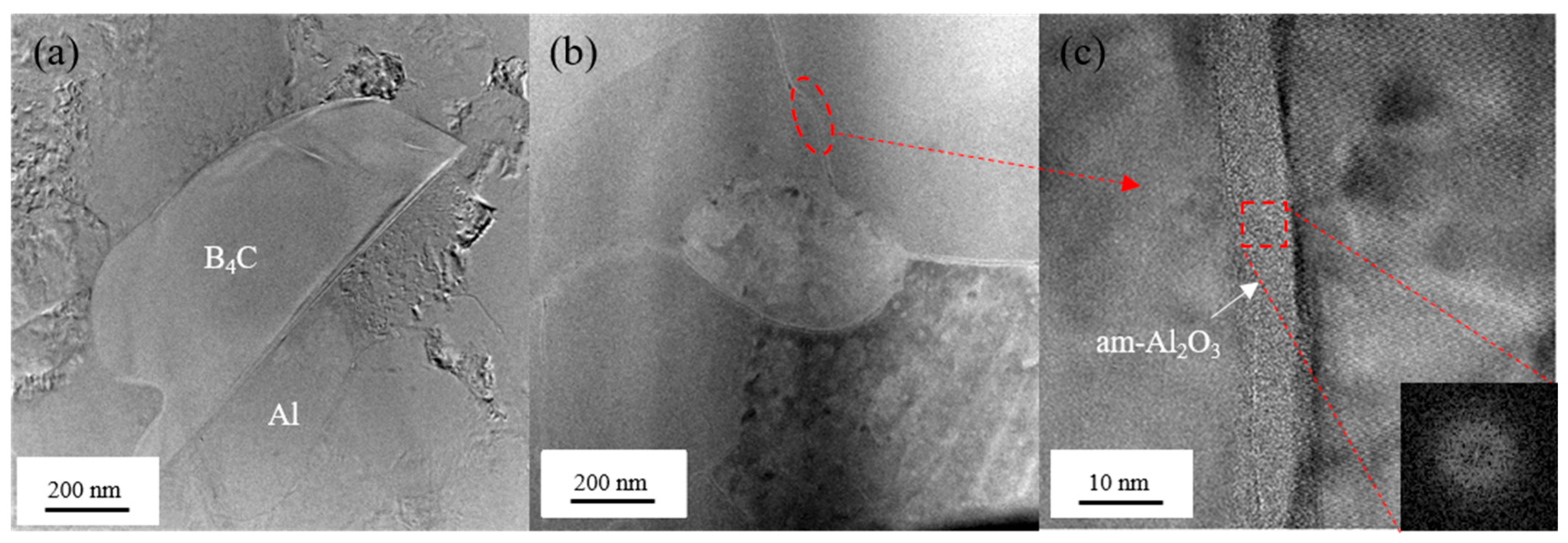
3.1. Microstructure and Properties of Forged Composites
3.2. Microstructure and Properties of Extruded Composites
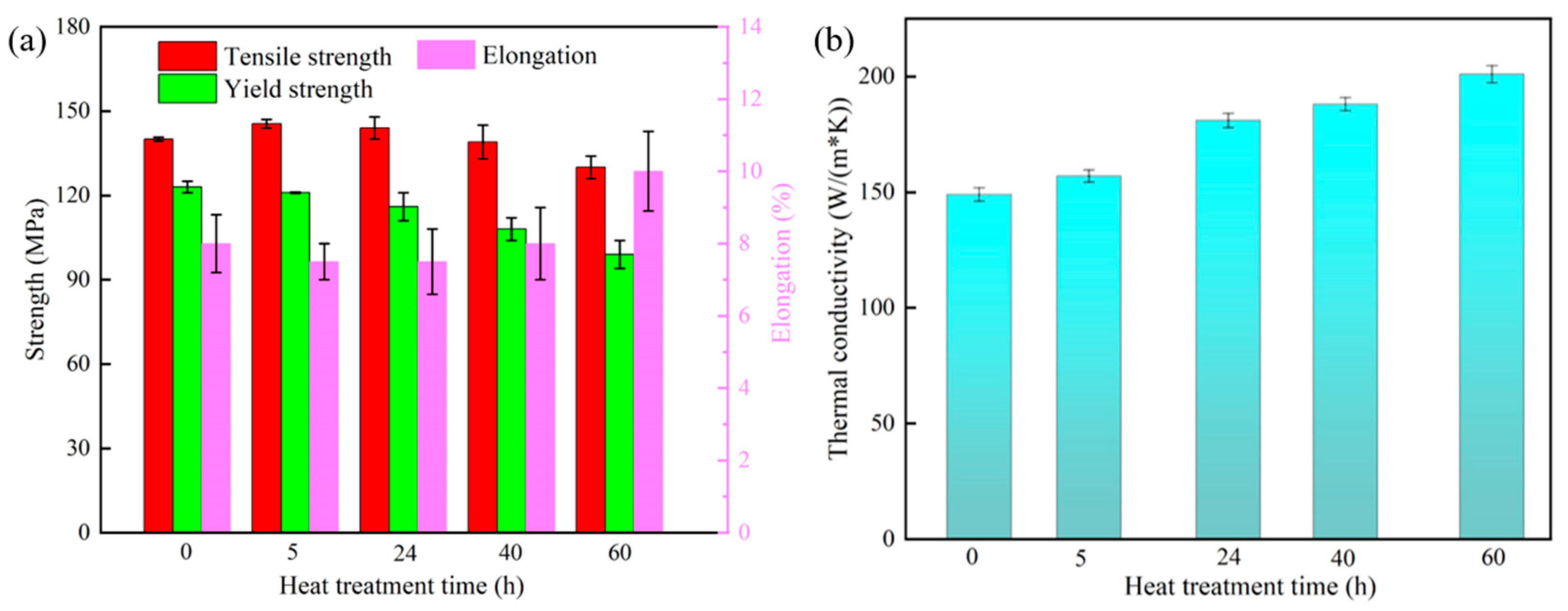
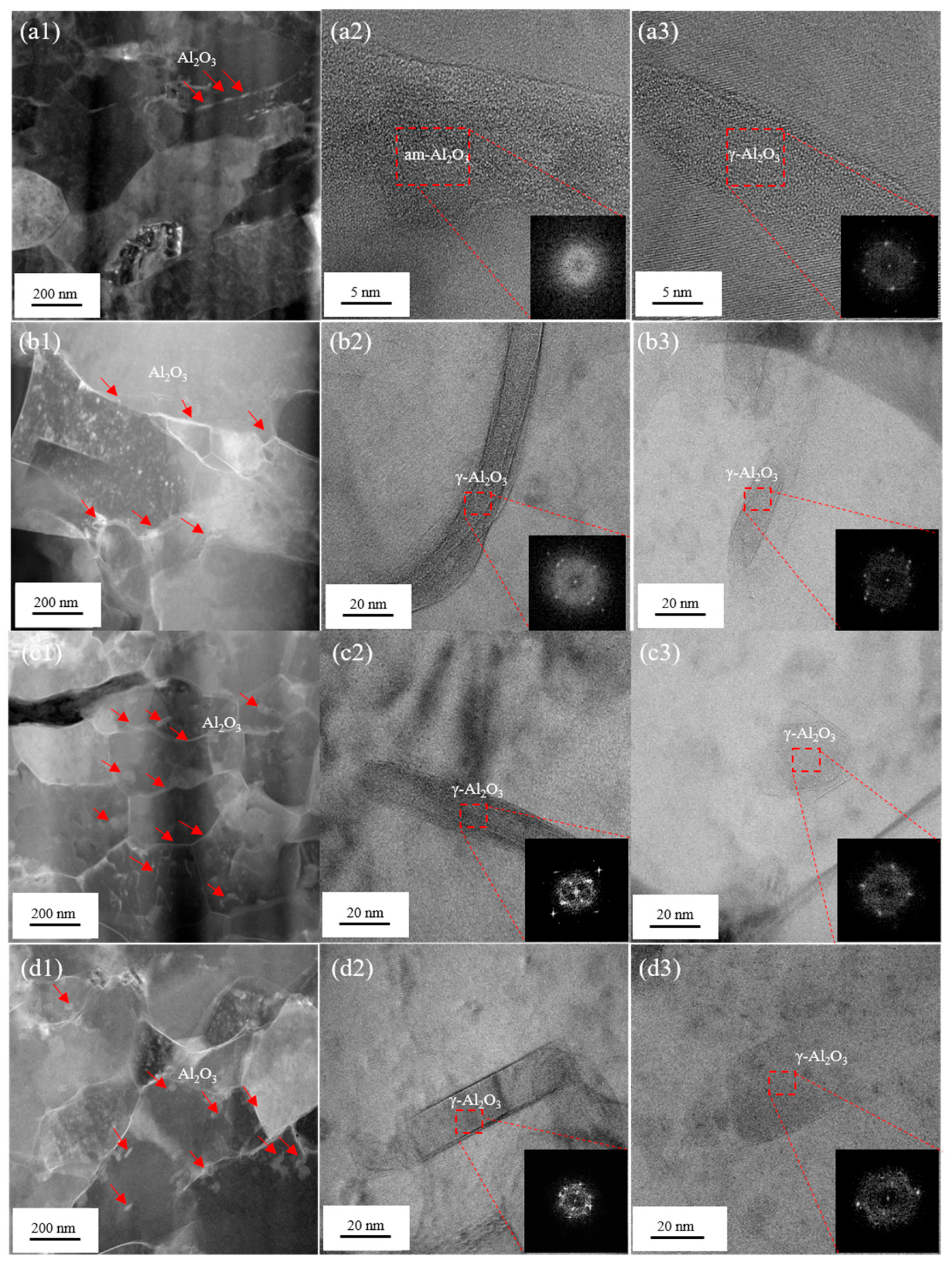
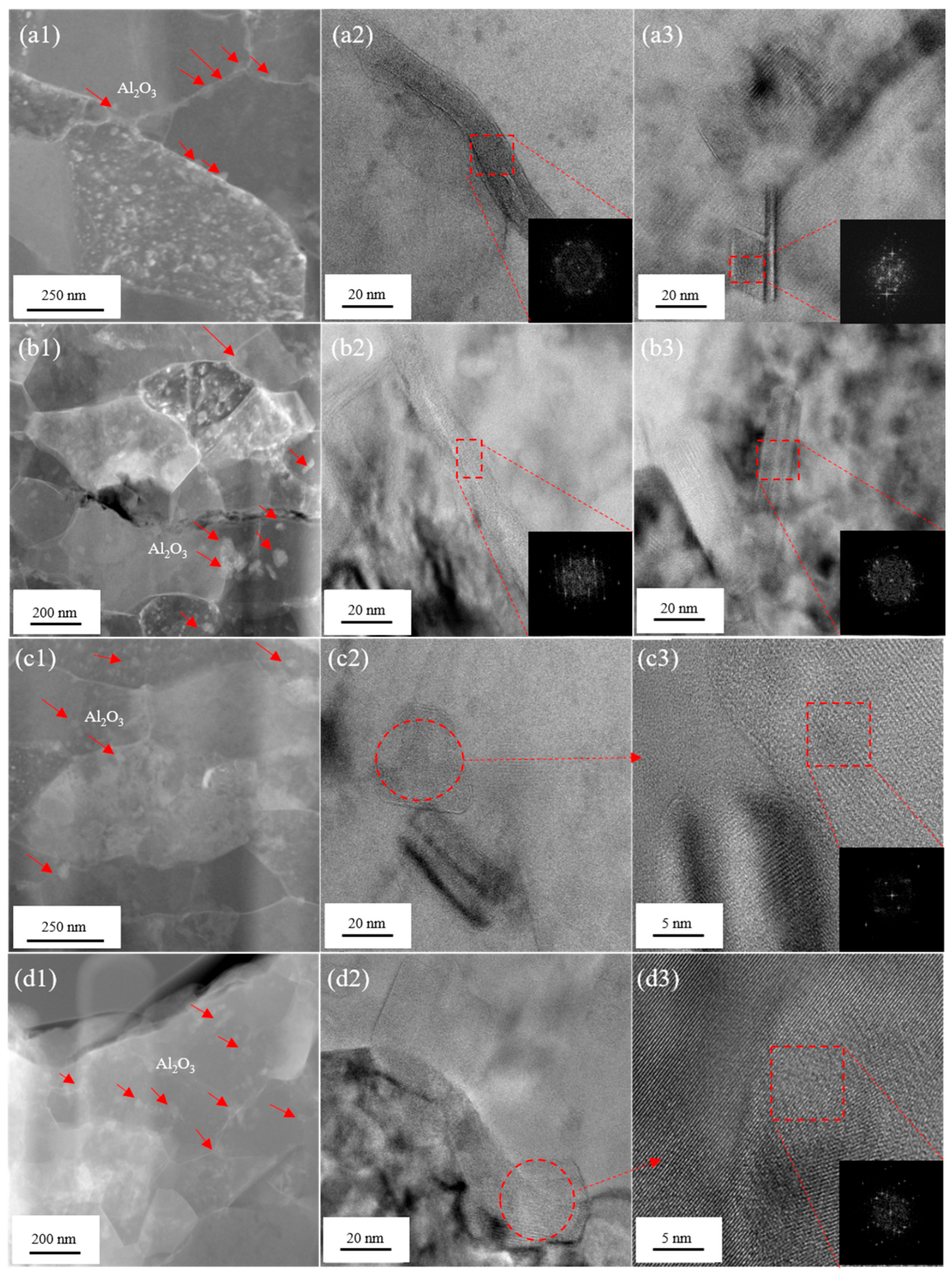
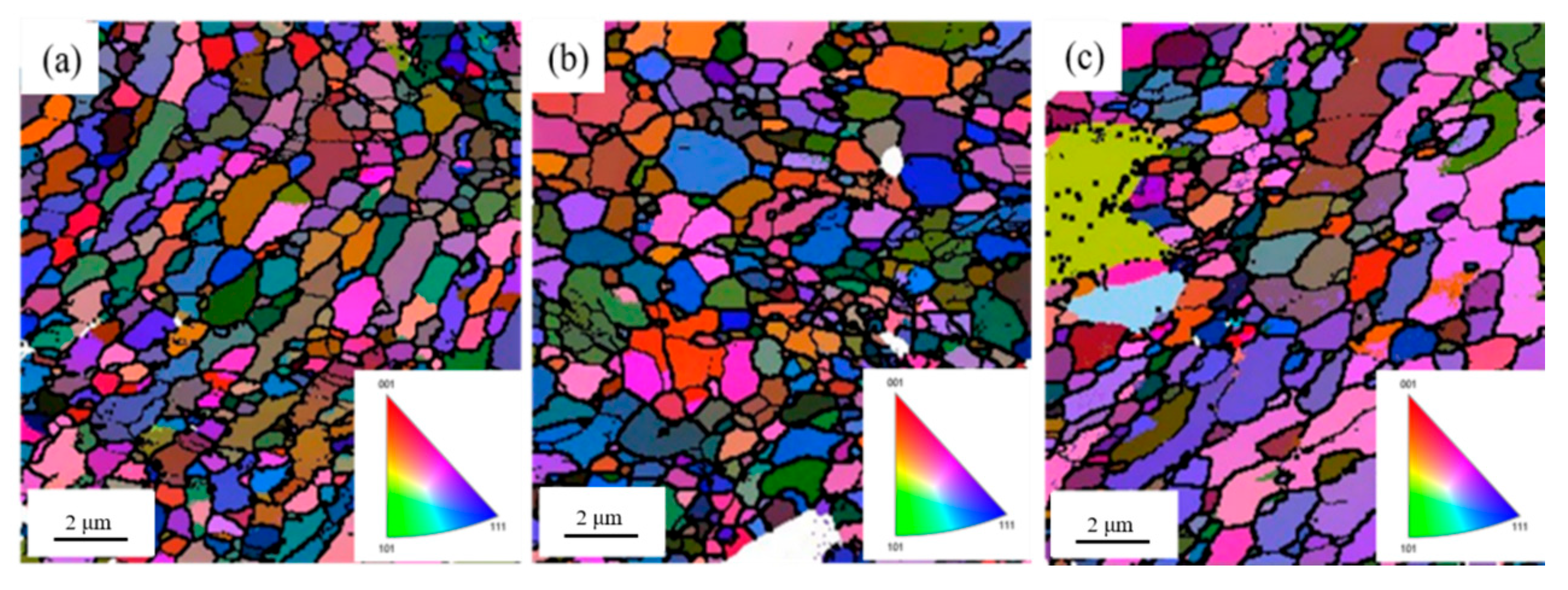
3.3. Microstructure and Properties of Heat-Treated Composites
4. Conclusions
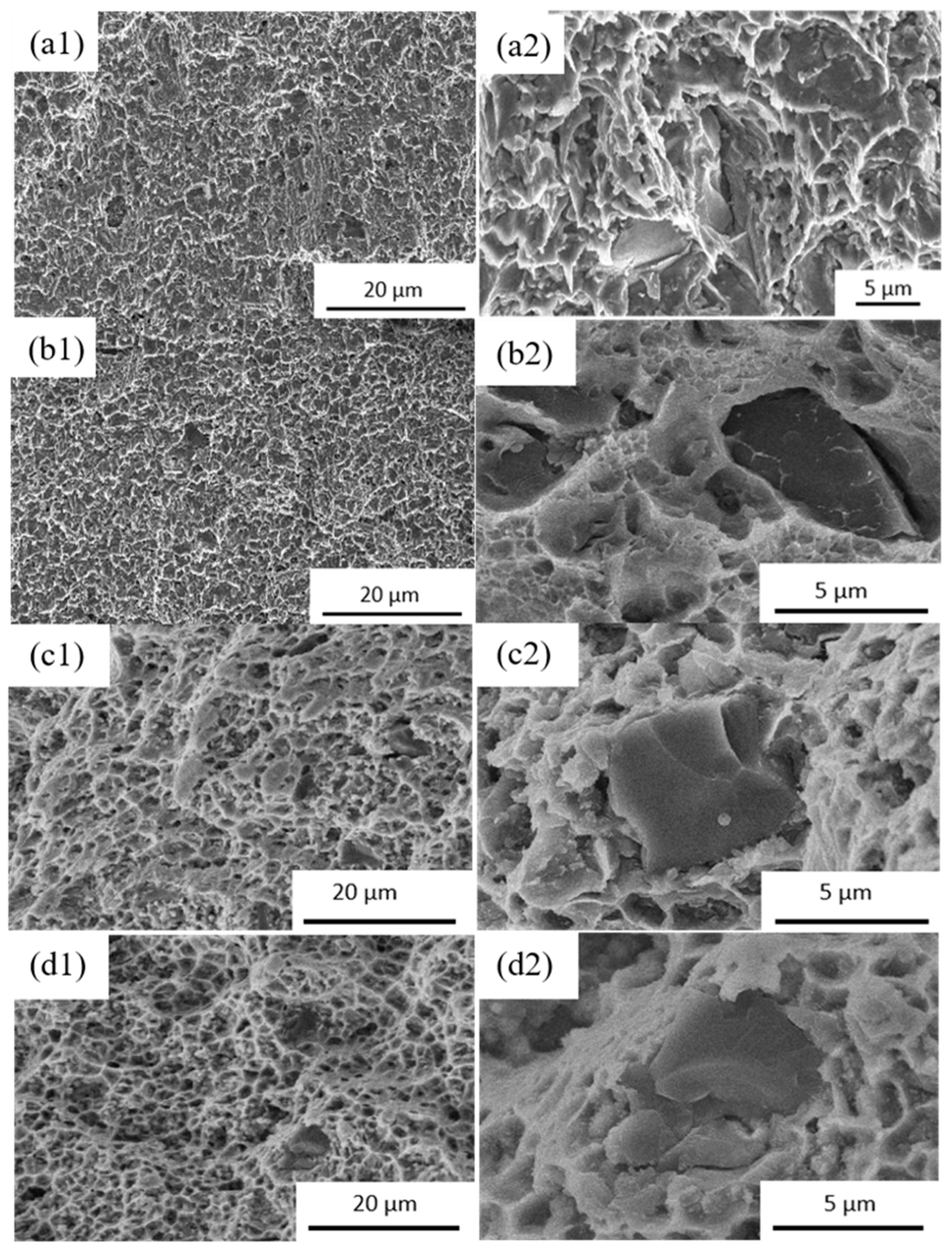
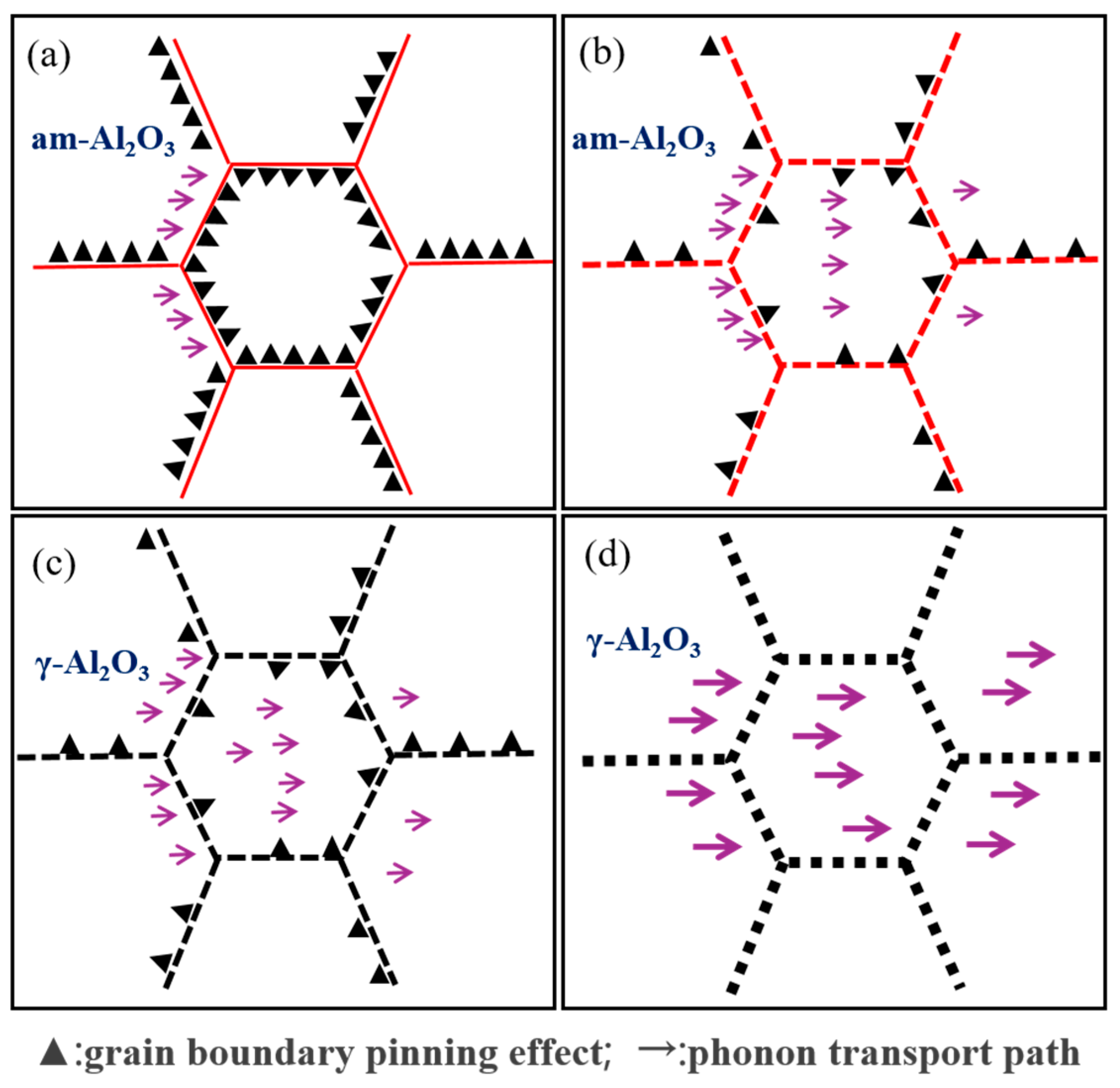
- In as-forged composites, amorphous Al2O3 distributes continuously along the grain boundaries of the matrix, forming a strong pinning effect that significantly enhances high-temperature strength (exhibiting a tensile strength of 149 MPa at 350 °C). However, this continuous network structure blocks the thermal conduction pathways in the aluminum matrix, resulting in a low thermal conductivity of only 100 W/(m·K) at 350 °C.
- During hot extrusion, am-Al2O3 in B4C/Al composites breaks into flakes (100–200 nm) distributed along the grain boundaries. This distribution not only retains partial pinning effects (inhibiting grain coarsening) but also constructs continuous thermal conduction pathways in the aluminum matrix, increasing the composite’s thermal conductivity to approximately 144 W/(m·K). At 350 °C, the composite demonstrates excellent high-temperature mechanical properties, with a tensile strength of 129 MPa and an elongation at break of 8%.
