Sodium Percarbonate for Eco-Efficient Cyanide Detoxification in Gold Mining Tailings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
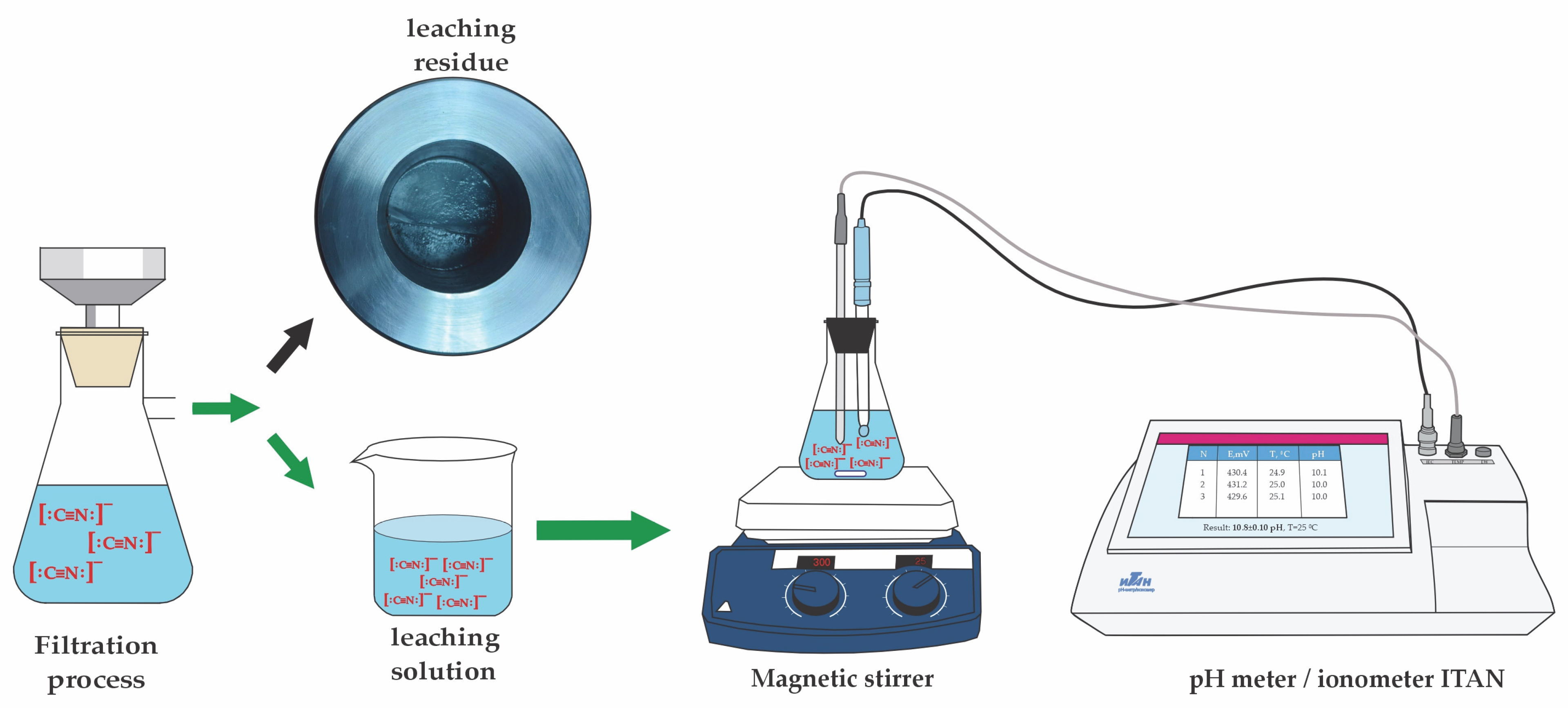
2.2. Analytical Techniques
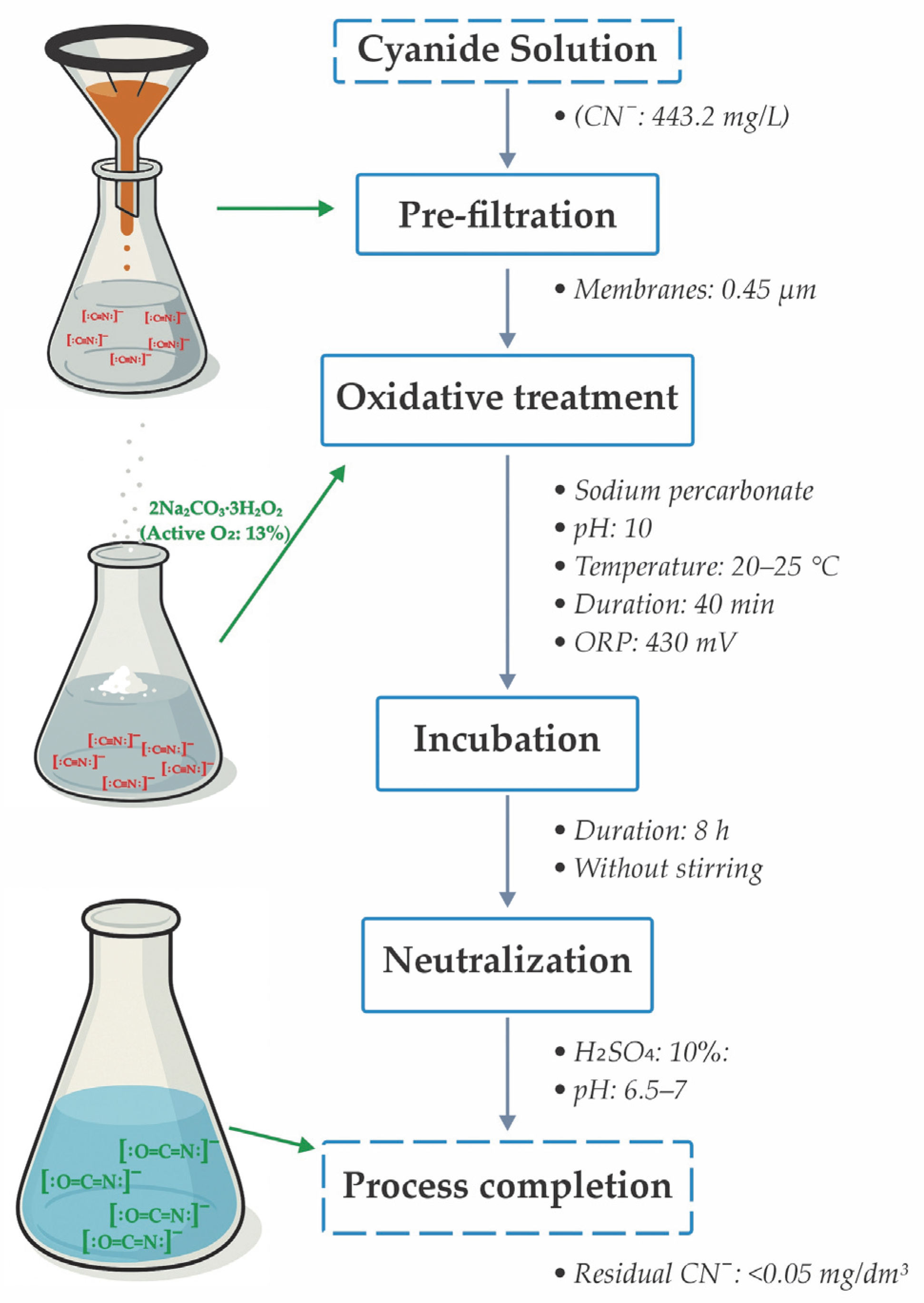
2.3. Experimental Method
2.4. Optimized Experimental Design for the Detoxification Process
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Tailings
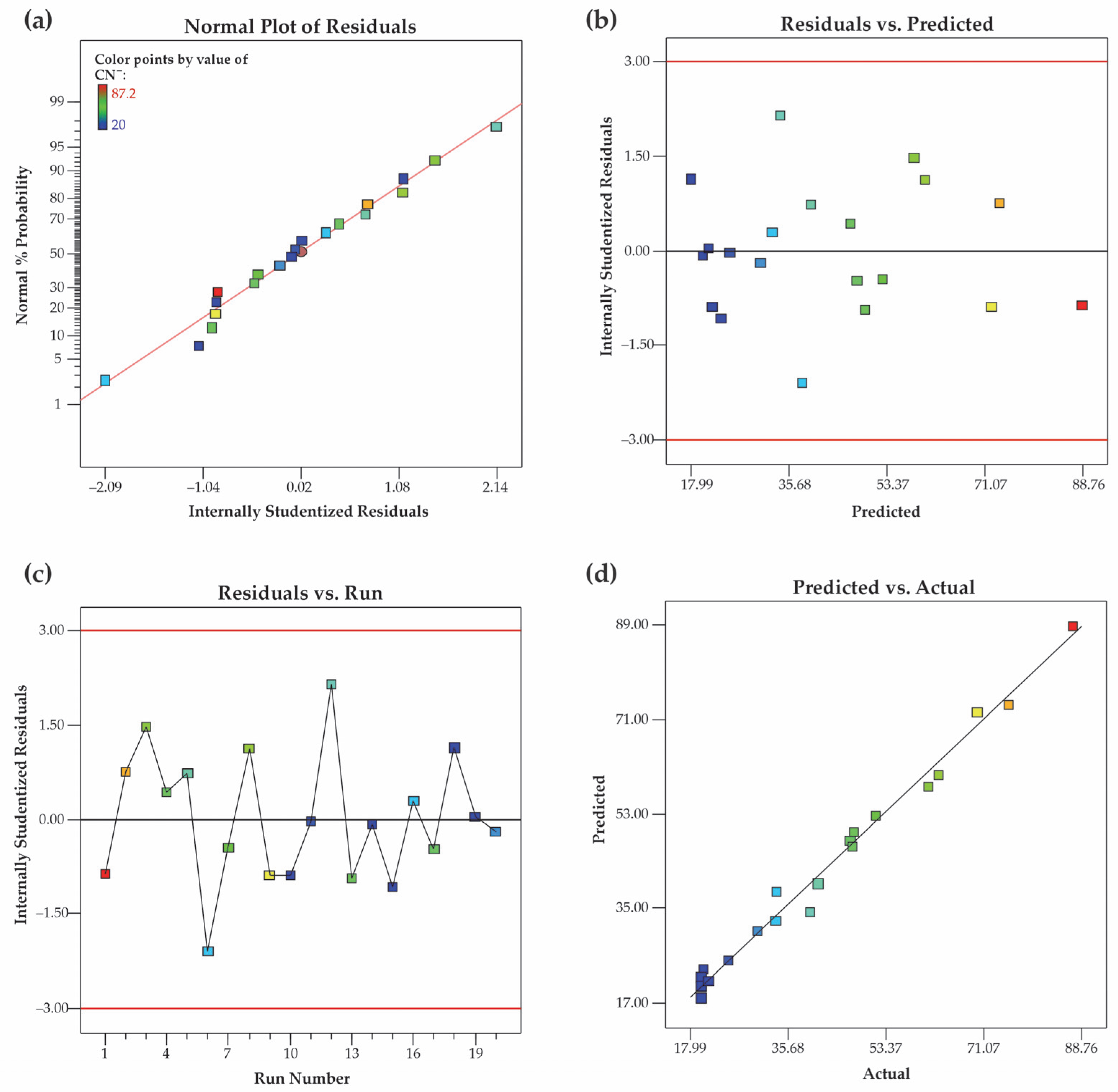
3.2. Statistical Analysis and Model Fitting
3.2.1. Data Analysis
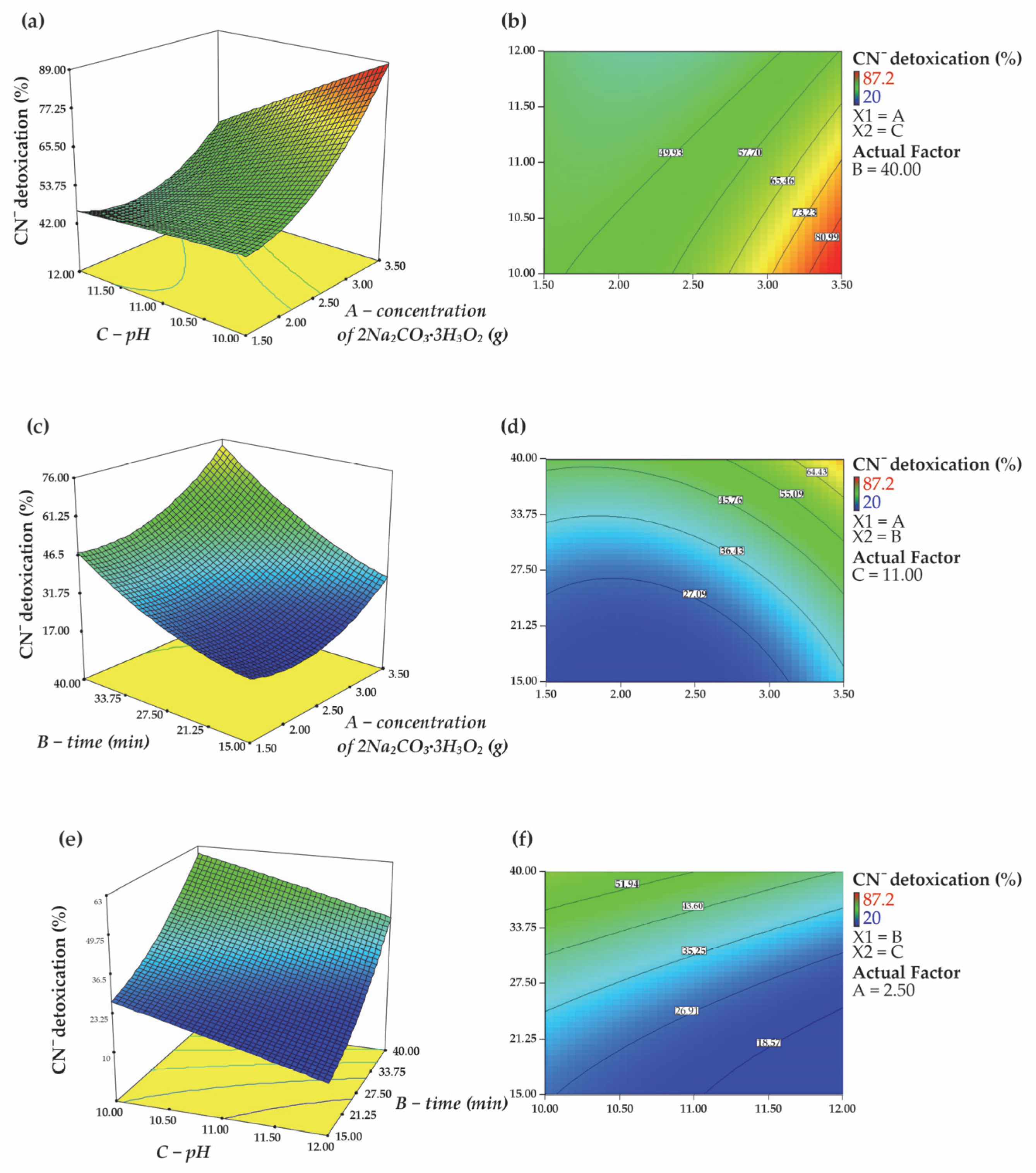
3.2.2. Internal Relationships Between Factors
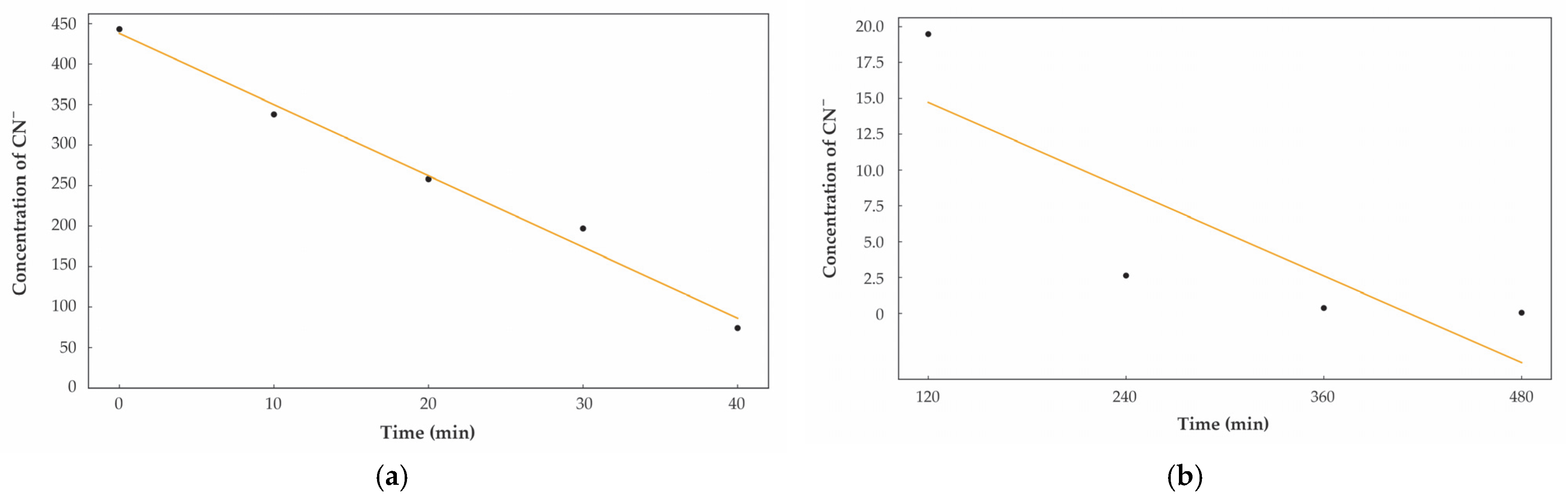
3.3. Kinetic Evolution and Prolonged Detoxification Efficacy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santanu, P.; Atanu, P.; Kumaresh, G. Supramolecular gels in cyanide sensing: A review. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 584–602. [Google Scholar]
- Antonini, E.; Brunori, M.; Rotilio, G.C.; Greenwood, C.; Malmström, B.G. The Interaction of Cyanide with Cytochrome Oxidase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1971, 23, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajamanikandan, R.; Sasikumar, K.; Kosame, S.; Ju, H. Optical Sensing of Toxic Cyanide Anions Using Noble Metal Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaca-Escobar, K.; Arregui-Almeida, D.; Espinoza-Montero, P. Chemical, ecotoxicological characteristics, environmental fate, and treatment methods applied to cyanide-containing wastewater. NPJ Clean Water 2024, 7, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seney, C.S.; Bridges, C.C.; Aljic, S.; Moore, M.E.; Orr, S.E.; Barnes, M.C.; Joshee, L.; Uchakina, O.N.; Bellott, B.J.; McKallip, R.J.; et al. Reaction of Cyanide with Hg0-Contaminated Gold Mining Tailings Produces Soluble Mercuric Cyanide Complexes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 2834–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.T. Cyanide: Social, industrial and economic aspects. Gold Bull. 2001, 34, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, M.