Abstract
Deep eutectic solvents are widely employed in the recycling and reuse of spent lithium-ion battery cathode materials because of their non-toxicity, low cost, and recyclability. Although DESs have a high recovery rate for metals and are more environmentally friendly, they typically require a longer time or higher temperatures. High temperature and pressure considerably improve leaching efficiency in traditional aqueous systems; this study investigates whether the same is true in DES systems. The physicochemical properties of a DES composed of choline chloride (ChCl) and malonic acid (MA) (1:1) were measured before and after high-temperature and high-pressure treatments, along with their effects on the leaching efficiency of cathode materials for spent lithium-ion batteries (LIBs). The results show that after treatment, the 632.03 cm−1 twisted vibration peak of C-O was red-shifted to 603 cm−1 and the alkyl chain of the DES was lengthened, whereas the 1150.52 cm−1 C-O peak was blue-shifted to 1219 cm−1 and the hydrogen-bonding effect was weakened. At long reaction times, crystals appeared inside the DES. Over time, the crystals increased in size and became less dense, and the color of the material changed from clear to blue to green. After pressurization treatment, the conductivity of the DES increased considerably over its value at atmospheric pressure. The leaching efficiency of Li, Co, Ni, and Mn were 53.20, 47.24, 26.27, and 48.57%, respectively, at 3 h of leaching at atmospheric pressure. The leaching efficiency increased to 78.20, 79.74, 69.76, and 81.80%, respectively, after being pressurized at 3.3 MPa. On this basis, the reaction time was extended to 6 h, and the leaching efficiency of Li, Co, Ni, and Mn were 96.41, 97.62, 98.13, and 97.34%, respectively, trending towards complete leaching. The leaching efficiency of spent LIB cathode materials in DESs was considerably improved under pressurized conditions, providing an efficient method for recovering spent LIB cathode materials using DESs.
1. Introduction
Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) are formed from mixtures of hydrogen bond donors (HBDs) and hydrogen bond acceptors (HBAs), which together exhibit a considerably lower melting temperature at the eutectic point than their constituents [1]. DESs are widely employed for the recovery and reuse of metallurgical secondary resources because of their non-toxicity [2], low cost [3], recyclability [4], and selective solvation of metal oxides [5,6]. Zürner et al. [7] employed a DES comprising ChCl and oxalic acid for extracting precious metals (Fe, Zn, Pb, Cu, In, and Sn) from zinc flue dust. The leaching efficiency of all metals was higher than 80% when reacting at 323 K for 48 h. In addition, DESs have shown excellent results in the preparation of nano-metal oxides. For example, Zhao et al. [8,9,10,11] used a DES based on ChCl and urea as an ion-exchange reaction medium to prepare Ni3(PO4)2–Ni2P2O7 nanoparticles loaded in mesoporous and amorphous forms. DESs can also be employed in the recycling and reuse of spent LIB cathode materials, such as LCO, NCM, and LFP. Tran et al. [12] discovered that a DES composed of ChCl and ethylene glycol was capable of extracting metals (lithium and cobalt) from spent LCO. Leaching occurred through the coordination of the HBAs (ChCl) with chloride ions. The leaching efficiency for both metals was high; however, the leaching process was time-consuming (≥24 h) and required elevated temperatures (>50 °C). Several leaching processes and the leaching efficiency of valuable metals in LIB cathode materials extracted using DESs under atmospheric pressure are shown in Table 1. Long reaction times limit the application of DESs in the recycling and reuse of spent LIB cathode materials.

Table 1.
Several leaching processes and the leaching efficiency of valuable metals in LIB cathode materials in DESs under atmospheric pressure.
Improving the dissolution rate in DESs require new approaches to hydrometallurgy. In 2006, Abbot [17] proposed the ChCl–MA DES, which has great potential in the dissolution of metal oxides. ChCl–MA is a typical DES. Because it has a higher acidity than DESs prepared by combining with other substances, it can provide more protons to the oxygen-atom acceptor, and thus, change the coordination structure of the metal. This is beneficial for increasing the dissolution rate of metal oxides. In addition, the DES can be used as either a leachate or reducing agent to break the covalent bonds of metal oxides when recycling spent LIB cathode materials [18,19].
Pressure hydrometallurgy is an emerging short-process intensive technology; its development is a key emerging trend in modern hydrometallurgy [20]. The process encompasses the processing of polymetallic sulfide and oxide ores, as well as intricate low-grade substances, under high temperature and pressure settings. In addition to recovering primary metals, it is capable of preferentially dissolving and isolating any associated rare or valuable elements. Pressure hydrometallurgy has been widely used in various aspects of material preparation to extract aluminum, uranium, copper, zinc, nickel, cobalt, tungsten [21,22], and various rare metals [23]. It is gaining importance because it has a short process flow [24], is environmentally friendly [25], and offers a high metal recovery rate [26].
To enhance the DES metal leaching efficiency for LIB cathode materials and reduce reaction times, it is crucial to explore new research directions in hydrometallurgy. This paper presents a preliminary study of the structural stability of the ChCl–MA DES at high temperatures and pressures and the effect on the leaching efficiency of cathode materials from spent NCM.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials and Instruments
The following materials and equipment were sourced for the study: malonic acid (AR, Sinopharm Group Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), choline chloride (AR, Shanghai Aladdin Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), anhydrous ethanol (AR, Shanghai McLean Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), 18,650 LiNixCoyMnzO2 (NCM) spent LIBs (battery recycling center in China), standard solutions of Li, Ni, Mn, Co (1000 µg/mL, national standard sample), deionized water, and an FA2004N analytical electronic balance (Shanghai Precision Scientific Instruments Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), LC-DZF-6020A vacuum drying oven (Shanghai Li-Chen Bangxi Instrument Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), Stemi 305 stereoscopic microscope (Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany), YSCLF-100 mL miniature magnetic reactor (Shanghai Shenkou Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), TGA/DSCI differential thermal analyzer (NETZSCH, Selb, Germany), Bruker ALPHA II Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectrometer (Bruker (Beijing) Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China), DDSJ-307F digital conductivity meter (Juyihui Supply Chain (Qingdao) Co., Ltd., Qingdao, China), OTF-1200X miniature open tube furnace (Hefei Kejing Material Technology Co., Ltd., Hefei, China), DF-101S collective magnetic stirrer (Dingxinyi Experimental Equipment Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China), ICAP 7400 inductively coupled plasma spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific (China) Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), and EM 30+ scanning electron microscope (COXEM, Beijing, China).
