Optimization of Deposition Parameters for Ni-P-WC-BN(h) Composite Coatings via Orthogonal Experimentation and Wear Behavior of the Optimized Coating
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
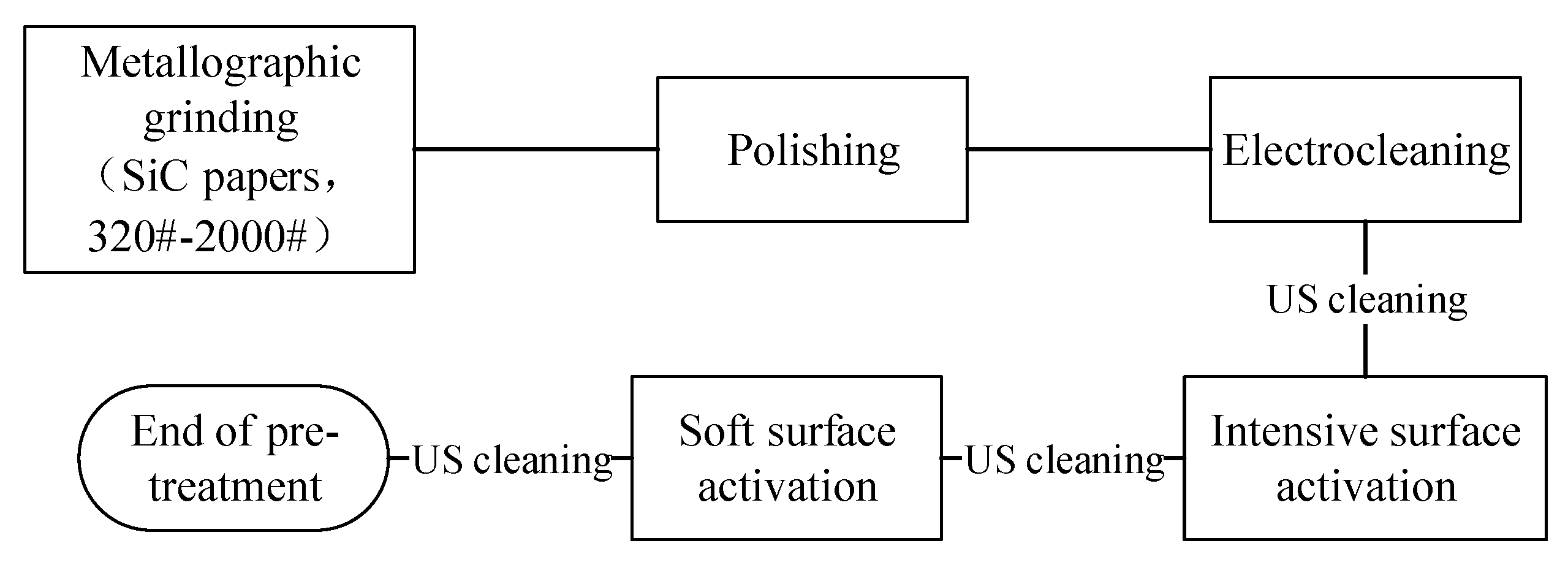
2.1. Preparation of Coating
2.2. Characterization of Coating Properties
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization Design
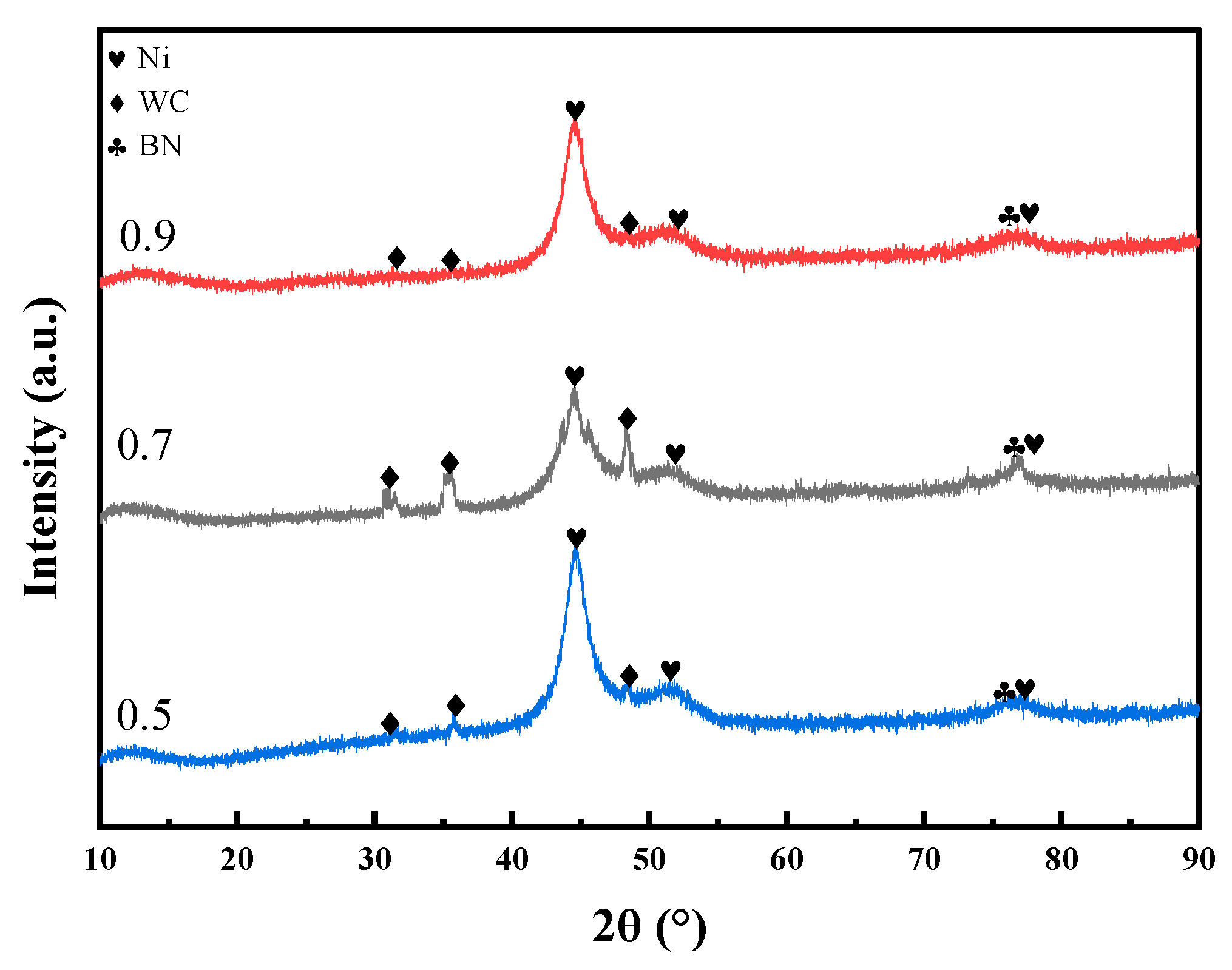
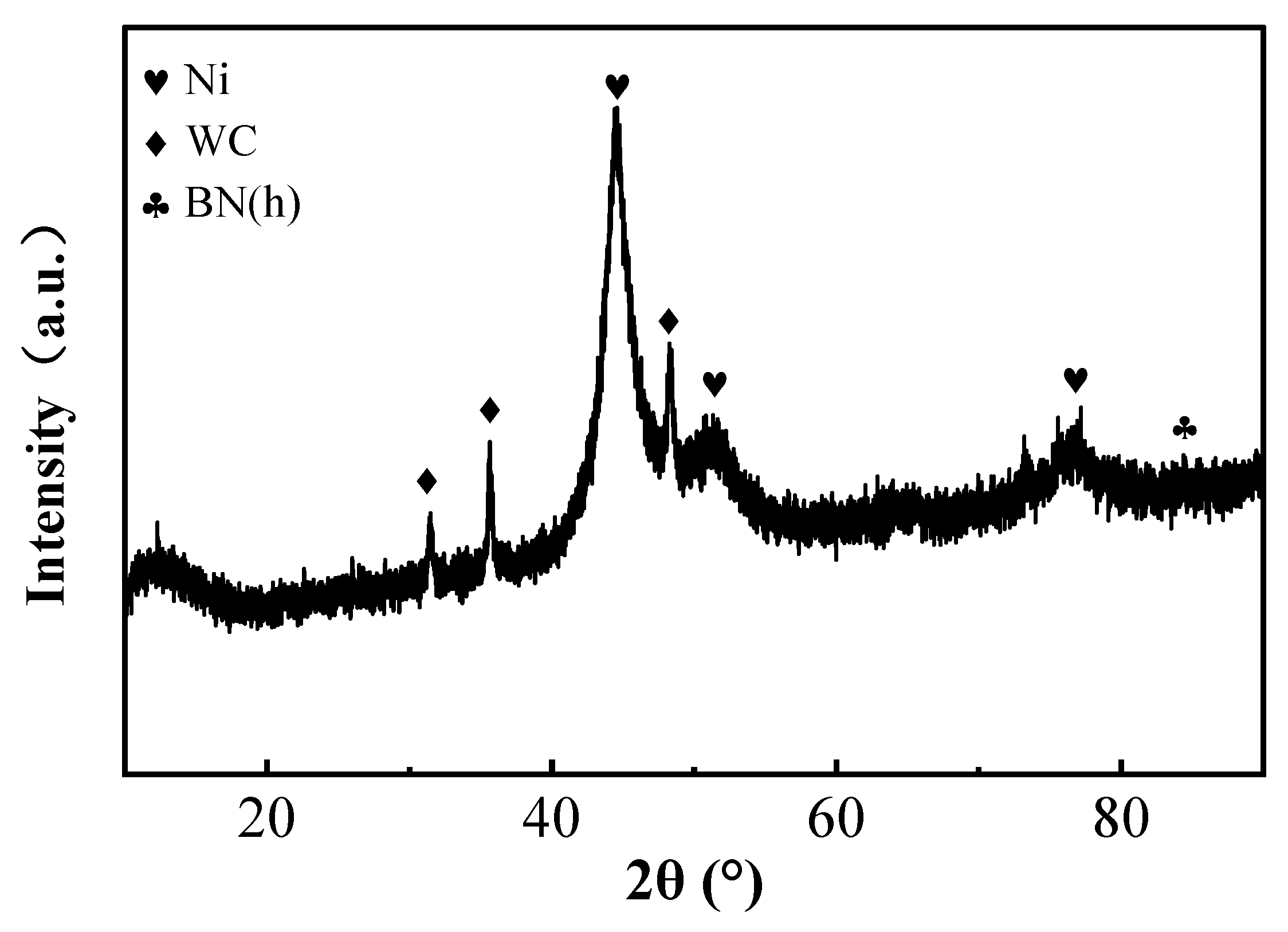
3.2. XRD Analysis
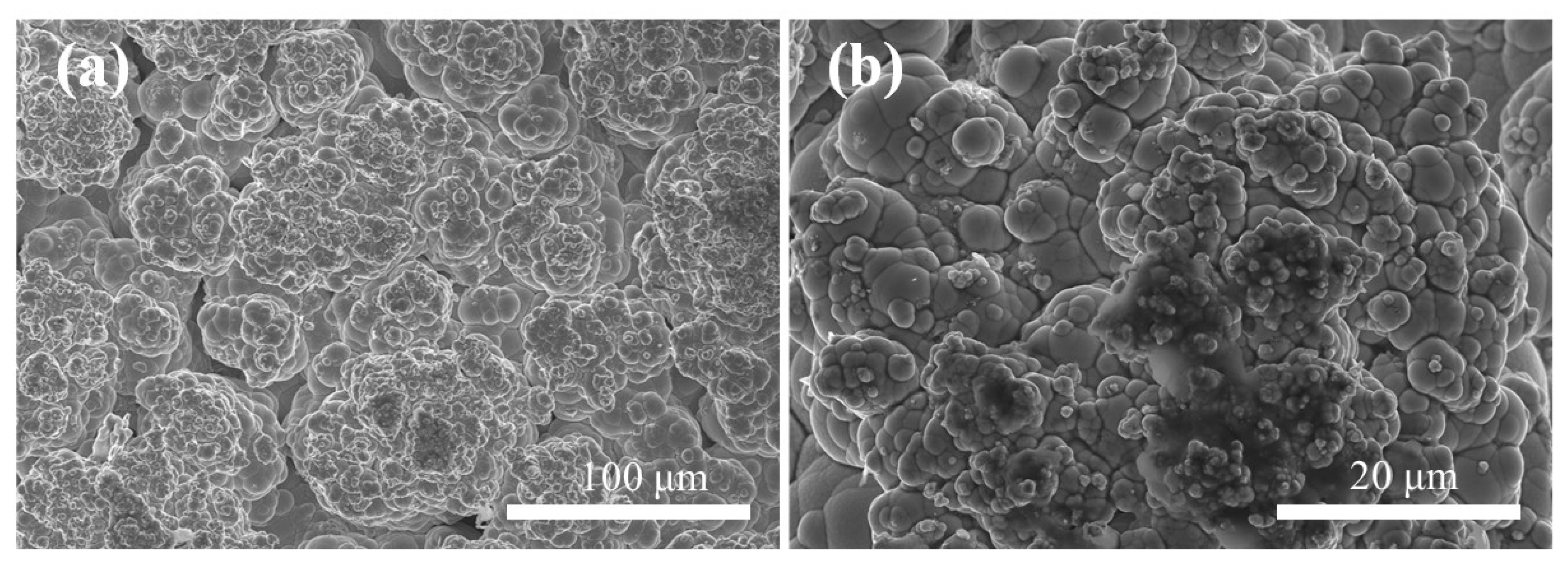
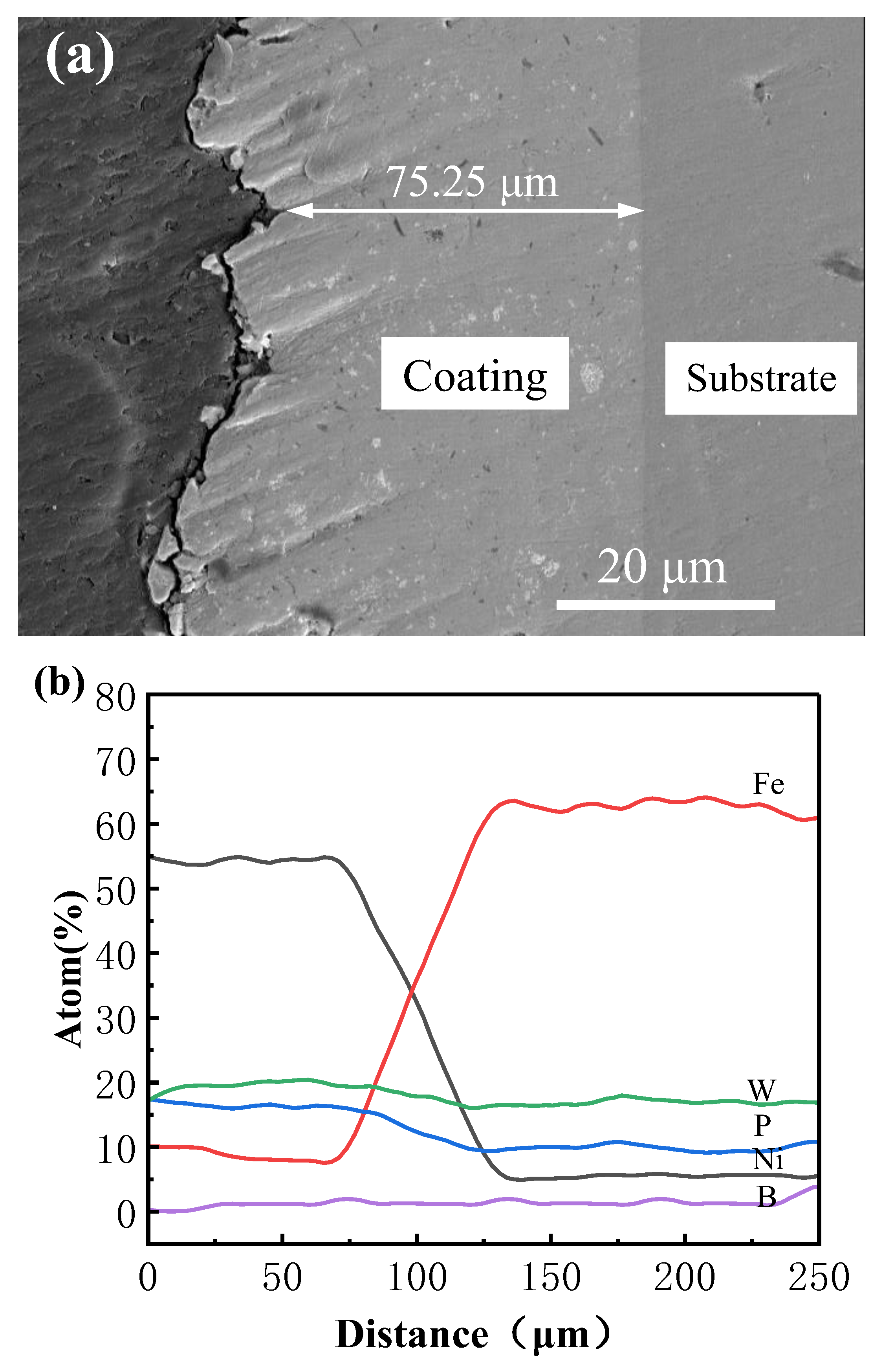
3.3. Surface and Cross-Sectional Morphology
3.4. Microhardness
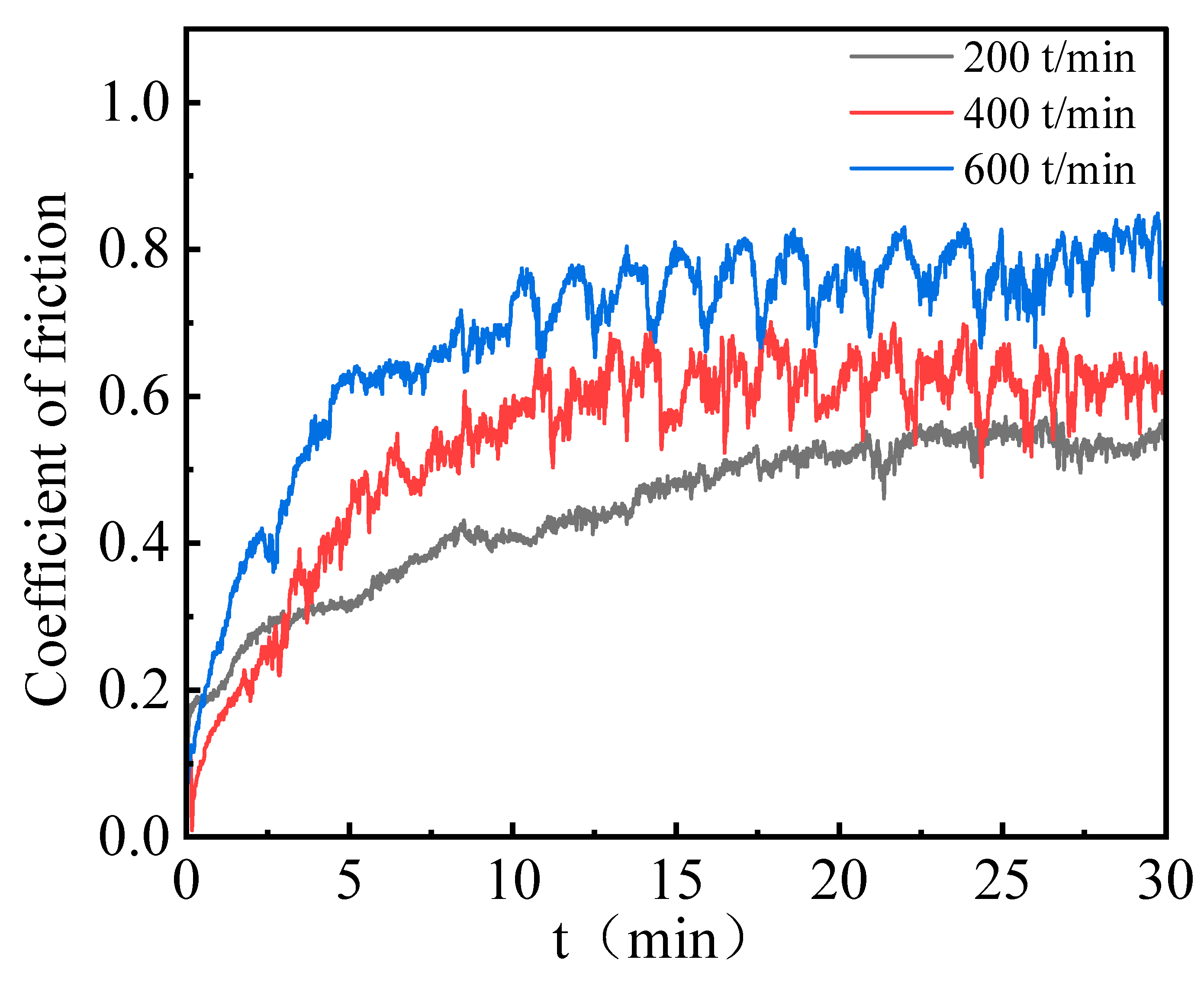
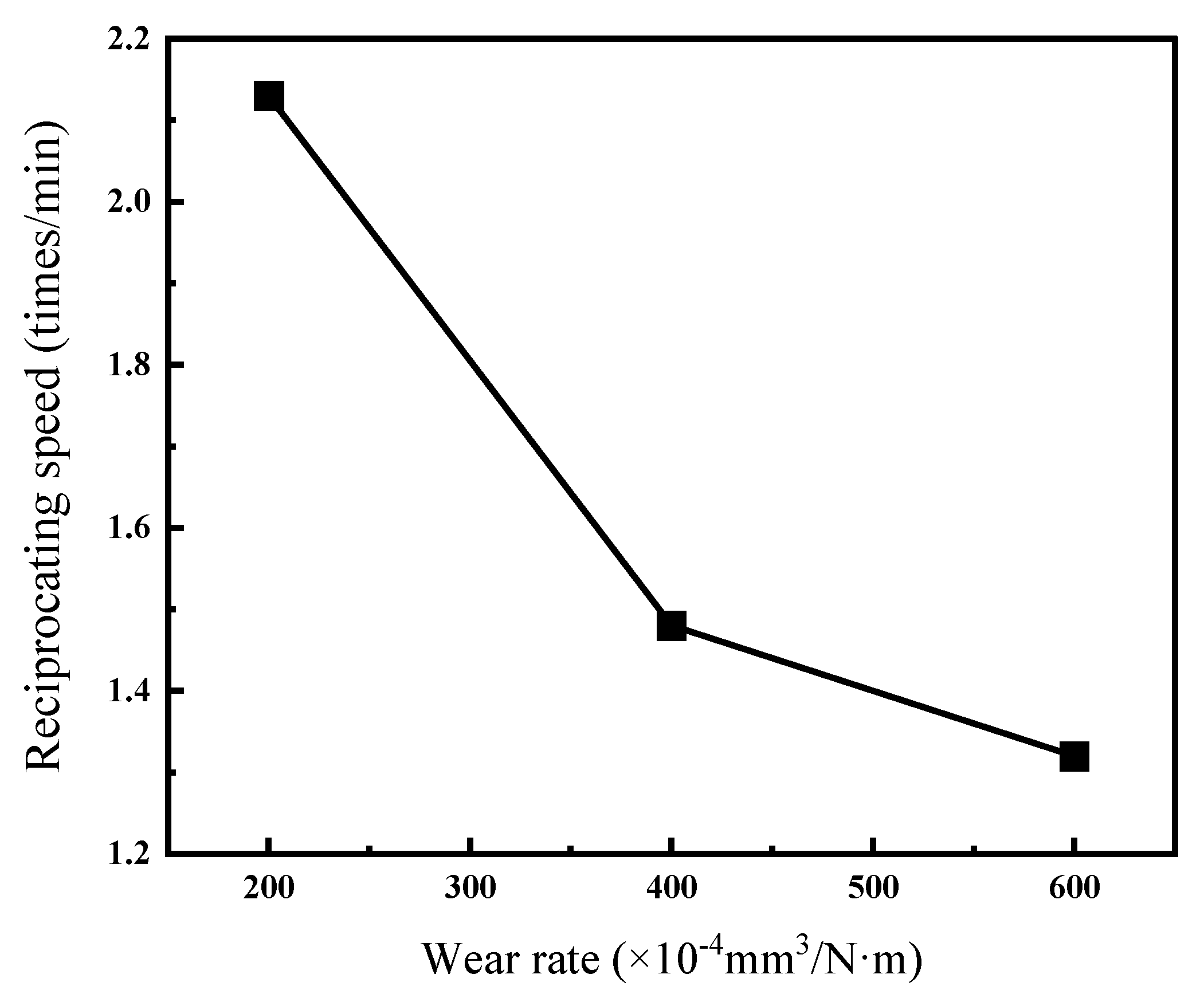
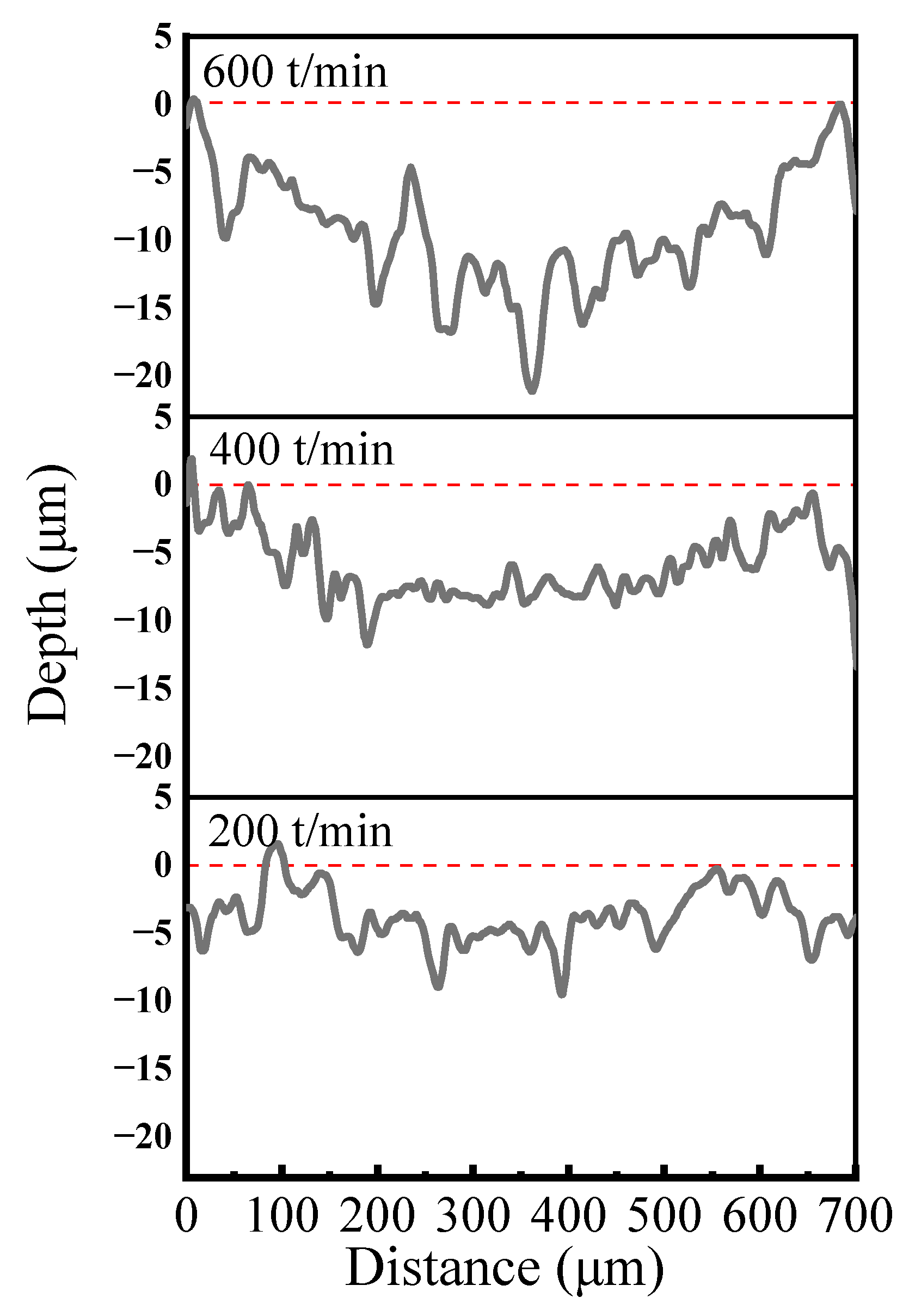
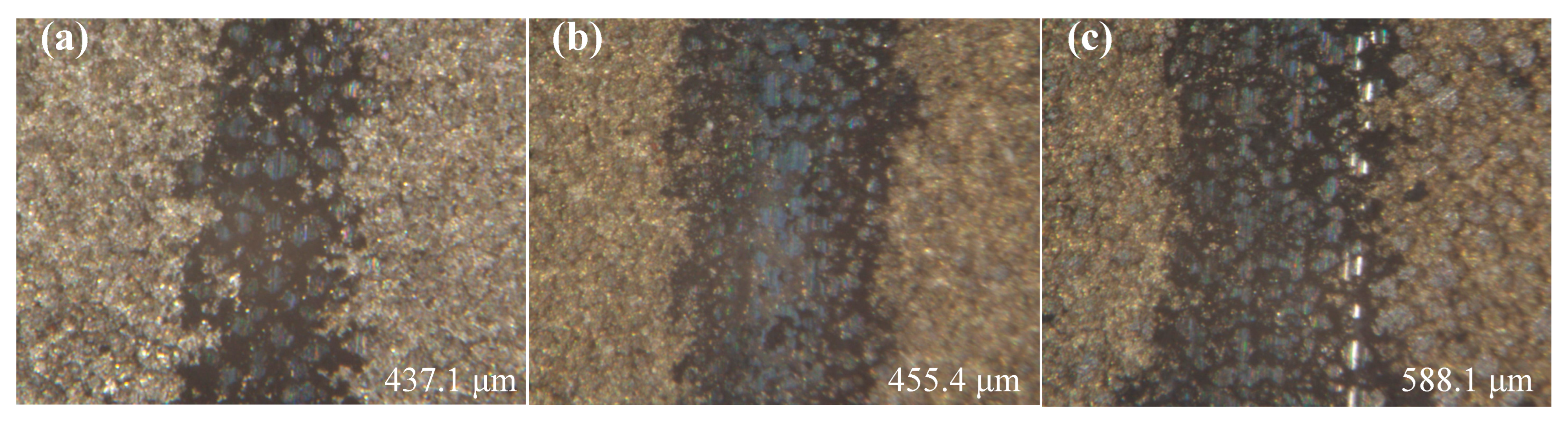
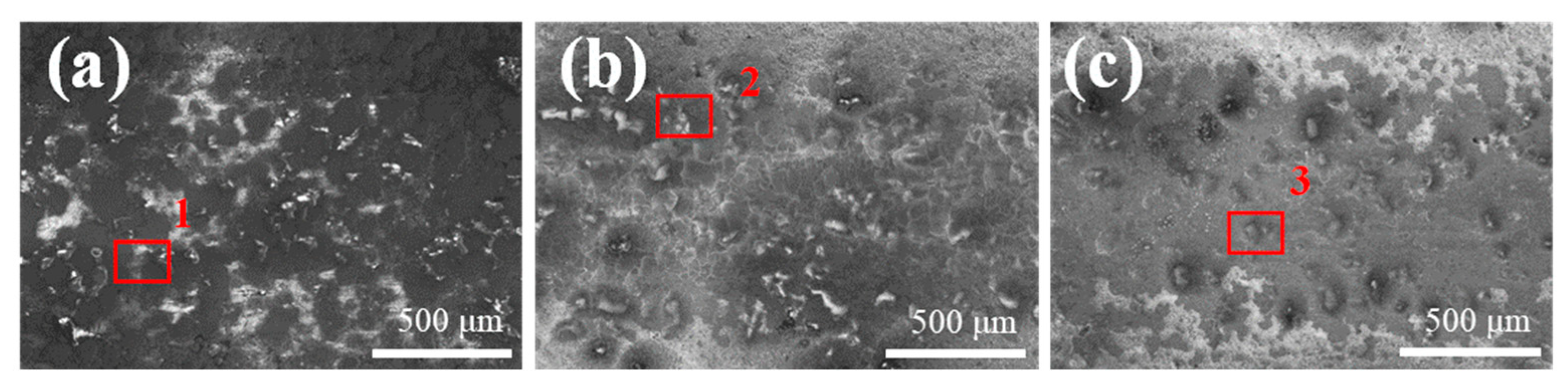
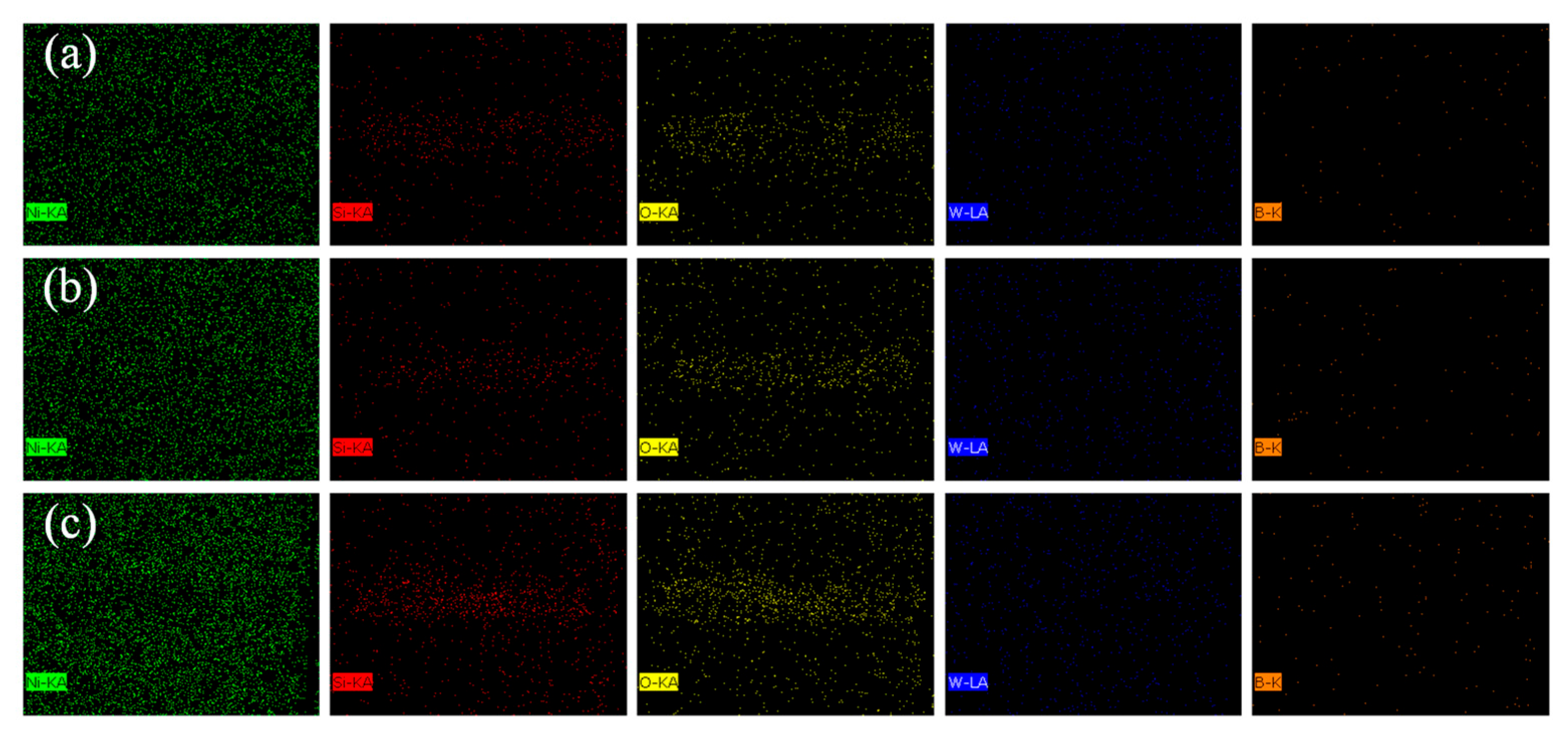
3.5. Wear Behavior
4. Conclusions
- Range analysis and ANOVA results showed that the influence of the four parameters on microhardness followed the order: current density (A) > duty cycle (D) > ultrasonic power (C) > temperature (B). The optimal parameter combination was determined to be A3B3C1D2, corresponding to a current density of 3 A·dm−2, a bath temperature of 55 °C, an ultrasonic power of 210 W, and a pulse duty cycle of 0.7. Under these conditions, the coating exhibited improved deposition quality, structural uniformity, and overall performance.
- The microhardness of the Ni–P–WC–BN(h) coating prepared under the optimal parameters reached 1244.3 HV1, which is approximately twice that of the 20CrMnTi substrate, indicating a significant improvement in mechanical strength.
- Tribological performance tests were conducted under a constant friction load of 320 g at reciprocating speeds of 200, 400, and 600 times/min. With increasing reciprocating speed, the COF increased, and the concentrations of O and Si elements in the wear track region also rose, indicating intensified oxidative processes. These results suggest that the predominant wear mechanisms involve abrasive wear, oxidative wear, and adhesive wear.