Strategies for the Recovery of Tungsten from Wolframite, Scheelite, or Wolframite–Scheelite Mixed Concentrates of Spanish Origin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Leaching of Wolframite Concentrate
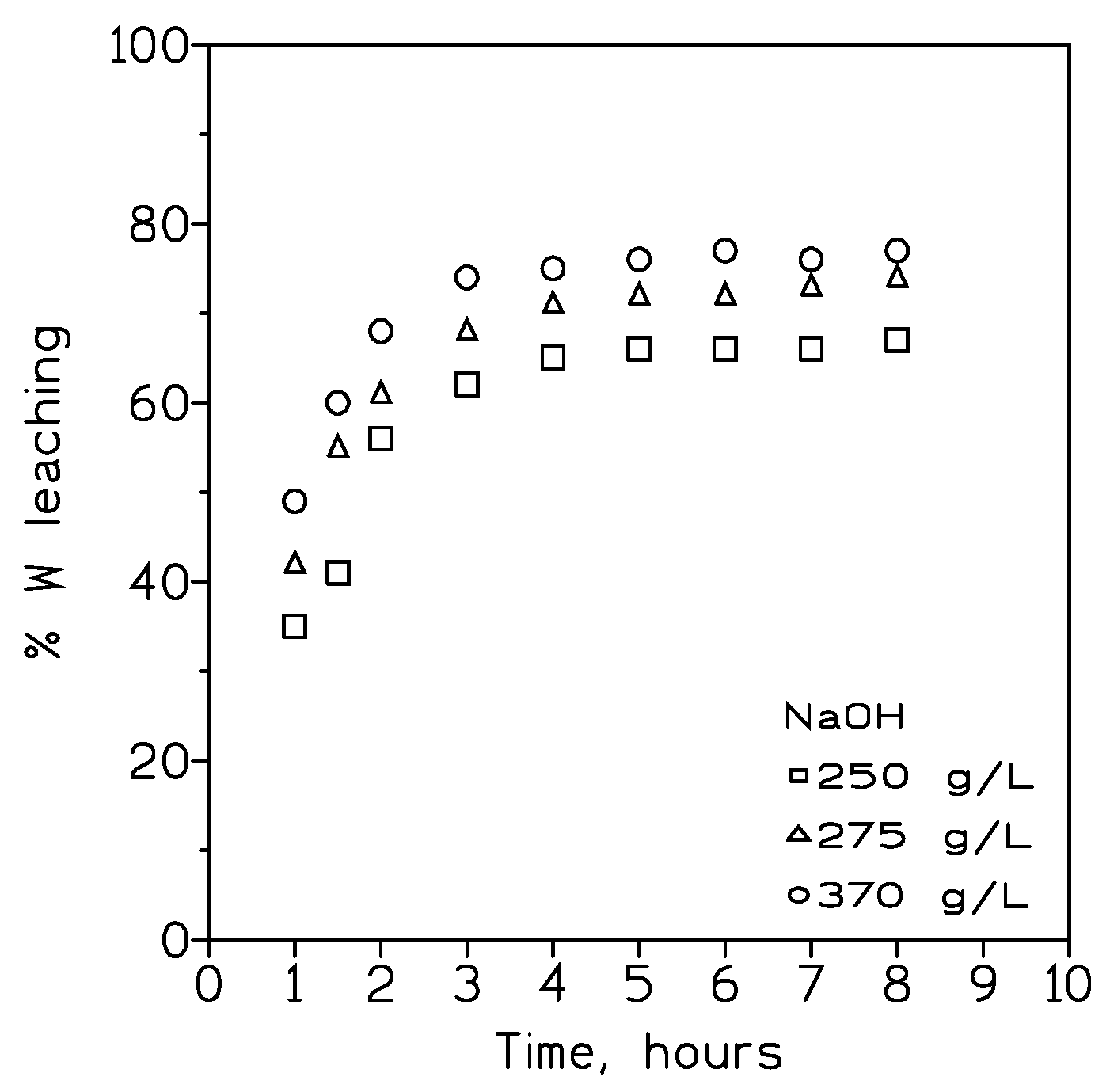
3.1.1. Influence of the Leaching Agent
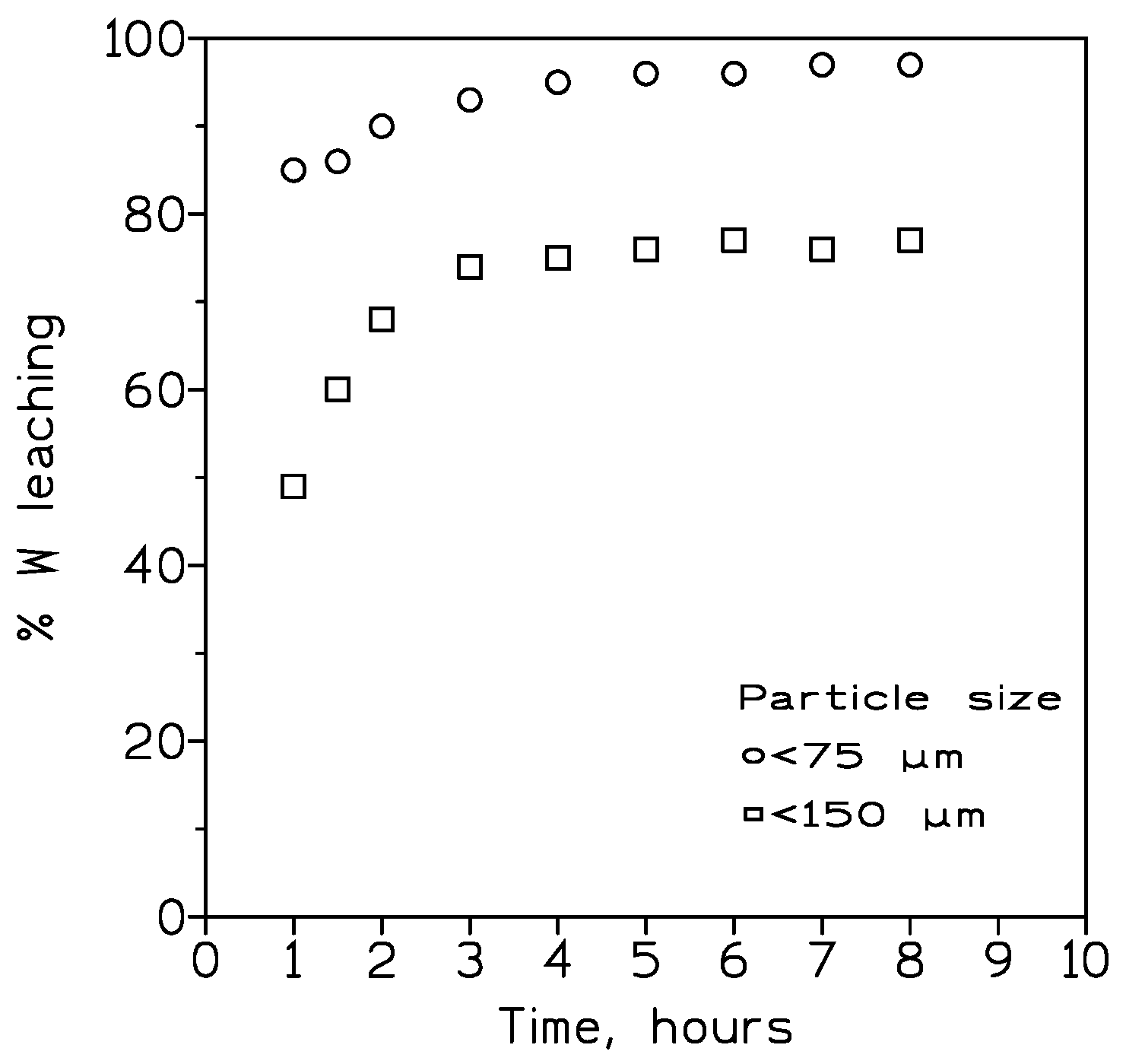
3.1.2. Influence of the Particle Size
3.2. Leaching of the Scheelite Concentrate
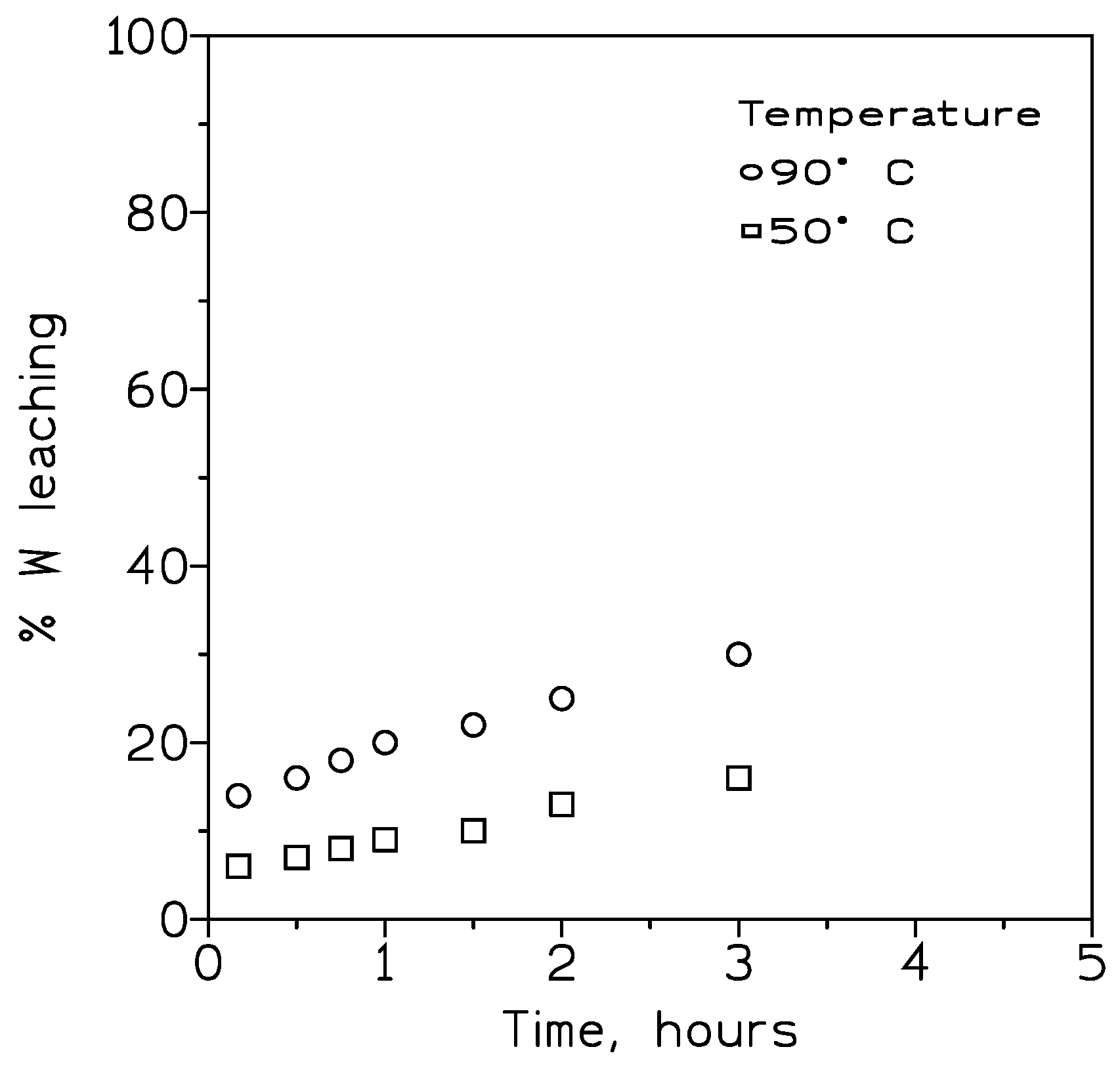
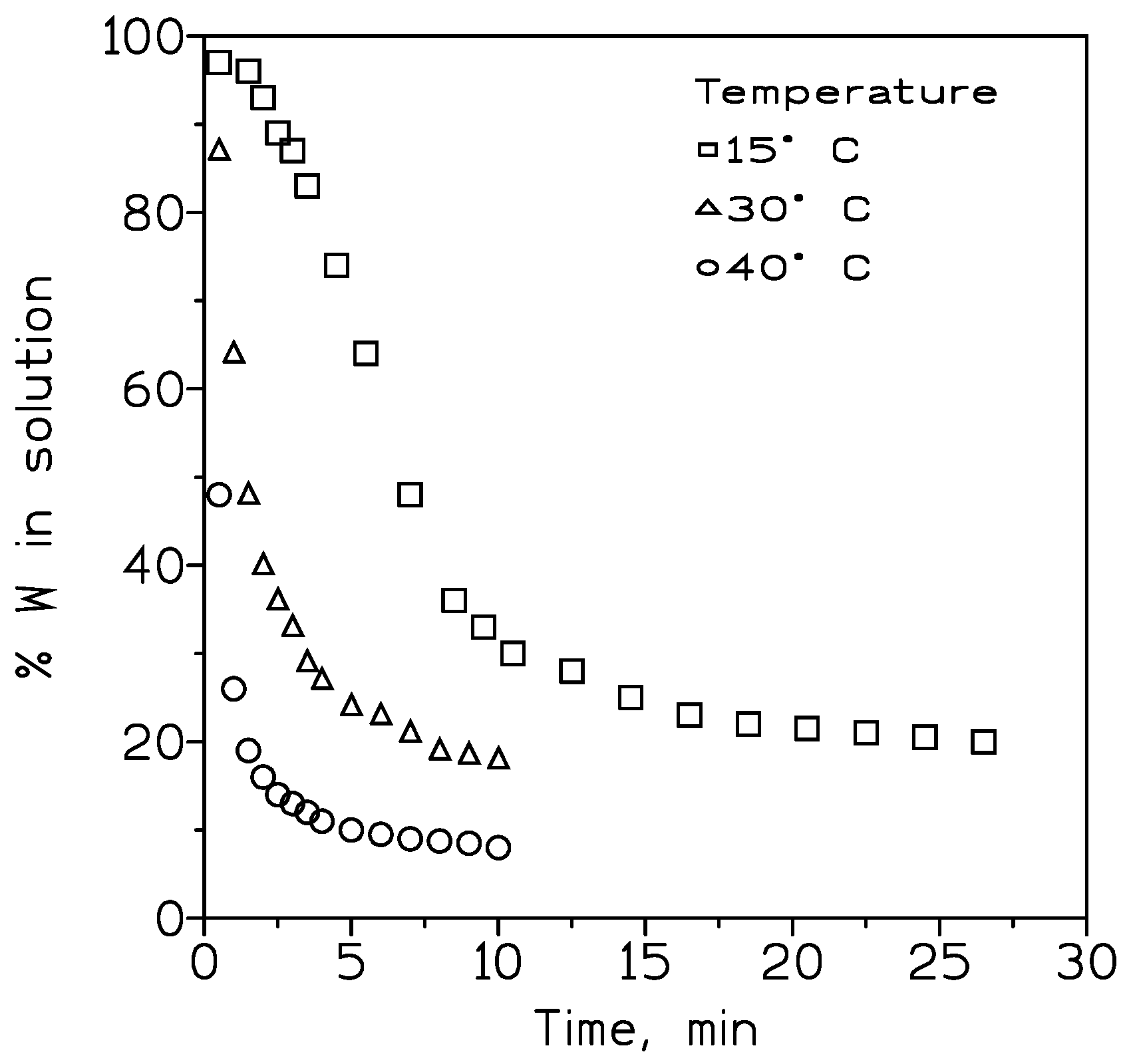
3.2.1. Influence of the Temperature on Tungsten Recovery
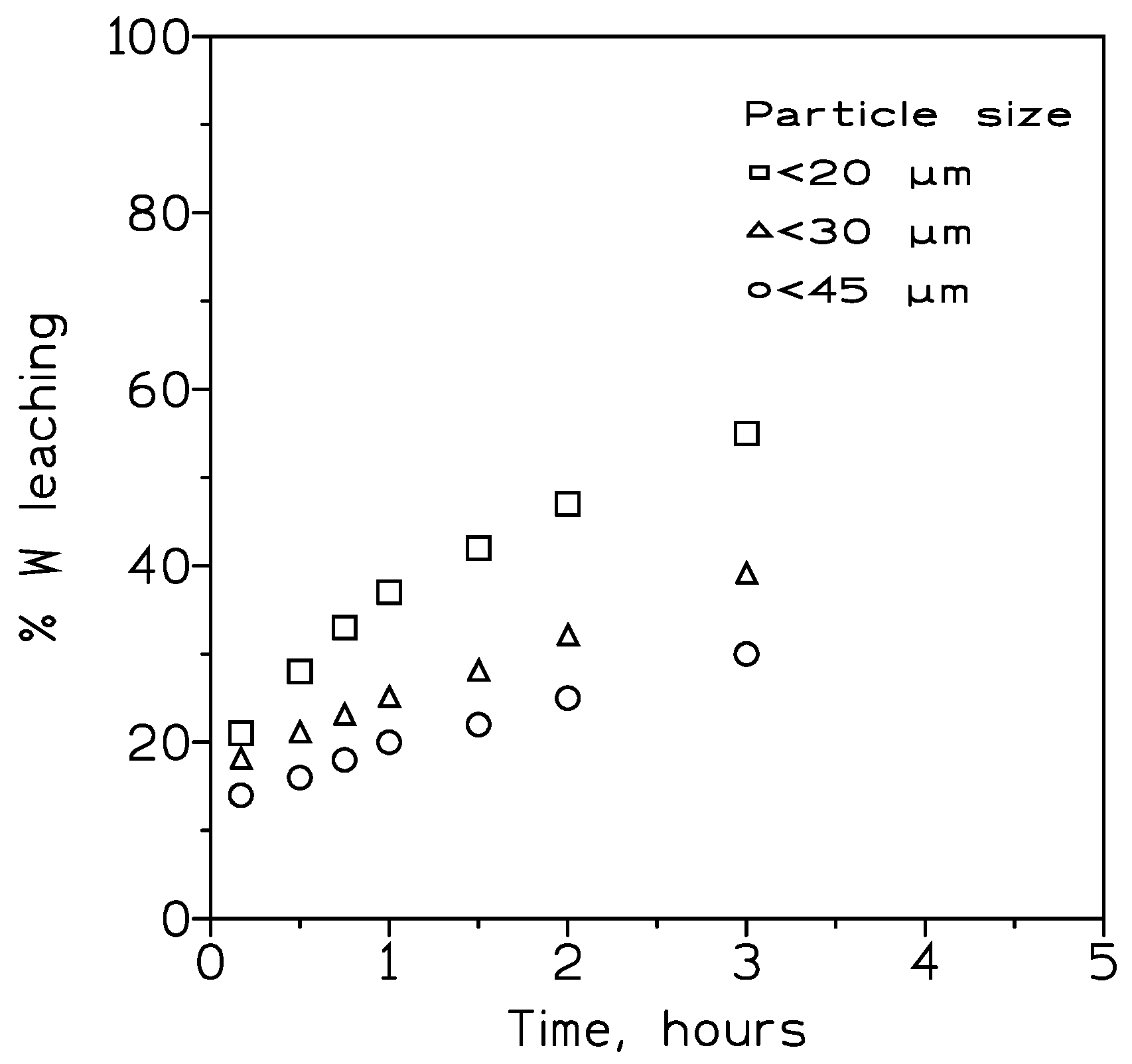
3.2.2. Influence of the Particle Size
3.2.3. Influence of the Leachant on Tungsten Recovery
3.3. Leaching of a Scheelite–Wolframite Concentrate. Acidic Medium
3.3.1. Influence of the HCl Concentration on Tungsten Leaching
3.3.2. Influence of the Pulp Density on Tungsten Recovery
3.4. Leaching of a Scheelite–Wolframite Concentrate. Alkaline Medium
3.5. Pyro-Hydrometallurgical Treatment of the Mixed Concentrate
3.5.1. Roasting of the Concentration in Sodium Carbonate Media
3.5.2. Leaching of the Roasted Materials
3.6. Treatment of the Leachates
3.6.1. Acidic Medium
3.6.2. Alkaline Medium
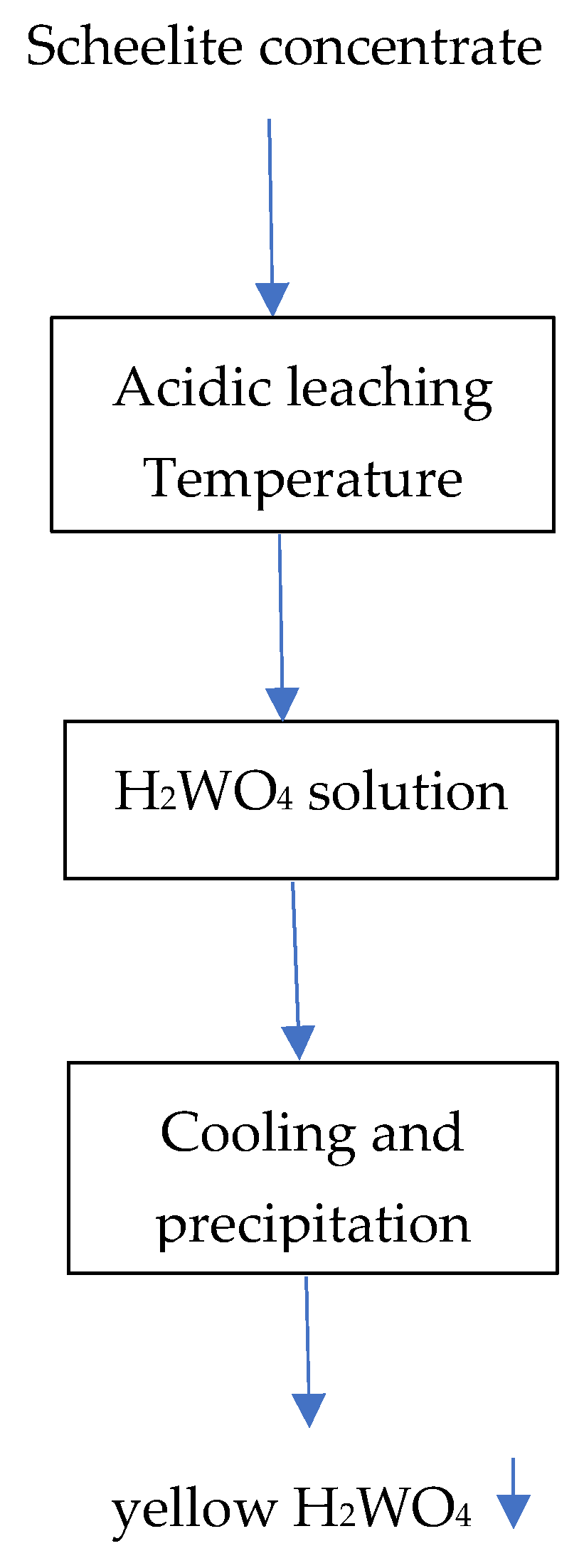
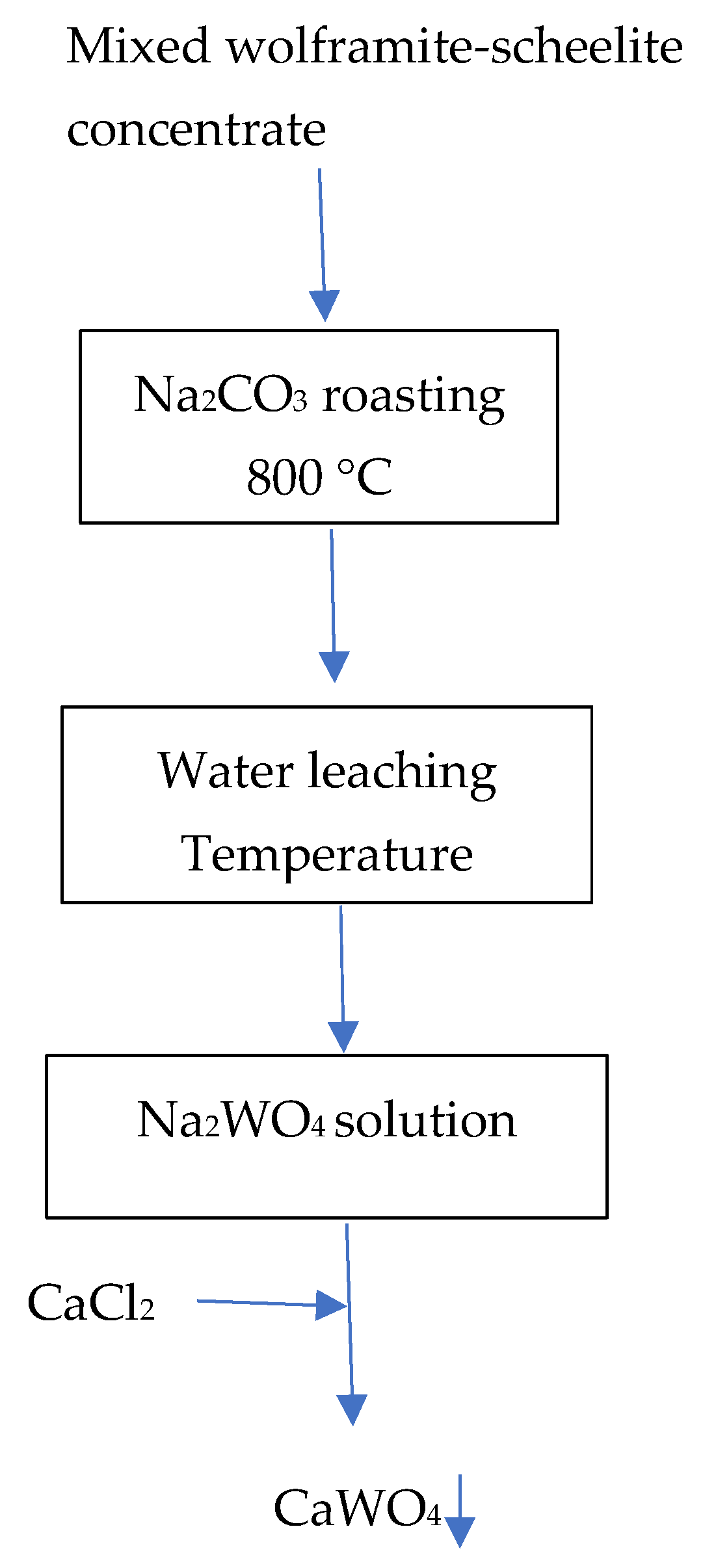
3.7. General Flowsheets
