Characterization of Thermophysical Properties and Crystallization Behavior of Industrial Mold Fluxes
Abstract
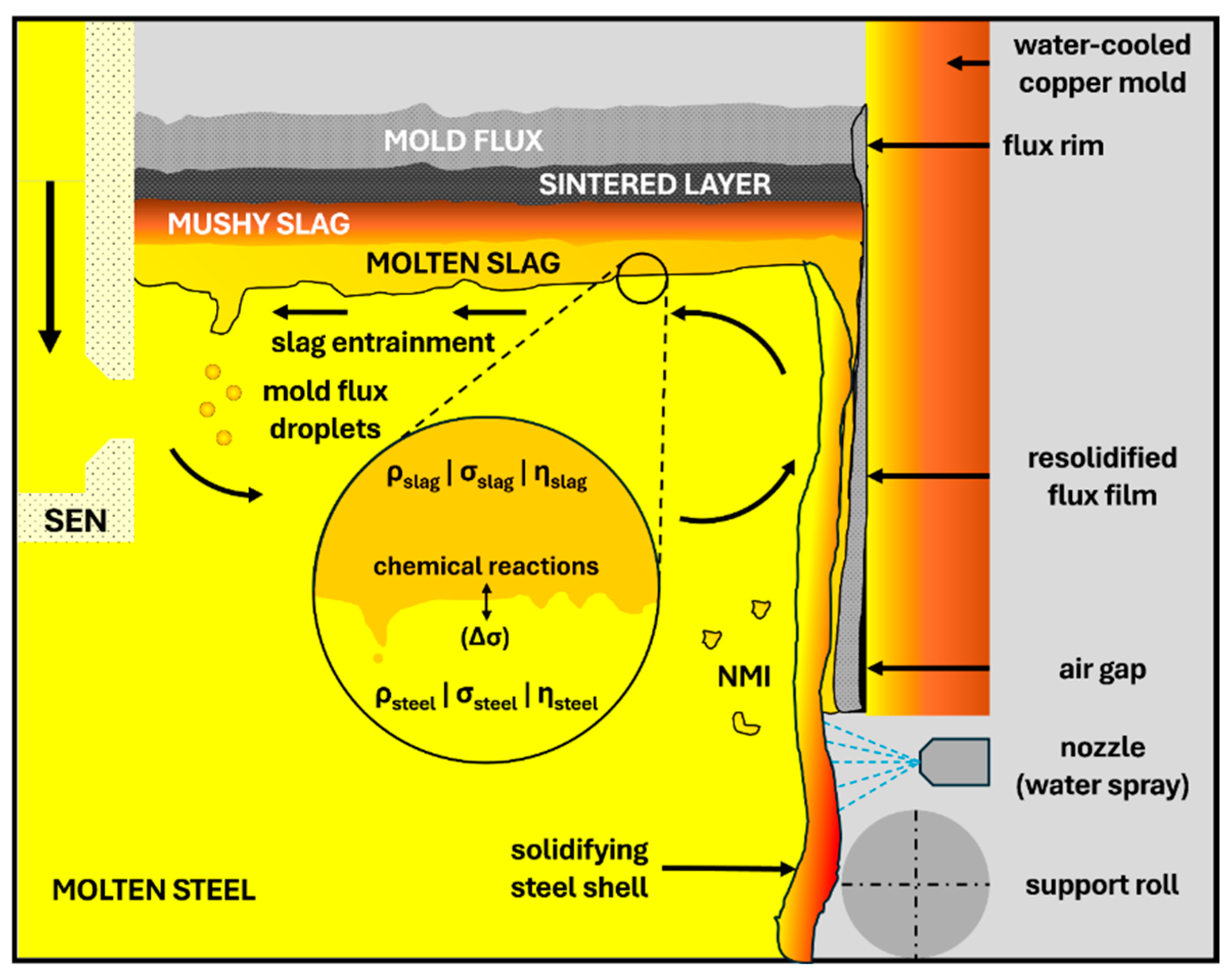
1. Introduction
- -
- Group 1: contact with liquid steel (thermal insulation, prevention of reoxidation, inclusion entrapment).
- -