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.2.1. Preparation of DESs
Because ChCl strongly absorbs water, the appropriate amounts of MA and ChCl were kept in a vacuum drying oven at 90 °C for 24 h before use. With ChCl as the HBA and MA as the HBD (see structural formula in Figure 1), a DES system with a 1:1 ratio of ChCl to MA was configured before each experiment (because DESs with a 1:1 ratio of HBA to HDA typically enhance acidity or reducibility through a strong hydrogen bonding network, thereby improving metal leaching efficiency [27]); 10.40 g of fully dried MA and 13.96 g of ChCl (as weighed with an analytical balance) were combined in a 50 mL beaker. After being covered with a plastic wrap, the beaker was placed in a vacuum drying oven at 90 °C for 3 h until the powder was completely dried and turned into a colorless transparent liquid, which was cooled to room temperature and poured into a 30 mL PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) beaker as a reserve.
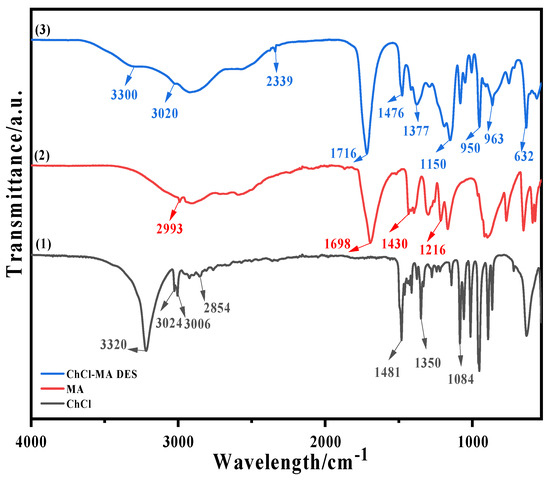
Figure 1.
FTIR curves of (1) ChCl, (2) MA, and (3) ChCl–MA DES.
FTIR curves of ChCl, MA, and the ChCl–MA DES are shown in Figure 1. Curve (1) is the FTIR curve of ChCl. The peak observed at 3320 cm−1 corresponds to the stretching vibration of O-H bonds. The peaks at 3024 cm−1 and 3006 cm−1 represent the stretching vibrations of two -CH2 groups attached to -OH. The peak located at 2854 cm−1 signifies the stretching vibration of a CH3 group connected to N. The peak at 1481 cm−1 is attributed to the bending vibration of methylene groups (CH2). The peak observed at 1350 cm−1 corresponds to the bending vibration of methyl groups (CH3). Finally, the peak at 1084 cm−1 indicates the stretching vibration of C-O bonds.
Curve (2) is the FTIR curve of MA. The peak at 2993 cm−1 corresponds to the stretching vibration of O-H bonds. At 1698 cm−1, the peak signifies the stretching vibration of C=O bonds. The peak observed at 1430 cm−1 is attributed to the bending vibration of C-H bonds. Finally, the peak at 1216 cm−1 represents the stretching vibration of C-O bonds.
Curve (3) is the FTIR curve of the ChCl–MA DES. The broad peak at 3300 cm−1 indicates that ChCl and MA form a large number of hydrogen bonds during the preparation of DESs [28], which may include H-O⋯H, N-H⋯Cl, and OH-Cl. Hydrogen bonds can reduce the lattice energy of ChCl and play an important role in the formation of DESs. The peak at 3020 cm−1 is the stretching vibration peak of MA’s O-H. A distinct and sharp short peak was observed at 2339 cm−1, which may have been noise produced by carbon dioxide in the air. The highly strong and sharp peak at 1716 cm−1 was due to C=O stretching; this result also proves that hydrogen bonds were generated in the DES. Distorted C-H vibrational peaks occurred at 1476 and 1377 cm−1. The peak at 1150 cm−1 was a distorted C-O vibrational peak and that at 950 cm−1 was the C-C absorption peak in ChCl. An asymmetric telescopic vibrational peak of C-N occurred at 863 cm−1 [29,30], and a twisted vibrational peak of C-O was observed at 632.03 cm−1.
2.2.2. Pressurization
The configured DES was placed in a sealed autoclave, and the nut tightened to ensure proper closure. The airtightness of the pressurized autoclave was checked prior to the test. If it was adequate, the air outlet was closed, and high-purity nitrogen was passed through the air inlet. After the pressure in the kettle reached 0.2 MPa, the air inlet was closed. Heat was applied until the temperature reached 120 °C, after which the temperature range was maintained within a fluctuation range of ±1 °C. After the reaction, when the temperature dropped below 60 °C, a wet wag was used as a buffer and placed at the outlet to avoid the splashing of reactants. The air outlet knob was opened to release the pressure in the autoclave. The nut was loosened, and the autoclave cover was opened. The DES was removed and weighed, samples were extracted, and their morphology was observed.
2.2.3. Pre-Experimentation
To investigate the variation in pressure and temperature with time, the DES was heated after 0.2 MPa of nitrogen gas was introduced and was maintained in the autoclave for 5 h. The results are shown in Figure 2.
