Carbon Steel A36 Planar Coupons Exposed to a Turbulent Flow Inside a 90° Pipe Elbow in a Testing Rack: Hydrodynamic Simulation and Corrosion Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Coupons and Reverse Osmosis Solutions
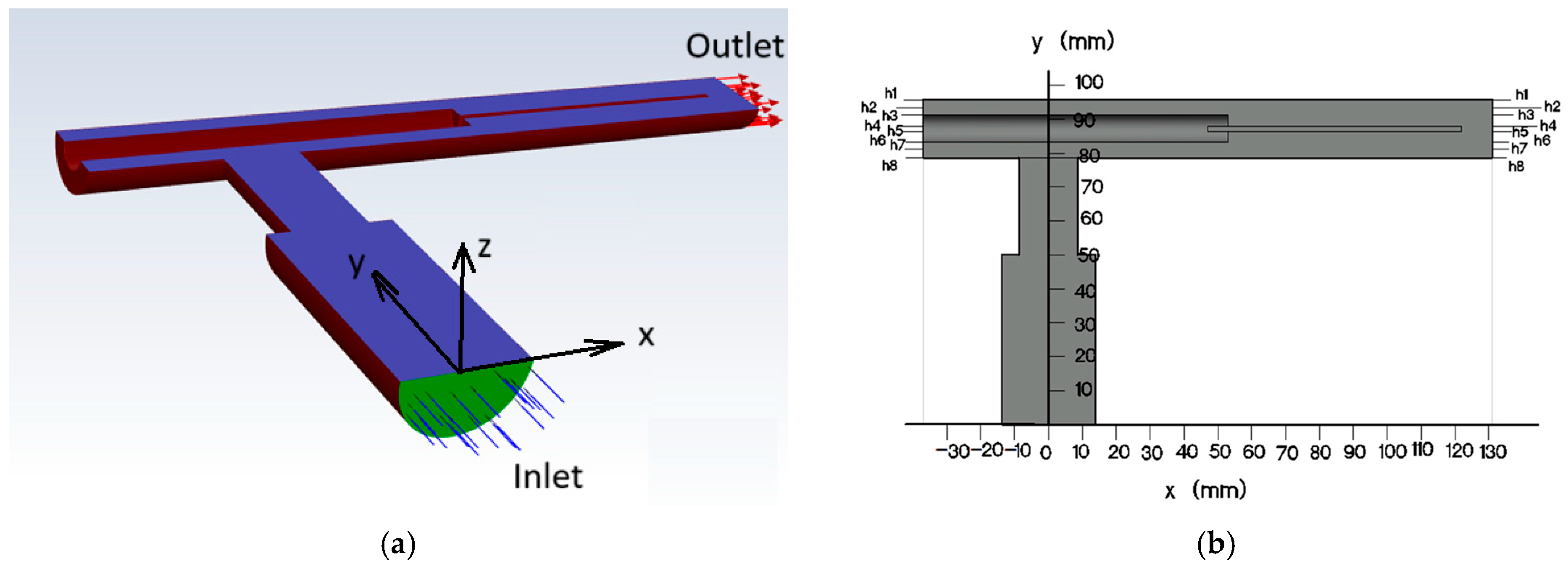
2.2. Experimental Apparatus
2.3. Fluid Flow Simulation Along the Coupon Compartment
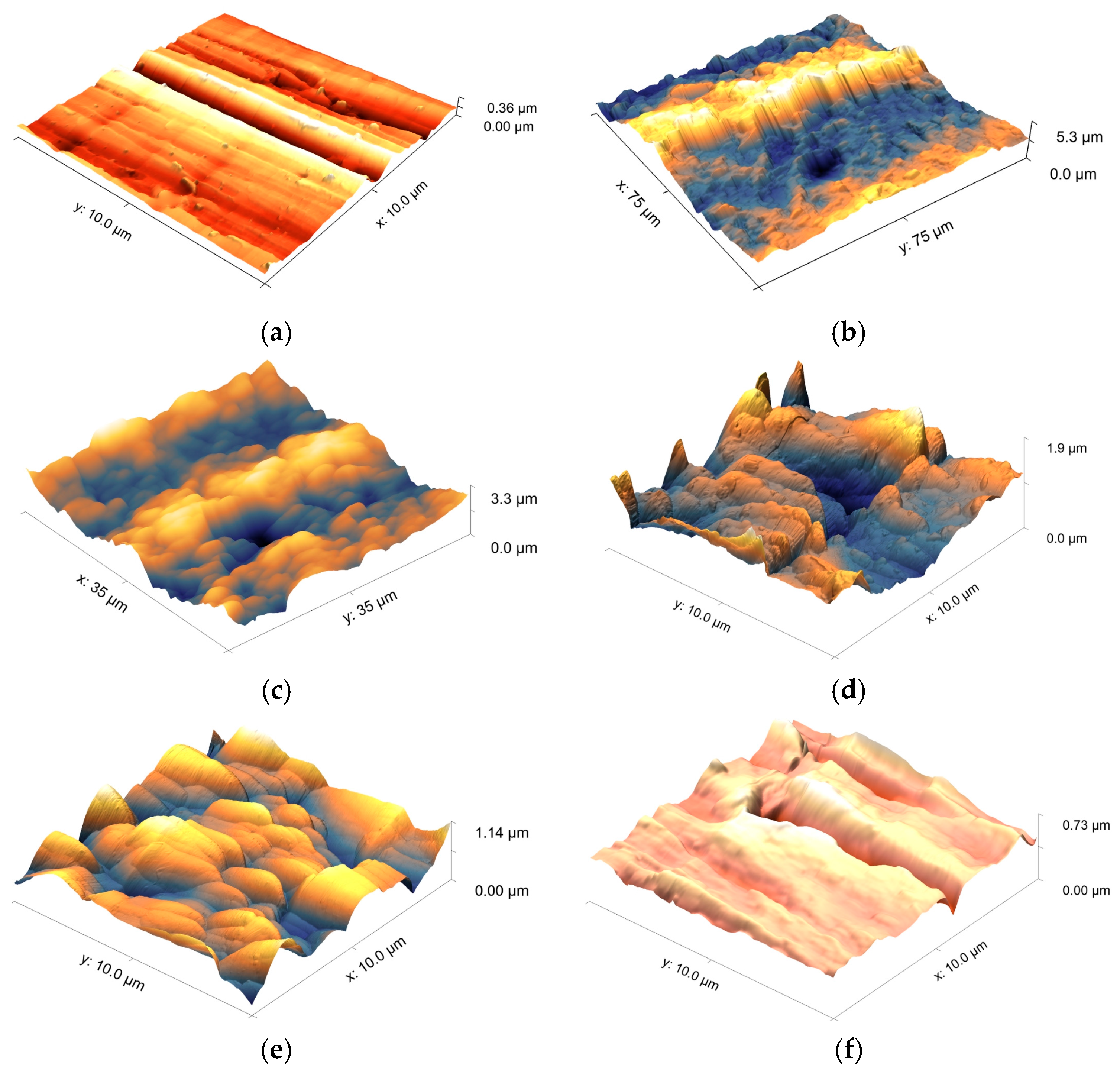
2.4. Surface Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
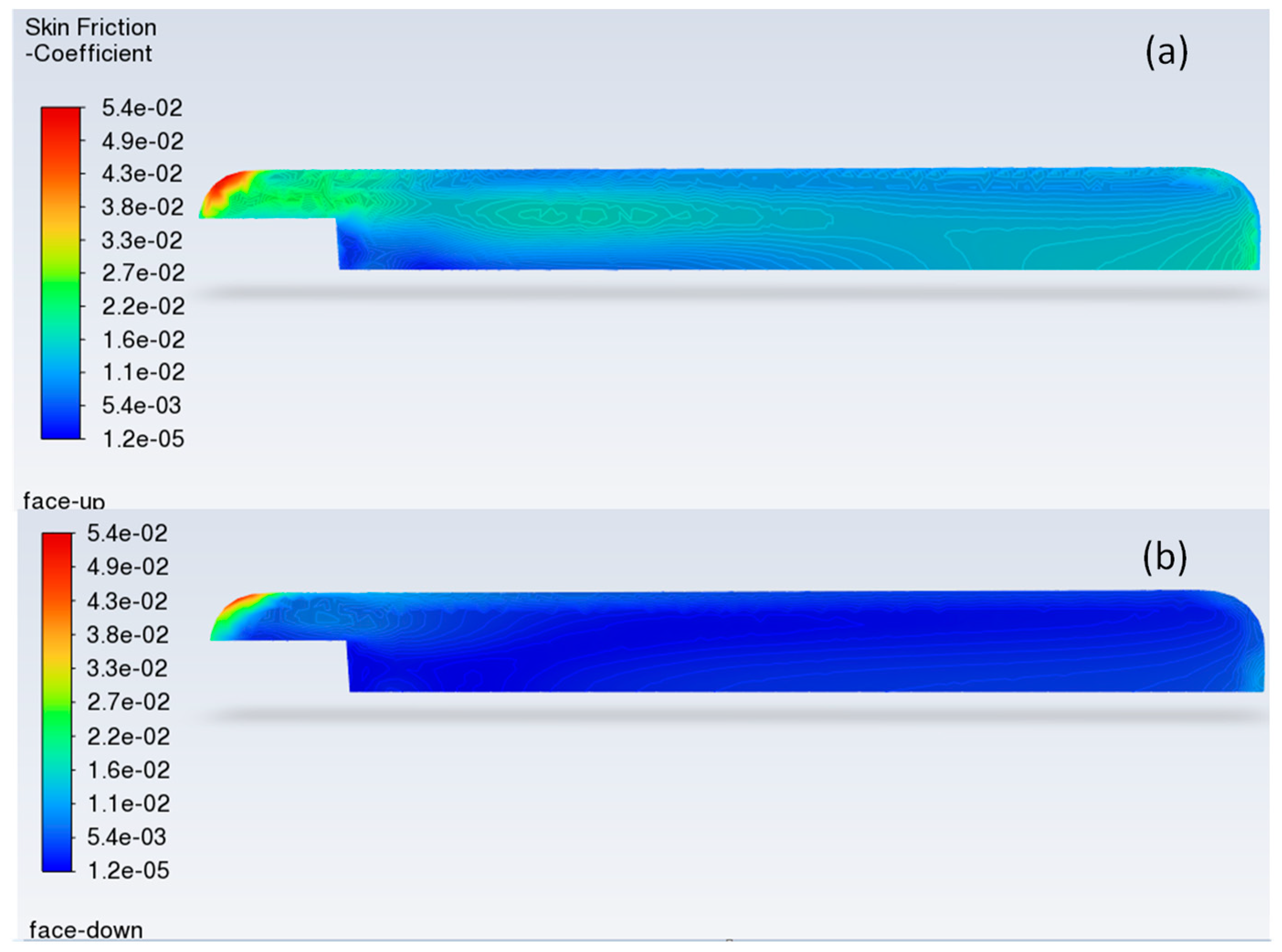
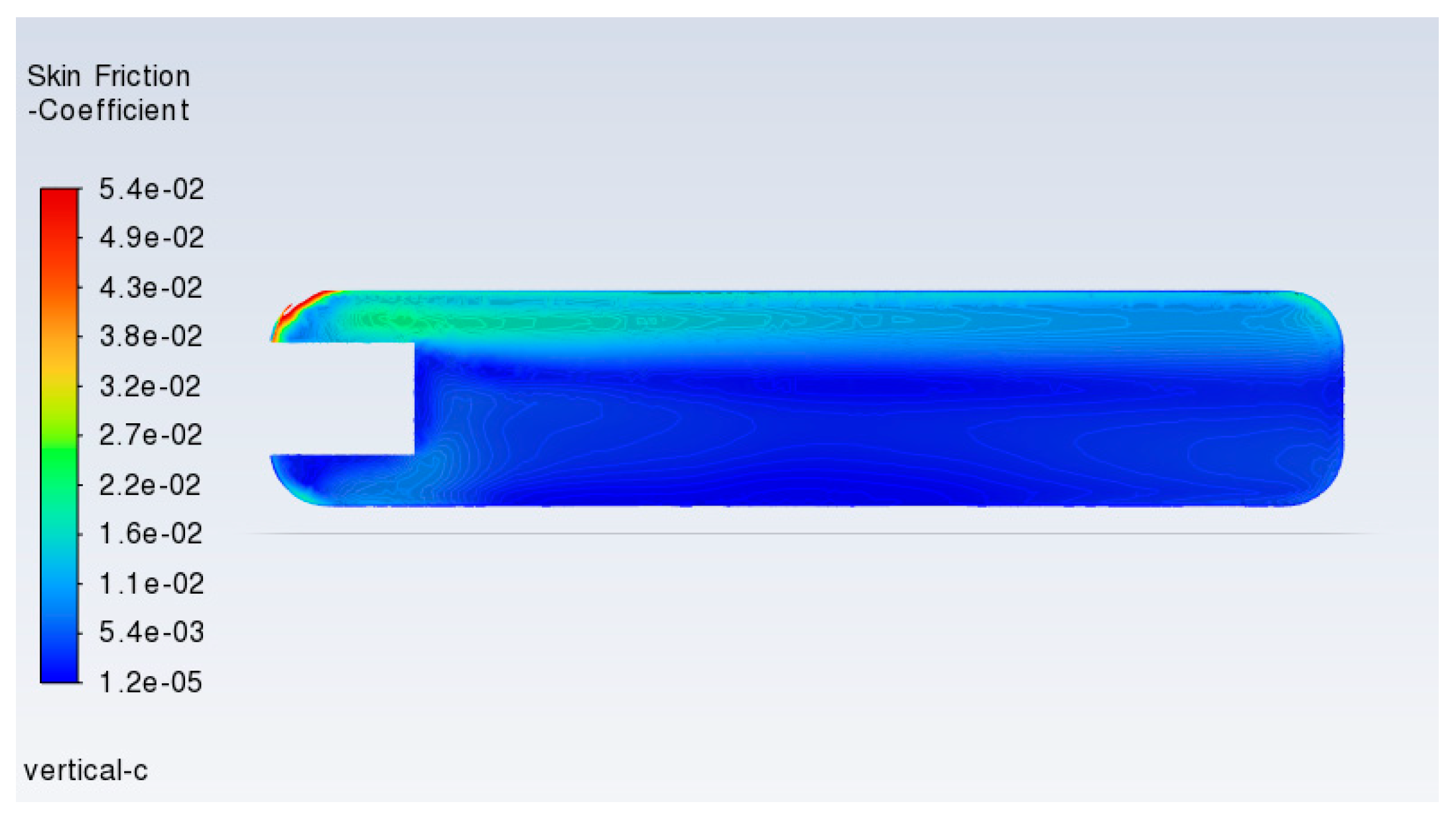
3.1. Hydrodynamic Simuations
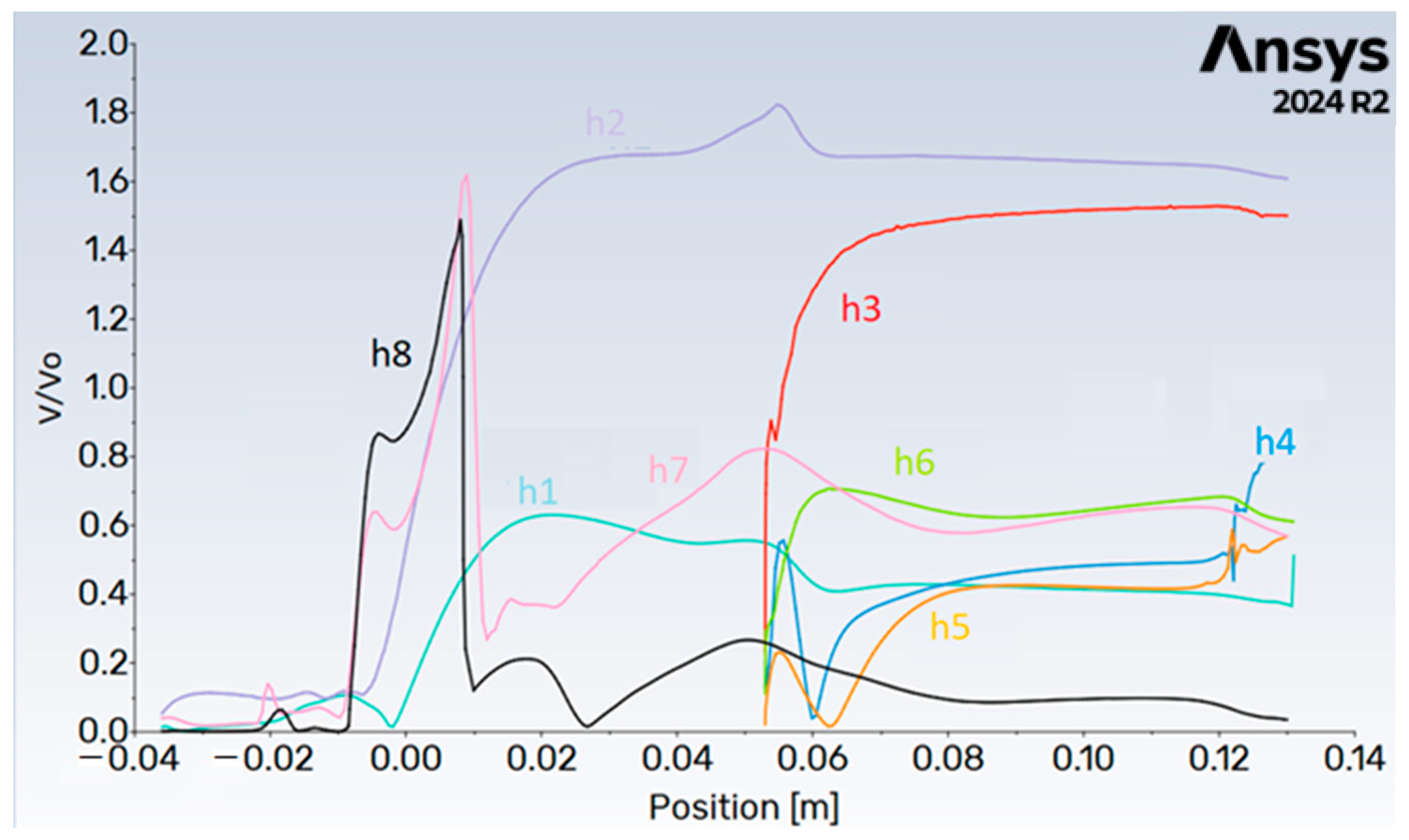
3.1.1. Velocity Distribution and Vorticity
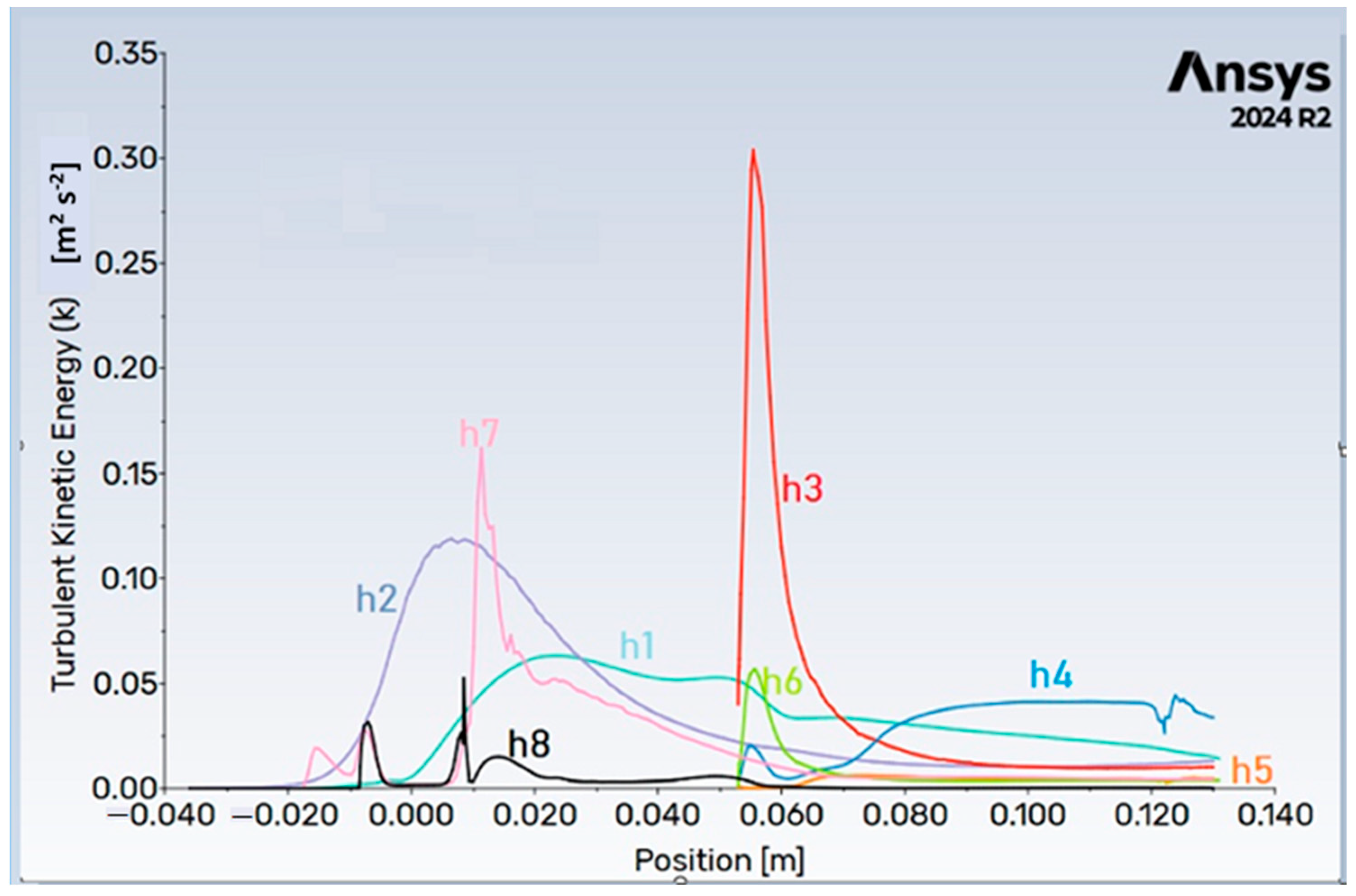
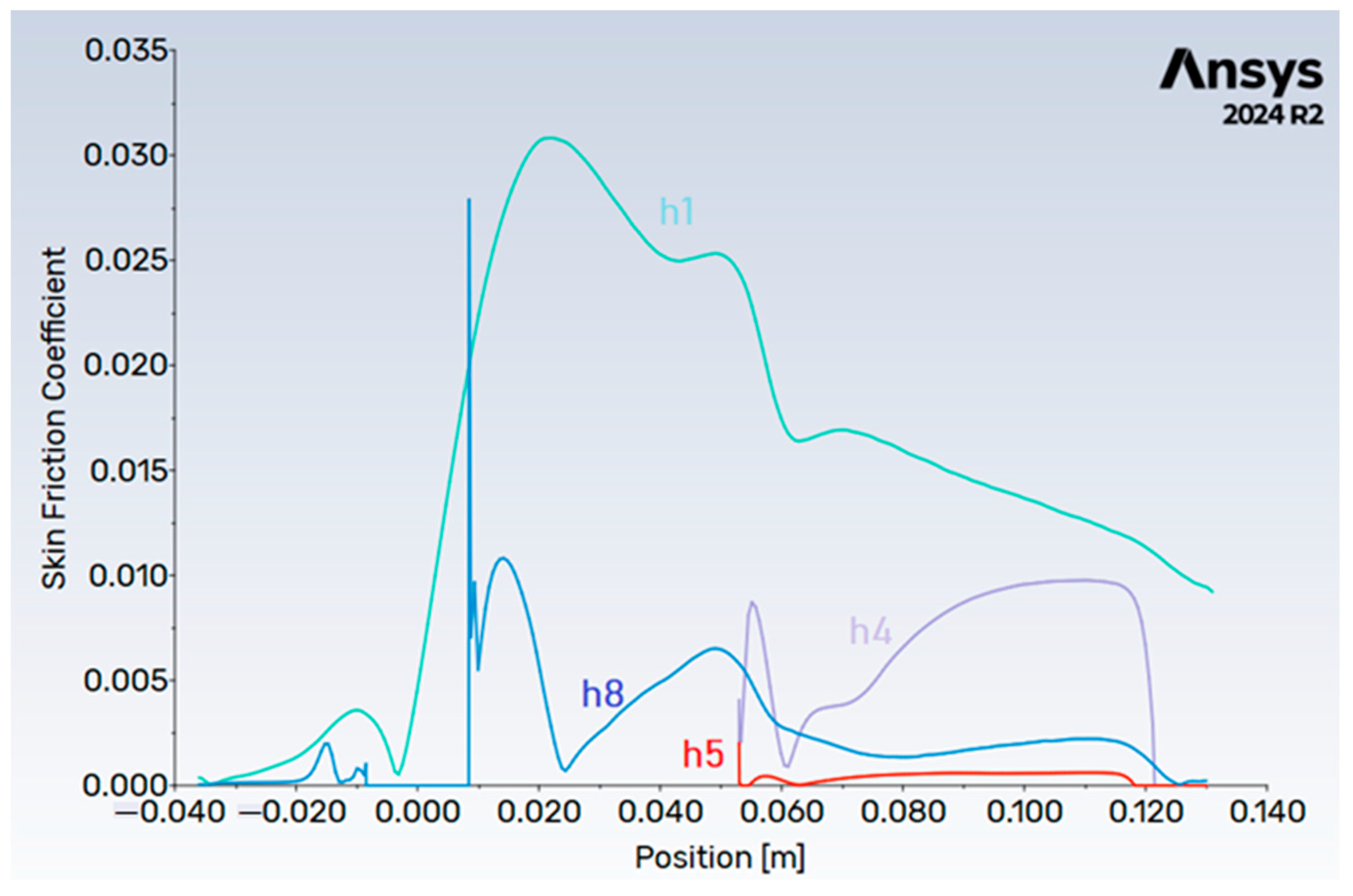
3.1.2. RANDS Parameters
3.1.3. Turbulence and Reynolds Number
3.2. Hydrodynamic Effect on Coupon Corrosion Rate
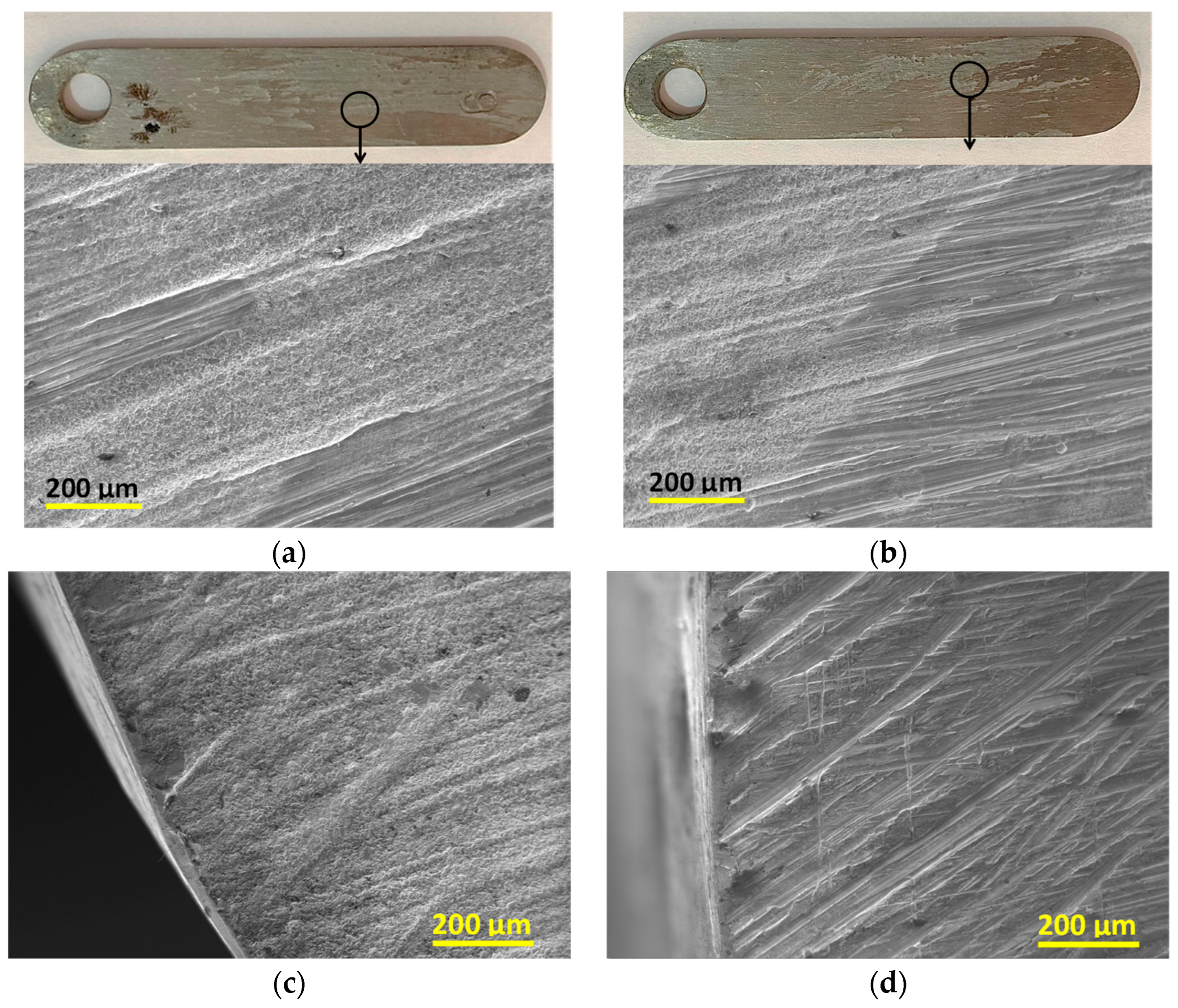
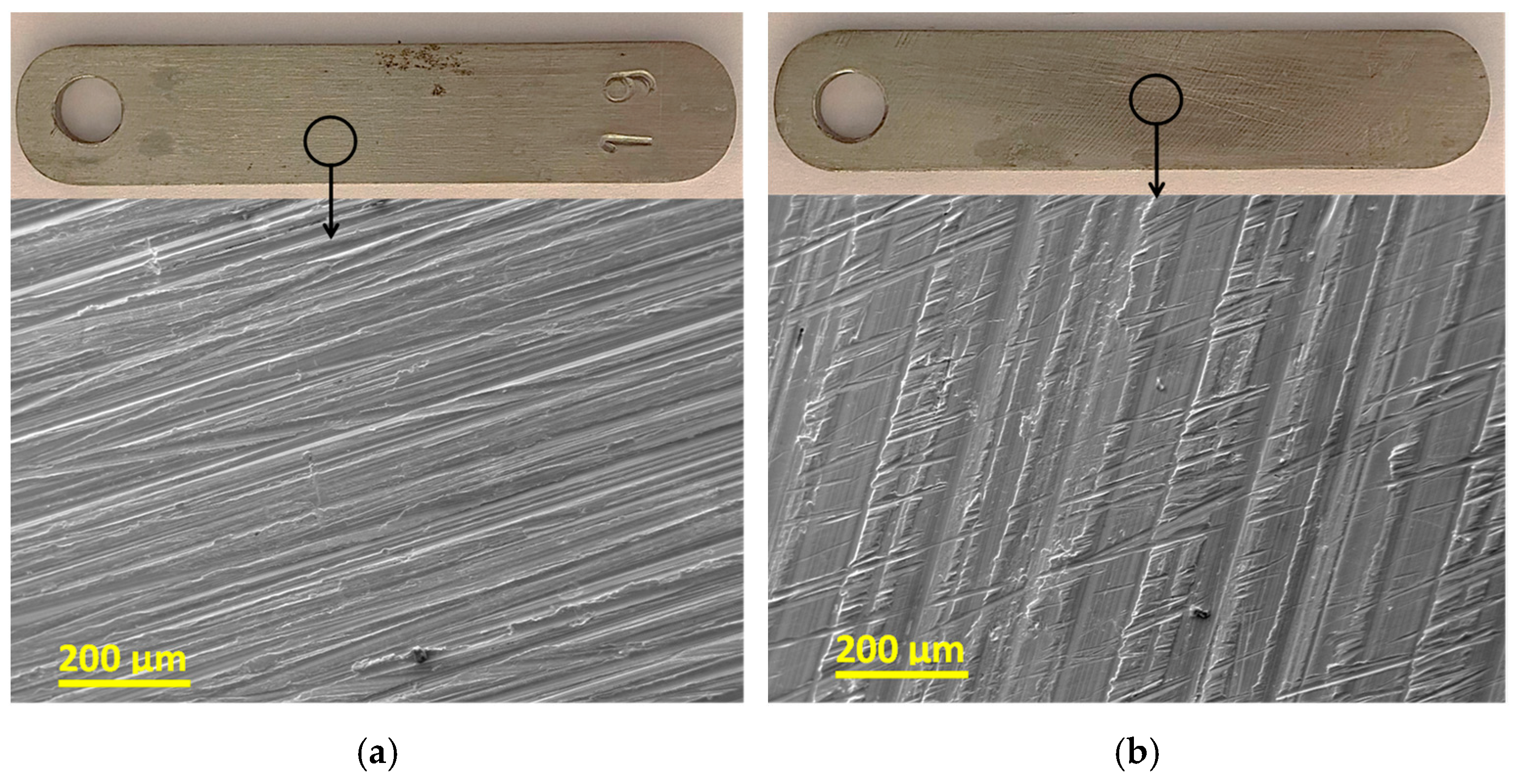
3.3. Morphological Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- The generation term iswhere is the vorticity magnitude, defined as
- The dissipation term iswhere .
- The generation term for is formulated aswhere , , , .
- The dissipation termwhere , , , strain rate is , is the vorticity with respect to axis .
