Atomic Revealing of the Dissolution Behavior of Spinel Oxides on the 316L Surface in Alkaline High-Temperature and High-Pressure Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Specimens
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. DFT Calculation
3. Results and Discussion
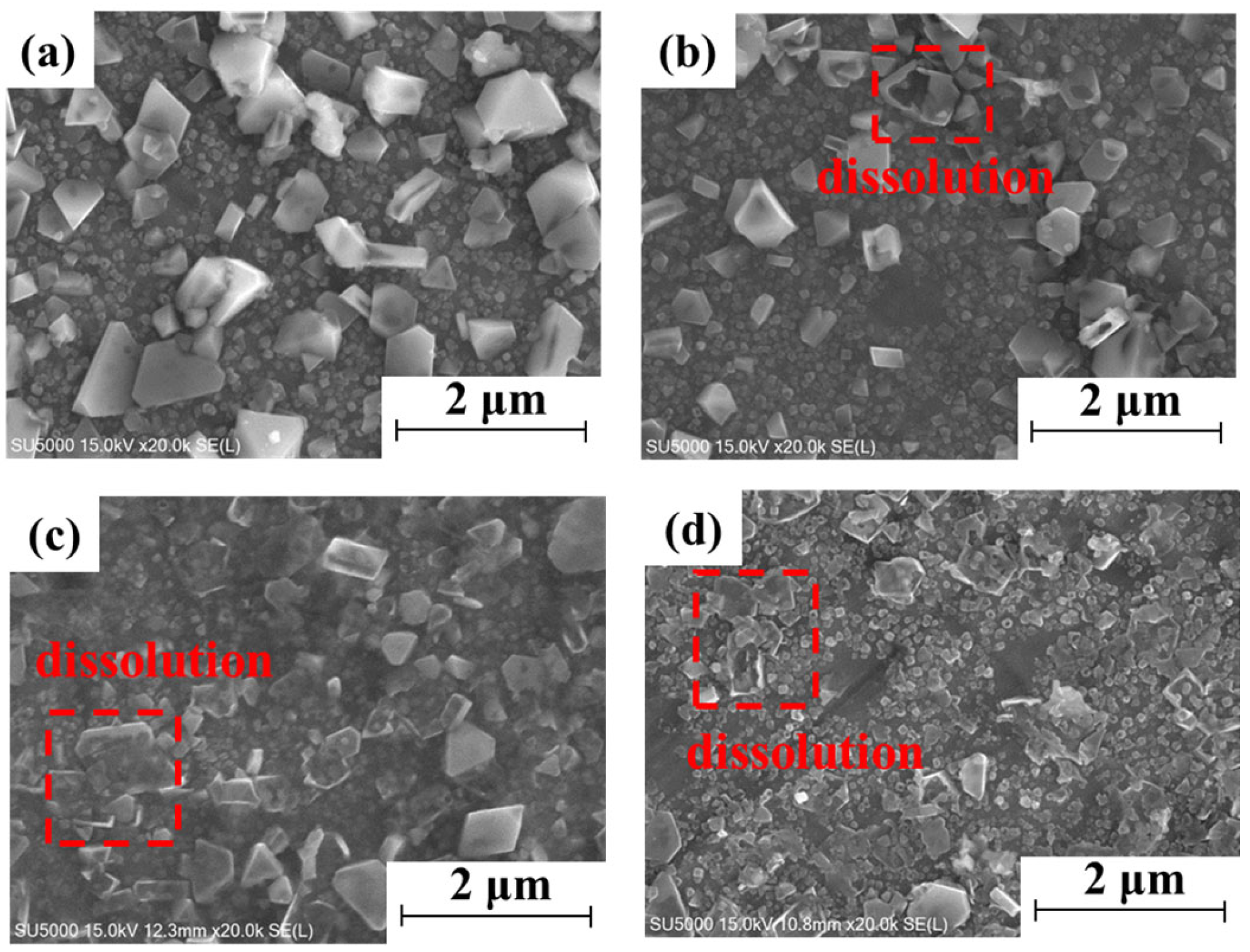
3.1. Exposure Experimental Results
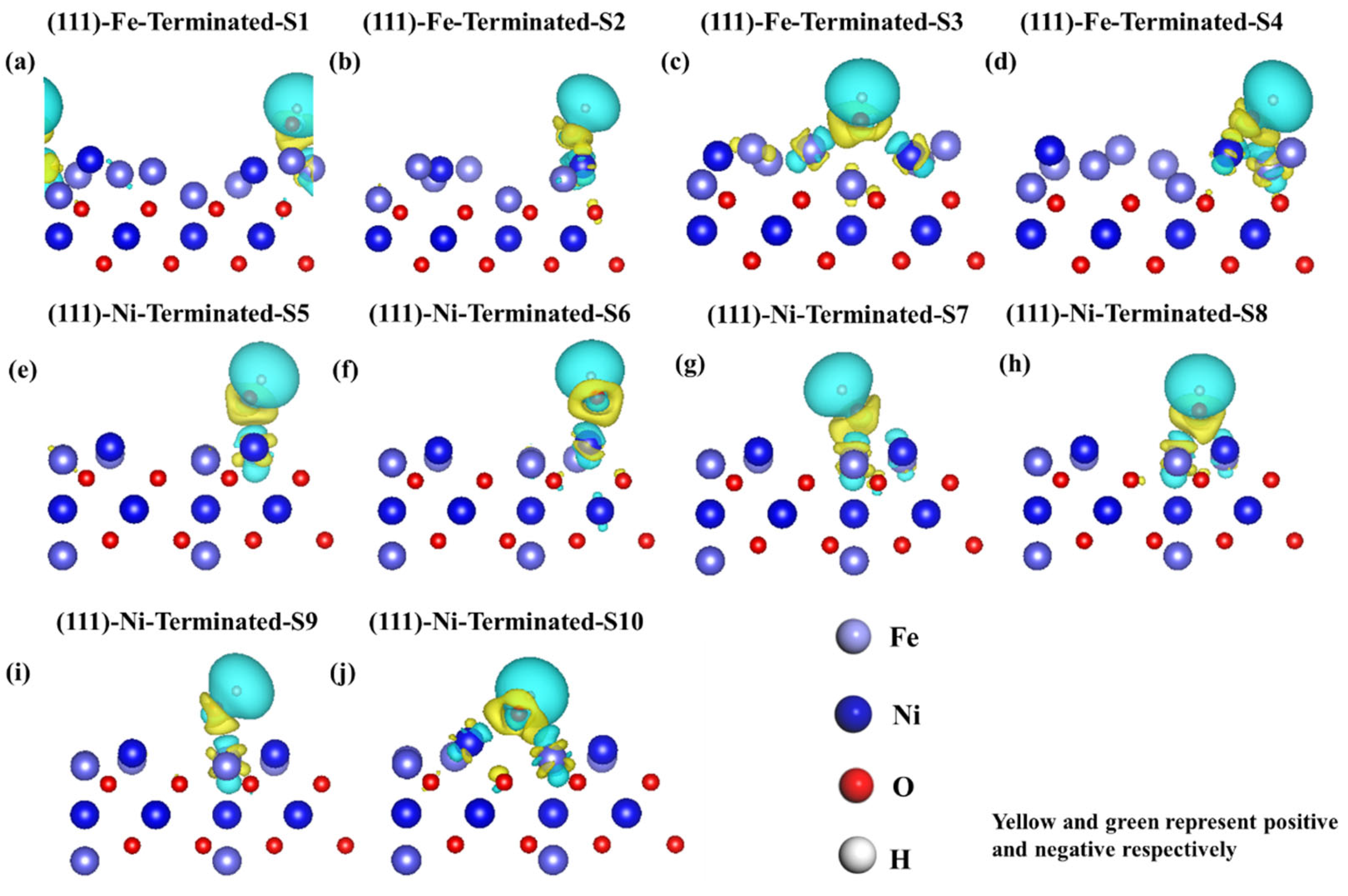
3.2. DFT Calculation Results
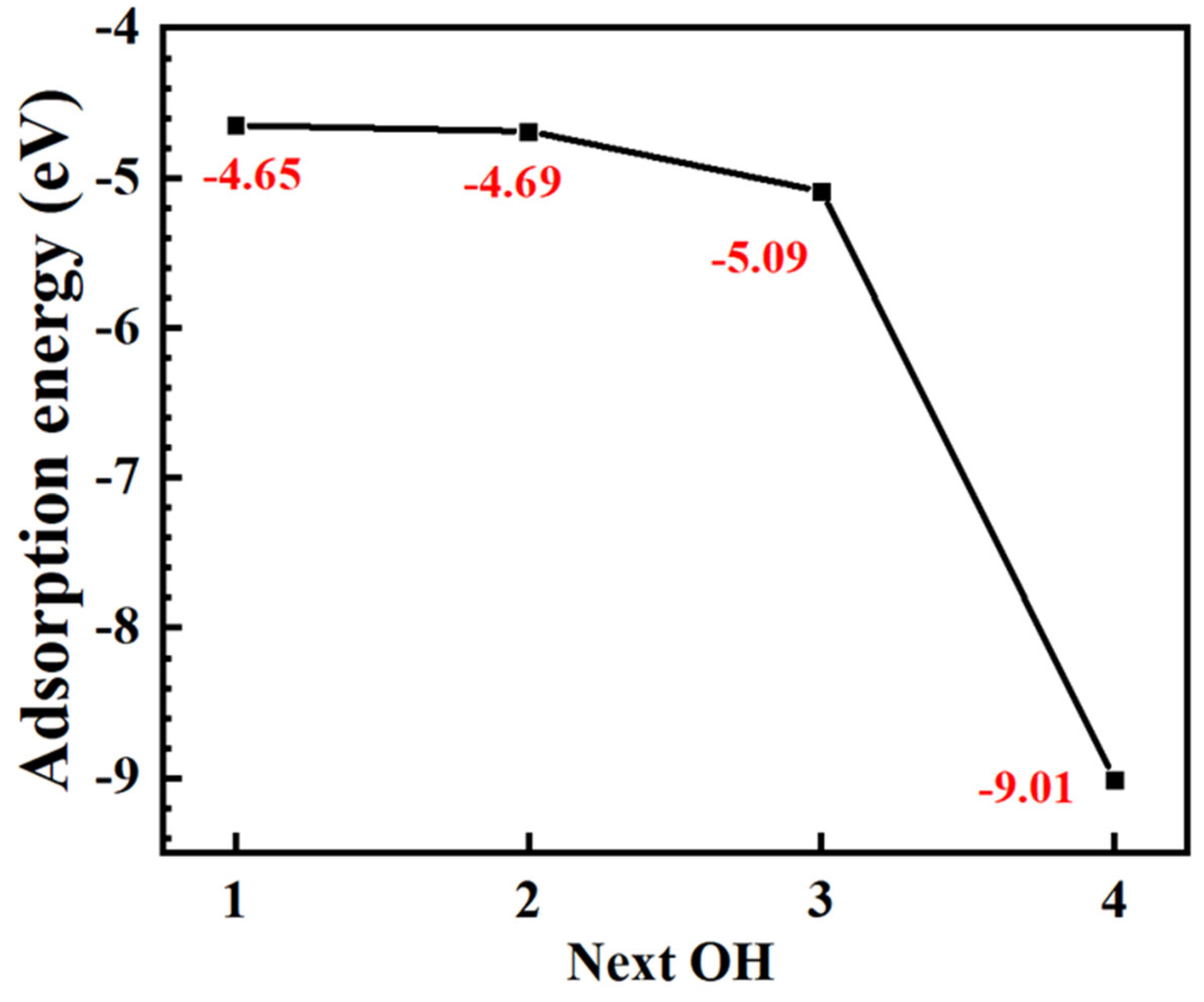
3.3. Dissolving Mechanism of Spinel Oxides in Alkaline Solution
4. Conclusions
- The oxide film on the surface of the 316L SS is a double-layer structure. The outer oxide layer is Fe-rich spinel oxide, and the inner layer is Cr-rich oxide;
- The inner oxide layer is dense and thickens with increasing exposure time. The outer oxide layer is loosely distributed and dissolved after 336 h;
- The thickness of the inner oxide layer increases with exposure time and stabilizes at approximately 100 nm;
- OH− is strongly adsorbed onto NiFe2O4. With increasing coverage, OH is more easily adsorbed.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herman, S.D.; Mehrotra, A.K. A heat-transfer model for tube fouling in the radiant section of once-through steam generators. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 99, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedeji, O.E.; Kumar, A.; Perdicakis, B.; Sanders, R.S. Investigation of solid particle erosion-related failures in once-through steam generators (OTSGs) in oil sands in-situ production: The limitations of the API RP 14E guideline in OTSG design or operational decision-making. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 101, 6135–6150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrodnikov, A.V.; Toshinsky, G.I.; Komlev, O.G.; Dragunov, Y.; Stepanov, V.; Klimov, N.; Generalov, V.; Kopytov, I.; Krushelnitsky, V. Innovative nuclear technology based on modular multi-purpose lead–bismuth cooled fast reactors. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2008, 50, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, A.; Takaki, N.; Sekimoto, H. A feasible core design of lead bismuth eutectic cooled CANDLE fast reactor. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2009, 36, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldhoff, J.F.; Hirsch, T.; Pitz-Paal, R.; Valenzuela, L. Transient models and characteristics of once-through line focus Systems. Energy Procedia 2015, 69, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Xin, L.; Lu, Y.; Shoji, T.; Takeda, Y.; Otsuka, Y.; Mutoh, Y. The synergy of corrosion and fretting wear process on Inconel 690 in the high temperature high pressure water environment. J. Nucl. Mater. 2018, 502, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Qiu, G.; Yu, H.; Zhou, P.; Wang, S.; Zhang, K.; Guo, Q.; Ren, L.; Xu, J. The Fouling Behavior of Steam Generator Tube at Different Positions in the High-Temperature Water. Metals 2021, 11, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Su, M.; Yan, P.; Zou, L.; Schreiber, D.K.; Baer, D.R.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, G.; Wang, Y.; Bruemmer, S.M.; et al. Atomic origins of water-vapour-promoted alloy oxidation. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.; Zhang, T.; Yuan, Y.; Guo, Q.; Liu, Z.; Liu, F.; Xu, J.; Shoji, T. Effects of dissolved oxygen on the corrosion-related unidentified deposit formed of 304 SS in the flow accelerated zone under the simulated secondary water chemistry. Corros. Commun. 2024, 16, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.; Bai, Z.; Wei, S.; Yuan, Y.; He, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Xu, J. Effects of pH on the corrosion behavior of 316L SS in SMRs for boron-free lithium-containing high-temperature water: Experiments and calculations. Surf. Interfaces 2025, 56, 105750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.H.; Peng, Q.J.; Sato, T.; Shoji, T. An ATEM study of oxidation behavior of SCC crack tips in 304L stainless steel in high temperature oxygenated water. J. Nucl. Mater. 2005, 347, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yuan, S.; Wu, R.; Wei, S.