- Group 2: contact with solidified steel (lubrication between the solidified steel shell and the mold, heat transfer control).
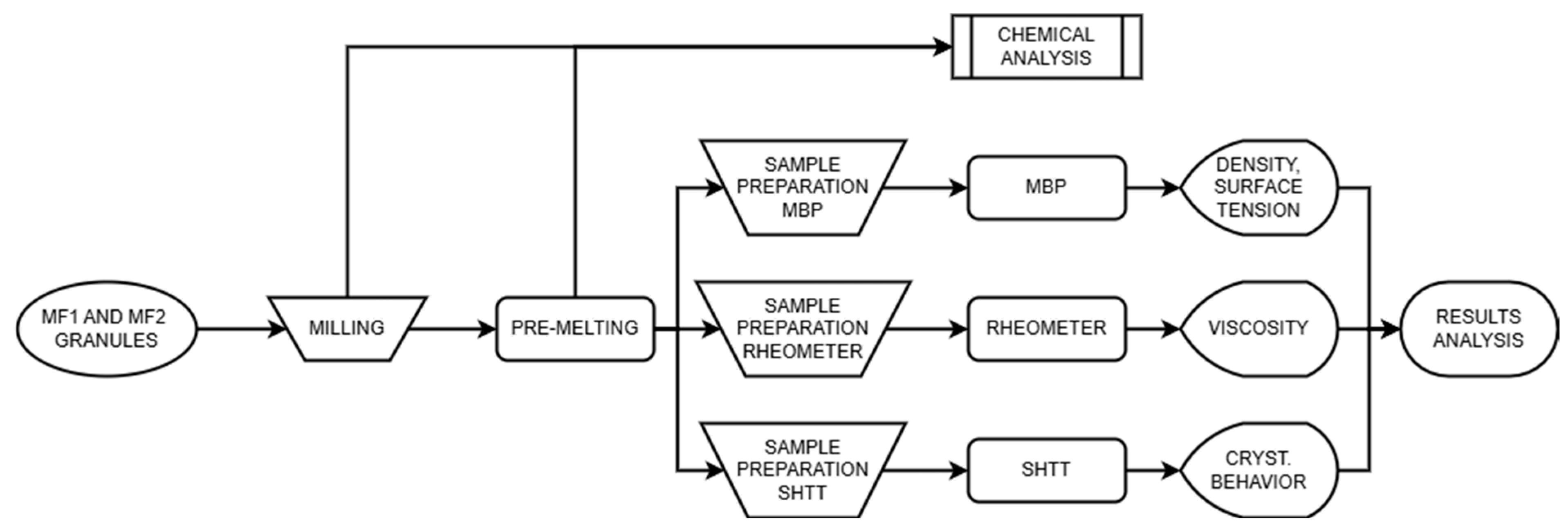
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
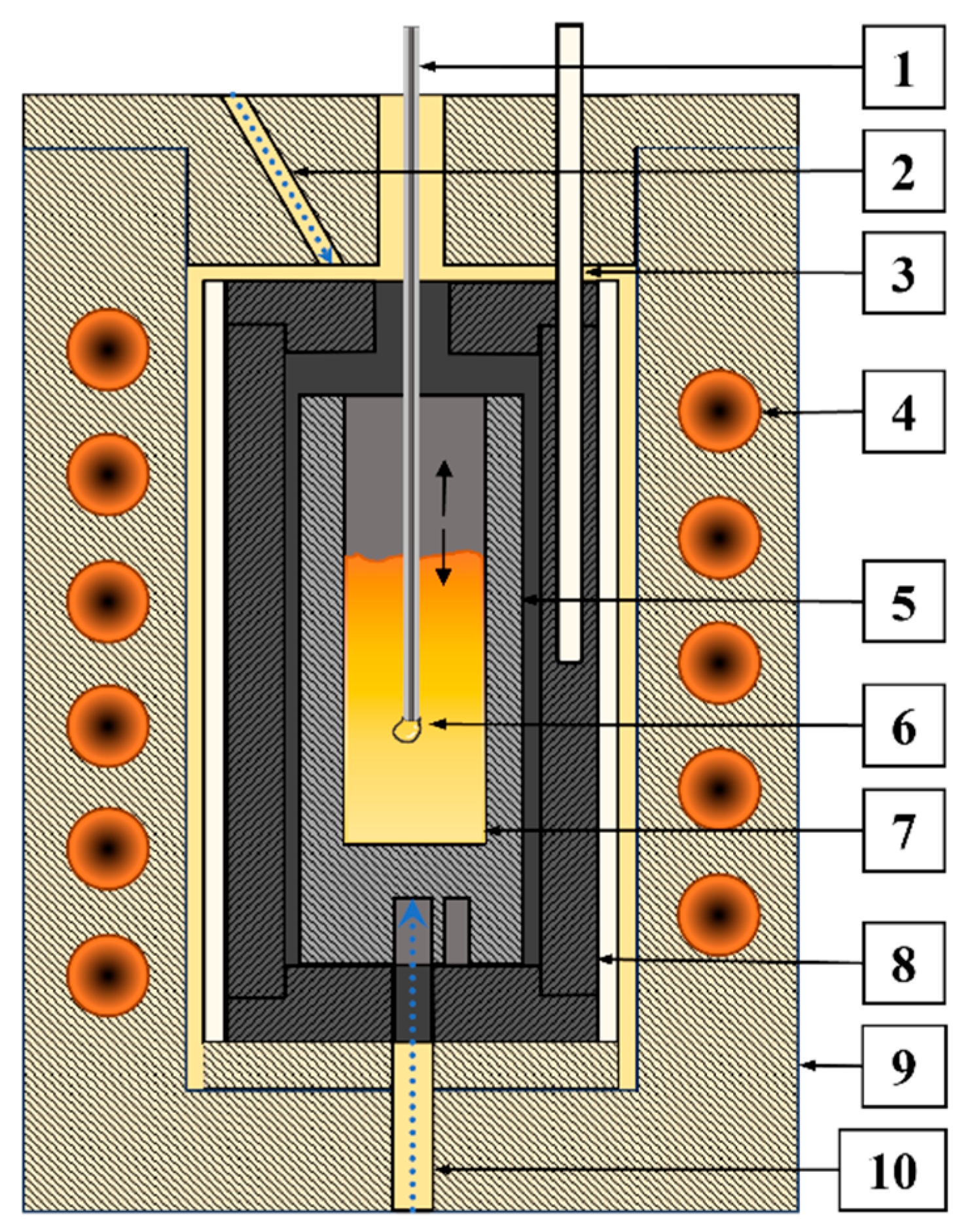
2.2. Rotating Bob Viscometry (RBV)
