Abstract
In this paper, we propose the use of burnishing internal cylindrical surfaces with a hard tool in a mandrel shape. The burnishing force is exerted mainly by the press slide, which has pushing properties, moving the burnisher through the hollow tube. The burnishing of hollow surfaces is used as the finishing step for elements such as tubes. The purpose of using the burnishing method may be, for example, to increase the smoothness and accuracy of the object, for the improvement of its functional and operational properties, for economic reasons, or to increase its resistance to corrosion and fatigue. The depth of plastic deformation and the accuracy of processing are the main differences in the machining effects for individual burnishing methods. The selection of the burnishing conditions depends on the method of exerting pressure from the burnishing elements on the machined surface, which can be elastic or rigid. Computer simulations of the burnishing process were performed in FORGE® NxT 2.1 software. A numerical analysis was performed using a three-dimensional triangular mesh. The theoretical and experimental research was determined to have very good compatibility, as determined by the numerically calculated results and by the mean deviation of residual stress method. This research analyzed the stress and strain state after the burnishing process, and a depth of deformation of approximately 20 μm to 30 μm in the material was determined.
1. Introduction
The commonly implemented development and research activity consists of producing newer and more functional products. The development and application of innovative processes, services, and projects are of importance. Products are all types of objects that begin in the design and production phase, then are made and used, and after use, they are disposed of or reprocessed. Examples of products include airplanes, ships, cars, machine tools, gears, shafts, and bushings, as well as gasoline, electricity, gas, etc. A product must meet the expectations of the future user, characterized by a set of utility features. In the case of machines and devices, their capabilities and performance, such as durability, maintenance, and reliability, result from the features represented by the assemblies that create the structure. Assemblies and subassemblies constitute a set of kinematic pairs, while the set of functional features is determined by the features of the individual kinematic pairs [1,2,3,4].
In their book, Burakowski T. and Wierzchoń T. [4] point out that the formation of the functional features of the surface layer in the technological process is an important problem, as it is desirable for the elements of the kinematic pairs to fulfill their intended functions for as long as possible. The surface layer of the cooperating elements created in the technological process has a significant impact on their functional features, which determine the durability of the entire machine, including [4,5,6,7,8,9] wear resistance, fatigue strength, movement resistance, corrosion resistance, etc. In research on the finishing process, it is important to determine the influence of technological, mechanical, and strength conditions on the condition of the surface layer [10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. The technology of burnishing is a simple, fast, and cost-effective process of shaping the technological surface layer, and it is used to improve the surface quality of manufactured machine elements [17]. The impact of the burnishing tool on the workpiece is most often modeled using solutions for elastic–plastic and rigid–plastic bodies [18,19,20,21]. Numerical simulations of the mechanical shaping process of the technological surface layer are of increasing interest in research and industry as they provide a better understanding of the surface treatment, analysis, and prediction of the impact of the burnishing parameters on various surface integrity properties [5,6,7,8,21,22,23,24]. The burnishing process consists of the action of a hard and smooth burnishing element (e.g., ball, roller, disc, burnisher mandrel) on the machined surface. Slide burnishing [17,24] push-through involves pushing the burnishing element, which has a larger dimension than the hole.
In the book by Korzyński M. [17], the author analyzed the process of slide burnishing. It is a type of finishing plastic processing particularly applicable to metals and their alloys. It is divided into redrawing and sliding smoothing. It can be performed as pushing and pulling burnishing using a burnishing pusher, a ball, or a burnishing broach. In slide burnishing, slippage occurs between the machined surface and the burnishing part. Burnishing is performed by pressing, with an appropriate force, a hard and smooth burnishing element onto the machined surface, which slides over the machined surface, causing sliding friction and the plastic deformation of the surface irregularities. Burnishing elements for this type of processing are hard and have a low coefficient of sliding friction. Sliding smoothing is used for the processing of holes, shafts, surfaces, and shaped planes characterized by high hardness.
In the book by Przybylski W. [24], it is noted that the following tools are used for the slide burnishing of holes in series and in mass production: balls, mandrel burnishers, and multi-element sliding burnishers. As a result of burnishing, elastic and plastic deformation states occur in the surface layer.
The purposes of burnishing are strengthening, improving smoothness, obtaining appropriate dimensional tolerance for better lubrication, and improving the appearance of the surface layer [4,25,26]. Based on our own research [8,9,10] and the literature [27,28,29,30], it can be stated that relative deformation during burnishing and rolling processes significantly affects the parameters of the geometric structure of the surface and the relative hardening of the surface layer [24,25,30,31,32]. For higher values of relative deformation, higher values of the relative hardening of the surface layer are obtained [28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35]. Using higher values of relative deformation, a lower surface roughness can be obtained, and therefore, higher values of the surface roughness reduction index can then occur [29,35,36,37].
This article considered the burnisher mandrel as the element for sliding burnishing. It is a rotating or non-rotating element with a complex shape, and its working area may be a section of a sphere or an axisymmetric solid. Burnishing methods can be divided into groups due to the mechanics of the machining process: static methods, where, during burnishing, the forces have constant values and dynamic methods, and whose burnishing forces are variable in time. The burnishing process, compared to machining, is a quick and safe process, performed at low temperatures, and does not leave waste in the form of chips, sparks or harmful dust [4,24,26]. Burnishing, as a chipless process, does not cause any material loss and allows obtaining surfaces with low roughness and increased strength properties [27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35].
An important physical aspect of the surface layer is the residual stresses in the resulting product, which significantly affect the fatigue life of machine elements. The analysis of the research results presented in [8,17,19,24] showed that compressive residual stresses are created in the surface layer of holes in machine elements processed by burnishing. Such stresses contribute to the increase in the working time of elements exposed to variable loads. In order to effectively control the quality of the surface layer of products using technological parameters, a process model should be developed. In this case, process modeling using finite element methods can be particularly useful.