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Lyu, X. A review of gold extraction using alternatives to cyanide: Focus on current status and future prospects. Miner. Eng. 2022, 176, 107336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Guo, X.; Tian, Q.; Zhang, L. A systematic review of gold extraction: Fundamentals, advancements, and challenges toward alternative lixiviants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 440, 129778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooiman, M.B.; Miller, J.D. The chemistry of gold solvent extraction from cyanide solution using modified amines. Hydrometallurgy 1986, 16, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisler, R.; Wiemeyer, S.N. Cyanide Hazards to Plants and Animals from Gold Mining and Related Water Issues. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2004, 183, 21–54. [Google Scholar]
- Brüger, A.; Fafilek, G.; Restrepo, B.O.J.; Rojas-Mendoza, L. On the volatilisation and decomposition of cyanide contaminations from gold mining. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Chung, H.; Choi, S.; Bahn, Y.; Son, J. Evaluation of exposure to cyanogenic glycosides and potential hydrogen cyanide release in commercially available foods among the Korean population. Food Chem. 2024, 456, 139872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyirenda, K.K. Toxicity Potential of Cyanogenic Glycosides in Edible Plants. IntechOpen 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Ding, J.; Qian, P.; Li, Q.; Ye, S.; Chen, Y. Comprehensive recovery of metals from cyanidation tailing. Miner. Eng. 2014, 70, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Luque-Almagro, V.M.; Moreno-Vivián, C.; Roldán, M.D. Biodegradation of cyanide wastes from mining and jewellery industries. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 38, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Q.; Li, Z.; Chi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H. Cyanide Release Characteristics of Solid Waste in Gold Smelting Process. Minerals 2022, 12, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittan, M.; Plenge, G. Estimating Process Design Gold Extraction, Leach Residence Time and Cyanide Consumption for High Cyanide-Consuming Gold Ore. Miner. Metall. Process. 