Composition Optimization and Microstructure-Property Investigation of Al-3.0Ce-xCa-yMn Alloy Exhibiting High Hot Tearing Resistance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Computational and Design Aspects of Alloy Composition
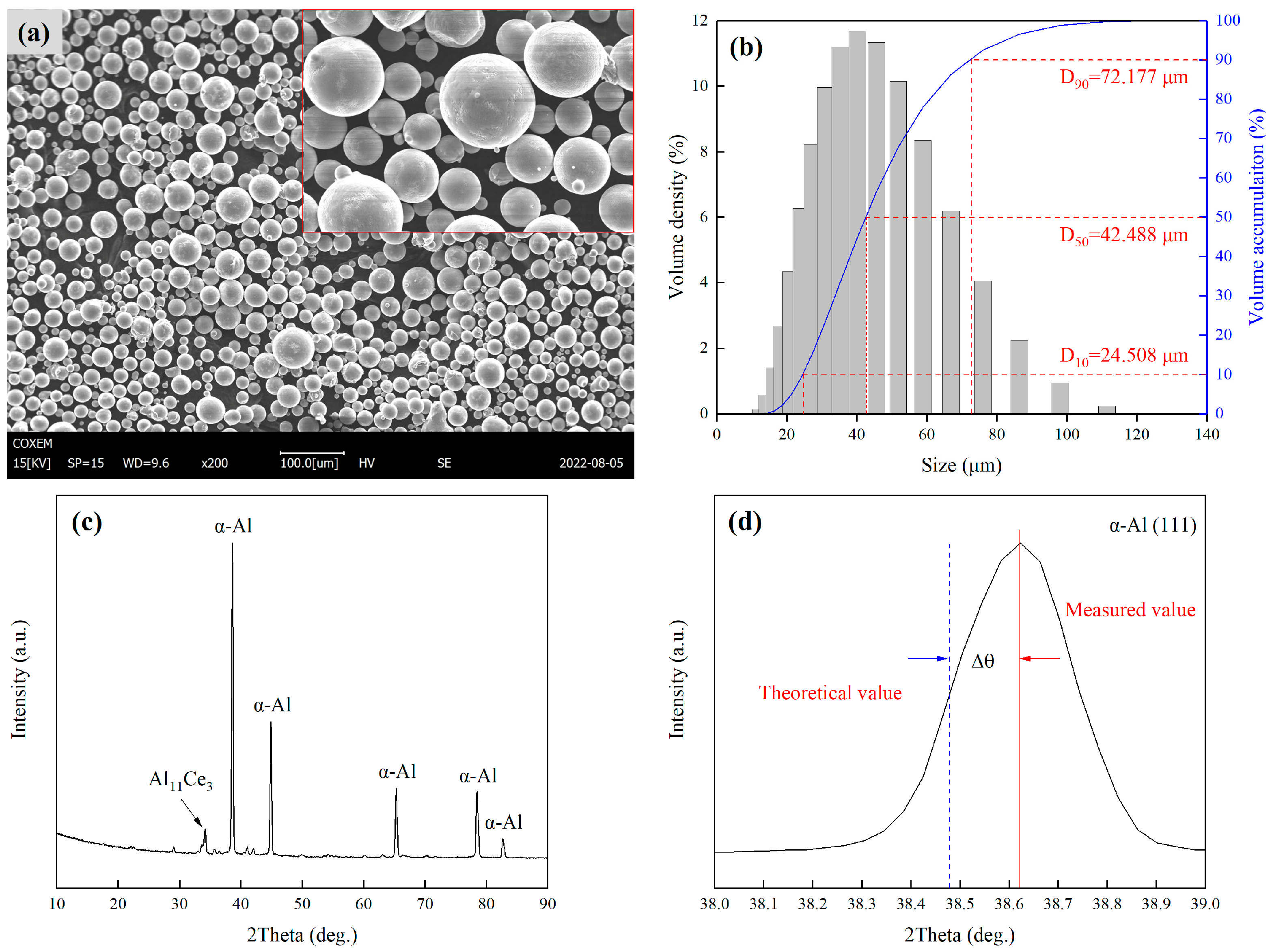
2.2. Characteristics of Pre-Alloyed Powders
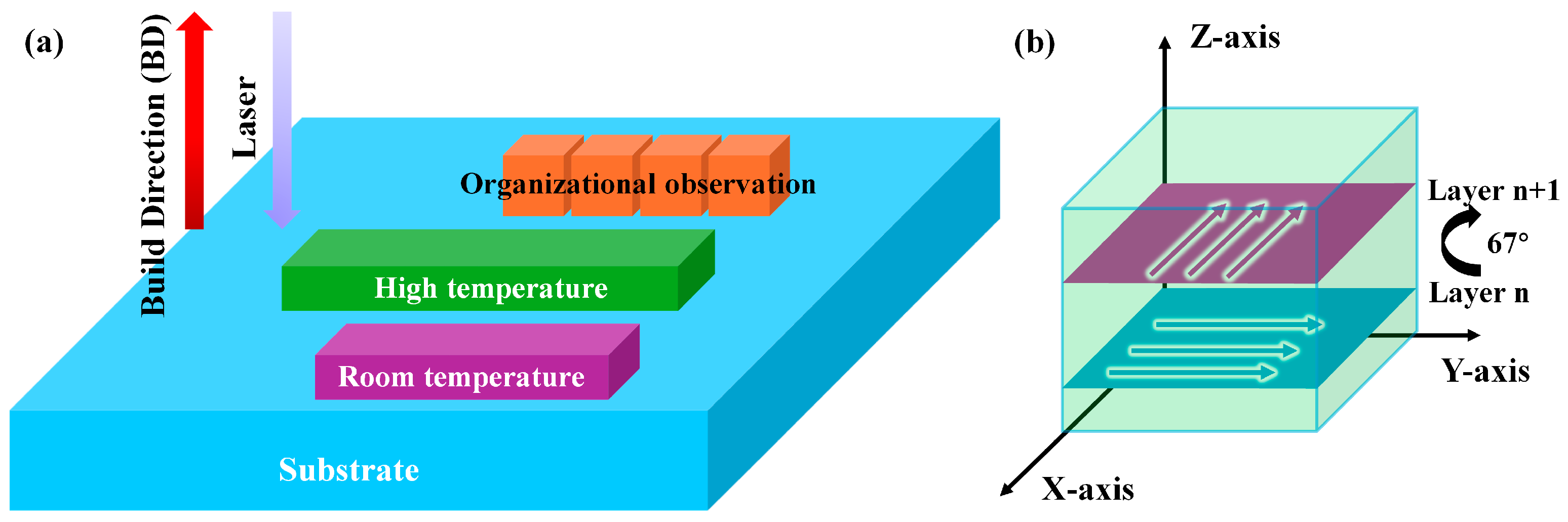
2.3. The Procedural Sequence for the LPBF Manufacturing of the Al-3.0Ce-0.8Ca-1.9Mn Alloy