The article presents the results of numerical analysis of the static pressure-slide burnishing process. The mode of interaction of a rigid tool with a specific curvature of the burnishing element with the deformed object was determined. At the contact point of the burnishing element with the inner surface of the steel tube, the temperature distribution, the deformation state and the stress state were determined using the commercial software FORGE® NxT 2.1 [38] based on the finite element method FEM [2,5,22,30,31,32,38].
Slide burnishing allows for improving the geometric parameters of the hole, reducing the surface roughness, increasing the hardness of the surface layer, and creating compressive residual stresses. This treatment is characterized by high efficiency, simple technological equipment, and the possibility of machining holes with a non-straight axis. The burnishing element has a larger dimension than the hole by the value of the burnishing press-in. The burnishing element has a larger dimension than the hole in terms of the amount of interference. The burnishing pressure is the difference between the dimensions of the tool and the dimensions of the workpiece after the preceding machining, defined as the average measurement value in three planes.
The experimental studies were conducted on a Hydraulic Punching and Shearing Machine MX340G (Prada Nargesa, Girona, Spain) (Figure 1). The sliding burnishing was carried out with lubrication with machine oil. A burnisher and a force meter were screwed to the piston rod, and a sample in the form of a tube was mounted in a holder. The piston rod with the mandrel burnisher performed vertical movements up and down, simultaneously pushing the mandrel through the tube. It is difficult to find in the literature [2], apart from our own works [8], where balls were used for burnishing, as well as references to the use of the FORGE® NxT 2.1 program in burnishing with a mandrel. The shape of the burnishing tool and the process parameters were selected based on our own [8] research and literature analysis [17,24]. Therefore, the presented research results are considered to provide added value to existing knowledge.
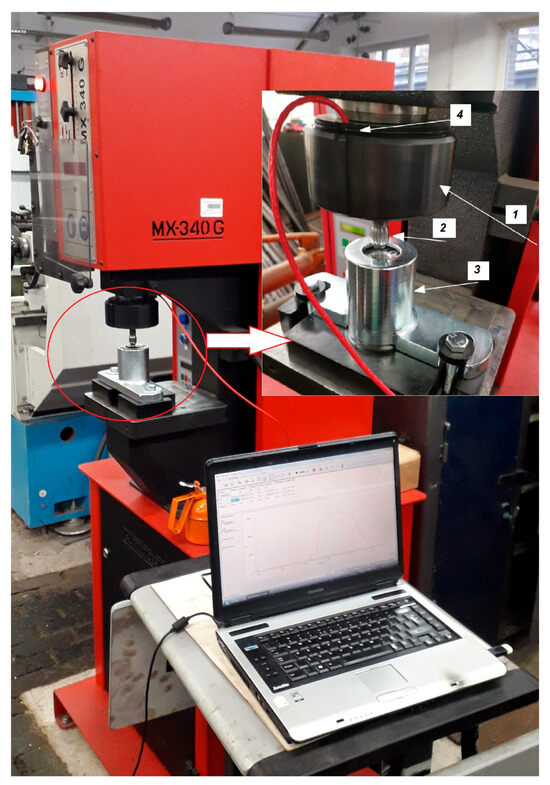

Figure 1.
The Narges Hydraulic Press, model MX-340G, where 1—piston rod of a hydraulic press, 2—burnisher mandrel, 3—sample holder in the form of a steel tube, 4—dynamometer with load sensor.
2. Numerical Analysis of Slide Burnishing Process
The conditions reaching the plastic state in complex stress states were given by H. Tresca (the maximum tangential stress reaches a limiting value) and M.T. Huber and R. Mises (the stress intensity reaches a certain constant value). The hypothesis regarding the relationship between stresses and strains was independently formulated by M.T. Huber (1904), R. Mises (1913) and H. Hencky (1924) [3,8,17,24]. It can be expressed as follows: “Plastic deformation at a given point in the body occurs when the octahedral tangential stress at that point reaches a value characteristic for a given material, i.e., when the reduced stress reaches the yield point from the uniaxial state”. In the numerical modeling, it was taken into account on the basis of the Hertz model, which is a modification of the Bussinesq model, that the burnishing force is distributed over a specific contact surface of the spherical tool with the workpiece in the elastic–plastic half-space. Theoretical analysis of the burnishing was carried out numerically. The commercial package based on the finite element method; FORGE® NxT 2.1 [38] was used. Numerical modeling and experimental research of the slide burnishing process consisted in determining the effect of a rigid tool, i.e., a mandrel burnisher made of 20CrMo4 steel with a specific curvature and an external diameter of 17 mm, on the deformed object tube made of C45 unalloyed steel (Figure 2). The chemical composition of the burnisher and steel samples was determined using a Solaris-CCD Plus spark-excited optical emission spectrometer (Table 1).
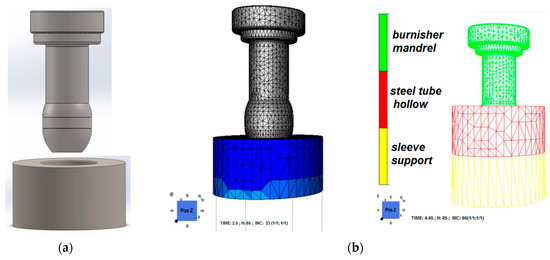
Figure 2.
The three-dimensional model: (a) burnisher mandrel and tube, (b) the triangular mesh for the simulation.

Table 1.
