1. Introduction
As a disruptive new technology, Additive Manufacturing (AM) has been recognized as a viable production method for mass customization [
1,
2]. AM is the process of joining materials to make parts from 3D model data [
3]. In contrast to the subtractive and forming methods of production, material is joined layer upon layer in AM processes to form the final product. This departure from conventional manufacturing has profound product and supply chain impacts [
4,
5,
6]. Product impacts of adopting AM are well recognized, but the operational impacts are relatively less known [
7,
8]. This study is inspired by the need to understand the operational implications of AM adoption.
Metal AM refers to a collective term for several distinct processes with different operating principles, capabilities, and implementation requirements. The mainstream metal AM technologies are Powder Bed Fusion (PBF), Directed Energy Deposition (DED), Material Extrusion (MEX), Sheet Lamination, Material Jetting, Binder Jetting (BJ), and Vat Photopolymerization [
3]. PBF (%54), DED (%16), BJ (%16), and MEX (%10) are the most commonly used AM technologies for producing metal parts [
9,
10], with their suitability depending on application, performance requirements, and the industry sector [
11].
As the need for one-off manufactured parts increases, companies are adopting AM to establish metal 3D printing capabilities [
12]. The differences in technologies provide variation in production processes, which necessitate careful consideration of both costs and externalities for selecting the best alternative on the pathway towards adopting metal AM. Cost remains a major barrier to the widespread adoption of AM technologies [
13]. There is a need for understanding when and how different metal AM processes can compete with traditional manufacturing, specifically CNC machining.
Cost analysis of metal AM-based production is limited to a handful of papers. The existing studies are mostly generic and conceptual [
14]. Among the most relevant studies, [
15] developed a cost model for the evaluation of monitoring tools in metal AM processes. Reference [
16] explored the cost competitiveness of MEX for the production of metal parts using a case study. A comprehensive techno-economic analysis was conducted by [
17] to compare PBF and MEX, considering quality, ease of use, setup time, and costs. Reference [
18] conducted regression analysis using costs and complexity metric values for post-processing cost modelling in Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS). Reference [
19] conducted a literature review for the conceptual cost modeling of PBF and DED. AM is not a solution that fits all application areas and industry sectors. Case studies are required to explore the nuances of adopting metal AM technologies for different production scenarios and use cases. Addressing this practical need is the main aim of the present study.
The keyword analysis of 2477 articles published to date on the Web of Science databases (
Figure 1) suggests that PBF and DED are the most studied metal AM technologies in the academic literature, considering the highest frequency of the use of the keywords and the greatest correlation with metal AM. The present study aims to compare the most prevalent AM technologies for producing metal parts through a case study. The research question under investigation is as follows: how do WAAM and PBF perform compared to CNC for small batches of steel parts with high complexity? A steel robotic gripper is considered as a case study to explore this question. A simulation model is developed to model the system’s dynamics at machine-level resolution, considering cost-per-part, externalities, and lead time with hourly resolution. To the authors’ knowledge, a shop floor-level analysis of PBF and WAAM has not been conducted. The novelty of this study is the cost analysis based on a practical case study and a modeling approach that accounts for the complex, interconnected operational factors influencing costs.
The rest of this article is structured into 4 sections.
Section 2 delves into the developed simulation model, providing details about equations, flows, stocks, etc.
Section 3 validates the model through a case study and presents the results.
Section 4 discusses the practical implications. Finally,
Section 5 concludes the study, lists its limitations, and provides suggestions for future research.
2. Cost Modeling
This study utilizes case study data to draw generalizable conclusions about the cost performance of PBF and WAAM in producing steel parts. The objective is to measure the value added of different production processes in terms of cost and lead time, and to analyse how different scenarios influence their competitiveness. This includes investigating the changes in production throughput, machine availability, and costs, considering various production technologies.
The cost model is developed within the system dynamics framework and is modelled using the Vensim software. System dynamics provides a framework to model the complex, interconnected operational factors that influence costs over time. As one of the most widely used methods for cost modeling and analysis [
20,
21], system dynamics helps in estimating costs, identifying cost drivers, and analyzing the impact of various operations management decisions on overall costs.
