Microstructure and Mechanical Behaviors of Fiber-Laser-Welded QP980-QP1180 Steels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
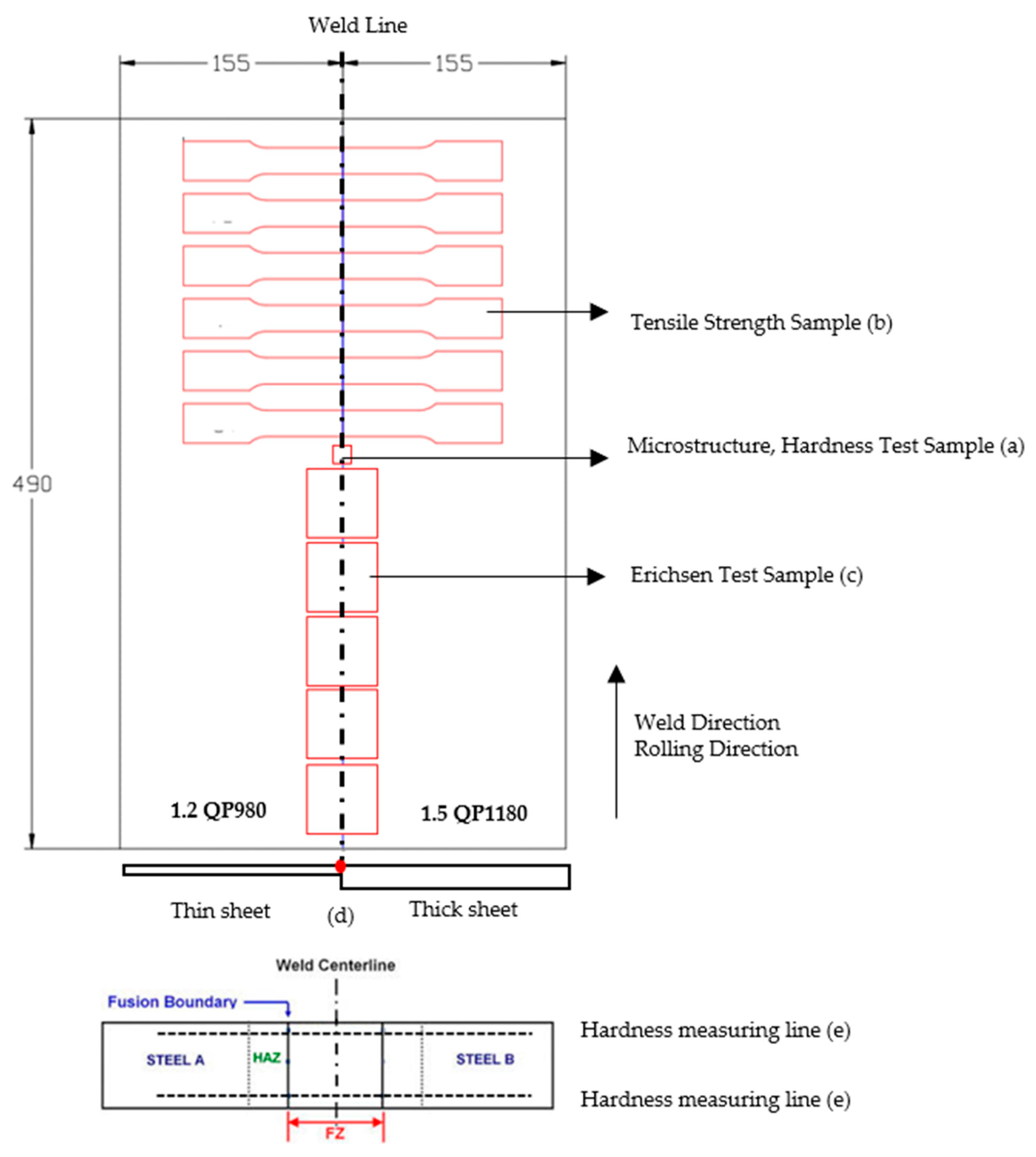
2.1. Materials and Laser Welding Process
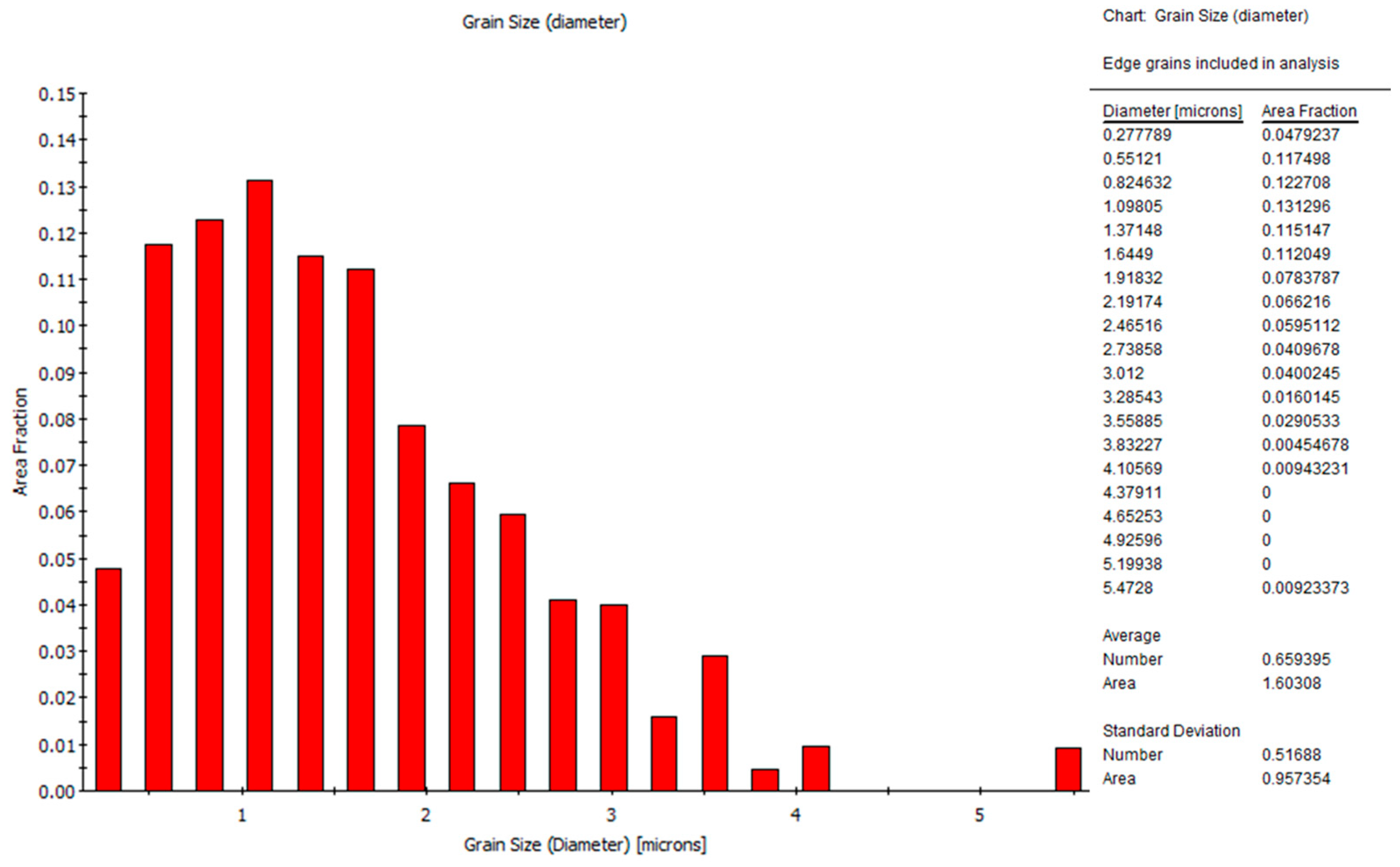
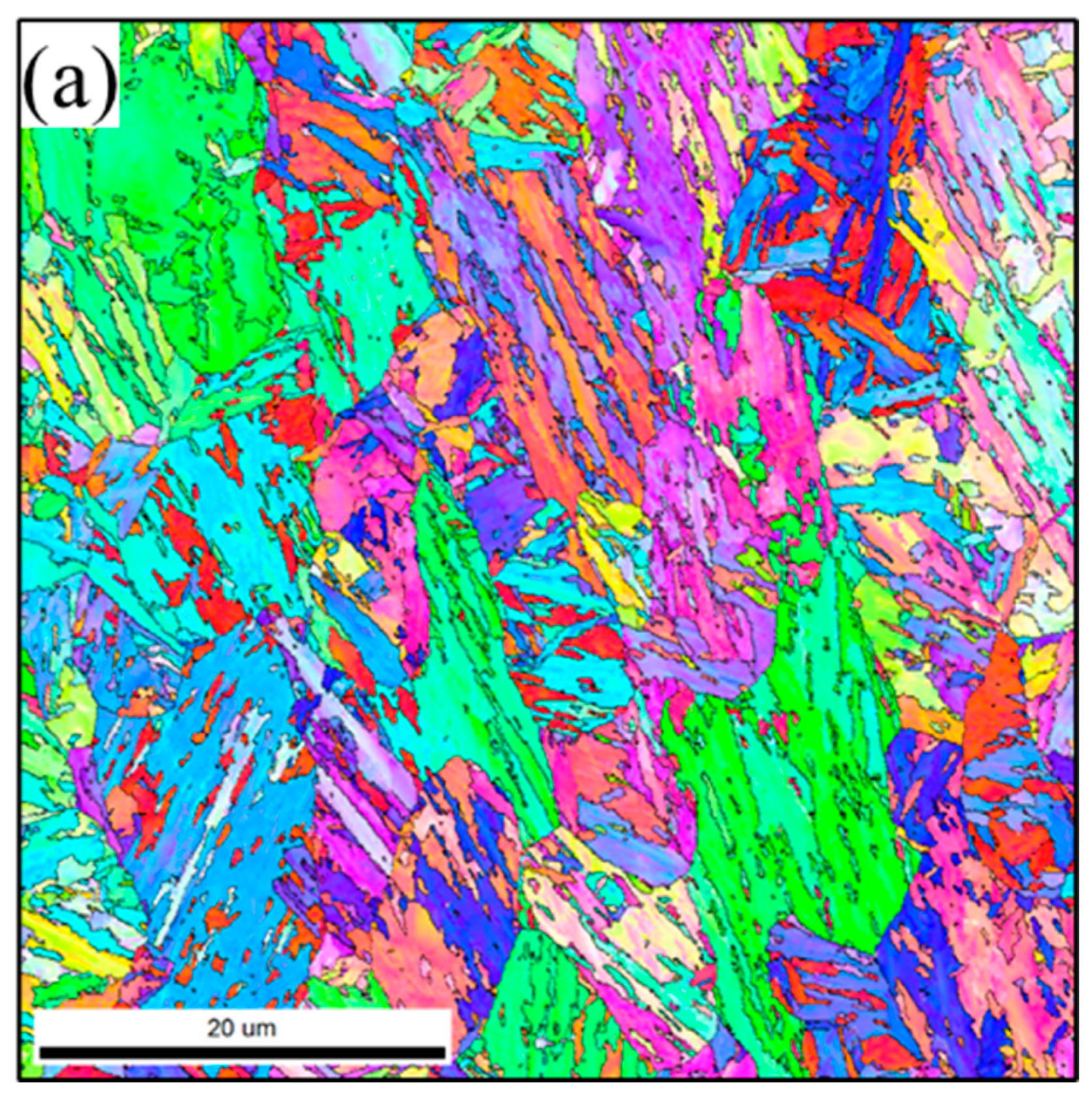
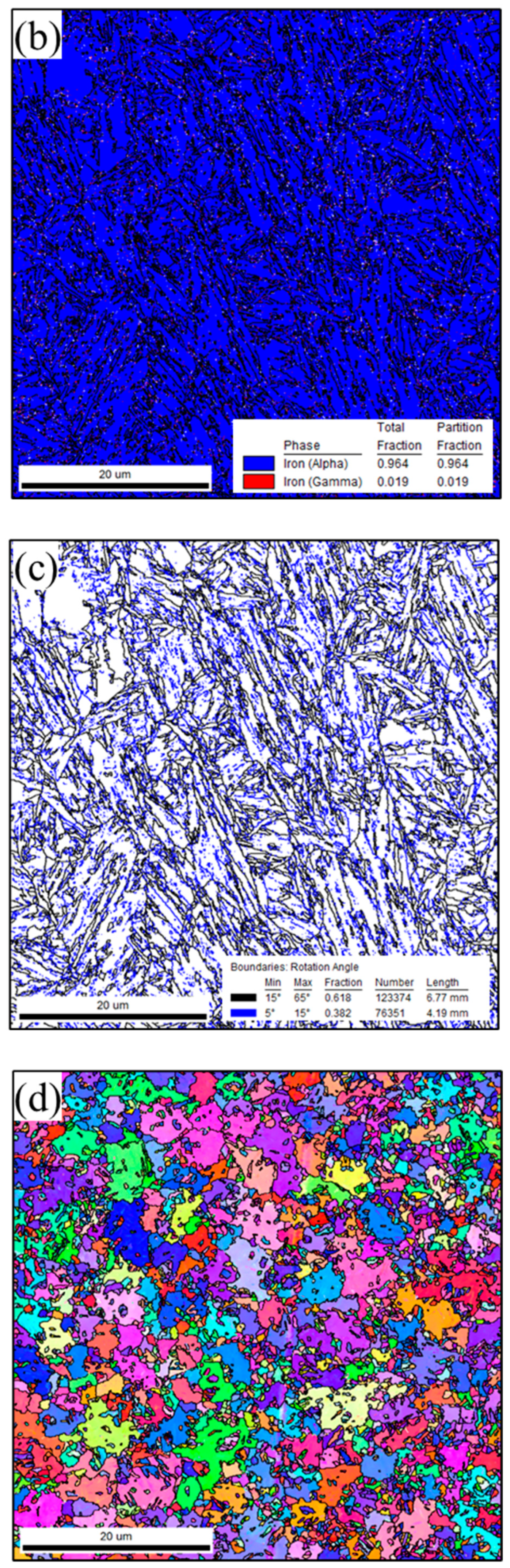
2.2. Microstructural Characterizations
2.3. Mechanical Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Metallographic Characterization
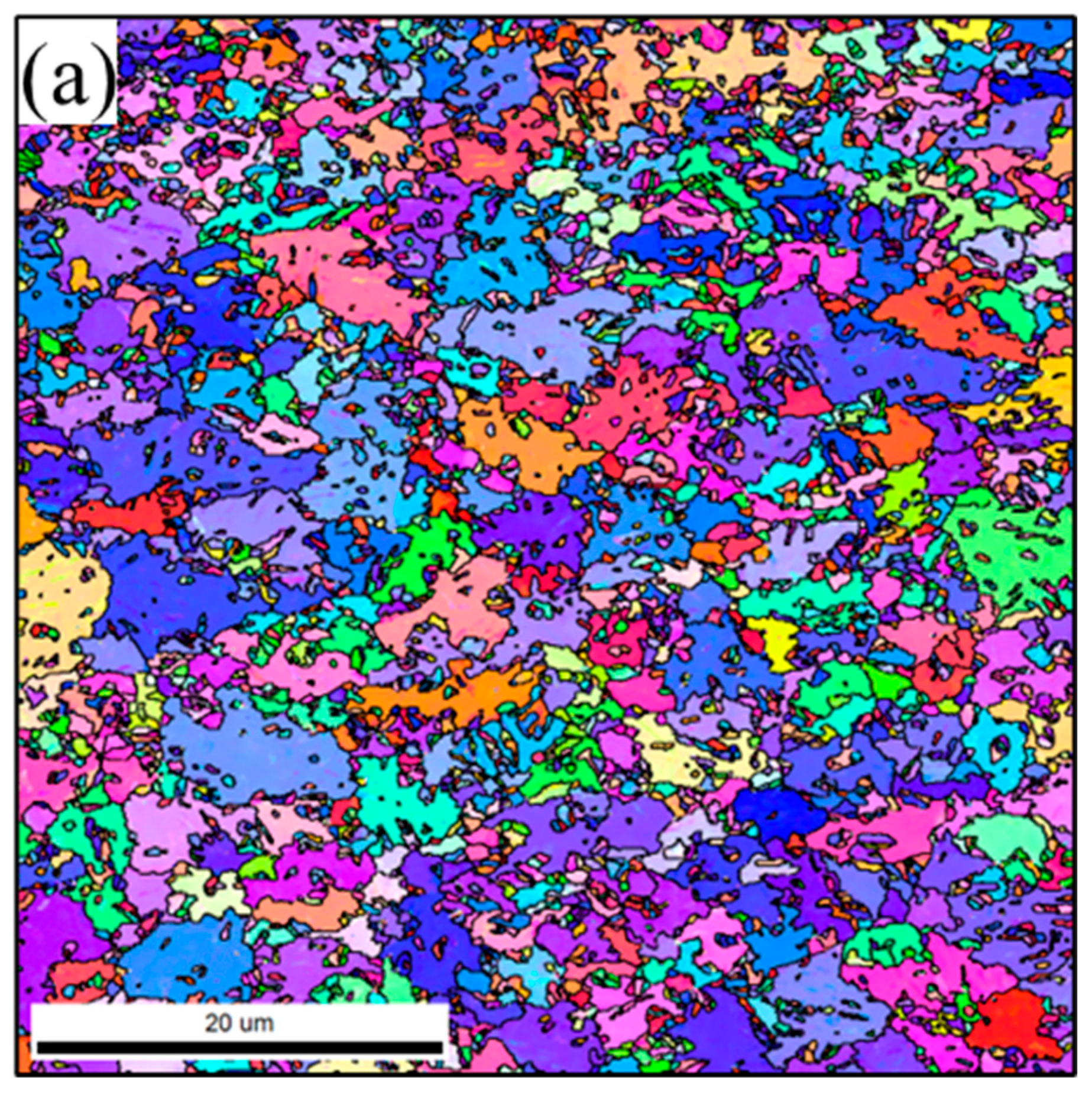