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Yu, H.; Sun, D. Effect of surface hemispherical dent depth on the microstructure evolution and stress corrosion cracking of heat transfer tubes in steam generator. Corros. Sci. 2024, 230, 111950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, T.W.; Babbar, V.K.; Underhill, P.R. A pulsed eddy current probe for inspection of support plates from within Alloy-800 steam generator tubes. Am. Inst. Phys. 2014, 55, 112–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebardast, H.R.; Rogak, S.; Asselin, E. Electrochemical detection of corrosion product fouling in high temperature and high pressure solution. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 100, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.B.; Jang, C. Effect of dissolved hydrogen on the early corrosion behavior of 316 stainless steel in simulated PWR environments. J. Nucl. Mater. 2024, 591, 154907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Arjmand, F.; Zhang, L.; Abe, H. Investigation of the corrosion behavior of 304 L and 316 L stainless steels at high-temperature borated and lithiated water. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2015, 53, 1435–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, T.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, D.; Si, J.; Zhang, X.; Yu, H.; Shoji, T.; et al. Fouling on the secondary side of nuclear steam generator tube: Experimental and simulated study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 590, 153143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, D.D. The Point Defect Model for the Passive State. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1992, 139, 3434–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Han, E.H.; Wu, X. Effects of crevice geometry on corrosion behavior of 304 stainless steel during crevice corrosion in high temperature pure water. Corros. Sci. 2016, 111, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Han, E.H.; Ke, W. Effects of Surface State and Applied Stress on Stress Corrosion Cracking of Alloy 690TT in Lead-containing Caustic Solution. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2012, 28, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Nong, J.; Guo, Q.; Liu, Z.; Liu, F.