References
- ASTM D 2688-05; ASTM International Standard Test Method for Corrosivity of Water in the Absence of Heat Transfer (Weight Loss Method). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2005.
- Benamor, A.; Talkhan, A.G.; Nasser, M.; Hussein, I.; Okonkwo, P.C. Effect of temperature and fluid speed on the corrosion behavior of carbon steel pipeline in Qatari oilfield produced water. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 808, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El–Gammal, M.; Mazhar, H.; Cotton, J.S.; Shefski, C.; Pietralik, J.; Ching, C.Y. The hydrodynamic effects of single–phase flow on flow accelerated corrosion in a 90-degree elbow. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2010, 240, 1589–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khunphakdee, P.; Chalermsinsuwan, B. Review of flow accelerated corrosion mechanism, numerical analysis, and control measures. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 197, 519–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhang, R.; Si, X. Effects of fluid dynamics parameters on flow-accelerated corrosion at elbow of carbon steel pipeline. Mater. Res. Express 2024, 11, 056520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elemuren, R.; Evitts, R.; Oguocha, I.; Kennell, G.; Odeshi, A.; Gerspacher, R. Influence of flow velocity on erosion–corrosion performance of 90° carbon steel elbows in potash brine. In Proceedings of the Canadian Society for Mechanical Engineering International Congress, Toronto, ON, Canada, 27–30 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Slaimana, Q.J.M.; Hasan, B.O. Study on corrosion rate of carbon steel pipe under turbulent flow conditions. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 88, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.; Zhang, R.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, K. Effects of local velocity components on flow–accelerated corrosion at 90° elbow. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 16557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.; Han, S.; Lee, G.; Maeng, W. Hydrodynamic parameters affecting flow-accelerated corrosion in elbows. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2024, 57, 103293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansys Fluent; Academic Version 2024 R2; Fluid Simulation Software; Ansys Fluent, Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2024.