2015, 32, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, D.; Anderson, C.G. A Review of the Cyanidation Treatment of Copper-Gold Ores and Concentrates. Metals 2020, 10, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.A. The fate of cyanide in leach wastes at gold mines: An environmental perspective. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 57, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Valoys, A.C.; Arrocha, J.; Monteza-Destro, T.; Vargas-Lombardo, M.; Esbrí, J.M.; Garcia-Ordiales, E.; Jiménez-Ballesta, R.; García-Navarro, F.J.; Higueras, P. Environmental challenges related to cyanidation in Central American gold mining; the Remance mine (Panama). J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 113979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuyucak, N.; Akcil, A. Cyanide and removal options from effluents in gold mining and metallurgical processes. Miner. Eng. 2013, 50–51, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Deep treatment technology for cyanidation barren solution from a gold enterprise. Gold 2019, 40, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Q.; Jiang, S.; Fang, R.; Liu, S.; Wu, X. An environmental-friendly approach to remove cyanide in gold smelting pulp by chlorination aided and corncob biochar: Performance and mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamelkina, M.A.; Herraiz-Carboné, M.; Cotillas, S.; Lacasa, E.; Sáez, C.; Tuunila, R.; Sillanpää, M.; Häkkinen, A.; Rodrigo, M.A. Treatment of mining wastewater polluted with cyanide by coagulation processes: A mechanistic study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 237, 116345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anning, C.; Wang, J.; Chen, P.; Batmunkhi, I.; Lyu, X. Determination and detoxification of cyanide in gold mine tailings: A