Figure 2 shows the model that captures shop-floor dynamics and operations at the machine level. The model considers a monthly time horizon with hourly resolution to compare the production of identical parts under the same demand and sourcing conditions. Using feedback loops and exploring the dynamic relationships between various cost elements, the developed cost model enables informed adoption decision-making.
In this figure, the first layer (i.e., the machine level) represents the details of material flows and manufacturing processes over an hourly timescale, considering one month. The key production parameters, such as setup time, batch size, print time per part, and machine utilization, are adjusted separately for different AM technologies. The model facilitates the analysis of the production-related behavior and results for various input parameters. We now elaborate on the model elements and their corresponding formulations.
2.1. Stocks, Flows, and Operational Parameters
The production system is modelled through a set of interconnected stocks and flows that represent the movement of parts and materials on the shop floor. Stocks show the accumulation of operational values to describe the system at a certain point in time. The main stocks are:
Raw material inventory (kg): Available raw material used for production.
Demand queue: Parts awaiting the printing process.
Printing Work-In-Process (WIP): Parts currently undergoing printing.
Finished goods inventory: Parts that have completed all production stages.
In addition to these, the cumulative cost stock is defined to accumulate the total processing costs over time, including machine depreciation, material cost, labour, energy use, and consumables. Following [
10], the pre- and post-processing tasks (e.g., support removal, machining, cleaning, and heating for addressing porosity and residual stresses [
22]) are included in the setup time, eliminating the need for a separate post-processing stock and queue.
The flows connect the stocks, representing the movement of material and parts through the production stages. They are driven by machine capacity, raw material availability, and processing lead times. The model has been established using the following main flows.
Material delivery rate: Raw materials supplied to the production system, considering the forecasted needs.
Material consumption rate: Raw materials consumed within the printing process, depending on production start rate and material usage per part.
Printing start rate: The number of parts entering the printing process, determined by the minimum of machine capacity, raw material availability, and outstanding demand.
Printing completion rate (printing + embedded finishing): The number of parts completed from printing, considering the effective printing time per part.
Effective printing time per part: Each production stage is associated with a lead time, summing the setup time with the actual print time per part.
Given these stocks and flows, a capacity-constrained production system with a fixed, passive demand input is modelled. Demand is established through a demand queue to determine the desired production rate. The demand does not directly influence cost per part, lead time, or backlog accumulation. This is because the production process is subject to machine availability and raw material supply.
While the queue allows the system to meet demand, the model does not include backlog accumulation or penalties for unmet orders. Backlog and order fulfillment delays are relevant at the supply chain level, which falls beyond the scope of the present analysis. That is, any unmet demand will not be carried over, and hence demand functions more like a production target than a dynamic driver. In so doing, variations in demand level do not impact cost or time metrics under the following assumptions.
- -
The model stops at the shop floor. Upstream supplier delays and downstream warehousing or transport are not represented. That is, material enters through a constant “delivery rate”.
- -
One month is considered to capture the short-term production dynamics. Long-term learning effects and capacity growth fall beyond the scope of this study.
- -
Demand is imposed externally and is assumed to be constant and deterministic; unmet demand is neither back-ordered nor penalised.
- -
Machine availability is expressed via the utilization parameter; preventive or corrective maintenance events are not considered.
- -
Zero scrap or rework is allowed. That is, the parts from every build are assumed to be fully functional.
- -
Pre-processing activities are folded into the “effective printing time” parameter. This simplification treats the entire production cycle (pre-, post-, and setups) as a time block.
The following parameters are defined to run the model: Setup time, Batch size, Printing time per part, Machine power consumption, Material utilization, Labor requirements for printing and post-processing, and consumable costs. These parameters have to be adjusted depending on the production technology. All values are based on real industrial data, ensuring that the simulation outcomes reflect realistic production scenarios.
4. Discussions and Practical Implications
The comparative analysis of PBF, DED, and CNC for producing robot grippers showed that cost performance changes under different operating scenarios. PBF is more cost-competitive than CNC machining if the build capacity is fully utilized. This is because the fixed overhead of a PBF task (i.e., machine preparation, cooldown, and powder handling) is spread over fewer parts, limiting the economy-of-scale advantage of AM over CNC machining. In this study, PBF achieved an approximate per-part cost of 2725 NOK under full build utilization, cheaper than CNC, with about 5624 NOK cost per part. This requirement, however, may reduce the competitiveness of PBF for small and medium-sized enterprises, considering that maintaining a full chamber size may not be applicable.