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grohol, M.; Veeh, C. Study on the Critical Raw Materials for the EU 2023—Final Report; European Commission—Directorate-General for Internal Market, Industry, Entrepreneurship and SMEss, Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huo, G.; Guo, X.; Chen, J. A review of flowsheets for tungsten recovery from scheelite, wolframite and secondary resources and challenges for sustainable production. Hydrometallurgy 2025, 234, 106455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, H.; Peng, Z.; Duan, A.; Zhang, T.; Gong, Z. Leaching of scheelite concentrate for tungsten extraction. Minerals 2025, 15, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alguacil, F.J.; Alonso, M. Recovery of tungsten from raw and secondary materials using hydrometallurgical processing. Metals 2025, 15, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chang, J.; Wei, Y.; Qiao, J.; Yue, X.; Fan, H.; Zhang, L.; Guo, X. Green and efficient recovery of tungsten from spent SCR denitration catalyst by Na2S alkali leaching and calcium precipitation. Adv. Sust. Syst. 2025, 9, 2400895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Pu, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lei, X.; Hu, H.; Chen, Z. Extraction of tungsten from tungsten fine mud by caustic soda autoclaving. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 6901–6907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, J.; Sun, Q.; Yang, Y.; Si, Q.; Liang, C.; Liu, G.; Mi, A.; Wang, S. Recycling efficiency optimization of tungsten-filled vinyl-methyl-silicone-based flexible gamma ray shielding materials. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2025, 57, 103163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, T.; Sun, F.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; He, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Z. Synthesis of intermediatevalence tungsten oxides via carbon reduction and their dissolution behavior in hydrogen peroxide. Int. J. Refract. Met. H. 2025, 131, 107191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.-Y.; Mu, P.-P.; Liu, H.; Chachina, S.B.; Zhang, X.-G.; Zhang, S.-G.; Pan, D. Extraction and response surface methodology optimization of tungsten and molybdenum from spent fluidized catalytic cracking catalysts. Tungsten 2025, 7, 268–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Yi, B.; Hu, X.; Fang, L.; Yu, S.; Yu, S.; Wu, D. Advanced sequential treatment approach for enhanced recovery in tungsten-nickel electroplating wastewater. J. Water Proc. Eng. 2025, 71, 107421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, T.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hu, H.; Liang, Y. Factors affecting purity of ammonium paratungstate (APT) prepared from wolframite ((Fe,Mn)WO4) concentrate by NaHSO4·H2O roasting, water/ammonia leaching and evaporation crystallization. Hydrometallurgy 2025, 234, 106467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, L.; Wu, S.; Guan, W.; Wang, M.; Wu, X. A novel pyro-hydrometallurgy process for efficient recovery of tungsten, vanadium, and titanium from spent SCR catalysts. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xi, X.; Nie, Z. 1T/2H-Mo1-xWxS2 obtained from secondary resources and its superior piezoelectric catalysis. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimova, L.; Oleinikova, T.; Terentyeva, I.; Korabayev, A.; Tussupbekova, T. Study of the efficiency of using pelletizing poor scheelite ore for leaching tungsten. Acta Metall. Slovaca 2025, 31, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncer, I.M.; Yue, H.; Liu, J. An optimisation study for leaching synthetic scheelite in H2SO4 and H2O2 solution. Can. Metall. Q. 2025, 64, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Liu, L.; Chen, M. The tungsten tailings remediation by soilless plant establishment: Varied aggregation structure, heavy metal mobilization, and microbial community structure. Ecol. Eng. 2025, 213, 107565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Edraki, M.; Golev, A. Characterization, potential valuable metals recovery and remediation of historic wolframite mining waste. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 129009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Qiu, Y.; He, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, A.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; He, L.; Sun, F.; Zhao, Z. Research on the ammonia-free solvent extraction of tungsten from sodium tungstate solution using TBP. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 513, 162869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, L.; Hu, W.; Wang, C.; Hou, X.; Li, H. Separation of vanadium, tungsten, and arsenic from alkaline leachate of spent SCR catalysts via coextraction and stepwise stripping. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 352, 127991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Lu, X. Tungsten adsorption on goethite: Insights from first-principles molecular dynamics simulations. Inorg. Chem. 2025, 64, 5331–5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Q.; Yang, B.; Li, X.M.; Gao, F.; Hao, X. A self-driven Ni(OH)2/CB/PVDF film for highly efficient adsorption of tungsten via hydroxyl ligand exchange. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 352, 128163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Ma, L.; Xi, X.; Nie, Z. The adsorption and separation of tungsten and molybdenum by chitosan and chitosan-D301: Experiments and DFT theoretical calculation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 68, 161511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.-F.; Alguacil, F.J.; Martinez, S.; Caravaca, C. Production of high-grade tin in a new electrolytic plant. In Hydrometallurgy´94, Proceedings of the ‘Hydrometallurgy’94’ Symposium, Institution of Mining and Metallurgy and the Society of Chemical Industry, Cambridge, UK, 11–15 July 1994; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1994; pp. 939–946. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.; Tang, K.; Zhang, L.; Xia, Z.; Liu, S. Separation of cobalt and tungsten from grinding waste of cemented carbide by a midly process of chloridizing roasting and water leaching combining. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2025, 132, 107303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.-T.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J.-L.; Zhou, Q.-S.; Qi, T.-G.; Peng, Z.-H.; Liu, G.-H.; Li, X.-B. Leaching of WO3 from sulfuric acid converted product of scheelite on NH3·H2O–NH4HCO3 solution. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2025, 25, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.I.; Moreira, A.; Costa, S.C. Leaching of synthetic scheelite by hydrochloric acid without the formation of tungstic acid. Hydrometallurgy 2003, 70, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahruman, C.; Yusufoglu, I. Leaching kinetics of synthetic CaWO4 in HCl solutions containing H3PO4 as chelating agent. Hydrometallurgy 2006, 81, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Li, L.; Cao, Q. Recovery of rhenium and tungsten from calcium tungstate containing rhenium via hydrochloric acid decomposition. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2025, 60, 480–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
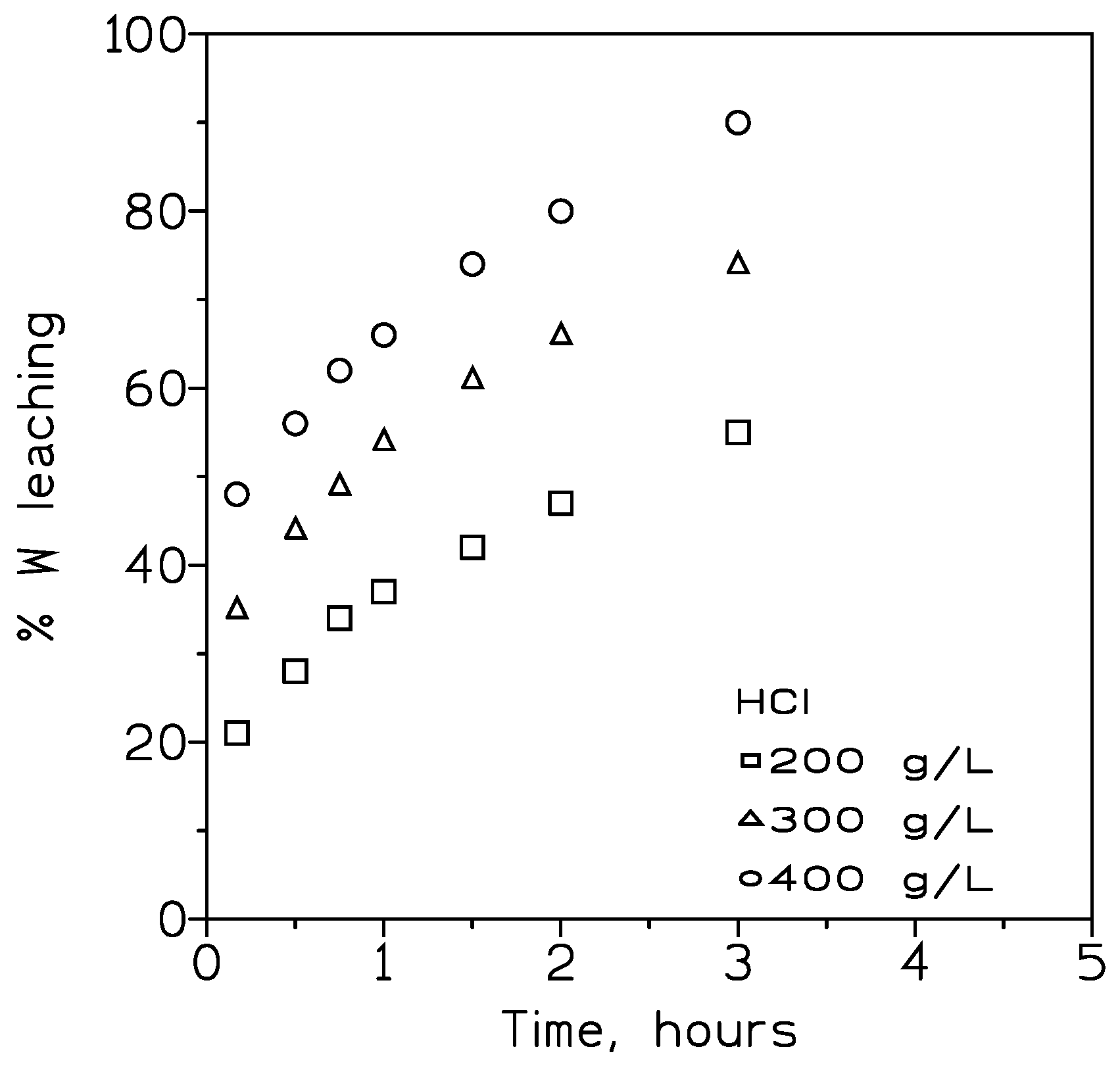
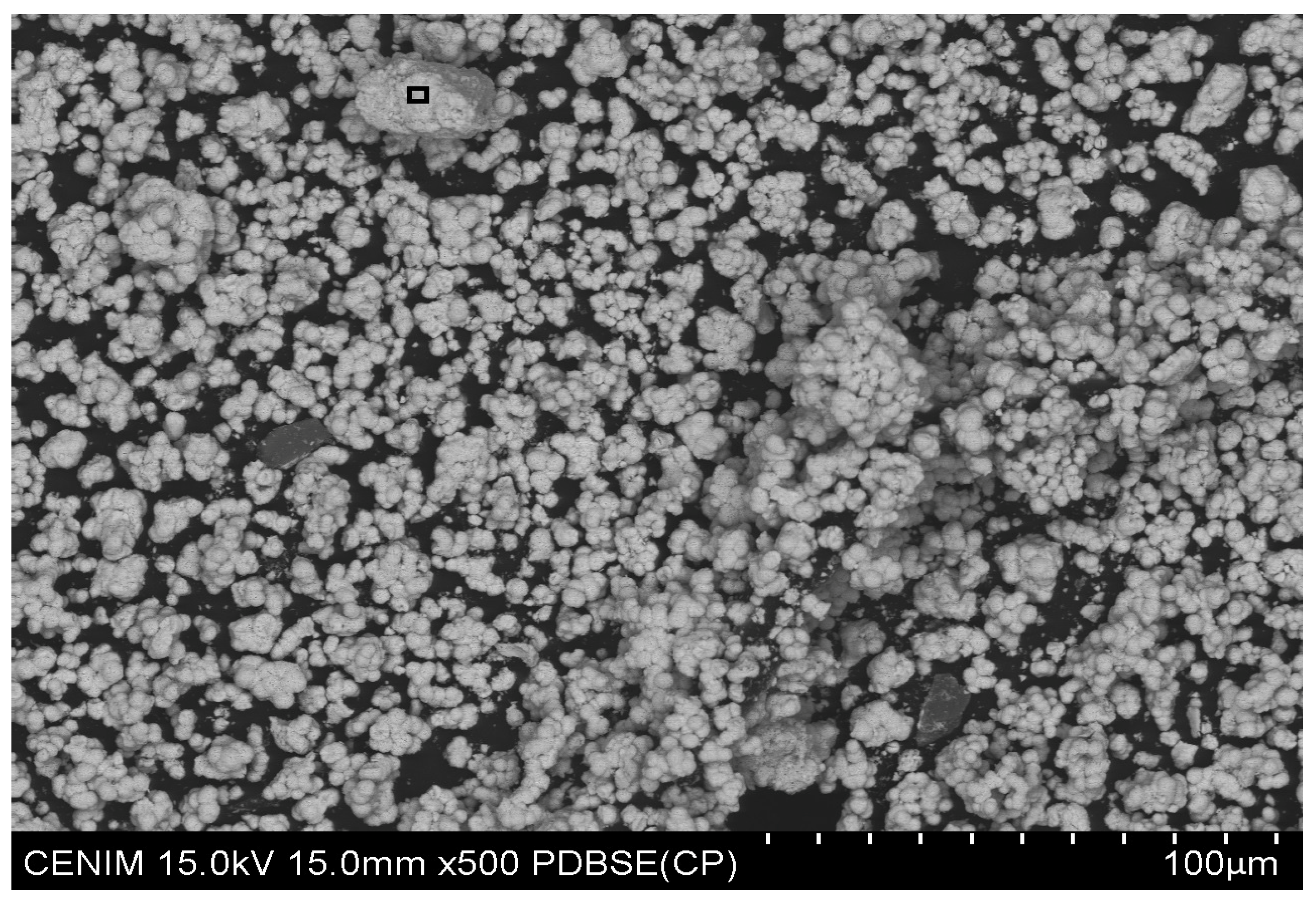
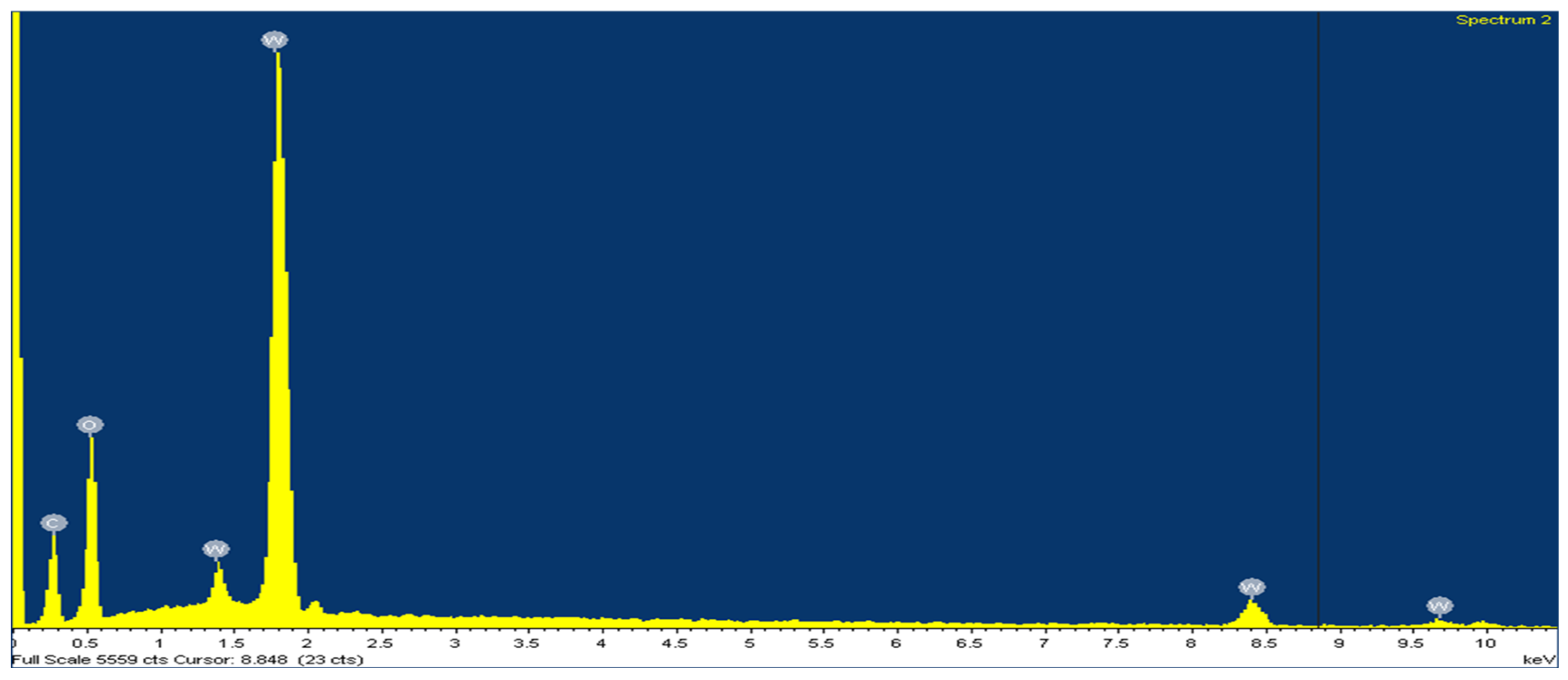
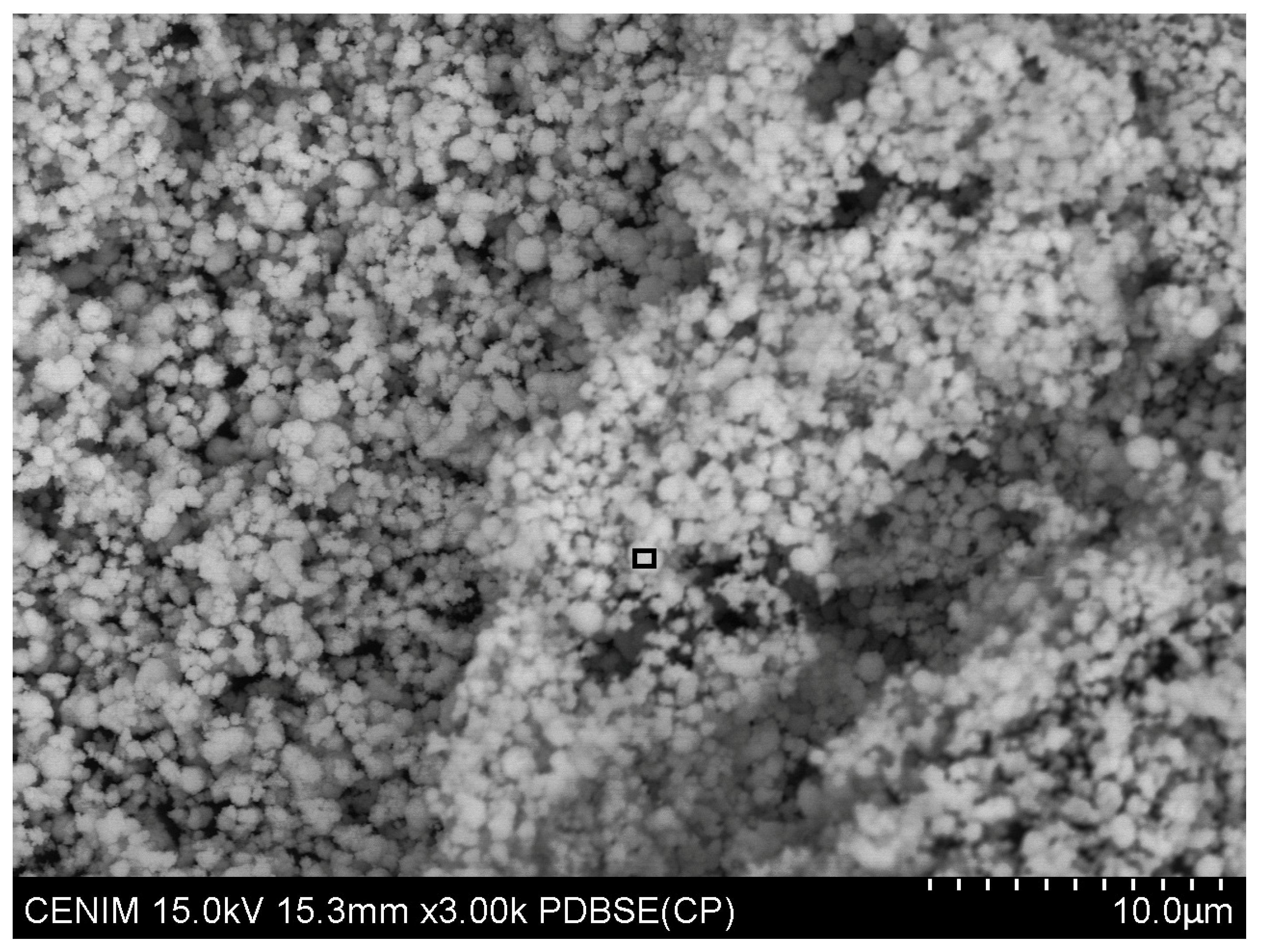
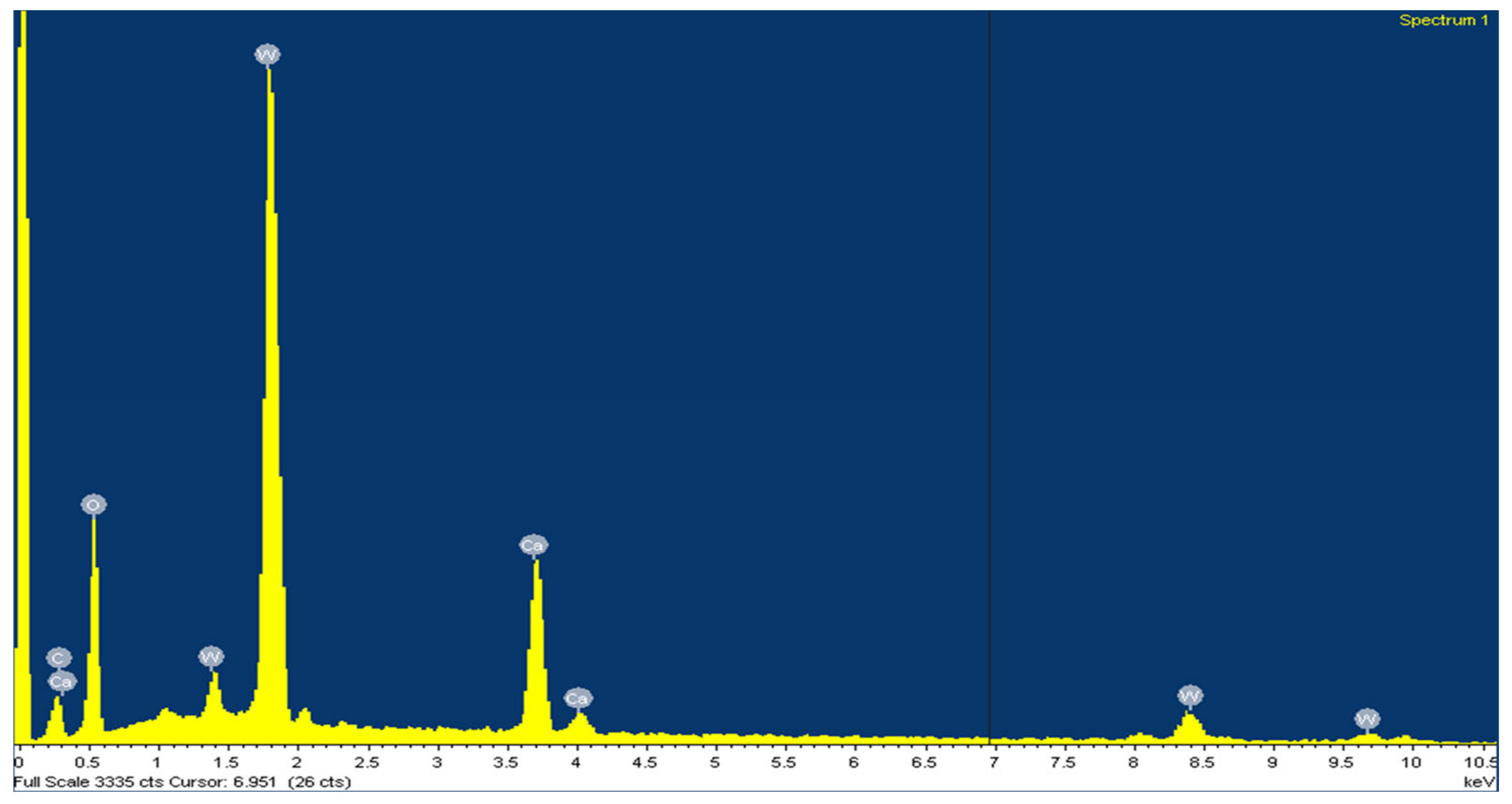