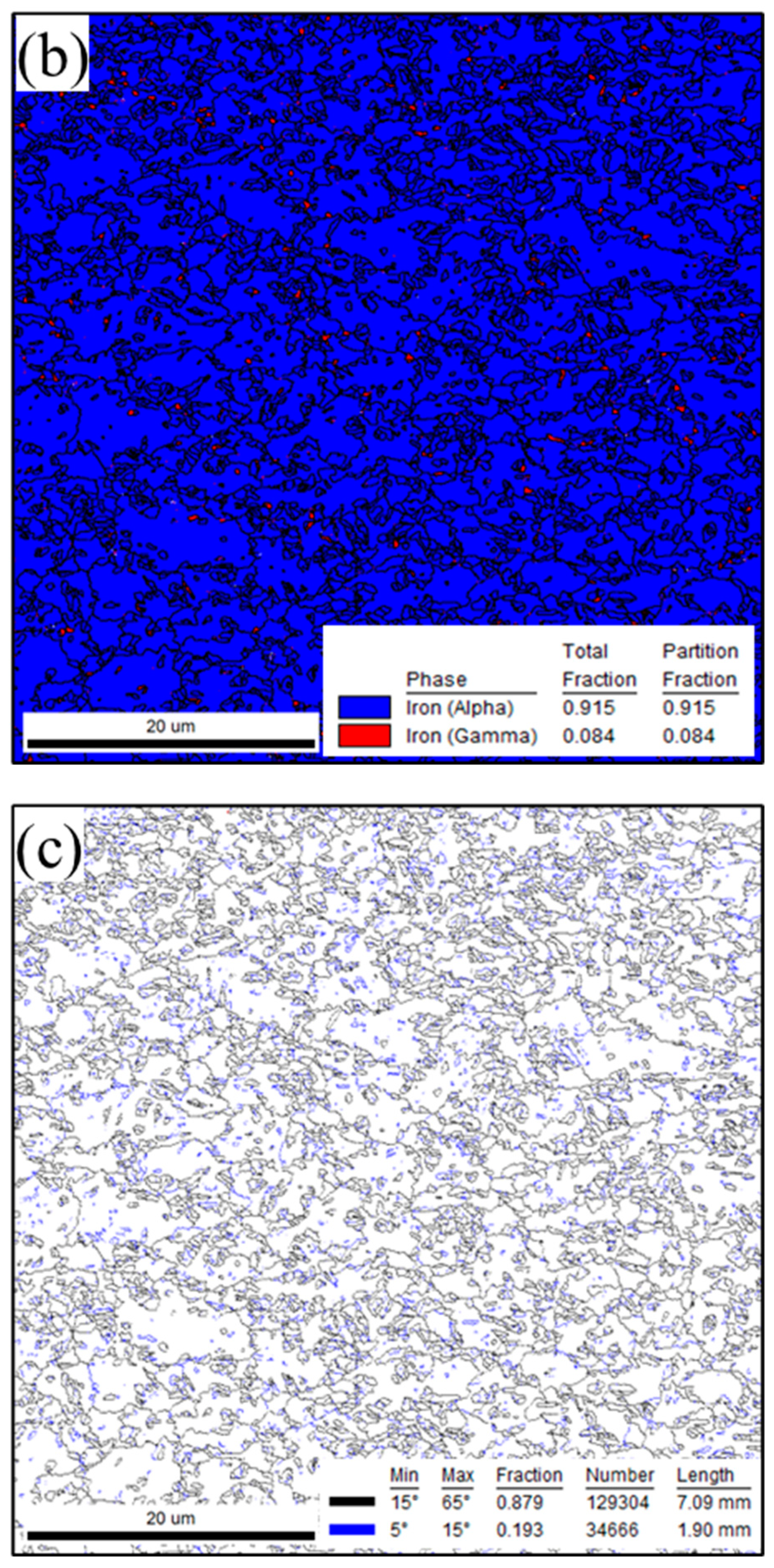
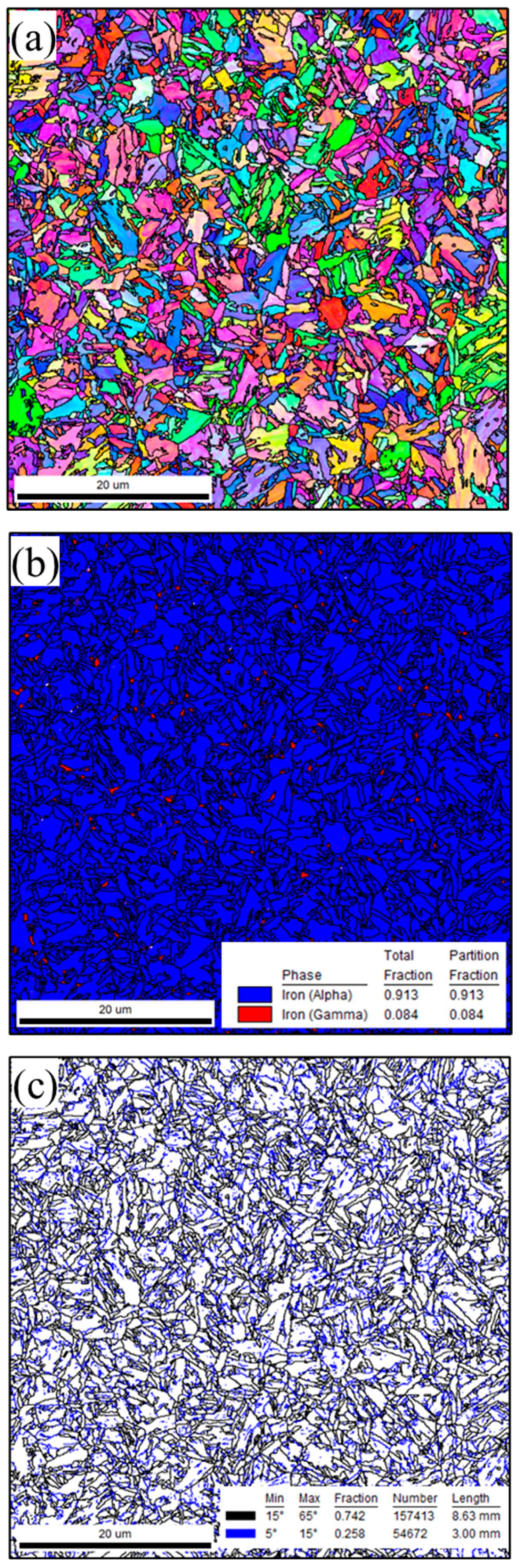
3.1.1. Microstructure of BMs
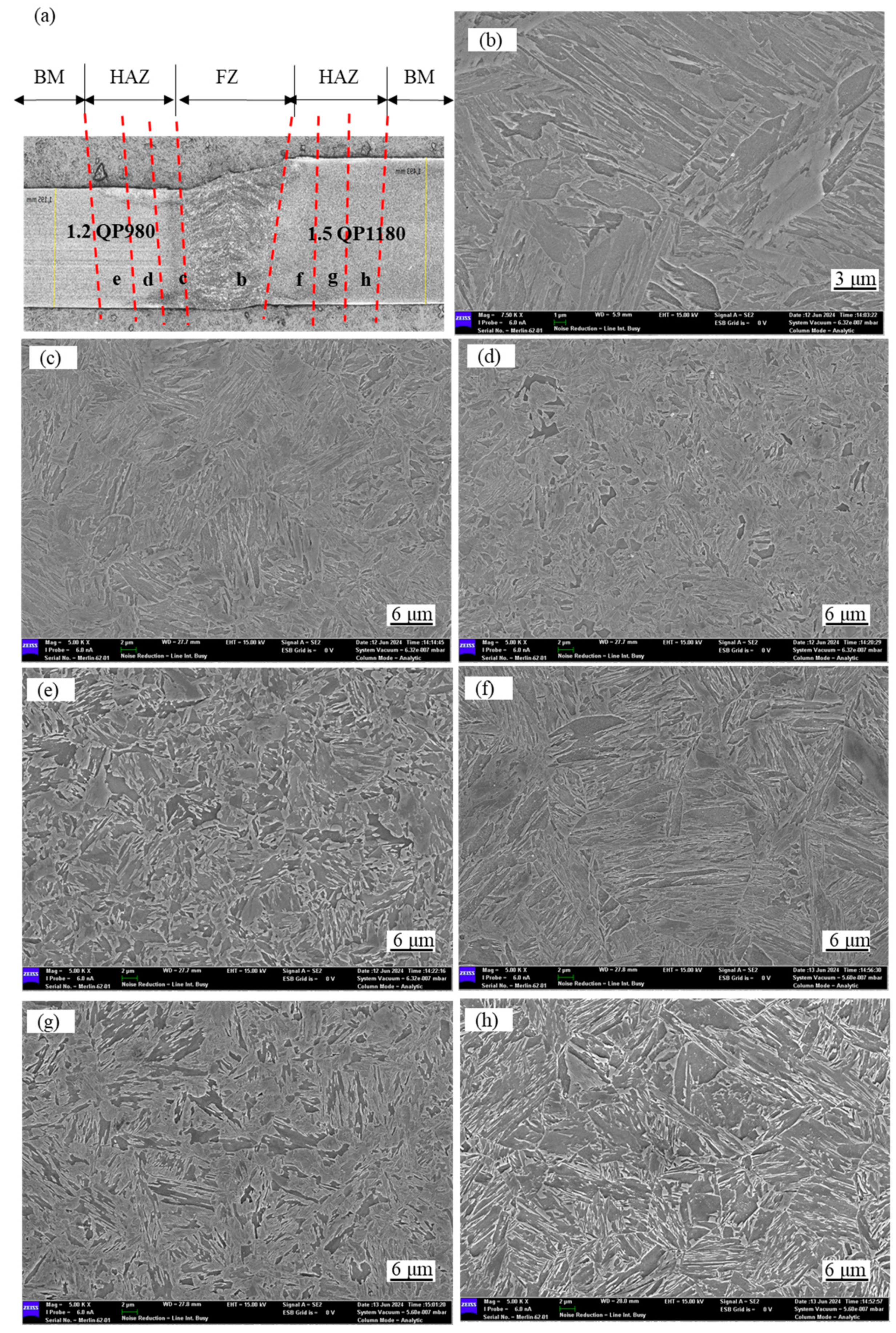
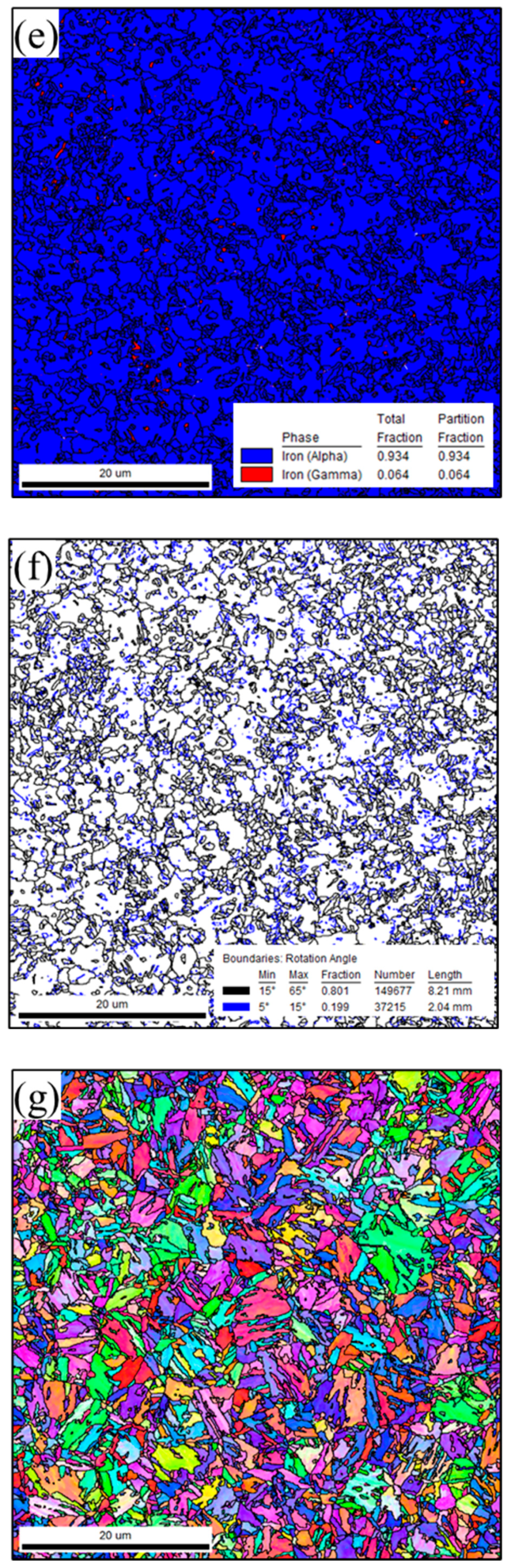
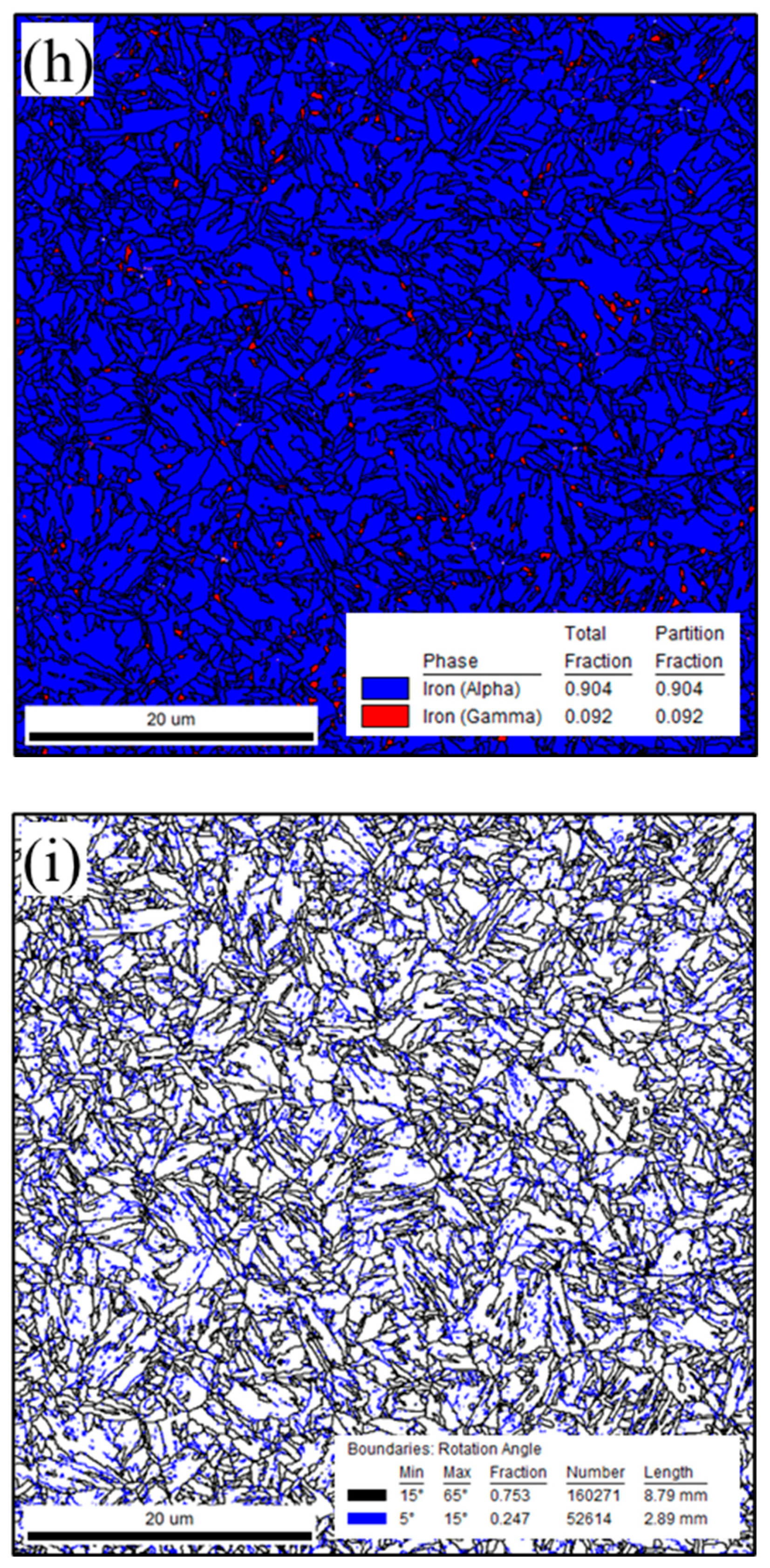
3.1.2. Microstructure of Laser-Welded 1.2 mm QP980 and 1.5 mm QP1180 Steels
3.2. Mechanical Characterization
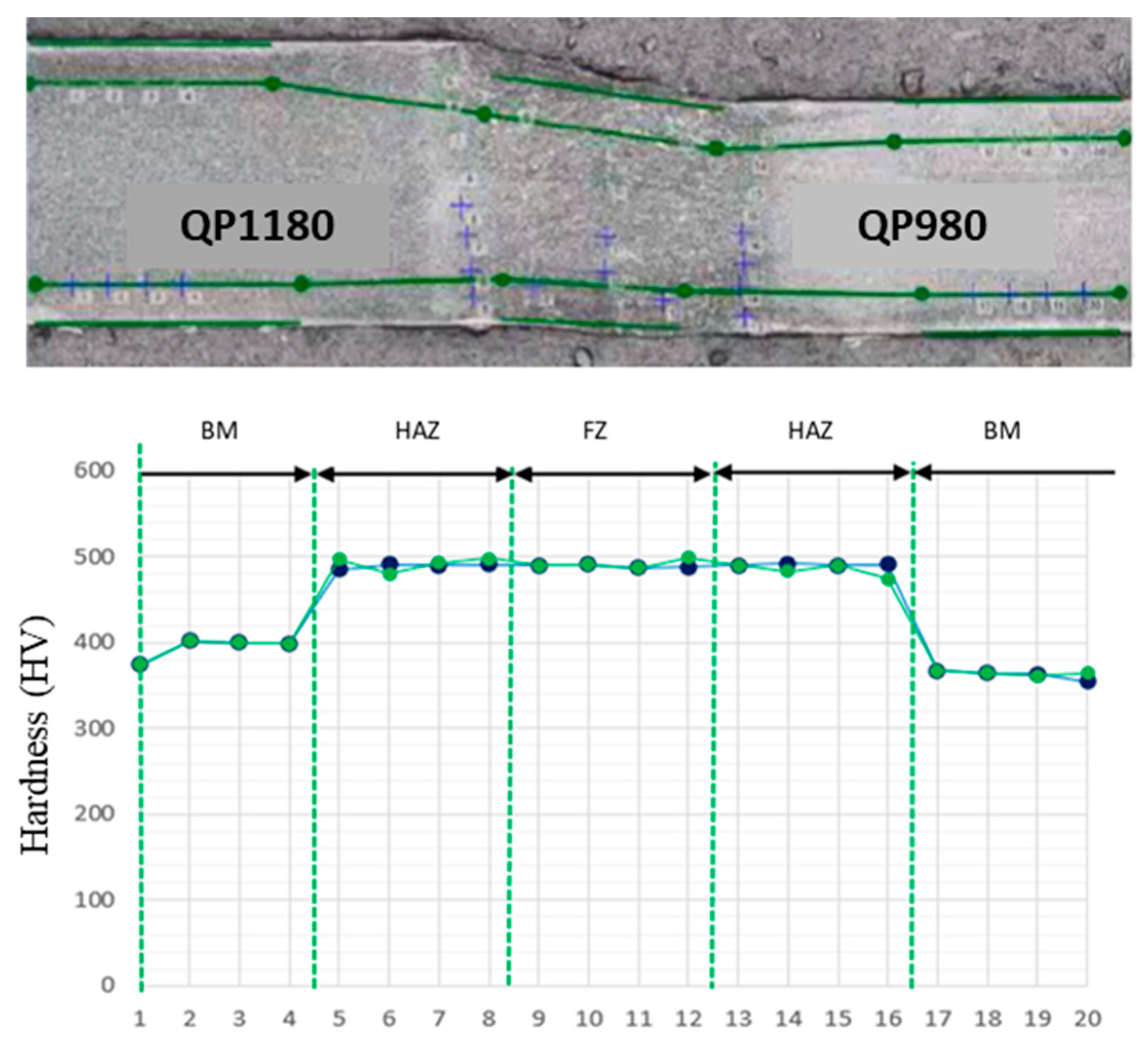
3.2.1. Microhardness Measurement
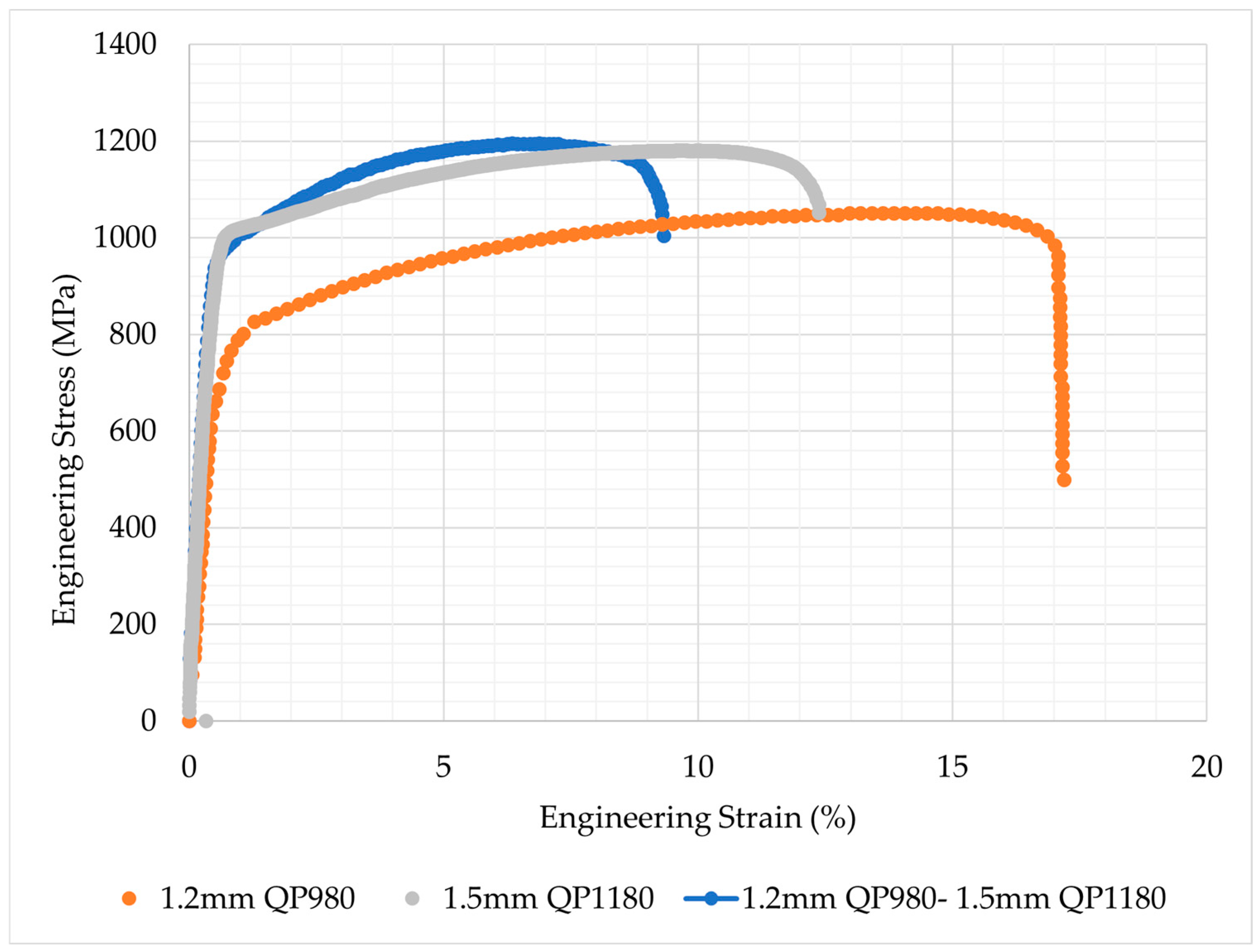
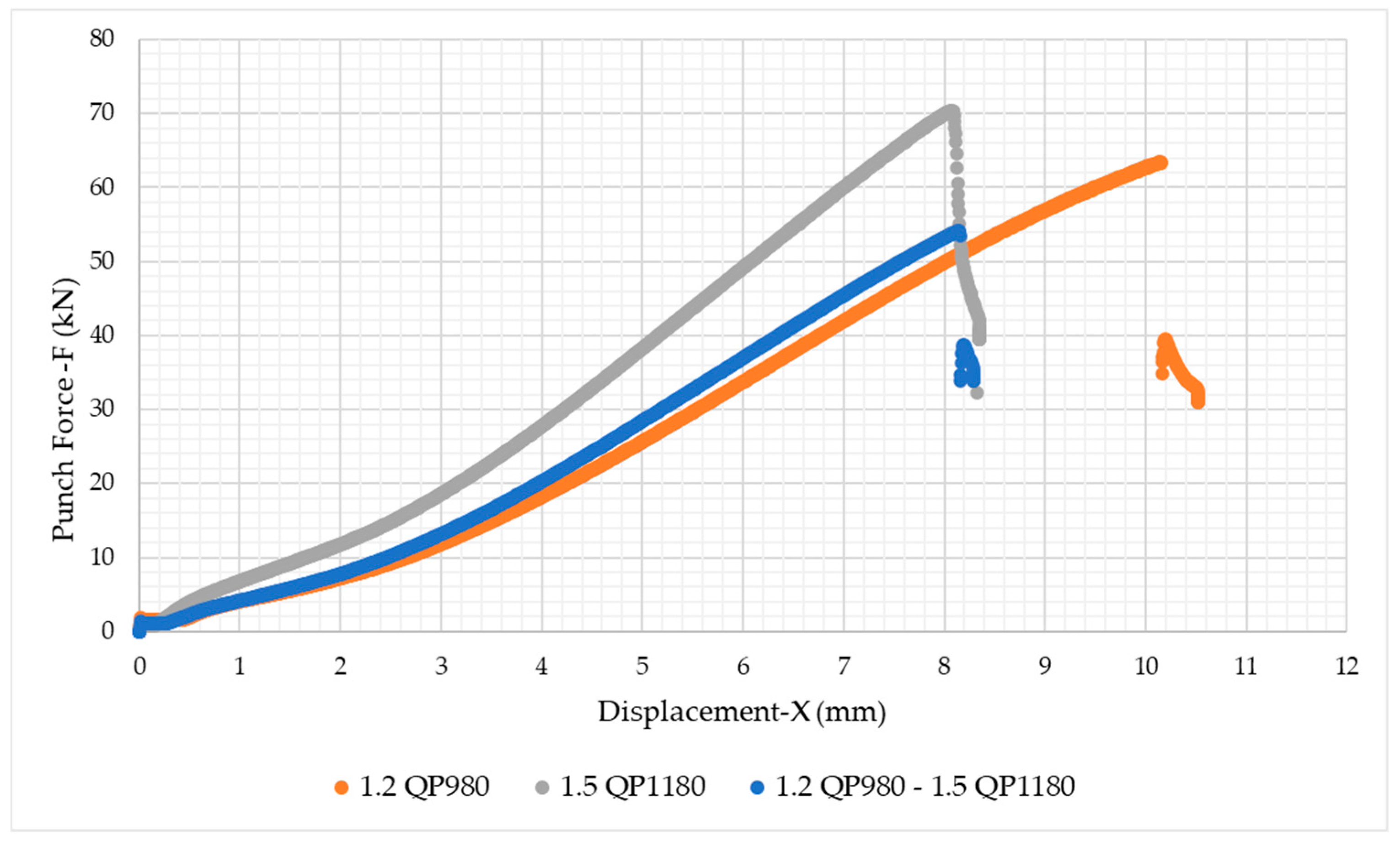
3.2.2. Tensile Tests
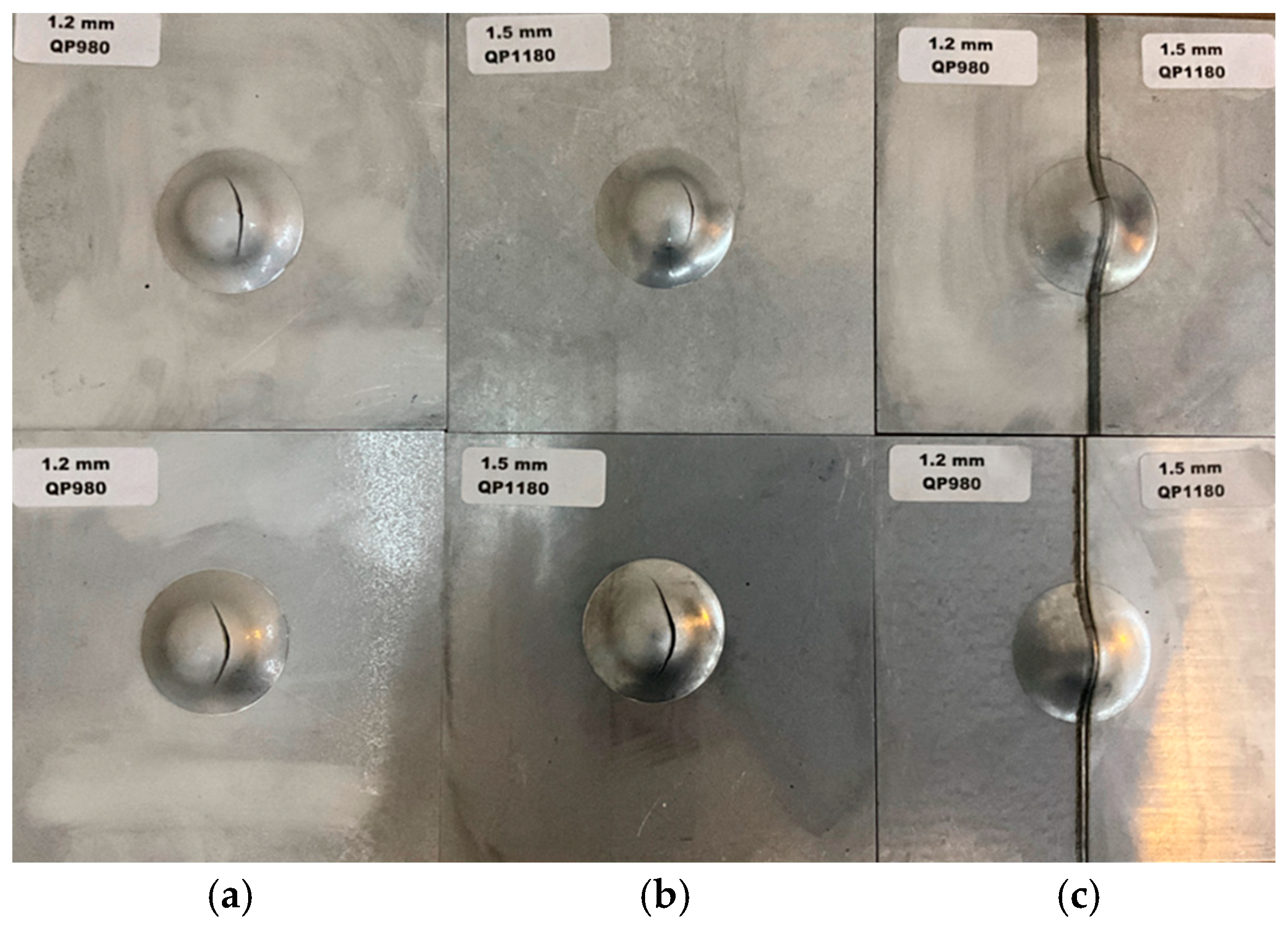