The DED-WAAM recorded a flat cost of around 1702 NOK per part, the lowest of the compared methods. Nevertheless, the result should be interpreted with caution. In practice, arc-based WAAM is a process primarily suited for producing large-scale parts, as it offers very high deposition rates and lower material cost. This comes at the expense of lower precision and surface quality. WAAM is, therefore, suitable for producing bulky parts, such as those in the shipbuilding and heavy machinery industries. The WAAM-produced parts have rough resolution and surface finish, requiring extensive post-processing (i.e., machining) to meet dimensional tolerances. The flat cost model in the present study may not reflect how costs might scale with part size or quantity due to the simplified cost model for the additional finishing steps.
Unlike PBF, DED-WAAM struggles to batch many parts in one build, as each part should be deposited individually or sequentially. Therefore, producing multiple small parts using WAAM results in a nearly linear cost function (concerning material and time). While WAAM showed a low nominal cost in the comparative analysis, the low cost of 1702 NOK per part may have been impacted by the limited data or simplifications rather than a definitive economic advantage.
Laser-based DED technologies are expected to perform better for producing small, complex parts with intricate geometries. Using a focused laser to melt metal powder or wire feedstock makes it possible to produce parts with higher precision and finer resolution than WAAM. This is mostly due to thinner deposition beads and smaller features, although at lower deposition rates and higher equipment cost than WAAM. Laser-based DED bridges the gap between WAAM and PBF in terms of accuracy, while it still deposits faster and at larger scales than PBF. Laser powder-blown DED offers excellent geometrical accuracy and usage for small feature deposition [
25], whereas WAAM’s poor resolution (on the order of 1 mm and above) [
26] necessitates extensive post-processing for fine details. In line with these results, one can conclude that Laser-based DED will be a more appropriate production method than PBF and CNC but with higher costs than WAAM (i.e., due to costlier equipment and slower build rates).
Another important discussion concerns the design of the part. The gripper was designed for AM processes, with a design strategy favoring laser-based AM processes for complex geometries (i.e., intricate internal channels, undercuts, fine details). CNC machining is limited in addressing such features. Achieving greater geometric complexity with subtractive manufacturing drives up cost due to more complicated tool paths and fixturing. The part geometry was designed for AM, which inflated CNC machining time and price. The results are therefore design-specific, and a CNC-friendly redesign can narrow the gap.
Overall, the decision of which AM technology to adopt is multifaceted, involving the analysis of practical requirements in addition to the technical constraints [
11,
27]. Therefore, the most cost-effective technology is case-specific. For example, the company should evaluate whether a component’s complexity justifies AM adoption, considering a higher unit cost. That is, on-demand production of highly customized components in time-sensitive situations can justify a higher cost for metal AM [
28].
It is also important to analyze whether a large production run favors investing in tooling for CNC or alternative solutions. For example, the use of a hybrid approach (i.e., printing the near-net shape part using AM and then machining critical surfaces using traditional manufacturing) may be the best compromise. In the particular case of a robot gripper, the study result is supportive of using PBF as an economically viable alternative, whereas using DED-WAAM for producing a small part may be misleadingly cheap, given the practical considerations.
Beyond the technology-specific findings, it is also necessary to reflect on the modeling assumptions behind the cost results. Cost modeling for metal AM remains inherently difficult because outcomes are highly sensitive to company setup, operator expertise, and process-specific factors such as downtime, scrap, and demand fluctuations. In this study, simplified conditions of constant demand, no downtime, and no scrap were applied to make the results comparable across PBF, WAAM, and CNC. While such idealized scenarios are commonly used in early-stage AM cost models and provide a useful baseline, they should be interpreted with caution, as CNC will often regain cost advantage once real-world variability and yield losses are taken into account.
