Influence of Welding Speed on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Laser-Welded Joints in 316L Stainless Steel Sheets
Abstract
1. Introduction
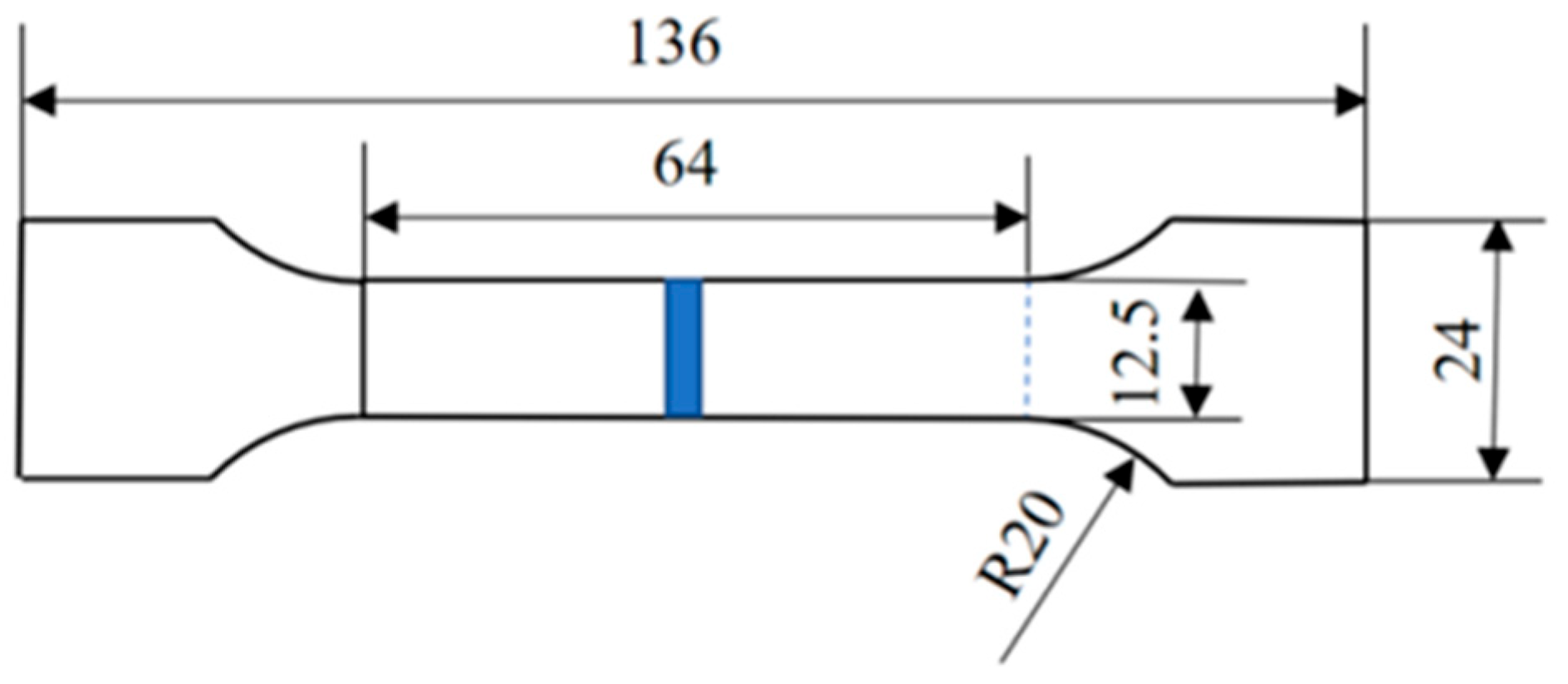
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Setup
3. Results and Discussion
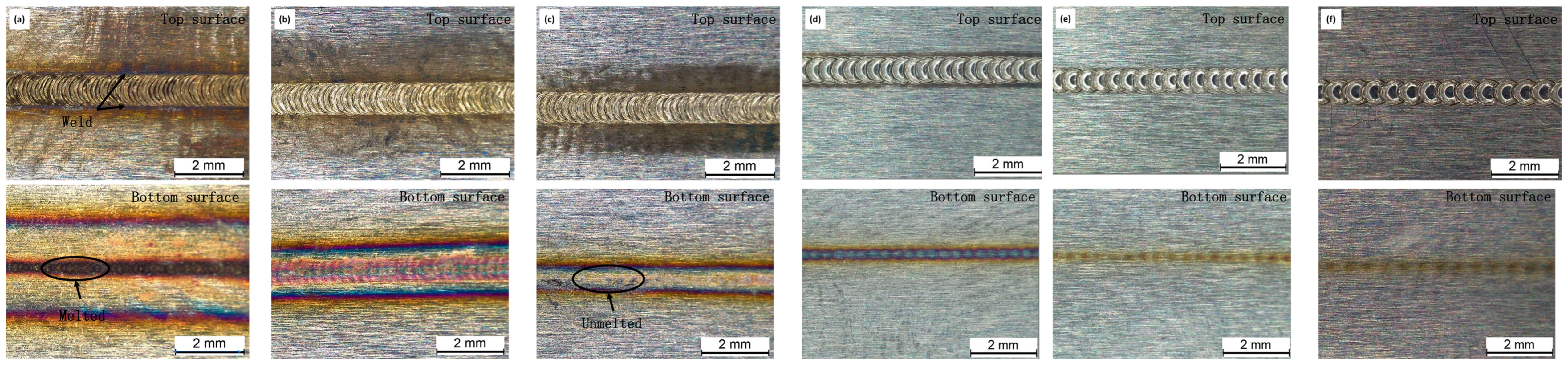
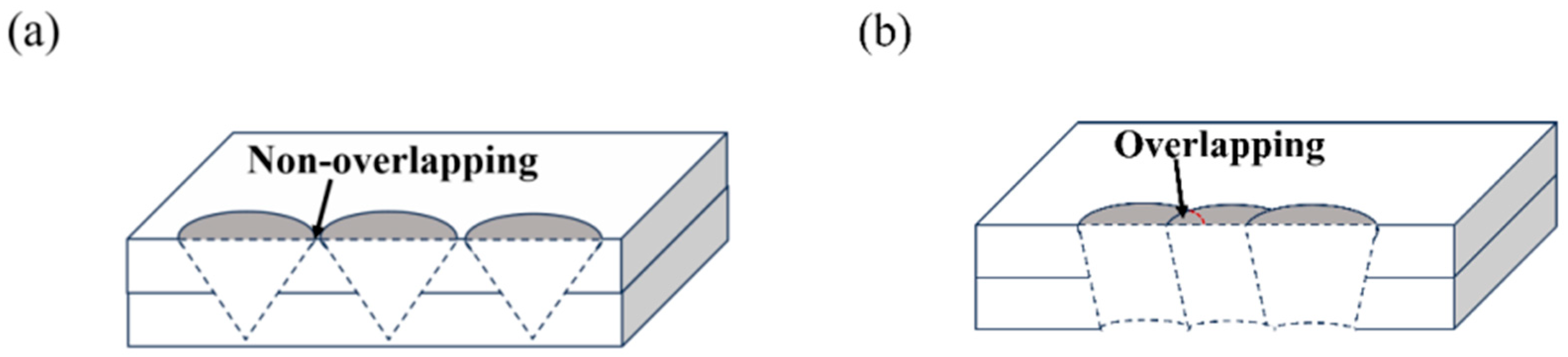
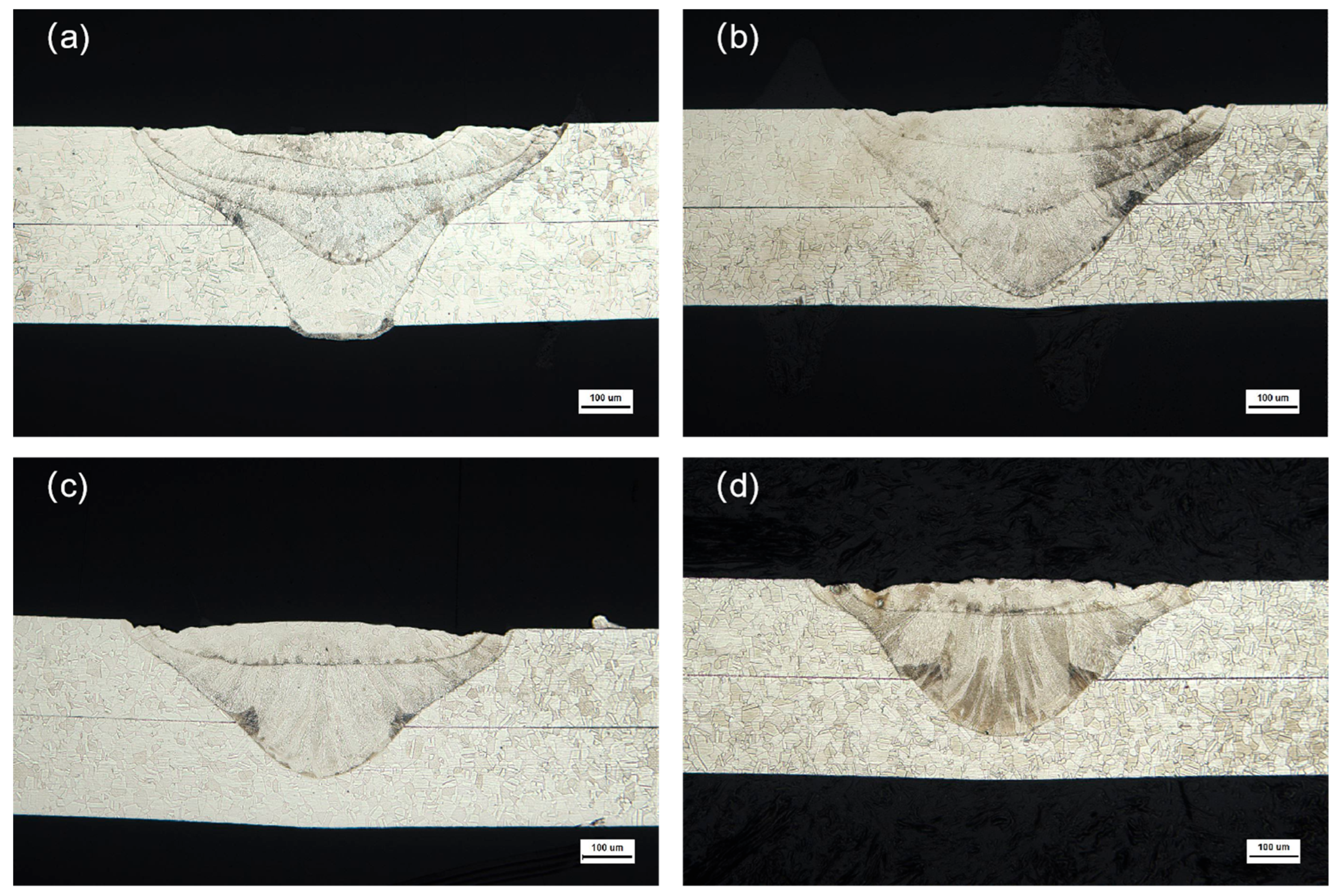
3.1. Effect of Welding Speed on Macromorphology
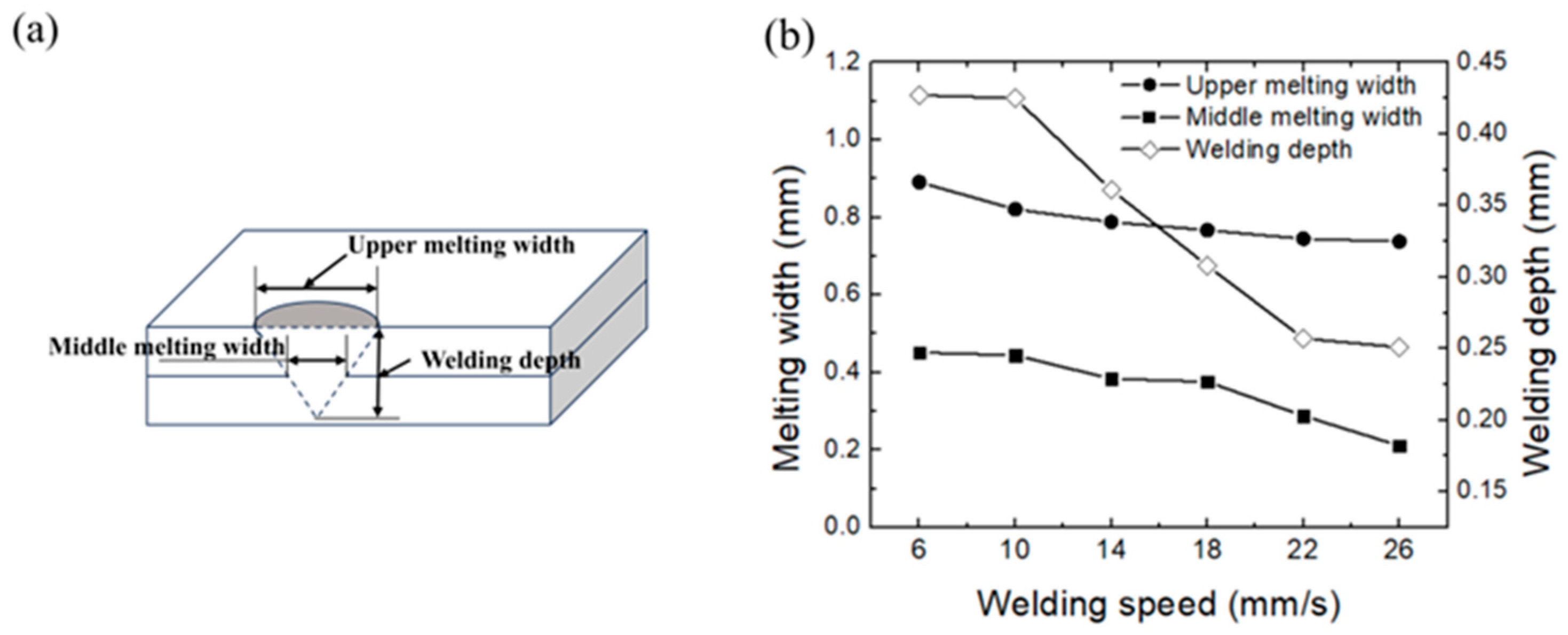