2.3. Maximum Bubble Pressure (MBP) Method
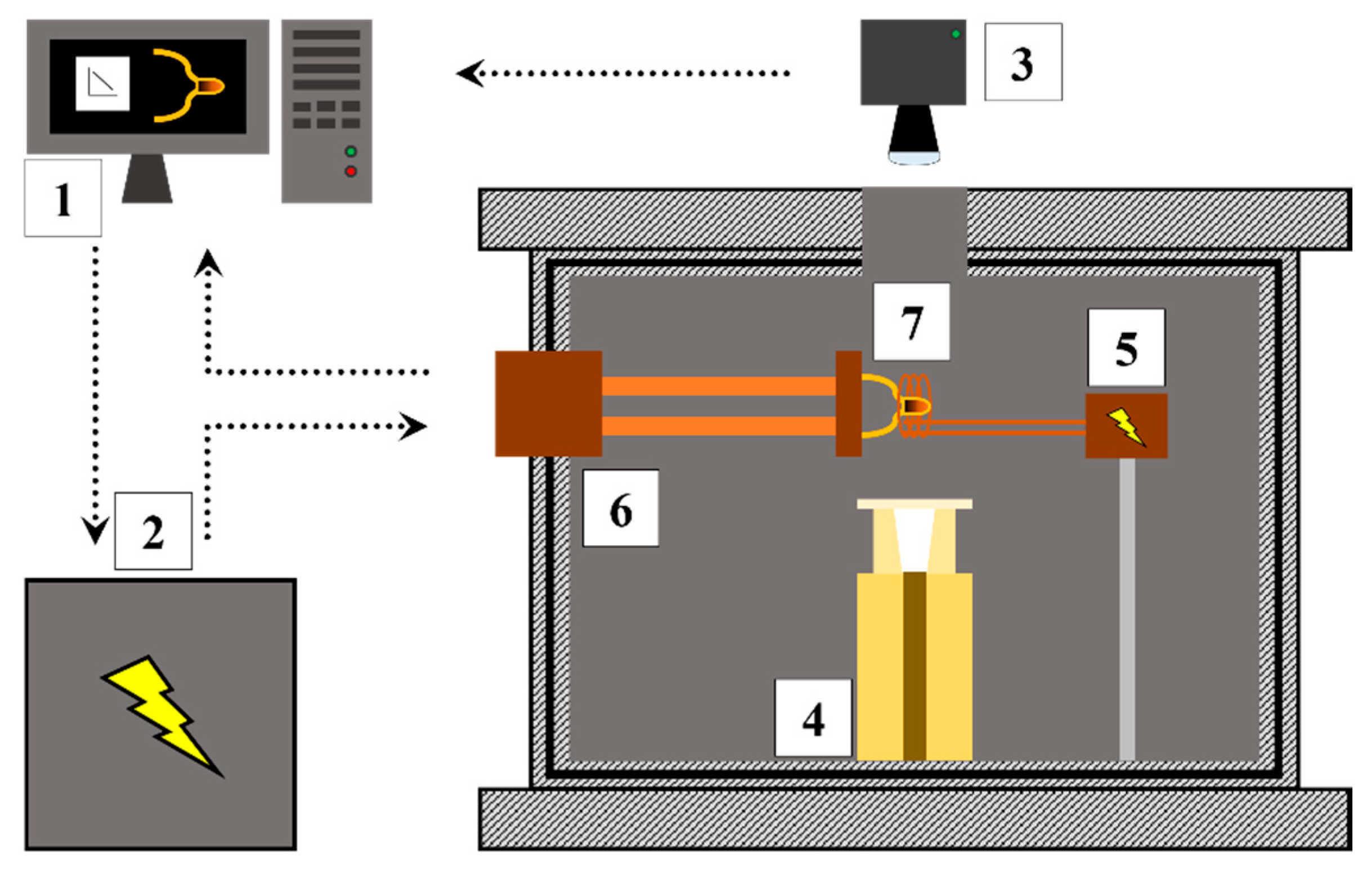
2.4. Single Hot Thermocouple Technique (SHTT)
3. Results and Discussion
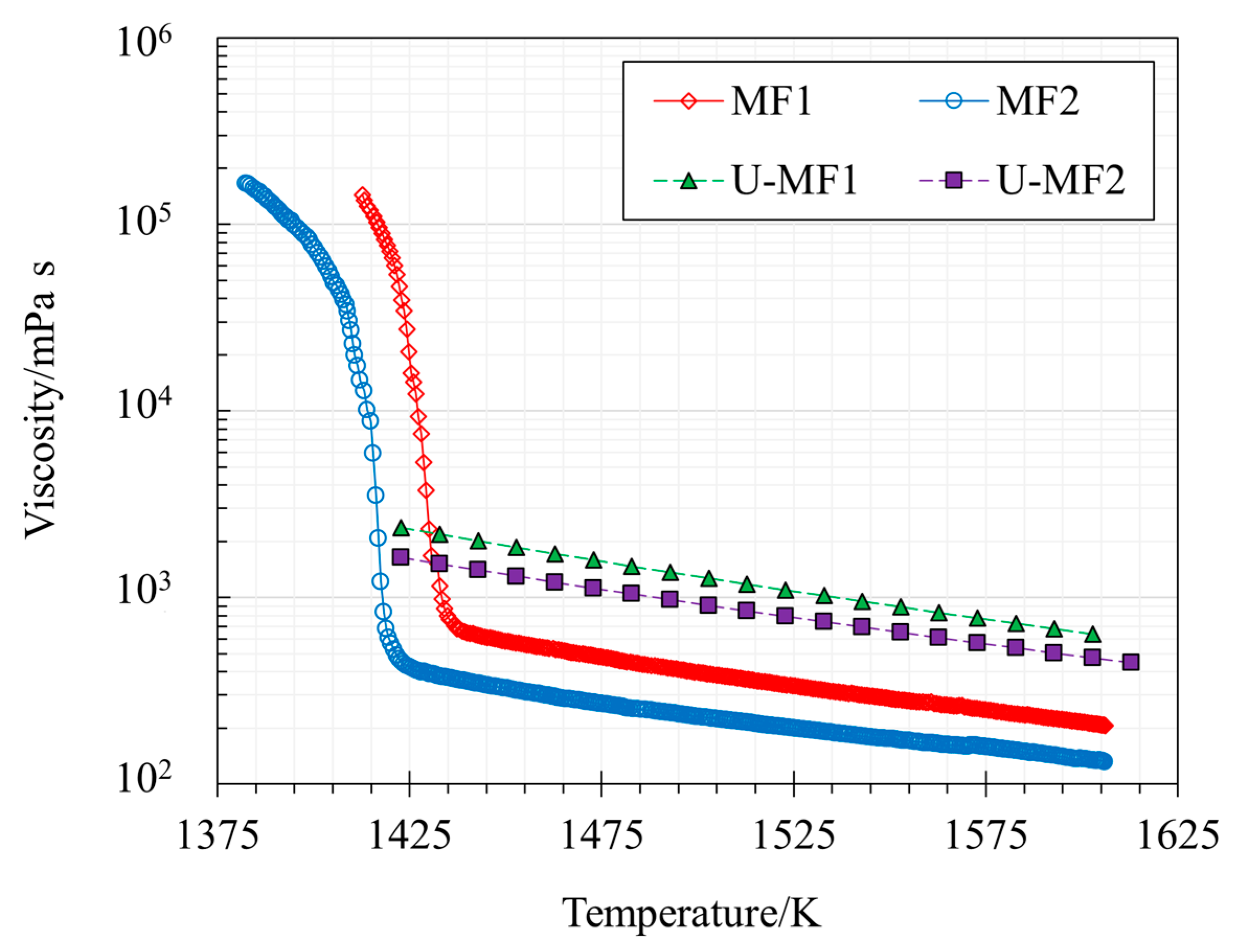
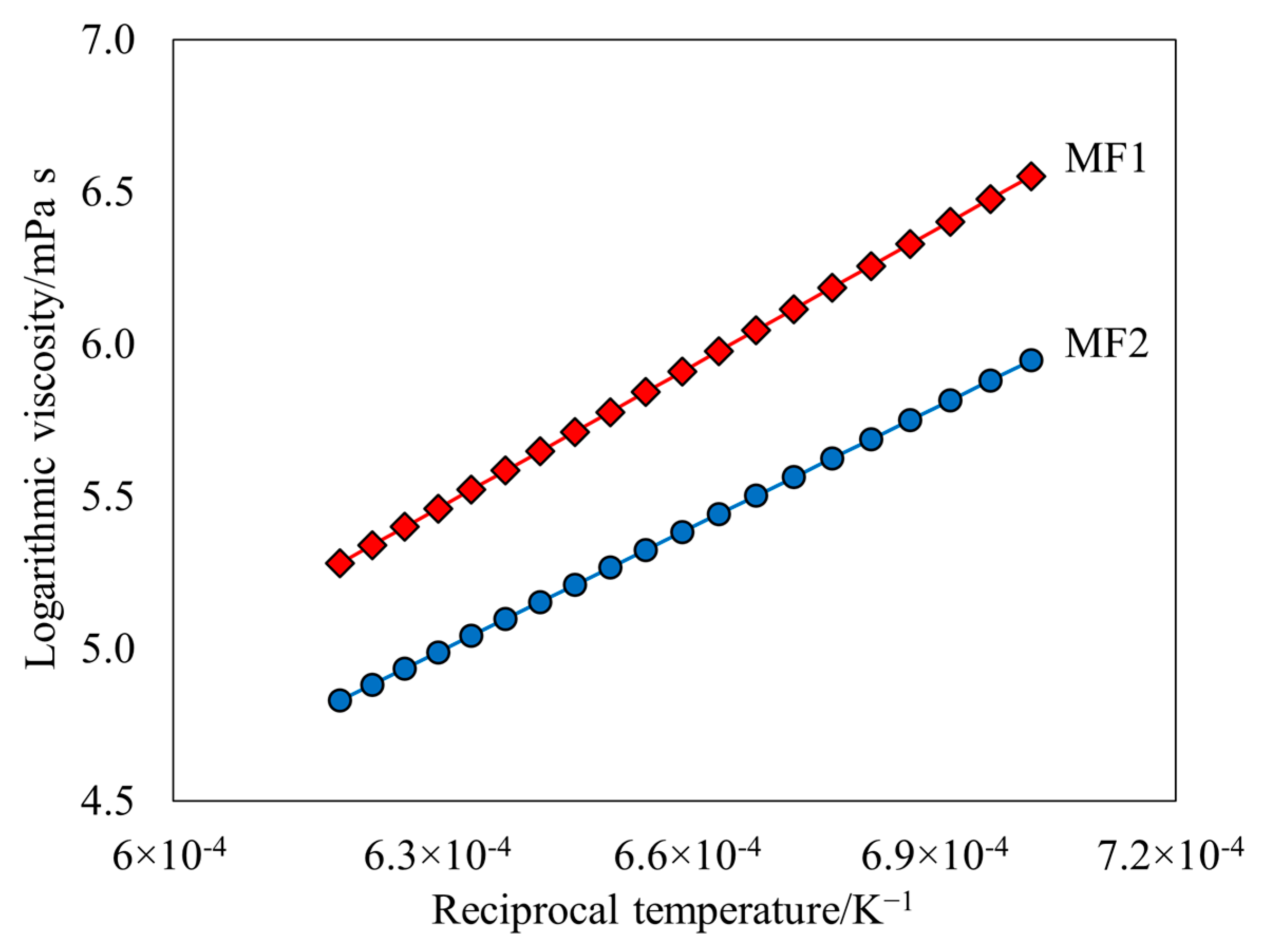
3.1. Viscosity, Structure, and Transition Temperatures
