Effects of Laser Process Parameters on Melt Pool Thermodynamics, Surface Morphology and Residual Stress of Laser Powder Bed-Fused TiAl-Based Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure and Simulation Model
- (1)
- The powder particles follow a normal size distribution and are randomly distributed within the powder bed.
- (2)
- The molten metal is treated as an incompressible Newtonian fluid exhibiting laminar flow characteristics.
- (3)
- Both the solid and liquid phases are regarded as continuous media.
- (4)
- The attenuation of laser energy due to scattering and absorption by the powder particles is neglected.
- (5)
- Given the significant size difference between the reinforcing particles and the TiAl matrix powders, explicitly resolving both particle sizes would require extremely fine meshing, leading to a prohibitive number of elements and computational cost. Therefore, the reinforcing particles are assumed to have the same size as the TiAl powders, and the TiAl powder size is used as the reference for mesh generation.
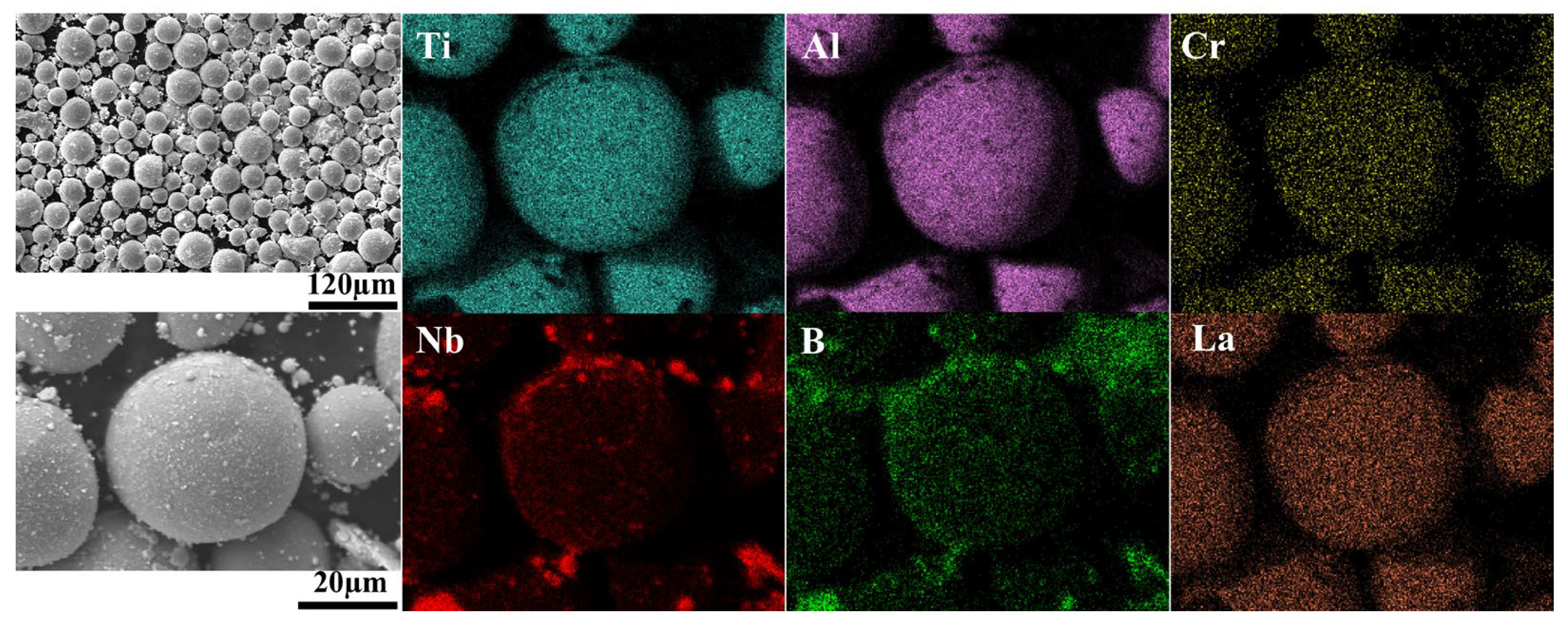
2.1. Experiment
2.1.1. Raw Materials and Ball Milling Treatment
2.1.2. LPBF Consolidation
2.1.3. Microstructure Characterization
2.2. Powder Bed Model
2.3. Material Thermophysical Parameters
2.4. Governing Equations
2.5. Boundary Conditions
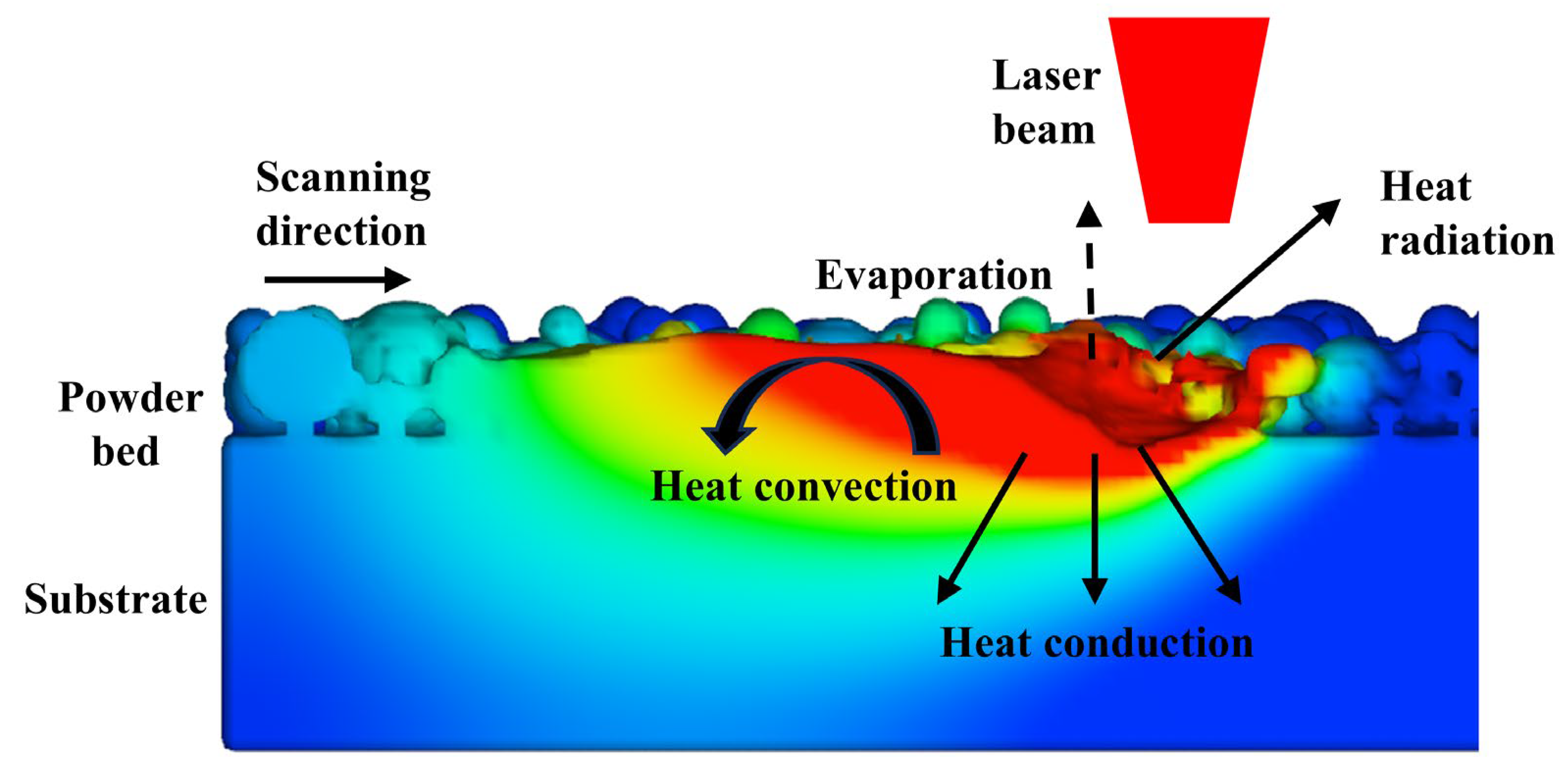
2.6. Thermal Source Model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Melt Pool Flow Behavior and Temporal Evolution
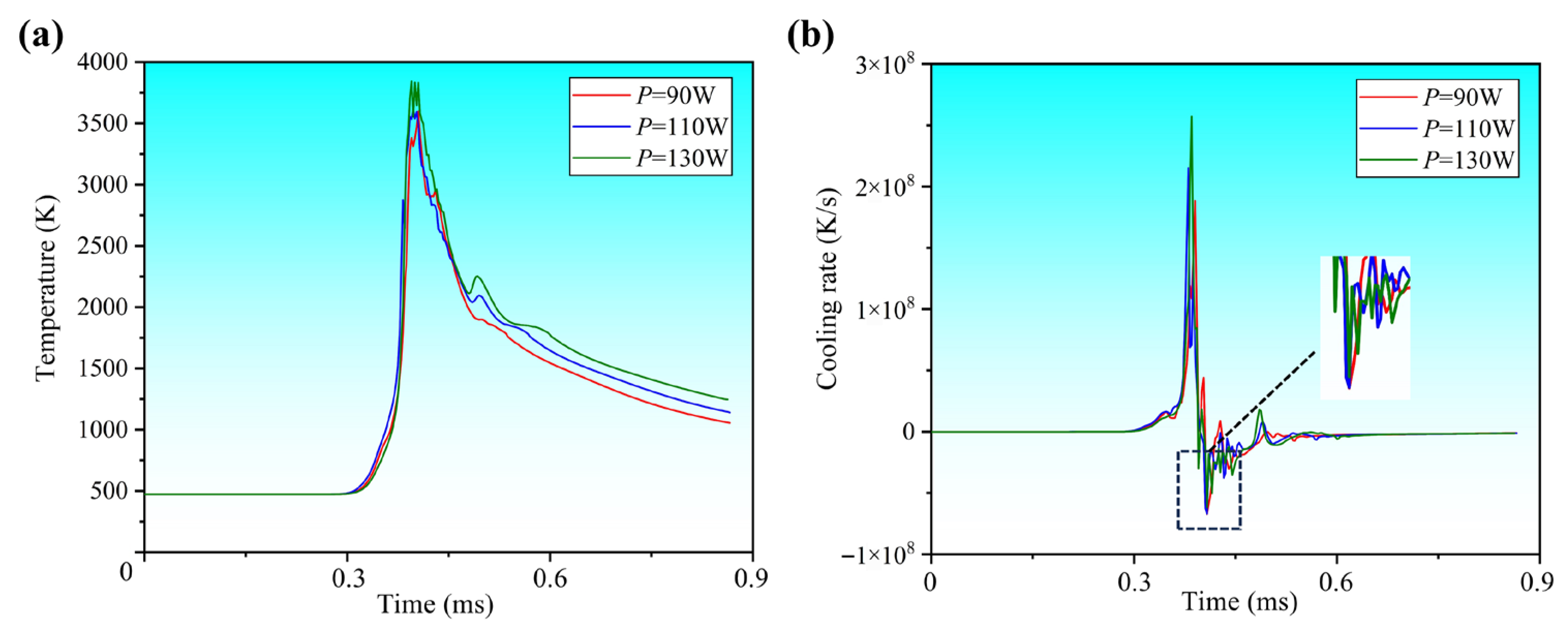
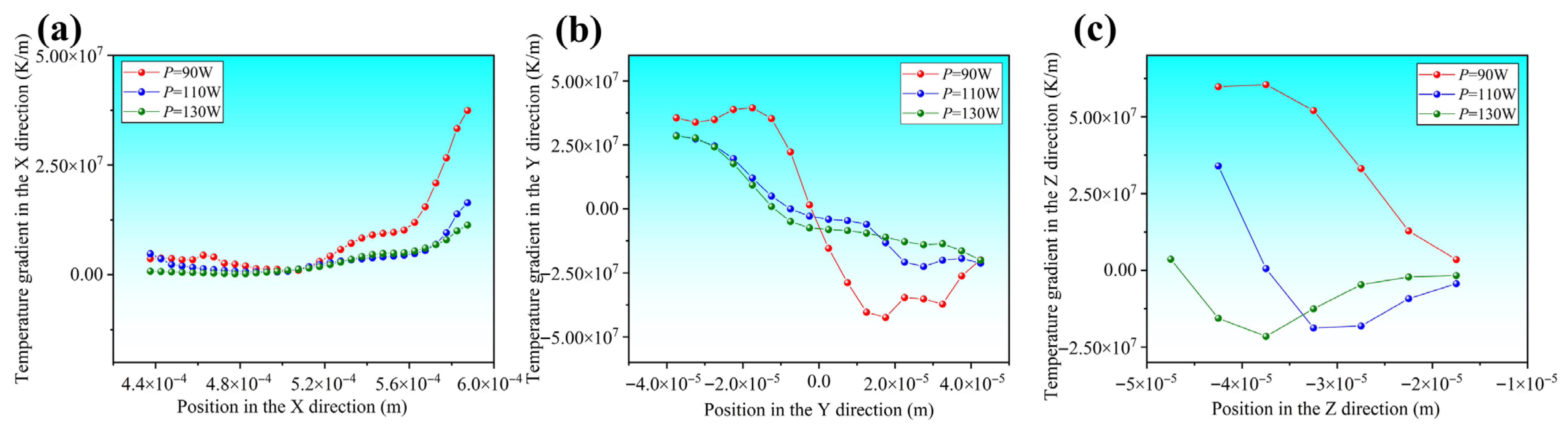