3.2. Effect of Welding Speed on Weld Microstructure
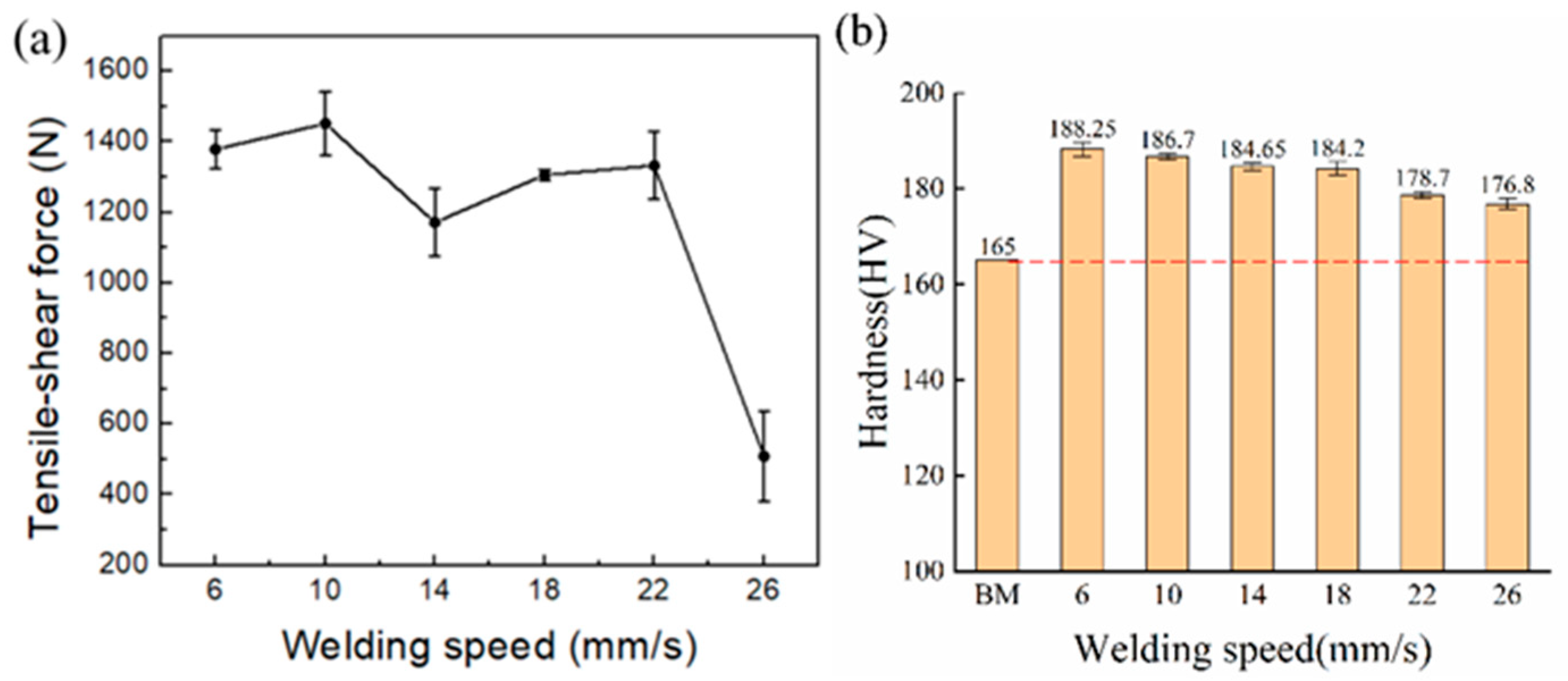
3.3. Effect of Welding Speed on Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
- I
- Welding speeds between 10 mm/s and 14 mm/s provide the best balance between sufficient heat input, appropriate overlap factor, and favorable mechanical performance, without causing defects such as burn-through or incomplete fusion. At a welding speed of 6 mm/s, the weld surface exhibits a fish scale morphology (commonly observed in pulsed laser welding [19]), while the bottom surface achieves full penetration but displays burn-through defects and oxidation. As the welding speed increases, reduced heat input leads to partial penetration with localized burn marks induced by single-pulse thermal conduction to the substrate. This aligns with Ref. [19], where excessive heat input at low speeds exacerbates burn-through, emphasizing the critical role of pulse parameter optimization (e.g., power, pulse duration) in weld morphology control.
- II
- Increasing welding speed reduces heat input, causing decreases in upper melt width, middle melt width, and penetration depth until a threshold heat input stabilizes the penetration depth. No discernible heat-affected zone (HAZ) is observed due to the ultra-thin sheet geometry (0.2 mm) and rapid cooling. Ferritic columnar grains at the fusion boundary exhibit epitaxial growth perpendicular to the fusion line, while the weld core comprises short-lath ferrite and globular ferrite arranged in parallel. Compared to Ref. [20], where δ-ferrite transitions from skeletal to lathy morphology with increasing speed, the distinct globular-lath duplex structure here arises from thinner material (0.2 mm vs. 0.5 mm) and higher cooling rates. Ref. [21] attributes phase evolution to carburization-induced carbon diffusion, but in this study, hardness enhancement (6–14% over base metal) stems from grain refinement rather than carburization effects.
