Uranium(VI), Thorium(IV), and Lanthanides(III) Extraction from the Eudialyte Concentrate Using the N,O-Hybrid Heterocyclic Reagents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Remarks
2.2. Liquid Extraction Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phase Stability of the Extraction Systems
3.2. Extraction of Actinides and Lanthanides from Model Solutions
3.3. Determination of Solvation Numbers Using L
- -
- Organic phase: 0.05 mol/L solution of ligand L1 in meta-nitrobenzotrifluoride;
- -
- Aqueous phase: nitric acid content of 4 mol/L; it is necessary to dilute the concentrated solution of the eudialyte ore concentrate recovery by three times, due to the phase instability of the extraction systems at high nitric acid contents;
- -
- Stripping of the organic phase with 0.1 mol/L nitric acid solution for selective re-extraction of Zr(IV), Hf(IV) and Ti(IV).
- -
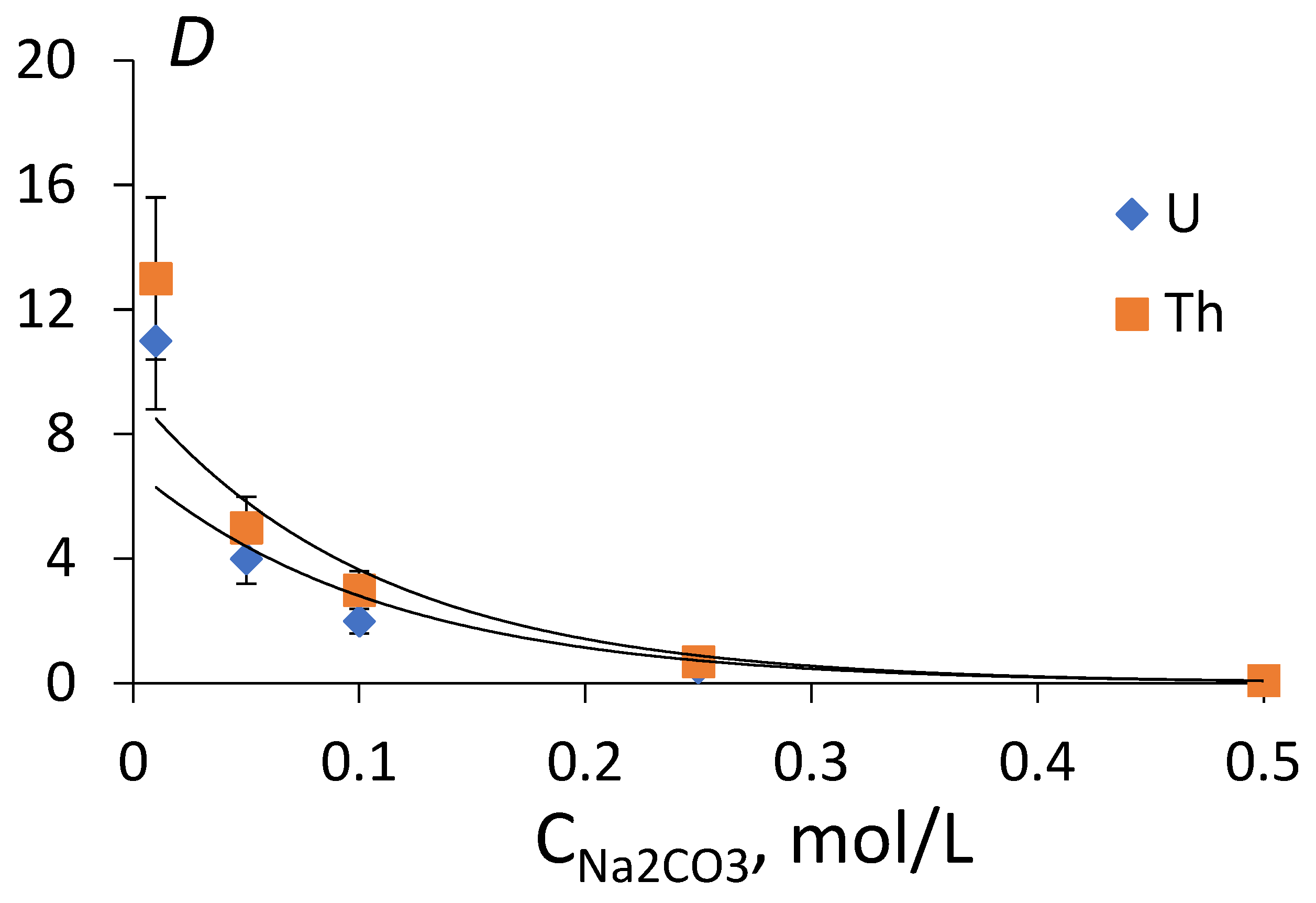
- Re-extraction of uranium and thorium—0.5 mol/L sodium carbonate solution.
