Aluminum Surface Corrosion Behavior and Microstructural Evolution in Dissimilar AA6016-T4 Aluminum to DP600 Steel via Refill Friction Stir Spot Welding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
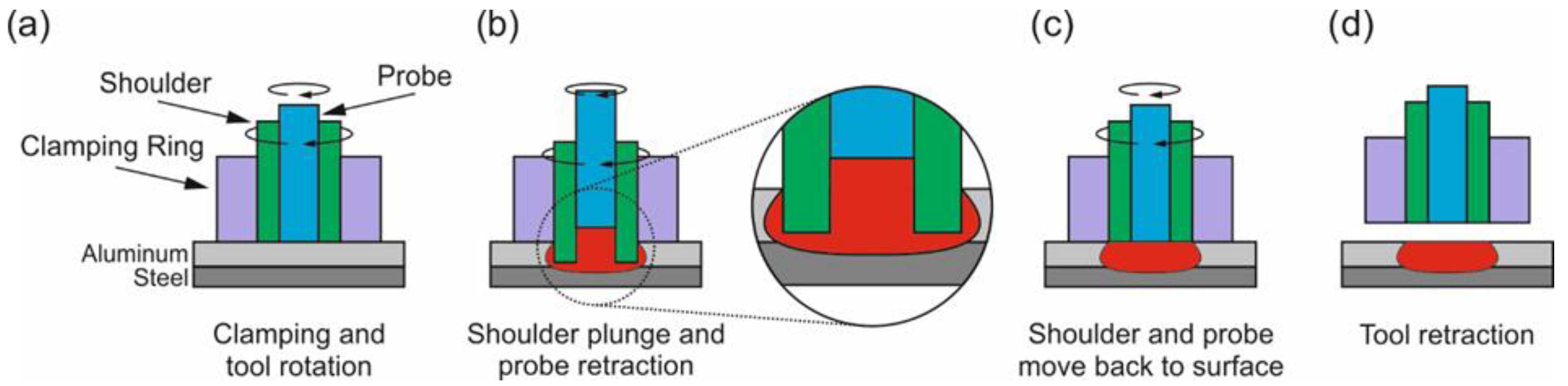
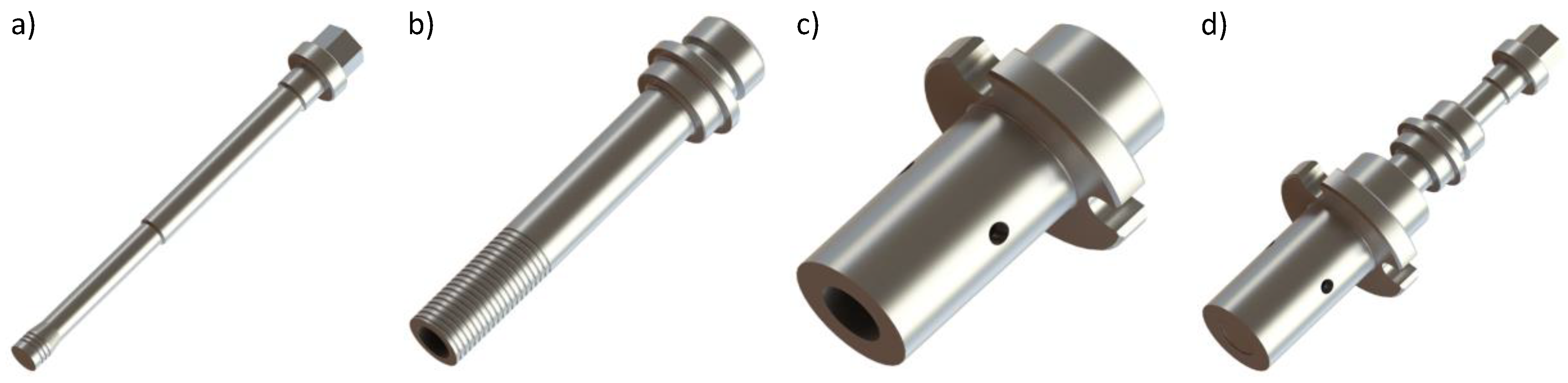
2.1. Base Materials and Welding Process