- Ko, T.; Choi, H.G.; Bai, R.; Joseph, D.D. Finite element method simulation of turbulent wavy core–annular flows using a k–ω turbulence model method. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2002, 28, 1205–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, D.C. Formulation of the k–ω turbulence model revisited. AIAA J. 2008, 46, 2823–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqr, K.M.; Kassem, H.I.; Aly, H.S.; Wahid, M.A. Computational study of decaying annular vortex flow using the R ε/k–ε turbulence model. Appl. Math. Model. 2012, 36, 4652–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ajmal, T.S.; Arya, S.B.; Udupa, K.R. Effect of hydrodynamics on the flow accelerated corrosion (FAC) and electrochemical impedance behavior of line pipe steel for petroleum industry. Int. J. Press. Vessels Pip. 2019, 174, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshtkar, K.; Nematollahi, M.; Erfaninia, A. CFX study of flow accelerated corrosion via mass transfer coefficient calculation in a double elbow. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 7036–7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, H.P.; Divya, T.; Sahaya, R.R.; Kain, V.; Barua, D.K. CFD study of flow accelerated corrosion in 3D elbows. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2014, 69, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F.C.; Pereira, J.M.C.; Pereira, J.C.F. Vorticity transport in laminar steady rotating plumes. Phys. Fluids 2020, 32, 043604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, G.; Qin, W.; Pan, D.; Si, X. Empirical model of flow-accelerated corrosion at elbow of carbon steel pipeline based on dimensional analysis. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2024, 201, 110462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoesmith, D.W. Kinetics of Aqueous Corrosion, Corrosion: Fundamentals, Testing, and Protection; ASM International: Russell, OH, USA, 2003; Volume 13A. [Google Scholar]
- Chilton, T.H.; Colburn, A.P. Mass transfer (absorption) coefficients prediction from data on heat transfer and fluid friction. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1934, 26, 1183–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El–Feki, A.A.; Walter, G.W. Corrosion Rate Measurements under Conditions of Mixed Charge Transfer plus Diffusion Control Including the Cathodic Metal Ion Deposition Partial Reaction. Corros. Sci. 2000, 42, 