review. Waste Manag. Res. 2019, 37, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, K.; Xie, F.; Wang, W.; Chang, Y.; Lu, D.; Gu, X.; Chen, C. The detoxification and utilization of cyanide tailings: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 302, 126946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyuchi, M.M.; Sukdeo, N.; Stinner, W. Potential to remove heavy metals and cyanide from gold mining wastewater using biochar. Phys. Chem. Earth 2022, 126, 103110. [Google Scholar]
- Khodadad, A.; Teimoury, P.; Abdolahi, M.; Samiee, A. Detoxification of Cyanide in a Gold Processing Plant Tailings Water Using Calcium and Sodium Hypochlorite. Mine Water Environ. 2008, 27, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; AO, X.; Wang, L. A Study of Treatment of High-Cyanide-Containing Wastewater and Application Thereof. Available online: https://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD2005&filename=HGGS200502013&uniplatform=OVERSEA&v=43gIbe2CU4ydtIgYAeghQPlNw3WW-_tQSLHGq4JWEc5C6IbOBrcEWP9ohbEul-EM (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Chen, X.; Ren, Y.; Qu, G.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ning, P. A Review of Environmental Functional Materials for Cyanide Removal by Adsorption and Catalysis. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 157, 111298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkinbayeva, A.; Kenzhaliyev, B.; Smailov, K.; Aimagambetov, A.; Kamenov, B.; Saulebekkyzy, S.; Tolegenova, N.; Putri, P.S.R. An overview of biological cyanide elimination from tailing wastewater as a promising tool for sustainable utilization. Water Res. X 2025, 29, 100400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe-Ramírez, D.; Cristiani-Urbina, E.; Morales-Barrera, L. Biodegradation of Free Cyanide by a New Isolated Alkaliphilic Bacillus licheniformis Strain. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 15, 33–49. [Google Scholar]
