Effect of Oxidative Roasting on Selective Leaching of Lithium from Industrially Shredded Lithium Iron Phosphate Blackmass
Abstract
1. Introduction
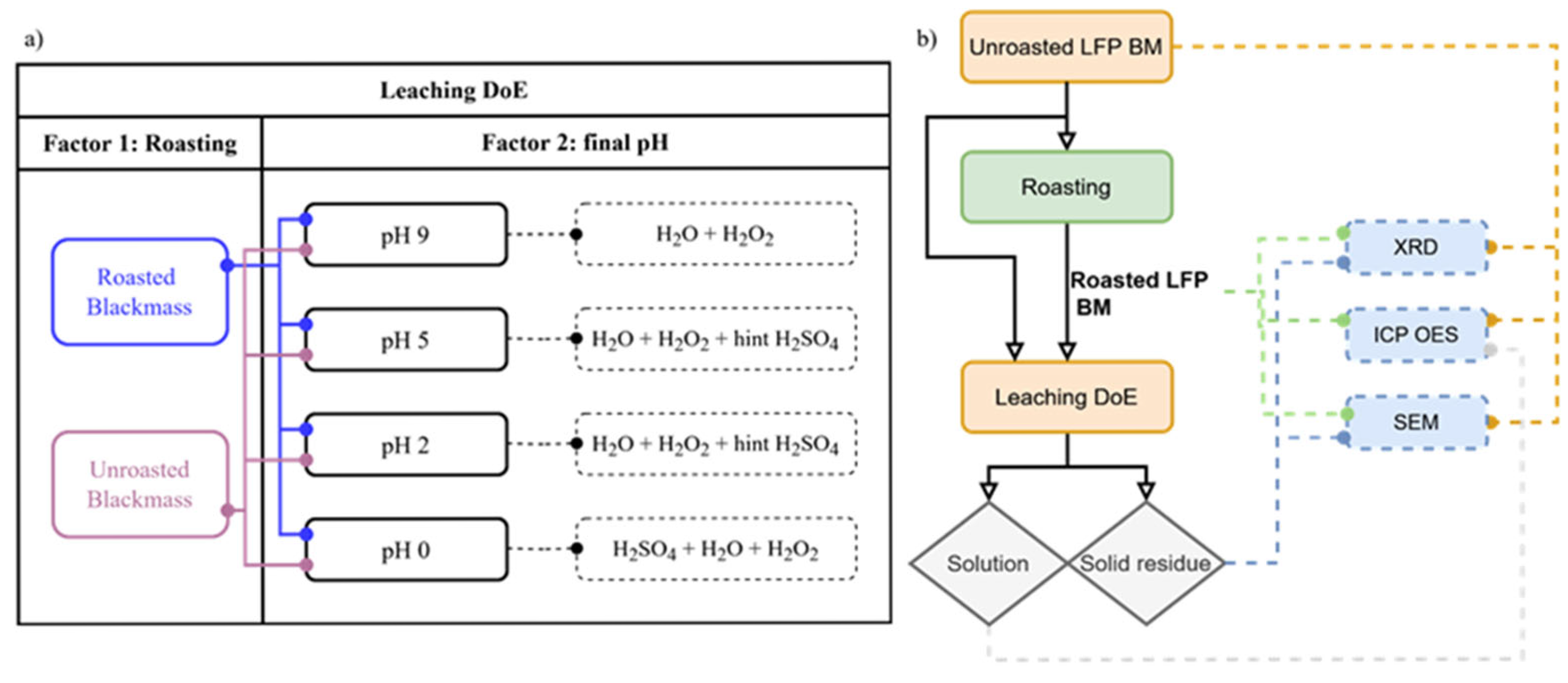
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Characterization
- Chemical composition—determined by ICP-OES (Spectro CIROS Vision, Spectro Analytical Instruments GmbH, Kleve, Germany) after digestion in aqua regia;
- Carbon content—determined by combustion method for carbon analysis (ELTRA CS 2000, ELTRA GmbH, Haan, Germany);