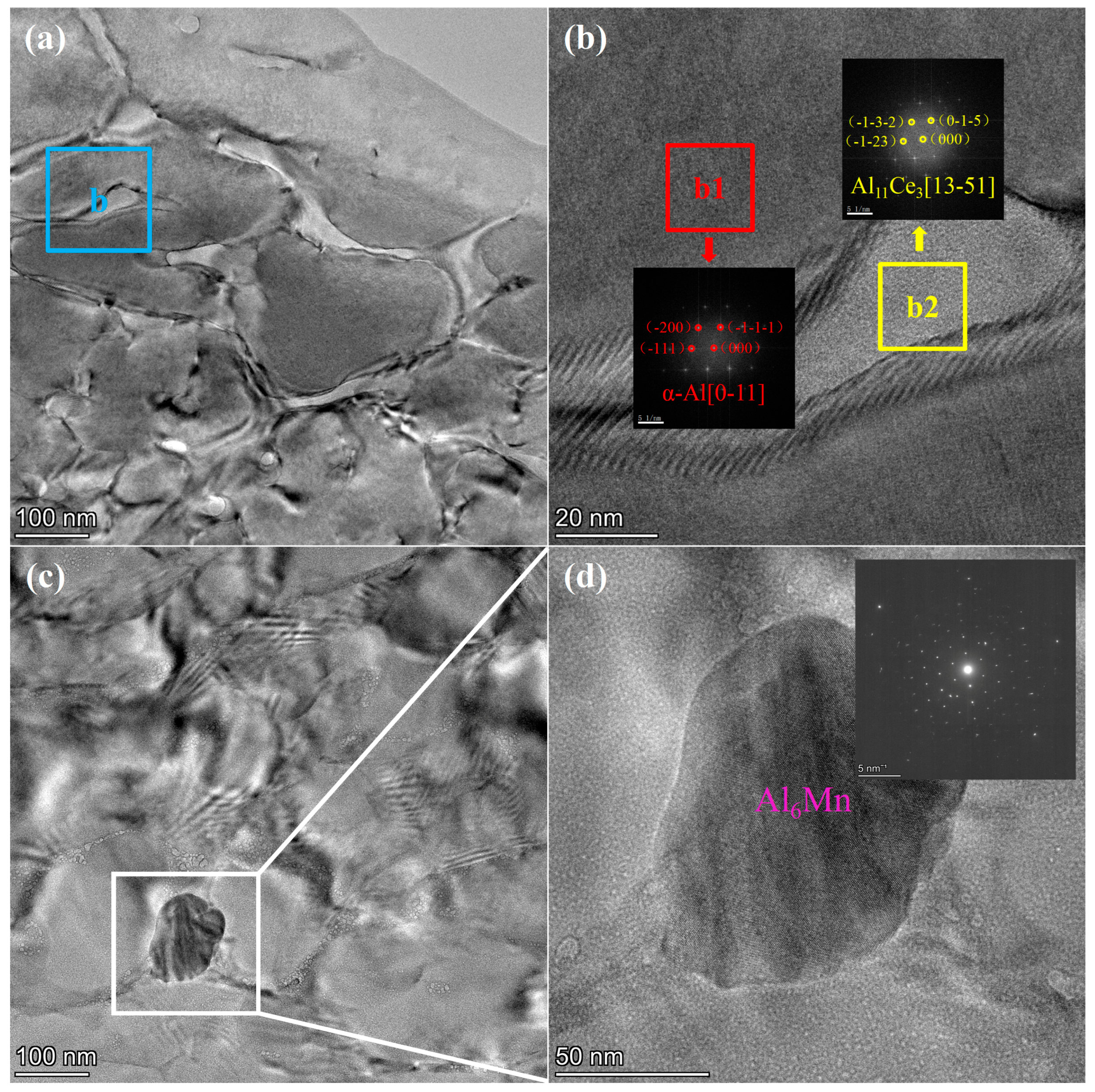
2.4. Microstructural Characterization
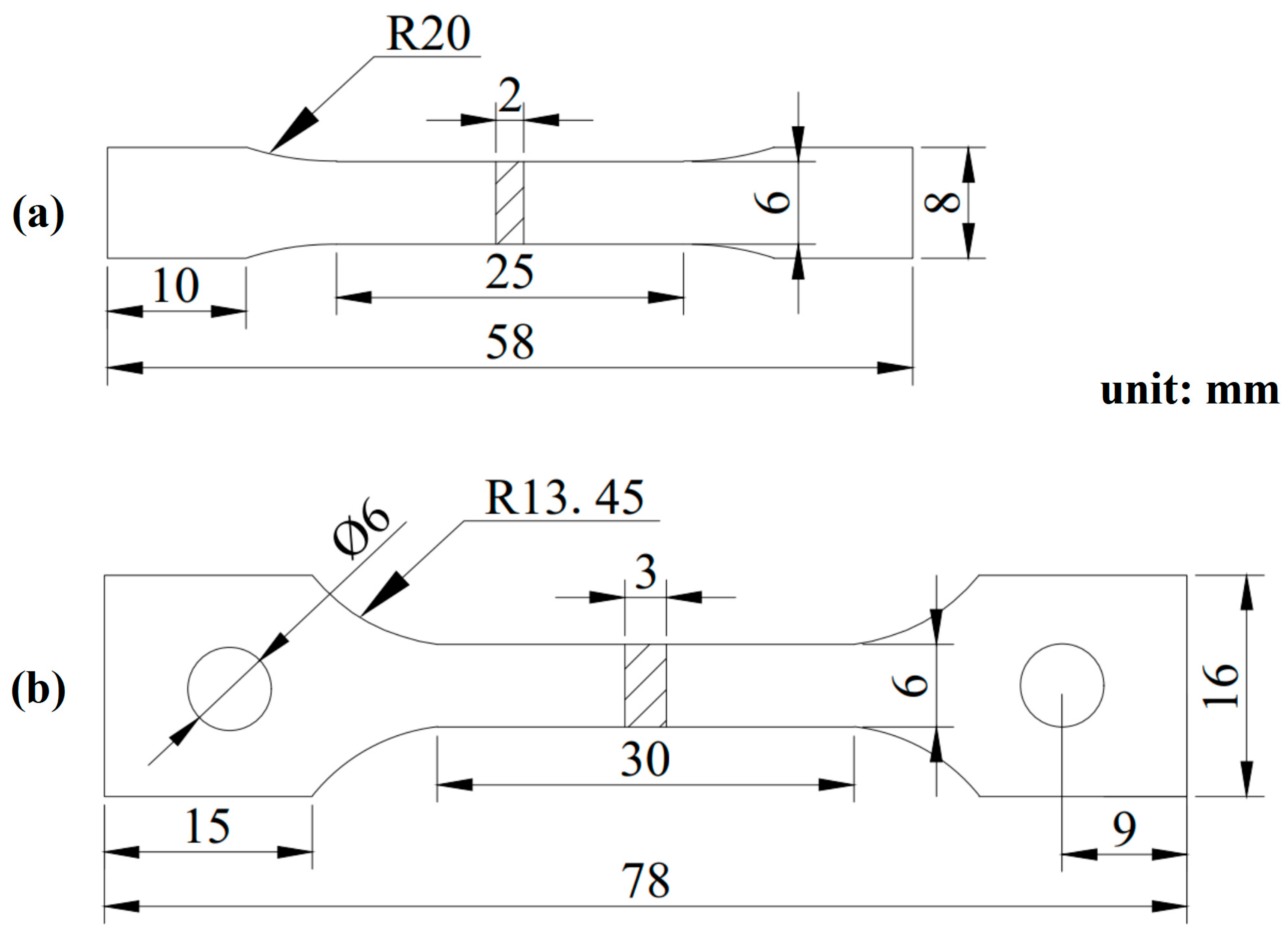
2.5. Mechanical Properties Testing
3. Theoretical Calculations
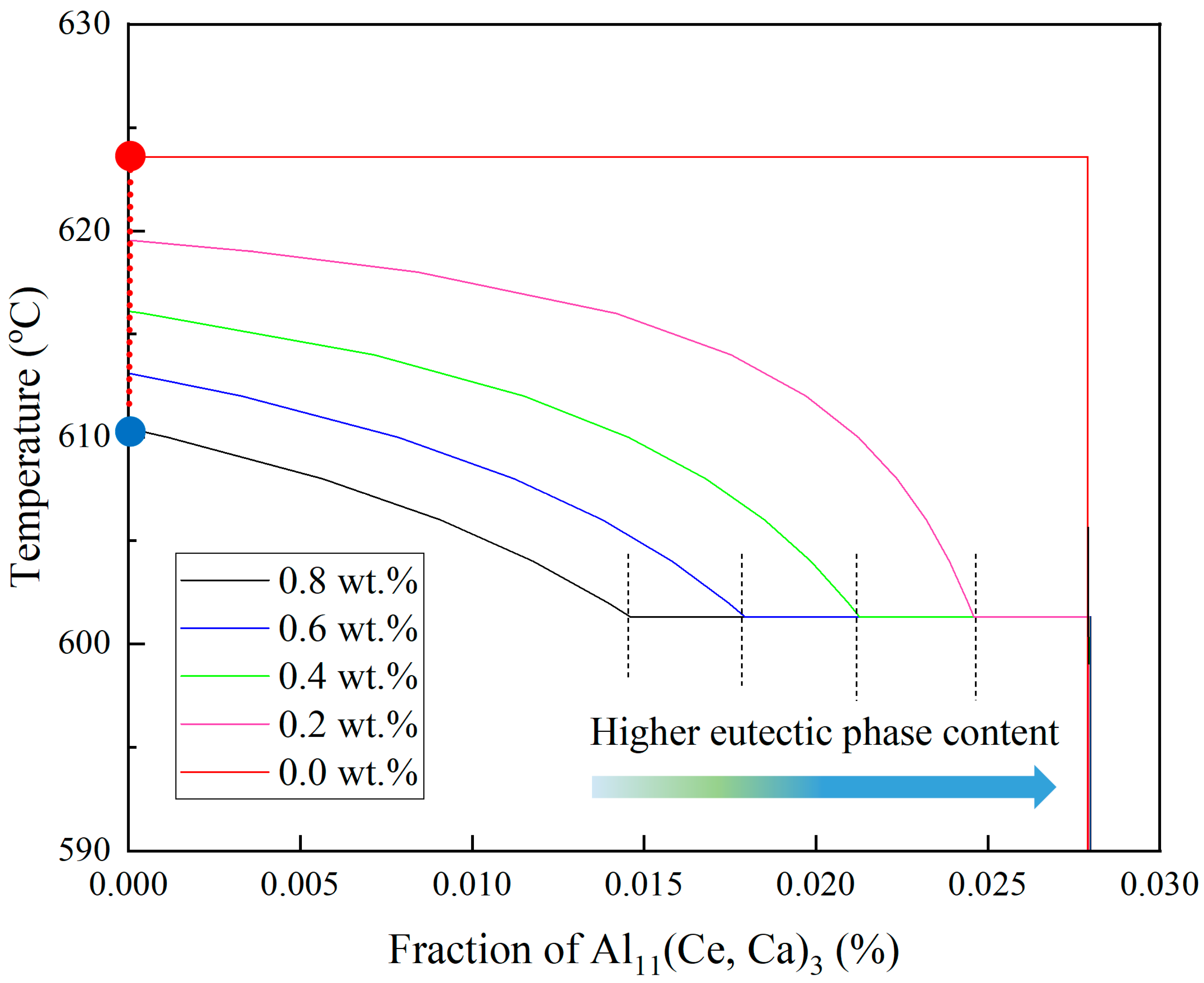