The chemical composition of materials used in numerical and experimental investigation, weight %.
The tests had the same external diameter of 45 mm, and samples with a height of 25 mm were used. The target internal diameter after burnishing should be 17 mm. The burnishing press-in was a value of 0.1 mm. This is a difference in the dimension measured on three planes, before and after burnishing.
Figure 2 shows examples of elements with and without STL meshes applied. The specificity of the software means that despite the tool material being assigned to the model, the boundary parameters and the density of the finite element mesh are crucial for the quality of the calculations.
In the first stage of creating the simulation, three-dimensional models were made on which an STL (STereoLithography) was applied, thanks to which it was possible to accurately apply the finite element method triangular mesh to the designed elements in the FORGE® NxT 2.1 software. A three-dimensional triangular mesh was used. The mesh is switched to the appropriate number of freedom nodes. The coarse mesh option was selected on the outer diameter, while the fine mesh option was set on the inner diameter. The mesh density inside the tube was 0.4 mm. Mesh generation is based on global element size, tolerance and local mesh control settings, which allow for defining different sizes of parts, edges, faces and vertices. The software calculates the global element size of the model, taking into account volume and surface area. Tests were carried out to see how the shape of deformation changes and the results with mesh density. The effect of mesh size was analyzed; the higher the density, the more accurate the calculations. Too thick a FEM mesh leads to large errors. The mesh was densified in areas where large losses of stability occur (deformation and stress), which allowed for an increase in accuracy without a significant increase in computation time. An analysis was carried out in which place the largest deformations and stresses can be expected, and in these areas, the mesh was densified. Data from the use of different meshes was compared, taking into account the results, as well as the time in performing numerical calculations.
Boundary conditions and load were assigned to the geometric points of the sleeve and the burnisher, thanks to which an additional node was created there. Places where maximum stresses occur require more iterations of mesh refinement. On the external plane of the tool, the mesh elements are less refined, which also significantly affects the time of complex numerical calculations. Tests were carried out to determine the change in the shape of deformation; the results were obtained with mesh refinement. An analysis was carried out of where the greatest deformations and stresses can be expected, and in these areas, the sieve was refined. The comparison of data from the use of different meshes took into account the results, the number of nodes, and the time in performing numerical calculations. Therefore, mesh generation used computing capabilities of the FORGE® NxT 2.1 software.
The rheological characteristics of C45 unalloyed steel and 20CrMo4 bearing steel (Table 2) were entered into the commercial numerical program using the Hensel–Spittel function [6,7,8,22,38]:
where:
σp—yielding stress; ε—strain; —strain rate; T—temperature; K0, m1, m2, m3, m4—material coefficients determined by approximation of plastometric experiments.

Table 2.
The coefficients determining the rheological properties of steels used in research.
Table 2.
The coefficients determining the rheological properties of steels used in research.
| Material | K0 | m1 | m2 | m3 | m4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C45 | 1523.4 | −0.00269 | −0.12651 | 0.14542 | −0.05957 |
| 20CrMo4 | 1233.1 | −0.00254 | −0.05621 | 0.14550 | −0.03240 |
The computer simulations of surface plastic processing were performed at ambient temperature. Friction forces were modeled based on the Tresca solution and determined from the following formula [22]:
τ—friction stress, [MPa]; σ0—initial yield stress, [MPa]; σn—normal stress, [MPa]; μ—coefficient of friction; m—friction factor.
A mathematical model was used to simulate three-dimensional plastic flow of metal during sliding burnishing, in which the mechanical state of the deformed material was described using the Norton–Hoff law [8,23], presented by equation:
where:
Sij—stress deviator; —strain rate tensor; —strain rate; —strain; —initial strain; T—temperature; K0, m0, n0, β0—material constants relating to the characteristic properties of a given material.
The computer program used for the tests has built-in thermomechanical models, and requires defining boundary conditions that determine the correctness of numerical calculations. The FORGE® NxT 2.1 commercial package uses models consisting of a finite element mesh whose basic element is a triangle. The following parameters were used in the tests: tool feed rate from 2 mm/s to 10 mm/s, friction factor value 0.2, heat exchange coefficient with air 10 [W/K·m2], contact heat transfer coefficient 3000 [W/K·m2], initial tool temperature 25 °C, initial ambient temperature 20 °C. The boundary conditions were as follows: properties of the tested material, friction conditions, kinetic and thermal parameters, and tool properties.
3. Research Results
A numerical analysis of the burnishing process of hollow steel tubes is a very important issue due to the cognitive aspect of physical phenomena in the material subjected to surface plastic working. In computer simulations of the slide burnishing process, the coefficient and friction factor were adopted based on previous research on numerical modelling and literature data [8,10,17,24]. The Tresca model was used in numerical calculations, for which the friction factor was 0.2 for the (steel-steel) tube and a burnisher mandrel was used. Numerical modelling was carried out for given boundary conditions: a specific tool feed rate from 2 mm/s to 10 mm/s, ambient temperature, burnishing press-in 0.1 mm and a mandrel burnisher with an external diameter of 17 mm.
After numerical tests of sliding push-burnishing, the distributions of strain rate and strain intensity and stress intensity for the given absolute deformation (burnishing press-in) were determined. After computer simulations of burnishing, the temperature distribution was determined for unalloyed C45 steel (cold working), where the maximum temperature value at the interface between the tool and the workpiece was 30°C (Figure 3). The source of heat released in the deformation zone is the work of plastic deformation. In practice, about 15% of this energy is transformed into heat in the area of plastic deformation. During an intensive course of the surface plastic processing process, a momentary increase in the temperature value occurs in the surface layer of the material at the contact with the tool, caused not only by the work of deformation, but also by the friction of the burnishing element against the machined surface. After the tests were performed, the state of strain and stress was determined on the contact surface of the burnishing element with the processed element in the shape of non-alloy hollow steel tubes.