- Hai, L.; Fang, X.; Zhao, X.; Xu, B.; Cheng, T. Experimental analysis on cyanide removal of gold tailings under medium-temperature roasting. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaya-Abril, A.; Biełło, K.; Rodríguez-Caballero, G.; Cabello, P.; Sáez, L.P.; Moreno-Vivián, C.; Luque-Almagro, V.M.; Roldán, M.D. Bacterial tolerance and detoxification of cyanide, arsenic and heavy metals: Holistic approaches applied to bioremediation of industrial complex wastes. Microb. Biotechnol. 2024, 17, e14399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrov, V.F.; Chepaikin, E.G.; Bezrukov, G.M. Method of Treatment of Cyanide-Containing Waste Water of Gold Mining Industry Enterprises. RU Patent 2450979C2, 20 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kim, R.; Han, K.N. Advances in Hydrometallurgical Gold Recovery through Cementation, Adsorption, Ion Exchange and Solvent Extraction. Minerals 2024, 14, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.J.; Pomberger, A.; Felton, K.C.; Grainger, R.; Barecka, M.; Chamberlain, T.W.; Bourne, R.A.; Johnson, C.N.; Lapkin, A.A. A Brief Introduction to Chemical Reaction Optimization. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 3089–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, S.G. Optimizing Chemical Reactions. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 3645–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenzhaliyev, B.; Koizhanova, A.; Fischer, D.; Magomedov, D.; Yerdenova, M.; Smailov, K.; Abdyldayev, N. Study of efficiency of organic activator application to process difficult-to-beneficiate polymetallic ridder ores. Transit. Met. Chem. 2025, 50, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulvaliev, R.A.; Surkova, T.Y.; Baltabekova, Z.; Yessimova, D.M.; Stachowicz, M.; Smailov, K.M.; Dossymbayeva, Z.D.; Ainur, B. Effect of Amino Acids on the Extraction of Copper from Sub-Conditional Raw Materials. Complex Use Miner. Resour. 