| Concentrate | % Tungsten | Others |
|---|---|---|
| wolframite | 50 | Sn (2%) |
| scheelite | 23 | Quartz, magnetite, hematite, rutile |
| mixed scheelite–wolframite | 23 | Sn (42%), Pb (0.8%), Fe (3%) |
| [HCl], M | Temperature, °C | Two Hours | Four Hours |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 M | 20 | 0 | 0.05 |
| 6 M | 40 | 0.08 | 0.1 |
| 6 M | 80 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| 12 M | 20 | 0.04 | 0.8 |
| 12 M | 40 | 1 | 1 |
| 12 M | 80 | 56 | 69 |
| Time, Hours | 16.7 wt% (28 g W) | 8.4 wt% (14 g W) | 4.2 wt% (7 g W) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 56 | 21 | 14 |
| 4 | 69 | 23 | 14 |
| Time, Hours | 16.7 wt% (28 g W) | 8.4 wt% (14 g W) | 4.2 wt% (7 g W) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
| 4 | 9 | 13 | 14 |
| 6 | 10 | 16 | 18 |
| 8 | 12 | 21 | 21 |
| Test | Temperature, °C | Time, Hours | Excess Na2CO3, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 600 | 2 | 30 |
| 2 | 600 | 1 | 40 |
| 3 | 600 | 2 | 40 |
| 4 | 700 | 2 | 20 |
| 5 | 700 | 2 | 30 |
| 6 | 800 | 2 | 40 |
| 7 | 800 | 1 | 20 |
| 8 | 800 | 2 | 20 |
| 9 | 800 | 1 | 30 |
| 10 | 800 | 2 | 30 |
| 11 | 800 | 1 | 40 |
| 12 | 800 | 2 | 40 |
| 13 | 800 | 2 | 20 |
| 14 | 800 | 2 | 40 |
| Test (With Respect to Table 4) | Pulp Density, wt% | % W Leached |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25 (29 g W) | 71 |
| 16.7 (23 g W) | 75 | |
| 12.5 (17 g W) | 80 | |
| 5 | 25 (29 g W) | 75 |