3.1. Eutectic Precipitation Temperature
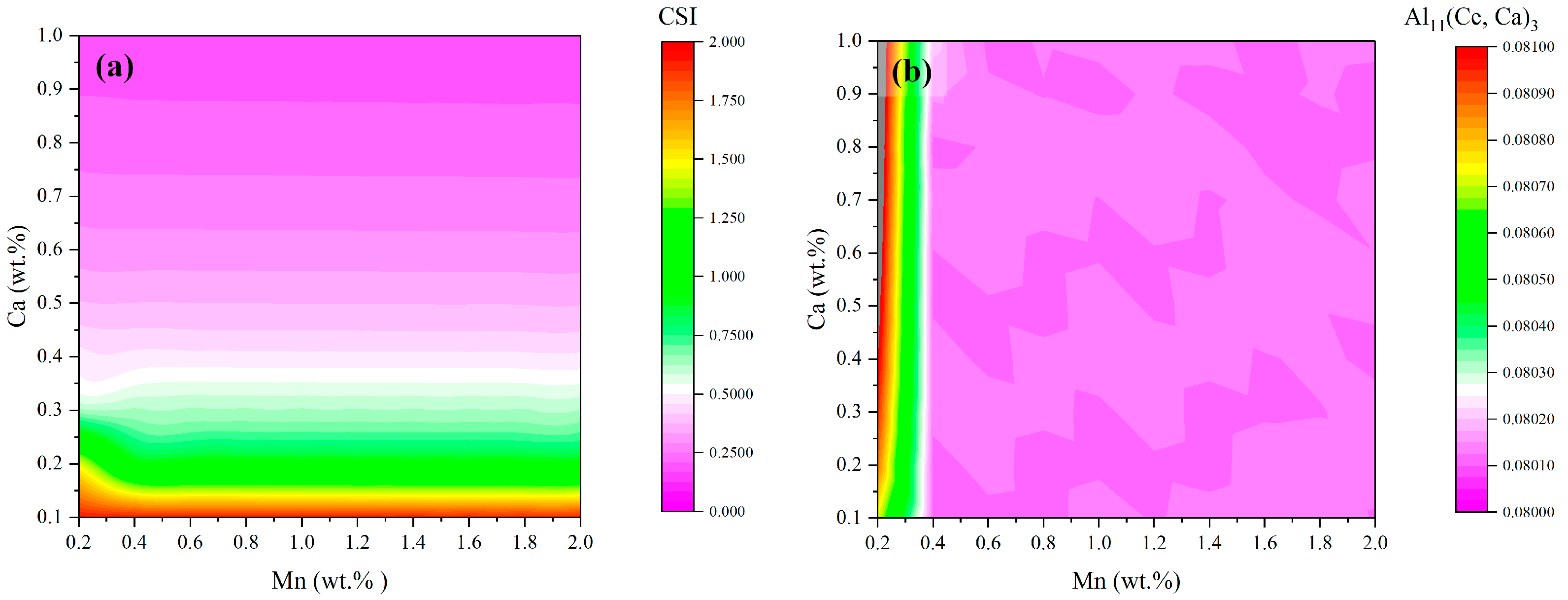
3.2. Hot Tearing Susceptibility and Volume Fraction of Al11(Ce, Ca)3 Eutectic Phase
4. Results and Discussion
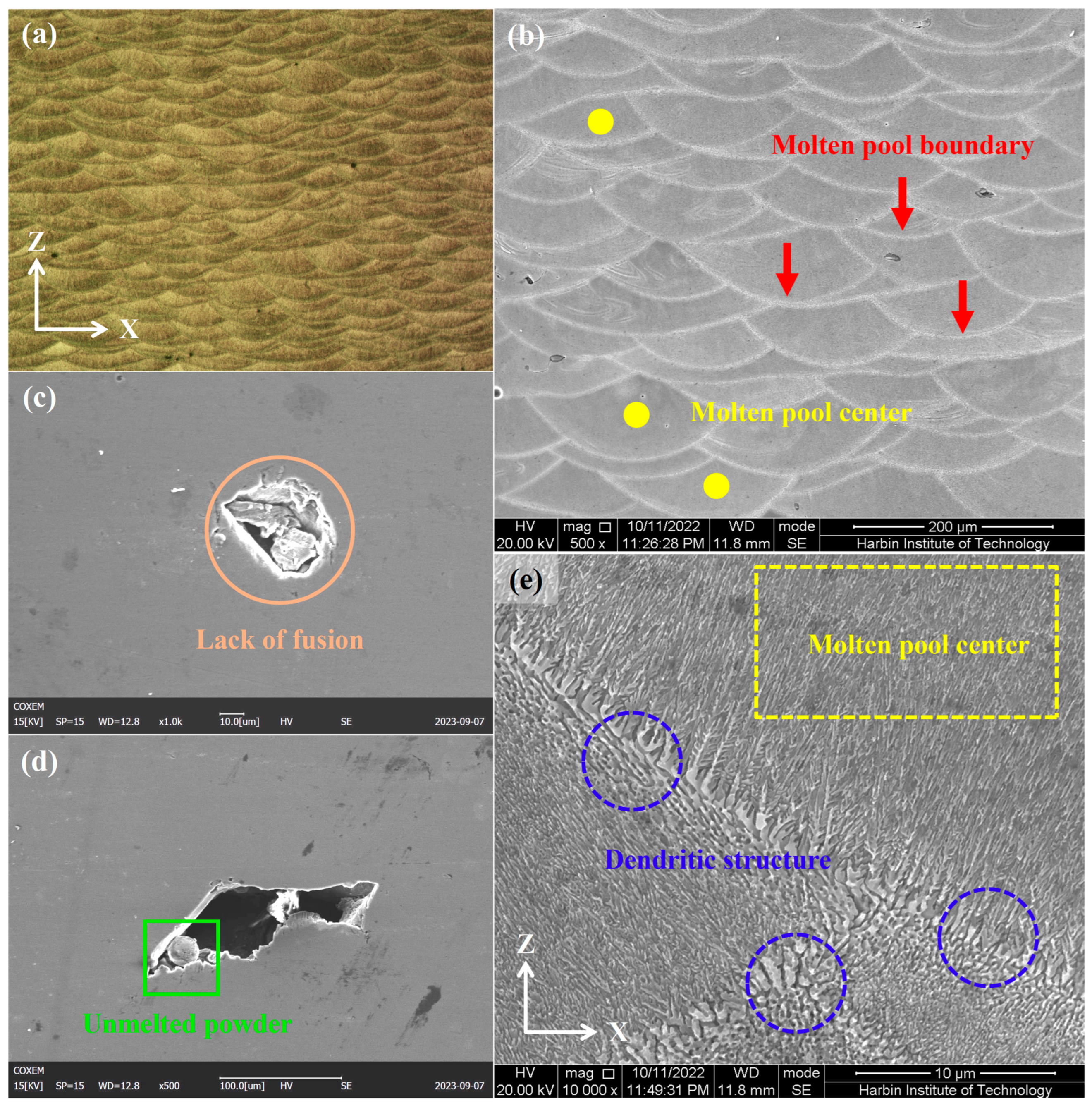