2024, 335, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenzhaliyev, B.; Ultarakova, A.; Lokhova, N.; Mukangaliyeva, A.; Kassymzhanov, K. Optimized Hydrometallurgical Extraction of Molybdenum via Mechanoactivation and Nitric–Sulfuric Leaching. Processes 2025, 13, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciuttolo, C.; Cano, D.; Custodio, M. Socio-Environmental Risks Linked with Mine Tailings Chemical Composition: Promoting Responsible and Safe Mine Tailings Management Considering Copper and Gold Mining Experiences from Chile and Peru. Toxics 2023, 11, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 5667-3:2024; Water Quality — Sampling — Part 3: Preservation and Handling of Water Samples. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024.
- KnowItAll IR Spectral Libraries. Wiley Science Solutions. Available online: https://sciencesolutions.wiley.com/solutions/technique/ir/ (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Nakamoto, K. Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds; Mir: Moscow, Russia, 1991; p. 536. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, M.D. Advantages in Gold Ore Processing, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Perth, Australia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Wu, D.; Wang, Z. Investigation of the Leaching Kinetics of Zinc from Smithsonite in Ammonium Citrate Solution. Metals 2024, 14, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenzhaliyev, B.; Surkova, T.; Berkinbayeva, A.; Baltabekova, Z.; Smailov, K.; Abikak, Y.; Saulebekkyzy, S.; Tolegenova, N.; Omirbek, T.; Dosymbaeva, Z. Innovative Methods for Intensifying the Processing of Zinc Clinker: Synergy of Microwave Treatment and Ultrasonic Leaching. Metals 2025, 15, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.J.; Wu, D.D.; Li, S.Y.; Ma, W.H.; Wang, R.Z. Effect of process variables on leaching behavior and kinetics of silver element from waste photovoltaic modules. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 335, 126062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenzhaliyev, B.; Berkinbayeva, A.; Baltabekova, Z.; Moldabayeva, G.; Smailov, K.; Saulebekkyzy, S.; Tolegenova, N.; Karim, D.; Omirbek, T. Investigation of Phase Transformations in Technogenic Raw Materials Under Microwave Treatment for Enhanced Zinc Leaching. Processes 2025, 13, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Lu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Yu, H.; Ma, P.