5. Conclusions
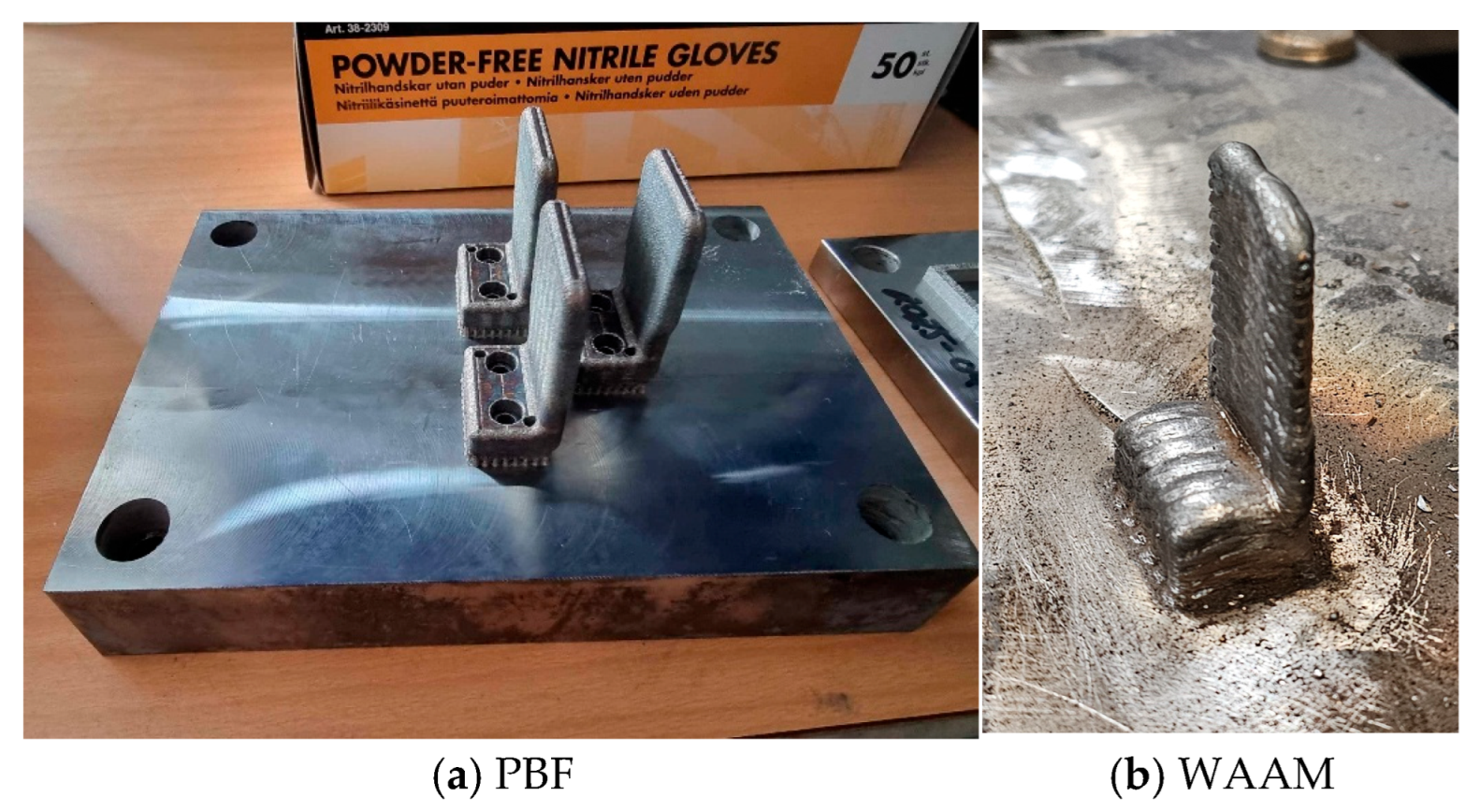
This study compared PBF and DED AM technologies with CNC machining to explore the most cost-effective machines for establishing 3D print farms. A robot steel gripper was used as a case study for a shop floor-level cost and externalities analysis. It was found that the unit cost of PBF becomes significantly cheaper than the quoted CNC price when the build chamber is full (i.e., 72 parts). Printing a single part using PBF raised the cost significantly. Therefore, a high build utilization rate is deemed necessary to benefit from cost advantages. The cost estimate of producing the part using WAAM-DED showed an advantage over PBF for medium- to large-sized items that do not have complex internal features and do not require heavy post-processing. For small, intricate shapes, the laser-based DED route is expected to be superior, offering finer resolution at a higher but more realistic cost.