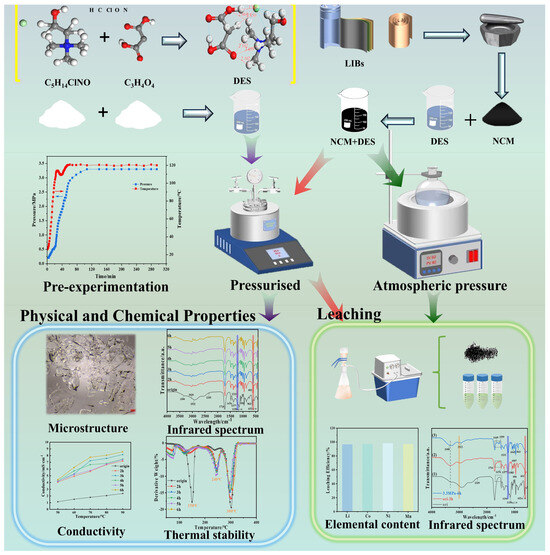
Figure 2.
Schematic experiments and analytical procedures showing the physical and chemical properties of DESs under pressure and their use for recovering spent NCM cathode materials.
Initially, the temperature curve rose rapidly; then, it began to slowly decline. After reaching approximately 113 °C, it declined by approximately 5 °C; this was due to the characteristics of the high-pressure reactor itself (ensuring the safety of the experiment), which suppressed the temperature surge. After about 55 min, the temperature gradually increased to 120 °C and remained stable.
The change in pressure was more straightforward. For 20 min, the increase in pressure was uniform. This may have been caused by the increasing average speed of the nitrogen molecules in the autoclave as the temperature increased, which led to an increase in the number of molecules striking the plane of impact per unit time, and therefore, increasing the pressure in the kettle [31]. During the 20 min of heating prior to the holding period, the pressure increased sharply. This phenomenon occurred because the DES gradually began to boil during the heating period, resulting in gasification. At this time, the thermal movement of the DES gas molecules intensified. At high temperatures, MA decomposes into acetic acid and CO2; when this happens, the original DES system is destroyed, and the emergence of gas expansion causes the pressure to increase sharply. In the holding stage, more molecules in the system are able to cross the potential barrier. These activated molecules intensify thermal movement and increase the diffusion rate. Therefore, the pressure in the autoclave continued to increase until it gradually stabilized at approximately 3.3 MPa.
2.2.4. Dissolution of Cathode Materials
To ensure equipment safety, the 18,650 used LIBs were discharged in a saturated sodium chloride solution for 24 h and then placed in a drying oven for drying. After drying, the batteries were disassembled, and the positive electrode of the batteries was placed in a tube furnace at 400 °C for roasting so as to facilitate the separation of the NCM powder from the aluminum foil. The chemical composition of the NCM battery cathode material used is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Chemical composition of NCM cathode material used.
The effect of pressure on the leaching efficiency of leached metals was investigated by adding 1 g of the cathode material to 20 mL of the DES. This was conducted under the following conditions: a leaching time of 3 h, temperature of 120 °C, rotational speed of 500 rpm, and at pressures of 3.1 and 3.3 MPa, respectively.
Equation (1) for the metal leaching efficiency is given below:
where represents the leaching efficiency for each valent metal (%), denotes the mass concentration of each valent metal ion in the leaching solution (gL), V denotes the volume of the leaching solution (L), M indicates the mass of the experimental waste (g), and is the mass percentage of valent metal elements in the waste (wt.%). Two parallel tests were performed for each leaching experiment, and the average value was used.
2.2.5. Performance Testing
The DES was initially pressurized to 0.2 MPa (the insulation pressure is around 3.3 MPa) using a miniature magnetic reactor and held for 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 h; the microscopic morphologies and conductivities of the DES at the different reaction times were measured using a stereoscopic microscope and a digital conductivity meter.
2.3. Characterization Analysis
2.3.1. FTIR-ATR
Fourier-transform infrared attenuated total reflectance (FTIR-ATR) spectroscopy is a powerful technique for obtaining the infrared spectra of absorbing/emitting liquids or gases; in our analysis, we measured in the long range of 4000–400 cm−1 with a resolution of 2 cm−1.
2.3.2. TG
Thermogravimetry (TG) is a technique used to analyze the thermal stability and composition of samples by measuring the change in the mass of the sample as the temperature varies under programmed control. This experiment used a TGA/DSCI differential thermal apparatus with nitrogen as the environment, a heating range of 30 to 500 °C, and a heating rate of 10 °C/min.
2.3.3. ICP-OES
Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) can determine the content of multiple elements in the same test sample. In this experiment, the leaching efficiency of Li, Ni, Mn, and Co in the cathode materials from spent LIBs were mainly measured.
2.3.4. SEM
In this study, the surface morphology and structure of the samples was investigated using a KOXEM EM 30+ emission scanning electron microscope with a test voltage of 0–20 kV and a magnification of 5000–10,000×.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FTIR-ATR Analysis of DESs
The FTIR-ATR spectra of DESs before and after pressurization are shown in Figure 3. Without high-pressure treatment, ChCl and MA formed a large number of hydrogen bonds, such as H⋯OH, N-H⋯Cl, OH⋯Cl, OH⋯C=O [28,32]. This led to a decrease in the lattice energy of ChCl (a key factor in the formation of the DES). The liquid had a weak broad peak at 3300 cm−1 which is the peak of the O-H stretching vibration.
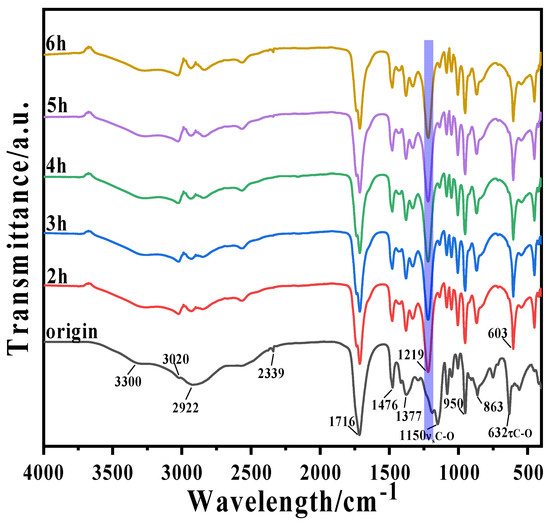
Figure 3.
FTIR-ATR curves of DESs with different reaction times at 120 °C and 3.3 MPa.