| 16.7 (23 g W) | 80 | |
| 12.5 (17 g W) | 84 | |
| 10 | 25 (29 g W) | 80 |
| 16.7 (23 g W) | 86 | |
| 12.5 (17 g W) | 91 | |
| 12 | 25 (29 g W) | 94 |
| 16.7 (23 g W) | 98 | |
| 12.5 (17 g W) | 99 | |
| 14 | 25 (29 g W) | 60 |
| 16.7 (23 g W) | 69 | |
| 12.5 (17 g W) | 73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alguacil, F.J.; Alonso, M.; Lozano, L.J.; Robla, J.I. Strategies for the Recovery of Tungsten from Wolframite, Scheelite, or Wolframite–Scheelite Mixed Concentrates of Spanish Origin. Metals 2025, 15, 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080819
Alguacil FJ, Alonso M, Lozano LJ, Robla JI. Strategies for the Recovery of Tungsten from Wolframite, Scheelite, or Wolframite–Scheelite Mixed Concentrates of Spanish Origin. Metals. 2025; 15(8):819. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080819
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlguacil, Francisco Jose, Manuel Alonso, Luis Javier Lozano, and Jose Ignacio Robla. 2025. "Strategies for the Recovery of Tungsten from Wolframite, Scheelite, or Wolframite–Scheelite Mixed Concentrates of Spanish Origin" Metals 15, no. 8: 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080819
APA StyleAlguacil, F. J., Alonso, M., Lozano, L. J., & Robla, J. I. (2025). Strategies for the Recovery of Tungsten from Wolframite, Scheelite, or Wolframite–Scheelite Mixed Concentrates of Spanish Origin. Metals, 15(8), 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080819