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, H.; Guo, Q.; Wang, C.; Cao, G.; Liu, Y. Preparation and performance of PANI/CNTs composite coating on 316 stainless steel bipolar plates by pulsed electrodeposition. Prog. Org. Coat. 2023, 182, 107611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.Z. Study on the Performances of Ni-Co-P/BN(h)Nanocomposite Coatings Made by Jet Electro-deposition. Procedia CIRP 2018, 68, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Jin, S.; Wu, R.; Ma, X.; Pang, M.; Yu, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Krit, B.; Betsofen, S.; et al. Enhancing tribological performance of micro-arc oxidation coatings on Mg-Li alloy with h-BN incorporation. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 13760–13771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kul, M.; Oskay, K.O.; Erden, F.; Akça, E.; Katırcı, R.; Köksaı, E.; Akıncı, E. Effect of Process Parameters on the Electrodeposition of Zinc on 1010 Steel: Central Composite Design Optimization. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 9779–9795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xia, W.; Li, B.; Li, M.; Hong, M.; Zhang, Z. Influences of Co and process parameters on structure and corrosion properties of nanocrystalline Ni-W-Co ternary alloy film fabricated by electrodeposition at low current density. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 439, 128457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.N.; Wu, M.H.; Li, Z. Optimization of Process Parameters of Ni-TiN-CeO2 Binary Nanocomposite Coatings by Ul-trasound-pulse Electrodeposition. In Advanced Materials and Process Technology, PTS 1–3, Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ADME 2012), Taiyuan, China, 16–18 August 2012; Liu, X., Bai, Z., Shuang, Y., Zhou, C., Shao, J., Eds.; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Wollerau, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.-Q.; Chi, G.-X.; Wei, D.-B.; DI, S.