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Shoji, T. Atomic insights into the preferential dissolution of Laves phase of 9% Cr heat resistant steels in the strong alkaline solution. Corros. Sci. 2024, 227, 111791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Ming, H.; Zhang, Z.; Han, E. Effect of pH on corrosion behavior of 316 L stainless steel in hydrogenated high temperature water. Mater. Corros. 2017, 69, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wu, X.; Han, E.H.; Wei, Y. Effects of pH and dissolved oxygen on electrochemical behavior and oxide films of 304SS in borated and lithiated high temperature water. Corros. Sci. 2012, 59, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, J.; Ren, Y.; Bai, Z.; Wei, S.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Xu, J.; Shoji, T. Combined dual-exposure test and DFT investigations into effects of interstitial hydrogen on oxide film of Alloy 600 in high temperature water. Corros. Sci. 2024, 238, 112371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, F.J.; Carvalho, V.E.; Costa, B.V.; de Castilho, C. Temperature dependent structure of low index copper surfaces studied by molecular dynamics simulation. Braz. J. Phys. 2004, 34, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obot, I.B.; Gasem, Z.M.; Umoren, S.A. Understanding the mechanism of 2-mercaptobenzimidazole adsorption on Fe (110), Cu (111) and Al (111) Surfaces: DFT and molecular dynamics simulations approaches. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 2367–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, N.; Kokalj, A. Chemistry of the interaction between azole type corrosion inhibitor molecules and metal surfaces. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 137, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Guo, Q.; Li, X.; Xu, J.; Shoji, T. Experiments and DFT calculations on the effects of interstitial hydrogen on Ti corrosion products in high temperature water. Corros. Sci. 2024, 232, 112014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.J.; Ding, K.N.; Zhang, Y.F.; Li, J.Q. A DFT study of acetonitrile adsorption and decomposition on the TiO2 (110) surface. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2011, 111, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Gao, W.; Jiang, Q. A universal picture for ejecting atoms on metallics. Acta Mater. 