- Heat treatment enhances the high-temperature mechanical properties and thermal conductivity of B4C/Al composites by regulating the distribution, size, morphology, and crystalline state of nano-Al2O3 within the aluminum matrix. Notably, the nano-Al2O3 undergoes sequential phase transformations during heat treatment: lamellar am-Al2O3 → lamellar γ-Al2O3 → short-rod γ-Al2O3 → spherical γ-Al2O3. The 500 °C/24 h heat treatment process emerges as the key optimization window, enabling the composite to simultaneously attain high strength (144 MPa) and high thermal conductivity (181 W/(m·K)) at 350 °C.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Samrah, M.G.; Tawfic, A.F.; Chidiac, S.E. Spent nuclear fuel interim dry storage; Design requirements, most common methods, and evolution: A review. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2021, 160, 108408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Yang, G.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, J. The Advancement of Neutron-Shielding Materials for the Transportation and Storage of Spent Nuclear Fuel. Materials 2022, 15, 3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, Y.N.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, Y.T.; Wang, Q.Z.; Xiao, B.L.; Ma, Z.Y. Enhancing high-temperature strength of B4C–6061Al neutron absorber material by in-situ Mg(Al)B2. J. Nucl. Mater. 2019, 526, 151788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaedi, H.; Ibrahim, M.; Ammar, H.; Samuel, A.; Soliman, M.; Almajid, A.; Samuel, F. Effect of testing temperature on the strength and fracture behavior of Al-B4C composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2015, 50, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangolu, S.; Rao, A.; Prabhu, N.; Deshmukh, V.P.; Kashyap, B.P. Effects of temperature and strain rate on compressive flow behavior of aluminum-boron carbide composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2014, 48, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.G.; Stgeorges, L.; Roux, M. Mechanical Behavior of High Boron Content Al-B4C Metal Matrix Composites at Elevated Temperatures. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2012, 706–709, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Shang, Q.; Tan, J.; Dong, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, G.; Yu, P.; Jiang, B.; Tang, A.; Pan, F. Breaking the trade-off between mechanical properties and thermal conductivity of magnesium alloys via regulating the partial Gibbs energy of alloying elements. Acta Mater. 