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J. Biodegradation of Cyanide by a New Isolated Aerococcus viridans and Optimization of Degradation Conditions by Response Surface Methodology. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhatskiy, Y.; Знак, З.О.; Sozanskyi, M.; Shepida, M.; Gogate, P.R.; Tsymbaliuk, V. Activated Periodates and Sodium Percarbonate in Advanced Oxidation Processes of Organic Pollutants in Aqueous Media: A Review. Chem. Chem. Technol. 2024, 18, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabalka, G.W.; Reddy, M.S.; Chen, Y. Sodium Percarbonate. e-EROS. [CrossRef]
- Ospanov, K.; Smailov, K.; Nuruly, Y. Patterns of Non-Traditional Thermodynamic Functions ΔrG0/n and ΔfG0(Averaged) Changes for Cobalt Minerals. Chem. Bull. Kazakh Natl. Univ. 2020, 96, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Yang, H.; Tong, L. Removal of Cyanide in Gold Cyanide Residues through Persulfate-Advanced Oxidation Process. Minerals 2023, 13, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Chemical Compounds | Au | Cu | As | Fe | Ag | Zn | Stotal | S2 | CNfree | CNS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration, mg/L | 0.101 | 4.74 | 7.0 | 3.7 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 658.2 | 246.7 | 443.2 | 257.5 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Concentration (g) | 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5 *, 4.0 |
| Time (min) | 10, 20 *, 30, 40 |
| pH | 10, 11 *, 12 |
| Factors | Symbol | Coding Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Concentration 2Na2CO3·3H2O2 (g) | A | 1.5 | 2.75 | 4.0 |
| Time (min) | B | 10 | 25 | 40 |
| pH | C | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F Value | p-Value Prob > F | Standard Error | 95% CI (Lower–Upper) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 7758.88 | 9 | 862.10 | 84.50 | <0.0001 | - | - |