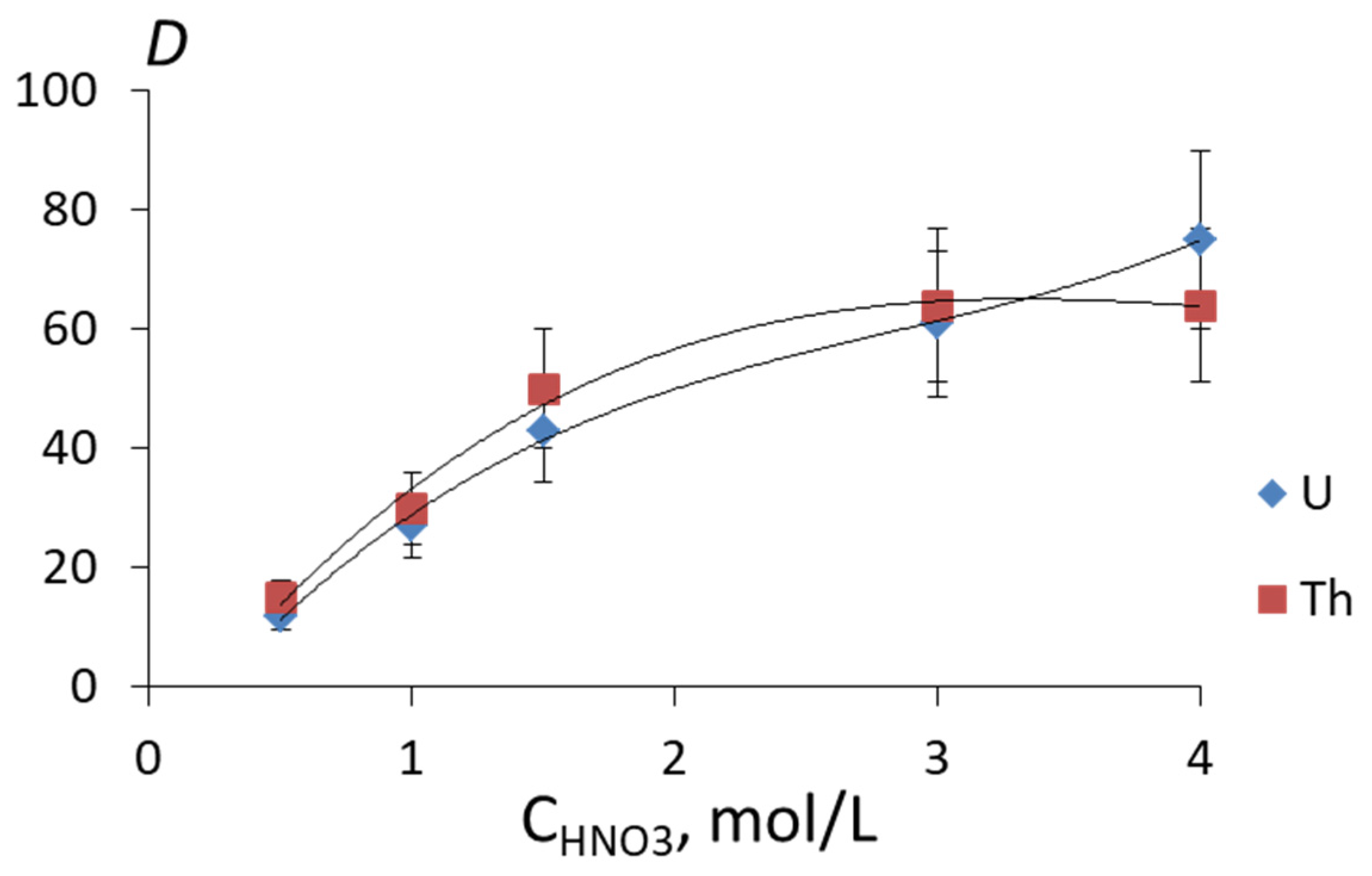
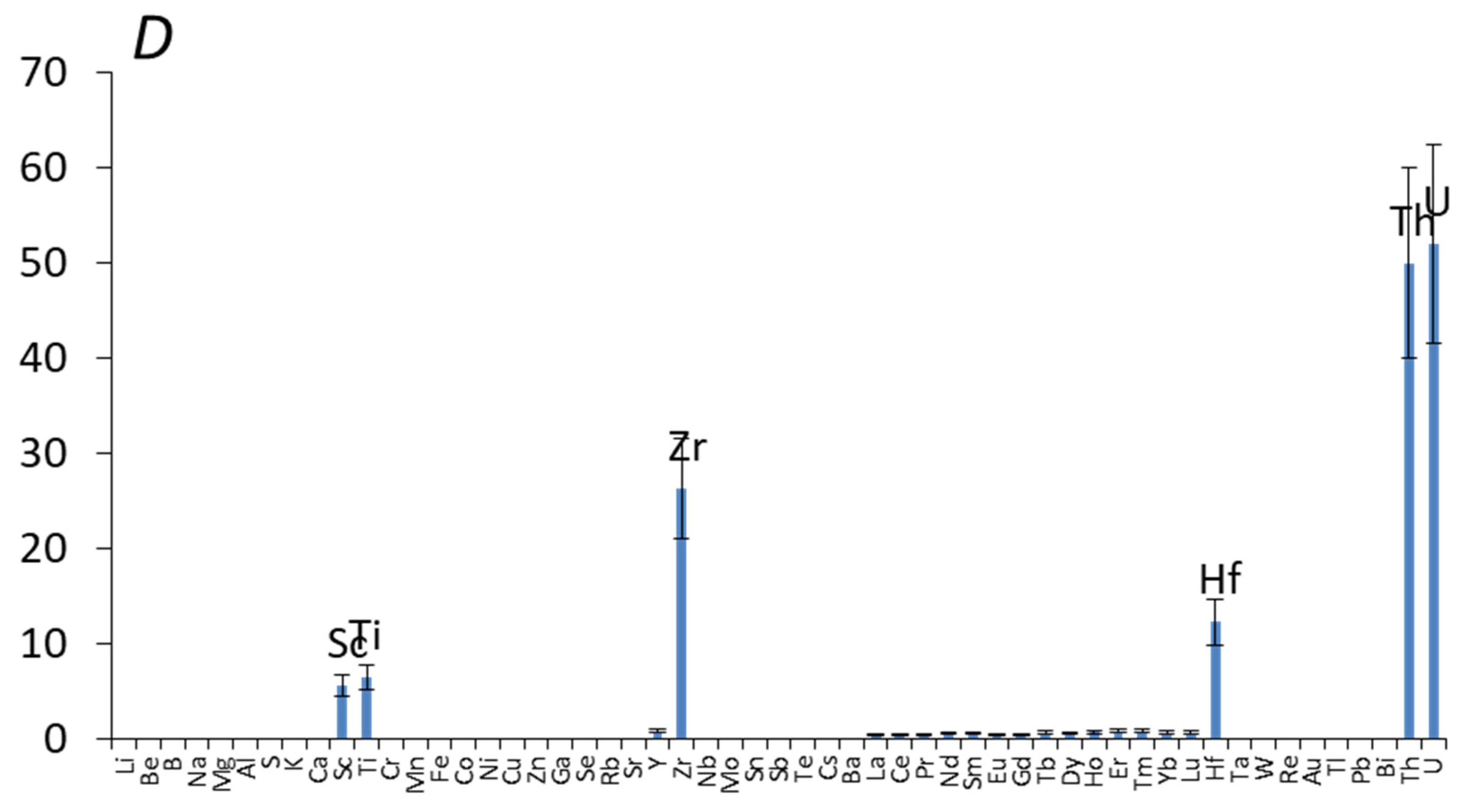
3.4. Extraction of Metals from Eudialyte Nitric Acid Solution
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhiltsov, S.S. Policy of Western States in Central Asia: The Role of Rare-Earth Metals. Post-Sov. Issues 2024, 11, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryukov, V.A.; Yatsenko, V.A.; Kryukov, Y.V. Rare Earth Industry—How to take advantage of opportunities. Gorn. Promyshlennost = Russ. Min. Ind. 2020, 5, 68–84. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepf, V. Rare Earth Elements; Springer Theses; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanova, O.A.; Sirotin, D.V. Metal Industry Development in the Conditions of Formation of New Technological and Institutional Trends. KnE Mater. Sci. 2019, 5, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, K.J.; DeYoung, J.H., Jr.; Seal, R.R., II; Bradley, D.C. Critical Mineral Resources of the United States-Economic and Environmental Geology and Prospects for Future Supply; U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1802; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2017; 797p. [CrossRef]
- Paulick, H.; Machacek, E. The global rare earth element exploration boom: An analysis of resources outside of China and discussion of development perspectives. Resour. Policy 2017, 52, 134–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machacek, E.; Richter, J.L.; Lane, R. Governance and Risk–Value Constructions in Closing Loops of Rare Earth Elements in Global Value Chains. Resources 2017, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsonov, N.Y. Global Chains of Supply of Rare-Earth and Rare Metals as High-Tech Raw Materials Within the Framework of International Industrial Cooperation. Prostranstvennaya Ekon. = Spat. Econ. 2018, 3, 43–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toishybek, A.M.; Baigenzhenov, O.S.; Turan, M.D.; Kurbanova, B.; Merkibayev, Y.S. A review of recovery technologies of rare and rare earth metals from wastes generated in titanium and magnesium production. Complex Use Miner. Resour. 