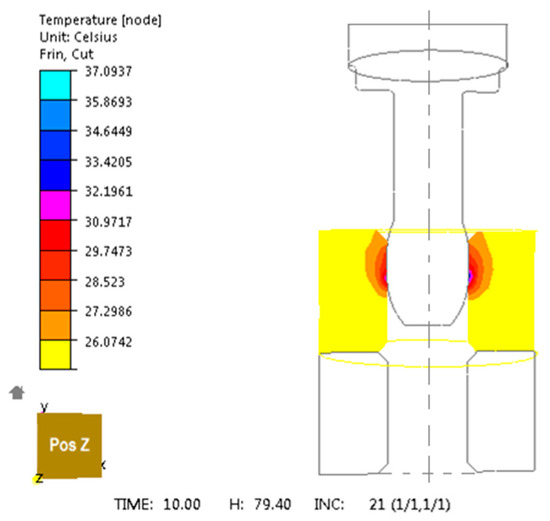
Figure 3.
Temperature distribution for unalloyed steel C45 in computer simulation of sliding push-burnishing during 10 s for a burnisher mandrel.
After analyzing the results of numerical research presented in Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9, it can be stated that an increase in the intensity of deformation and strain rate and stress intensity is observed in the top layer of the tube on its inner side at the contact with the burnishing element. Analysis of the depth of plastic deformation in the burnishing process is a fundamental issue in theoretical, analytical and numerical considerations for the correct design of surface plastic processing technology. Depth of plastic deformation and the degree of hardening as well as the machining accuracy constitute the main differences in machining effects for individual burnishing methods. Many functional properties of burnished products depend on the depth of plastic deformation in the surface layer, including fatigue strength. The depth of the plasticized zone results from the Bussinesq solution and depends on the maximum tangential stress. In accordance with the direction of the burnishing force, the reduced stresses reach the maximum value on the surface of the workpiece and decrease with increasing distance from the surface of the processed element.
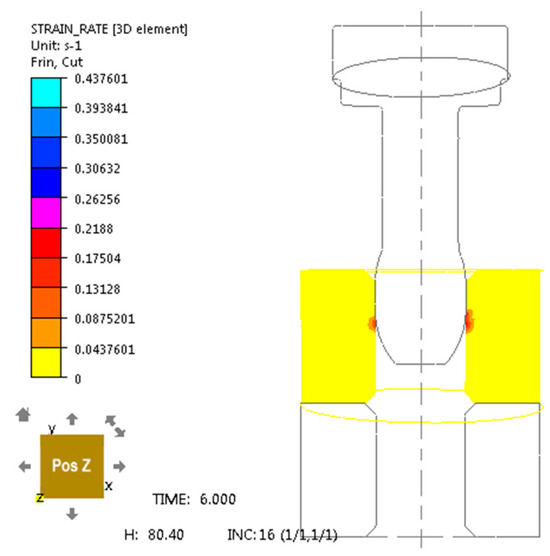
Figure 4.
Strain rate distribution for unalloyed steel C45 in computer simulation of sliding push-through burnishing over 6 s for a burnisher mandrel.
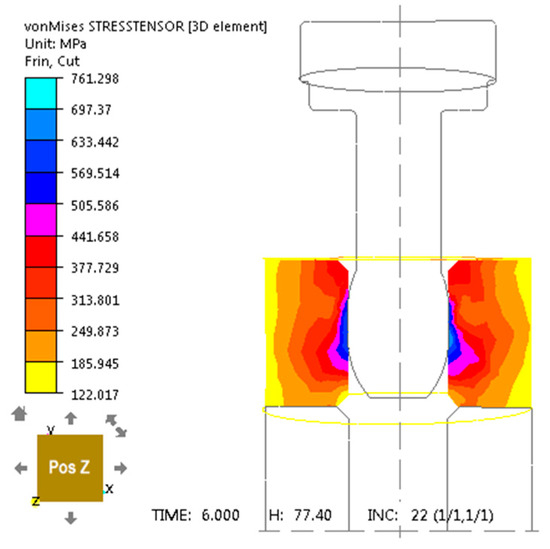
Figure 5.
Von Mises stress tensor distribution for unalloyed steel C45 in computer simulation of sliding push-through burnishing over 6 s for a burnisher mandrel.
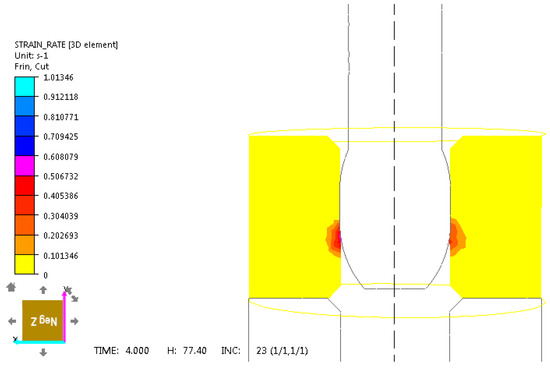
Figure 6.
Strain rate distribution for unalloyed steel C45 in computer simulation of sliding push-through burnishing over 4 s for a burnisher mandrel.
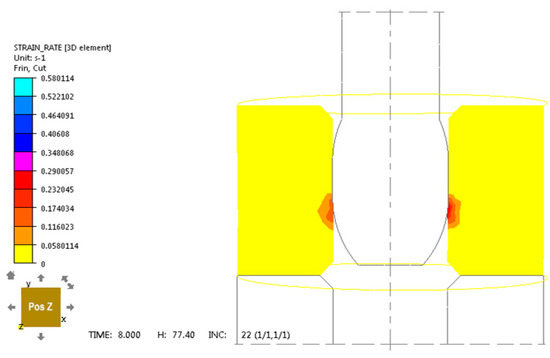
Figure 7.