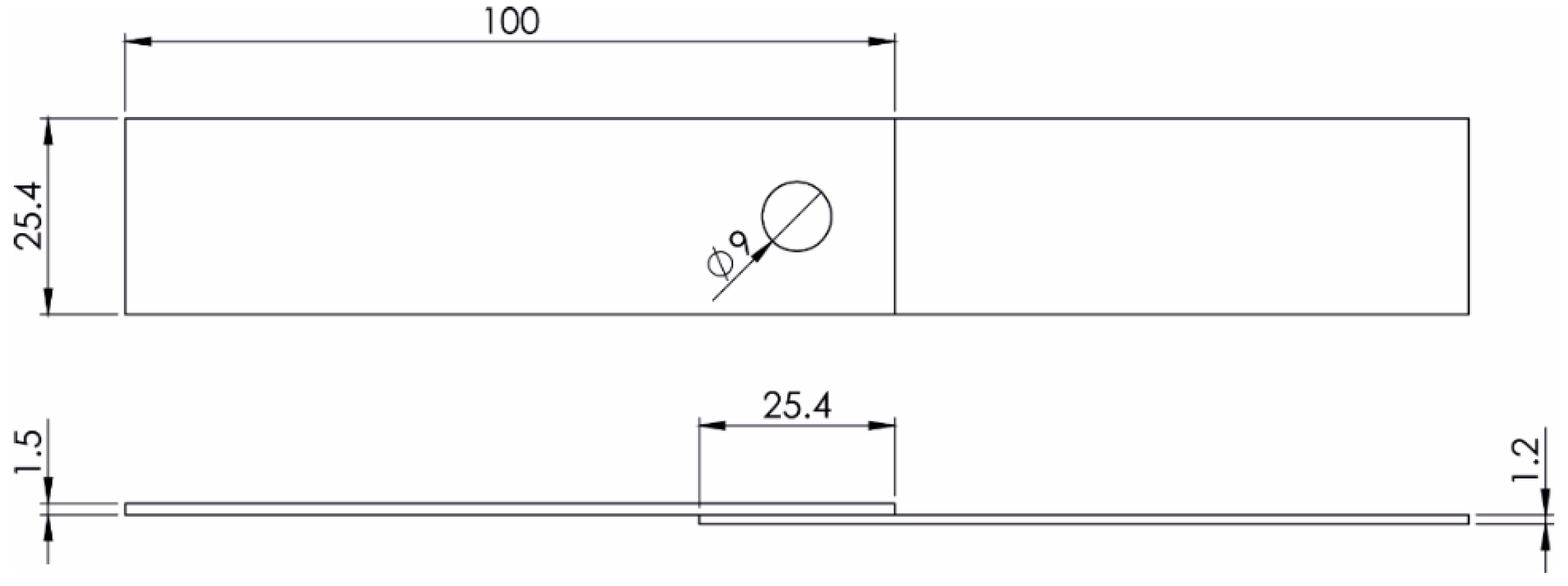
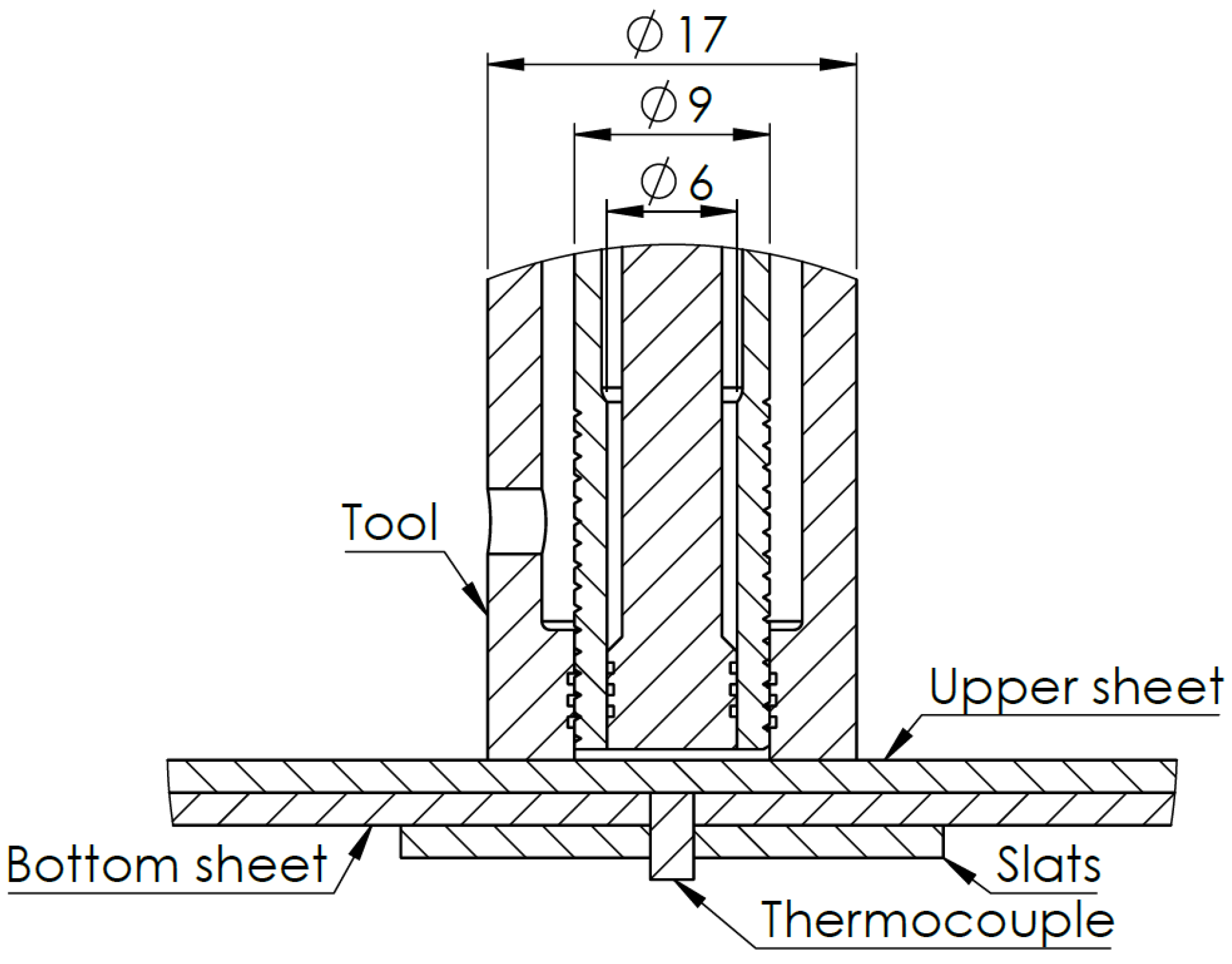
2.2. Quasi-Static Lap Shear Tests and Thermal Characterization
2.3. Hardness and Microstructure Characterization
2.4. Potentiodynamic Anodic Polarizaton Tests
3. Results and Discussion
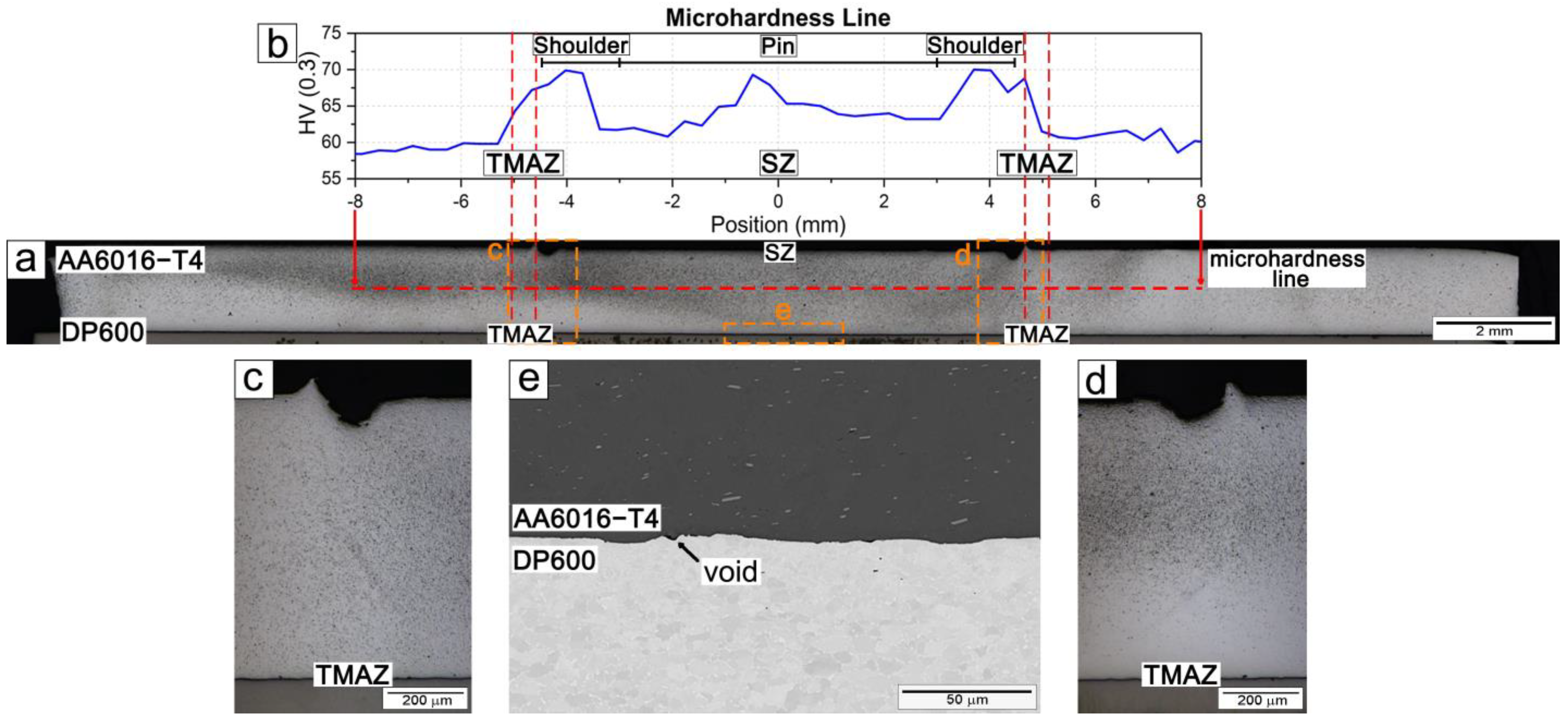
3.1. Interface Characterization
