Compressive Strength and Metallurgical Properties of Pellets with Added Oolitic Hematite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials and Chemical Composition
2.2. Experimental Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Compressive Strength Results
3.2. Reduction Expansion Rate Test Results
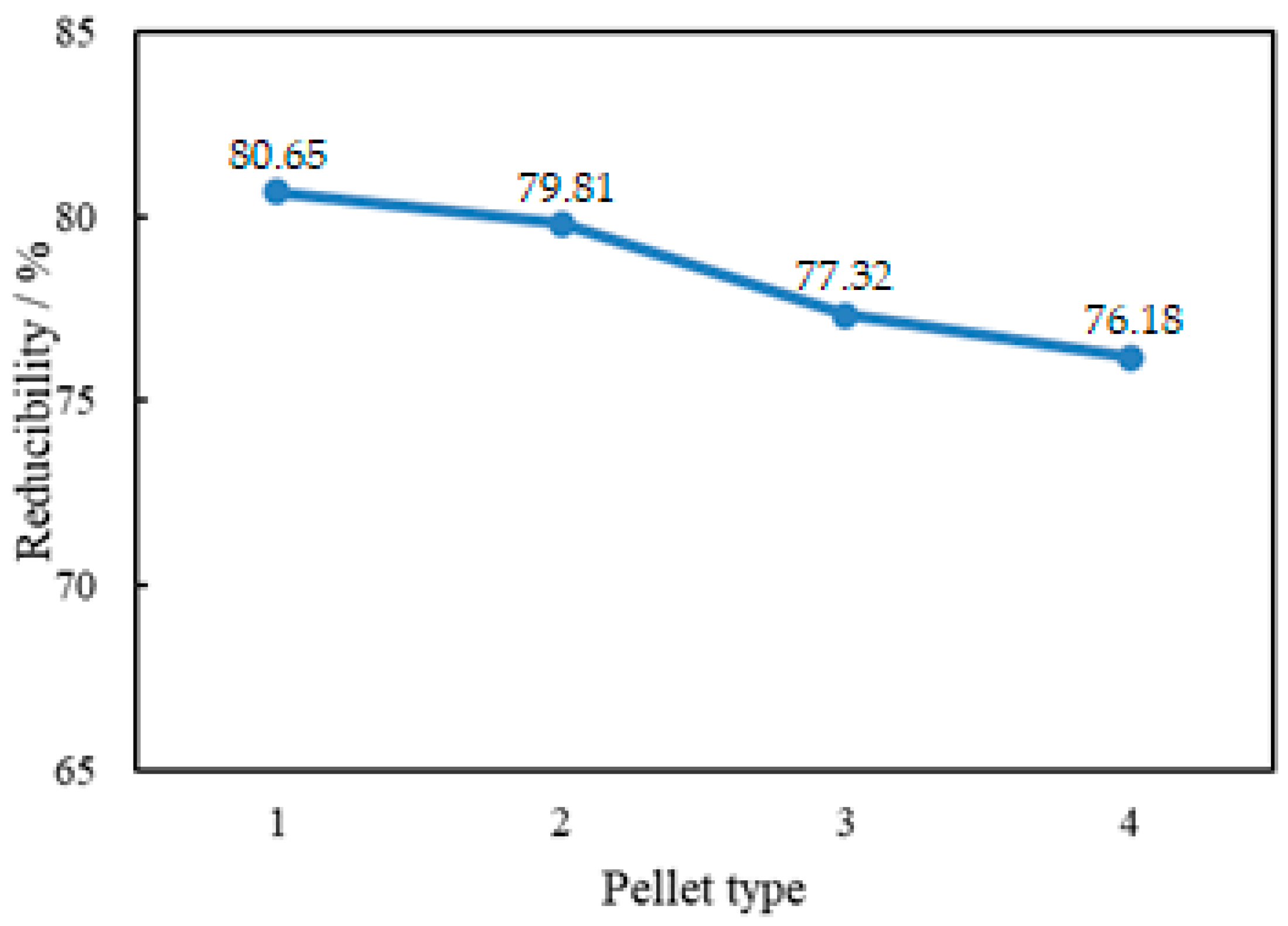
3.3. Reducibility Test Results
3.4. Softening and Dripping Performance Test Results
3.5. Results Analysis
4. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, Y.S.; Han, Y.X.; Gao, P.; Zhou, M. Study on Process Mineralogy of a High Phosphorus Oolitic Hematite Ore. J. Northeast. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2013, 34, 1773–1776. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.F. Basic Research for Direct Reduction of Carbon Bearing Pellets of High Phosphorus Oolitic Hematite by Gas Based Shaft Furnace Process. Ph.D. Thesis, Central Iron & Steel Research Institute, Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.B. Phosphorus Migration Behavior in Pre-Reduction Sintering Process of Bayan Obo Iron Concentrate. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia University of Science & Technology, Baotou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.Z.; Li, J.; Li, F. Effect of Dephosphorization Agent on Gasification and Dephosphorization of High Phosphorus Iron Ore Pellets. Iron Steel Vanadium Titan. 