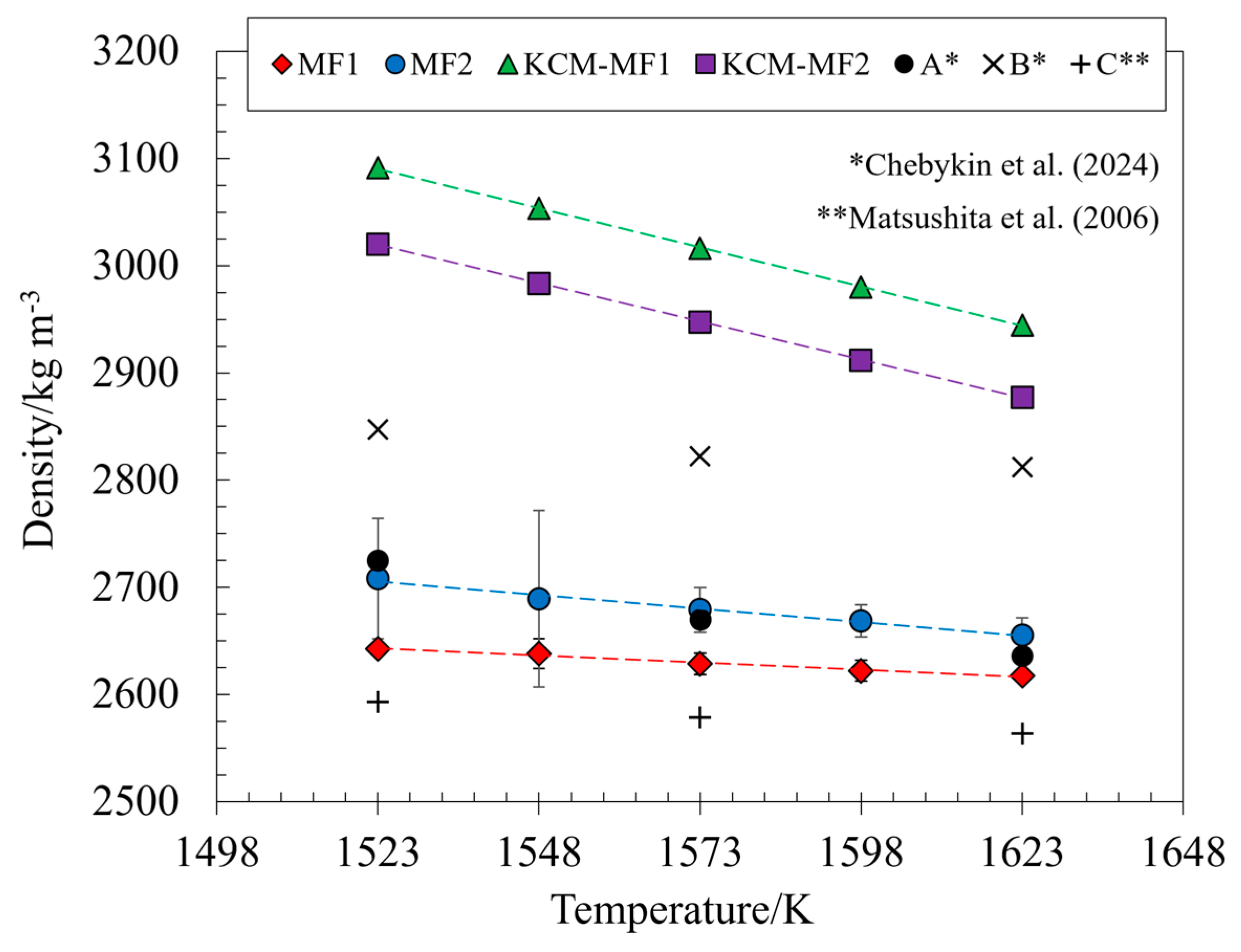
3.2. Density
3.3. Surface Tension
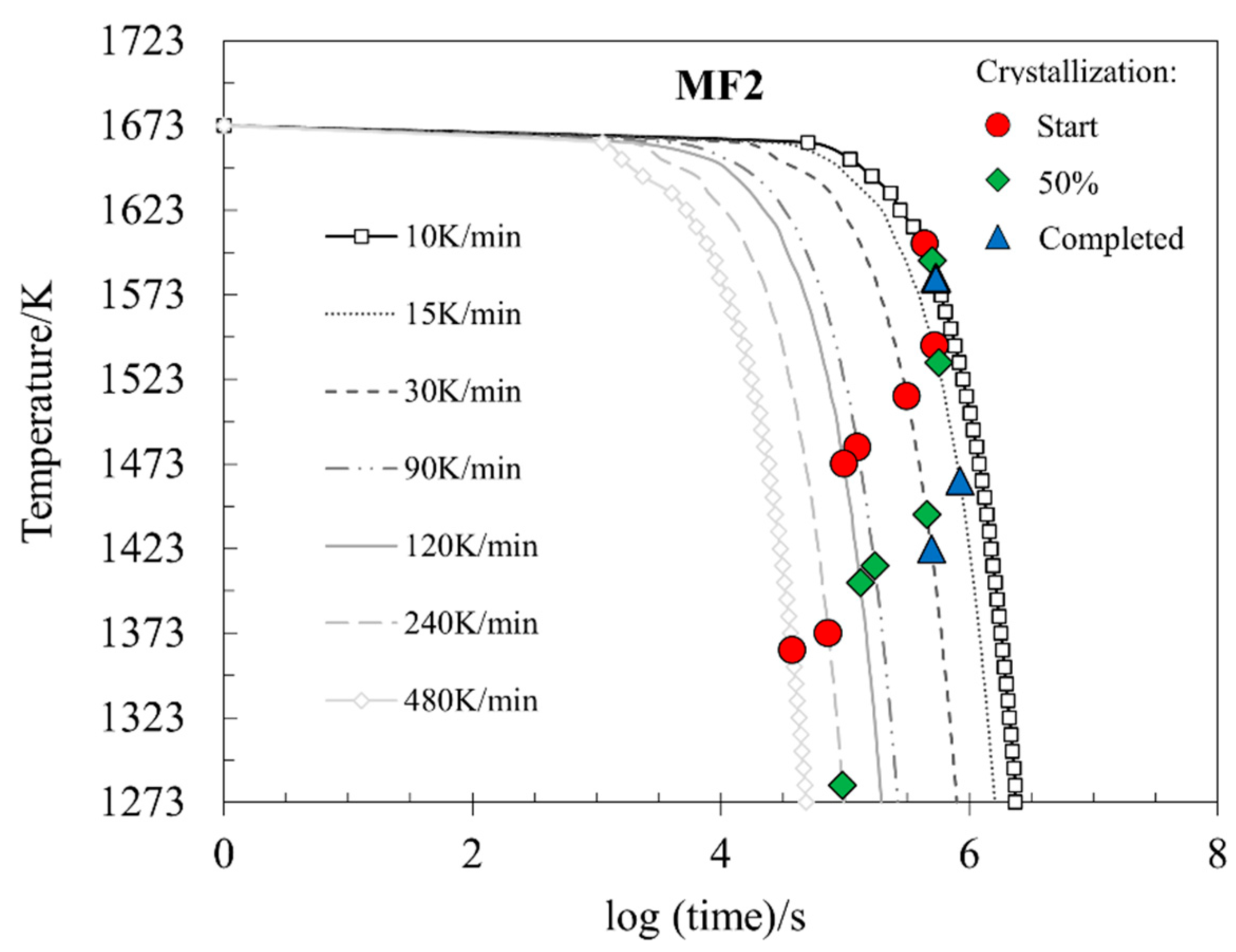
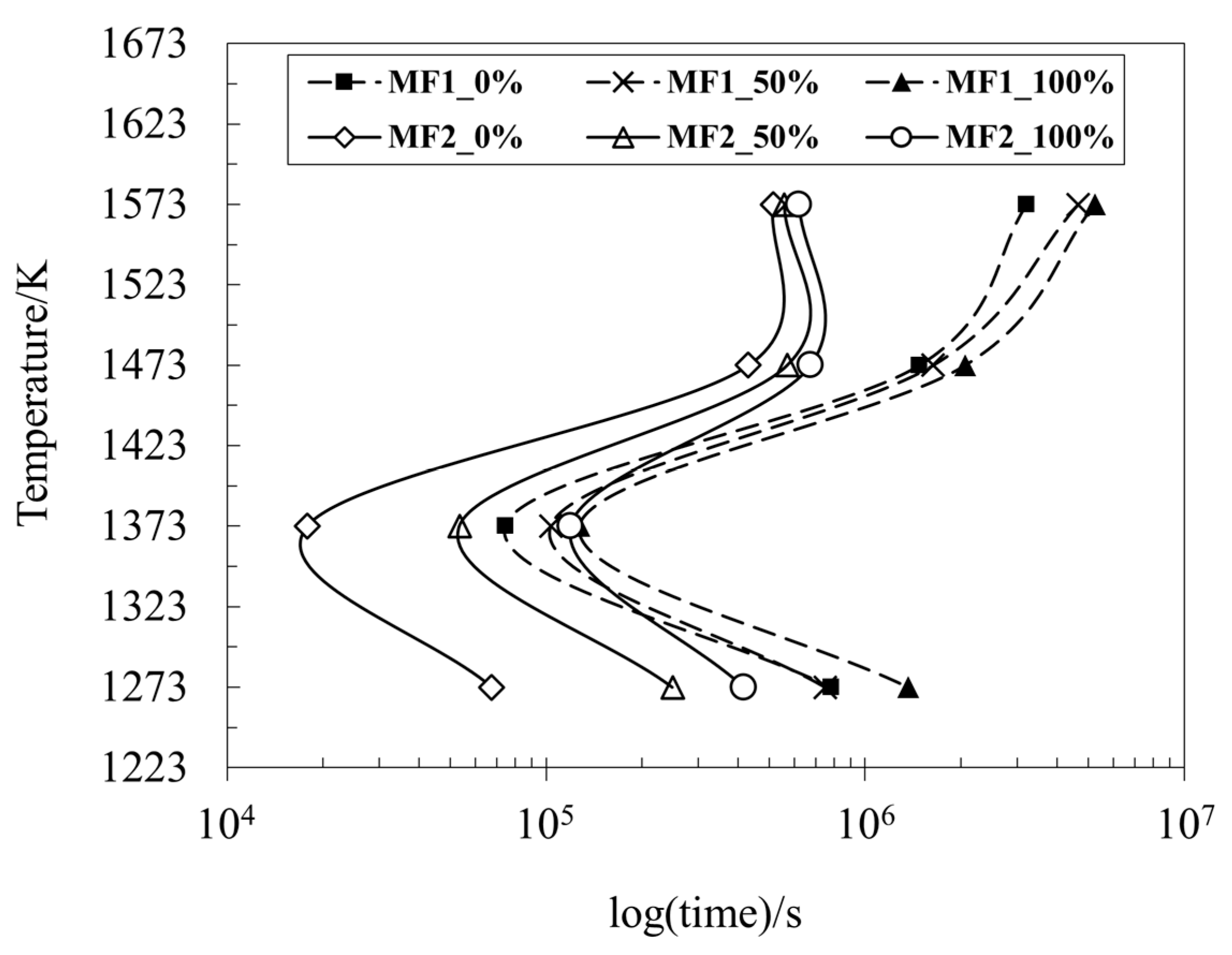
3.4. Crystallization Behavior
4. Conclusions
- The dynamic viscosity was successfully measured and showed that both samples present a breaking temperature. Tbr MF1 is higher than MF2, with values of 1439 K and 1425 K, respectively.
- Arrhenius equations for MF1 and MF2 are as follows:
- Arrhenius analysis indicated that MF1 has a higher Ea, 127.64 kJ mol−1 in comparison to 112.11 kJ mol−1 for MF2.