1055–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, F.G. About Boussinesq’s turbulent viscosity hypothesis: Historical remarks and a direct evaluation of its validity. Comptes Rendus Mécanique 2007, 335, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Taylor, R.; Nithiarasu, P. The Finite Element Method for Fluid Dynamics, 8th ed.; Butterworth–Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2025. [Google Scholar]






| Run | Flow, L s−1 | Inlet Diameter, mm | Final Diameter, mm | Flow Velocity, m s−1 | Re |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.28 | 28 | 17 | 1.47 | 24,939 |
| 2 | 0.14 | 28 | 17 | 0.73 | 12,470 |
| 3 | 0.07 | 28 | 17 | 0.37 | 6235 |
| Volume-Averaged Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Re | Coupon Position | Vorticity Magnitude <VM>, s−1 | Turbulent Kinetic Energy <k>, m2 s−2 | Specific Dissipation Rate <w>, s−1 |
| 24,939 | Horizontal | 357.4 | 0.01580 | 1623.9 |
| Vertical | 317.5 | 0.01701 | 1413.2 | |
| 12,470 | Horizontal | 203.5 | 0.00311 | 1054.2 |
| Vertical | 176.2 | 0.00360 | 849.6 | |
| 6235 | Horizontal | 109.3 | 0.00042 | 739.3 |
| Vertical | 97.5 | 0.00058 | 563.1 | |
| Run | Coupon Position | Mass Flow, kg s−1 | , m s−1 | <f> | mc, m s−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Horizontal | 0.28 | 1.4 | 1.1 × 10−2 | 1.2 × 10−4 |