3.2. Melt Pool Morphology and Dynamic Response Under Different Laser Powers
3.3. Melt Pool Morphology and Dynamic Response Under Different Scanning Speeds
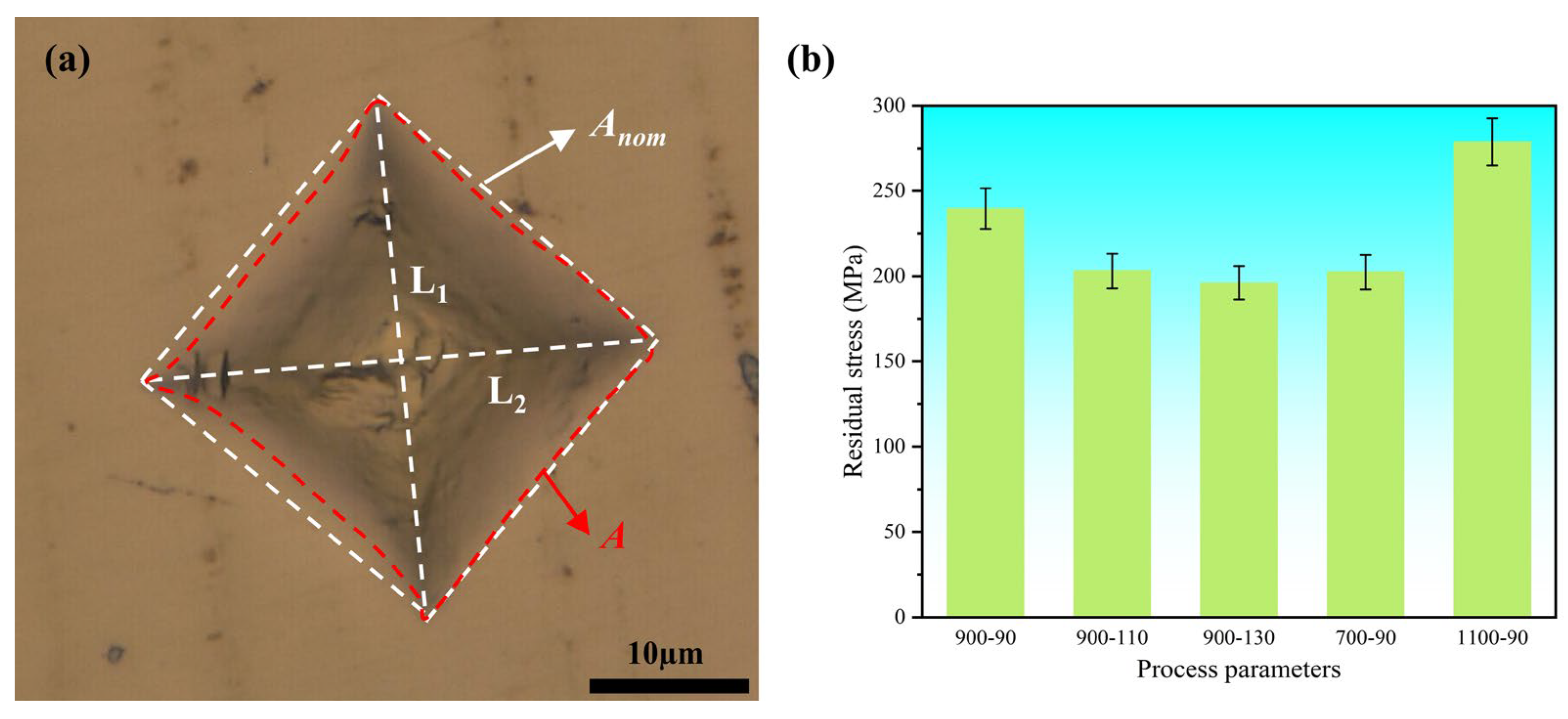
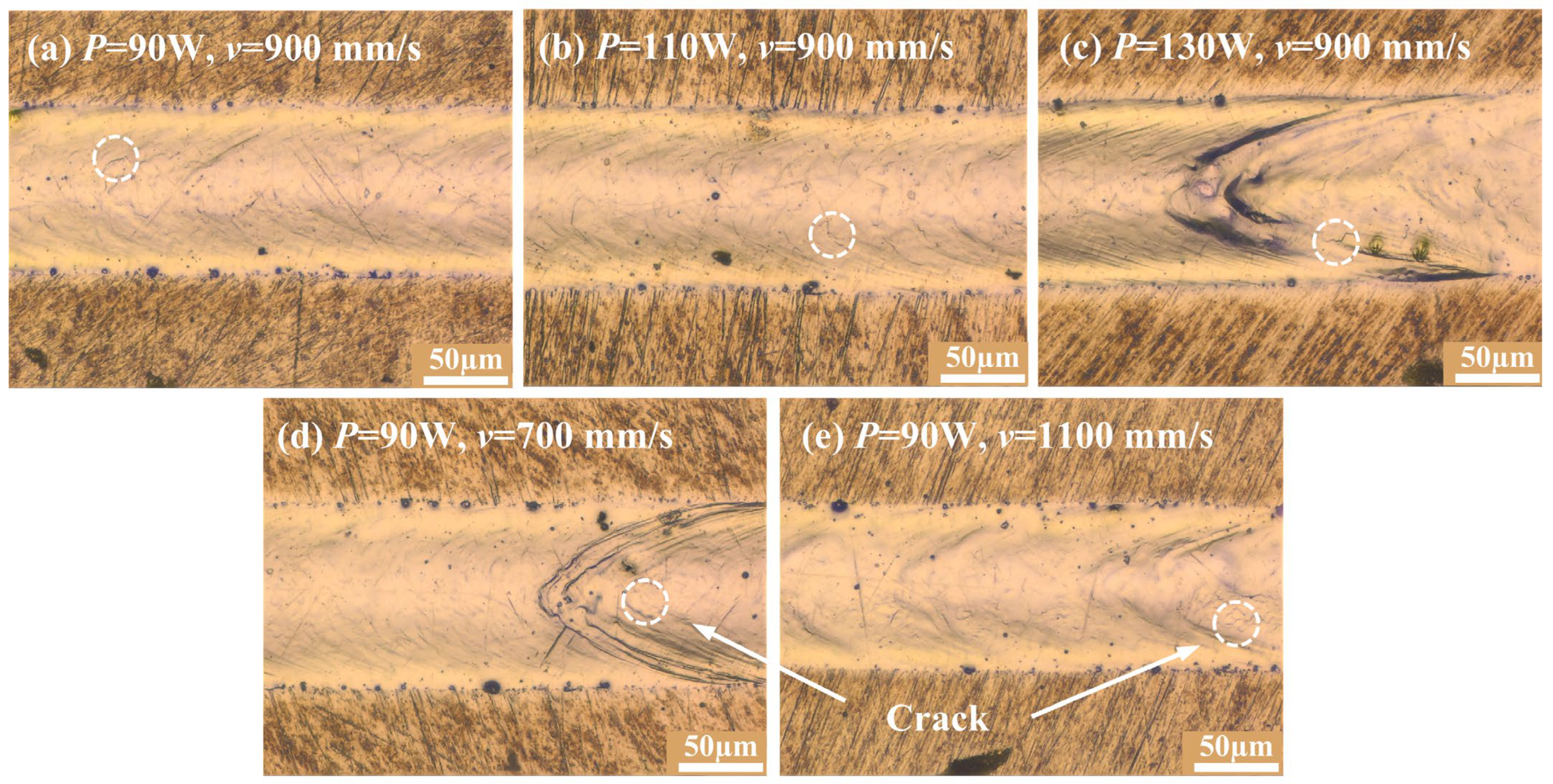
3.4. Single-Track Experimental Validation and Mechanisms of Defect Control
4. Conclusions
- Melt pool dynamics are strongly governed by recoil pressure and Marangoni convection. The competition and coupling between these two items jointly determine the temporal evolution of melt pool morphology during laser scanning.
- Process parameters significantly affect melt pool geometry and thermal history. A combination of high laser power and low scanning speed can produce a wider and deeper melt pool as well as enhanced convection and heat dissipation, consequently reducing the cooling rate and temperature gradient. Conversely, low laser power with high scanning speed results in a narrower and shallower melt pool. In this case, the limited heat-affected zone accelerates heat conduction, leading to a higher cooling rate and a steeper temperature gradient.