- The average density values for MF1 varied from 2642.35 ± 4.98 kg m−3 to 2617.56 ± 3.50 kg m−3, while for MF2 it varied from 2708.30 ± 56.06 kg m−3 to 2655.58 ± 16.07 kg m−3, between 1523 and 1623 K.
- The dependence of the density on temperature for the mold fluxes is as follows:
- The surface tension of the MF1 sample decreased from 299.40 ± 3.11 mN m−1 to 290.76 ± 2.11 mN m−1. Similarly, the surface tension of MF2 declined from 347.97 ± 3.37 mN m−1 to 304.81 ± 91.72 mN m−1.
- The dependence of the surface tension on temperature is:
- The SHTT results showed that the increase in the cooling rate was responsible for the decrease in the crystallization temperatures for all stages and in both samples.
- Both samples presented crystals; MF1 presented a longer incubation time than MF2 due to its higher content of glass-forming oxides, which resist crystallization.
- Complete glass formation is possible in the system MF1 at cooling rates above 21 K s−1 and in MF2 above 18 K s−1.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chebykin, D.; Heller, H.P.; Schulz, K.; Endo, R.; Volkova, O. Viscosity, Density, Surface Tension, and Crystallization Behavior of Commercial Mold Fluxes. Steel Res. Int. 2024, 96, 2400103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lu, B.; Xiao, D. A Review of Mold Flux Development for the Casting of High-Al Steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2016, 47, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.C.; Fox, A.B.; Li, Z.; Thackray, R.P. Performance and Properties of Mould Fluxes. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2005, 32, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.C. Structure and Properties of Slags Used in the Continuous Casting of Steel: Part 1 Conventional Mould Powders. ISIJ Int. 2016, 56, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandaleze, E.; Di Gresia, G.; Santini, L.; Martín, A.; Benavidez, E. Mould Fluxes in the Steel Continuous Casting Process. In Science and Technology of Casting Processes; Srinivasan, M., Ed.; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 205–233. [Google Scholar]
- Hibbeler, L.C.; Thomas, B.G. Investigation of Mold Flux Entrainment in CC Molds due to Shear Layer Instability; Association for Iron & Steel Technology: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, B.G. Modeling of the Continuous Casting of Steel-Past, Present, and Future. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2002, 33B, 795–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemann, R.; Heller, H.P.; Lachmann, S.; Seetharaman, S.; Scheller, P.R. Slag Entrainment in Continuous Casting and Effect of Interfacial Tension. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2012, 39, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemann, R.; Schwarze, R.; Heller, H.P.; Scheller, P.R. Model Investigations on the Stability of the Steel-Slag Interface in Continuous-Casting Process. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2013, 44, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Thackray, R.; Mills, K.C. A Test to Determine Crystallinity of Mould Fluxes. In Proceedings of the VII International Conference on Molten Slags, Fluxes and Salt, Cape Town, South Africa, 25–28 January 2004; The South African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2004; pp. 813–820. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, W.; Zhou, L.; Lu, B.; Kang, Y.B. Effects of MnO on Crystallization, Melting, and Heat Transfer of CaO-Al2O3-Based Mold Flux Used for High Al-TRIP Steel Casting. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2014, 45, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, G.L.; Liu, Y.C.; Yen, S.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Su, Y.H.; Lu, M.J.; Lin, S.K. Reactivity and Thermo-Physical Properties of MnO-Modified CaO-Al2O3-Based Mold Fluxes for Advanced High-Strength Steels. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 12091–12101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, W.; Zhou, K. Effect of Al2O3 on the Crystallization of Mold Flux for Casting High Al Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. E 2015, 2, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.C.; Bao, G.D.; Sadaf, S.; Mao, S.S.; Wu, T. Combing Role of MgO and Al2O3 on Viscosity and Its Correlation to Structure of Fluorine-Free Mold Fluxes. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B Metall. 2023, 59, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shao, H.; Zhou, L.; Luo, H.; Wu, H. Rheological Behavior of the CaO-Al2O3-Based Mold Fluxes with Different Na2O Contents. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 26880–26887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, H.P.; Schürmann, M.; Scholl, K.; Haustein, N.; Lychatz, B.; Falkus, J. Calibration Problems with the Viscosity Measurement of Liquid Metallurgical Slags. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 790, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebykin, D.; Heller, H.P.; Dubberstein, T.; Korobeinikov, I.; Volkova, O. Viscosity Measurement of Slags Using Rotating Bob and Vibrating Finger Viscometer. ISIJ Int. 2017, 57, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehorov, A.; Wei, X.; Bellé, M.R.; Volkova, O. Influence of SiO2-Adding on the Thermophysical Properties and Crystallization Behavior of Ladle Slags. Steel Res. Int. 2023, 95, 2300173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.d.R.; Vilela, A.C.F.; Heck, N.C.; Heller, H.P.; Volkova, O. Solidification Behavior of CaO–SiO2–Al2O3 Mold Fluxes Containing MgO and Low TiO2 Content Using Single Hot Thermocouple Technique (SHTT): Continuous-Cooling-Transformation (CCT) and Viscosity Analysis. Steel Res. Int. 2018, 89, 1700246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levchenko, M.; Kovtun, O.; Angelini, A.; Markus, H.P.; Sosin, D.; Endo, R.; Volkova, O. Effect of SiO2 and Al2O3 on the Thermophysical Properties and the Foaming Index of Electric Arc Interface Slag from the Production of Construction Steel. Steel Res. Int. 2024, 96, 2400476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellé, M.R.; Neubert, L.; Sherstneva, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Nishi, T.; Yamano, H.; Weinberg, M.; Volkova, O. Density, Surface Tension, and Viscosity of Liquid Low-Sulfur Manganese–Boron Steel via Maximum Bubble Pressure and Oscillating Crucible Methods. Steel Res. Int. 2024, 96, 2400252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubberstein, T.; Heller, H.P. The Thermophysical Properties of Liquid TRIP/TWIP-Steel Alloys Using the Maximum Bubble Pressure Method. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2013, 15, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klug, J.L.; Hagemann, R.; Heck, N.C.; Vilela, A.C.F.; Heller, H.P.; Scheller, P.R. Solidification Behaviour of Slags: The Single Hot Thermocouple Technique. J. Manuf. Sci. Prod. 2014, 13, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klug, J.L.; Hagemann, R.; Heck, N.C.; Vilela, A.C.F.; Heller, H.P.; Scheller, P.R. Fluorine-Free Mould Powders for Slab Casting: Crystallization Control in the CaO-SiO2-TiO2-Na2O-Al2O 3 System. Steel Res. Int. 2012, 83, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.d.R.; Heck, N.C.; Vilela, A.C.F.; Heller, H.P.; Volkova, O. Water-CaO-Al2O3 Join Interaction: Crystallization Behavior Investigation Using the Single Hot Thermocouple Technique (SHTT). Cryst. Res. Technol. 2022, 57, 2100003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbain, G. Viscosity Estimation of Slags. Steel Res. 1987, 58, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, M.; Görnerup, M.; Seetharaman, S. Viscosity Measurements of Some Mould Flux Slags. ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Mills, K.C.; Afrange, O.D.C.; Lörz, H.P.; Carli, R. Break Temperatures of Mould Fluxes and Their Relevance to Continuous Casting When Viscosity Measurements Are Carried out During. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2000, 27, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondratiev, A.; Ilyushechkin, A. Flow Behaviour of Crystallising Coal Ash Slags: Shear Viscosity, Non-Newtonian Flow and Temperature of Critical Viscosity. Fuel 2018, 224, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaf, S.; Wu, T.; Zhong, L.; Liao, Z.Y.; Wang, H.C. Effect of Basicity on the Structure, Viscosity and Crystallization of CaO-SiO2-B2O3 Based Mold Fluxes. Metals 2020, 10, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kromhout, J.A.; Schimmel, R.C. Understanding Mould Powders for High-Speed Casting. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2018, 45, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, T.M.; Cho, J.W.; Alloni, M.; Casagrande, S.; Carli, R. Structure and Its Effect on Viscosity of Fluorine-Free Mold Flux: Substituting CaF2 with B2O3 and Na2O. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2020, 529, 119756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, W.; Gao, M.; Du, S.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, J. Effect of CaO/SiO2 and Al2O3/SiO2 Mass Ratios on Structure and Viscosity of Mold Flux for Continuous Casting High-Mn High-Al Steel. Steel Res. Int. 2024, 96, 2400740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.C. The Influence Slags of Structure on the Physico-Chemical Properties of. ISIJ Int. 1993, 33, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.C.; Karagadde, S.; Lee, P.D.; Yuan, L.; Shahbazian, F. Calculation of Physical Properties for Use in Models of Continuous Casting Process-Part 1: Mould Slags. ISIJ Int. 2016, 56, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Paradis, P.-F.; Mukai, K.; Seetharaman, S. Density Measurements of Mould Flux Slags by Electrostatic Levitation Method. ISIJ 2006, 46, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.C.; Keene, B.J. Physical Properties of BOS Slags. Int. Mater. Rev. 1987, 32, 1–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Q. A Density Estimation Model for Molten Silicate Slags. High Temp. Mater. Process. 2007, 26, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mills, K.C. Estimation of Physicochemical Properties of Coal Slags and Ashes. In ACS Symposium Series: Mineral Matter and Ash in Coal; Vorres, K.S., Ed.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1986; pp. 195–214. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.; Min, Y.; Jiang, M. The Temperature and Structure Dependence of Surface Tension of CaO-SiO2-Na2O-CaF2 Mold Fluxes. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2018, 49, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, M.; Tanaka, T.; Holappa, L.; Hämäläinen, M. Surface Tension Evaluation of Molten Silicates Containing Surface-Active Components (B2O3, CaF2 or Na2O). ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutale, C.T.; Claudon, T.; Cramb, A.W. Observation of the Crystallization Behavior of a Slag Containing 46 Wt Pct CaO, 46 Wt Pct SiO2, 6 Wt Pct Al2O3, and 2 Wt Pct Na2O Using the Double Hot Thermocouple Technique. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2005, 36, 417–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Network Formers | SiO2 | 17–56 | Alkalis | Na2O | 0–25 |
| Al2O3 | 0–13 | Li2O | 0–5 | ||
| B2O3 | 0–19 | K2O | 0–2 | ||
| Fe2O3 | 0–6 | Fluidizing | F MnO | 2–15 0–5 | |
| Network Modifiers | CaO | 22–45 | |||
| MgO | 0–10 | ||||
| BaO | 0–10 | Melting control | C | 2–20 | |
| SrO | 0–5 |
| Flux Components | As-Received Granules (~1 mm) | After Pre-Melting | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MF1 | MF2 | MF1 | MF2 | |
| CaO | 32.91 | 31.74 | 38.77 | 40.89 |
| SiO2 | 32.34 | 32.68 | 34.72 | 36.30 |
| Fe2O3 | 1.81 | 0.99 | 1.61 | 0.93 |
| MgO | 1.47 | 1.88 | 1.53 | 2.07 |
| Al2O3 | 6.79 | 3.76 | 7.07 | 4.33 |
| MnO | 2.71 | 0.16 | 2.38 | 0.09 |
| TiO2 | 0.16 | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.19 |
| K2O | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.16 |
| Na2O | 5.54 | 3.76 | 7.81 | 8.53 |
| P2O5 | 0.44 | 0.48 | 0.07 | 0.05 |
| CaF2 | 6.79 | 8.93 | 5.64 | 6.11 |
| C | 8.59 | 14.34 | 0.03 | 0.14 |
| S | 0.16 | 0.71 | 0.14 | 0.19 |
| Zn | 0.11 | 0.12 | - | - |
| CaO/SiO2 | 1.02 | 0.97 | 1.12 | 1.13 |