3.2. Surface Characterization
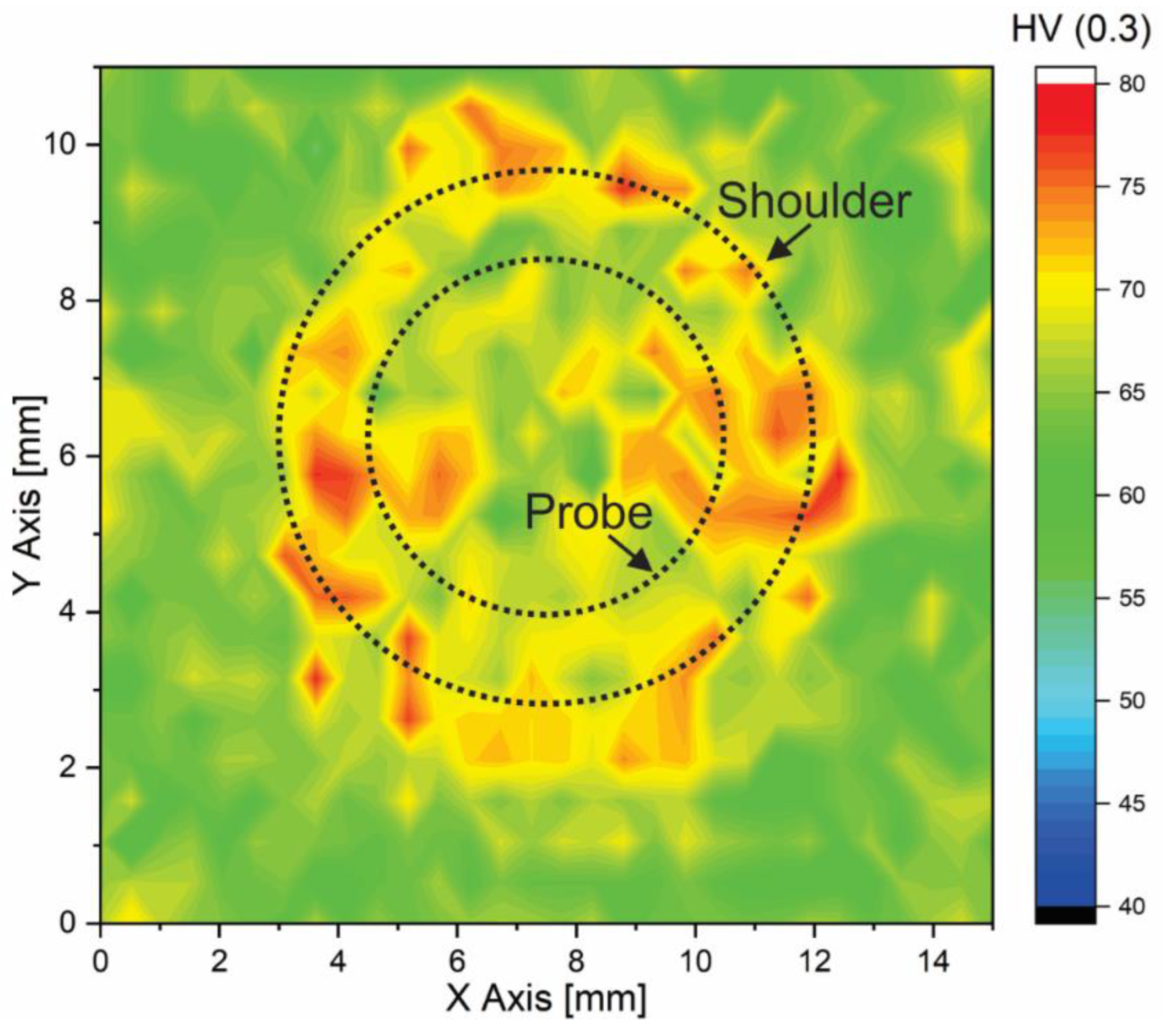
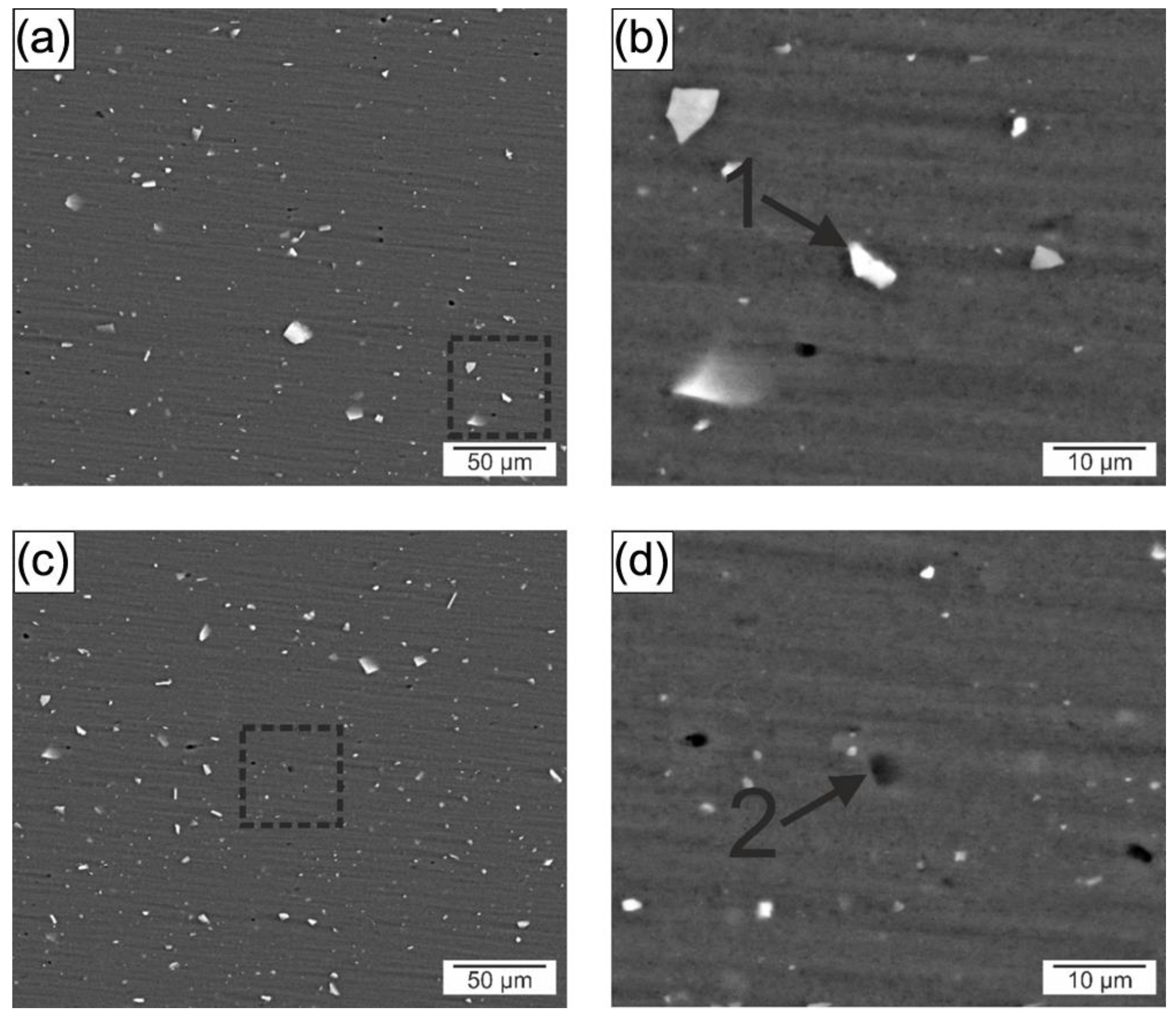
3.2.1. Microstructure and Hardness Characterization
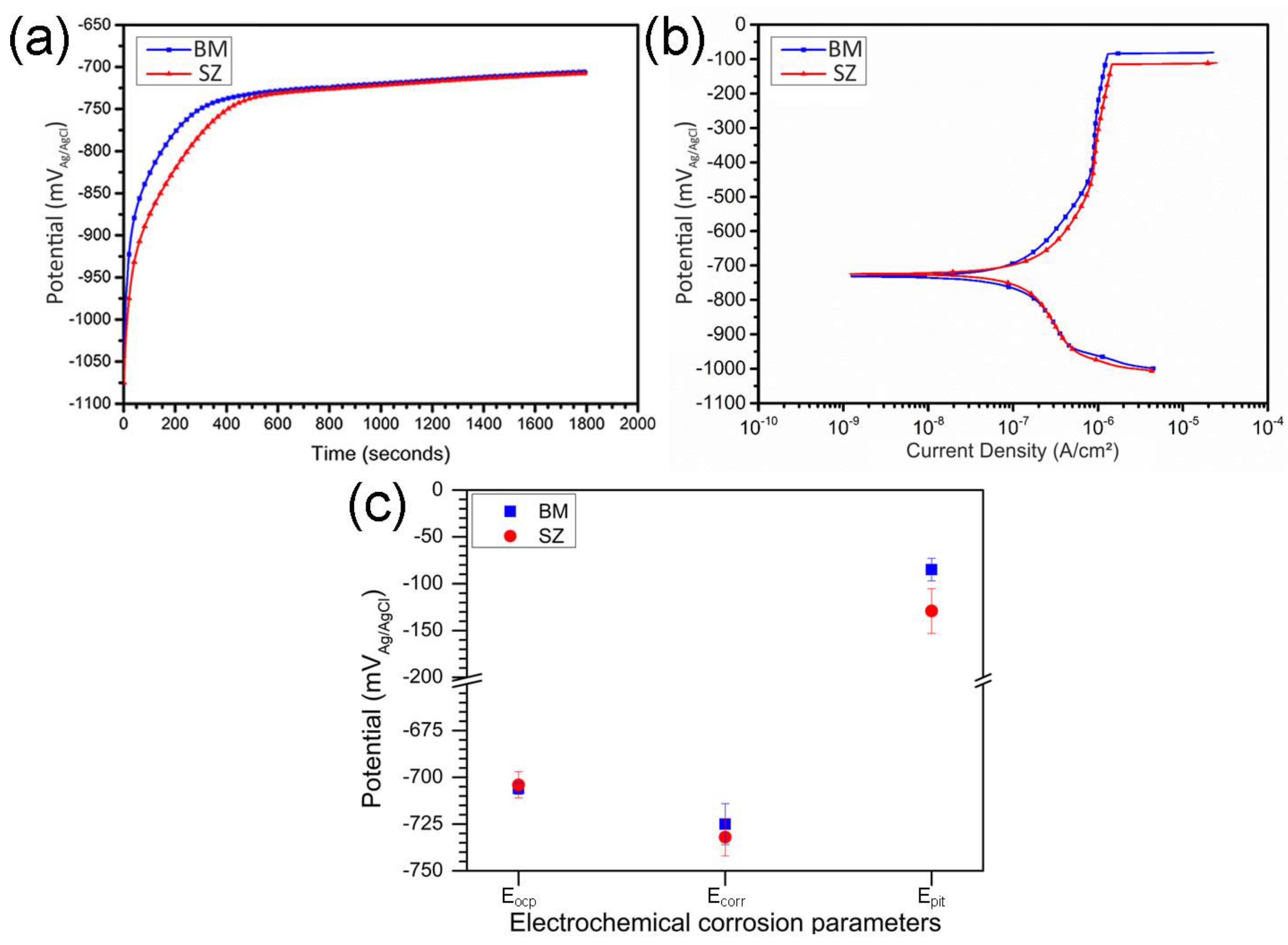
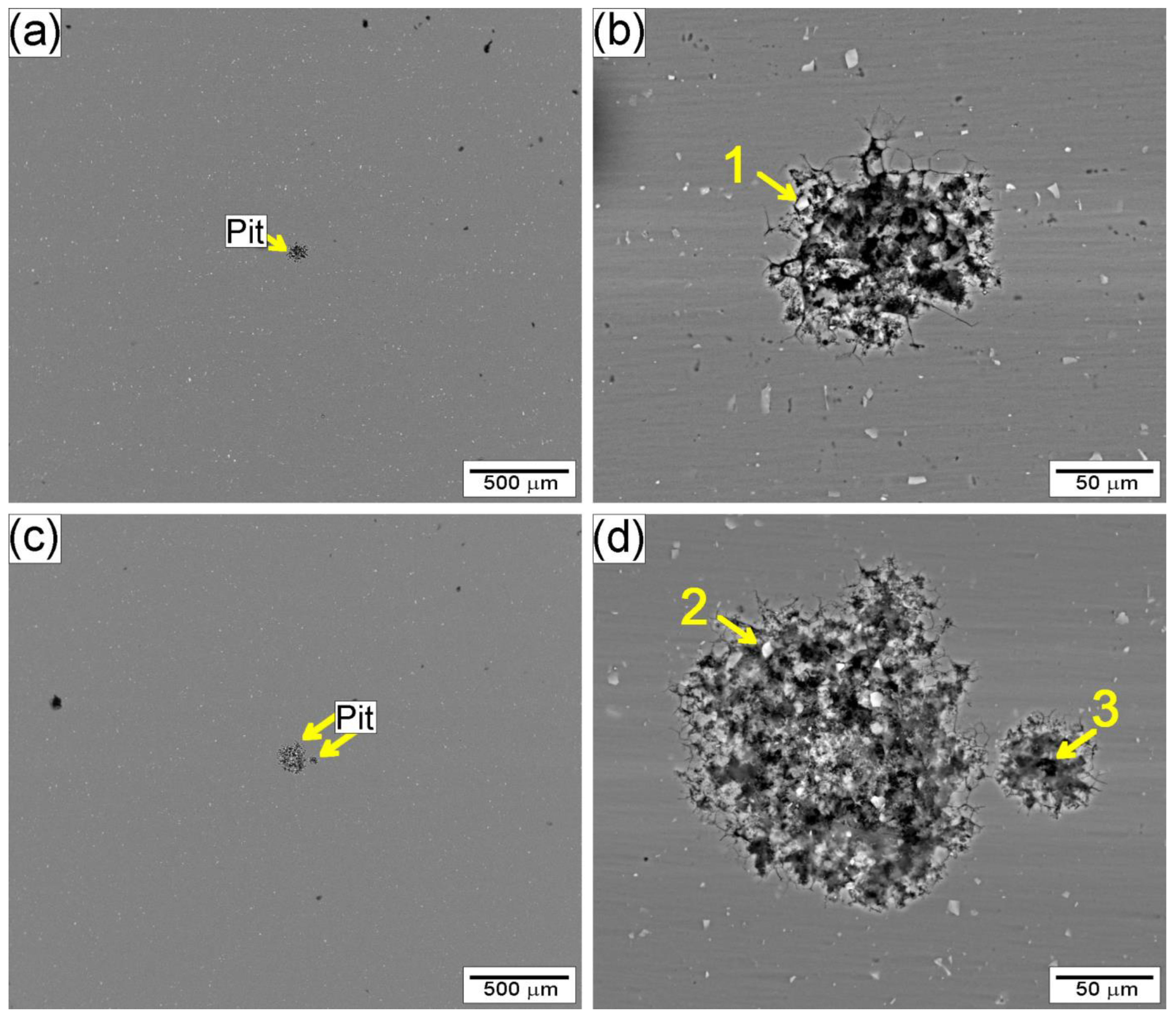
3.2.2. Corrosion Characterization
4. Conclusions