Strain rate distribution for unalloyed steel C45 in computer simulation of sliding push-through burnishing over 8 s for a burnisher mandrel.
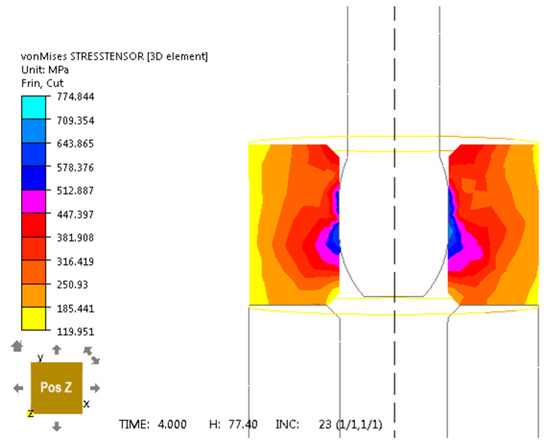
Figure 8.
Von Mises stress tensor distribution for unalloyed steel C45 in computer simulation of sliding push-through burnishing over 4 s for a burnisher mandrel.
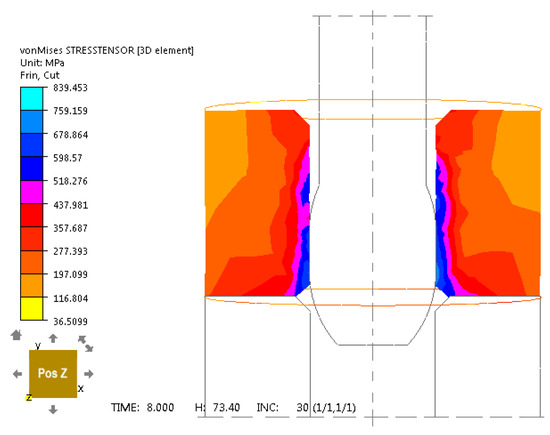
Figure 9.
Von Mises stress tensor distribution for unalloyed steel C45 in computer simulation of sliding push-through burnishing over 8 s for a burnisher mandrel.
Analyzing the depth of plastic deformation in the burnishing process is important for the correct design and development of burnishing technology. In order to determine the depth of the zone of plastic deformation used in numerical analysis based on the finite element method, it was analytically determined, by analyzing the results of computer simulations of the slide burnishing process, that the maximum values of strain and absolute compressive stress occur at a depth from the machined surface tubes of about 20 μm to 30 μm.
In Figure 10 it can be seen that the strain intensity value increases with the increase in the burnishing tool speed, reaching maximum values of 10 mm/s. In Figure 11 it can be seen that the stress intensity value is stabilized for all speeds. The highest stress intensity values are achieved for a tool feed rate of 6 mm/s.
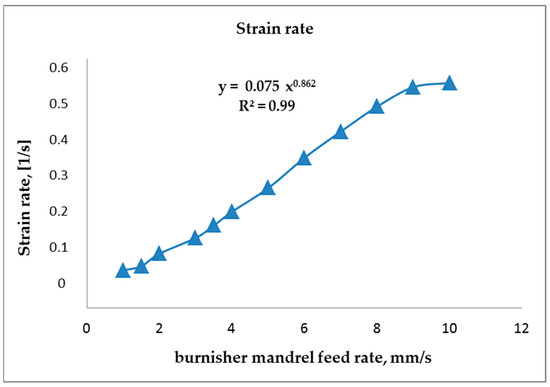
Figure 10.
The dependence of the strain rate on the tool feed rate for C45 unalloyed steel for a burnisher mandrel diameter of 17 mm.
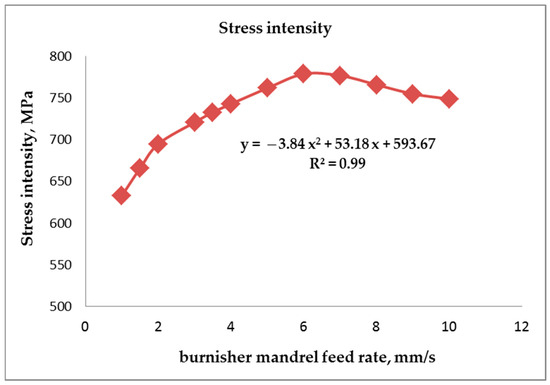
Figure 11.
The stress intensity dependence as a function of tool feed rate for C45 unalloyed steel for a burnisher mandrel diameter of 17 mm.
We determined a numerical solute ion for contact and deformation of bodies on the basis of the theory of plasticity and elasticity. Based on numerical analysis, we determined the depth of the plastic deformation zone. For the required boundary conditions and specific areas of research, determined on the basis of their own numerical slide burnishing, the relationship was determined between the depth of the zone of plastic deformation and the deformation and burnishing press-in.
4. Experimental Verification of the Theoretical Model
In order to determine the residual stresses after experimental burnishing, a mechanical method was used. This method consists in calculating stresses based on the tube deformations caused by the occurrence of these stresses. Each metal forming process causes the formation of residual stresses in the manufactured products. Residual stresses can be a source of deformation. It is important to determine whether the residual stresses from the previous processing stage are the cause of an uncontrolled change in shape before the next operation.