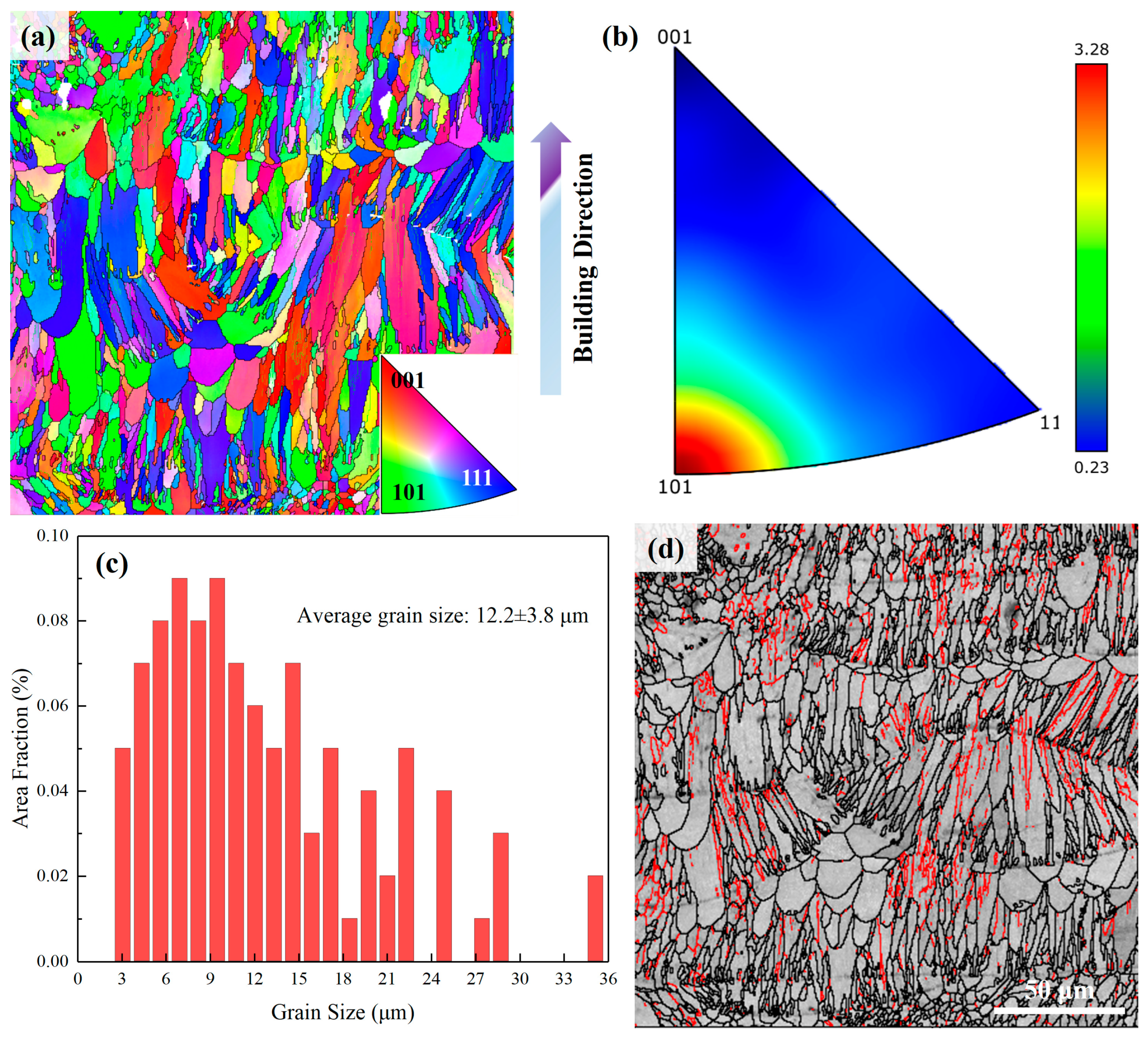
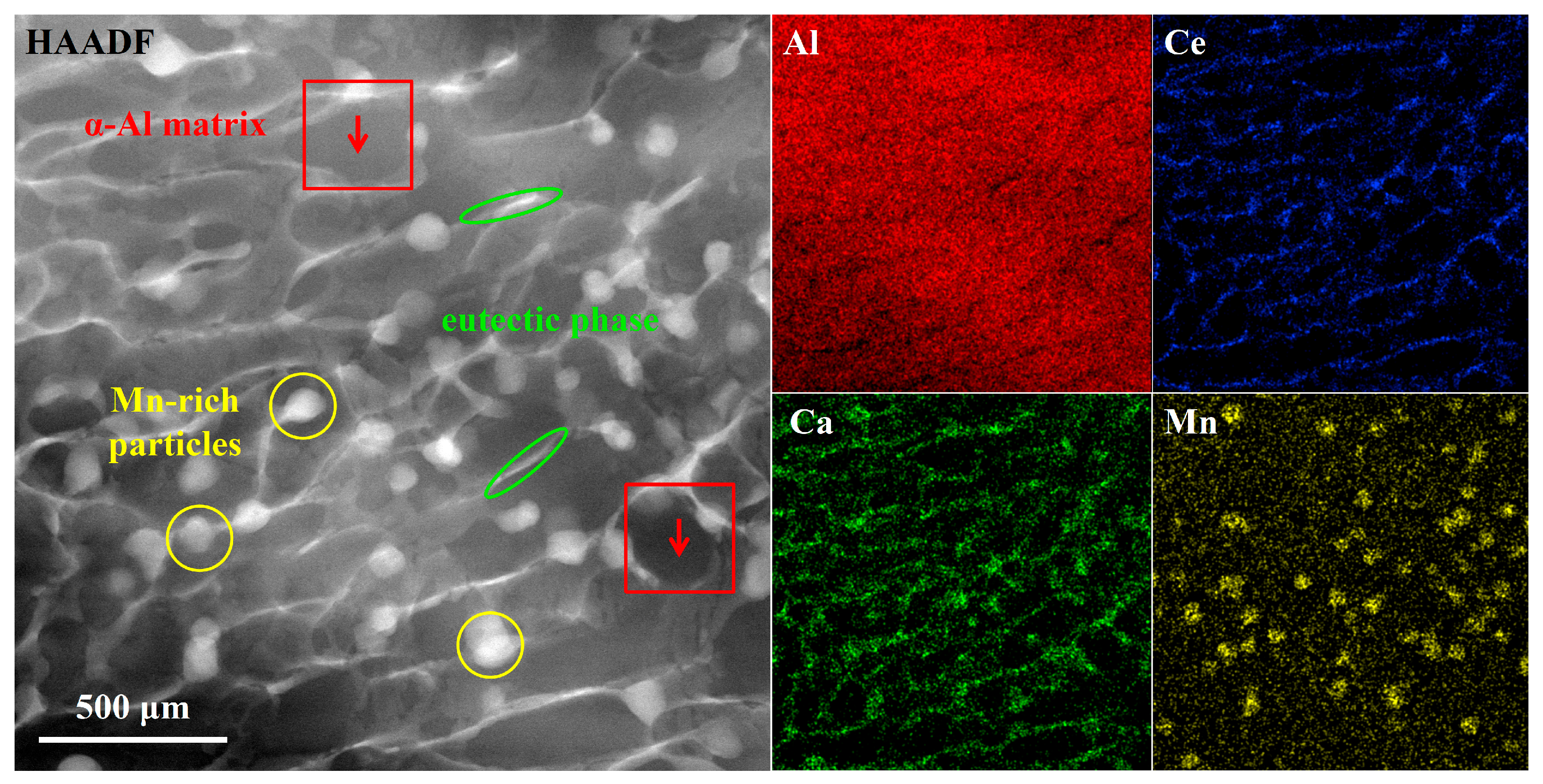
4.1. Microstructure
4.2. Mechanical Properties
4.3. Strengthening and Toughening Mechanisms of Al-3Ce-0.8Ca-1.9Mn Alloy
5. Conclusions
- In LPBF processing, the incorporation of Ca element significantly reduces the eutectic precipitation temperature of Al-Ce alloys, effectively suppressing the hot cracking tendency of the alloy, thereby laying a crucial foundation for achieving high-quality forming.