- Fluorine content—determined by Ion Chromatography (811 Compact IC pro, Deutsche Metrohm GmbH & Co., KG, Filderstadt, Germany);
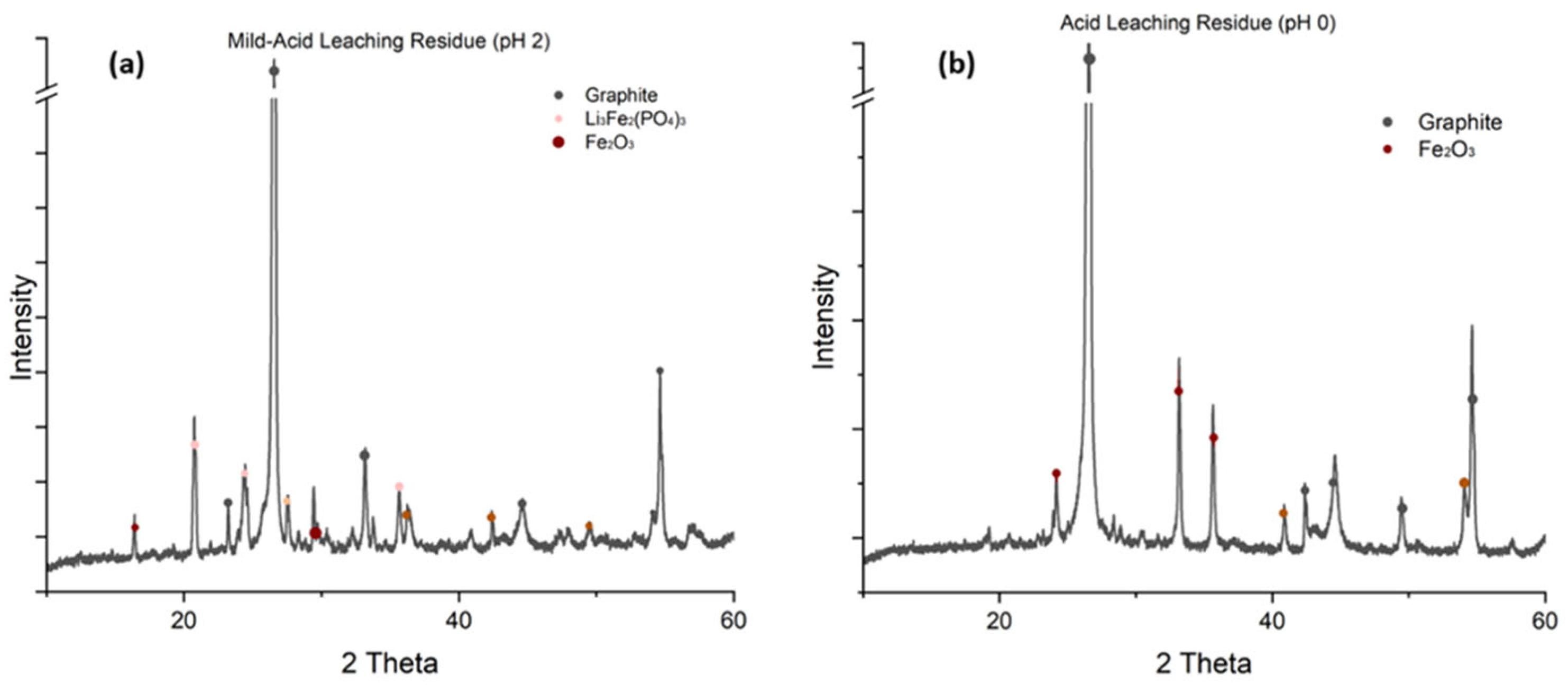
- Phases/compounds—determined by X-Ray Diffractometry (Rigaku SmartLab 9 kW, Bangkok, Thailand) with measurements every 0.5° with radiation Cu Kα;
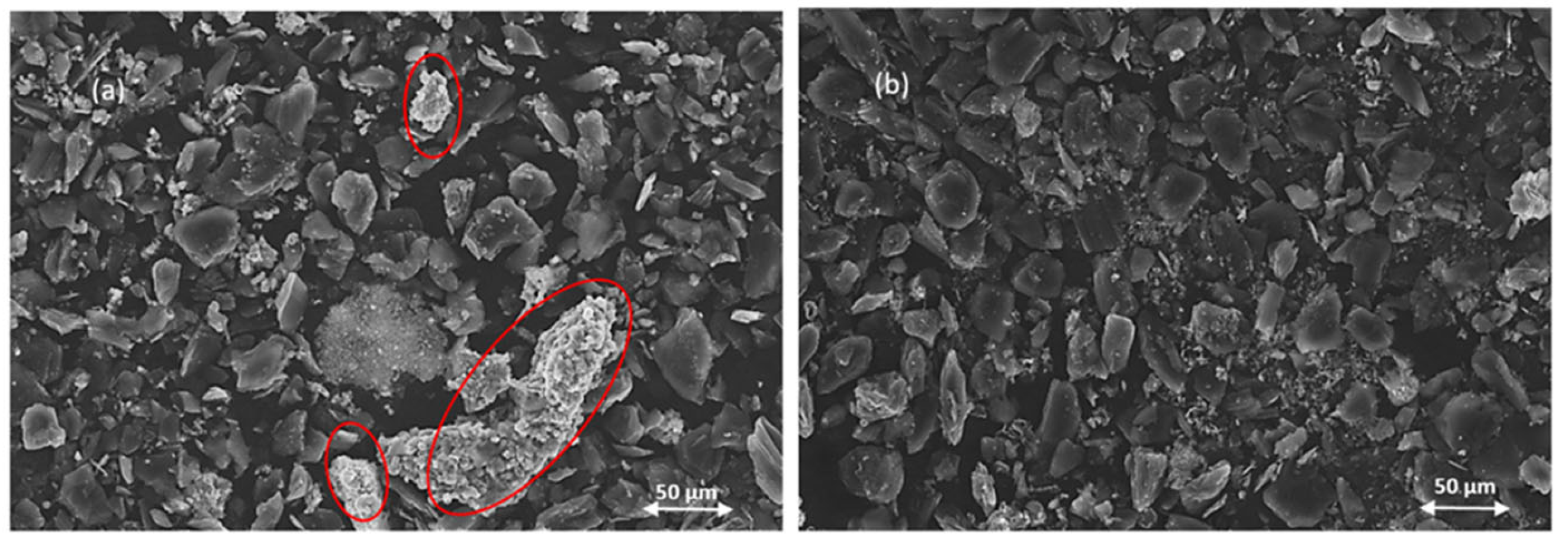
- Morphology of particles—determined by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) (JEOL model JSM-6610 LV, Bangkok, Thailand).