2020, 41, 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 14201-2018; Iron Ore Pellets for Blast Furnace and Direct Reduction Feedstocks—Determination of the Crushing Strength. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- GB/T 13240-2018; Iron Ore Pellets for Blast Furnace Feedstocks, Determination of the Free-Swelling Index. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- GB/T 13241-2017; Iron Ores—Determination of Reducibility. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- GB/T 34211-2017; Iron Ores—Method for Determination of Iron Reduction Softening Drippinger Performance Under Load. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Chen, X.L.; Gan, M.; Fan, X.H.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, G.G. Concretion properties of organic-binder oxidated pellets and strengthen measures. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2009, 40, 550. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.-J.; Xing, Z.-X.; Yang, H.; Xue, X.-X. Effects of high proportion unground sea sand ore on the preparation process and reduction performance of oxidized pellets. Minerals 2021, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Tao, J.; Fan, C.; Ding, L.; Long, H.; Yang, T.; Yu, Z. Analysis of the titanium-bearing pellets prepared by a waste titanium-based catalyst and vanadium titanomagnetite. Chin. J. Eng. 2023, 45, 1740–1749. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Han, C.C.; Yang, A.M.; Liu, W.X.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Liu, L.J. Effect of SiO2 on quality of magnesian acid pellets. J. Iron Steel Res. 2017, 29, 872–877. [Google Scholar]
- Qing, G.L.; Wang, C.D.; Hou, E.J.; Liu, H.S.; Ma, L.; Wu, Q. Compressive strength and metallurgical property of low silicon magnesium pellet. J. Iron Steel Res. 2014, 26, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.H. Principles of Iron and Steel Metallurgy; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2013; p. 438. [Google Scholar]
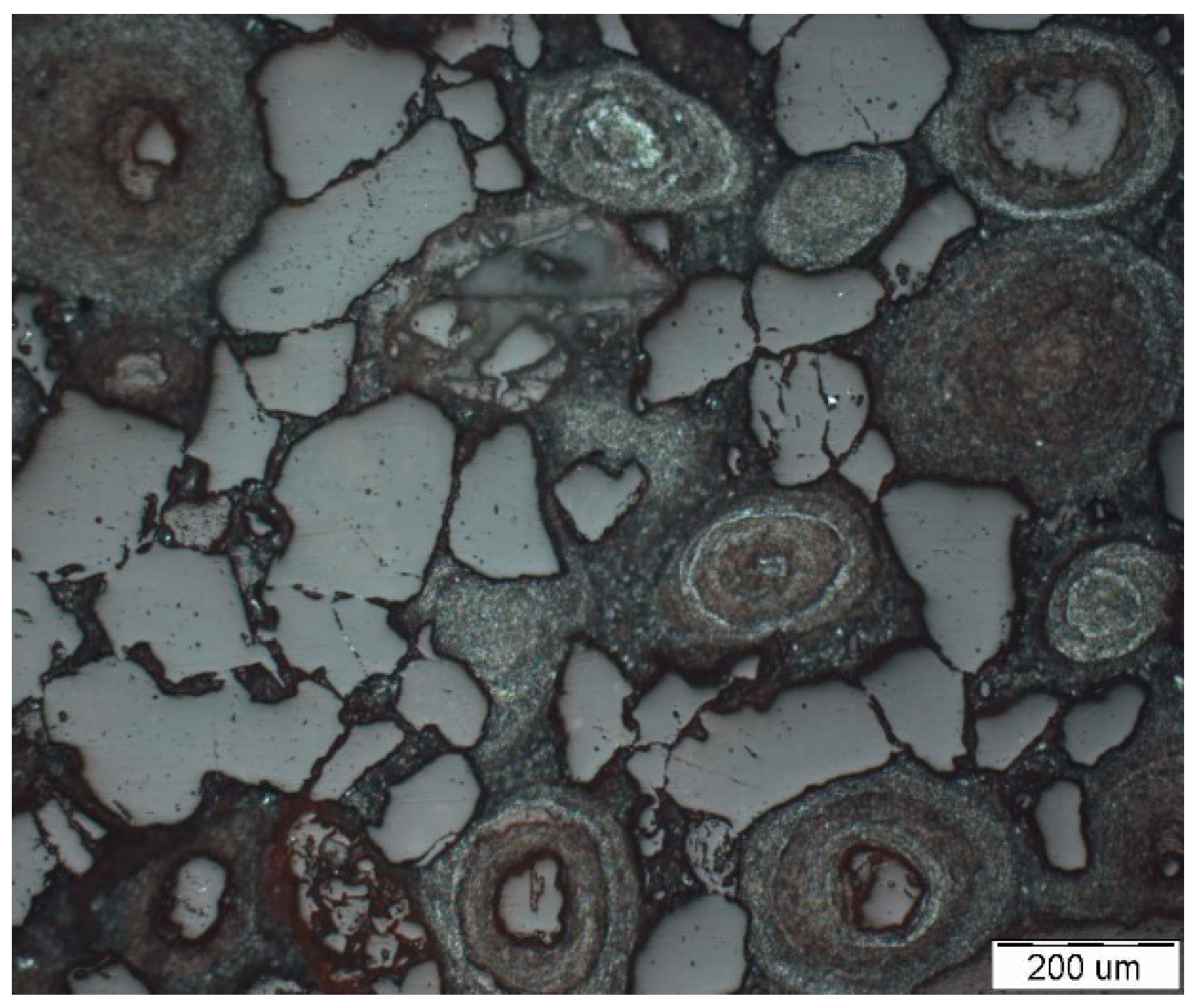


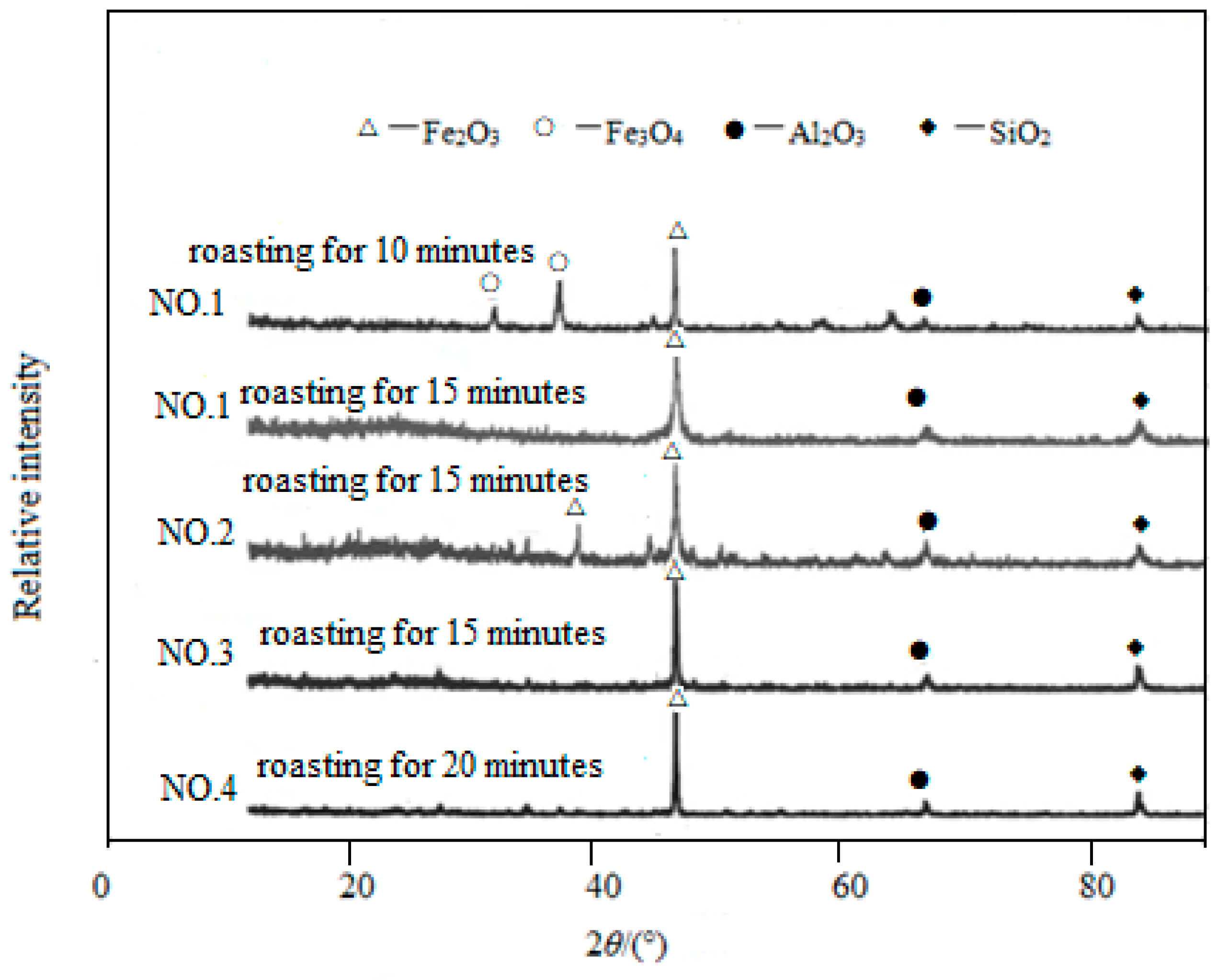

| Raw Materials | TFe | FeO | SiO2 | CaO | MgO | Al2O3 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iron concentrate | 65.58 | 23.40 | 2.49 | 0.015 | 0.038 | 0.07 | 0.03 |
| Oolitic hematite | 55.29 | 0.89 | 18.17 | 1.18 | 0.29 | 5.98 | 0.56 |
| Bentonite | 2.76 | - | 57.38 | 3.01 | 1.98 | 14.23 | - |
| Scheme | Oolitic Hematite/% | Iron Concentrate/% | Bentonite/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 99.0 | 1.0 |
| 2 | 6.0 | 93.0 | 1.0 |
| 3 | 8.0 | 91.0 | 1.0 |
| 4 | 10.0 | 89.0 | 1.0 |
| 5 | 12.0 | 87.0 | 1.0 |
| Pellet Type | T10/°C | T40/°C | ΔT/°C | Dripping Temperature/°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO. 1 | 1079 | 1195 | 116 | 1232 |
| NO. 2 | 1087 | 1210 | 123 | 1295 |
| NO. 3 | 1104 | 1287 | 183 | 1338 |
| NO. 4 | 1120 | 1362 | 242 | 1405 |
| Pellet Type | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | TFe | FeO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO. 1 | 2.98 | 0.16 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 65.13 | 2.28 |
| NO. 2 | 5.32 | 1.97 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 64.09 | 0.70 |
| NO. 3 | 7.07 | 3.25 | 0.22 | 0.31 | 63.78 | 0.68 |
| NO. 4 | 9.12 | 4.50 | 0.31 | 0.45 | 62.83 | 0.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, F. Compressive Strength and Metallurgical Properties of Pellets with Added Oolitic Hematite. Metals 2025, 15, 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15030303
Yang F. Compressive Strength and Metallurgical Properties of Pellets with Added Oolitic Hematite. Metals. 2025; 15(3):303. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15030303
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Fu. 2025. "Compressive Strength and Metallurgical Properties of Pellets with Added Oolitic Hematite" Metals 15, no. 3: 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15030303
APA StyleYang, F. (2025). Compressive Strength and Metallurgical Properties of Pellets with Added Oolitic Hematite. Metals, 15(3), 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15030303