| Vertical | 0.28 | 1.4 | 7.1 × 10−3 | 7.9 × 10−5 | |
| 2 | Horizontal | 0.14 | 0.7 | 1.3 × 10−2 | 7.4 × 10−5 |
| Vertical | 0.14 | 0.7 | 9.4 × 10−3 | 5.2 × 10−5 | |
| 3 | Horizontal | 0.07 | 0.35 | 1.4 × 10−2 | 3.8 × 10−5 |
| Vertical | 0.07 | 0.35 | 1.3 × 10−2 | 3.5 × 10−5 |
| Run | mc, m s−1 | icorr, A m−2 | IE, % | , mmol O2 L−1 | , mmol O2 L−1 | kc, m s−1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Inhibitor | With Inhibitor | Without Inhibitor | With Inhibitor | Without Inhibitor | With Inhibitor | Without Inhibitor | With Inhibitor | |||
| 1 | 1.2 × 10−4 | 3.1 | 1.14 | 63.2 | 0.131 | 0.048 | 0.087 | 0.170 | 1.8 × 10−4 | 3.5 × 10−5 |
| 7.9 × 10−5 | 2.95 | 1.07 | 63.7 | 0.194 | 0.070 | 0.025 | 0.148 | 6.1 × 10−4 | 3.7 × 10−5 | |
| 2 | 7.4 × 10−5 | 1.72 | 0.32 | 81.4 | 0.120 | 0.022 | 0.099 | 0.196 | 9.0 × 10−5 | 8.4 × 10−6 |
| 5.2 × 10−5 | 1.65 | 0.33 | 80.0 | 0.164 | 0.033 | 0.055 | 0.186 | 1.6 × 10−4 | 9.2 × 10−6 | |
| 3 | 3.8 × 10−5 | 1.39 | 0.85 | 38.8 | 0.191 | 0.117 | 0.028 | 0.102 | 2.6 × 10−4 | 4.3 × 10−5 |