2.2. Roasting in Air Atmosphere
2.3. Leaching Procedure
3. Results
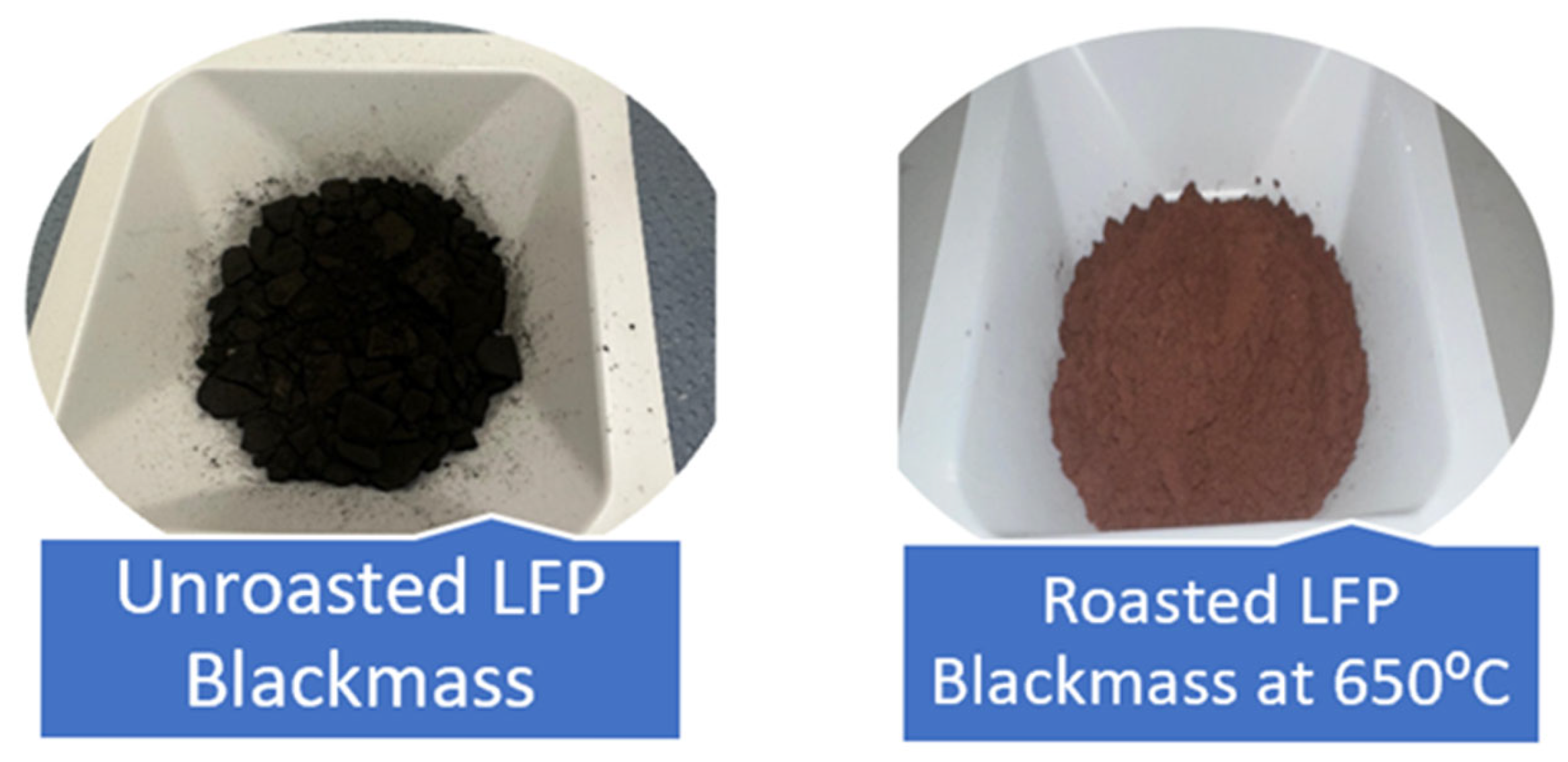
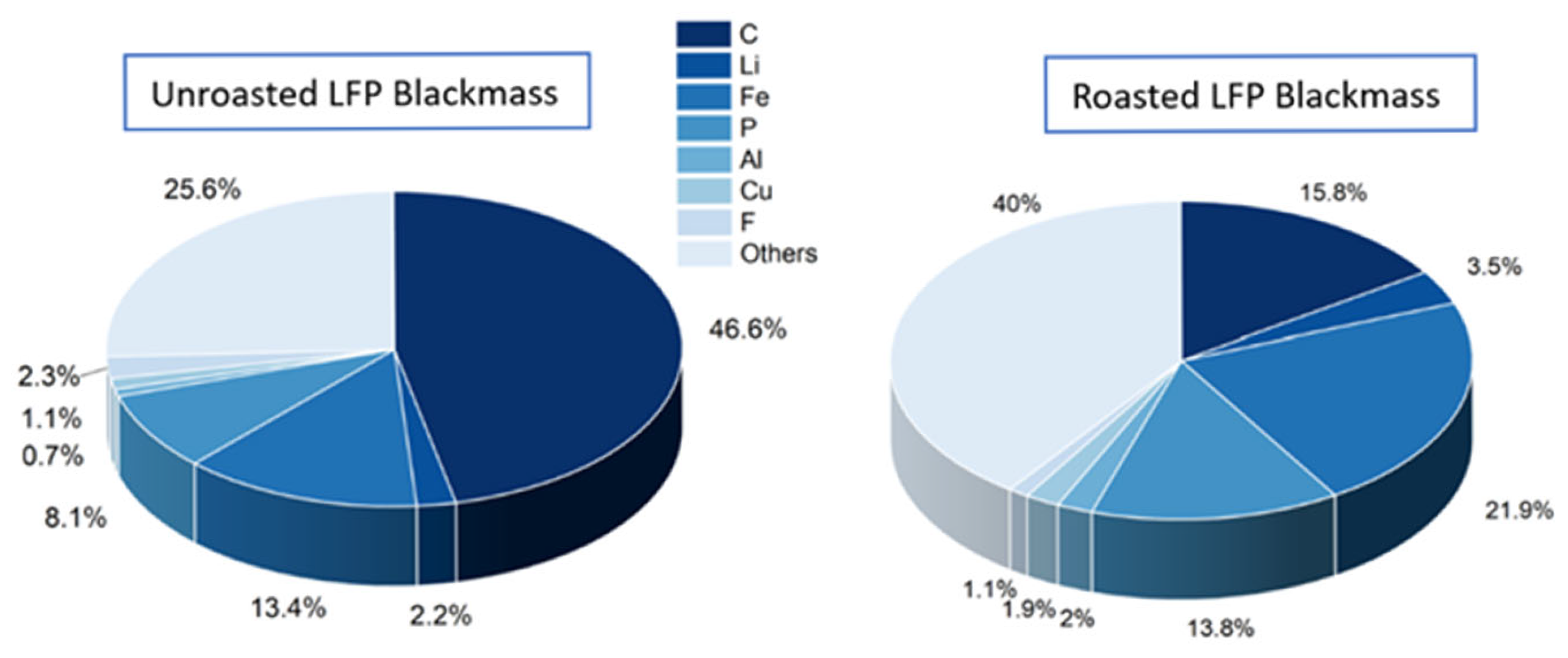
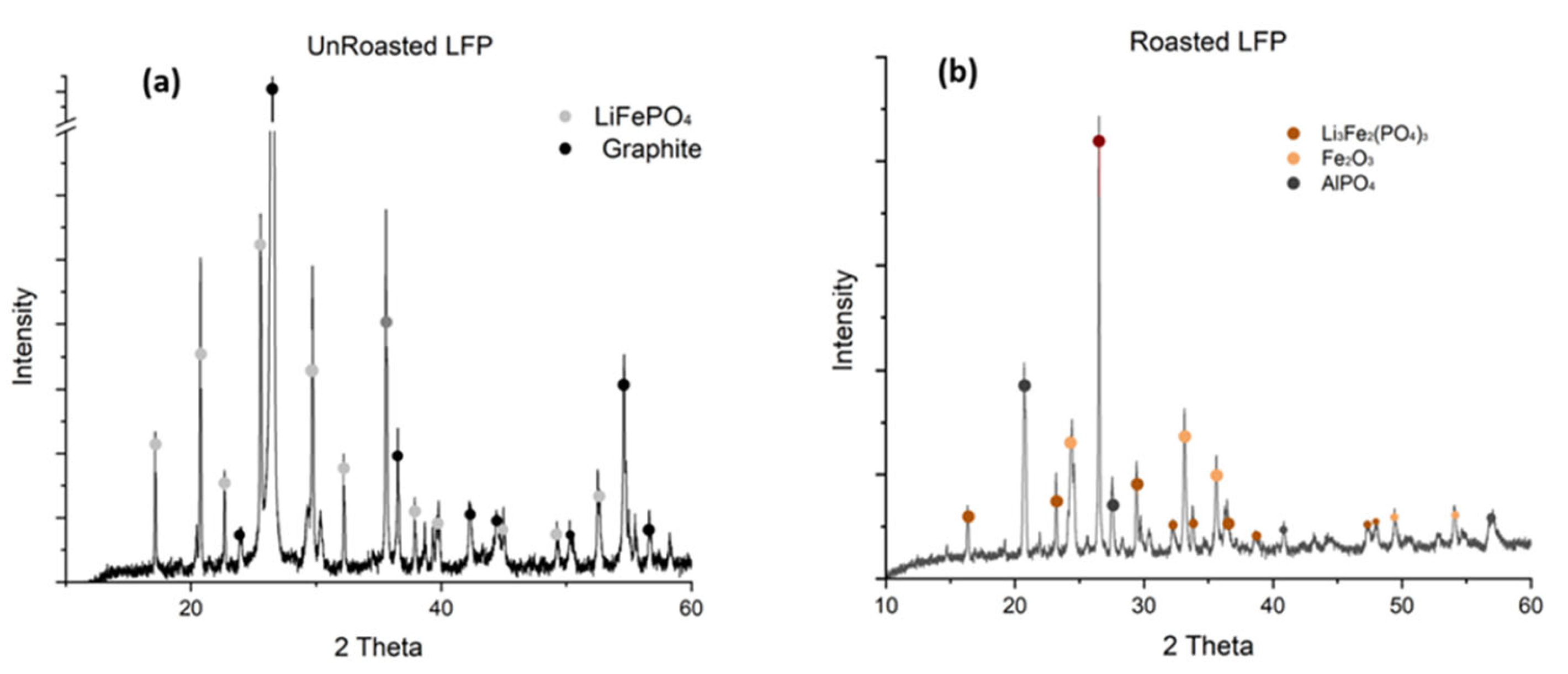
3.1. LFP Blackmass Characterization and Roasting Effect
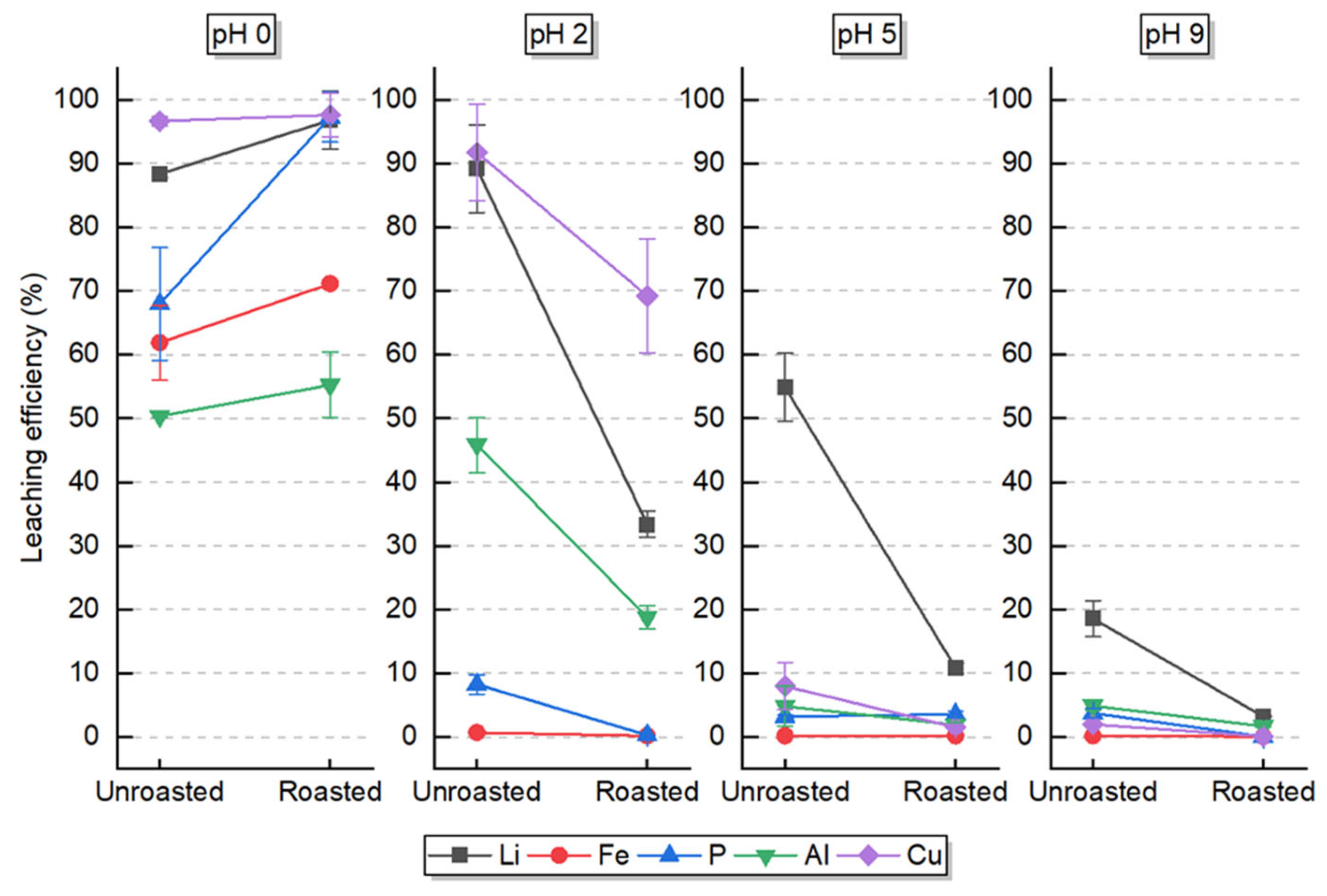
3.2. Selectivity of Lithium Leaching
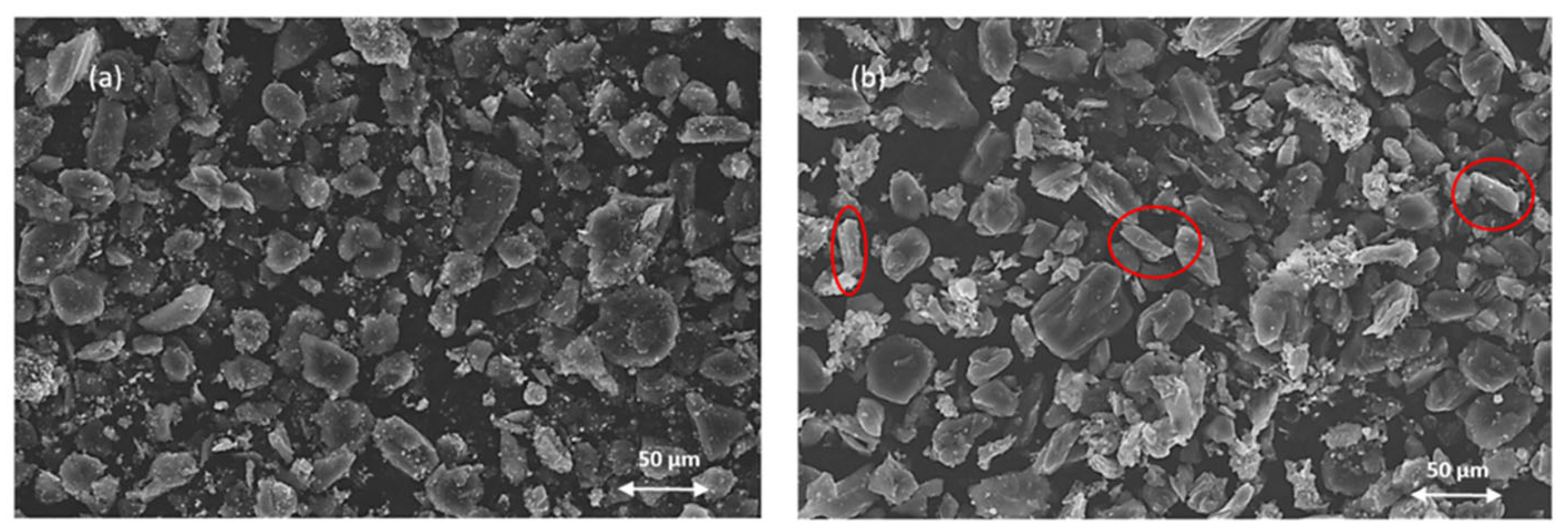
3.3. Characterization of Solid Residues
4. Discussion
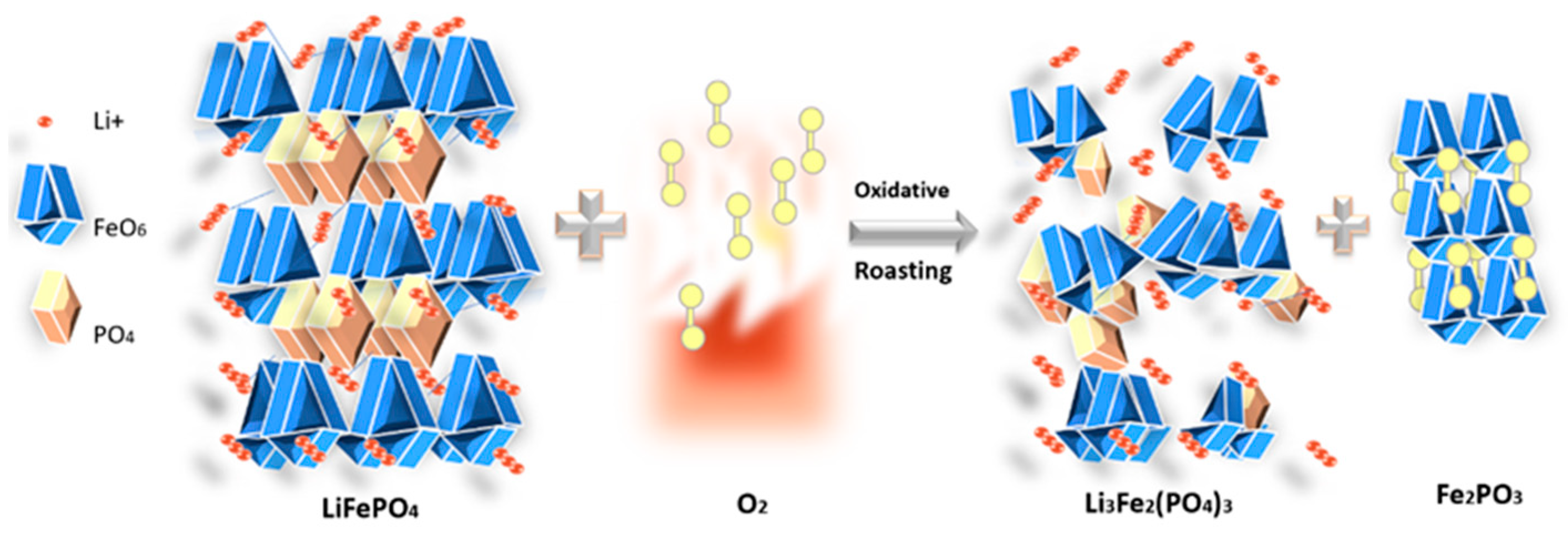
4.1. Oxidative Roasting Mechanism and Phase Transformations
4.2. Selective Leaching Behavior
4.3. Impurity Behavior and Selectivity
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holzer, A.; Windisch-Kern, S.; Ponak, C.; Raupenstrauch, H. A Novel Pyrometallurgical Recycling Process for Lithium-Ion Batteries and Its Application to the Recycling of LCO and LFP. Metals 2021, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billmann, L. Comparative Study of Li-Ion Battery Recycling Processes; ACCUREC Recycling GmbH: Krefeld, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, J.; Ulmala, S.; Wan, X.; Partinen, J.; Lundström, M.; Jokilaakso, A. Selective Sulfation Roasting for Cobalt and Lithium Extraction from Industrial LCO-Rich Spent Black Mass. Metals 2023, 13, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, F.; Pietrantonio, M.; Pucciarmati, S.; Puzone, M.; Fontana, D. Lithium iron phosphate batteries recycling: An assessment of current status. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 51, 2232–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaines, L.; Richa, K.; Spangenberger, J. Key issues for Li-ion battery recycling. MRS Energy Sustain. 