After high-temperature and high-pressure treatment, the distorted vibration peak of C-O at 632.03 cm−1 in the original sample was red-shifted to approximately 603 cm−1; this may be related to the formation of H-O…H hydrogen bonds [33]. Alternately, it may be due to the transfer of electrons from proton acceptor to proton donor C-H antibonding orbitals (i.e., to alkyl chain elongation), leading to elongation of the C-H bond and an accompanying vibrational red-shift [34]. The C-O peak at 1150.52 cm−1 in the original sample exhibited an obvious blue-shift to approximately 1219 cm−1; this suggests that the high-temperature and high-pressure conditions weakened the hydrogen bonding in the DESs to some extent, leading to the reconstruction of the hydrogen bonding network and increasing the fluidity and reactivity of the solvent, which is more conducive to the leaching of NCM.
3.2. Effect of Reaction Time on the Morphology of DESs
The macroscopic morphology of the DES changed with the reaction times at 120 °C, as documented in Figure 4. At room temperature, the untreated solvent was colorless and transparent, contained bubbles (this was due to the squeezing of the dropper during sampling), and had a freezing point of 10 °C [35]. Figure 4a shows the morphological characteristics of the DES when it was immediately removed from the autoclave and cooled to 60 °C after the reaction was completed. As can be seen in Figure 4a, the color of the DES changed markedly with reaction time, becoming first minty blue, then an increasingly deep grassy green. Figure 4b shows that the morphological characteristics of the DES after being taken out and left to stand at room temperature after a 12 h standing time. The DES underwent a phase transition from pure liquid into a solid–liquid mixture, with crystals forming within the solvent. This transformation may be attributed to the high-temperature and high-pressure treatment: the C-O blue-shift at 1150.52 cm−1 weakened hydrogen bonding and raised the solidification point. Consequently, some crystals emerged in the liquid phase, while a portion of the solvent supercooled into a metastable liquid and ultimately into an amorphous glass, thus forming a stable solid–liquid mixture [36]. The internal crystals of the solvent appeared milky white with 2 h of reaction. After a reaction time of 3 h, the crystals appeared slightly blue; moreover, the internal crystals were no longer confined within but began to cover the surface of the liquid, forming a sandy and slightly porous layer. With longer reaction times, the crystals became light green. The reason for the color change may be that the presence of a conjugated system in the DES, along with the existence of polar groups (e.g., -COOH), high temperature, and high pressure, increased the polarity of the molecules. Therefore, the mobility of the electrons in the large π-bonds was enhanced, lowering the energy required for molecular excitation, red-shifting the absorbed light quanta and producing the effect of a deep color [37]. After removal and standing for 72 h at room temperature, as shown in Figure 4i, the size of crystals gradually decreased (to make it easier to observe, some crystals were adhered to the glass container wall). The corresponding microstructure is shown in Figure 4c–h.
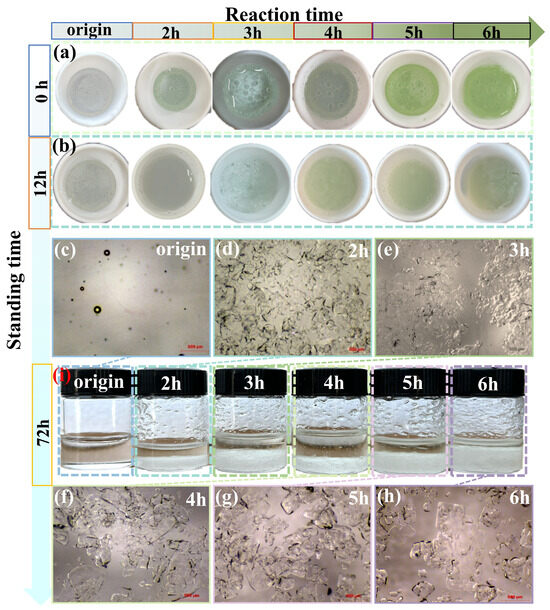
Figure 4.
Morphology of ChCl–MA DES after different reaction times at 120 °C: (a) immediately removed from autoclave upon reaction completion and cooled to 60 °C; (b) removed from autoclave upon reaction completion and left standing for 12 h at room temperature; and (c–h) microscopical morphology of DES under 40-magnification microscope after standing for 72 h and (i) corresponding macroscopic morphology at room temperature. Note: “origin” refers to DES that has not undergone any processing.
The change in the microscopic morphology of the DES with reaction time is shown in Figure 4c–h. Examination using a Stemi 305 body-vision microscope at 40× magnification revealed no crystals and a small number of air bubbles inside the original sample. After a reaction time of 2 h, a large number of transparent crystals appeared inside the liquid; they were small and tightly arranged, with rounded and non-angled boundaries, and mostly in the form of elliptical cakes or rounded rectangles, about 100 μm in length. A small number of long strips, about 250 μm in length, were also detected.
The arrangement began to disperse after a reaction time of 3 h. The crystals increased in size, the number of cake-like crystals decreased, and massive crystals (approximately 300 μm in length) appeared. After a reaction time of 4 h, the crystals size continued to grow, the length of the blocky crystals became approximately 400 μm, and prismatic corners appeared. Large crystals began to accumulate, while there were still some small crystals. After a reaction time of 5 h, the small crystals increased in size, with most of the crystals exhibiting a very regular, square-like lamellar structure, approximately 350 μm long; in addition, the density was reduced. After a reaction time of 6 h, the change was more obvious; there were large crystals, approximately 800 μm long. Irregular tetragonal lamellar crystals were dominant. Their size was slightly reduced (to approximately 300 μm), and the distribution was relatively sparse. This suggests that the high temperature and pressure weakened hydrogen bonding, increasing the mobility of the solvent layer. At the same time, the number of free particles increased, and the volume expanded. Thus, the crystals grew bigger and sparser [38].