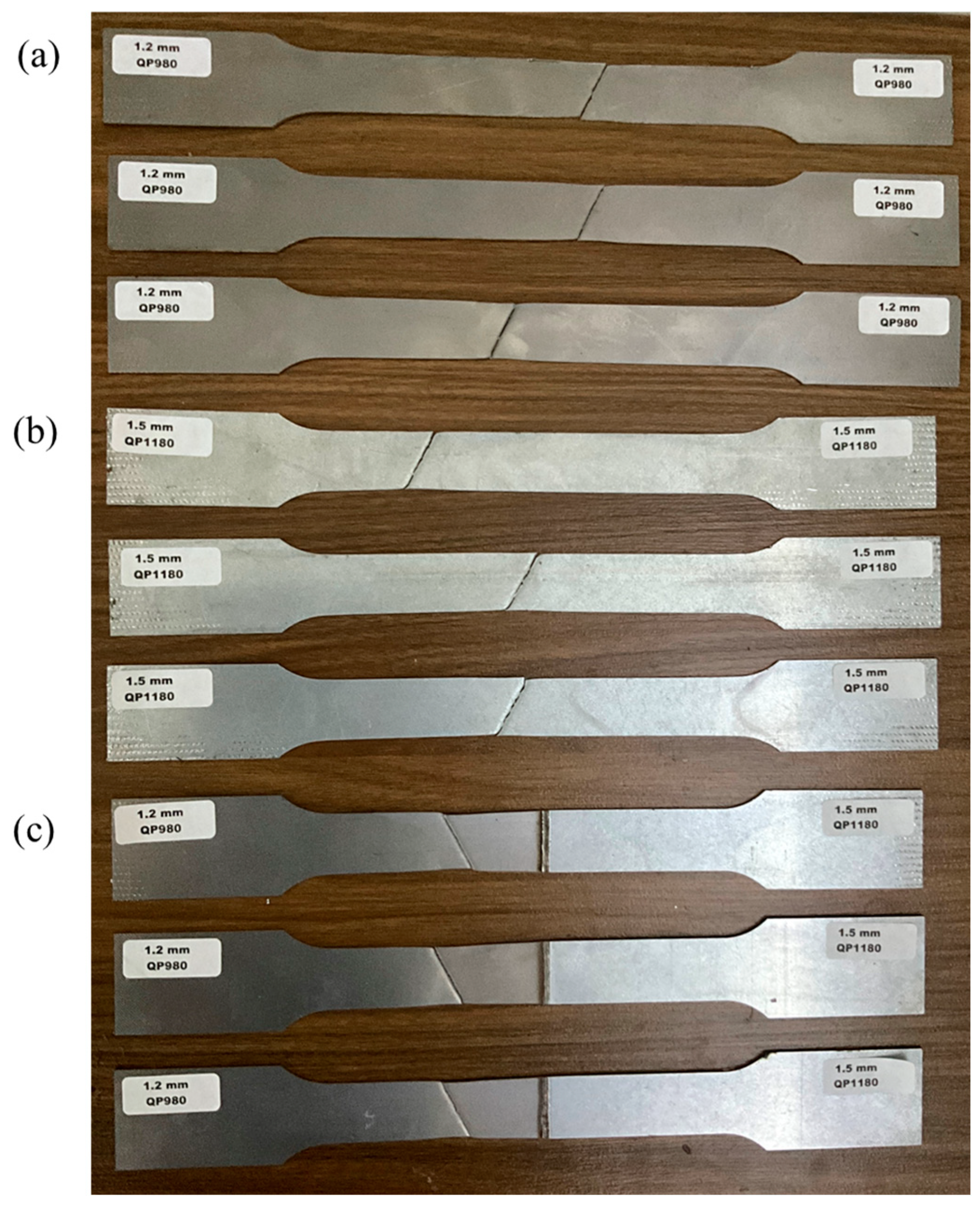
3.2.3. Erichsen Tests
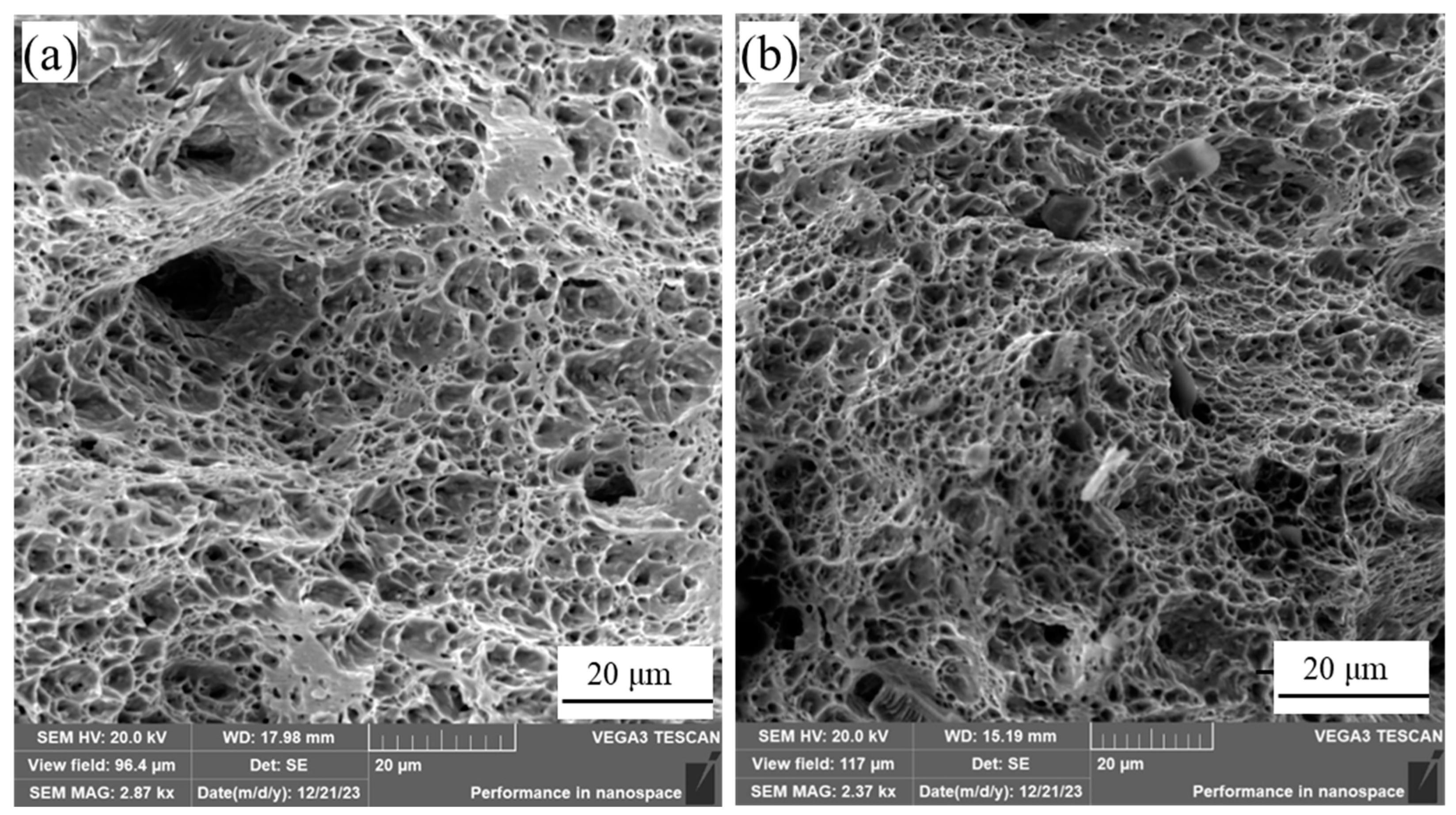
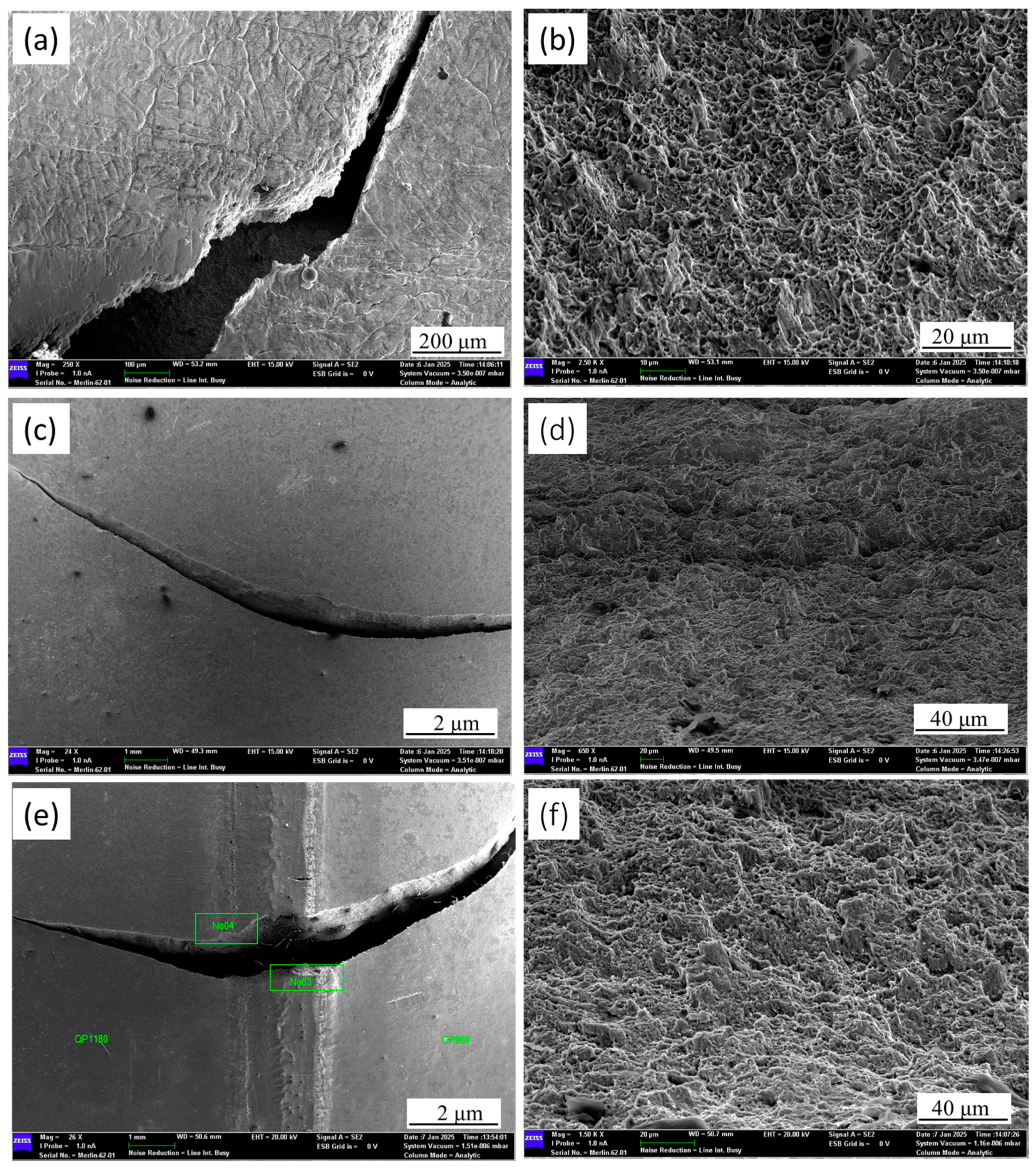
3.3. Fractography
4. Conclusions
- (a)
- Laser welding 1.2 mm QP980 and 1.5 mm QP1180 steels resulted in a microstructure that consisted of a lath M phase in FZ. The microstructure of QP980 and QP1180 steels consists of the M phase at the supercritical HAZ and is transformed into a microstructure that consists of RA, F, and M in the sub-critical HAZ.
- (b)