- Defect-free welds were achieved under the selected parameters, reaching an ultimate lap shear force of 4.6 ± 0.25 kN. The joints exhibited a mixed fracture mode, predominantly ductile, with limited brittle regions near the shoulder/pin interface.
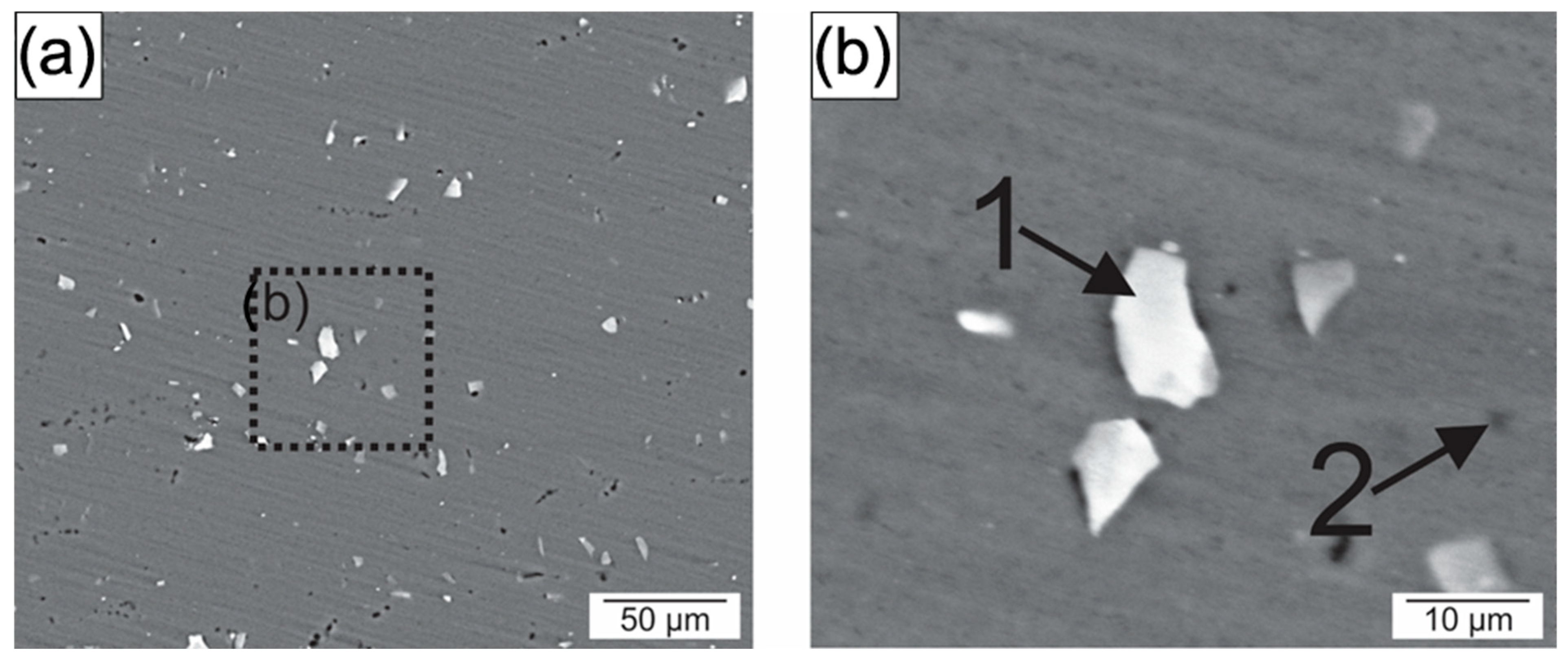
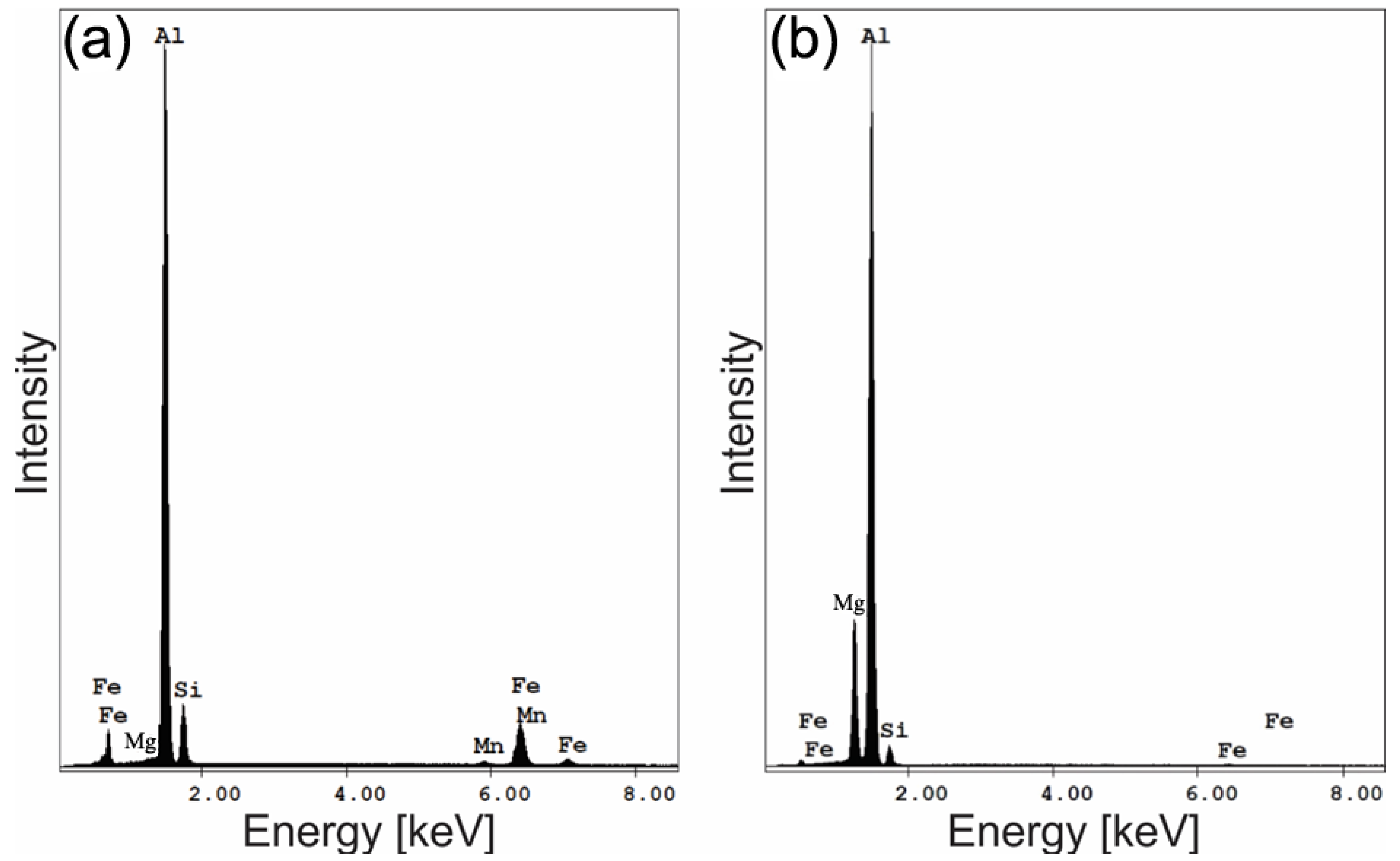