2018, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.D.M.; Villen-Guzman, M.; Vereda, C.; Rodríguez-Maroto, J.; Paz-García, J. Towards Sustainable Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling: Advancements in Circular Hydrometallurgy. Processes 2024, 12, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greil, R.; Chai, J.; Rudelstorfer, G.; Mitsche, S.; Lux, S. Water as a Sustainable Leaching Agent for the Selective Leaching of Lithium from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 7806–7816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, W.M. (Ed.) CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 97th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Cai, C.; Peng, G.; Hu, J.; Hou, H.; Liu, B.; Liang, S.; Xiao, K.; Yuan, S.; Yang, J. Hydrometallurgical recovery of spent lithium-ion batteries: Environmental strategies and sustainability evaluation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 6105–6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, D.; Lai, Y.; Chen, Y. Oxidizing roasting behavior and leaching performance for the recovery of spent lifepo4 batteries. Minerals 2020, 10, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Jing, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C. Facile and efficient recovery of lithium from spent LiFePO4 batteries via air oxidation–water leaching at room temperature. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasuno, T.; Kitada, A.; Shimokawa, K.; Murase, K. Suppression of Silver Dissolution by Contacting Different Metals during Copper Electrorefining. J. MMIJ 2014, 130, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Zhu, X.; Xu, M.; Li, J.; Wang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liao, Q. Recycling of spent LiFePO4 batteries by oxidizing roasting: Kinetic analysis and thermal conversion mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larouche, F.; Tedjar, F.; Amouzegar, K.; Houlachi, G.; Bouchard, P.; Demopoulos, G.P.; Zaghib, K. Progress and Status of Hydrometallurgical and Direct Recycling of Li-Ion Batteries and Beyond. Materials 2020, 13, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, W.; Lu, D.; Ren, G.; Tu, Y. Application of Roasting Flotation Technology to Enrich Valuable Metals from Spent LiFePO4 Batteries. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 25590–25599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Luo, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Xu, C.; Guo, J.; Cheali, P.; Xia, X. Progress, challenges, and prospects of spent lithium-ion batteries recycling: A review. J. Energy Chem. 2024, 89, 144–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Nakajima, A.; Zhang, Z.; Watanabe, M. Organic Acid-Based Hydrothermal Leaching of LiFePO4 Cathode Materials. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2024, 8, 2300421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Liu, Z.; Gu, J.; Yuan, H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y. A facile new process for the efficient conversion of spent LiFePO4 batteries via (NH4)2S2O8-assisted mechanochemical activation coupled with water leaching. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Ge, P.; Wang, L.; Sun, W.; Bu, Y.; Sun, M.; Yang, Y. The Recycling of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: Crucial Flotation for the Separation of Cathode and Anode Materials. Molecules 2023, 28, 4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Obuz, H.E.; Keber, S.; Tekmanli, F.; Mettke, L.N.; Yagmurlu, B. Concepts for the Sustainable Hydrometallurgical Processing of End-of-Life Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) Batteries. Sustainability 2024, 16, 11267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliamentary Research Service. New EU Regulatory Framework for Batteries: Setting Sustainability Requirements. Briefing, 5 September 2024. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/thinktank/en/document/EPRS_BRI(2021)689337 (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Obuz, H.; Tekmanlı, F.; Mettke, L.; Müller, M.; Yagmurlu, B. Investigation of Recycling Behavior of Lithium Iron Phosphate Batteries with Different Thermal Pre-Treatments. Mater. Proc. 2023, 15, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xing, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Guo, H.; Kuang, G. Recovery of lithium, iron, and phosphorus from spent LiFePO4 batteries using stoichiometric sulfuric acid leaching system. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 7350–7358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, B.; Park, H.-K.; Na, T.; Heo, S.; Kim, R.; Yoon, H.-S.; Chung, K.W.; Park, K. Selective leaching behavior of Nd from spent NdFeB magnets treated with combination of selective oxidation and roasting processes. Hydrometallurgy 2024, 227, 106320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallmeister, C.; Friedrich, B. Holistic Investigation of the Inert Thermal Treatment of Industrially Shredded NMC 622 Lithium-Ion Batteries and Its Influence on Selective Lithium Recovery by Water Leaching. Metals 2023, 13, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-F.; Chen, M.; Zhao, J.-J.; Zhou, F.-Y.; Wang, H.-Y.; Qu, X.; Cai, Y.-Q.; Zheng, Z.-Y.; Wang, D.-H.; Yin, H.-Y. Revealing role of oxidation in recycling spent lithium iron phosphate through acid leaching. Rare Met. 2025, 44, 2059–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woeste, R.; Drude, E.-S.; Vrucak, D.; Klöckner, K.; Rombach, E.; Letmathe, P.; Friedrich, B. A techno-economic assessment of two recycling processes for black mass from end-of-life lithium-ion batteries. Appl. Energy 2024, 361, 122921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Ge, Z.; Zhang, S.; Song, B.; Tian, Y.; Deng, W.; Zou, G.; Hou, H.; Ji, X. Advances and perspectives towards spent LiFePO4 battery recycling. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Jing, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C. Recovery and regeneration of LiFePO4 from spent lithium-ion batteries via a novel pretreatment process. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2021, 28, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Teng, T.; Xiao, L.; Shen, L.; Ran, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, H. Recovery of LiFePO4 from used lithium-ion batteries by sodium-bisulphate-assisted roasting. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ru, J.; Hua, Y.; Cheng, M.; Lu, L.; Wang, D. Priority Recovery of Lithium From Spent Lithium Iron Phosphate Batteries via H2O-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Carbon Neutralization 2025, 4, e186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yuan, X.; Tay, C.Y.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Duan, C. Selective recycling of lithium from spent lithium-ion batteries by carbothermal reduction combined with multistage leaching. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 314, 123555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Marthi, R.; Mahandra, H.; Chae, S.; Traversy, M.; Sadri, F.; Choi, Y.; Ghahreman, A. Direct selective leaching of lithium from industrial-grade black mass of waste lithium-ion batteries containing LiFePO4 cathodes. Waste Manag. 2023, 171, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Zhao, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Q.; Mu, D.; Li, R.; Dai, C. Optimized Li and Fe recovery from spent lithium-ion batteries via a solution-precipitation method. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 43613–43625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| p-Value | Li | Fe | P | Al | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor 1: roasting | 0.000 | 0.44 | 0.15 | 0.001 | 0.13 |