A useful, cheap and simple method of average deviations presented in the works of [8,13,39,40] was used. The basics of analytical modeling using the method of average deviations and a computer program allowing for quick calculations and determining the level of residual stresses in tubes are presented. After burnishing, the external and internal dimensions were measured. The samples were then cut along the forming surface and their outer diameter was measured. The data were substituted into the equation [13,39]:
where:
- E—modulus elasticity (E = 210 GPa, for steel);
- gt—thickness of the wall [mm];
- D—outer diameter tube before slitting after burnishing [mm];
- D1—outer diameter burnishing tube and after cutting [mm].
Figure 12 shows a diagram of a sample for calculating residual stresses. There is also a view of the steel tubes after burnishing and then after cutting. After the tests, samples were cut and the external diameter was measured and we calculated residual stress.
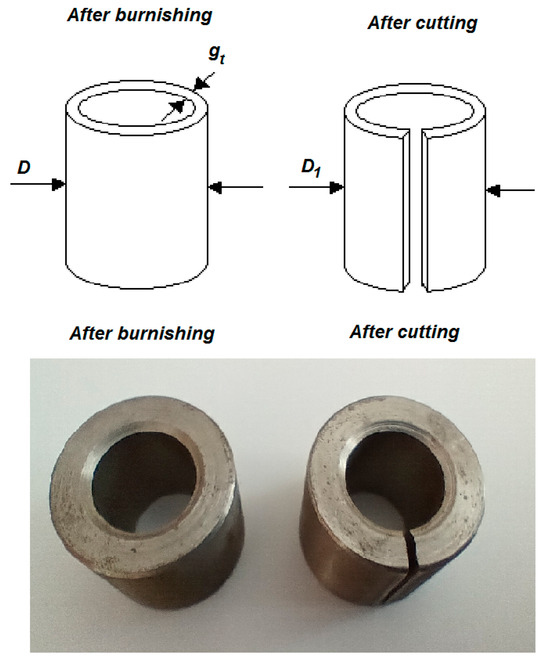
Figure 12.
The schema and view of the tube made of unalloyed C45 steel after burnishing and also after cutting.
After burnishing and processing, samples were cut and the external diameter measured and we calculated residual stress.
After performing calculations using Equation (4), the values of residual stresses in the tubes after burnishing were determined; they were in the range of σC = 17.11–24.18 MPa. The residual stresses calculated numerically after the conducted computer simulations of burnishing were in the range of σC = 18.02–25.11 MPa. These are permissible values, because they are lower than the limit value of the allowable residual stress for the mean deviation method. The given values of residual stresses remaining in the tubes after the sliding burnishing were lower than the limit value of the allowable residual stress for the mean deviation method σC < 35 MPa. The work in [39] presented ranges of residual stress acceptability as follows: σC < 35 MPa—acceptable; σC = 35–70 MPa—borderline; σC > 70 MPa—unacceptable.
The microstructure of the surface layer of C45 steel was characterized by the marked depth of deformation at 500× magnification. The presented microstructure is characteristic of the effects of the burnishing process. However, the depth of deformation is original for the given process and its parameters used in the tests. It can be seen that the deformation occurs at a depth of about 20 μm to 30 μm. The ferrite–pearlitic microstructure can be observed after normalizing annealing and surface plastic deformation. The pearlite grains form upwards, showing the deformation zone (Figure 13).
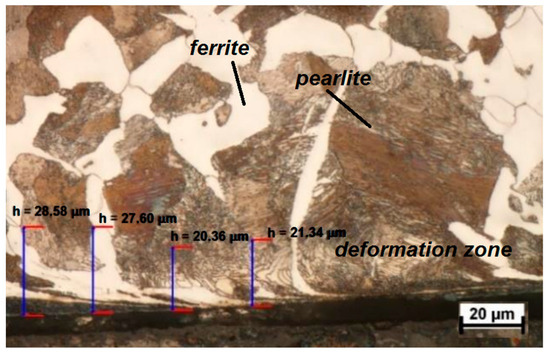
Figure 13.
The ferrite–pearlitic microstructure of the surface layer of C45 steel with the marked depth of deformation at 500× magnification.
5. Discussion
Numerical modeling of the burnishing was performed in the FORGE® NxT 2.1 program, because it allows the analysis of physical models that take into account geometric nonlinearities induced by large deformations and nonlinear material characteristics. Simulations were performed for sleeve-type samples. The model was fixed in the Y-axis plane, moved in the X-axis plane. Displacement variables were obtained at nodes and extrapolated to the rest of the element using shape functions, which have additional nodes in the middle of the edges and better represent the discretization curvatures. The constitutive model is a linear study of elasticity and plasticity with the adopted von Mises criterion. The mechanical state of the deformed material is described by the Norton–Hoff relationship. The rheological properties of the materials are introduced by means of the Hensel–Spittl function.
The analysis of the burnishing sliding push was conducted analytically and numerically. In the original approach, a burnisher mandrel, with a specially designed geometry, radius of rounding and curvature creating the burnishing part, was used. We present in this work an analysis of the deformation and stress field in a steel tube during the sliding burnishing sliding process. The considered problem was to conduct a numerical analysis of the burnishing process.
After conducting a numerical analysis of the burnishing process of sliding pushing of steel tubes, it was determined that the most intense state of stress and deformation occurs at the contact surface (steel–steel) of the tool and the inner layer of the tube. After slide burnishing the surface layer, compressive residual stress results from the increased specific volume of the material in a plastic state. The maximum absolute value stresses occur near the surface subjected to burnishing. The presence of compressive stresses in the surface layer is preferred due to improved performance, especially the increase in fatigue strength of machine parts. It was also determined that with the increase in tool feed speed in the range from 2 mm/s to 10 mm/s, the strain rate values increase significantly. On the other hand, with the increase in tool feed speed, the stress intensity values change slightly, reaching maximum values for a speed of 6 mm/s. The maximum strain rate values occur at a speed of 10 mm/s.