2025, 289, 120894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Akhtar, S.; Wang, P.; He, Z.; Jiao, X.; Ge, S.; Yuan, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Thermal conductivity of binary Al alloys with different alloying elements. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 177257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Hou, H.; Zhao, Y. Simultaneously improving thermal conductivity, mechanical properties and metal fluidity through Cu alloying in Mg-Zn-based alloys. J. Magnes. Alloys 2024, 12, 3823–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Pan, A. Study on Preparation, Microstructure and Tensile Properties of B4C/6061Al Composites. Hot Work. Technol. 2021, 50, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Suo, X.; Liao, H.; Hu, Y.; Dixit, U.; Petrov, P. Formation of Al15Mn3Si2 phase during solidification of a novel Al-12%Si-4%Cu-1.2%Mn heat-resistant alloy and its thermal stability. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 2910–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morri, A.; Ceschini, L.; Messieri, S.; Cerri, E.; Toschi, S. Mo addition to the A354 (Al-SiCu-Mg) casting alloy: Effects on microstructure and mechanical properties at room and high temperature. Metals 2018, 8, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CCeschini, L.; Morri, A.; Toschi, S.; Seifeddine, S. Room and high temperature fatiguebehaviour of the A354 and C355 (Al-Si-Cu-Mg) alloys: Role of microstructure and heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 653, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Li, Q. Effect of Remelting Temperature and Stirring Time on the Microstructure of Al-B4C Composites. Contemp. Chem. Ind. 2018, 47, 2510–2513. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W. Research on the Fabrication of Al-B4C-Al2O3 Composites by Liquid Process and Solid-State Distribution Technology. Master’s Thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, X.X. High-Temperature Strengthened Aluminum Matrix Boron Carbide Composite Materials: Design, Preparation, and Performance Study. Ph.D. Thesis, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Balog, M.; Simancik, F.; Krizik, P.; Nosko, M.; Rajner, W.; Walcher, M.; Qian, M. Novel ultrafine-grained aluminium metal matrix composites prepared from fine atomized Al powders. In Proceedings of the TMS 2014 Annual Meeting & Exhibition, San Diego, CA, USA, 16–20 February 2014; pp. 1425–1430. [Google Scholar]
- Balog, M.; Krizik, P.; Nosko, M.; Hajovska, Z.; Riglos, M.; Rajner, W.; Liu, D.; Simancik, F. Forged HITEMAL: Al-based MMCs strengthened with nanometric thick Al2O3 skeleton. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 613, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, Y.N.; Zhou, Y.T.; Li, X.N.; Ma, G.N.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, Q.Z.; Wang, D.; Xiao, B.L.; Ma, Z.Y. Enhancing High-Temperature Strength and Thermal Stability of Al2O3/Al Composites by High-Temperature Pre-treatment of Ultrafine Al Powders. Acta Metall. Sin. 2020, 33, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, Y.N. High-Temperature Neutron Absorbing (B4C+Al2O3)/Al Composites: Preparation and Processing Research. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, H. Future perspective regarding nuclear power and fuel cycle in Japan and the world. At. Energy Soc. Jpn. 2018, 60, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, K.; Sunghwan, C.; Junhee, H. Performance evaluation of METAMIC neutron absorber in spent fuel storage rack. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2018, 50, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Li, Q.; Liu, W.; Shu, G.; Wang, X. Microstructure and mechanical properties of B4C/Al composite at elevated temperature strengthened with in situ Al2O3 network. Rare Met. 2020, 39, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, Y.N.; Zhou, Y.T.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, Q.Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, W.G.; Xiao, B.L.; Ma, Z.Y. Enhancing high-temperature strength of (B4C+Al2O3)/Al designed for neutron absorbing materials by constructing lamellar structure. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 183, 107674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, Y.N.; Zhou, Y.T.; Liu, Z.Y.; Ma, G.N.; Wang, D.; Wang, Q.Z.; Wang, W.G.; Xiao, B.L.; Ma, Z.Y. Enhancing strength and ductility synergy through heterogeneous structure design in nanoscale Al2O3 particulate reinforced Al composites. Mater. Des. 2019, 166, 107629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, Y.N.; Zhou, Y.T.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, Q.Z.; Wang, W.G.; Wang, D.; Xiao, B.L.; Ma, Z.Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of (B4C+Al2O3)/Al composites designed for neutron absorbing materials with both structural and functional usages. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 773, 138840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, B.; Tao, H.; Peter, K.; Maria, V.; Brandon, D.; Hanry, Y.; Julie, M.; Enrique, J. On the thermal stability of ultrafine-grained Al stabilized by in-situ amorphous Al2O3 network. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 648, 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM B962; Standard Test Methods for Density of Compacted or Sintered Powder Metallurgy (PM) Products Using Archimedes’ Principle. American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM International): West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023.
