Research on the Solidification Structure of the Zn-19Al-6Mg Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Thermodynamic Calculation
- (1)
- Selection of modules and databases: For the variable-temperature phase diagram of the Zn-xAl-yMg ternary alloy, the “phase diagram” module is selected. After entering the module, the “TCAl7.1” database is used for calculation. The determination of the database represents the determination of the phase diagram calculation model, and then the calculation parameters can be set.
- (2)
- Parameter setting: When calculating the phase diagram, ensure that the degrees of freedom are 0. For the temperature-varying phase diagram of the Zn-Al-Mg ternary alloy, it is necessary to set its component content, temperature, pressure, and molar mass. The Zn-Al-Mg ternary alloy is based on Zn. However, since the database “TCAl7.1” is an Al-based alloy database, when setting the component content, the two elements Zn and Mg are determined. Then, through the function x·ω(Mg) − y·ω(Al) = 0, the contents of Al and Mg elements are correlated, and the temperature, pressure, and molar mass are set. After setting the initial conditions, the parameters in the phase diagram, their variation ranges, and their step sizes are set, and finally the phase diagram calculation is carried out.
- (3)
- Phase diagram optimization: For variable-temperature phase diagrams, after obtaining the complete phase diagram through software calculation, the coordinate axes of the phase diagram are selectively truncated and the microstructure is calibrated based on the alloy composition under study.
- (4)
- Phase diagram output: Save the obtained phase diagram to the computer.
2.2. Induction Melting Furnace Smelting Zn-19Al-6Mg Alloy
2.3. A Test Block Was Cut in the Middle of the Bar Zn-19Al-6Mg Alloy Sample, and DSC Differential Thermal Analysis Experiment Was Carried out
2.4. Microstructure Observation and EDS Analysis of Zn-19Al-6Mg Alloy