2023, 327, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Dou, Z.; Xie, W.; Lan, C.; Li, G. Summary of the Research Progress on Advanced Engineering, Processes, and Process Parameters of Rare Earth Green Metallurgy. Materials 2024, 17, 3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosinski, A.; Kowalczyk, J.; Mazanek, C. Development of the Polish wasteless technology of apatite phosphogypsum utilization with recovery of rare earths. J. Alloys Compd. 1993, 200, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukeur, A.; Szymczyk, A.; Berbar, Y.; Amara, M. Extraction of rare earth elements from waste products of phosphate industry. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 256, 117857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammache, Z.; Berbar, Y.; Bensaadi, S.; Trari, M.; Amara, M. Recovery of light rare earth elements by leaching and extraction from phosphate mining waste (Fluorapatite and Carbonate-Fluorapatite). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2020, 171, 103937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonin, M.A.; Nechaev, A.V.; Yakimenko, I.A.; Belova, V.V. Extraction of Rare Earth Elements from Chloride Solutions Using Mixtures of P507 and Cyanex 272. Compounds 2024, 4, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jeon, H.S.; Lee, M.S. Solvent extraction of Pr and Nd from chloride solution by the mixtures of Cyanex 272 and amine extractants. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 150, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wei, H.; Liao, W. Synergistic extraction and separation of rare earths from chloride medium by the mixture of HEHAPP and D2EHPA. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 174, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogarko, L.N. Features of eudialyte ore formation in high-alkaline magmas of the Lovozero deposit (Kola peninsula). Dokl. Earth Sci. 2021, 496, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.-Y.; Yang, Y.-H.; Marks, M.A.; Liu, Z.-C.; Zhou, Q.; Ge, W.-C.; Yang, J.-S.; Zhao, Z.-F.; Mitchell, R.H.; Markl, G. In situ U–Pb, Sr, Nd and Hf isotopic analysis of eudialyte by LA-(MC)-ICP-MS. Chem. Geol. 2010, 273, 8–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksenov, S.M.; Rastsvetaeva, R.K.; Mitchell, R.H.; Chakrabarty, A. Crystal structure of manganese-rich variety of eudialyte from Suchina Hill, India, and manganese ordering in eudialyte-group minerals. Crystallogr. Rep. 2014, 59, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, J.; Wu, F.