- III
- Within the welding speed range of 6–22 mm/s, the tensile–shear strength fluctuates slightly, with fractures consistently occurring in the base material, indicating weld integrity exceeding parent metal strength. At 26 mm/s, the minimum tensile–shear force (509 N) correlates with incomplete fusion due to insufficient heat input, consistent with Ref. [22], where low power density–long duration (LPDL) modes mitigate porosity and enhance bonding. Ref. [23] reports residual stress concentration in HAZ for thicker plates, but the absence of HAZ here ensures uniform hardness distribution across the weld, highlighting advantages of laser welding for ultra-thin 316L sheets.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rännar, L.-E.; Koptyug, A.; Olsén, J.; Saeidi, K.; Shen, Z. Hierarchical structures of stainless steel 316L manufactured by Electron Beam Melting. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 17, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczotkarz, N.; Mrugalski, R.; Maruda, R.W.; Królczyk, G.M.; Legutko, S.; Leksycki, K.; Dębowski, D.; Pruncu, C.I. Cutting tool wear in turning 316L stainless steel in the conditions of minimized lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2021, 156, 106813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Silva, E.M.F.; Da Fonseca, G.S.; Ferreira, E.A. Microstructural and selective dissolution analysis of 316L austenitic stainless steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 4317–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, T.; Panton, B.; Lippold, J. Analysis of the laser welding keyhole using inline coherent imaging. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 82, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakmanesh, M.R.; Shamanian, M. Effects of Process Parameters on the Tensile-Shear Strength of Pulsed Laser Welded Thin 316L Stainless Steel Foils. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2017, 70, 2389–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamov, E.M.; Mishin, M.A.; Shiganov, I.N.; Taksants, M.; Efimov, E. Features of pulsed laser welding with deep fusion penetration. Weld. Int. 2019, 33, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, C.; Duan, J. Combined pulse laser: Reliable tool for high-quality, high-efficiency material processing. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 153, 108209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Song, Y.T.; Wei, J.; Xin, J.J.; Wu, H.P.; Salminen, A.; Handroos, H. Design and Analysis of the Laser Robotic Welding System for ITER Correction Coil Case. J. Fusion Energy 2015, 34, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Akbari, M.; Karimipour, A.; Karimi, A.; Soleimani, A.; Afrand, M. Effects of the laser parameters on the mechanical properties and microstructure of weld joint in dissimilar pulsed laser welding of AISI 304 and AISI 420. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 103, 103081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Tao, W.; Luo, H.; Yang, S. Effect of welding speed on microstructure and mechanical behavior of laser welded Al-Si coated 22MnB5 steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 154, 108344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, S.; Rajendran, R.; Shashi Kumar, S. Effect of travel speed on the microstructure and mechanical properties of laser beam welded nitronic-50 stainless steel joints. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2023, 237, 1847–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Wang, S.; Sun, W.; Geng, Z.; Xin, J.; Ke, L. Effect of welding speed on microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melting Inconel 625 alloy laser welded joint. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 2093–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köse, C.; Kacar, R. Effect of welding speed on the mechanical properties and microstructure of laser welded AISI 316L stainless steel. J. Fac. Eng. Archit. Gazi Univ. 2015, 30, 225–235. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, P.; Du, X.; Kan, Y.; Peng, L.; Lai, X. Modeling and Experimental Study of Laser Welding Distortion of Thin Metallic Bipolar Plates for PEM Fuel Cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 4850–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, O.; Shakeri, M.; Imen, S.J.; Aval, H.J. Small-scale resistance seam welding of stainless steel bipolar plates of PEM fuel cells. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 13822–13835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Shin, Y.C. Laser keyhole welding of stainless steel thin plate stack for applications in fuel cell manufacturing. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2015, 20, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 228.1-2021; Metallic materials-Tensile testing-Part 1: Method of test at room temperature. State Administration for Market Regulation & Standardization Administration of the P.R.C.: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Torkamany, M.J.; Hamedi, M.J.; Malek, F.; Sabbaghzadeh, J. The effect of process parameters on keyhole welding with a 400 W Nd : YAG pulsed laser. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2006, 39, 4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, F.; Tan, C.; Zhou, Y.N.; Peng, P. Effect of heat input modes on microstructure, mechanical properties and porosity of laser welded NiTi-316L joints: A comparative study. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 848, 143426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Lee, M.; Kim, C.K.; Song, S.; Cha, S.C.; Park, H.J.; Kim, J.-H.; Jeong, B. Effect of Carburization on the Microstructure and Laser Weldability of 316L Stainless Steel. J. Korean Weld. Join. Soc. 2023, 41, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanciu, E.M.; Pascu, A.; Roată, I.C.; Iatan, C.; Moldovan, E.R.; Tierean, M.H. Millisecond pulsed laser welding of AISI 316 stainless steel. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1251, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragavendran, M.; Vasudevan, M. Effect of Laser and Hybrid Laser Welding Processes on the Residual Stresses and Distortion in AISI Type 316L(N) Stainless Steel Weld Joints. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2021, 52, 2582–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Guo, X.; Lei, Y.; Lin, J.; Fu, H.; Xiao, R.; Huang, T.; Shin, Y.C. Welding deformation of ultra-thin 316 stainless steel plate using pulsed laser welding process. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 119, 105583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| C | Si | Mn | S | P | Cr | Ni | Mo | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.013 | 0.605 | 1.304 | 0.002 | 0.029 | 16.64 | 10.01 | 2.085 | Bal. |
| Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Ultimate tensile strength (MPa) | 495 |
| Yield strength (MPa) | 182 |
| Elongation (%) | 40 |
| Microhardness (HV) | 165 |
| Parameter (Unit) | Value |
|---|---|
| Peak power (kW) | 1.2 |
| Pulse frequency (Hz) | 50 |
| Pulse width range (ms) | 2 |
| Welding speed (mm/s) | 6–26 |
| Position of the laser spot | On the surface |
| V (mm/s) | D (mm) | T (ms) | Qf (%) | HI (J/mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 0.925 | 2 | 87.2 | 20.0 |
| 10 | 0.863 | 2 | 77.3 | 12.0 |
| 14 | 0.775 | 2 | 65.1 | 8.6 |
| 18 | 0.783 | 2 | 56.0 | 6.7 |
| 22 | 0.746 | 2 | 44.3 | 5.5 |
| 26 | 0.700 | 2 | 30.9 | 4.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Nie, Y.; Feng, Q.; Liang, X.; Lei, H.; Niu, S.; Lou, M. Influence of Welding Speed on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Laser-Welded Joints in 316L Stainless Steel Sheets. Metals 2025, 15, 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060624
Liu J, Nie Y, Feng Q, Liang X, Lei H, Niu S, Lou M. Influence of Welding Speed on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Laser-Welded Joints in 316L Stainless Steel Sheets. Metals. 2025; 15(6):624. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060624
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jianqiang, Yu Nie, Qiaobo Feng, Xiuyu Liang, Haiyang Lei, Sizhe Niu, and Ming Lou. 2025. "Influence of Welding Speed on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Laser-Welded Joints in 316L Stainless Steel Sheets" Metals 15, no. 6: 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060624
APA StyleLiu, J., Nie, Y., Feng, Q., Liang, X., Lei, H., Niu, S., & Lou, M. (2025). Influence of Welding Speed on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Laser-Welded Joints in 316L Stainless Steel Sheets. Metals, 15(6), 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060624