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
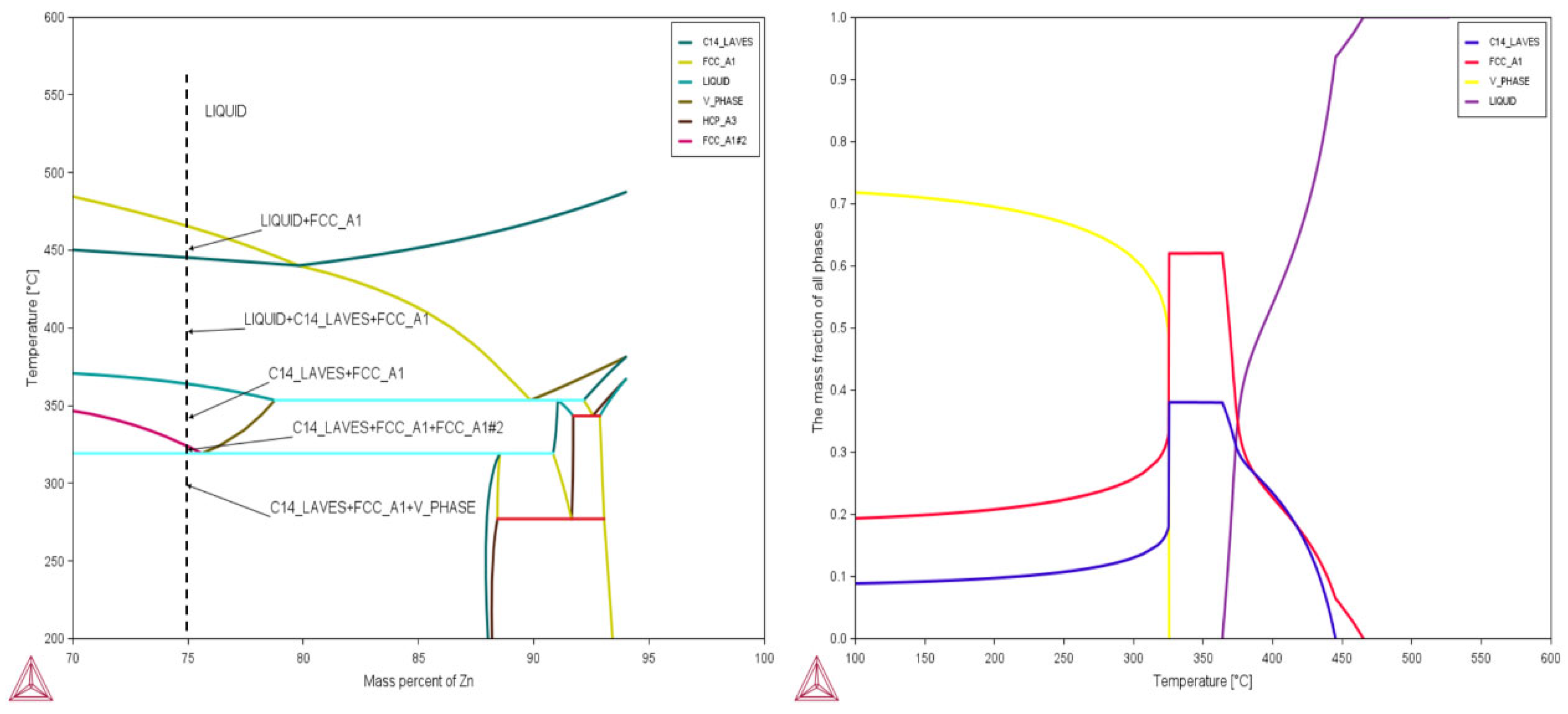
3.1. Calculation and Analysis of Phase Diagram of Zn-19Al-6Mg-Coated Alloy
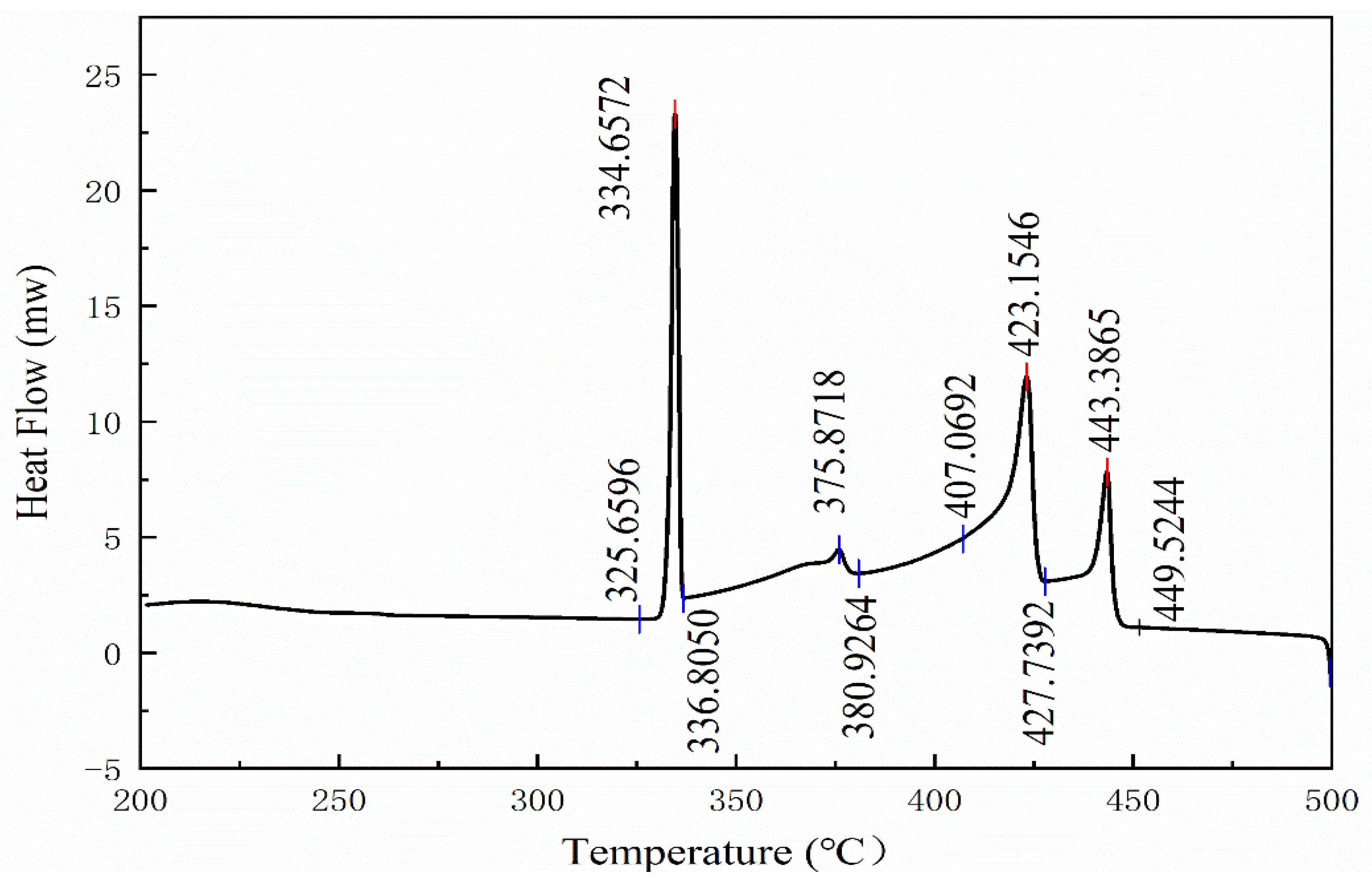
3.2. Verification of Thermodynamic Calculation Results
3.3. Observation and Analysis of Microstructure of Zn-19Al-6Mg Coating Alloy
4. Conclusions
- (1)
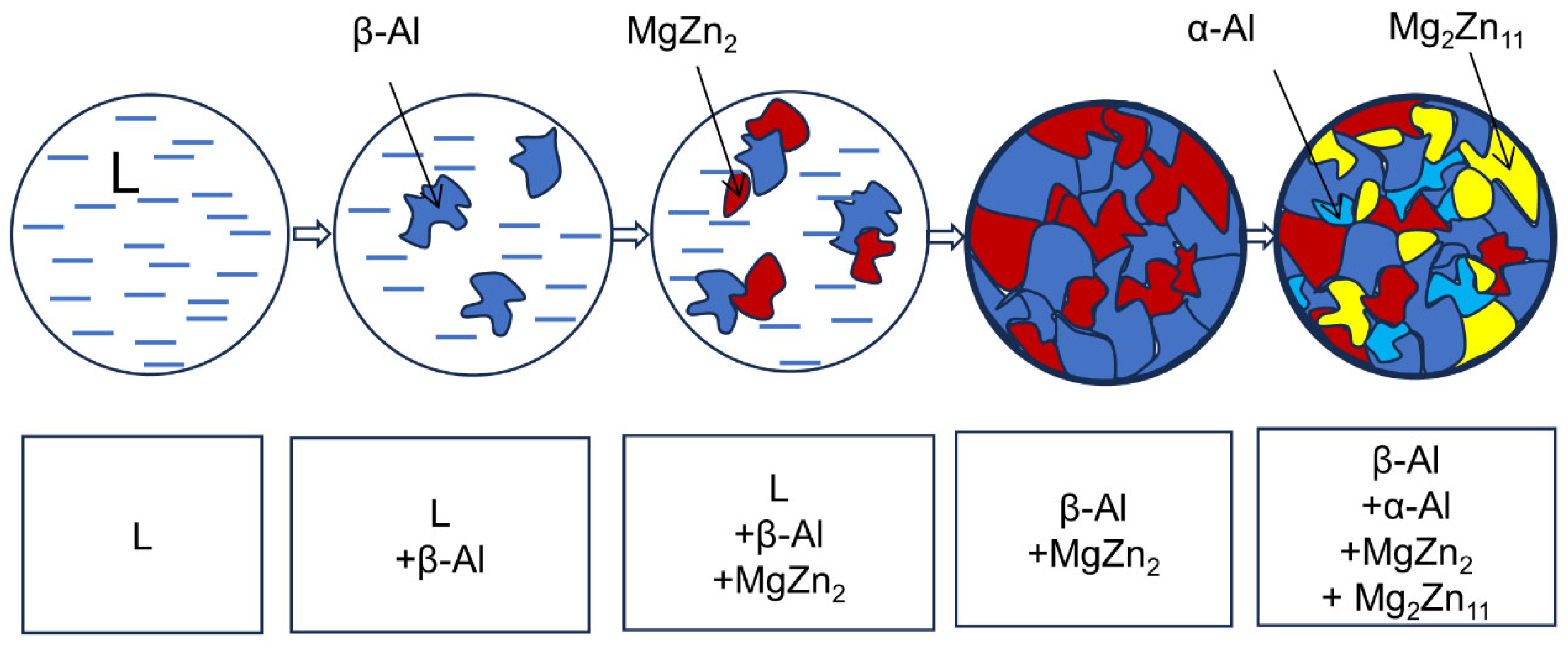
- The solidification microstructure of the Zn-19Al-6Mg alloy consists of an β-Al phase, α-Al phase, MgZn2 phase, and Mg2Zn11 phase.
- (2)
- The microstructure formation path of the Zn-19Al-6Mg alloy at room temperature is L→β-Al→β-Al + MgZn2→MgZn2 + β-Al + α-Al + Mg2Zn11.
- (3)
- During the formation of the solidification structure of the Zn-19Al-6Mg alloy, the primary β-Al phase precipitates Zn and forms the α-Al phase. Due to the cooling rate in the actual transformation process, the precipitated Zn cannot completely form Mg2Zn11 with the MgZn2 phase, resulting in the Zn-rich phase in some regions of the structure.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, G.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, H.; Gao, J.; Wu, G.; Mao, X. Study on Corrosion Behavior and Mechanism of Ultrahigh-Strength Hot-Stam** Steel Based on Traditional and Compact Strip-Production Processes. Materials 2023, 16, 3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Luo, M.; Lan, P.; Tang, H.; Zhang, J. Characteristics and evolution of the spot segregations and banded defects in high strength corrosion resistant tube steel. Acta Met. Sin 2019, 55, 762–772. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Q. Enhanced Corrosion Protection of Steel Strip through Advanced Zn-Mg Alloy Coatings manufactured by Continuous Physical Vapor Deposition: A Review. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 328, 129884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Salgın, B.; Kooi, B.J.; Pei, Y. Genesis and mechanism of microstructural scale deformation and cracking in ZnAlMg coatings. Mater. Des. 2020, 186, 108364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Salgın, B.; Ahmadi, M.; Kooi, B.J.; Pei, Y. Unraveling dislocation mediated plasticity and strengthening in crack-resistant ZnAlMg coatings. Int. J. Plast. 2021, 144, 103041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Salgın, B.; Kooi, B.J.; Pei, Y. The effect of grain refinement on the deformation and cracking resistance in Zn–Al–Mg coatings. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 840, 142995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosek, T.; Nazarov, A.; Goodwin, F.; Šerák, J.; Thierry, D. Improving corrosion stability of ZnAlMg by alloying for protection of car bodies. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 306, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.W.; Cooman, B.D. State-of-the-knowledge on coating systems for hot stamped parts. Steel Res. Int. 2012, 83, 412–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marder, A.R. The metallurgy of zinc-coated steel. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2000, 45, 191–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munroe, P.R.; Laksmi, C.S.; Gleeson, B. Effects of 0.1 and 0.2 wt.% aluminium addition to zinc on the interdiffusion between zinc and iron at 400 C. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 251, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Liu, Y.; Tu, H.; Wu, C.; Su, X.; Wang, J. The Effects of B on the Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Zn-6Al-3Mg Alloy Coating. Steel Res. Int. 2024, 95, 2400180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wei, J.; Tian, G.; Qie, R.; Yan, L.; Zhao, A. Effect of al content on microstructure and corrosion resistance of Zn-Al-Mg alloy. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 02670836241292174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouki, A.; Ben Ali, M.; El Maalam, K.; Aouadi, K.; Benabdallah, I.; El Fatimy, A.; Naamane, S. Optimizing corrosion protection: Performance comparison of Zn and Zn-Al-Mg alloys Hot-Dip galvanized coatings. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1007, 176371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.W.; Gao, B.; Tu, G.F.; Sun, S.C.; Yin, S.H.; Hu, L. The Effects of RE and Si on the Thickness and Cross Section Morphology of Zn-6Al-3Mg Alloy Coating. Key Eng. Mater. 2013, 562, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.X.; Ma, X.H.; Bai, J.T.; Du, T.; Ma, R.; Du, A.; Zhao, A.; Fan, Y.; Li, G. Study of the corrosion behavior and mechanism of a hot-dipping Zn–6Al–3Mg alloy coating in 3.5 wt% neutral NaCl solution. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 464, 129576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, G.; Sun, H.; Teng, X.; Zhao, Z. Effect of Ti and Zr elements with equal mass ratio on microstructure and corrosion resistance of Zn-11Al-3Mg alloy. Mater. Corros. 2021, 72, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dong, A.; Zhu, G.; Chu, S.; Qian, H.; Hu, C.; Sun, B.; Wang, J. Investigation of the corrosion behaviors of continuously hot-dip galvanizing Zn–Mg coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 3989–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuda, K.; Goto, Y.; Saito, M.; Takebayashi, H.; Konishi, T.; Fukuda, Y.; Nakamura, F.; Kawanishi, K.; Ueda, K.; Shindo, H. New Corrosion-Resistant Zn-Al-Mg Alloy Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet. Corros. Sci. Technol. 