3.3. Effect of Reaction Time on Conductivity of DESs
Conductivity, a critical physical characteristic of solvents, refers to the degree of ease with which electrical charges can move within a substance [39]. The effects of temperature and reaction time on the conductivity (σ) of the various DESs are illustrated in Figure 5a. The conductivity always increased considerably with temperature, as expected [40,41]. The conductivity of a DES is due to the migration of ions; with an increase in temperature, the kinetic energy of the ions is enhanced, and movement in an electric field becomes easy [42]. Before being subjected to high-temperature and high-pressure treatment, the solvent had a relatively low conductivity. However, after undergoing this treatment, its conductivity considerably increased. When the temperature was higher than 70 °C, the conductivity of the DESs followed the order σ6h > σ3h > σ4h > σ5h > σ2h > σorigin. The conductivity of the DES with a reaction time of 6 h at 90 °C reached the maximum value within the range of test conditions in this study.
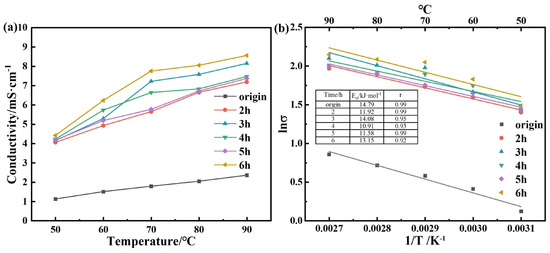
Figure 5.
(a) Effect of temperature and reaction time on the electrical conductivity of the DESs; (b) logarithm of the conductivity σ of DESs with different reaction times plotted against . The inset shows the conductivity activation energies and correlation coefficients r.
The logarithm of conductivity is plotted against in Figure 5b. A strong linear correlation is observed, as evidenced by the high coefficient of determination (R2 > 0.92). This agrees with the Arrhenius formula [37]
where represents the conductivity (mS/cm), stands for a constant, denotes the activation energy of conductivity (kJ/mol), is the gas constant, and is the thermodynamic temperature (K).
The corresponding conductivity activation energies and correlation coefficients r were obtained after fitting using Figure 5a and Equation (2); the results are shown in the Figure 5b. fell in the range of 10.91–14.79 kJ/mol. The conductivity activation energies are the largest in the origin DES, which is 14.79 kJ/mol. After high-temperature and pressure treatment, the conductivity activation energy of this DES decreased, indicating an increase in its electrical conductivity.
3.4. Effect of Reaction Time on Thermal Stability of DESs
The thermal stability of DESs plays a crucial role in determining whether they can be applied at high temperatures, which directly impacts their potential economic and environmental benefits.
The weight loss ratio of the DESs increased slightly with reaction time (Figure 6a). At the beginning of each group of experiments, the base mass of the DES was about 23 g. After a reaction time of 2 h, the weight loss ratio was 15.50%, increasing to 18.01% as the reaction time was extended to 6 h. This is because in the process of heating and incubation, molecules of vaporized DES continually hit the wall of the autoclave. Therefore, the DES adhered to the autoclave wall and was charred to a certain extent under the high temperature and pressure; some of it escaped when the air outlet was opened. Because of the small size of the reaction vessel and the low actual capacity of the samples, the weight loss was rather high.
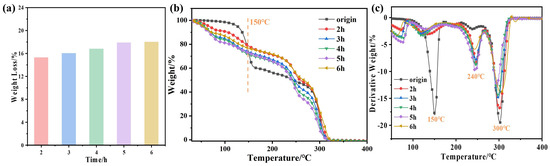
Figure 6.
(a) Effect of reaction time on the weight loss ratio of the DES at 120 °C; (b) thermogravimetric and (c) differential thermogravimetric curves of DESs with different reaction times.
Thermogravimetric (TG) lines of the DES at different reaction times are shown in Figure 6b. The DES decomposed gradually with increasing temperature. The maximum decomposition rate occurred at the peak temperature value (referred to as in the figure), which represents the temperature corresponding to the highest rate of decomposition; determines the maximum temperature at which the DES can remain liquid without decomposing [43].
MA has a relatively low ability to form hydrogen bonds with ChCl; the hydrogen bonds that it does manage to form break when the temperature increases to a certain level. The DES that had not been treated with high temperature and pressure had a = 110.2 °C, at which point the hydrogen bonds were already broken. Note that two phases are clearly visible in Figure 6b: they represent the volatilization and decomposition of the HBD (i.e., MA), respectively, [38] and have weight loss ratios of 38.6% and 17.5%, respectively. The chemical reaction mechanism can be described as follows:
In the first phase, . At this time, the decomposition rate of MA was the fastest, until it was completely decomposed at 270 °C [33]. The second phase (decomposition of ChCl as a residual component) started at 270 °C. At , the ChCl decomposition rate reached its maximum value and began to decrease; the ChCl had decomposed completely by about 320 °C, with a weight loss ratio of 43.9% [44,45]. The chemical reaction mechanism can be described as follows:
Below 150 °C, for the DES subjected to high-temperature and high-pressure treatment for 3 h (as there is not much regularity, we can select this DES (Figure S1)), the TG curves of the solutions shifted relative to the original DES in the direction of low temperature. Moreover, was obviously smaller than ; the short-term thermal stability of the solvents became worse because of the weakening of the intermolecular force (hydrogen bonding) with which the thermal stability of DESs has a positive correlation. High temperature and pressure caused the characteristic peak of C-O at 1150 cm−1 to be blue-shifted, weakening the hydrogen bonding that prevents the molecules from escaping. This affected the thermal decomposition of the DES and lowered its temperature of decomposition [45]. In the range 40.6–100 °C, when the hydrogen bonds began to break, the hydroxyl groups began to crack to generate water, and thus part of the MA began to decompose. Simultaneously, the hydroxyl groups (-OH) present in ChCl may have undergone esterification reactions with the carboxylic acid group of succinic acid, generating monoesters or diesters of succinic acid, while releasing water molecules:
with and a weight loss of 13.4%. When the temperature was 100–150 °C, . At this time, the decomposition rate reached its maximum value and began to decrease; decomposition was completed at about 320 °C with a weight loss ratio of 44.2%. The DTG curve in Figure 6c is consistent with the above. In general, the short-term thermal stability of the DESs deteriorated after high-temperature and high-pressure treatment.