- The aluminum stir zone (SZ) displayed refined equiaxed grains and increased hardness relative to the base metal, reflecting the combined influence of plastic deformation and dynamic recrystallization. Fe-rich precipitates were fragmented, whereas Mg2Si precipitates showed slight coarsening under the welding thermal cycle.
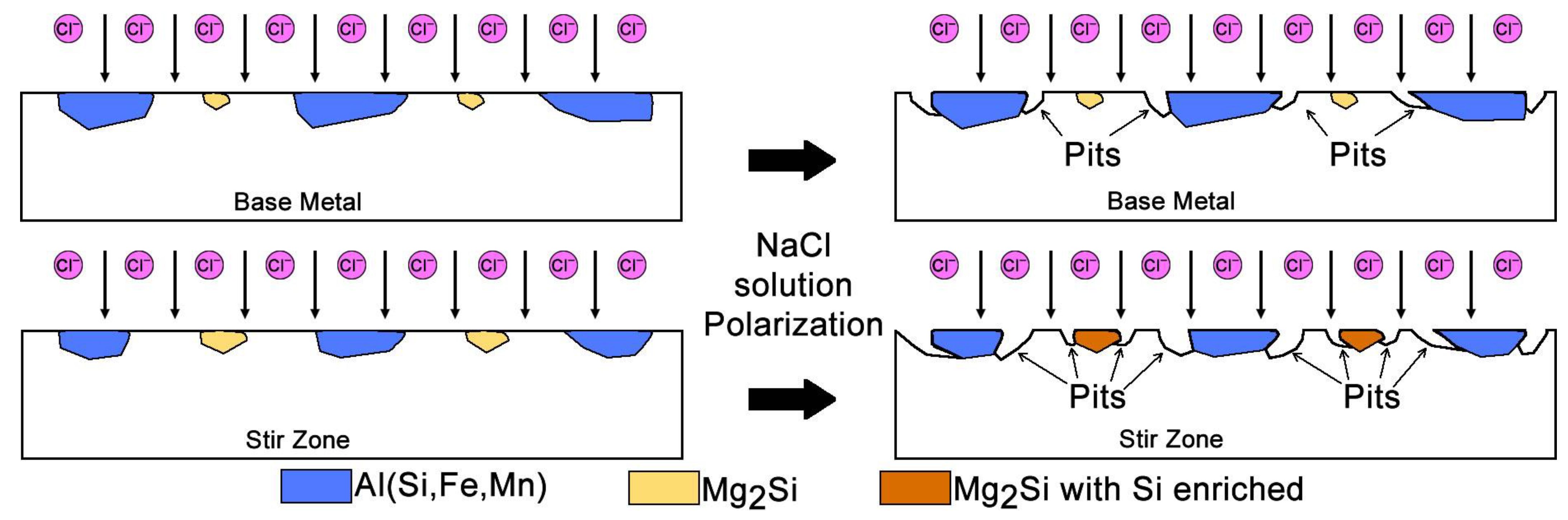
- Electrochemical tests indicated similar corrosion potentials (Ecorr) for the SZ and base metal, but a lower pitting potential (Epit) in the SZ. Pit initiation occurred primarily near Al(Fe, Mn)Si and coarsened Mg2Si precipitates, explaining the modest reduction in localized corrosion resistance.