- Different defect formation mechanisms emerge across varying process windows. Under conditions of high power and low scanning speed, vigorous metal evaporation and pronounced recoil pressure trigger surface ripples and uneven topography, which serve as stress concentration sites and markedly elevate crack density. In contrast, under low power and high scanning speed conditions, although higher residual stresses develop due to enhanced cooling rates and thermal gradients, grain refinement is promoted, thereby partially inhibiting crack initiation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bewlay, B.P.; Nag, S.; Suzuki, A.; Weimer, M.J. TiAl alloys in commercial aircraft engines. Mater. High Temp. 2016, 33, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habel, U.; Heutling, F.; Kunze, C.; Smarsly, W.; Das, G.; Clemens, H. Forged Intermetallic γ-TiAl Based Alloy Low Pressure Turbine Blade in the Geared Turbofan. In Proceedings of the 13th World Conference on Titanium; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Appel, F. Effect of Al content and Nb addition on the strength and fault energy of TiAl alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 329, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.C.; Lin, J.P.; Li, S.J.; Chen, G.L. Effects of Nb and Al on the microstructures and mechanical properties of high Nb containing TiAl base alloys. Intermetallics 2002, 10, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.L.; Li, G.Y.; Zhang, L.Q.; Lin, J.P.; Song, X.P.; Ye, F.; Chen, G.L. Influence of Y addition on the long time oxidation behaviors of high Nb containing TiAl alloys at 900 °C. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1586–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, R.; Chen, D.; Su, Y.; Ding, H.; Guo, J.; Fu, H. The characteristics and mechanisms of creep brittle-ductile transition in TiAl alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 767, 138393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, P.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Lin, J. Fabrication of high strength TiAl alloy with nano-lamellar and ultra-fine-grained microstructure by selective electron beam melting. J. Mater. Res. Technol.-JMRT 2025, 35, 7156–7166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprio, L.; Demir, A.G.; Chiari, G.; Previtali, B. Defect-free laser powder bed fusion of Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb with a high temperature inductive preheating system. J. Phys. Photonics 2020, 2, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhan, Q. Enhanced strength and ductility in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys fabricated by laser powder bed fusion using a synergistic grain-refining strategy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 124, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Z.; Fang, Z.; Ma, C.; Xie, Z.; Peng, X.; Wang, Q.; Miao, X.; Wu, M. Influence of LaB6 inoculant on the thermodynamics within the molten pool and subsequent microstructure development and cracking behavior of laser powder bed fused TiAl-based alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol.-JMRT 2023, 27, 2363–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Tan, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, Y.; Wang, F.; Wu, T.; Yang, X.; Fan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. The significant impact of grain refiner on γ-TiAl intermetallic fabricated by laser-based additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 46, 102172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.A.; Li, Y.; Lu, Y.; Xie, X.; Gan, Z.; Mojumder, S.; Wagner, G.J.; Liu, W. Physics guided heat source for quantitative prediction of IN718 laser additive manufacturing processes. npj Comput. Mater. 2024, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePond, P.J.; Fuller, J.C.; Khairallah, S.A.; Angus, J.R.; Guss, G.; Matthews, M.J.; Martin, A.A. Laser-metal interaction dynamics during additive manufacturing resolved by detection of thermally-induced electron emission. Commun. Mater. 2020, 1, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Mao, B.; Mushongera, L.; Kundin, J.; Liao, Y. Laser powder bed fusion of titanium aluminides: An investigation on site-specific microstructure evolution mechanism. Mater. Des. 2021, 201, 109501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Choe, J.; Kim, S.; Hong, J.; Choi, Y. Understanding crack formation mechanisms of Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb single tracks during laser powder bed fusion. Met. Mater.-Int. 2021, 27, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Li, G.; Wang, P.; Zeng, Z.; Tang, Y. Numerical simulation of melt pool size and flow evolution for laser powder bed fusion of powder grade Ti6Al4V. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2023, 223, 103971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yan, R.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, K. Powder-spreading dynamics and packing quality improvement for laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Powder Technol. 2021, 389, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klassen, A.; Forster, V.E.; Juechter, V.; Körner, C. Numerical simulation of multi-component evaporation during selective electron beam melting of TiAl. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 247, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saari, H.; Seo, D.; Blumm, J.; Beddoes, J. Thermophysical property determination of high temperature alloys by thermal analysis. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2003, 73, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novakovic, R.; Giuranno, D.; Mohr, M.; Fecht, H. Thermodynamic evaluation of the surface tension and viscosity of liquid quaternary alloys: The Ti-Al-Cr-Nb system. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 2023, 35, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, P.-F.; Ishikawa, T.; Yoda, S. Non-contact measurements of surface tension and viscosity of niobium, zirconium, and titanium using an electrostatic levitation furnace. Int. J. Thermophys. 2002, 23, 825–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Ma, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Dai, D.; Wang, Q.; Xu, X.; Wu, M. Role of Ti-6Al-4V addition in modulating crack sensitivity, solidification microstructure and mechanical properties of laser powder bed fused γ-TiAl alloys. Vacuum 2025, 231, 113758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badini, C.; Santero, T.; Rosito, M.; Padovano, E. Laser Powder Bed Fusion of Pure Titanium: Optimization of Processing Parameters by Means of Efficient Volumetric Energy Density Approach. Metals 2024, 14, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arblaster, J.W. The thermodynamic properties of niobium. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 2017, 38, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zhuo, Z.; Xie, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wu, M. Effect of scanning strategy on the thermo-structural coupling field and cracking behavior during laser powder bed fusion of Ti48Al2Cr2Nb alloys. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 110372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, R.K.; Mohr, M.; Dong, Y.; Hecht, U.; Matson, D.M.; Hyers, R.; Bracker, G.; Lee, J.; Schneider, S.; Xiao, X.; et al. Thermophysical properties of the TiAl-2Cr-2Nb alloy in the liquid phase measured with an electromagnetic levitation device on board the International Space Station, ISS-EML. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2021, 112, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Yao, D.; Luo, H.; An, X.; Fu, H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; et al. Numerical investigation on effects of operating conditions and final dimension predictions in laser powder bed fusion of molybdenum. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 76, 103783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Xie, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y. Mesoscale numerical simulation and experimental study on the selective laser melting process of 17-4PH stainless steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol.-JMRT 2025, 35, 2443–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairallah, S.A.; Anderson, A.T.; Rubenchik, A.; King, W.E. Laser powder-bed fusion additive manufacturing: Physics of complex melt flow and formation mechanisms of pores, spatter, and denudation zones. Acta Mater. 2016, 108, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Aoyagi, K.; Yamanaka, K.; Chiba, A. A survey on basic influencing factors of solidified grain morphology during electron beam melting. Mater. Des. 2022, 221, 110927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaghefi, E.; Hosseini, S.; Prorok, B.; Mirkoohi, E. Geometrically-informed predictive modeling of melt pool depth in laser powder bed fusion using deep MLP-CNN and metadata integration. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 119, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, S.; Larsson, P.-L. On the determination of residual stress and strain fields by sharp indentation testing: Part I: Theoretical and numerical analysis. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 2179–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, R.; Venkateshwarlu, M.; Petley, V.; Verma, S. Strain hardening exponents and strength coefficients for aeroengine isotropic metallic materials—A reverse engineering approach. J. Mech. Behav. Mater. 2014, 23, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzogbewu, T.C. Additive manufacturing of TiAl-based alloys. Manuf. Rev. 2020, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L. Crack initiation mechanism of laser powder bed fusion additive manufactured Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy. Mater. Charact. 2023, 195, 112415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L. Understanding melt pool characteristics in laser powder bed fusion: An overview of single-and multi-track melt pools for process optimization. Adv. Powder Mater. 2023, 2, 100137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.S.; Liu, E.W.; Du, Y.L.; Liu, T.T.; Liao, W.H. Cracking mechanism and a novel strategy to eliminate cracks in TiAl alloy additively manufactured by selective laser melting. Scr. Mater. 2021, 204, 114151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staron, P.; Stark, A.; Schell, N.; Spoerk-Erdely, P.; Clemens, H. Thermal expansion of a multiphase intermetallic Ti-Al-Nb-Mo alloy studied by high-energy X-ray diffraction. Materials 2021, 14, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakout, M.; Elbestawi, M.A.; Veldhuis, S.C. A study of the relationship between thermal expansion and residual stresses in selective laser melting of Ti-6Al-4V. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 52, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-S. Effect of grain size reduction on high temperature oxidation of binary two-phase alloys. J. Chin. Nonferrous Met. Soc. 2001, 5, 644–648. Available online: http://refhub.elsevier.com/S0030-3992(19)30546-8/h0180 (accessed on 1 November 2025).