-Y.; McCammon, C.; Wenzel, T.; Marks, M.A.W.; Pfaff, K.; Jacob, D.E.; Markl, G. The compositional variability of eudialyte-group minerals. Miner. Mag. 2011, 75, 87–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogarko, L.N. Geochemistry of Rare Earth Metals in the Ore Eudialyte Complex of the Lovozero Rare Earth Deposit. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2020, 491, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastsvetaeva, R.K.; Chukanov, N.V. Classification of eudialyte-group minerals. Geol. Ore Depos. 2012, 54, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, O.; Ferraris, G.; Gault, R.A.; Grice, J.D.; Kampf, A.R.; Pekov, I.V. The nomenclature of eudialyte-group minerals. Can. Miner. 2003, 41, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöqvist, A.S. The Tale of Greenlandite: Commemorating the Two-Hundredth Anniversary of Eudialyte (1819–2019). Minerals 2019, 9, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanturiya, V.A. Scientific substantiation and development of innovative processes for the extraction of zirconium and rare earth elements in the deep and comprehensive treatment of eudialyte concentrate. J. Min. Inst. 2022, 256, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balinski, A.; Wiche, O.; Kelly, N.; Reuter, M.A.; Scharf, C. Separation of rare earth elements from contaminants and valuable components by in-situ precipitation during the hydrometallurgical processing of eudialyte concentrate. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 194, 105345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balinski, A.; Atanasova, P.; Wiche, O.; Kelly, N.; Reuter, M.A.; Scharf, C. Recovery of REEs, Zr(+Hf), Mn and Nb by H2SO4 leaching of eudialyte concentrate. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 186, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Stopic, S.; Gronen, L.; Friedrich, B. Recovery of Zr, Hf, Nb from eudialyte residue by sulfuric acid dry digestion and water leaching with H2O2 as a promoter. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 181, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voßenkaul, D.; Birich, A.; Müller, N.; Stoltz, N.; Friedrich, B. Hydrometallurgical Processing of Eudialyte Bearing Concentrates to Recover Rare Earth Elements Via Low-Temperature Dry Digestion to Prevent the Silica Gel Formation. J. Sustain. Met. 2016, 3, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davris, P.; Stopic, S.; Balomenos, E.; Panias, D.; Paspaliaris, I.; Friedrich, B. Leaching of rare earth elements from eudialyte concentrate by suppressing silica gel formation. Miner. Eng. 2017, 108, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Stopic, S.; Gronen, L.; Milivojevic, M.; Obradovic, S.; Friedrich, B. Neural Network Modeling for the Extraction of Rare Earth Elements from Eudialyte Concentrate by Dry Digestion and Leaching. Metals 2018, 8, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silin, I.; Dertmann, C.; Cvetković, V.S.; Stopic, S.; Friedrich, B. Prevention of Silica Gel Formation for Eudialyte Study Using New Digestion Reactor. Minerals 2024, 14, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safiulina, A.M.; Semenov, A.A.; Lizunov, A.V.; Lesina, I.G.; Goryunov, E.I.; Goryunova, I.B.; Bodrin, G.V.; Brel, V.K.; Tananaev, I.G. Recovery and Separation of Rare Metals during the Processing of Eudialyte Concentrate with New Reagents of a Series of Phosphoryl Ketones. Radiochemistry 2022, 64, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisova, N.E.; Fedoseev, A.M.; Kostikova, G.V.; Matveev, P.I.; Starostin, L.Y.; Sokolova, M.N.; Evsiunina, M.V. Solvent Extraction and Conformation Rigidity: Actinide(IV) and Actinide(VI) Come Together. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 20774–20784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, A.; Xu, C.; Xiao, C. Separation and complexation of f-block elements using hard-soft donors combined phenanthroline extractants. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 496, 215404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GSO 8363-2003; APPROVED TYPE STANDARD SAMPLE OF URANIUM OXIDE COMPOSITION (COMMON URANIUM). JSC High-Tech Research Institute of Inorganic Materials named after academician A.A. Bochvar (JSC “VNIINM”): Moscow, Russia, 2014.