- The Al/steel interface exhibited a continuous metallurgical bond with minimal voids. No intermetallic layer was detected by SEM, suggesting that if present, it is of nanometric thickness and requires high-resolution characterization.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheah, L.W. Cars on a Diet: The Material and Energy Impacts of Passenger Vehicle Weight Reduction in the US. PhD Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Polmear, I.; St John, D.; Nie, J.F.; Qian, M. Light Alloys: Metallurgy of the Light Metals; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho, R.S.; Kostka, A.; dos Santos, J.F.; Pyzalla, A.R. EBSD technique visualization of material flow in aluminum to steel friction-stir dissimilar welding. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-Y.; Choi, D.H.; Yeon, Y.-M.; Jung, S.-B. Dissimilar friction stir spot welding of low carbon steel and Al-Mg alloy by formation of IMCs. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2009, 14, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şık, A. Comparison between microstructure characteristics and joint performance of AZ31 magnesium alloy welded by TIG and friction stir welding (FSW) processes. Kov. Mater. 2013, 51, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Li, W.; Shen, Z.; Su, Y.; Yang, X. Refill friction stir spot welding of aluminum alloys: State-of-the-art and Perspectives. Weld. World 2023, 67, 1853–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Q.; Yang, H.K.; Andriia, A.; Lo, H.H.; Li, J.X. Refill friction stir spot welding (RFSSW): A review of processing, similar/dissimilar materials joining, mechanical properties and fracture mechanism. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2024, 31, 1825–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.S.; Li, S.B.; Tang, L.N.; Wang, H.M. Refill Friction Stir Spot Welding of Similar and Dissimilar Alloys: A Review. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2020, 33, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, W.S.; Vioreanu, M.C.; Lutz, M.R.A.; Cipriano, G.P.; Amancio-Filho, S.T. The influence of tool wear on the mechanical performance of AA6061-T6 refill friction stir spot welds. Materials 2021, 14, 7252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacchi, G.S.; Silva, R.; Plaine, A.H.; Suhuddin, U.F.H.; Alcântara, N.G.; Sordi, V.L.; Rovere, C.A.D. Refill friction stir spot welded AA5754-H22/Ti-6Al-4V joints: Microstructural characterization and electrochemical corrosion behavior of aluminum surfaces. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 22, 100759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaine, A.H.; Suhuddin, U.F.H.H.; Alcântara, N.G.; dos Santos, J.F. Fatigue behavior of friction spot welds in lap shear specimens of AA5754 and Ti6Al4V alloys. Int. J. Fatigue 2016, 91, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsche, S.; Schindler, F.; de Carvalho, W.S.; Amancio-Filho, S.T. Wear mechanisms and failure analysis of a tool used in refill friction stir spot welding of AA6061-T6. Wear 2025, 560–561, 205610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosendo, T.; Parra, B.; Tier, M.A.D.; da Silva, A.A.M.; dos Santos, J.F.; Strohaecker, T.R.; Alcântara, N.G. Mechanical and microstructural investigation of friction spot welded AA6181-T4 aluminium alloy. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaine, A.H.H.; Gonzalez, A.R.R.; Suhuddin, U.F.H.F.H.; dos Santos, J.F.F.; Alcântara, N.G.G. The optimization of friction spot welding process parameters in AA6181-T4 and Ti6Al4V dissimilar joints. Mater. Des. 2015, 83, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Ding, Y.; Gopkalo, O.; Diak, B.; Gerlich, A.P. Effects of tool design on the microstructure and mechanical properties of refill friction stir spot welding of dissimilar Al alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 252, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amancio-Filho, S.T.; Camillo, A.P.; Bergmann, L.; Dos Santos, J.F.; Kury, S.E.; Machado, N.G. Preliminary Investigation of the Microstructure and Mechanical Behaviour of 2024 Aluminium Alloy Friction Spot Welds. Mater. Trans. 2011, 52, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Yang, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction spot welded 6061-T4 aluminum alloy. Mater. Des. 2014, 54, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhuddin, U.; Fischer, V.; Kroeff, F.; dos Santos, J.F. Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction spot welds of dissimilar AA5754 Al and AZ31 Mg alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 590, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Chen, S.; Song, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Z. Refilled friction stir spot welding of aluminum alloy to galvanized steel sheets. Mater. Des. 2016, 94, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacchi, G.S.; Plaine, A.H.; Silva, R.; Sordi, V.L.; Suhuddin, U.F.H.; Alcântara, N.G.; Kuri, S.E.; Rovere, C.A.D. Effect of friction spot welding (FSpW) on the surface corrosion behavior of overlapping AA6181-T4/Ti-6Al-4V joints. Mater. Des. 2017, 131, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.M.; Wei, R.P. Galvanic coupling of model alloys to aluminum—A foundation for understanding particle-induced pitting in aluminum alloys. Electrochim. Acta 1999, 45, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchheit, R.G.; Boger, R.K.; Carroll, M.C.; Leard, R.M.; Paglia, C.; Searles, J.L. The electrochemistry of intermetallic particles and localized corrosion in Al alloys. JOM 2001, 53, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, G.S. Pitting Corrosion of Metals: A Review of the Critical Factors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1998, 145, 2186–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Kang, S.B. The solidification process of Al-Mg-Si alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 1997, 32, 1443–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillel, G.; Kalabukhov, S.; Frage, N.; Zaretsky, E.; Meshi, L. Direct observation of initial stages of precipitation hardening process in commercial Al 6061 alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 10395–10406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.L.; Wei, Z.L.; Li, J.F.; Li, C.X.; Tan, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, Z.Q. Corrosion mechanism associated with Mg2Si and Si particles in Al-Mg-Si alloys. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2011, 21, 2559–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paglia, C.S.; Buchheit, R.G. A look in the corrosion of aluminum alloy friction stir welds. Scr. Mater. 2008, 58, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharavi, F.; Matori, K.A.; Yunus, R.; Othman, N.K.; Fadeifard, F. Corrosion evaluation of friction stir welded lap joints of AA6061-T6 aluminum alloy. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2016, 26, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, S.; Hihara, L.H. Microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion of friction stir welded 6061 Aluminum Alloy. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1511.05507. [Google Scholar]
- ASM Handbook. Volume 2: Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and Special-Purpose Materials, 10th ed.; ASM International: Novelty, OH, USA, 1990.
- ASM Handbook. Volume 1: Properties and Selection: Irons, Steels, and High-Performance Alloys, 10th ed.; ASM International: Novelty, OH, USA, 1990; Volume 1, p. 1063.
- AWS D17.2/D17.2M:2013; Specification for Resistance Welding for Aerospace Applications, 2nd Edition. American Welding Society: Doral, FL, USA, 2013.