Overall, cost comparisons across PBF, DED-WAAM, and CNC depend heavily on part design, quantity, and machine utilization. The following generalizations can be drawn from the comparative analysis.
- -
PBF offers excellent design freedom and parallel production but incurs high fixed costs per build and suffers if underutilized.
- -
CNC excels in consistent production with economies of scale through repeated runs, but complex internal features may favour AM.
- -
A rough but fast method, such as DED-WAAM, is cost-efficient for large, simple shapes yet ill-suited to fine details. A laser DED provides higher precision at a higher cost, potentially fitting small parts better.
This study has several limitations. First, the quality and source of data varied across the three manufacturing methods, potentially impacting the robustness of the comparisons. While PBF costs were derived from detailed modeling, the WAAM cost was based on assumptions considering the limited know-how in the new DED technology. Future research should offer empirical analysis for a more consistent comparison between WAAM and PBF. Additionally, since the present study focused on single-component WAAM builds to avoid distortion, future sensitivity analyses could examine multi-part configurations to assess how thermal interactions influence microstructure, mechanical performance, and dimensional stability. More empirical analysis on other AM technologies, especially BJ and MEX, would also be required to help extend the industrial reach of AM. The second limitation comes from the inherent differences in material and process conditions, in particular, the material forms and properties of the three different manufacturing methods. Using carbon steel with different characteristics (i.e., fine powdered 17-4 PH stainless steel by PBF, 316L stainless steel by CNC, and wire ESAB Purus 45 by WAAM) might have resulted in variations in mechanical properties, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy. In the case of the robotic gripper, the mechanical properties, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy of both printed parts were perceived as acceptable. Analyzing these characteristics was beyond the scope of our cost analysis and should be considered in future research. Third, the post-processing steps were simplified for WAAM. In future research, the post-processing activities should be modeled in more detail. Additionally, future work may benefit from examining a broader range of production volumes and design variations. Such an analysis should evaluate the cost competitiveness of different AM technologies under mass production scenarios. Finally, a comparative analysis including laser-based DED data will further our understanding of the MAM technologies’ competitiveness. As the next suggestion for future research, practical aspects, like machine maintenance, learning effects, and supply availability and quality, should be considered for comparing MAM technologies. Finally, this study focused solely on cost performance. Future research should also investigate energy use and environmental impacts to provide a more comprehensive evaluation of AM technologies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S., P.P., and W.D.S.; methodology, M.S.; validation, P.P. and W.D.S.; formal analysis, M.S.; investigation, P.P.; resources, W.D.S.; data curation, M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, P.P.; writing—review and editing, M.S., P.P., and W.D.S.; visualization, M.S.; supervision, P.P.; project administration, P.P.; funding acquisition, P.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study received financial support from the Interreg Aurora Program for implementing DED AM in future manufacturing with grant reference number 20358021 (IDiD project).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The steel robotic grippers were 3D printed at the Department of Industrial Engineering, UiT The Arctic University of Norway, and at the Kerttu Saalasti Institute, University of Oulu. We gratefully acknowledge the related technical and equipment support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lacroix, R.; Timonina-Farkas, A.; Seifert, R.W. Utilizing Additive Manufacturing and Mass Customization under Capacity Constraints. J. Intell. Manuf. 2023, 34, 281–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tan, Y.; Willis, S.; Bahshwan, M.; Folkes, J.; Kalossaka, L.; Waheed, U.; Myant, C. Toward Mass Customization Through Additive Manufacturing: An Automated Design Pipeline for Respiratory Protective Equipment Validated Against 205 Faces. Int. J. Bioprint. 2021, 7, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO/ASTM 52900; Additive Manufacturing—General Principles—Fundamentals and Vocabulary. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- Kang, K.; Kong, X.T.R.; Tan, B.Q. Impact of additive manufacturing on supply chain resilience. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2025, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonar, H.; Khanzode, V.; Akarte, M. Additive Manufacturing Enabled Supply Chain Management: A Review and Research Directions. Vis. J. Bus. Perspect. 2022, 26, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braziotis, C.; Rogers, H.; Jimo, A. 3D Printing Strategic Deployment: The Supply Chain Perspective. Supply Chain. Manag. Int. J. 2019, 24, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhejazy, P. Additive Manufacturing in the Supply Chain. In The Palgrave Handbook of Supply Chain Management; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 1383–1403. [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi, M.; Caterino, M.; Macchiaroli, R. Additive Manufacturing and Supply Chain Configuration: Modelling and Performance Evaluation. J. Ind. Eng. Manag. 2022, 15, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherdo, L. Metal 3D Printers in 2024: A Comprehensive Guide. Available online: https://www.aniwaa.com/buyers-guide/3d-printers/best-metal-3d-printer/ (accessed on 5 October 2025).