- The microstructure of the Al-3Ce-0.8Ca-1.9Mn alloy is predominantly characterized by an α-Al matrix and Al-Ce-Ca ternary eutectic compounds, complemented by a homogeneous dispersion of nanoscale spherical Al6Mn precipitates within the matrix.
- The Al-3Ce-0.8Ca-1.9Mn alloy demonstrates an exceptional synergy of strength and ductility across both room temperature and elevated temperature regimes. Notably, the room temperature yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, and elongation to fracture attained values of 321 ± 15 MPa, 429 ± 8 MPa, and 10.9 ± 2.3%, respectively.
- The superior mechanical performance of the Al-3Ce-0.8Ca-1.9Mn alloy is predominantly ascribed to the synergistic interplay of hetero-deformation induced strengthening derived from the eutectic structure, grain boundary strengthening conferred by the ultrafine-grained microstructure, and precipitation strengthening imparted by nanoscale Al6Mn precipitates.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michi, R.A.; Plotkowski, A.; Shyam, A.; Deho, R.R.; Babu, S.S. Towards high-temperature applications of aluminium alloys enabled by additive manufacturing. Int. Mater. Rev. 2022, 67, 3298–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poplawsky, J.D.; Milligan, B.K.; Allard, L.F.; Shin, D.; Shower, P.; Chisholm, M.F.; Shyam, A. The synergistic role of Mn and Zr/Ti in producing θ′/L12 co-precipitates in Al-Cu alloys. Acta Mater. 2020, 194, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Costan, E.; van Huis, M.A.; Xu, Q.; Zandbergen, H.W. Atomic Pillar-Based Nanoprecipitates Strengthen AlMgSi Alloys. Science 2006, 312, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, G.; Sun, J. Recent Progress in High-Temperature Resistant Aluminum-Based Alloys: Microstructural Design and Precipitation Strategy. Acta Metall. Sin. 2021, 57, 129–149. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Wen, J.; Zhang, J.; Song, B.; Shi, Y. Additive manufacturing of heat-resistant aluminum alloys: A review. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2024, 6, 062013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Liu, K.; Chen, X.-G. Recent advances in cost-effective aluminum alloys with enhanced mechanical performance for high-temperature applications: A review. Mater. Des. 2025, 253, 113869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, Z.C.; Rios, O.R.; Weiss, D.; Turchi, P.E.A.; Perron, A.; Lee, J.R.I.; Li, T.T.; Hammons, J.A.; Bagge-Hansen, M.; Willey, T.M.; et al. High performance aluminum-cerium alloys for high-temperature applications. Mater. Horiz. 2017, 4, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Michi, R.A.; Dunand, D.C. Cast near-eutectic Al-12.5 wt.% Ce alloy with high coarsening and creep resistance. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 767, 138440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.H.; Yahata, B.D.; Hundley, J.M.; Mayer, J.A.; Schaedler, T.A.; Pollock, T.M. 3D printing of high-strength aluminium alloys. Nature 2017, 549, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboulkhair, N.T.; Simonelli, M.; Parry, L.; Ashcroft, I.; Tuck, C.; Hague, R. 3D printing of Aluminium alloys: Additive Manufacturing of Aluminium alloys using selective laser melting. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 106, 100578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, M.E.; Gupta, M.K.; Robak, G.; Moj, K.; Krolczyk, G.M.; Kuntoğlu, M. Development of lattice structure with selective laser melting process: A state of the art on properties, future trends and challenges. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 81, 1040–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Seet, H.L.; Liu, T.; Liao, W.; Ramamurty, U.; Nai, S.M.L. Recent progress on the additive manufacturing of aluminum alloys and aluminum matrix composites: Microstructure, properties, and applications. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2023, 190, 104047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisco, K.; Plotkowski, A.; Yang, Y.; Leonard, D.; Stump, B.; Nandwana, P.; Dehoff, R.R.; Babu, S.S. Microstructure and properties of additively manufactured Al-Ce-Mg alloys. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, R.; Yuan, T.; Ke, L.; Bai, J.; Yang, K. A comprehensive overview of additive manufacturing aluminum alloys: Classifications, structures, properties and defects elimination. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 919, 147464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, S.; Wu, T.; Michi, R.A.; An, K.; Yu, D.; Allard, L.F.; Rakhmonov, J.U.; Poplawsky, J.D.; Fancher, C.M.; Dunand, D.C.; et al. An additively manufactured near-eutectic Al-Ce-Ni-Mn-Zr alloy with high creep resistance. Acta Mater. 2024, 268, 119787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, S.; Meng, X.; Xu, S. Trace Ca alloying enhance simultaneously strength and ductility of squeeze-cast Al-5Cu-0.5Mn-based alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 191, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akopyan, T.K.; Sviridova, T.A.; Belov, N.A.; Letyagin, N.V.; Korotitskiy, A.V. Intermetallic compounds in equilibrium with aluminum in Al-Ca-Cu ternary alloying system. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2024, 34, 1380–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belov, N.; Akopyan, T.; Tsydenov, K.; Sviridova, T.; Cherkasov, S.; Kovalev, A. Effect of Ca addition on structure, phase composition and hardness of Al-6%Cu-2%Mn sheet alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1009, 176955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akopyan, T.K.; Belov, N.A.; Letyagin, N.V.; Sviridov, T.A.; Cherkasov, S.O. New quaternary eutectic Al-Cu-Ca-Si system for designing precipitation hardening alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 993, 174695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, B.; Tao, X.; Yao, Z.; Belov, N.; van der Zwaag, S.; Liu, Z. Ca-modified Al-Mg-Sc alloy with high strength at elevated temperatures due to a hierarchical microstructure. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 16145–16157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurkin, P.K.; Letyagin, N.V.; Yakushkova, A.I.; Samoshina, M.E.; Ozherelkov, D.Y.; Akopyan, T.K. Remarkable thermal stability of the Al-Ca-Ni-Mn alloy manufactured by laser-powder bed fusion. Mater. Lett. 2021, 285, 129074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.V.; Rometsch, P.; Davies, C.H.J.; Huang, A.; Wu, X. Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure and anisotropy in mechanical properties of A357 alloy produced by selective laser melting. Mater. Des. 2018, 154, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spierings, A.B.; Dawson, K.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Wegener, K. Influence of SLM scan-speed on microstructure, precipitation of Al3Sc particles and mechanical properties in Sc- and Zr-modified Al-Mg alloys. Mater. Des. 2018, 140, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kou, S. Effect of diffusion on susceptibility to cracking during solidification. Acta Mater. 2015, 100, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, S.; Plotkowski, A.; Sisco, K.; Leonard, D.N.; Allard, L.F.; Michi, R.A.; Poplawsky, J.D.; Dehoff, R.; Shyam, A. Elevated temperature ductility dip in an additively manufactured Al-Cu-Ce alloy. Acta Mater. 2021, 220, 117285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Lei, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Tian, Z.; Liang, J.; Zhang, X.; Qin, X. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a novel Sc and Zr modified 7075 aluminum alloy prepared by selective laser melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 768, 138478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yang, M.; Li, R.; Jiang, P.; Yuan, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, Y. Plastic accommodation during tensile deformation of gradient structure. Sci. China Mater. 2021, 64, 1534–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwary, C.S.; Pandey, P.; Sarkar, S.; Das, R.; Samal, S.; Biswase, K.; Chattopadhyay, K. Five decades of research on the development of eutectic as engineering materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2022, 123, 100793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Al | Ce | Ca | Mn | Fe | Si | Cu | Mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bal. | 3.03 | 0.79 | 1.88 | <0.2 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| Laser Power/W | Scan Speed/mm/s | Layer Thickness/mm | Scan Space/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 370 | 900 | 0.03 | 0.13 |
| Ce/wt.% | Ca/wt.% | Mn/wt.% | Al | Density (g/cm3) | Vm (cm3/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | balance | 2.74918 | 10.0582 |
| 3.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | balance | 2.74504 | 10.0801 |
| 3.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | balance | 2.7409 | 10.1021 |
| 3.0 | 0.6 | 0.0 | balance | 2.73678 | 10.1241 |
| 3.0 | 0.8 | 0.0 | balance | 2.73267 | 10.1462 |
| 3.0 | 0.0 | 1.9 | balance | 2.78357 | 10.0333 |
| 3.0 | 0.2 | 1.9 | balance | 2.77932 | 10.0555 |
| 3.0 | 0.4 | 1.9 | balance | 2.77508 | 10.0777 |
| 3.0 | 0.6 | 1.9 | balance | 2.77086 | 10.0999 |
| 3.0 | 0.8 | 1.9 | balance | 2.76664 | 10.1221 |
| Temperature/°C | Yield Strength/MPa | Ultimate Tensile Strength/MPa | Elongation/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Room temperature | 321 ± 15 | 429 ± 8 | 10.9 ± 2.3 |
| 250 | 214 ± 11 | 242 ± 12 | 16.8 ± 2.4 |
| 300 | 196 ± 7 | 224 ± 6 | 16.7 ± 4.6 |
| 350 | 154 ± 19 | 161 ± 22 | 16.8 ± 3.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Teng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, M. Composition Optimization and Microstructure-Property Investigation of Al-3.0Ce-xCa-yMn Alloy Exhibiting High Hot Tearing Resistance. Metals 2025, 15, 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111195
Wei X, Zhang S, Wang X, Teng Y, Zhang W, Wang M. Composition Optimization and Microstructure-Property Investigation of Al-3.0Ce-xCa-yMn Alloy Exhibiting High Hot Tearing Resistance. Metals. 2025; 15(11):1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111195
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Xiaoxiao, Suhui Zhang, Xiaofei Wang, Yulin Teng, Wanwen Zhang, and Mengmeng Wang. 2025. "Composition Optimization and Microstructure-Property Investigation of Al-3.0Ce-xCa-yMn Alloy Exhibiting High Hot Tearing Resistance" Metals 15, no. 11: 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111195
APA StyleWei, X., Zhang, S., Wang, X., Teng, Y., Zhang, W., & Wang, M. (2025). Composition Optimization and Microstructure-Property Investigation of Al-3.0Ce-xCa-yMn Alloy Exhibiting High Hot Tearing Resistance. Metals, 15(11), 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111195