- Langdon, T.G. Grain boundary sliding revisited: Developments in sliding over four decades. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Aspect | Experimental Work | Modeling Approach (CFD + DEM) |
|---|---|---|
| Strengths | Provides direct observation of melt pool morphology and defects. Enables validation of numerical results through metallographic and microstructural evidence. Captures real material behavior under complex thermal conditions. | Allows detailed analysis of melt pool dynamics, including Marangoni convection, recoil pressure, and surface tension effects. Provides time-resolved temperature and velocity fields difficult to access experimentally. Enables parametric optimization of process parameters with reduced cost. |
| Weaknesses | Limited temporal and spatial resolution during in situ monitoring. High equipment cost and limited reproducibility due to process fluctuations. Difficult to isolate the effect of individual parameters. | Simplifications in boundary conditions and material property definitions. Computationally expensive, especially for realistic powder beds. Accuracy depends on calibration with experimental data. |
| Opportunities | Can be combined with in situ high-speed imaging or synchrotron-based observation to provide real-time validation. Offers database support for material design and defect control. | Integration with machine learning for predictive modeling. Extension to multi-layer or multi-track simulations for improved process understanding. Potential to develop digital twins for process optimization. |
| Threats | Equipment limitations or operator variability may affect repeatability. Experimental uncertainty in temperature and melt pool measurement. | Numerical instability when coupling multiple physical fields. Lack of comprehensive thermo-physical data for TiAl alloys at high temperature. Model assumptions may limit generalization to other alloys or process conditions. |
| Serial Number | Laser Power (W) | Scanning Speed (mm/s) | Hatch Space (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 90 | 900 | |
| 2 | 110 | 900 | |
| 3 | 130 | 900 | |
| 4 | 90 | 700 | |
| 5 | 90 | 1100 | |
| 6 | 90 | 900 | 60 |
| 7 | 110 | 900 | 60 |
| 8 | 130 | 900 | 60 |
| 9 | 90 | 700 | 60 |
| 10 | 90 | 1100 | 60 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Evaporation temperature (Tv) | 3142 K [18] |
| Ambient temperature (T0) | 300 K |
| Latent heat of fusion (Lm) | 4.0 × 105 J/kg [19] |
| Molar mass | 0.04199 kg/mol |
| Latent heat of vaporization(Lv) | 10.65 MJ/kg [18] |
| Stefan-Boltzmann constant (σ0) | 5.67 × 10−8 W/(m2·K4) |
| Surface tension coefficient (σm) | 1.28 N/m [20,21] |
| Surface tension temperature dependence (∂σ/∂t) | −2.4 × 10−4 N/(m·K) |
| Solidus temperature (Ts) | 1734 K [22] |
| Liquid temperature (Tl) | 1825 K [22] |
| Laser beam radius (r) | 40 µm |
| Laser absorptivity | 0.5 [23] |
| Temperature (K) | Density (kg/m3) [8] | Specific Heat (J/kg·K) [10,24,25] | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) [10,24,25] | Viscosity (kg/(m·s)) [26] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 4186.7 | |||
| 373 | 608.7 | 19 | ||
| 573 | 4172.6 | 640.5 | 21.5 | |
| 723 | 4164.2 | 664.3 | 23.3 | |
| 873 | 4156.7 | 688.4 | 25 | |
| 973 | 737.4 | 26.7 | ||
| 1073 | 4145.4 | 761.2 | 27.6 | |
| 1173 | 799.9 | 28.6 | ||
| 1273 | 4135.1 | 856.4 | 27.4 | |
| 1473 | 4124.8 | 1070.9 | 29.5 | |
| 1600 | 11.5 | |||
| 1700 | 6.93 | |||
| 1773 | 6.1 | |||
| 1820 | 5.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Xie, Z.; Wu, M.; Ma, C. Effects of Laser Process Parameters on Melt Pool Thermodynamics, Surface Morphology and Residual Stress of Laser Powder Bed-Fused TiAl-Based Composites. Metals 2025, 15, 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111234
Xu X, Xie Z, Wu M, Ma C. Effects of Laser Process Parameters on Melt Pool Thermodynamics, Surface Morphology and Residual Stress of Laser Powder Bed-Fused TiAl-Based Composites. Metals. 2025; 15(11):1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111234
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xiaolong, Ziwen Xie, Meiping Wu, and Chenglong Ma. 2025. "Effects of Laser Process Parameters on Melt Pool Thermodynamics, Surface Morphology and Residual Stress of Laser Powder Bed-Fused TiAl-Based Composites" Metals 15, no. 11: 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111234
APA StyleXu, X., Xie, Z., Wu, M., & Ma, C. (2025). Effects of Laser Process Parameters on Melt Pool Thermodynamics, Surface Morphology and Residual Stress of Laser Powder Bed-Fused TiAl-Based Composites. Metals, 15(11), 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111234