- Ghadge, A.; Karantoni, G.; Chaudhuri, A.; Srinivasan, A. Impact of Additive Manufacturing on Aircraft Supply Chain Performance. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2018, 29, 846–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sæterbø, M.; Solvang, W.D. Metal Additive Manufacturing Adoption in SMEs: Technical Attributes, Challenges, and Opportunities. J. Manuf. Process 2024, 128, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, H.; Baricz, N.; Pawar, K.S. 3D Printing Services: Classification, Supply Chain Implications and Research Agenda. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2016, 46, 886–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, M.; Todorov, I.; Kapletia, D. Application of Additive Manufacturing for Mass Customisation: Understanding the Interaction of Critical Barriers. Prod. Plan. Control 2018, 29, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureijs, R.E.; Roca, J.B.; Narra, S.P.; Montgomery, C.; Beuth, J.L.; Fuchs, E.R.H. Metal Additive Manufacturing: Cost Competitive Beyond Low Volumes. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2017, 139, 081010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colosimo, B.M.; Cavalli, S.; Grasso, M. A Cost Model for the Economic Evaluation of In-Situ Monitoring Tools in Metal Additive Manufacturing. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 223, 107532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sæterbø, M.; Solvang, W.D. Evaluating the Cost Competitiveness of Metal Additive Manufacturing—A Case Study with Metal Material Extrusion. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2023, 45, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenti, P.; Puccio, D.; Semeraro, Q.; Colosimo, B.M. A Techno-Economic Approach for Decision-Making in Metal Additive Manufacturing: Metal Extrusion versus Single and Multiple Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 9, 185–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, R.C.; Niknam, S.A. Applying Design Complexity Metrics for Post-Processing Cost Modeling in Metal Additive Manufacturing. Manuf. Lett. 2024, 41, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, N.; Salvi, H.; Karaş, B.; Fairoz, I.; Shokrani, A. Cost Modelling for Powder Bed Fusion and Directed Energy Deposition Additive Manufacturing. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2024, 8, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafokosi, K.R.M.; Pretorius, J.-H.C.; Chattopadhyay, G. Modeling of Impact of Operations and Maintenance on Safety, Availability, Capacity, and Cost of Railways-A System Dynamics Approach. J. Rail Transp. Plan. Manag. 2024, 31, 100463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Luo, M. Cost Estimation Model of Prefabricated Construction for General Contractors Based on System Dynamics. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2025, 32, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltaggaz, A.; Cloutier, J.; Deiab, I. Thermal Post-Processing of 4140 Alloy Steel Parts Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting (SLM). In Proceedings of the Canadian Society for Mechanical Engineering International Congress 2021, Charlottetown, PE, Canada, 27–30 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, S.; Shahvari, O.; Marufuzzaman, M.; Francis, J.; Bian, L. Sustainable Design of On-Demand Supply Chain Network for Additive Manufacturing. IISE Trans. 2019, 51, 744–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladani, L. Additive Manufacturing of Metals: Materials, Processes, Tests, and Standards; DEStech Publications: Lancaster, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.J.; Saldana, C. Thin Wall Deposition of IN625 Using Directed Energy Deposition. J. Manuf. Process 2020, 56, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.P.; Gouveia, F.M.; Santos, T.G. Micro Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (µ-WAAM). Addit. Manuf. Lett. 2022, 2, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhejazy, P.; Kravetc, T.; Sarkis, J. Performance evaluation of 3D print farms in additive manufacturing-based supply chains. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2025, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sæterbø, M.; Pourhejazy, P. The impact of Metal Additive Manufacturing Adoption on the Steel Supply Chain. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2025, 59, 2238–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).