-C. Influence of processing parameters on coating surface roughness of aluminum alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2009, 19, s392–s397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Dai, L.; Yin, Y.; Xu, Z.; Lv, Y.; Liao, Z.; Wei, G.; Zhong, F.; Yuan, M. Electrodeposition and wear behavior of NiCoW ternary alloy coatings reinforced by Al2O3 nanoparticles: Influence of current density and electrolyte composition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 431, 128030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barut, U.; Karslioglu, R. Influence of current type on tribological and corrosion properties of nickel boron coatings produced by electrodeposition. Met. Mater. 2019, 57, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, I.K.; Azam, M.U.; Lawal, D.U.; Samad, M.A. Optimization of SiC Concentration and Process Parameters for a Wear-Resistant UHMWPE Nancocomposite. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 45, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, T.V.; Dobrocký, D.; Pokorny, Z.; Kusmic, D.; Nguyen, V.T. Effect Of Plasma Nitriding On Mechanical And Tribological Properties of 42CrMo4 Steel. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Advanced Batteries, Accumulators and Fuel Cells (ABAF 2016), Brno, Czech Republic, 28–31 August 2016; pp. 231–238. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S.; Xu, K.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Y. A novel electrochemical deposited Fe Ni coating designed by laser-induced periodic current density: Effect of microstructure on microhardness and wear resistance improvement. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 468, 129785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Mao, Q.; Nie, J.; Zhao, Y. Electrodeposition of nanocrystalline Ni and NiCr alloy coatings: Effects of Cr content on microhardness and wear resistance improvement. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 3584–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, M. Effect of current density on properties of Ni–P-Al2O3-PTFE nanocomposite coatings by jet electrodeposition. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 125, 5743–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zuo, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, J.; Xiong, J. The effects of electrodeposition current density on properties of Ni–CNTs composite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 3246–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, K.; Li, F.; Liu, J.; Cao, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, B. Preparation and mechanism of Cu-GO laminated composite films with high thermal conductivity by intermediate nickel and silver layers via electrodeposition and ultrasonic spraying method. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 472, 129960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, B. Influence of Electrodeposition Conditions on the Microstructure and Hardness of Ni-B/SiC Nanocom-posite Coatings. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 3486–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.K.; Urumarudappa, S.K.J.; Kamal, S.; Widiadita, Y.; Mahamud, A.; Saito, T.I.; Bovornratanaraks, T. Effect of Pulse Electrodeposition Parameters on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ni–W/B Nanocomposite Coatings. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Fan, M.; Lu, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Q. Preparation and investigation of pulse co-deposited duplex nanoparticles reinforced Ni-Mo coatings under different electrodeposition parameters. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 29629–29640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Yoo, H.J. Formation of bilayer Ni–SiC composite coatings by electrodeposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1998, 108–109, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Perepezko, J. Al-based amorphous alloys: Glass-forming ability, crystallization behavior and effects of minor alloying additions. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 707, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Payne, B.P.; Grosvenor, A.P.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R.; Smart, R.S.C. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2717–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Peng, X.; Qin, Y.; Feng, J.; Wang, Z. Quantifying adhesion energy of mechanical coatings at atomistic scale. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 258, 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wang, S.; Shan, W.; Li, Z. Effect of the Pulse Duty Cycle on the Microstructure and Properties of a Jet Electrodeposited Nanocrystalline Copper Coating. Mater. Trans. 2020, 61, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, S.K.; Srivastava, A.K.; Pant, R.P.; Halder, S.K.; Singh, B.P.; Gupta, A.K. Synthesis of boron nitride nanotubes employing mechanothermal process and its characterization. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 5243–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, S.K.; Srivastava, A.K.; Mathur, R.B. Growth of Boron Nitride Nanotubes Having Large Surface Area Using Mechanothermal Process. World J. Nano Sci. Eng. 2011, 01, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ren, A.; Kang, M.; Fu, X.; Zhang, F.; Yang, W.; Pan, T. Preparation of Ni–B composite coating doped with hydrothermally modified synthetic WC@MoS2 powders via ultrasonic-assisted jet electrodeposition for corrosion protection. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 44, 103674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Pei, Z.; Song, G.; Liu, Z.; Gu, W.; Gong, J. Wear resistance of electro-brush plated Ni/diamond nanocomposite coatings. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2025, 153, 111992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liang, B.; Gao, Y.; Zou, J.; Hua, R.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Q. Pulse electrodeposition of a duplex-layer structured composite nickel-based coating with improved corrosion and abrasion resistance. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 10515–10524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.-C.; Cheng, C.-H. Preparation and tribocorrosion behavior of electrodeposited Ni–W/SiC composite coatings. Wear 2024, 558–559, 205571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; He, Y.; Song, R.; Li, H.; Liu, B.; Zhou, H.; Yan, L. Study of mechanical character and corrosion properties of La2O3 nanoparticle reinforced Ni-W composite coatings. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 652, 129799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, S.; Basu, A. Effect of multiple dissimilar nanoparticles in Ni–W alloy matrix composite coating and evaluation of surface-mechanical, corrosion, and hydrophobic properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 278, 125585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shang, C.; Wang, F.; Zheng, T.; Nie, C.; Qiao, Y.; Sun, G.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y. The wear behavior and corrosion resistance properties of Ni-based composite coatings modified with CeO2 and MoS2 nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 719, 137017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.; Andersson, J.M.; M’SAoubi, R.; Kryzhanivskyy, V.; Johansson-Jöesaar, M.P.; Johnson, L.J.; Odén, M.; Rogström, L. Adhesive wear of TiAlN coatings during low speed turning of stainless steel 316L. Wear 2023, 524–525, 204838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, J.; Cao, S.; Song, X.; Yan, X.; Nie, F.; Peng, Z. Wear behavior of coated cermet/carbide tools during high-speed turning of 18CrNiMo7-6 steel and its associated surface integrity evaluations. Wear 2025, 576–577, 206121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Hu, X.; Yin, Y.; Lei, T. Preparation of the electroless Ni–P and Ni–Cu–P coatings on engine cylinder and their tribological behaviors under bio-oil lubricated conditions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 258, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilie, F.; Ipate, G.; Manaila, F.C. Tribological Properties Study of Solid Lubrication with TiO2 Powder Particles. Materials 2022, 15, 7145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uniyal, P.; Gaur, P.; Yadav, J.; Khan, T.; Ahmed, O.S. A Review on the Effect of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles on Tribological Properties of Biolubricants. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 12436–12456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Li, S.-E.; Sun, G.-X.; Zhao, L.; Hu, C.-Q.; Zhang, W.; Tong, G.-D.; Chen, X.-G.; Han, S.; et al. Effects of nanostructuring on mechanical and tribological behaviors of FeCoNi medium-entropy alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2024, 34, 3963–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Pang, X.; Xu, Y.; Lu, H.; Jiang, P.; Yang, J.; Liao, Z. Microstructure, mechanical and tribological properties of in situ MoB reinforced Cu-Al matrix composites. Tribol. Int. 2023, 177, 107941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




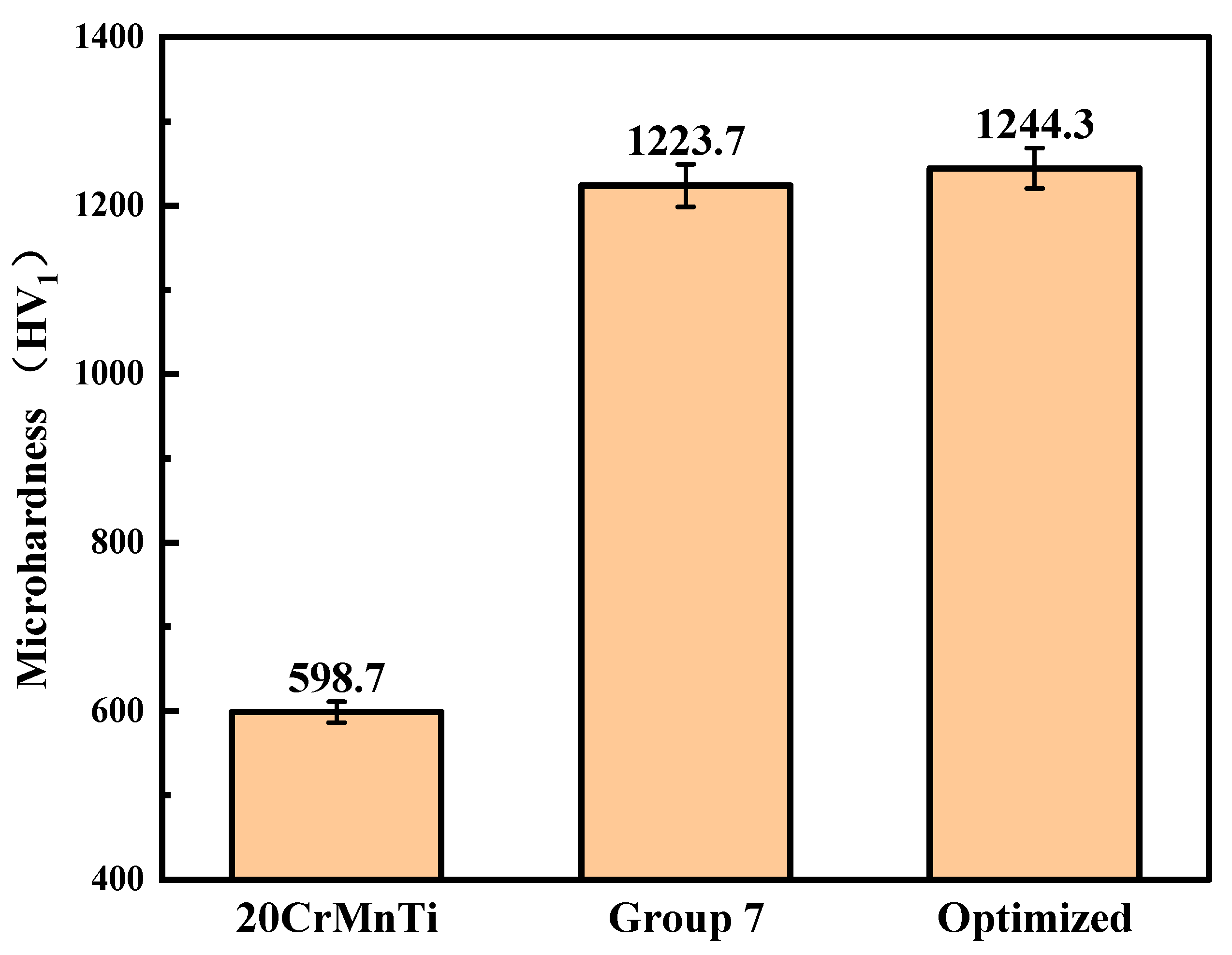
| Element | Concentration (g·L−1) |
|---|---|
| NiSO4·6H2O | 230 |
| NiCl2·6H2O | 30 |
| H3PO3 | 35 |
| NaH2PO2·H2O | 8 |
| NaC6H8O7·H2O | 80 |
| H3BO3 | 30 |
| C12H25NaSO4 | 0.1 |
| SC(NH2)2 | 0.02 |
| Level/Factor | Current Density (A·dm−2) | Temperature (°C) | Ultrasonic Power (W) | Duty Cycle |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 45 | 210 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 2 | 50 | 240 | 0.7 |
| 3 | 3 | 55 | 270 | 0.9 |
| Test Number | Current Density (A·dm−2) | Temperature (°C) | Ultrasonic Power (W) | Duty Cycle |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 45 | 210 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 1 | 50 | 270 | 0.7 |
| 3 | 1 | 55 | 240 | 0.9 |
| 4 | 2 | 45 | 270 | 0.9 |
| 5 | 2 | 50 | 240 | 0.5 |
| 6 | 2 | 55 | 210 | 0.7 |
| 7 | 3 | 45 | 240 | 0.7 |
| 8 | 3 | 50 | 210 | 0.9 |
| 9 | 3 | 55 | 270 | 0.5 |
| Test Number | Current Density (A·dm−2) | Temperature (°C) | Ultrasonic Power (W) | Duty Cycle | Microhardness (HV1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 45 | 210 | 0.5 | 813.4 |
| 2 | 1 | 50 | 270 | 0.7 | 961.5 |
| 3 | 1 | 55 | 240 | 0.9 | 811.5 |
| 4 | 2 | 45 | 270 | 0.9 | 949.3 |
| 5 | 2 | 50 | 240 | 0.5 | 822.3 |
| 6 | 2 | 55 | 210 | 0.7 | 998.2 |
| 7 | 3 | 45 | 240 | 0.7 | 1223.7 |
| 8 | 3 | 50 | 210 | 0.9 | 1186.7 |
| 9 | 3 | 55 | 270 | 0.5 | 1178.6 |
| k1 | 862.13 | 995.47 | 999.43 | 938.10 | |
| k2 | 9923.27 | 990.17 | 1029.80 | 1061.13 | |