After burnishing, metallographic sections were also made. Metallographic tests were performed. The effect of the process on the deformation of the surface layer was determined. Example results are shown in Figure 13.
The metallographic specimens were made perpendicular to the deformation direction. The sample preparation did not affect the structure change. The deformation zone is dependent on the structure and the burnishing process. Numerical modelling was experimentally verified and a high agreement was found between the numerically calculated results and the results determined by the strain analysis and the mean deviation of residual stress method. After microstructural tests and numerical analysis, strain depth measurements were performed. The stresses determined during numerical modeling were compared to the experimental study. A good agreement was found between the numerically calculated results and the results determined by microstructural tests and analysis of the mean residual stress deviation method.
6. Summary and Conclusions
The paper assessed the influence of the burnishing process based on the elastic–plastic deformation model on the properties of the surface layer. To these ends, a numerical implementation of finite element methods in the FORGE® NxT 2.1 software was used. The stress and strain state after the cold slide burnishing process was analyzed. Based on the developed mathematical model, the depth of deformation in the material was determined. To determine the plastic zone in the burnished element and to determine the state of deformation, as well as the depth of plastic deformation zone, numerical analysis based on the finite element method was used.
The numerical modeling was verified experimentally and a very good agreement was found between the numerically calculated results and those determined by the mean deviation of residual stress method. Based on the numerical analysis, it was possible to establish that burnishing affects the deformation fields and the stress state in the material. The intensity of deformation for the elastic–plastic body model remains closely dependent on the intensity of the equivalent stress.
- (1)
- After slide burnishing, compressive stresses are constituted in the surface layer, resulting from the increased specific volume of the material in the plastic state.
- (2)
- The maximum stresses in terms of absolute value occur near the surface subjected to burnishing treatment.
- (3)
- The presence of compressive stresses in the surface layer is beneficial due to the improvement of functional properties, especially the increase in fatigue strength of machine elements, but also in tribological wear.
- (4)
- After sliding burnishing, plastic deformations and internal stresses are constituted in the surface layer from the inside of the steel tube at a specific depth depending on the burnishing press-in.
- (5)
- It was found in numerical analysis and after experimental tests that plastic deformation occurs at a depth of approximately 20 μm to 30 μm.
- (6)
- The tubes after the experimental burnishing process were cut along the sample and the outer diameter was measured and the residual stresses were calculated. The values of residual stresses remaining in the tubes after the slide burnishing were lower than the limit value of the allowable residual stress for the mean deviation method from 35 MPa.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.C.D. and W.K.-M.; methodology, T.C.D.; software, W.K.-M.; validation, T.C.D. and W.K.-M.; formal analysis, T.C.D.; investigation, T.C.D. and W.K.-M.; resources, T.C.D.; data curation, T.C.D.; writing—original draft preparation, T.C.D.; writing—review and editing, T.C.D.; visualization, T.C.D.; supervision, T.C.D.; project administration, T.C.D.; funding acquisition, T.C.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Antosz, K.; Kluz, R.; Trzepieciński, T.; Bucior, M. Modeling of the influence of burnishing parameters on the surface roughness of rollers made of 42CrMo4 steel. Adv. Mech. Mater. Eng. 2022, 38, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra-Becerraa, E.; Aguilera Ojedaa, C.O.; Saldaña-Roblesb, A.; Reveles-Arredondoa, J.F.; Barco-Burgosc, J.; Vidal-Lessoa, A. A review of numerical simulation of ball burnishing process. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2023, 218, 103926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarski, T. Mechanika Plastycznego Płynięcia Metali; Oficyna Wydawnicza Politechniki Warszawskiej: Warszawa, Poland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Burakowski, T.; Wierzchoń, T. Surface Engineering of Metals: Principles, Equipment, Technologies; CRC Press LLC.: London, UK; New York, NY, USA; Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Doroszko, M.; Seweryn, A. A new numerical modelling method for deformation behaviour of metallic porous materials using X-ray computed microtomography. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 689, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyja, H.; Banaszek, G.; Grynkevych, V.A.; Danchenko, V.N. Modelowanie Procesów Kucia Swobodnego; Monografie Politechnika Częstochowska: Częstochowa, Poland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dyja, H.; Mróz, S.; Rydz, D. Technologia i Modelowanie Procesów Walcowania Wyrobów Bimetalowych; Monografie Politechnika Częstochowska: Częstochowa, Poland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dyl, T. Numeryczna i Eksperymentalna Analiza Procesu Nagniatania z Wykorzystaniem Teorii Sprężystości i Plastyczności; Prace Naukowe Akademii Morskiej w Gdyni: Gdynia, Poland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dyl, T.; Starosta, R.; Rydz, D.; Koczurkiewicz, B.; Kuśmierska-Matyszczak, W. The experimental and numerical research for plastic working of nickel matrix composite coatings. Materials 2020, 13, 3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyl, T.; Rydz, D.; Szarek, A.; Stradomski, G.; Fik, J.; Opydo, M. The Influence of Slide Burnishing on the Technological Quality of X2CrNiMo17-12-2 Steel. Materials 2024, 17, 3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzyura, V.; Maruschak, P.; Slavov, S.; Dimitrov, D.; Semehen, V.; Markov, O. Evaluating Some Functional Properties of Surfaces with Partially Regular Microreliefs Formed by Ball-Burnishing. Machines 2023, 11, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattouh, M. Some Investigation on the Ballizing Process. Wear 1989, 134, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garstka, T.; Dyl, T. Circumferential residual stresses in tubes estimated by means of deflection method. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2006, 2, 199–203. Available online: https://www.imim.pl/files/archiwum/Vol2_2006/art04.pdf (accessed on 19 May 2025).