2022, 228, 117792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shen, T.; Yao, C.; Chang, H.; Wei, K.; Niu, L.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Z. Corrosion behavior of ferritic–martensitic steels SIMP and T91 in fast-flowing steam. Corros. Sci. 2021, 187, 109474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jin, P.; Shen, T.; Wang, Z. Microstructural evolution of early-stage oxide film on 15–15Ti austenitic stainless steel under 500 ℃ steam. Corros. Sci. 2022, 207, 110557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wu, X.; Han, E.H. Effects of temperature on the oxide film properties of 304 stainless steel in high temperature lithium borate buffer solution. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 2840–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romedenne, M.; Lambeets, S.; Song, M.; Roach, C.; Devaraj, A.; Pillai, R. Revealing the elusive role of water vapor in the oxidation behavior of a Mn-Si containing NiCr alloy at 950 °C. Corros. Sci. 2023, 221, 111348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Wang, S.Z.; Li, X.D.; Lu, J.M. Corrosion of an Austenitic Heat-Resistant Steel HR3C in High-Temperature Steam and Supercritical Water. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 908, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyurin, A.G. Estimation of the Effect of Molybdenum on Chemical and Electrochemical Stability of Iron-Based Alloys. Prot. Met. 2003, 39, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | N | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 0.31 | 0.94 | 0.012 | 0.001 | 16.93 | 12.2 | 2.43 | 0.02 | Bal. |
| Parameter | Parameter Range |
|---|---|
| Inner water | |
| Dissolved oxygen (DO) | 0 ppb |
| pH | 9.6 ± 0.1 |
| Flow rate | 10 ± 0.5 L/h |
| Pressure | 9 ± 0.2 MPa |
| Temperature | 300 ± 0.5 °C |
| Adsorption Sites | Adsorption Energy (eV) | d (Fe-O) Å | d (Ni-O) Å | d (H-O) Å |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | −3.03 | 1.76 | -- | 0.98 |
| S2 | −3.43 | 2.01 | -- | 0.97 |
| S3 | −3.45 | 1.80 | -- | 0.98 |
| S4 | −3.45 | 1.80 | -- | 0.98 |
| S5 | −3.46 | -- | 1.84 | 0.98 |