| 3.5 × 10−5 | 1.34 | 0.89 | 33.6 | 0.200 | 0.133 | 0.019 | 0.086 | 3.7 × 10−4 | 5.4 × 10−5 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cáceres, L.; Leinenweber, G.; Soliz, A.; Landaeta, E. Carbon Steel A36 Planar Coupons Exposed to a Turbulent Flow Inside a 90° Pipe Elbow in a Testing Rack: Hydrodynamic Simulation and Corrosion Studies. Metals 2025, 15, 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060583
Cáceres L, Leinenweber G, Soliz A, Landaeta E. Carbon Steel A36 Planar Coupons Exposed to a Turbulent Flow Inside a 90° Pipe Elbow in a Testing Rack: Hydrodynamic Simulation and Corrosion Studies. Metals. 2025; 15(6):583. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060583
Chicago/Turabian StyleCáceres, Luis, Genny Leinenweber, Alvaro Soliz, and Esteban Landaeta. 2025. "Carbon Steel A36 Planar Coupons Exposed to a Turbulent Flow Inside a 90° Pipe Elbow in a Testing Rack: Hydrodynamic Simulation and Corrosion Studies" Metals 15, no. 6: 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060583
APA StyleCáceres, L., Leinenweber, G., Soliz, A., & Landaeta, E. (2025). Carbon Steel A36 Planar Coupons Exposed to a Turbulent Flow Inside a 90° Pipe Elbow in a Testing Rack: Hydrodynamic Simulation and Corrosion Studies. Metals, 15(6), 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060583