| Sample | SiO2 | CaO | MgO | Al2O3 | Na2O | F | LiO2 | B2O3 | Bal. | CaO/SiO2 | η1573 K/mPa s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A [1] | 33.76 | 42.18 | 2.2 | 3.43 | 9.09 | 9.11 | 0.33 | - | 0.6 | 1.25 | 123 |
| B [1] | 41.03 | 36.94 | 5.63 | 4.57 | 4.88 | 5.71 | - | - | 2.71 | 0.90 | 500 |
| F1 [30] | 36.74 | 42.26 | 2 | 4 | 8 | - | 1 | 6 | - | 1.15 | 171 |
| F3 [30] | 33.62 | 45.38 | 2 | 4 | 8 | - | 1 | 6 | - | 1.35 | 280 |
| I [31] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.80 | 160 |
| II [31] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.85 | 140 |
| A [32] | 34.93 | 31.8 | 2.53 | 3.58 | - | 15.74 | - | - | 11.42 | 1.23 | 620 |
| B [32] | 31.49 | 30.68 | 2.57 | 3.3 | 1.67 | 10.77 | - | 4.49 | 15.03 | 1.22 | 490 |
| C [32] | 26.99 | 30.32 | 2.26 | 3.46 | 3.4 | 4.71 | - | 9.02 | 19.84 | 1.25 | 770 |
| D [32] | 22.97 | 29.03 | 2.13 | 3.48 | 4.79 | - | - | 13.54 | 24.06 | 1.26 | 770 |
| Vr-1 [33] | 49.22 | 25.81 | 1.35 | 2.47 | 8.33 | 8.24 | 4.58 | - | - | 0.52 | 227 |
| Vr-2 [33] | 46.29 | 28.45 | 1.26 | 2.46 | 9.25 | 7.93 | 4.36 | - | - | 0.61 | 169 |
| Vr-3 [33] | 42.54 | 30.33 | 1.54 | 2.42 | 9.54 | 8.96 | 4.67 | - | - | 0.71 | 125 |
| Vr-4 [33] | 40.49 | 33.45 | 1.14 | 2.28 | 9.39 | 8.35 | 4.90 | - | - | 0.83 | 81 |
| Vr-5 [33] | 35.85 | 36.69 | 1.42 | 2.53 | 9.93 | 8.65 | 4.98 | - | - | 1.02 | 71 |
| AS-1 [33] | 49.22 | 25.81 | 1.35 | 2.47 | 8.33 | 8.24 | 4.58 | - | - | 0.52 | 227 |
| AS-2 [33] | 40.95 | 24.35 | 1.32 | 10.02 | 9.65 | 8.49 | 5.22 | - | - | 0.59 | 98 |
| AS-3 [33] | 33.95 | 23.89 | 1.58 | 16.56 | 9.95 | 9.25 | 4.82 | - | - | 0.70 | 132 |
| AS-4 [33] | 29.13 | 24.58 | 1.18 | 22.32 | 9.55 | 8.65 | 4.59 | - | - | 0.84 | 177 |
| AS-5 [33] | 26.11 | 23.67 | 1.19 | 26.31 | 9.34 | 8.61 | 4.77 | - | - | 0.91 | 229 |
| MF1 | 34.72 | 38.77 | 1.53 | 7.07 | 7.81 | 5.64 | - | - | 4.24 | 1.12 | 251 |
| MF2 | 36.30 | 40.89 | 2.07 | 4.33 | 8.53 | 6.11 | - | - | 1.75 | 1.13 | 159 |
| Sample | Arrhenius Equation | Ea/kJ mol−1 | A/mPa s |
|---|---|---|---|
| MF1 | 127.72 | 0.0144 | |
| MF2 | 112.11 | 0.0294 |
| Sample | CaO | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | MgO | Al2O3 | MnO | P2O5 | TiO2 | K2O | Na2O | CaF2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MF1 | 36.11 | 35.49 | 1.99 | 1.61 | 7.45 | 2.98 | 0.48 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 6.08 | 7.45 |
| MF2 | 37.42 | 38.53 | 1.16 | 2.22 | 4.43 | 0.19 | 0.57 | 0.29 | 0.22 | 4.43 | 10.53 |
| MF1 * | 38.77 | 34.77 | 1.61 | 1.53 | 7.08 | 2.38 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 7.82 | 5.65 |
| MF2 * | 41.03 | 36.43 | 0.93 | 2.08 | 4.35 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 8.56 | 6.13 |
| Sample | Basicity (CaO/SiO2) | (Λcorr) | NBO/T | Q | (%cryst.) | Tliq | Tbr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| as-received granules | MF1 | 1.02 | 0.6759 | 1.75 | 2.25 | 0 | 1450 | 1384 |
| MF2 | 0.97 | 0.6664 | 2.05 | 1.95 | 4.7 | 1477 | 1409 | |
| after pre-melting | MF1 | 1.12 | 0.6727 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1440 | 1428 |
| MF2 | 1.13 | 0.6976 | 2.4 | 1.6 | 55 | 1436 | 1470 | |
| T/K | MF1 | MF2 | KCM-MF1 [37] | KCM-MF2 [37] | A [1] | B [1] | C [36] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1523 | 2642.35 ± 4.98 | 2708.30 ± 56.06 | 3091.35 | 3020.19 | 2725 | 2847 | 2593 |
| 1548 | 2638.26 ± 13.95 | 2689.25 ± 82.42 | 3053.34 | 2983.18 | - | - | - |
| 1573 | 2628.61 ± 9.89 | 2679.03 ± 20.65 | 3016.25 | 2947.08 | 2670 | 2822 | 2578 |
| 1598 | 2622.18 ± 9.90 | 2668.62 ± 15.14 | 2980.05 | 2911.83 | - | - | - |
| 1623 | 2617.56 ± 3.50 | 2655.58 ± 16.07 | 2944.70 | 2877.42 | 2636 | 2812 | 2563 |
| T/K | MF1 | MF2 | KCM-MF1 | KCM-MF2 | A [1] | B [1] | 1 [40] | 2 [40] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1523 | 299.40 ± 3.11 | 347.97 ± 3.37 | 288.68 | 277.90 | 445.6 | 524.7 | - | - |
| 1548 | 297.29 ± 1.17 | 329.80 ± 20.12 | 287.37 | 276.72 | - | - | - | - |
| 1573 | 295.16 ± 1.48 | 320.43 ± 10.23 | 286.07 | 275.55 | 434.8 | 549 | - | - |
| 1598 | 293.32 ± 2.18 | 319.24 ± 21.41 | 284.76 | 274.37 | - | - | - | - |
| 1623 | 290.76 ± 2.11 | 304.81 ± 32.57 | 283.45 | 273.20 | 437.9 | 522.4 | 417 | 448 |
| Cooling Rates (K min−1) | 10 | 15 | 30 | 90 | 120 | 240 | 480 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystallization Temperatures (K) | MF1 | Start | 1240 | 1200 | 1100 | 1090 | 1060 | 1050 | 1030 |
| 50% | 1100 | 1090 | 1050 | 1040 | 1020 | 1010 | - | ||
| Completed | 1070 | 1040 | 1030 | 1030 | 1010 | - | - | ||
| MF2 | Start | 1330 | 1270 | 1240 | 1210 | 1200 | 1100 | 1090 | |
| 50% | 1320 | 1260 | 1170 | 1140 | 1130 | 1010 | - | ||
| Completed | 1310 | 1190 | 1150 | - | - | - | - | ||
| Sample | Basicity (CaO/SiO2) | NBO/T | Glass Formers | Crystalline Formers | Nucleating Agents | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| as-received granules | MF1 | 1.02 | 1.75 | 48.38 | 51.45 | 0.17 |
| MF2 | 0.97 | 2.05 | 44.89 | 54.82 | 0.29 | |
| after pre-melting | MF1 | 1.12 | 2 | 45.91 | 53.96 | 0.12 |
| MF2 | 1.13 | 2.4 | 41.85 | 57.96 | 0.19 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bellé, M.R.; Yehorov, A.; Chebykin, D.; Zotov, D.; Volkova, O. Characterization of Thermophysical Properties and Crystallization Behavior of Industrial Mold Fluxes. Metals 2025, 15, 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070715
Bellé MR, Yehorov A, Chebykin D, Zotov D, Volkova O. Characterization of Thermophysical Properties and Crystallization Behavior of Industrial Mold Fluxes. Metals. 2025; 15(7):715. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070715
Chicago/Turabian StyleBellé, Matheus Roberto, Anton Yehorov, Dmitry Chebykin, Dmytro Zotov, and Olena Volkova. 2025. "Characterization of Thermophysical Properties and Crystallization Behavior of Industrial Mold Fluxes" Metals 15, no. 7: 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070715
APA StyleBellé, M. R., Yehorov, A., Chebykin, D., Zotov, D., & Volkova, O. (2025). Characterization of Thermophysical Properties and Crystallization Behavior of Industrial Mold Fluxes. Metals, 15(7), 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070715