3.5. Effect of Pressure on the Leaching Efficiency of Spent LIB Cathode Materials in DES
Having established that the structure of DESs remained stable after high-temperature and high-pressure treatment, along with an increase in the electrical conductivity and a decrease in the short-term thermal stability, further research was conducted to determine whether DESs can enhance the metal leaching efficiency of spent LIB cathode materials under these conditions.
Comparative experiments were conducted on atmospheric pressure leaching and pressure leaching at a temperature of 120 °C, liquid–solid ratio 20 mL/g, and stirring speed of 500 rpm. Leaching was performed for 3 h; the leaching effectiveness can be observed in Figure 7a.
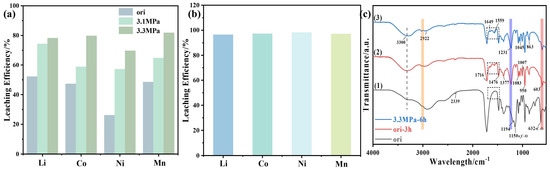
Figure 7.
(a) Effect of pressure on leaching efficiency of spent LIB cathode materials in DESs at 120 °C and reaction time of 3 h; (b) leaching efficiency of spent LIB cathode materials at a reaction time of 6 h at 120 °C; (c) FTIR profiles of different leaching solutions at 120 °C: (1) ChCl–MA DES; (2) reaction at atmospheric pressure for 3 h; (3) reaction at 3.3 MPa for 6 h.
It is evident that pressure plays a crucial role in determining leaching efficiency. As the pressure increases, the leaching rate also increases accordingly. Under normal pressure, the leaching efficiency of metals is relatively low; for example, the leaching efficiency of Li, Co, Ni, and Mn were 53.20, 47.24, 26.27, and 48.57%, respectively. When the insulation pressure was 3.1 MPa, the leaching efficiency of Li, Co, Ni, and Mn increased considerably, reaching 74.43, 58.87, 57.19, and 64.78%, respectively. When the insulation pressure was 3.3 MPa, the leaching efficiency of Li, Co, Ni, and Mn increased to 78.20, 79.74, 69.76, and 81.80%, respectively. On this basis, the reaction time was extended to 6 h; the leaching efficiency of each element is shown in Figure 7b. After a reaction time of 6 h, the leaching efficiency of Li, Co, Ni, and Mn were 96.41, 97.62, 98.13, and 97.34%, respectively, indicating a trend toward complete leaching. It can be inferred that increasing pressure is a feasible approach to enhancing the metal leaching efficiency of DESs on spent LIB cathode materials.
Figure 7c shows the changes in the functional groups before and after leaching from deep eutectic solvents under different reaction conditions. Curve (1) represents the original infrared spectrum of the deep eutectic solvent, curve (2) represents the infrared spectrum of the leach solution after 3 h of reaction at atmospheric pressure, and curve (3) represents the infrared spectrum of the leach solution after 6 h of reaction at a pressure of 3.3 MPa. The strength of the O-H group at 3300 cm−1 is slightly reduced after leaching. This result may be attributed to the reaction between the DES and metal oxides, where the proton hydrogen of the hydroxyl group in the hydrogen bond combines with oxygen to form water. Consequently, the metal salt replaces the original hydrogen site in the hydroxyl group, indicating that the hydrogen bond is involved in the leaching process. Further, after pressurizing the leach solution, the intensity of the O-H group is reduced, indicating that more hydrogen bonds are involved in the reaction, which correlates with improved leaching efficiency. Meanwhile, the stretching vibration peaks of C=C appeared at 1649 cm−1 and 1559 cm−1. In addition, the twisted vibrational peak of C-O at 632.03 cm−1 was red-shifted, and the C-O peak at 1150.52 cm−1 showed an obvious blue shift and moved to approximately 1219 cm−1, which is consistent with the effect of high temperature and high pressure on the DES structure. Therefore, it can be assumed that the hydrogen bond inside the DES is crucial to the overall process of leaching waste ternary LIB cathode materials.
SEM analysis was utilized to characterize the morphology of the cathode material and leach residue. Figure 8a–c illustrates that a notable alteration occurred in the surface morphology of the cathode material powder following leaching. Prior to leaching, the powder consisted of irregular block-shaped crystals of different sizes, with some of the crystals clustered into spheres that adhered to each other (Figure 8a). During the leaching process, these globular clusters were successively dissolved by the DES and the grains began to disperse (Figure 8b,c). The change was more pronounced under pressurized conditions, as shown in Figure 8c, where the shape was directly disrupted into an amorphous form that was more dispersed. This result is due to the enhanced permeability of the DES to the pores of the cathode electrode material under high-pressure conditions, promoting the contact between DES and the interior of the material.
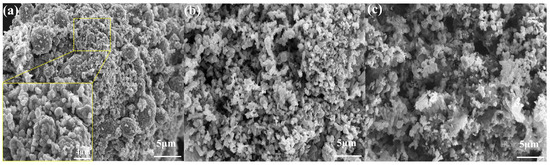
Figure 8.
SEM of (a) raw cathode materials, (b) leach residue of atmospheric pressure leaching for 3 h at 120 °C, and (c) leach residue of pressurized leaching for 3 h at 120 °C.
Moreover, when DESs extract waste NMC cathode materials, it is a complex reaction that involves the coupling of mass transfer and chemical reactions. The MA in DES provides H+, which reacts with O2− in the cathode material, damaging the crystal structure of the material. The chemical reaction mechanism can be described as
At the same time, Cl− and malonate ions (C3H2O42−) act as ligands to form stable complexes with transition metal ions (such as [NiCl2] and [Co (C3H2O4)], reducing the activity of metal ions and pushing the dissolution equilibrium towards the positive reaction direction [46]. High temperatures enhance the activity of H⁺ in DES, making it easier to damage the crystal structure of the NCM materials and promoting the dissolution of Li⁺ and transition metal ions. Simultaneously, under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions, the coordination ability of Cl− and malonate ions (C3H2O42−) may be enhanced, forming more stable complexes with transition metal ions (such as [NiCl4]2− or [Co(C3H2O4)2]2−), pushing the dissolution equilibrium towards the positive reaction direction.