- The hardness of the BMs of QP980 and QP1180 were measured as 380 Hv and 400 Hv, respectively. The microhardness of the FZ of the joint was measured as 510 Hv. This value is considerably higher than those of both BMs. The hardness value of the HAZ reflected a limited variation through the HAZ of both the QP980 and QP1180 sides. The HAZ hardness values decreased sharply to the BM hardness levels by the end of the sub-critical HAZ.
- (c)
- The yield and tensile strengths of the welded steels were measured as 816.6 MPa and 1194.2 MPa, respectively. The uniform elongation and elongation at break values of these steels were determined as 6.9% and 9.3%, respectively.
- (d)
- The laser-welded pair showed an Erichsen index of 6.98 mm, which is 70% of that of the 1.2 QP980 steel. This value is acceptable for industrial applications of QP steel. The lower Erichsen index of the pair is mainly attributed to the full M microstructure of the weld seam, leading to the early onset of fracture at the biaxial tensile loading of the Erichsen test.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHSS | Advanced High-Strength Steel |
| BIW | Body in White |
| BM | Base Metal |
| EBSD | Electron Backscatter Diffraction |
| EL | Elongation |
| F | Ferrite |
| FZ | Fused Zone |
| HAGB | High Angle Grain Boundaries |
| HAZ | Heat-Affected Zone |
| Hv | Microhardness Vickers |
| LME | Liquid Metal Embrittlement |
| M | Martensite |
| QP | Quenching and Portioning |
| RA | Retained Austenite |
| TM | Tempered Martensite |
| TRIP | Transformation-Induced Plasticity |
| UTS | Ultimate Tensile Strength |
| YS | Yield Strength |
References
- Billur, E.; Çetin, B.; Gürleyik, M. New Generation Advanced High Strength Steels: Developments, Trends and Constraints. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2016, 2, 50–62. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission and CRU. European Commission and CRU. Available online: https://commission.europa.eu/index_en (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Stellantis. Stellantis: Official Global Website. Available online: https://www.stellantis.com/en/company/dare-forward-2030/care (accessed on 18 July 2024).