- ASTM E384-11; Standard Test Method for Knoop and Vickers Hardness of Materials. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- ASTM E112-13; Standard Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- Lee, W.-J.; Pyun, S.-I. Effects of sulphate ion additives on the pitting corrosion of pure aluminium in 0.01 M NaCl solution. Electrochim. Acta 2000, 45, 1901–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Su, W.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Z. Friction stir brazing: A novel process for fabricating Al/steel layered composite and for dissimilar joining of Al to steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2011, 42, 2850–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, X.; Al, D.; Fssw, S.K. Interface Behavior and Impact Properties of Dissimilar Al/Steel Keyhole-Free FSSW Joints. Metals 2019, 9, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Chen, J.; Ding, Y.; Hou, J.; Shalchi Amirkhiz, B.; Chan, K.; Gerlich, A.P. Role of interfacial reaction on the mechanical performance of Al/steel dissimilar refill friction stir spot welds. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2018, 23, 462–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubit, A.; Bucior, M.; Wydrzyński, D.; Trzepieciński, T.; Pytel, M. Failure mechanisms of refill friction stir spot welded 7075-T6 aluminium alloy single-lap joints. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 94, 4479–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitturi, V.; Pedapati, S.R.; Awang, M. Investigation of Weld Zone and Fracture Surface of Friction Stir Lap Welded 5052 Aluminum Alloy and 304 Stainless Steel Joints. Coatings 2020, 10, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.M.; Loureiro, A.; Leitao, C.; Leal, R.M.; Chaparro, B.M.; Vilaça, P. Influence of friction stir welding parameters on the microstructural and mechanical properties of AA 6016-T4 thin welds. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 1913–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, L.; Li, T. Microstructure and failure mechanisms of refill friction stir spot welded 7075-T6 aluminum alloy joints. Mater. Des. 2013, 44, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, G.P.; Robinson, J.S. Residual stress reduction in 7175-T73, 6061-T6 and 2017A-T4 aluminium alloys using quench factor analysis. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 153–154, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Threadgill, P.L.; Leonard, A.J.; Shercliff, H.R.; Withers, P.J. Friction stir welding of aluminium alloys. Int. Mater. Rev. 2009, 54, 49–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.S.S.; Ma, Z.Y.Y. Friction stir welding and processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2005, 50, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.Q.; Sun, T.; Meng, F.Q.; Jiang, X.W.; Chou, T.H.; Ju, J.; Gan, J.; Yang, T.; Li, M.S.; Shen, Z.K.; et al. Microstructural evolution and wear behavior of friction stir processed L12 strengthened AlFeCrCuNi-type high-entropy alloy. Mater. Charact. 2024, 216, 114250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, F.; Xin, S.; Tu, X.; Wang, H.; Guo, P.; Hou, H.; Lian, Z.; Zhang, L.; Hou, W. Low-temperature superplastic deformation mechanism of ultra-fine grain Ti-6Al-4V alloy by friction stir processing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 7413–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallais, C.; Denquin, A.; Bréchet, Y.; Lapasset, G. Precipitation microstructures in an AA6056 aluminium alloy after friction stir welding: Characterisation and modelling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 496, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sri Ram Vikas, K.; Ramanab, V.S.N.V.; Mohammedc, R.; Reddyd, G.M.; Raoe, K.S. Influence of post weld heat treatment on microstructure and pitting corrosion behavior of dissimilar Aluminium alloy friction. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 15, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Yan, J.; Sutton, M.A.; Reynolds, A.P. Banded microstructure in AA2024-T351 and AA2524-T351 aluminum friction stir welds. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 364, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donatus, U.; Thompson, G.E.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Cassell, A.; Beamish, K. Corrosion susceptibility of dissimilar friction stir welds of AA5083 and AA6082 alloys. Mater. Charact. 2015, 107, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Menshawy, K.; El-Sayed, A.-W.A.; El-Bedawy, M.E.; Ahmed, H.A.; El-Raghy, S.M. Effect of aging time at low aging temperatures on the corrosion of aluminum alloy 6061. Corros. Sci. 2012, 54, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarlak, H.; Atapour, M.; Esmailzadeh, M. Corrosion behavior of friction stir welded lean duplex stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2015, 66, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aballe, A.; Bethencourt, M.; Botana, F.J.; Cano, M.J.; Marcos, M. Localized alkaline corrosion of alloy AA5083 in neutral 3.5% NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 2001, 43, 1657–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalera-Lozano, R.; Pech-Canul, M.I.A.; Pech-Canul, M.I.A.; Montoya-Davila, M.; Uribe-Salas, A. The Role of Mg2Si in the Corrosion Behavior of Al-Si-Mg Alloys for Pressureless Infiltration. Open Corros. J. 2010, 3, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.-H.H.; Ma, A.-B.B.; Lu, F.-M.M.; Saito, N.; Watazu, A.; Song, D.; Zhang, P.; Nishida, Y. Improving corrosion resistance of Al-11mass%Si alloy through a large number of ECAP passes. Mater. Corros. 2011, 62, 848–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Alloy | Al | Fe | C | Mg | Si | Cu | Mn | Mo | Cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA6016 | Bal. | 0.5 | - | 0.25–0.6 | 1–1.5 | 0.2 | 0.2 | - | 0.1 |
| DP600 | 0.03–0.1 | Bal. | 0.04–0.12 | - | 0.4–1.4 | 0.15 | 0.9–2 | 0.05–0.3 | 0.1–0.5 |
| Refill FSSW Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Tool rotational speed (rpm) (Ω) | 1000 |
| Shoulder plunge depth (mm) | 1.3 |
| Plunging and retracting speed of the shoulder (mm/s) | 4 |
| Dwell time (s) | 1 |
| Region | Al | Si | Fe | Mg | Mn | Precipitates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 75.1 | 12.33 | 12.1 | 0.5 | 1.2 | Al(Fe, Mn)Si |
| 2 | 81.4 | 6.6 | 0.5 | 11.5 | - | Mg2Si |
| Region | Al | Si | Fe | Mg | Mn | Precipitates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 73.9 | 11.33 | 13.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | Al(Fe, Mn)Si |
| 2 | 74.2 | 11.3 | 0.2 | 14.1 | 0.2 | Mg2Si |
| Weldment Region | Eocp (mVAg/AgCl) | Ecorr (mVAg/AgCl) | Epit (mVAg/AgCl) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BM | −706 ± 3 | −725 ± 12 | −85 ± 12 |
| SZ | −704 ± 7 | −732 ± 10 | −129 ± 24 |
| Region | Al | Si | Fe | Mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 76.7 | 10.6 | 10.4 | 0.6 |
| 2 | 77.8 | 10.9 | 10.7 | 0.6 |
| 3 | 75.2 | 24.1 | - | 0.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Carvalho, W.S.; Vacchi, G.d.S.; Suhuddin, U.F.H.; Silva, R.d.; Magalhães, D.C.C.; Rovere, C.A.D. Aluminum Surface Corrosion Behavior and Microstructural Evolution in Dissimilar AA6016-T4 Aluminum to DP600 Steel via Refill Friction Stir Spot Welding. Metals 2025, 15, 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15121288
de Carvalho WS, Vacchi GdS, Suhuddin UFH, Silva Rd, Magalhães DCC, Rovere CAD. Aluminum Surface Corrosion Behavior and Microstructural Evolution in Dissimilar AA6016-T4 Aluminum to DP600 Steel via Refill Friction Stir Spot Welding. Metals. 2025; 15(12):1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15121288
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Carvalho, Willian S., Guilherme dos Santos Vacchi, Uceu F. H. Suhuddin, Rodrigo da Silva, Danielle C. C. Magalhães, and Carlos A. D. Rovere. 2025. "Aluminum Surface Corrosion Behavior and Microstructural Evolution in Dissimilar AA6016-T4 Aluminum to DP600 Steel via Refill Friction Stir Spot Welding" Metals 15, no. 12: 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15121288
APA Stylede Carvalho, W. S., Vacchi, G. d. S., Suhuddin, U. F. H., Silva, R. d., Magalhães, D. C. C., & Rovere, C. A. D. (2025). Aluminum Surface Corrosion Behavior and Microstructural Evolution in Dissimilar AA6016-T4 Aluminum to DP600 Steel via Refill Friction Stir Spot Welding. Metals, 15(12), 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15121288