| k3 | 1196.33 | 996.10 | 952.50 | 982.50 | |
| R | 334.20 | 5.93 | 77.30 | 1123.03 |
| Considerations | SS | df | MS | F | Threshold Value | Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microhardness (HV1) | Current density | 189,992.329 | 2 | 94,996.1645 | 2982.798 | 9 | * |
| Temperature | 63.696 | 2 | 31.848 | 1.000 | 9 | ||
| Ultrasonic power | 9100.162 | 2 | 4550.081 | 142.869 | 9 | * | |
| Duty cycle | 23,291.762 | 2 | 11,645.881 | 365.671 | 9 | * |
| Reciprocating Speed (Times/min) | Load (g) | Wear Rate (×10−4 mm3/N·m) |
|---|---|---|
| 200 | 320 | 2.13 |
| 400 | 320 | 1.48 |
| 600 | 320 | 1.32 |
| Location | Elemental Atomic Fraction at. /% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | W | O | Si | P | C | N | B | |
| 1 | 37.47 | 4.86 | 41.91 | 3.87 | 2.31 | 4.61 | 2.90 | 1.03 |
| 2 | 17.83 | 3.29 | 56.82 | 4.46 | 1.55 | 9.84 | 5.40 | 1.80 |
| 3 | 16.91 | 3.16 | 63.51 | 4.91 | 1.08 | 5.55 | 4.63 | 0.48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Lin, J. Optimization of Deposition Parameters for Ni-P-WC-BN(h) Composite Coatings via Orthogonal Experimentation and Wear Behavior of the Optimized Coating. Metals 2025, 15, 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070714
Li Y, Liu Z, Li Y, Lin J. Optimization of Deposition Parameters for Ni-P-WC-BN(h) Composite Coatings via Orthogonal Experimentation and Wear Behavior of the Optimized Coating. Metals. 2025; 15(7):714. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070714
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yingyue, Zehao Liu, Yana Li, and Jinran Lin. 2025. "Optimization of Deposition Parameters for Ni-P-WC-BN(h) Composite Coatings via Orthogonal Experimentation and Wear Behavior of the Optimized Coating" Metals 15, no. 7: 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070714
APA StyleLi, Y., Liu, Z., Li, Y., & Lin, J. (2025). Optimization of Deposition Parameters for Ni-P-WC-BN(h) Composite Coatings via Orthogonal Experimentation and Wear Behavior of the Optimized Coating. Metals, 15(7), 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070714