- Grochała, D.; Grzejda, R.; Józwik, J.; Siemiątkowski, Z. Improving the degree of surface isotropy of parts manufactured using hybrid machining processes. Coatings 2025, 15, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grudzień, J.; Grochała, D.; Grzejda, R.; Kochmański, P. Testing the effectiveness of hybrid milling and surface burnishing in improving the wear resistance of machine parts made of structural steel. Lubricants 2024, 12, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerez-Mesa, R.; Fargas, G.; Roa, J.J.; Llumà, J.; Travieso-Rodriguez, J.A. Superficial Effects of Ball Burnishing on TRIP Steel AISI 301LN Sheets. Metals 2021, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzyński, M. Nagniatanie Ślizgowe; Wydawnictwo Naukowo—Techniczne: Warszawa, Poland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kucharska, B. Identification of surface stress in the exhaust system pipe made by hydroforming technology based on diffractometric measurements. Eksploat. I Niezawodn.—Maint. Reliability 2019, 21, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukiełka, L. Teoretyczne i Doświadczalne Podstawy Powierzchniowego Nagniatania Tocznego z Elektrokontaktowym Nagrzewaniem; Wydawnictwo Uczelniane Wyższej Szkoły Inżynierskiej: Koszalin, Poland, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kułakowska, A.; Bohdal, Ł. Surface Characterization of Carbon Steel after Rolling Burnishing Treatment. Metals 2024, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximov, J.; Duncheva, G.; Anchev, A.; Dunchev, V.; Anastasov, K.; Daskalova, P. Effect of Roller Burnishing and Slide Roller Burnishing on Surface Integrity of AISI 316 Steel: Theoretical and Experimental Comparative Analysis. Machines 2024, 12, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mróz, S. Proces Walcowania Prętów z Wzdłużnym Rozdzielaniem Pasma; Monograph; Monografie Politechnika Częstochowska: Częstochowa, Poland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Naif, A. Interaction of electric current with burnishing parameters in surface integrity assessment of additively manufactured Inconel 718. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2024, 230, 114474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybylski, W. Technologia Obróbki Nagniataniem; Wydawnictwo Naukowo—Techniczne: Warszawa, Poland, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Ramezani, M.; Mohd Ripin, Z.; Pasang, T.; Jiang, C.P. Surface engineering of metals: Techniques, characterizations and applications. Metals 2023, 13, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Calleja, A.; López de Lacalle, L.N.; Pereira, O.; González, H.; Urbikain, G.; Laye, J. Burnishing of FSW Aluminum Al–Cu–Li Components. Metals 2019, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Lopez de Lacalle, L.N.; Celaya, A.; Lamikiz, A.; Albizuri, J. Surface improvement of shafts by the deep ball-burnishing technique. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 2817–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachin, B.; Rao, C.M.; Naik, G.M.; Puneet, N.P. Influence of slide burnishing process on the surface characteristics of precipitation hardenable steel. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez Egea, A.J.; Rodríguez, A.; Celentano, D.; Calleja, A.; López de Lacalle, L.N. Joining metrics enhancement when combining FSW and ball-burnishing in a 2050 aluminium alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 367, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoblik, R.; Rydz, D.; Stradomski, G. Analysis of asymmetrical rolling process of multilayer plates. Solid State Phenom. 2010, 165, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stradomski, G.; Rydz, D.; Dyja, H. Bimetal plate St3S+Cu. Metalurgija 2005, 44, 147–150. Available online: https://hrcak.srce.hr/file/188854 (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Stradomski, G.; Fik, J.; Lis, Z.; Rydz, D.; Szarek, A. Wear Behaviors of the Surface of Duplex Cast Steel after the Burnishing Process. Materials 2024, 17, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, M.J.; Su, C. Dynamic reliability evaluation of buried corroded pipeline under rockfall impact. Eksploat. I Niezawodn.—Maint. Reliab. 2022, 24, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winiarski, G.; Gontarz, A.; Skrzat, A.; Wójcik, M.; Wencel, S. Analysis of a New Process for Forming Two Flanges Simultaneously in a Hollow Part by Extrusion with Two Moving Dies. Metals 2024, 14, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Zhao, H.; Chen, Y.; Chang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Modification of Johnson–Cook Constitutive Parameters in Ball Burnish Simulation of 7075-T651 Aluminum Alloy. Metals 2023, 13, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaleski, K. Technologia Nagniatania Dynamicznego; Wydawnictwo Politechniki Lubelskiej: Lublin, Poland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zaleski, K.; Lipski, J. Modelling on the Ballizing Process of Holes in Workpieces Made of C45 Steel; Management and Control of Manufacturing, Processes; Świć, A., Lipski, J., Eds.; Lubelskie Towarzystwo Naukowe: Lublin, Poland, 2011; pp. 114–124. [Google Scholar]
- FORGE® Reference Guide Release; Transvalor S.A., Parc de Haute Technologie, Sophia–Antipolis: 2024. Available online: https://www.transvalor.com/en/forge (accessed on 24 September 2024).
- Walton, H.W. Deflection Methods to Estimate Residual Stress. In Handbook of Residual Stress and Deformation of Steel; Totten, G., Howes, M., Inoue, T., Eds.; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2002; pp. 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.M.; Ding, H. Experimental and Numerical Study of the Subsurface Deformation and Residual Stress during the Roller Burnishing Process. Procedia CIRP 2020, 87, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).