- ASTM E1461; Standard Test Method for Thermal Diffusivity by the Flash Method. American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM International): West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- Kentaro, F.L.; Diran, A. Thermal and Electrical Conductivity of Aluminum Alloys: Fundamentals, structure-property relationships, and pathways to enhance conductivity. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 924, 147766. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, N.; Laachachi, A.; Ferriol, M.; Lutz, M.; Toniazzo, V.; Ruch, D. Review of thermal conductivity in composites: Mechanisms, parameters and theory. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 61, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, A.H.; Thomas, A.M.; Mike, F.; Peter, P.; William, E.L.; Mike, R.; Salvatore, G. Thermal conductivity of WC: Microstructural design driven by first-principles simulations. Acta Mater. 2025, 283, 120517. [Google Scholar]
- Madeleine, B.; Marc, B. Particle pinning during grain growth-A new analytical model for predicting the mean limiting grain size but also grain size heterogeneity in a 2D polycrystalline context. Acta Mater. 2024, 277, 120174. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.Y.; Chen, H.; Fu, W.J.; Zhou, L.M.; Deng, Y.Q. Effect of titanium element on the interfacial reactions and properties of B4C/Al composites fabricated by selective laser melting. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2025, 333, 130385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.L.; Wu, Q.L.; Li, X.; Wang, X.Q.; Shi, Y.X.; Zhou, Y.; Wen, S.F.; Shi, Y.S. Crack suppression and ductility modification of additive manufactured Ti6Al4V/W heterostructure interface via Nano-TiC reinforcement. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2025, 180, 109852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, W.; Kim, G.; Jung, Y.S.; Ahn, S.J. Experimental emulation of 10B(n, α)7Li reaction-induced microstructural evolution of Al-B4C neutron absorber used in the dry storage of spent nuclear fuel. J. Nucl. Mater. 2024, 593, 154977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Heat Treatment Temperature (°C) | Heat Treatment Time (h) |
|---|---|
| 500 | 5, 24, 40, 60 |
| 580 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 |
| Density | Tensile Strength | Yield Strength | Elongation | Thermal Conductivity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forged composites | 99.26% | 149 ± 1.9 MPa | 109 ± 4.5 MPa | 5 ± 0.7% | 100 ± 1.8 W/(m·K) |
| Extruded composites | 99.66% | 129 ± 1.0 MPa | 96.5 ± 3.0 MPa | 8 ± 0.7% | 144 ± 2.7 W/(m·K) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, C.; Li, L.; Li, Q. Synergistic Optimization of High-Temperature Mechanical Properties and Thermal Conductivity in B4C/Al Composites Through Nano-Al2O3 Phase Transformation and Process Engineering. Metals 2025, 15, 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080874
Huang C, Li L, Li Q. Synergistic Optimization of High-Temperature Mechanical Properties and Thermal Conductivity in B4C/Al Composites Through Nano-Al2O3 Phase Transformation and Process Engineering. Metals. 2025; 15(8):874. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080874
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Chunfa, Lingmin Li, and Qiulin Li. 2025. "Synergistic Optimization of High-Temperature Mechanical Properties and Thermal Conductivity in B4C/Al Composites Through Nano-Al2O3 Phase Transformation and Process Engineering" Metals 15, no. 8: 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080874
APA StyleHuang, C., Li, L., & Li, Q. (2025). Synergistic Optimization of High-Temperature Mechanical Properties and Thermal Conductivity in B4C/Al Composites Through Nano-Al2O3 Phase Transformation and Process Engineering. Metals, 15(8), 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080874