- Grajcar, A.; Morawiec, M.; Różański, M.; Stano, S. Twin-spot laser welding of advanced high-strength multiphase microstructure steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2017, 92, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonstein, N. Dual-Phase Steels in Automotive Steels; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017; pp. 169–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butuc, M.C.; Vincze, G.; Santos, R.; Pereira, A.; Santos, A.D.; Amaral, R.L.; Barlat, F. Formability of third generation advanced high strength steel: Experimental and theoretical approach. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 281, 109559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao Steel Company. Baowu Open Innovation. Available online: http://rd.baosteel.com/zypt/en/ability/see/abilityDetailsBSSF5/1/318362afb3924a479c3bb4407ce48f6a (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- World Auto Steel. The Latest Global Formability Diagram. Available online: https://www.worldautosteel.org/ahss-insights-blog-the-new-global-formability-diagram (accessed on 3 March 2022).
- Demir, S.; Doruk, E. New generation steels for light weight vehicle safety related applications. Mater. Test. 2024, 66, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.B.; Chen, Y.A.; Sheng, J.; Li, D.Z.; Lu, H.H.; Bai, P.K.; Huang, Z.Q.; Li, J.Y.; Zhao, C. A comprehensive overview of high strength and toughness steels for automobile based on QP process. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 2216–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shome, M.; Tumuluru, M. Introduction to Welding and Joining of Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS) in Welding and Joining of Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS); Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2015; pp. 1–8. ISBN 9780857098580. [Google Scholar]
- Aydin, H.; Tutar, M.; Davut, K.; Bayram, A. Effect of welding current on microstructure and mechanical properties of 15% deformed TWIP steel joined with electrical resistance spot welding. J. Fac. Eng. Archit. Gazi Univ. 2021, 35, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncel, O.; Aydın, H.; Çetin, Ş. Nd: Yag lazer kaynağı ile birleştirilen DP600 çeliğinde darbe süresinin mikroyapı ve mekanik özelliklerine etkisi. In Proceedings of the 9th International Automotive Technologies Congress, OTEKON, Bursa, Türkiye, 7–8 May 2018; Available online: https://www.otekon.org/dokuman/books/9thOtekonBook.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2018).
- Farabi, N.; Chen, D.L.; Zhou, Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of laser welded dissimilar DP600/DP980 dual-phase steel joints. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.W.; Liu, M.; Zhang, H.; Xie, G.M.; Xue, P.; Wu, L.H.; Zhang, Z.; Ni, D.R.; Xiao, B.L.; Ma, Z.Y. Welding behavior of an ultrahigh-strength quenching and partitioning steel by fusion and solid-state welding methods. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 1289–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertem, R.U. Investigation of The Effect of The Laser Welding Parameters Change on Welding Seam for Stainless Steel. Sigma J. Eng. Nat. Sci. 2013, 31, 583–593. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/sigma/issue/65813/1026759 (accessed on 1 December 2013).
- Turan, M.K.; Yuce, C.; Karpat, F. Numerical and experimental investigation of the effect of heat input on weld bead geometry and stresses in laser welding. Mater. Test. 2024, 66, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.L.; Lu, Y.; Xue, R.J.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, Y.Z.; Nian, B.G.; Ma, C. Microstructure Characterization and Mechanical Properties of Laser Welded Super High Strength QP980 Automotive Steel. Solid State Phenom. 2023, 354, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, M.; Jia, Q.; Chi, J.; Shi, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, H. Local microstructure and mechanical characteristics of HAZ and tensile behavior of laser welded QP980 joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 854, 143862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Wan, Z.; Peng, P.; Jia, Q.; Zou, G.; Peng, Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of fiber laser welded QP980 steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 256, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tian, J.; Yang, S.; Mu, S. Effect of water-cooling assistance on fatigue behavior of laser welded QP980 steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 2060–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahrani, M.M.; Ranjbarnodeh, E.; Ketabchi, M.; Ghassemali, E. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of laser-welded joints of 1.2 GPa-class quenching and partitioning steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 170, 110257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Yang, J.G.; Song, K.J.; Liu, X.S.; Fang, H.Y. Acceleration of regeneration treatment for nanostructured bainitic steel by rotary impacting trailed welding. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2014, 214, 2935–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farabi, N.; Chen, D.L.; Zhou, Y. Tensile properties, and work hardening behavior of laser-welded dual-phase steel joints. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2012, 21, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Peng, P.; Guo, W.; Xia, M.; Tan, C.; Wan, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. HAZ Characterization and Mechanical Properties of QP980-DP980 Laser Welded Joints. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. Ji Xie Gong Cheng Xue Bao 2021, 34, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, S.; Zhong, H.; Xiao, S.; Li, D. Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Corrosion Behavior of Laser-Welded Dissimilar Joints Between DP980 and QP980 Steel. Steel Res. Int. 2022, 93, 2100541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, M.; Li, L.; Wu, Z. Investigation on microstructure and properties of dissimilar joint between TRIP800 and QP980 fabricated by laser welding. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2021, 26, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Guo, W.; Wan, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zou, G.; Tian, Z.; Zhou, Y.N. Microstructure, and mechanical properties of laser welded dissimilar joints between QP, and boron alloyed martensitic steels. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 259, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Huang, R.; Sun, Y.; Tan, C.; Wu, L.; Chen, B.; Song, X.; Li, G. Microstructure, and mechanical properties of fiber laser welded QP980/press-hardened 22MnB5 steel joint. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 10079–10090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ma, L.; Peng, P.; Jia, Q.; Wan, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, W. Microstructural evolution and deformation behavior of fiber laser welded QP980 steel joint. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 717, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dak, G.; Pandey, C. A critical review on dissimilar welds joints between martensitic and austenitic steel for power plant application. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 58, 377–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Li, Y.; Yi, W.; Shi, S.; Dai, Y.; Liu, C.; Ren, M.; He, C. Biaxial Very High Cycle Fatigue Testing and Failure Mechanism of Welded Joints in Structural Steel Q345. Crystals 2024, 14, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Výrostková, A.; Homolová, V.; Pecha, J.; Svoboda, M. Phase evolution in P92 and E911 weld metals during ageing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 480, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saray, O.; Purcek, G.; Karaman, I.; Maier, H.J. Formability of ultrafine-grained interstitial-free steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 4194–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.O.; Pereira, A.B.; Butuc, M.C.; Vincze, G.; Festas, A.J.; Moreira, L.P. Development of a device compatible with universal testing machine to perform hole expansion and Erichsen cupping tests. Machines 2019, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Steel Grade | Coating | Thickness |
|---|---|---|
| QP980 | Uncoated | 1.2 mm |
| QP1180 | GI (hot-dip galvanized coating) | 1.5 mm |
| Sample | Yield Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Uniform Elongation (%) | Elongation to Failure (%) | Fracture Location | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.2 QP980 | 801.3 | ± | 2.3 | 1050.7 | ± | 2.3 | 14.7 | ± | 0.2 | 17.2 | ± | 0.5 | BM | |
| 1.5 QP1180 | 1042.4 | ± | 25.8 | 1180.0 | ± | 5.5 | 9.7 | ± | 0.4 | 12.4 | ± | 0.5 | BM | |
| 1.2 QP980–1.5 QP1180 | 816.6 | ± | 45.8 | 1194.2 | ± | 21.9 | 6.9 | ± | 2.6 | 9.3 | ± | 1.7 | QP980-BM | |
| Sample | Punch Force (F) (kN) | Erichsen Index (mm) | Fracture Location | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.2QP 980 | 60.81 | ± | 1.9 | 9.99 | ± | 0.4 | BM |
| 1.5QP 1180 | 71.79 | ± | 1.9 | 8.62 | ± | 0.2 | BM |
| 1.2 QP980-1.5 QP1180 | 42.55 | ± | 10.2 | 6.98 | ± | 1.0 | Weld seam |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Çelik, H.; Saray, O. Microstructure and Mechanical Behaviors of Fiber-Laser-Welded QP980-QP1180 Steels. Metals 2025, 15, 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15020174
Çelik H, Saray O. Microstructure and Mechanical Behaviors of Fiber-Laser-Welded QP980-QP1180 Steels. Metals. 2025; 15(2):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15020174
Chicago/Turabian StyleÇelik, Hafize, and Onur Saray. 2025. "Microstructure and Mechanical Behaviors of Fiber-Laser-Welded QP980-QP1180 Steels" Metals 15, no. 2: 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15020174
APA StyleÇelik, H., & Saray, O. (2025). Microstructure and Mechanical Behaviors of Fiber-Laser-Welded QP980-QP1180 Steels. Metals, 15(2), 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15020174