- Chizhevskaya, S.V.; Chekmarev, A.M. Non-traditional methods of treating high-silicon ores containing rare elements. In Proceedings of the Hydrometallurgy ’94, Cambridge, UK, 11–15 July 1994; pp. 219–228. [Google Scholar]
- Altshuler, G.N.; Malyshenko, N.V.; Popova, A.N. The Ion-Exchange Properties of Polymeric Zirconium Phosphate and Zirconium Dioxide. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 2018, 9, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, J.J.; Seaborg, G.T.; Morss, L.R. The Chemistry of the Actinide Elements; Chapman and Hall Ltd.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1986; 990p, ISBN 10: 0412105500. [Google Scholar]
- Goryunov, E.I.; Safiulina, A.M.; Morgalyuk, V.P.; Goryunova, I.B.; Molchanova, G.N.; Baulina, T.V.; Matrosov, E.I.; Petrovskii, P.V.; Nifant’ev, E.E.; Tananaev, I.G.; et al. N-(n-alkyl)-N′-diphenylphosphorylureas as a new type of extractants for preconcentration of actinides and lanthanides. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2008, 57, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisova, N.E.; Ivanov, A.V.; Matveev, P.I.; Smirnova, A.A.; Belova, E.V.; Kalmykov, S.N.; Myasoedov, B.F. Screening of the Structure of Americium Extractants Based on a 2,2′-Bipyridyl Scaffold: A Simple Way to a N2,O2-Tetradentate Ligands Library for Rational Design of An/Ln Extractants. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 1983–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakirova, G.G.; Mladentsev, D.Y.; Borisova, N.E. Palladium-Catalyzed C–P Cross-Coupling between (Het)aryl Halides and Secondary Phosphine Oxides. Synthesis 2019, 51, 2379–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopkina, E.A.; Pozdeev, A.S.; Kalle, P.; Kirsanov, D.; Smol’yanov, N.A.; Kirsanova, A.A.; Kalmykov, S.N.; Petrov, V.G.; Borisova, N.E.; Matveev, P.I. Sensing and extraction of hazardous metals by di-phosphonates of heterocycles: A combined experimental and theoretical study. Dalton Trans. 2023, 52, 12934–12947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Element | Si | Al | Fe | Zr | Mn | Ca | Na | K | Ti | U |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | 49.97 | 11.65 | 11.55 | 8.67 | 3.81 | 3.13 | 2.63 | 2.01 | 1.96 | 0.012 |
| Element | Sr | Cl | Nb | Mg | P(V) | Hf | Ba | Mo | Ta | Th |
| wt.% | 1.25 | 0.675 | 0.503 | 0.309 | 0.292 | 0.122 | 0.064 | 0.039 | 0.031 | 0.023 |
| Element | S | Ni | La − Lu + Y | La − Nd | Sm − Lu +Y | Y | ||||
| wt.% | 0.023 | 0.017 | 1.22 | 0.77 | 0.45 | 0.403 | ||||
| Element | La − Nd | Ce | Sm − Lu + Y | Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | 63.2 | 0.40 | 36.8 | 0.40 |
| Type of Ligand | HNO3 (mol/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 12 | |
| L1 | Stable | Emulsion | Emulsion | Emulsion | Emulsion |
| L2 | Stable | Stable | Emulsion | Emulsion | Emulsion |
| L3 | Stable | Emulsion | Sediment and emulsion | Sediment and emulsion | Sediment and emulsion |
| Type of Ligand | L1 | L2 | L3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SF(U, Th/REE) | 50–100 | 4 | 8 |
| Extractant | Ln(III) | Th(IV) | U(VI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 1.0–1.1 | 1.5 | 1.2 |
| L2 | 1.1–1.2 | 1.5 | 1.1 |
| L3 | 1.3–1.4 | 1.4 | 1.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Safiulina, A.M.; Lizunov, A.V.; Ivanov, A.V.; Borisova, N.E.; Matveev, P.I.; Aksenov, S.M.; Ivanets, D.V. Uranium(VI), Thorium(IV), and Lanthanides(III) Extraction from the Eudialyte Concentrate Using the N,O-Hybrid Heterocyclic Reagents. Metals 2025, 15, 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050494
Safiulina AM, Lizunov AV, Ivanov AV, Borisova NE, Matveev PI, Aksenov SM, Ivanets DV. Uranium(VI), Thorium(IV), and Lanthanides(III) Extraction from the Eudialyte Concentrate Using the N,O-Hybrid Heterocyclic Reagents. Metals. 2025; 15(5):494. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050494
Chicago/Turabian StyleSafiulina, Alfiya M., Alexey V. Lizunov, Alexey V. Ivanov, Nataliya E. Borisova, Petr I. Matveev, Sergey M. Aksenov, and Dmitry V. Ivanets. 2025. "Uranium(VI), Thorium(IV), and Lanthanides(III) Extraction from the Eudialyte Concentrate Using the N,O-Hybrid Heterocyclic Reagents" Metals 15, no. 5: 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050494
APA StyleSafiulina, A. M., Lizunov, A. V., Ivanov, A. V., Borisova, N. E., Matveev, P. I., Aksenov, S. M., & Ivanets, D. V. (2025). Uranium(VI), Thorium(IV), and Lanthanides(III) Extraction from the Eudialyte Concentrate Using the N,O-Hybrid Heterocyclic Reagents. Metals, 15(5), 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050494