| A—Concentration | 1283.40 | 1 | 1283.40 | 125.80 | <0.0001 | ±0.91 | (8.56–12.50) |
| B—pH | 581.43 | 1 | 581.43 | 56.99 | <0.0001 | ±1.09 | (−10.92–6.22) |
| C—Time | 1726.34 | 1 | 1726.34 | 169.22 | <0.0001 | ±1.64 | (18.42–25.60) |
| AB Interaction | 333.16 | 1 | 333.16 | 32.66 | 0.0002 | ±1.14 | (−9.18–4.29) |
| AC Interaction | 92.87 | 1 | 92.87 | 9.10 | 0.0130 | ±1.15 | (1.12–6.04) |
| A2—Quadratic | 77.11 | 1 | 77.11 | 7.56 | 0.0205 | ±3.13 | (1.85–15.81) |
| C2—Quadratic | 126.60 | 1 | 126.60 | 12.41 | 0.0055 | ±1.89 | (2.69–10.96) |
| Lack of Fit | 53.52 | 5 | 10.70 | 1.10 | 0.4200 | - | - |
| Pure Error | 48.50 | 5 | 9.70 | - | - | - | - |
| Residual Error | 102.02 | 10 | 10.20 | - | - | - | - |
| Cor Total | 7860.90 | 19 | - | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berkinbayeva, A.; Saulebekkyzy, S.; Kenzhaliyev, B.; Smailov, K.; Yessengaziyev, A.; Nurtazina, N.; Karim, D.; Birlikzhan, Y. Sodium Percarbonate for Eco-Efficient Cyanide Detoxification in Gold Mining Tailings. Metals 2025, 15, 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101162
Berkinbayeva A, Saulebekkyzy S, Kenzhaliyev B, Smailov K, Yessengaziyev A, Nurtazina N, Karim D, Birlikzhan Y. Sodium Percarbonate for Eco-Efficient Cyanide Detoxification in Gold Mining Tailings. Metals. 2025; 15(10):1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101162
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerkinbayeva, Ainur, Shynar Saulebekkyzy, Bagdaulet Kenzhaliyev, Kenzhegali Smailov, Azamat Yessengaziyev, Nargiza Nurtazina, Diana Karim, and Yerkem Birlikzhan. 2025. "Sodium Percarbonate for Eco-Efficient Cyanide Detoxification in Gold Mining Tailings" Metals 15, no. 10: 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101162
APA StyleBerkinbayeva, A., Saulebekkyzy, S., Kenzhaliyev, B., Smailov, K., Yessengaziyev, A., Nurtazina, N., Karim, D., & Birlikzhan, Y. (2025). Sodium Percarbonate for Eco-Efficient Cyanide Detoxification in Gold Mining Tailings. Metals, 15(10), 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101162