4. Conclusions
In this study, a DES containing ChCl and MA in a 1:1 ratio was prepared, and its various physicochemical properties at various reaction times were compared with those at atmospheric pressure. The results were as follows:
(1) After high-temperature and high-pressure treatment, the twisted vibration peak of C-O at 632.03 cm−1 in the original sample was red-shifted and the C-O peak at 1150.52 cm−1 showed an obvious blue-shift; the hydrogen bonding was weakened, leading to the reconstruction of the hydrogen bonding network and increasing the fluidity and reactivity of the solvent, which is more conducive to the leaching of NCM.
(2) High temperature and pressure changed the appearance of the DES from colorless to blue and then to green as the reaction time was extended, while a large number of crystals appeared inside the solvents, and the crystals became larger and less dense.
(3) The conductivity of the DES at atmospheric pressure was poor, but after high-temperature and pressure treatment it increased considerably, especially with an increase in temperature. The conductivity was largest at a reaction time of 6 h and a temperature of 90 °C.
(4) The weight loss of the DES increased with reaction time but not considerably. However, the short-term thermal stability of the DES deteriorated after high-temperature and high-pressure treatment.
(5) At a temperature of 120 °C and reaction time of 3 h, pressurization can improve the metal leaching efficiency of DES on spent LIB cathode materials. Compared with atmospheric pressure, an insulation pressure of 3.3 MPa considerably increased the leaching efficiency of Li, Co, Ni, and Mn from 53.20, 47.24, 26.27, and 48.57% to 78.20, 79.74, 69.76, and 81.80%, respectively. By increasing the reaction time, the leaching efficiency of Li, Co, Ni, and Mn can reach 96.41, 97.62, 98.13, and 97.34%, effectively approaching complete leaching. This offers an efficient method for recovering spent LIB cathode materials in DESs.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/met15040350/s1, Figure S1. (a) Thermogravimetric and (b) differential thermogravimetric curves of deep eutectic solvents with a holding time of 3 h.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.J.; methodology, D.J.; software, Y.B.; validation, L.J. and Y.L.; formal analysis, Y.B.; investigation, Y.B.; resources, L.J.; data curation, Y.L.; writing—original draft, Y.B.; writing—review and editing, D.J.; visualization, C.C.; supervision, D.J.; project administration, C.C.; funding acquisition, Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the financial support from the Graduate Research and Innovation Projects in Jiangsu Province (No. KYCX23_3872).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank Dongjie Zhou for his contributions to the validation of and in ensuring the accuracy of our results, and Jiahao Liu for his efforts in the investigation, which provided critical insights. We also extend our gratitude to colleagues and mentors for their support and guidance throughout this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| DESs | deep eutectic solvents |
| LIBs | lithium-ion batteries |
| NCM | LiNixCoyMnzO2 |
| MA | malonic acid |
| ChCl | choline chloride |
| LCO | LiCoO2 |
| LFP | LiFePO4 |
References
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V.J.C.C. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 9, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudłak, B.A.E.; Owczarek, K.; Namieśnik, J.E.S.; Research, P. Selected issues related to the toxicity of ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 11975–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Gou, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z. Esterification of cellulose using carboxylic acid-based deep eutectic solvents to produce high-yield cellulose nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zuo, M.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Xiong, C.; Zen, X.; Sun, Y.; Hu, L.; Liu, S.; Lei, T.J.C. Green Processing of Lignocellulosic Biomass and Its Derivatives in Deep Eutectic Solvents. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 2696–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateli, I.M.; Jenkin, G.; Hartley, J.M.; Abbott, A.J.G.C. Electrochemical oxidation as alternative for dissolution of metal oxides in deep eutectic solvents. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 8360–8368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liang, Q.; Yu, X.; Lü, Q.; Ma, L.; Qin, X.; Chen, G.; Li, B. Deep Eutectic Solvents for Boosting Electrochemical Energy Storage and Conversion: A Review and Perspective. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2011102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zürner, P.; Frisch, G. Leaching and Selective Extraction of Indium and Tin from Zinc Flue Dust Using an Oxalic Acid-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 5300–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Hamad, A.; Hayyan, M.; AlSaadi, M.A.; Hashim, M.A. Potential applications of deep eutectic solvents in nanotechnology. Chem. Eng. J. 2000, 273, 551–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, H.U.; Bibi, R.; Arain, M.B.; Safi, F.; Ullah, S.; Castro-Muñoz, R.; Boczkaj, G. Deep eutectic solvent (DES) with silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) based assay for analysis of lead (II) in edible oils. Food Chem. 2022, 379, 132085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S. Deep eutectic solvents as versatile media for the synthesis of noble metal nanomaterials. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2017, 6, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, H.; Shen, J. Synthesis of nickel phosphide nano-particles in a eutectic mixture for hydrotreating reactions. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 8137–8145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.K.; Rodrigues, M.T.F.; Kato, K.; Babu, G.; Ajayan, P.M.J.N.E. Deep eutectic solvents for cathode recycling of Li-ion batteries. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, Z.; Xu, Z. A novel method for screening deep eutectic solvent to recycle the cathode of Li-ion batteries. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 4473–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hu, T.; Shi, P.; Min, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, Q. Efficient Recovery of Value Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries by Combining Deep Eutectic Solvents and Coextraction. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 10, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Fan, M.; Gu, C.; He, W.; Meng, Q.; Wan, L.; Guo, Y. Selective Extraction of Transition Metals from Spent LiNixCoyMn1−x−yO2 Cathode via Regulation of Coordination Environment. Angew. Chem. 2022, 134, 202202558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Guo, M. A simple green method for in-situ selective extraction of Li from spent LiFePO4 batteries by synergistic effect of deep-eutectic solvent and ozone. Environ. Res. 2023, 239, 117393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; McKenzie, K.J.; Obi, S.U. Solubility of metal oxides in deep eutectic solvents based on choline chloride. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2006, 51, 1280–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateli, I.M.; Thompson, D.; Alabdullah, S.S.M.; Abbott, A.P.; Jenkin, G.R.T.; Hartley, J.M. The effect of pH and hydrogen bond donor on the dissolution of metal oxides in deep eutectic solvents. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 5476–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Du, R.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Dong, S.; Zhou, D.; Wang, S.; Li, C. High-efficiency leaching of valuable metals from waste Li-ion batteries using deep eutectic solvents. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, Y.; Smelter, S.D. Application of Pressurized Hydrometallurgical Technology in Zinc Smelting. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2021, 5, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Q.; Chen, L.; Xian, Y.; Wang, Y. Ultrasonic pretreatment for enhancing flotation separation of elemental sulfur and silver-bearing lead minerals from an oxidative pressure leaching residue of zinc sulfide. Miner. Eng. 2024, 205, 108495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Liao, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Pressure Sulfuric Acid Leaching of Manganese-Rich Slag with Pyrite as Additive. Min. Met. Explor. 2020, 37, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saida, S.; Kumar, B.; Roy, G.G.; Chakravarty, S.; Kundu, T.K. Synthesis of TiO2 from the Low-Grade Ilmenite Using the Mechanical Activation and Reductive Pressure Leaching in Low-Concentration H2SO4. Min. Met. Explor. 2023, 40, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Zhou, P.; Wu, D.; Wu, C. An Overview of Flashing Phenomena in Pressure Hydrometallurgy. Processes 2023, 11, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopić, S.R.; Friedrich, B.G. Pressure hydrometallurgy: A new chance to non-polluting processes. Vojn. Glas. 2011, 59, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Shi, L.; Qu, T.; Yang, Z.; Lin, L.; Xie, G.; Xu, B. Kinetics of Ni and Co Recovery via Oxygen-Enriched Pressure Leaching from Waste Lithium-Ion Batteries. Separations 2023, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, K.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Valix, M.; Tsang, D.C. Challenges in Recycling Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: Spotlight on Polyvinylidene Fluoride Removal. Glob. Chall. 2023, 7, 2200237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, M.I.; García-Díaz, I.; Rodríguez, M.L.; Gutiérrez, M.C.; del Monte, F.; López, F.A. Synthesis and Properties of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents via Heating-Stirring and Ultrasound. Molecules 2024, 29, 3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, H.M.; Förner, W. Analysis of the infrared and Raman spectra of phenylacetic acid and mandelic (2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetic) acid. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 78, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altamash, T.; Atilhan, M.; Aliyan, A.; Ullah, R.; Nasser, M.; Aparicio, S. Technology, A Detailed Experimental Study on Rheological, Thermodynamic and Gas Solubility Properties of Phenylacetic Acid Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2016, 40, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghatee, M.H.; Zare, M.; Moosavi, F.; Zolghadr, A.R. Temperature-Dependent Density and Viscosity of the Ionic Liquids 1-Alkyl-3-methylimidazolium Iodides: Experiment and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 3084–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, S.L.; Painter, P.; Colina, C.M. Experimental and Computational Studies of Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2014, 59, 3652–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tian, R.; Han, H.; Wu, K.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, H.; Liang, B. Preparation strategy and stability of deep eutectic solvents: A case study based on choline chloride-carboxylic acid. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 345, 131028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zheng, Q.; Tan, H.; Wang, X. Insight into the role of hydrogen bond donor in deep eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 399, 124332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, X. High pressure-induced glass transition and stability of choline chloride/malonic acidic deep eutectic solvents with different molar ratios. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 364, 120055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruinhorst, A.v.D.; Kollau, L.J.B.M.; Kroon, M.C.; Meuldijk, J.; Tuinier, R.; Esteves, A.C.C. A centrifuge method to determine the solid–liquid phase behavior of eutectic mixtures. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 149, 224505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, K.A.; Sadeghi, R. Database of deep eutectic solvents and their physical properties: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 384, 121899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobza, P.; Špirko, V.; Selzle, H.L.; Schlag, E.W. Anti-Hydrogen Bond in the Benzene Dimer and Other Carbon Proton Donor Complexes. J. Phys. Chem. A 1998, 102, 2501–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, M.; García-Díaz, I.; López, F. Properties and perspective of using deep eutectic solvents for hydrometallurgy metal recovery. Miner. Eng. 2023, 203, 108306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishov, A.; Makoś-Chełstowska, P.; Bulatov, A.; Andruch, V. Condensed matter, materials, surfaces, interfaces, biophysical, Deep Eutectic Solvents or Eutectic Mixtures? Characterization of Tetrabutylammonium Bromide and Nonanoic Acid Mixtures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 3889–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshina, J.L.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic Liquids: New Forms of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients with Unique, Tunable Properties. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 11894–11953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fronduti, M.; Del Giacco, T.; Rossi, E.; Tiecco, M.; Germani, R. Insights into the structural features of deep eutectic solvents: The eutectic point as an unicum in their physical properties and the surface tension as a method for its determination. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 379, 121679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Castañeda, J.; Negrón-Mendoza, A.; Frías, D.; Colín-García, M.; Heredia, A.; Ramos-Bernal, S.; Villafañe-Barajas, S. Chemical evolution studies: The radiolysis and thermal decomposition of malonic acid. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2015, 304, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Mellado, N.; Larriba, M.; Navarro, P.; Rigual, V.; Ayuso, M.; García, J.; Rodríguez, F. Thermal stability of choline chloride deep eutectic solvents by TGA/FTIR-ATR analysis. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 260, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xue, Z.; Wang, J.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, X.; Mu, T. Investigation on the thermal stability of deep eutectic solvents. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2018, 34, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Bian, X.; Han, W.; Cao, D.; Wen, Y.; Zhu, K.; Wang, S. The application of deep eutectic solvents in lithium-ion battery recycling: A comprehensive review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 188, 106690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).