| S6 | −3.32 | 1.74 | 1.81 | 0.97 |
| S7 | −3.45 | 1.80 | -- | 0.98 |
| S8 | −3.44 | 1.80 | -- | 0.98 |
| Adsorption Sites | Adsorption Energy (eV) | d (Fe-O) Å | d (Ni-O) Å | d (H-O) Å |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | −4.66 | 1.74 | -- | 0.98 |
| S2 | −4.94 | 1.87 | 2.01 | 0.98 |
| S3 | −4.85 | 1.88 | 1.88 | 0.98 |
| S4 | −4.25 | 1.90 | 1.89 | 0.98 |
| S5 | −0.48 | -- | 1.79 | 0.98 |
| S6 | −0.61 | 1.81 | -- | 0.98 |
| S7 | −0.43 | 1.84 | -- | 0.97 |
| S8 | −0.45 | 1.83 | -- | 0.97 |
| S9 | −0.49 | 1.82 | -- | 0.98 |
| S10 | −0.64 | 1.99 | 1.94 | 0.97 |
| Eject Energy | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (011)-Fe-Terminated | (011)-Ni-Terminated | (111)-Fe-Terminated | (111)-Ni-Terminated | (022)-Fe-Terminated | (022)-Ni-Terminated | ||||||
| Fe1 | 6.59 | Fe3 | 9.42 | Fe1 | 4.23 | Fe4 | 4.82 | Fe1 | 7.41 | Fe3 | 8.29 |
| Fe2 | 5.27 | Ni1 | 6.37 | Fe2 | 2.52 | Ni1 | 3.26 | Fe2 | 6.67 | Ni2 | 7.43 |
| -- | -- | Ni2 | 6.35 | Fe3 | 4.64 | -- | -- | Ni1 | 4.58 | -- | -- |
| -- | -- | Ni3 | 5.76 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Zhu, C.; Zou, X.; Wu, H.; Xu, J. Atomic Revealing of the Dissolution Behavior of Spinel Oxides on the 316L Surface in Alkaline High-Temperature and High-Pressure Water. Metals 2025, 15, 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060602
Zhang B, Zhu C, Zou X, Wu H, Xu J. Atomic Revealing of the Dissolution Behavior of Spinel Oxides on the 316L Surface in Alkaline High-Temperature and High-Pressure Water. Metals. 2025; 15(6):602. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060602
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bin, Congbin Zhu, Xiaoping Zou, Haodong Wu, and Jian Xu. 2025. "Atomic Revealing of the Dissolution Behavior of Spinel Oxides on the 316L Surface in Alkaline High-Temperature and High-Pressure Water" Metals 15, no. 6: 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060602
APA StyleZhang, B., Zhu, C., Zou, X., Wu, H., & Xu, J. (2025). Atomic Revealing of the Dissolution Behavior of Spinel Oxides on the 316L Surface in Alkaline High-Temperature and High-Pressure Water. Metals, 15(6), 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060602