2024, 23, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda, S.; Nishida, Y.; Nishimoto, M.; Muto, I.; Shoji, H. Initial dissolution of Mg-containing phase and corrosion product formation in cut-edge corrosion of Zn-11% Al-3% Mg-0.2% Si coated steel. Corros. Sci. 2023, 225, 111605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Q. Calculation and Experimental Verification of Zn-Al-Mg Phase Diagram. Coatings 2024, 14, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atapek, Ş.H.; Erişir, E.; Gümüş, S. Modeling and thermal analysis of solidification in a low alloy steel. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 114, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.-O.; Helander, T.; Höglund, L.; Shi, P.; Sundman, B. Thermo-Calc & DICTRA, computational tools for materials science. Calphad 2002, 26, 273–312. [Google Scholar]
- Minakshi, M.; Appadoo, D.; Martin, D.E. The anodic behavior of planar and porous zinc electrodes in alkaline electrolyte. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2010, 13, A77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Zn | Al | Mg | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target value (wt%) | 75% | 19% | 6% |
| Actual value (wt%) | 74.98% | 19.08 | 5.94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, J.; Xiao, J.; Yang, S.; Cao, K.; Wang, D.; Zhao, A. Research on the Solidification Structure of the Zn-19Al-6Mg Alloy. Metals 2025, 15, 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070769
Wei J, Xiao J, Yang S, Cao K, Wang D, Zhao A. Research on the Solidification Structure of the Zn-19Al-6Mg Alloy. Metals. 2025; 15(7):769. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070769
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Jianhua, Jun Xiao, Shaoguang Yang, Kuo Cao, Di Wang, and Aimin Zhao. 2025. "Research on the Solidification Structure of the Zn-19Al-6Mg Alloy" Metals 15, no. 7: 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070769
APA StyleWei, J., Xiao, J., Yang, S., Cao, K., Wang, D., & Zhao, A. (2025). Research on the Solidification Structure of the Zn-19Al-6Mg Alloy. Metals, 15(7), 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070769