| Factor 2: final pH | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Interaction (Roasting × Final pH) | 0.000 | 0.54 | 0.01 | 0.000 | 0.31 |
| Study | Feed Source | Li Recovery (%) | Fe/Li Molar Ratio | Key Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current Study | Industrial BM | 33–95 | 0.24–0.97 | H2SO4/H2O2, 20 °C, 40 g/L |
| Jing et al. [11] | Lab synthesized LFP | 95.4 | 0.05 | H2O2, neutral pH, 80 °C |
| Wang et al. [26] | Industrial BM | 97 | 1.02 | H2SO4, 60 °C |
| Zhang et al. [31] | Virgin LFP | 98 | 1.10 | H2SO4, 80 °C |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tasawar, A.; Dotto Munchen, D.; Birich, A.; Yeetsorn, R.; Friedrich, B. Effect of Oxidative Roasting on Selective Leaching of Lithium from Industrially Shredded Lithium Iron Phosphate Blackmass. Metals 2025, 15, 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070739
Tasawar A, Dotto Munchen D, Birich A, Yeetsorn R, Friedrich B. Effect of Oxidative Roasting on Selective Leaching of Lithium from Industrially Shredded Lithium Iron Phosphate Blackmass. Metals. 2025; 15(7):739. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070739
Chicago/Turabian StyleTasawar, Ayesha, Daniel Dotto Munchen, Alexander Birich, Rungsima Yeetsorn, and Bernd Friedrich. 2025. "Effect of Oxidative Roasting on Selective Leaching of Lithium from Industrially Shredded Lithium Iron Phosphate Blackmass" Metals 15, no. 7: 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070739
APA StyleTasawar, A., Dotto Munchen, D., Birich, A., Yeetsorn, R., & Friedrich, B. (2025). Effect of Oxidative Roasting on Selective Leaching of Lithium from Industrially Shredded Lithium Iron Phosphate Blackmass. Metals, 15(7), 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070739









